Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fusion 360 stl export failed
Exporting STL files from Fusion 360 can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, especially those engaged in international markets where precise modeling is critical. The issue of “Fusion 360 STL export failed” can arise unexpectedly, disrupting workflows and leading to costly delays in product development and production. This guide aims to equip buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the potential pitfalls associated with STL export failures, the underlying causes, and practical solutions to mitigate these issues.
In this guide, we will explore various types of STL export failures, their applications in different industries, and strategies for effective supplier vetting. Additionally, we will analyze the associated costs of resolving these export challenges and provide actionable insights for enhancing your workflow efficiency. By addressing common obstacles faced during the STL export process, this guide empowers B2B buyers—especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (e.g., Saudi Arabia, Brazil)—to make informed purchasing decisions.
Navigating the complexities of STL exports requires not just technical knowledge but also an understanding of the global market landscape. By leveraging the insights provided in this guide, businesses can enhance their operational capabilities, reduce downtime, and ultimately foster smoother collaborations with suppliers and partners. Equip your organization with the tools needed to overcome STL export challenges and thrive in a competitive marketplace.
Understanding fusion 360 stl export failed Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometry Errors | Inaccurate or corrupted geometry leading to failed exports. | 3D printing, prototyping | Pros: Identifies design flaws early. Cons: May require rework and additional time. |
| File Permission Issues | Lack of write permissions on local or network drives. | Collaboration across teams and locations | Pros: Encourages proper file management. Cons: Can halt workflows unexpectedly. |
| Export Format Conflicts | Issues due to incompatible file formats or settings. | Data exchange between design and manufacturing | Pros: Ensures compatibility with different systems. Cons: Requires knowledge of formats. |
| Large File Size | Exports failing due to excessive file size or complexity. | Detailed models in manufacturing and design | Pros: Captures intricate details. Cons: Slower processing and potential crashes. |
| Software Bugs and Glitches | Technical issues within Fusion 360 affecting export functionality. | Design iterations and client presentations | Pros: Regular updates can resolve issues. Cons: Unpredictable disruptions in workflow. |
What are the characteristics of Geometry Errors in STL Exports?
Geometry errors often arise when the model contains non-manifold edges, overlapping faces, or other defects that complicate the mesh structure. These issues are critical in B2B contexts, particularly in industries like 3D printing and rapid prototyping, where precision is paramount. Buyers should consider investing in software solutions or services that offer robust geometry validation tools to identify and rectify these errors before export.
How do File Permission Issues affect STL Export?
File permission issues typically occur when users attempt to save STL files in locations where they lack write access, such as network drives or restricted folders. This can significantly impact collaborative projects, especially for teams spread across different regions. To mitigate these challenges, B2B buyers should establish clear file management protocols and ensure that all team members have the necessary permissions to facilitate seamless workflows.
What are Export Format Conflicts and their implications?
Export format conflicts can arise when users attempt to export models in formats that are incompatible with their intended applications. This is particularly relevant in B2B settings where data exchange between design and manufacturing systems is common. Buyers should be aware of the specific requirements of their downstream processes and invest in training or resources that enhance their team’s understanding of file formats and export settings.
Why is Large File Size a concern in STL Exports?
Large file sizes can lead to export failures due to the complexity of the model exceeding software capabilities or system resources. In sectors like manufacturing and design, where detailed models are essential, this can pose a significant challenge. B2B buyers should consider optimizing their models or utilizing software that can handle large datasets efficiently to avoid delays in production timelines.
How do Software Bugs and Glitches impact STL Export?
Software bugs and glitches can disrupt the export process, leading to unexpected failures. This is particularly concerning for B2B operations where time is critical, such as in client presentations or product launches. Regular software updates and support from the vendor can help mitigate these issues, but buyers must also be prepared for potential disruptions and have contingency plans in place to ensure continuity in their projects.
Key Industrial Applications of fusion 360 stl export failed
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fusion 360 stl export failed | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Design validation for prototyping | Reduces time-to-market by identifying design flaws early | Need for high precision and compliance with safety standards |
| Automotive | Custom parts manufacturing | Enhances product customization and customer satisfaction | Consideration for material compatibility and cost-effectiveness |
| Medical Devices | 3D printing of prosthetics and implants | Improves patient outcomes through personalized solutions | Regulatory compliance and biocompatibility of materials required |
| Consumer Electronics | Rapid prototyping of electronic enclosures | Speeds up product development cycles and innovation | Sourcing materials that can withstand electronic components |
| Architecture & Construction | Visualization and model testing | Enhances client engagement and design accuracy | Demand for high-resolution outputs for client presentations |
How Does STL Export Failure Impact the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, STL export failures can hinder the design validation process for prototypes. When engineers cannot export STL files from Fusion 360, they face delays in identifying potential design flaws, which can significantly prolong the development timeline. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, ensuring compliance with strict safety standards is critical. Therefore, sourcing solutions that facilitate seamless STL exports is essential for maintaining project timelines and adhering to regulatory requirements.
