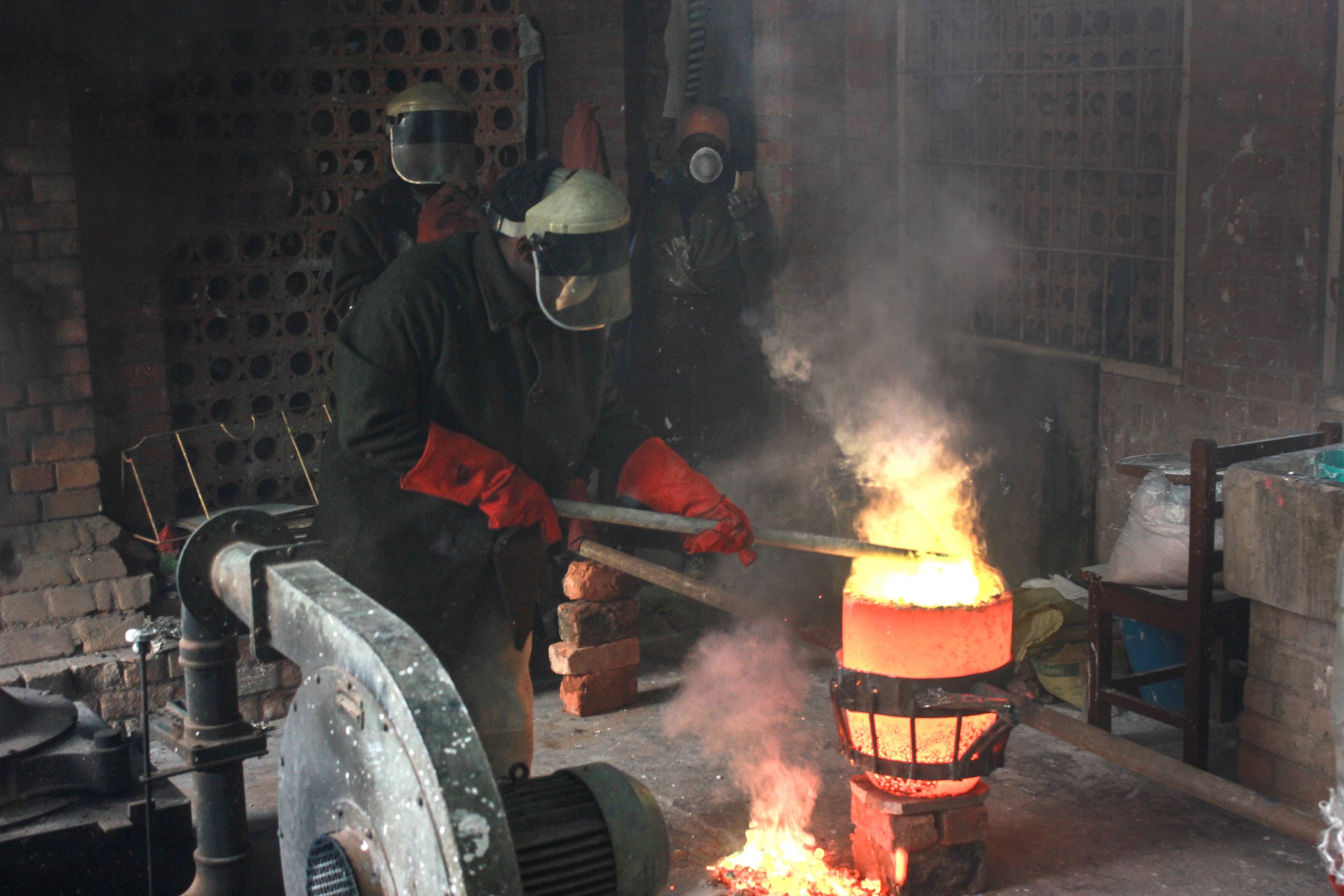
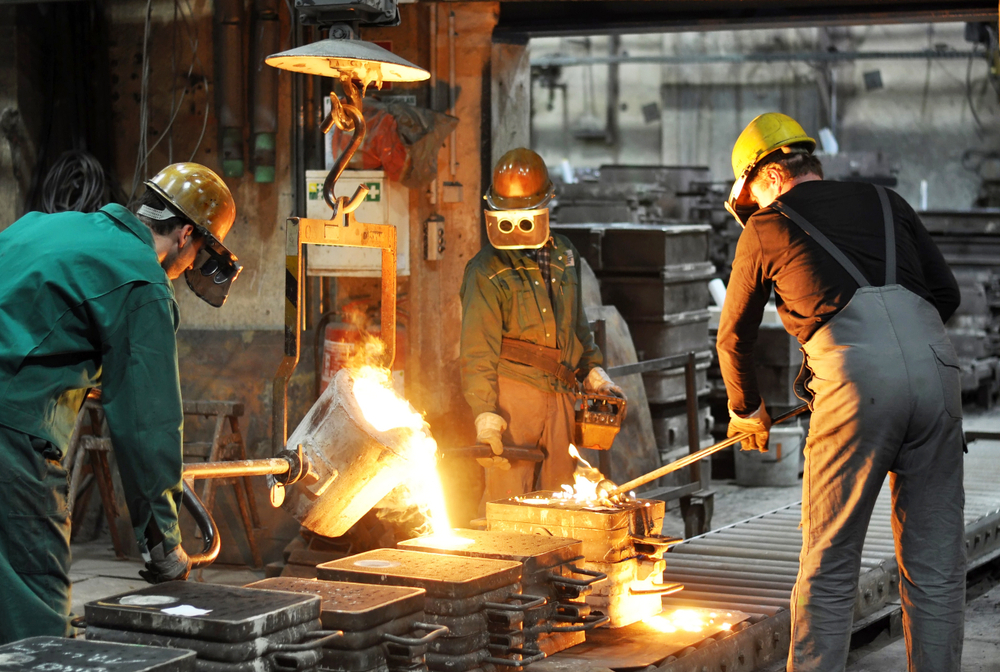
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fundicion de metales
The global market for fundición de metales presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers seeking to source high-quality metal castings efficiently. With a plethora of suppliers and processes available, navigating this landscape can be daunting, particularly when balancing cost, quality, and lead times. This guide is designed to equip you with the essential knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions.
In the following sections, we will explore various types of metal casting processes—including sand casting, pressure die casting, and investment casting—highlighting their applications across diverse industries. Additionally, we will provide insights into the critical factors for vetting suppliers, ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers capable of meeting your specifications. Understanding the cost structures associated with different casting methods will also be covered, enabling you to optimize your procurement strategy and budget effectively.
Whether you are based in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, this comprehensive guide will empower you to navigate the complexities of the metal casting market confidently. By arming yourself with the right information, you can enhance your supply chain resilience, reduce lead times, and ultimately drive greater value for your business.
