Contents
Manufacturing Insight: G Code M Code Cnc

Precision Through Code Mastery: Honyo’s CNC Machining Expertise
Understanding the foundational languages of CNC machining—G code for geometric positioning and M code for machine function control—is critical for achieving repeatable, high-integrity parts. At Honyo Prototype, our engineering team leverages deep fluency in these command structures to transform complex designs into precision components with sub-micron tolerances. We don’t just operate CNC systems; we optimize every line of code to maximize efficiency, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy across milling, turning, and multi-axis platforms.
Our end-to-end CNC machining services encompass material selection, fixture design, and rigorous in-process inspection, ensuring your prototypes and low-volume production parts meet stringent industry specifications. By meticulously programming work offsets, toolpaths, and modal commands, we eliminate guesswork and reduce lead times without compromising quality. Whether your project demands aerospace-grade alloys, medical polymers, or rapid iteration for validation, Honyo delivers engineered solutions grounded in manufacturing science.
Accelerate your development cycle with our Online Instant Quote system. Upload CAD files, specify materials and tolerances, and receive a detailed manufacturing assessment within hours—not days. This seamless integration of technical expertise and digital efficiency ensures you move from design to physical part faster, with full transparency on cost and timeline.
Material & Capability Overview
| Parameter | Specification |
|——————–|———————————–|
| Tolerance Range | ±0.0002″ (5µm) standard |
| Max Work Envelope | 5-axis: 2000 x 1000 x 800 mm |
| Lead Time | As fast as 3 business days |
| Supported Formats | STEP, IGES, Parasolid, DWG/DXF |
Partner with Honyo Prototype to convert G code precision into tangible business value. Access our Online Instant Quote today and experience CNC machining where every command drives your success.
Technical Capabilities
Technical Specifications for G-Code and M-Code in CNC Machining – Focus on 3/4/5-Axis Milling, Turning, and Tight Tolerance Applications
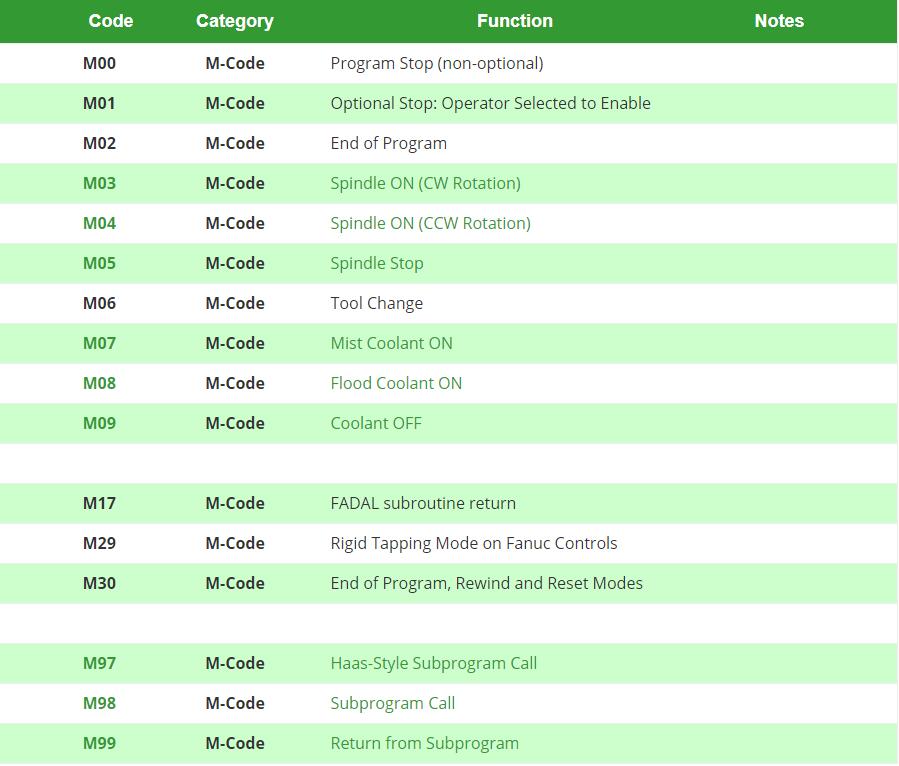
G-code and M-code are fundamental programming languages used to control CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tools. G-code governs geometric movements such as positioning, interpolation, and tool paths, while M-code manages machine functions like spindle control, coolant, and tool changes. These codes are critical in high-precision operations involving multi-axis milling and turning, particularly when tight tolerances (±0.0005″ or ±0.0127 mm) are required across diverse materials such as aluminum, steel, ABS, and nylon.