What Are the Implications for Automotive Custom Parts Manufacturing?
For automotive manufacturers, the inability to export STL files can disrupt the production of custom parts. This challenge limits the ability to create tailored solutions that enhance customer satisfaction and meet specific market demands. Buyers from regions such as South America and Africa should consider sourcing advanced training or software support to mitigate these export failures. Ensuring that the materials used in production are compatible with design specifications is also crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and reducing costs.
Why Is STL Export Failure Critical in Medical Device Production?
In the medical device industry, STL export failures can pose significant risks, particularly in the production of prosthetics and implants. The ability to create precise 3D models is vital for improving patient outcomes through personalized medical solutions. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing materials that comply with regulatory standards and ensure biocompatibility. Addressing STL export challenges swiftly is essential for maintaining the integrity of the design process and meeting the stringent requirements of the healthcare industry.
How Does STL Export Failure Affect Consumer Electronics Development?
In the consumer electronics field, rapid prototyping is essential for innovative product development. STL export failures can delay the creation of electronic enclosures, impacting the overall product development cycle. International B2B buyers should focus on sourcing materials that not only facilitate rapid prototyping but also ensure durability and performance under varying conditions. By addressing STL export issues, companies can enhance their innovation capabilities and respond more effectively to market demands.
What Role Does STL Export Failure Play in Architecture and Construction?
In architecture and construction, STL export failures can hinder the visualization and model testing phases. When architects cannot export accurate STL files, it can lead to miscommunication with clients and stakeholders, ultimately affecting project outcomes. For buyers in these sectors, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, it is crucial to source solutions that offer high-resolution outputs to improve client engagement and ensure design accuracy. Effective management of STL export processes can significantly enhance project delivery timelines and client satisfaction.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fusion 360 stl export failed’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Incomplete Model Exports Resulting in Production Delays
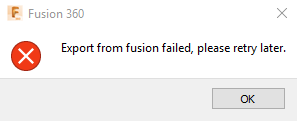
The Problem: A manufacturing company frequently encounters issues with exporting STL files from Fusion 360, leading to incomplete or corrupted files. This scenario is particularly frustrating when time-sensitive projects are involved, as delays in model exports can stall production schedules. The lack of a clear error message during the export process compounds the problem, leaving users guessing about the underlying issues and further delaying project timelines. This situation not only affects internal productivity but also strains relationships with clients expecting timely deliverables.
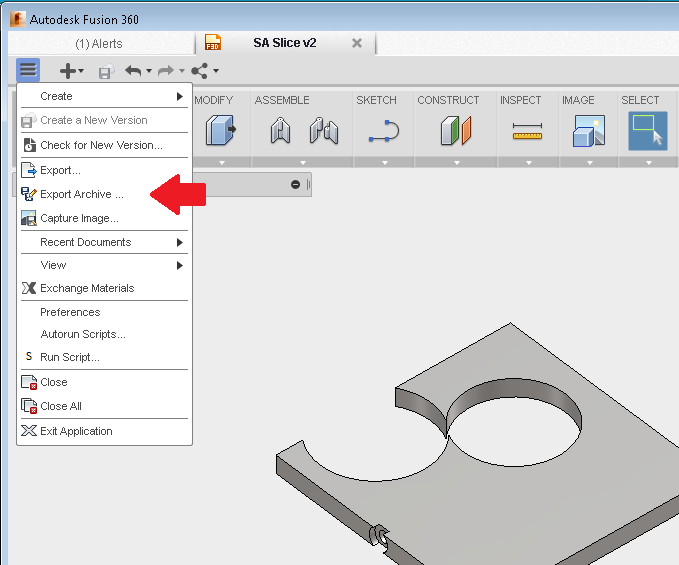
The Solution: To address this challenge, users should first ensure that the model is free of errors before initiating the export process. This can be achieved by utilizing Fusion 360’s built-in validation tools to check for non-manifold edges or other common geometric issues. Additionally, users can try exporting the model in smaller sections rather than as a single file, which may help isolate problematic components. If the export still fails, consider using the “Save As Mesh” option instead of the standard STL export. This alternative can sometimes bypass issues that the standard export encounters, allowing for successful file creation without compromising on quality.