Understanding fundicion de metales Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Uses sand molds; versatile for various sizes and shapes. | Automotive, machinery parts, art sculptures | Pros: Cost-effective, suitable for large parts. Cons: Surface finish may require additional machining. |
| Investment Casting (Lost Wax) | High precision and intricate designs using a wax pattern. | Aerospace, medical devices, jewelry | Pros: Excellent detail, smooth surface finish. Cons: Higher cost, longer lead times. |
| Die Casting | Utilizes high-pressure injection of molten metal into molds. | Mass production of small to medium parts | Pros: Fast production, consistent quality. Cons: High initial tooling costs. |
| Shell Molding | Thin-walled molds made from resin-bonded sand for better detail. | Automotive, industrial components | Pros: Good dimensional accuracy, smooth finish. Cons: More expensive than traditional sand casting. |
| Continuous Casting | Produces metal sections by continuously pouring molten metal. | Construction, railways, electrical conductors | Pros: High efficiency, reduced waste. Cons: Limited to specific shapes and sizes. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Sand Casting for B2B Buyers?
Sand casting is one of the oldest and most versatile metal casting methods. It involves creating molds from sand, which allows for the production of large and complex parts. This method is particularly advantageous for industries such as automotive and machinery, where large components are common. Buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of this method, especially for low to medium production volumes. However, they must also be aware that the surface finish may require additional machining to meet specific standards.