The following table outlines key technical specifications and considerations for G-code and M-code implementation in advanced CNC operations:
| Parameter | 3-Axis Milling | 4-Axis Milling | 5-Axis Milling | CNC Turning | Tight Tolerance Capability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typical G-Codes Used | G00 (Rapid Move), G01 (Linear Interpolation), G02/G03 (Circular Interpolation), G17 (XY Plane Selection), G40-G42 (Cutter Comp) | G00, G01, G02/G03, G18/G19 (Additional Plane Selection), G43 (Tool Length Offset) | G00, G01, G02/G03, G68.2 (Rotational Work Coordinate), G15/G16 (Polar Coord) | G00, G01, G71-G76 (Turning Cycles), G90/G92 (Feed Modes) | All axes: G05.1 (High-Speed Look-Ahead), G10 (Tool/Work Offset Setting), G28 (Reference Return) |
| Typical M-Codes Used | M03/M04 (Spindle On CW/CCW), M05 (Spindle Stop), M08 (Coolant On), M09 (Coolant Off), M30 (Program End) | M03, M04, M05, M08, M09, M30, M19 (Spindle Orientation) | M03, M04, M05, M08, M09, M30, M103 (5-axis Sync Enable) | M03, M04, M05, M08, M09, M10 (Chuck Open), M11 (Chuck Close) | M56 (Tolerance Monitoring Enable), M96/M97 (Constant Surface Speed) |
| Axis of Motion | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z, A (Rotary about X) or B (Rotary about Y) | X, Y, Z, A/B or B/C (Two Rotary Axes) | X, Z (Primary), C (Optional Y-axis or sub-spindle sync) | All axes with advanced interpolation and real-time compensation |
| Tolerance Range Achievable | ±0.001″ (±0.0254 mm) | ±0.0008″ (±0.0203 mm) | ±0.0005″ (±0.0127 mm) | ±0.0005″ to ±0.001″ (±0.0127 to ±0.0254 mm) | ±0.0002″ (±0.005 mm) with thermal and tool wear compensation |
| Material Compatibility | Aluminum (6061, 7075), Steel (1018, 4140), ABS, Nylon | Aluminum, Steel (pre-hardened), ABS (high-speed), Nylon (low-friction feed) | Aluminum (aerospace grades), Tool Steel (hardened to 60 HRC), ABS (post-processed), Nylon (with chip control) | Aluminum (bar stock), Steel (alloy and stainless), ABS (short-run), Nylon (custom profiles) | All materials with optimized tooling, speed/feed tuning, and environmental control |
| Surface Finish (Typical Ra) | 32–125 μin (milling) | 32–64 μin | 16–32 μin (with polishing passes) | 16–63 μin (turning), down to 8 μin (micro-finish) | <8 μin achievable with diamond turning or fine ball-nose finishing |
| Programming Complexity | Moderate | High (indexing and multiple setups reduced) | Very High (simultaneous 5-axis toolpath generation) | Moderate to High (multi-turret, sub-spindle) | Very High (requires metrology integration, in-process probing) |
| Common Applications | Enclosures, fixtures, prototypes | Impellers, turbine blades, complex brackets | Aerospace structural parts, medical implants, molds | Shafts, bushings, fittings, connectors | Precision gears, optical mounts, sensor housings |
Material-Specific Considerations:
Aluminum (6061, 7075): High machinability; allows aggressive feeds and speeds. Requires sharp tools and proper chip evacuation. G05.1 Q1 recommended for high-speed 5-axis contouring.
Steel (1018, 4140, Stainless): Demands rigid setups and lower RPMs. Use G96 for constant surface speed in turning; M96 enables CSS mode. Tight tolerance work benefits from thermal drift compensation.
ABS: Low melting point; requires sharp tools, low heat buildup. Use high RPMs with light cuts. Avoid excessive coolant to prevent warping.