Scenario 2: Permission Issues Causing Export Failures
The Problem: An architectural firm has several team members working on a collaborative project in Fusion 360, but they frequently face export failures due to permission issues related to file storage locations. When team members attempt to export STL files, they receive vague error messages, leading to confusion and wasted effort as they try to troubleshoot the problem. This scenario can create frustration among team members and hinder collaborative progress, especially if project deadlines are looming.
The Solution: To resolve permission-related export failures, it’s essential to first confirm that all team members have appropriate write permissions for the designated file storage locations. Encourage team members to save their projects locally and then upload them to a shared drive after successful exports. It may also be beneficial to set up a dedicated project folder with confirmed permissions for all users. If problems persist, consider using cloud storage solutions that offer robust access management features, ensuring that everyone involved in the project can seamlessly export files without encountering permission errors.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Identifying the Cause of Export Failures
The Problem: An engineering firm is grappling with frequent STL export failures from Fusion 360 without any clear indicators of what is causing the issue. Users report that the export process simply fails without error messages, leading to significant downtime as they attempt various troubleshooting methods. This lack of clarity not only frustrates the design team but also affects overall project timelines, as they are unable to pinpoint and resolve the underlying issues efficiently.
The Solution: To tackle the ambiguity surrounding export failures, users should adopt a systematic troubleshooting approach. Begin by checking the model’s complexity; overly intricate designs may exceed the software’s export capabilities. Simplifying the model can often resolve export issues. Additionally, users should review the Fusion 360 support forums and community discussions to see if others have encountered similar problems and what solutions have been effective. If the problem persists, reaching out to Autodesk support with specific details about the model and the export attempt can provide targeted assistance, enabling the team to quickly identify and rectify the underlying issues.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fusion 360 stl export failed
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Fusion 360 STL Export Failures?
When dealing with STL export failures in Fusion 360, the choice of material can significantly impact both the functionality of the design and the success of the export process. Here, we analyze four common materials: PLA, ABS, Nylon, and PETG, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does PLA Perform in Fusion 360 STL Exports?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch. It is widely used in 3D printing due to its ease of use and environmental benefits.
- Key Properties: PLA has a low melting point (around 180-220°C), making it suitable for low-temperature applications. It exhibits good rigidity and minimal warping.
- Pros & Cons: PLA is relatively inexpensive and easy to print, but it has lower heat resistance and can become brittle over time. Its biodegradability is a significant advantage for environmentally conscious projects.
- Impact on Application: PLA is not suitable for high-stress applications or environments that exceed its thermal limits. It is ideal for prototypes and decorative items.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental standards is crucial, especially in Europe, where regulations on biodegradable materials are stringent. Buyers should verify material certifications like ASTM D6400 for compostability.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of ABS?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a popular thermoplastic known for its toughness and impact resistance.
- Key Properties: ABS has a higher melting point (around 220-250°C) and excellent mechanical properties, making it suitable for functional parts.
- Pros & Cons: Its durability and resistance to impact are significant advantages. However, ABS can warp during printing and may emit fumes, necessitating good ventilation.
- Impact on Application: ABS is suitable for parts that require strength and durability, such as automotive components and consumer products.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like the Middle East and South America should be aware of local environmental regulations regarding emissions and waste disposal, as ABS may not comply with certain eco-friendly standards.
How Does Nylon Compare in Terms of Performance?
Nylon is a versatile engineering thermoplastic known for its strength and flexibility.
- Key Properties: Nylon has excellent tensile strength and abrasion resistance, with a melting point around 220-260°C. It is also resistant to many chemicals.
- Pros & Cons: Its flexibility and durability make it ideal for functional parts. However, nylon can absorb moisture, which may affect print quality and mechanical properties.
- Impact on Application: Suitable for applications requiring high strength and wear resistance, such as gears and functional prototypes.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with industry standards such as DIN or JIS is essential, particularly for buyers in Europe and Asia. Moisture control during storage and transport is also critical.
What Makes PETG a Preferred Choice for Exporting STL Files?
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) combines the best features of PLA and ABS, making it a popular choice for various applications.
- Key Properties: PETG has a melting point of around 230-250°C and offers good impact resistance and flexibility. It is also less prone to warping compared to ABS.
- Pros & Cons: PETG is easy to print and has excellent clarity, making it suitable for transparent applications. However, it can be more expensive than PLA and may require specific printing conditions.
- Impact on Application: Ideal for both functional and aesthetic parts, PETG is suitable for packaging, medical devices, and consumer products.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that PETG complies with relevant food safety standards if the application involves food contact. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding plastic use is essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Fusion 360 STL Export Failures
| Material | Typical Use Case for fusion 360 stl export failed | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Prototypes, decorative items | Biodegradable, easy to print | Low heat resistance, brittle | Low |
| ABS | Functional parts, automotive components | Toughness, impact resistance | Warping, fumes during printing | Med |
| Nylon | Gears, functional prototypes | High strength, abrasion resistance | Moisture absorption | High |
| PETG | Transparent applications, medical devices | Clarity, easy to print | Higher cost than PLA | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers navigating the complexities of STL export failures in Fusion 360, ensuring informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fusion 360 stl export failed
How Do Manufacturing Processes Impact STL Export Failures in Fusion 360?