How Does Investment Casting (Lost Wax) Benefit Specialized Industries?
Investment casting, also known as lost wax casting, is ideal for producing intricate and high-precision components. This method is widely used in aerospace, medical devices, and jewelry manufacturing due to its ability to create complex shapes with excellent surface finishes. For B2B buyers, the precision offered by investment casting can lead to reduced post-processing costs and improved product quality. However, the trade-off includes higher costs and longer lead times, which may affect production schedules.
Why Choose Die Casting for High-Volume Production?
Die casting is characterized by the injection of molten metal into high-pressure molds, making it suitable for mass production of small to medium-sized parts. Industries such as automotive and consumer goods benefit from this method due to its speed and consistency in quality. B2B buyers should weigh the initial tooling costs against the efficiency and lower per-unit costs achieved through high-volume runs. While die casting offers many advantages, it may not be the best choice for low-volume applications due to the upfront investment required.
What Advantages Does Shell Molding Offer in Metal Casting?
Shell molding involves creating thin-walled molds from resin-bonded sand, providing superior dimensional accuracy and a smooth finish. This method is particularly beneficial for automotive and industrial component manufacturers looking for high-quality parts. B2B buyers should consider shell molding when precision and surface quality are critical. However, it is generally more expensive than traditional sand casting, so buyers must evaluate their budget against the required quality levels.
How Does Continuous Casting Enhance Efficiency in Metal Production?
Continuous casting is a highly efficient method that produces metal sections by continuously pouring molten metal into a mold. This process is predominantly used in the construction and electrical industries for producing long metal shapes. B2B buyers can benefit from the reduced waste and high efficiency associated with continuous casting, making it a cost-effective option for large-scale production. However, its limitations in terms of shape and size may restrict its applicability for more complex designs.
Key Industrial Applications of fundicion de metales
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fundicion de metales | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine Blocks and Cylinder Heads | Enhanced durability and performance in high-stress environments | Need for precision engineering and compliance with safety standards |
| Aerospace | Turbine Components | Lightweight yet strong components that withstand extreme conditions | Certification requirements and material traceability are critical |
| Construction | Structural Steel Components | Cost-effective solutions for large-scale projects | Sourcing from reliable suppliers with robust quality assurance processes |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline Fittings and Valves | Corrosion resistance and reliability in harsh environments | Importance of sourcing materials that meet international standards |
| Consumer Goods | Kitchenware and Appliances | Design flexibility and enhanced aesthetic appeal | Need for quick turnaround times and scalability in production |
How is ‘fundicion de metales’ Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, fundicion de metales is crucial for manufacturing engine blocks and cylinder heads, which are essential components of vehicles. The casting process allows for the production of complex shapes that are both durable and lightweight, enhancing engine performance and fuel efficiency. Buyers in this industry must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality standards and regulations, particularly regarding material specifications and environmental compliance.
What Role Does Metal Casting Play in Aerospace Applications?
The aerospace industry relies heavily on fundicion de metales for producing turbine components, where precision and strength are paramount. These components must endure extreme temperatures and pressures, making the choice of material and casting method critical. International buyers need to prioritize suppliers who can provide certified materials and demonstrate compliance with rigorous aerospace standards to ensure safety and reliability in their products.
How is Metal Casting Beneficial for Construction Projects?
In construction, fundicion de metales is used to create structural steel components, which are vital for the integrity and safety of buildings and infrastructure. The casting process offers cost-effective solutions for producing large quantities of components with consistent quality. Buyers should focus on sourcing from suppliers that offer robust quality assurance processes and can provide timely deliveries to meet project deadlines.
Why is Metal Casting Important in the Oil & Gas Industry?
For the oil and gas sector, fundicion de metales is essential for manufacturing pipeline fittings and valves that must withstand corrosive environments and high pressures. The reliability of these components directly impacts operational safety and efficiency. Buyers should consider sourcing materials that meet international standards and ensure traceability, as well as evaluating suppliers’ experience in producing specialized components for the industry.