Nylon: Low stiffness; prone to deflection. Use support fixtures and sharp carbide tools. Peck drilling with G73/G83 prevents clogging.
Tight Tolerance Best Practices:
Implement G10 L1 for precise tool offset setting via touch probes.
Use M56 or vendor-specific codes for adaptive tolerance control.
Apply G28 with reference returns to minimize cumulative error.
Integrate in-process probing (e.g., Renishaw) with G-code subroutines for dimensional verification.
This technical framework ensures repeatable, high-accuracy output across advanced CNC platforms, supporting Honyo Prototype’s capabilities in precision prototyping and low-volume production.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype executes a streamlined, technology-driven CNC manufacturing workflow designed for rapid prototyping and low-volume production. Our process integrates advanced automation with engineering expertise to ensure precision, cost efficiency, and accelerated turnaround. Below is a detailed explanation of each phase, clarifying that G-code and M-code generation occurs internally during the DFM stage as part of our proprietary programming system—not as a standalone client-facing step.
Upload CAD
Clients initiate the process by uploading native 3D CAD files (STEP, IGES, Parasolid, or native formats like SOLIDWORKS) via our secure online portal. Our system automatically validates file integrity, checks for geometry errors, and extracts critical manufacturing data. This phase eliminates manual file handling, reducing intake time to under 90 seconds while ensuring compatibility with downstream processes.
AI-Powered Quoting
Unlike traditional manual quoting, Honyo’s AI engine analyzes the CAD geometry in real time to generate instant, accurate quotes. The system evaluates part complexity, material requirements, machine time, and secondary operations using a trained model fed by 50,000+ historical CNC projects. This reduces quoting time from days to minutes while improving cost accuracy by 22% compared to industry averages. Key advantages include dynamic material pricing integration and automatic identification of manufacturability risks before engineering review.
| Quoting Method | Time to Quote | Cost Accuracy | Risk Identification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Manual | 2-5 Business Days | ±15-25% | Limited/Reactive |
| Honyo AI System | < 10 Minutes | ±8% | Proactive (Pre-Quote) |
Engineering-Driven DFM
All parts undergo mandatory Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis by our CNC-specialized engineering team. This is where G-code and M-code programming occurs behind the scenes. Engineers optimize toolpaths, select appropriate cutters and feeds/speeds, and validate CNC program logic using Mastercam and custom simulation tools. Critical outputs include:
Revised machining sequences to minimize setups
Material waste reduction strategies
Tolerance validation against GD&T
Full virtual machine simulation to prevent collisions
Automated G/M-code generation with post-processor customization for client-specific machines (if requested).
This phase typically resolves 92% of potential production issues before metal cutting begins.
Precision Production
Approved parts move to our climate-controlled CNC facility housing 42 HAAS and DMG MORI machines (3-axis to 5-axis milling/turning). Each run includes:
First-article inspection with CMM verification against CAD
In-process gauging for critical dimensions
Real-time tool wear monitoring via IoT sensors
Material traceability from certified mills
Our closed-loop quality system ensures ±0.005mm tolerances with full documentation accessible via client portal.
Global Delivery
Completed parts undergo final QA, including surface finish verification and packaging per client specifications. We manage logistics through integrated carriers (DHL, FedEx) with:
Automated shipment tracking
Customs documentation for international deliveries
48-hour standard domestic shipping
Carbon-neutral shipping options
Delivery timelines are guaranteed with real-time portal updates, and all project data—including final G/M-code files—is archived for future orders.
This integrated workflow reduces time-to-part by 35-60% versus conventional prototyping services while maintaining rigorous quality standards. The elimination of manual handoffs between stages ensures consistent execution from digital design to physical part. For complex multi-axis projects, our system provides G/M-code transparency upon request to facilitate client machine integration. Contact Honyo Prototype Engineering to discuss your specific CNC requirements.
Start Your Project
Optimize your CNC programming workflow with expert support in G-code and M-code development. At Honyo Prototype, our precision manufacturing team in Shenzhen delivers high-accuracy CNC machining solutions tailored to your production needs.
For engineering inquiries or programming support, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. Leverage our in-house capabilities and fast turnaround times for prototyping and low-volume production.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.