Understanding the manufacturing processes involved in creating parts for 3D printing, particularly when using software like Fusion 360, is crucial for international B2B buyers. Export failures, such as those encountered during STL file generation, can often be traced back to issues in the design or the manufacturing workflow. By dissecting the main stages of manufacturing—material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing—buyers can better identify potential pitfalls and enhance their product development processes.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Relevant to STL Export?
-
Material Preparation: The first stage involves selecting the appropriate materials for 3D printing, which can include plastics, metals, or composites. Proper material selection is critical, as the characteristics of the chosen material can influence the export process. If the material properties do not align with the specifications required for STL files, issues may arise. For instance, certain materials may not translate well into mesh formats, leading to export failures.
-
Forming: In this stage, the design is transformed into a physical representation. Techniques such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) or subtractive methods (CNC machining) can be used. When forming, ensuring that the model is manifold (i.e., without holes or non-manifold edges) is vital. Non-manifold geometries are a common cause of STL export failures, as they cannot be accurately represented in 3D space.
-
Assembly: For complex designs, assembly may involve combining multiple parts. Each part must be designed with consideration for how it will be assembled. Misalignment or improper fit between parts can lead to complications during the export process. It is essential to verify that all components are correctly oriented and that their interfaces are properly defined to avoid issues.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes surface treatments or coatings that enhance the part’s aesthetic and functional qualities. While this stage may not directly impact the STL export, it can influence the design specifications and tolerances, which need to be maintained throughout the manufacturing process. Ensuring that finishing requirements are well understood can help mitigate potential errors during the export phase.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Preventing STL Export Failures?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to ensuring that the manufacturing processes yield products that meet the required specifications. For B2B buyers, particularly those in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, adhering to international standards is crucial.
-
Relevant International Standards: Compliance with ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system, is often a baseline requirement. This standard emphasizes a process approach and the importance of continuous improvement, which can significantly reduce the likelihood of STL export failures. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area or API standards for oil and gas equipment should be considered.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Implementing a robust QC framework is essential. Common checkpoints include:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Assessing raw materials before they enter production ensures that only materials meeting quality standards are used.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the manufacturing process itself helps catch defects early, preventing flawed models from proceeding to export.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product before it is exported can prevent STL export failures due to design flaws or material inconsistencies. -
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods can be employed to validate the quality of the manufactured parts. These may include dimensional inspections, non-destructive testing (NDT), and functional testing. Each method provides insights into different aspects of the part’s integrity and functionality, ensuring that potential export issues are identified and rectified before they escalate.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures is paramount. Here are actionable steps to verify QC practices effectively:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits allow buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices firsthand. This can include reviewing documentation, observing production workflows, and interviewing key personnel.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their QC processes, results of inspections, and any corrective actions taken. These reports offer transparency and build trust between buyers and suppliers.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Employing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. These inspectors can evaluate compliance with international standards and ensure that the manufacturing processes align with the buyer’s specifications.
What Are the Nuances of QC and Certification for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the landscape of quality assurance and certification can be complex, particularly for B2B buyers operating in different regions. Here are some considerations:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding the local regulations and cultural expectations around quality can help buyers make informed decisions. For instance, the certification process in Europe may differ significantly from that in Africa or South America.
-
Documentation and Traceability: Ensure that suppliers maintain comprehensive documentation throughout the manufacturing process. This includes material certificates, test reports, and compliance documentation. Traceability can enhance accountability and facilitate smoother resolution of any issues related to STL export failures.
-
Building Long-term Relationships: Establishing strong, collaborative relationships with suppliers can lead to improved quality outcomes. Regular communication and feedback loops can help suppliers understand buyer expectations and adapt their QC practices accordingly.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can significantly reduce the likelihood of STL export failures in Fusion 360, thereby enhancing their overall product development and supply chain efficiency.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fusion 360 stl export failed’
To address the challenges faced by B2B buyers encountering ‘Fusion 360 STL export failed’ issues, this guide provides a practical checklist. Each step is designed to facilitate a smoother export process, ensuring efficiency and quality in your design workflow.
Step 1: Identify the Problematic Model
Understanding which specific model is causing the STL export failure is crucial. Begin by isolating the model in question and attempting to export it separately. This allows you to determine whether the issue is model-specific or related to your Fusion 360 settings.