How Does Metal Casting Enhance Consumer Goods Manufacturing?
In the consumer goods sector, fundicion de metales is utilized for creating kitchenware and appliances that combine functionality with aesthetic appeal. The casting process allows manufacturers to produce intricate designs while maintaining durability. Buyers in this market should seek suppliers that can offer quick turnaround times and scalable production capabilities to meet fluctuating consumer demands while ensuring high-quality standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fundicion de metales’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Precision in Metal Casting
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges when it comes to achieving high precision in metal casting processes. This is particularly critical for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where even the slightest deviation can lead to catastrophic failures. Buyers may struggle with inaccurate patterns, leading to casting defects such as misalignment, porosity, or surface irregularities. These issues not only result in wasted materials and increased production costs but can also lead to costly recalls and damage to brand reputation.
The Solution: To enhance precision in metal casting, buyers should consider integrating advanced technologies such as 3D printing in the pattern-making phase. By using CAD software to design patterns, manufacturers can ensure accuracy and create complex geometries that traditional methods may not achieve. Additionally, investing in high-quality materials for both the patterns and molds is essential. Buyers should source materials specifically designed for their casting processes, ensuring that they can withstand the thermal and mechanical stresses involved. Finally, implementing a rigorous quality control process that includes dimensional inspections and non-destructive testing can help identify issues early, ensuring that only high-precision castings proceed to production.
Scenario 2: High Costs Associated with Metal Casting Processes
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the metal casting sector find themselves grappling with escalating costs, particularly in labor, materials, and energy consumption. Fluctuations in raw material prices can significantly impact overall production costs, while inefficient processes can lead to unnecessary expenditures. Buyers may also face challenges in meeting tight deadlines, forcing them to opt for more expensive solutions that compromise profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate these cost concerns, buyers should explore the possibility of automating parts of their casting processes. Automation can streamline workflows, reduce labor costs, and enhance consistency in production. Investing in energy-efficient equipment can also lead to significant savings on utility bills over time. Additionally, buyers should consider establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers who offer competitive pricing on raw materials. This approach not only helps stabilize costs but also allows for better negotiation terms. Finally, buyers can benefit from adopting lean manufacturing principles, which focus on minimizing waste and optimizing processes to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Material Selection for Specific Applications
The Problem: Selecting the right material for metal casting applications is a common pain point for B2B buyers, especially when the required properties of the final product are critical for performance. Buyers may struggle to understand the nuances between different metals and alloys, leading to suboptimal choices that affect durability, weight, and resistance to environmental factors. For example, using a non-ferrous alloy instead of a ferrous one may lead to issues with strength and longevity in high-stress applications.
The Solution: To address material selection challenges, buyers should begin with a thorough analysis of their application requirements, including factors such as strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal properties. Consulting with materials scientists or industry experts can provide valuable insights into the best choices for specific applications. It is also advisable to utilize material databases that offer comparative data on various metals and alloys. Additionally, buyers should consider prototyping with different materials before committing to large-scale production. This approach allows for testing and validation of the material’s performance in real-world conditions, ensuring that the final product meets all necessary specifications and requirements.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fundicion de metales
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Metal Casting?
When selecting materials for metal casting, understanding the properties and suitability of various metals is essential for achieving optimal product performance. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the metal casting industry, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
1. Aluminum Alloys
Key Properties: Aluminum alloys are known for their lightweight nature, excellent corrosion resistance, and good thermal and electrical conductivity. They can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum alloys is their low density, which contributes to reduced shipping costs and ease of handling. They also offer good machinability and can be cast into complex shapes. However, they have lower strength compared to ferrous metals and may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum alloys are commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and consumer products due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio. They are particularly effective in environments where corrosion resistance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN, particularly regarding alloy specifications. The availability of aluminum alloys may vary by region, and sourcing from local suppliers can reduce lead times.
2. Cast Iron
Key Properties: Cast iron is characterized by its high wear resistance, excellent castability, and good machinability. It can withstand high temperatures and has a high damping capacity, making it ideal for vibration-prone applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability and wear resistance of cast iron make it a preferred choice for heavy-duty applications, such as engine blocks and machinery bases. However, it is relatively brittle, which can lead to cracking under sudden impacts. Additionally, the weight of cast iron can increase shipping costs.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is widely used in construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries. Its ability to absorb vibrations makes it suitable for applications like machinery bases and tool holders.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the different grades of cast iron (e.g., gray, ductile) and their respective properties. Compliance with local standards is crucial, especially in regions with stringent manufacturing regulations.
3. Steel Alloys
Key Properties: Steel alloys offer high tensile strength, toughness, and ductility. They can be engineered to meet specific performance criteria, including high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The versatility of steel alloys allows for a wide range of applications, from construction to automotive. However, they can be more expensive than other materials and may require additional processing, such as heat treatment, to achieve desired properties.
Impact on Application: Steel alloys are commonly used in structural components, automotive parts, and heavy machinery due to their strength and durability. Their ability to be heat-treated enhances their performance in high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of specific steel grades and their compliance with international standards such as JIS and ASTM. Additionally, understanding local market conditions can influence sourcing decisions.
4. Bronze
Key Properties: Bronze is an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, known for its excellent corrosion resistance, low friction properties, and good machinability. It can withstand high temperatures and is suitable for marine applications.
Pros & Cons: The corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal of bronze make it ideal for decorative applications and marine environments. However, it is generally more expensive than other metals and can be more challenging to cast due to its lower fluidity.
Impact on Application: Bronze is commonly used in marine hardware, sculptures, and electrical connectors due to its resistance to corrosion and wear. Its low friction properties also make it suitable for bearings and bushings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific alloy compositions and their compliance with international standards. The availability of bronze may vary by region, and sourcing from reliable suppliers is essential for maintaining quality.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Metal Casting
| Material | Typical Use Case for fundicion de metales | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Automotive, aerospace, consumer products | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than ferrous metals | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Engine blocks, machinery bases | High wear resistance | Brittle and heavy | Medium |
| Steel Alloys | Structural components, automotive parts | High tensile strength | More expensive and requires processing | High |
| Bronze | Marine hardware, sculptures | Excellent corrosion resistance | More expensive and challenging to cast | High |
This guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers in selecting the most suitable materials for metal casting, ensuring compliance with local standards and optimizing product performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fundicion de metales
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Fundición de Metales?
The manufacturing process of fundición de metales involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality metal parts. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers looking to evaluate potential suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Fundición de Metales?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Manufacturers typically work with various metals, including ferrous metals (like iron and steel) and non-ferrous metals (such as aluminum, copper, and zinc). The choice of material often depends on the intended application of the final product, as each metal has unique properties that can affect performance and durability.
In addition to the primary metal, manufacturers may also use alloys, which combine two or more metals to achieve specific mechanical properties. For instance, aluminum alloys can provide enhanced strength and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for automotive and aerospace applications.
How Is the Forming Process Executed in Fundición de Metales?
The forming stage involves creating the pattern and mold, which are essential for shaping the metal.
-
Creating the Pattern: The process begins with the creation of a pattern, which serves as a model for the mold. Patterns can be made from various materials, including wood, plastic, or even 3D-printed models using advanced techniques. The pattern must consider the metal’s contraction during cooling, which requires it to be slightly larger than the intended final shape.
-
Mold Production: Once the pattern is prepared, the next step is mold creation. Molds can be either reusable (typically made of metal) or disposable (made of sand, plaster, or ceramic). For complex shapes, manufacturers may employ techniques like lost-wax casting, where a wax pattern is melted away to leave a hollow cavity for the metal.
-
Melting and Pouring the Metal: After the mold is ready, the metal is melted in a furnace. Different metals require varying temperatures for melting; for instance, aluminum melts at around 660°C, while iron requires about 1,540°C. Once melted, the metal is poured into the mold, where it cools and solidifies.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in Fundición de Metales?