- Tip: Review model complexity; overly intricate designs may exceed export capabilities.
Step 2: Check for Error Messages
Often, the software will provide minimal feedback when an export fails. Look for any error notifications that might offer clues regarding the failure. If no message appears, consider re-evaluating the export settings or trying a different export method.
- Tip: Document any error codes or messages for further troubleshooting or support requests.
Step 3: Simplify the Model Geometry
Complex geometries can hinder successful STL exports. Use Fusion 360’s tools to simplify the model, reducing the number of facets and triangles. This not only aids in successful exports but also improves printing performance.
- Tip: Utilize the “Reduce” feature under the mesh tools to maintain essential details while decreasing complexity.
Step 4: Verify Export Settings
Confirm that your export settings are appropriately configured. Select the correct output format (STL) and adjust the refinement options to balance quality and file size. Ensuring these settings align with your project requirements can prevent export failures.
- Tip: Experiment with different refinement settings to find the optimal balance for your model.
Step 5: Test Different Export Methods
If the standard export method fails, try using the “Save As Mesh” feature instead. This alternative approach may bypass issues related to the standard export process and provide a viable STL file.
- Tip: After saving as a mesh, check the file in a slicing software to ensure it’s usable for 3D printing.
Step 6: Check File Location and Permissions
Ensure that you have the necessary permissions to write files to your chosen export location. Exporting to a network drive or a location with restricted access may result in failure. Testing with a local directory can help isolate this issue.
- Tip: Always confirm write permissions by creating a simple test file in the intended directory before exporting.
Step 7: Seek Community and Professional Support
If issues persist, leverage community forums or professional support services for assistance. Engaging with other users who have faced similar challenges can provide insights or solutions that may not be immediately apparent.
- Tip: When seeking help, provide detailed information about your model, error messages, and the steps you’ve already taken.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their troubleshooting efforts when facing ‘Fusion 360 STL export failed’ issues, leading to more effective design and manufacturing processes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fusion 360 stl export failed Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Addressing Fusion 360 STL Export Failures?
When analyzing the costs associated with resolving Fusion 360 STL export failures, several key components must be considered. Materials include the software licenses and any additional tools required for troubleshooting or enhancing functionality. Labor costs involve the time spent by engineers and designers to diagnose and rectify the issues, which can vary significantly based on the complexity of the model and the skill level of the personnel involved.
Manufacturing overhead may encompass expenses related to software maintenance, updates, and IT support. Additionally, tooling costs could arise if specialized software tools are required for model optimization or error checking. Quality control (QC) is crucial, as ensuring the integrity of the exported STL files is essential for successful 3D printing or manufacturing. Finally, logistics costs may be relevant if physical prototypes are being shipped for validation or further testing, which could add to the overall expenditure.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Sourcing of Solutions for STL Export Failures?
Several factors influence pricing in the context of addressing STL export failures. Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) can significantly affect costs; larger orders may benefit from volume discounts, while smaller orders might incur higher per-unit costs. Specifications and customization of solutions—such as tailored software tools or specialized consulting services—can also drive up prices, as unique requirements often necessitate additional development time and resources.
The choice of materials and their quality can impact costs; for instance, higher quality software or services may come at a premium but can ultimately save money in the long run by reducing export failures. Supplier factors, such as reputation and support services, should not be overlooked, as reputable suppliers often provide additional value through customer support and reliability, justifying higher costs. Finally, understanding Incoterms is essential for international buyers, as they dictate shipping responsibilities and can affect overall pricing.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs When Dealing with STL Export Issues?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, a strategic approach to sourcing solutions for Fusion 360 STL export failures can lead to significant cost savings. Negotiation is key; understanding the market and leveraging competitive quotes from various suppliers can yield better pricing.
Considering cost-efficiency is essential, as the lowest initial price may not represent the best value over time. Evaluating the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes all expenses associated with the purchase, usage, and maintenance of a solution, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the financial implications.
Additionally, recognizing pricing nuances in international markets is crucial. Factors such as currency fluctuations, local regulations, and tariffs can influence pricing structures. Buyers should also be aware of potential hidden costs associated with cross-border transactions, such as customs duties or import taxes, which could impact the overall budget.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that prices for resolving Fusion 360 STL export failures can vary widely based on the specific circumstances of each case, including model complexity, the extent of required troubleshooting, and the geographical context of the buyer. Therefore, potential buyers should obtain tailored quotes and consider all variables when budgeting for these services.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fusion 360 stl export failed With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions for STL Export Issues
When facing challenges with exporting STL files in Fusion 360, businesses can benefit from exploring alternative solutions that may offer more reliability or efficiency. These alternatives can provide different functionalities, potentially reducing downtime and enhancing workflow. Below, we compare Fusion 360’s STL export failures with two viable alternatives: SolidWorks and Blender.