Once the metal has cooled, the finishing stage begins. This involves several processes designed to enhance the final product’s appearance and functionality:
-
Mold Removal: Depending on the type of mold used, the removal process can vary. For reusable molds, mechanical methods are often employed, while disposable molds may be broken away.
-
Surface Treatment: Common finishing techniques include grinding, polishing, and sandblasting. These processes help to remove any imperfections and achieve the desired surface finish.
-
Machining: For precision components, machining may be necessary to meet exact specifications. This can include drilling, milling, or turning to achieve the required dimensions and tolerances.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Fundición de Metales?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the fundición de metales process, ensuring that the final products meet industry standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on effective quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for European products or API standards for the oil and gas industry, can indicate compliance with relevant safety and performance requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Fundición de Metales?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks raw materials and components before they enter the production line, ensuring they meet predefined quality standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages helps identify any deviations from quality standards early in the process. This can involve regular inspections and tests of the molds, patterns, and the molten metal.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the casting process, FQC involves thorough inspections of the finished products. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests to confirm that the parts meet the required specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify a Supplier’s Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can verify a supplier’s quality control practices through several methods:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing process and quality assurance protocols firsthand. This can reveal insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting documentation of quality control processes, including inspection reports and certifications, can provide assurance of compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an extra layer of verification, ensuring that the supplier’s products meet the necessary quality benchmarks.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Factors such as local regulations, industry standards, and cultural practices can significantly impact the quality assurance processes of suppliers.
In some regions, local certifications may be as critical as international ones. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can navigate both local and international quality standards to facilitate smoother transactions and compliance with import regulations.
Furthermore, language barriers and differing business practices can complicate communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear lines of communication and setting explicit quality requirements can help bridge these gaps and foster successful international partnerships.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in fundición de metales is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions and establish strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fundicion de metales’
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring metal casting services. By following these steps, you can ensure that you select the right suppliers and processes that meet your technical and commercial needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications of the metal components you need, including dimensions, tolerances, and material types. This is critical as it ensures that potential suppliers understand your requirements and can provide accurate quotes. Additionally, identifying whether you require ferrous or non-ferrous metals will help narrow down your options.
Step 2: Research Casting Processes
Familiarize yourself with the various casting processes available, such as sand casting, investment casting, and die casting. Each method has distinct advantages and is suited for different applications, so understanding these will help you communicate your needs effectively to suppliers. Look for a process that aligns with your production volume and complexity of the design.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Pay attention to their experience in specific casting processes and the types of metals they work with to ensure they can meet your specifications.
- Check Certifications: Verify if the supplier holds relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) that demonstrate their commitment to quality and compliance with industry standards.
- Assess Production Capabilities: Confirm their production capacity and lead times to ensure they can meet your project deadlines.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Ask potential suppliers for samples or prototypes of previous work to assess their quality. This step is vital as it allows you to evaluate the craftsmanship and precision of their casting process. Ensure that the samples align with your specifications and quality expectations.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions regarding pricing structures and payment terms. Be transparent about your budget and inquire about volume discounts or long-term partnership agreements. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including shipping and handling, will help you make a more informed decision.
Step 6: Review Quality Control Processes
Inquire about the quality control measures implemented by the supplier throughout the casting process. A robust quality assurance system is essential to ensure that the final products meet the required standards. Look for suppliers who use modern testing methods, such as non-destructive testing (NDT), to ensure product integrity.
Step 7: Establish Communication Protocols
Set clear communication channels and expectations for updates throughout the production process. Effective communication is key to addressing any concerns or changes that may arise, ensuring that both parties remain aligned. Determine who will be your point of contact and establish a timeline for regular check-ins.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing metal casting services with confidence, ensuring they select the right partners to fulfill their manufacturing needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fundicion de metales Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Metal Casting Sourcing?
When considering sourcing for metal casting, understanding the cost structure is paramount. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of metals significantly impacts costs. Ferrous metals like steel are generally less expensive than non-ferrous metals such as aluminum and copper. Additionally, the quality and source of these materials can lead to fluctuations in price.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in the metal casting process, particularly for intricate designs and quality control. Labor costs vary widely based on geographical location and the complexity of the casting process.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Overhead costs can be substantial, especially in regions with high energy prices or stringent regulatory requirements.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs encompass the creation of molds and patterns, which can be a significant upfront investment. The type of tooling (reusable vs. disposable) also affects costs. For instance, 3D-printed patterns may reduce lead time but could have higher initial costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous QC processes is essential, especially for B2B transactions where specifications are critical. Investments in testing and inspection equipment can add to overall costs.
-
Logistics: Transporting raw materials and finished products can influence costs, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as shipping methods, distance, and customs duties need to be considered.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary based on the market dynamics and the level of competition. Understanding these margins can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Metal Casting Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in the metal casting industry:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs, but they also require upfront capital investment.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized components typically incur higher costs due to the additional labor and materials required. Standardized products may offer cost savings.
-
Materials: The choice of specific alloys or grades directly impacts costs. For instance, specialty alloys designed for high-performance applications are usually more expensive than standard materials.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific industry certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can incur higher costs due to additional testing and compliance processes.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers, as they determine who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs clearance. This can significantly impact the total landed cost.
What Tips Should Buyers Consider for Cost-Efficiency in Metal Casting?
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing, terms, and conditions. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price. Consider factors such as maintenance, durability, and performance, which can influence the overall cost over the product’s lifecycle.
-
Assess Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs can yield savings, but consider the trade-offs in quality and delivery times.
-
Understand Market Trends: Keep an eye on market trends affecting metal prices, such as supply chain disruptions or changes in demand, which can influence costs.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Whenever feasible, consider local suppliers to reduce logistics costs and lead times. This can be particularly beneficial for urgent projects.
Disclaimer
The prices and costs discussed are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure the most accurate and competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fundicion de metales With Other Solutions
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting the most suitable metal fabrication method for their specific needs. While fundición de metales (metal casting) remains a cornerstone of metal production, there are alternative solutions available that may offer distinct advantages depending on the application. This section explores these alternatives, enabling informed decision-making for businesses looking to optimize their manufacturing processes.
| Comparison Aspect | Fundición De Metales | 3D Metal Printing | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and detail for complex shapes. | Excellent for rapid prototyping and low-volume production. | High throughput and consistency for large production runs. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; cost-effective for large batches. | Higher per-unit costs; ideal for small batches. | High setup costs; economical for mass production. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and specialized equipment. | Requires CAD software and 3D printers; relatively easy to implement. | Complex setup and tooling required; longer lead times for molds. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance of molds and melting equipment needed. | Minimal maintenance; software and printer upkeep necessary. | Maintenance focused on molds; potential downtime for repairs. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for creating intricate designs and metal parts in various industries. | Best suited for prototyping and custom parts where design flexibility is crucial. | Optimal for high-volume production of identical parts with high precision. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Metal Printing?
3D metal printing has emerged as a compelling alternative to traditional metal casting. This technology allows for rapid prototyping and can produce highly complex geometries that are often challenging to achieve with conventional methods. One significant advantage is the ability to create parts without the need for tooling, which drastically reduces lead times. However, the downside includes higher per-unit costs, making it less suitable for large-scale production. 3D printing is best utilized in industries requiring customization and innovation, such as aerospace and medical devices.
How Does Injection Molding Compare to Fundición De Metales?
Injection molding is another viable alternative, particularly for high-volume production. This method involves injecting molten material into a mold, which then cools and solidifies. The primary advantage of injection molding is its efficiency in producing large quantities of consistent parts with minimal variance. However, the initial setup costs can be high due to the need for custom molds, making it less attractive for small production runs. Injection molding is commonly used in the manufacturing of plastic parts but can also handle certain metal alloys, making it a versatile option for manufacturers looking to scale their production effectively.
Conclusion: Which Metal Fabrication Solution Is Right for Your Business?