| Comparison Aspect | Fusion 360 STL Export Failed | SolidWorks | Blender |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Often fails with complex geometries; may lack error messages | Generally reliable; handles complex models well | Excellent for mesh modeling, but may require plugins for STL export |
| Cost | Subscription-based pricing; can be expensive for occasional users | High initial cost; maintenance fees apply | Free and open-source, offering significant cost savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Steeper learning curve; issues may require troubleshooting | User-friendly with comprehensive tutorials | Moderate learning curve; extensive community support available |
| Maintenance | Regular updates, but issues may persist | Frequent updates; stable performance | Active community provides ongoing support; frequent updates |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for integrated CAD workflows; when collaboration is key | Best for detailed engineering designs and simulations | Suited for artistic and complex mesh designs; great for 3D printing |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
SolidWorks
SolidWorks is a powerful CAD software widely recognized for its robust features, including excellent STL export functionality. Its performance with complex geometries is typically reliable, which minimizes the chances of export failures. However, SolidWorks comes with a higher price point, making it a less attractive option for smaller firms or those requiring infrequent use. The user interface is generally intuitive, and comprehensive tutorials are available, easing the learning curve for new users. SolidWorks is best suited for businesses engaged in detailed engineering projects where precision and reliability are critical.
Blender
Blender is a versatile open-source 3D modeling software that excels in mesh creation and manipulation. Its capabilities for exporting STL files are strong, particularly for creative projects or complex designs that require detailed mesh work. Since it is free, it offers significant cost savings for businesses, especially startups or freelancers. However, it may require additional plugins or manual adjustments for optimal STL export. While Blender has a moderate learning curve, it benefits from a vibrant community that provides extensive resources and support. It is ideal for businesses focused on artistic 3D modeling or those looking to prototype designs for 3D printing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for STL Export Needs
For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate solution for STL export issues hinges on specific business needs and use cases. If your primary focus is on engineering design with the need for reliability and precision, SolidWorks may be the best choice despite its higher cost. Conversely, if budget constraints are paramount and your work leans towards artistic modeling, Blender presents a compelling alternative. Understanding your workflow requirements and the nature of your projects will guide you in selecting the right tool to optimize your design processes and ensure successful STL exports.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fusion 360 stl export failed
What Are the Key Technical Properties Impacting Fusion 360 STL Export Failures?
When dealing with STL export failures in Fusion 360, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those in manufacturing and design. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
File Format Compatibility
The STL (Stereolithography) format is widely used for 3D printing, but not all software supports every version of this file type. Ensuring that Fusion 360 is compatible with the target printer’s software is vital. Exporting in the correct format can prevent failures and ensure seamless printing operations. -
Mesh Integrity
The integrity of the mesh structure is critical. A mesh should be manifold, meaning it has no holes or non-manifold edges, which can lead to export failures. B2B companies must ensure that their designs are free from these issues to avoid costly delays in production. -
Triangle Count
STL files represent 3D objects as a series of triangles. An excessively high triangle count can lead to export failures due to file size limits or processing power constraints. Optimizing triangle count while maintaining model fidelity is essential for efficient exporting and printing. -
Export Resolution
The resolution of the exported STL file can significantly impact both file size and detail. High-resolution exports yield detailed prints but can also lead to larger file sizes that may exceed software limits. Buyers should balance resolution with practicality based on their specific project needs. -
Material Specifications
Different materials used in 3D printing have unique properties that can affect the design and export process. Understanding the material’s thermal properties, tensile strength, and flexibility can inform design decisions that prevent STL export failures. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In 3D printing, maintaining appropriate tolerances is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly post-print. Poorly defined tolerances can lead to export issues, highlighting the need for precise engineering during the design phase.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Fusion 360 STL Export Failures?
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother communication and decision-making in B2B environments. Here are key terms relevant to STL export processes:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is important for ensuring that STL files meet specific standards required for integration into larger systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term denotes the smallest number of units that a supplier will sell. In the context of 3D printing, knowing the MOQ can help buyers determine the feasibility of producing parts based on their STL files. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to invite suppliers to bid on specific projects or products. B2B buyers should understand how to properly structure RFQs to ensure that their STL export requirements are clearly communicated to potential suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They are crucial for defining responsibilities regarding the delivery of goods, which can include the logistics of 3D printed parts. -
DPI (Dots Per Inch)
While primarily a term used in printing, DPI is also applicable in 3D printing to describe the resolution of a model. Higher DPI settings can yield more detailed prints but may complicate the export process. -
Post-Processing
This refers to any operations performed on a 3D printed part after the printing process, such as cleaning, painting, or finishing. Understanding post-processing requirements can help prevent STL export issues by ensuring that models are designed with these steps in mind.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, reducing the likelihood of STL export failures in Fusion 360 and enhancing their overall production efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fusion 360 stl export failed Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Affecting Fusion 360 STL Export Failures?
In recent years, the market for CAD software and 3D printing technologies has experienced significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing solutions. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international B2B buyers are focusing on optimizing design workflows, which has led to a surge in the adoption of software like Autodesk Fusion 360. However, challenges such as STL export failures have emerged as common pain points that can hinder production timelines and increase costs.
The primary drivers of these issues often stem from complex geometries, file corruption, or insufficient system resources, which are particularly impactful in regions where technical support may not be readily available. Emerging trends include the use of cloud-based platforms that allow for collaborative design, facilitating quicker troubleshooting for export issues. Additionally, the integration of AI and machine learning into CAD software is becoming more prevalent, providing automated solutions for error detection and optimization in design files.
B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing software solutions that offer robust support networks and community forums, enabling them to quickly resolve STL export failures. This trend emphasizes the importance of choosing platforms that not only provide powerful design tools but also foster a collaborative ecosystem for users to share solutions and best practices.
How Can B2B Buyers Embrace Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Fusion 360 STL Export Processes?
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is a growing concern for B2B buyers worldwide. As the industry shifts towards more sustainable practices, companies are under pressure to ensure their supply chains are not only efficient but also environmentally responsible. For those dealing with STL export failures in Fusion 360, considering the sustainability of materials and processes can mitigate environmental risks associated with 3D printing.
Ethical sourcing in the context of STL exports involves selecting suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled or biodegradable materials. Buyers should seek out suppliers who hold certifications like ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials in 3D printing not only reduces waste but also enhances a company’s reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
By embracing sustainability, B2B buyers can navigate market dynamics more effectively, ensuring that their operations align with global trends towards environmental responsibility. This approach not only addresses regulatory pressures but can also improve brand loyalty and open new market opportunities, particularly in regions where eco-friendly practices are highly valued.
What Is the Historical Context of STL Export Failures in CAD Software?
The evolution of CAD software and 3D printing technologies has significantly influenced the way designs are created and shared. Initially, STL (Stereolithography) files were introduced in the 1980s as a means of facilitating 3D printing processes. However, as software like Fusion 360 emerged, the complexity of design requirements increased, leading to more frequent STL export failures.
These failures often arise due to a combination of user error and software limitations. Over time, improvements in software capabilities have aimed to address these issues, including enhanced error reporting and automated troubleshooting features. As a result, users are now better equipped to understand the underlying causes of export failures, leading to more efficient design workflows.
The focus on user experience in software development has also led to the establishment of community forums and support networks, where users can share insights and solutions related to STL export challenges. Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as they seek to optimize their design processes and mitigate the risks associated with STL export failures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fusion 360 stl export failed
-
1. How do I solve the Fusion 360 STL export failure?
To troubleshoot STL export failures in Fusion 360, start by checking the model for any geometry issues. Ensure that the model is properly defined with no open edges or non-manifold geometry. You can also try exporting as a mesh or using the “Save As Mesh” option, ensuring that you select the appropriate bodies or components. Additionally, verify that you have the necessary permissions to save files in your chosen directory and try saving to a local drive rather than a network location. -
2. What should I do if I receive an error message when exporting STL files?
If you encounter an error message during the STL export process, first note the specifics of the error if provided. Common issues include file permissions, network issues, or model complexity. Ensure that you have selected a body or component before attempting to export. If the problem persists, consider simplifying the model by reducing the number of facets or checking for errors in the geometry. Engaging with the Autodesk community or technical support can also provide valuable insights. -
3. What is the best practice for customizing STL files for different 3D printers?
When customizing STL files for various 3D printers, consider the specific requirements of each printer, such as build volume, layer height, and material type. Use the slicing software associated with the printer to adjust settings like infill density, support structures, and print speed. It’s also advisable to maintain a balance between detail and printability, ensuring the model remains functional while meeting quality standards. Testing prototypes can help refine the settings before full-scale production. -
4. How do I ensure quality control when sourcing STL files internationally?
To ensure quality control when sourcing STL files from international suppliers, establish clear specifications and standards for the models. Use a quality assurance checklist that includes checks for geometry integrity, file format compatibility, and adherence to design requirements. Consider conducting sample prints before committing to larger orders to verify the model’s performance. Establishing strong communication channels with suppliers can also facilitate ongoing quality monitoring. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom STL file services?
Minimum order quantities for custom STL file services can vary significantly based on the supplier, project complexity, and production capabilities. Some suppliers may accept single-file orders, especially for prototyping, while others might have higher MOQs for bulk production. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and clarify their MOQ policies to find a suitable partner that aligns with your project requirements. -
6. What payment terms should I consider when working with STL file suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms with STL file suppliers, consider options such as upfront payments, deposits, or payment upon delivery. Establish clear terms regarding pricing, currency, and payment methods (e.g., wire transfer, credit card). Be mindful of potential currency exchange rates and international transaction fees. Additionally, consider using secure payment platforms that offer buyer protection, particularly when dealing with unfamiliar suppliers. -
7. How can I vet suppliers for STL file services in different regions?
Vetting suppliers for STL file services involves conducting thorough research into their background, experience, and client reviews. Look for certifications and industry affiliations that demonstrate their credibility. Additionally, request samples of their previous work to assess quality. Engaging with local industry associations or using platforms that facilitate supplier ratings can also provide insights into a supplier’s reliability and performance. -
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing STL files?
When sourcing STL files internationally, logistics considerations include shipping times, costs, and import/export regulations. Ensure that you understand the local laws regarding intellectual property and file sharing. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to customs or regulatory checks. Establishing a clear timeline for delivery and maintaining communication with your suppliers can help mitigate logistical challenges and ensure a smooth sourcing process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Fusion 360 Stl Export Failed Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Fusion 360 – 3D CAD, CAM, and CAE Tool
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Fusion 360 is a 3D CAD, CAM, and CAE tool that allows users to design and create 3D models. Users have reported issues with exporting STL and OBJ files for 3D printing, particularly with the software becoming unresponsive during the export process. Common troubleshooting steps include using the service tool to repair, resetting, reinstalling the software, and ensuring the latest version is install…
2. Bambu Lab – 3D Print Export Solutions
Domain: forum.bambulab.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Fusion 360, STL files, high refinement export, custom refinement, minimum error level, Bambu light gray basic PLA, X1C printer, silver silk filament, surface deviation settings, 3D Print Export feature.
3. Fusion 360 – Autodesk Translation Error Solutions
Domain: blog.jongallant.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: This company, Fusion 360 – Autodesk Translation Error Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Duet3D – 3D Printing Workflows
Domain: forum.duet3d.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Fusion360, SuperSlicer, and 3MF files are discussed in the context of 3D printing workflows. Users are trying to transition from STL to 3MF files, with the expectation that 3MF files can contain multiple parts for multi-color printing. Issues arise when attempting to export multiple bodies from Fusion360 as a single 3MF file, with users encountering errors and confusion over the export process. Th…
5. Prusa – 3D Printing Troubleshooting
Domain: forum.prusa3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: PrusaSlicer, Fusion 360, STL format, 3mf format, 3D printing, error message: ‘An object outside the print area was detected’, part dimensions: less than 2″ high and approx 1.5″ wide, troubleshooting suggestions include exporting as mesh in 3mf format and checking for remnants in the design.
6. Facebook – 3D Printing Issues
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – 3D Printing Issues, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Autodesk – Fusion 360 for Linux
Domain: github.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Autodesk Fusion 360 for Linux, Version: 2.0.15509 x86_64, Graphics card: Intel UHD Graphics 620, Driver version: 22.3.7, Operating system: Fedora 37, Desktop environment: GNOME 43.3, Issues: Stops working after a while, graphical area becomes gray with rendering glitches, corrupted visual elements when saving, file corruption messages, reproducible by locking the screen or leaving the part open fo…
8. All3DP – Fusion 360 STL Export Guide
Domain: all3dp.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Fusion 360 is a software by Autodesk that allows users to export STL files for 3D printing. The article provides a tutorial on three easy methods to export designs as STL files, emphasizing the simplicity of the process.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fusion 360 stl export failed
As businesses increasingly rely on advanced design software like Fusion 360, understanding the common challenges—such as STL export failures—becomes essential. The key takeaways for B2B buyers include recognizing the importance of file integrity and format compatibility, ensuring proper permissions for file saving, and utilizing community resources for troubleshooting. By addressing these issues proactively, companies can streamline their workflows and avoid costly delays.
Strategic sourcing plays a crucial role in optimizing these processes, allowing organizations to select the right tools and resources that align with their operational needs. It empowers businesses to leverage not only technology but also knowledge from global communities, enhancing their competitive edge in the market.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should remain vigilant and adaptable. Embracing best practices in software usage and collaboration will be vital for driving innovation and achieving sustainable growth. Equip your teams with the insights needed to overcome challenges, and consider partnerships that can further enhance your design capabilities. Take action today to ensure your organization is prepared for the future of design and manufacturing.