When choosing between fundición de metales and its alternatives, B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements, including production volume, desired part complexity, and budget constraints. Fundición de metales excels in creating intricate designs and is cost-effective for larger batches, while 3D metal printing offers flexibility for prototypes and custom parts. On the other hand, injection molding is unmatched in efficiency for mass production. By evaluating these factors, businesses can select the most appropriate solution to meet their operational goals and enhance their competitive edge in the market.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fundicion de metales
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Metal Casting?
When engaging in metal casting, understanding the critical technical properties is essential for ensuring the quality and performance of the final products. Here are some of the most significant specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of metals based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties. Common grades include various types of steel, aluminum alloys, and bronze. The selection of material grade is crucial because it directly affects the strength, durability, and corrosion resistance of the cast products. B2B buyers must ensure the chosen grade meets the specific requirements of their applications to avoid costly failures. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the manufacturing process. In metal casting, maintaining tight tolerances is vital for parts that must fit together or function in a specific way. Poor tolerance can lead to assembly issues or performance failures. Understanding tolerances helps buyers set clear expectations and ensures that suppliers can meet the required standards. -
Casting Surface Finish
Surface finish is the texture of the cast product’s surface, which can impact its aesthetic and functional properties. Common surface finishes include rough, polished, and anodized. A proper surface finish is essential for applications where appearance matters or where surface friction can affect performance. Buyers should specify their surface finish requirements to ensure compatibility with end-use conditions. -
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity refers to the ability of a material to conduct heat. Different metals have varying thermal properties, affecting how they perform in high-temperature applications. For example, copper has high thermal conductivity, making it suitable for heat exchangers, while aluminum is often chosen for its lightweight and moderate conductivity. Understanding thermal conductivity helps buyers select the appropriate material for temperature-sensitive applications. -
Ductility and Toughness
Ductility is the ability of a material to deform under tensile stress, while toughness measures its ability to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing. These properties are critical for applications requiring parts to withstand stress and strain, such as automotive components. Buyers should inquire about these properties to ensure the selected materials will perform adequately under operational conditions.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in Metal Casting?
Navigating the metal casting industry involves familiarizing oneself with specific jargon and trade terms that facilitate communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are several key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In metal casting, OEMs often require custom parts designed to fit their specific needs. Understanding the role of OEMs helps buyers identify potential suppliers who can meet their unique manufacturing requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant in metal casting, where production costs can be high. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to manage inventory levels and ensure they meet their production needs without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. Providing detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes and better negotiations. This process is crucial for B2B buyers to secure competitive pricing and favorable terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thus minimizing disputes and enhancing supply chain efficiency. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the total time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. In metal casting, lead times can vary significantly based on the complexity of the parts and the manufacturing processes involved. Buyers should account for lead times in their planning to ensure timely delivery and project execution.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions in the metal casting sector, ensuring they procure the right materials and services that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fundicion de metales Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Fundición de Metales Sector?
The global fundición de metales market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and economic shifts. Key market drivers include the growing automotive and aerospace industries, which increasingly rely on lightweight yet durable metal components. Additionally, the rising demand for custom and complex metal parts has led to the integration of advanced manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing and automation in traditional casting processes. This trend not only enhances production efficiency but also reduces lead times, making it particularly attractive to international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Emerging B2B sourcing trends in the sector include a shift towards digital platforms for procurement, enabling buyers to access a wider array of suppliers and streamline their purchasing processes. The adoption of Industry 4.0 principles, such as IoT integration and data analytics, is also becoming prevalent, allowing manufacturers to optimize their operations and improve quality control. For buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions and establishing competitive advantages in their respective markets.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Fundición de Metales Sector?
Sustainability has become a pressing concern in the fundición de metales sector, as environmental regulations tighten and consumers demand greener practices. The environmental impact of metal casting can be significant, encompassing energy consumption, emissions, and waste production. Consequently, international B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices. This includes implementing energy-efficient technologies, recycling scrap metal, and utilizing environmentally friendly materials in their processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers look for partners who adhere to fair labor practices and transparent supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are gaining traction. Moreover, the use of “green” materials, such as recycled alloys and eco-friendly coatings, is becoming a standard expectation. Buyers who align with suppliers that prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing not only mitigate risks but also enhance their brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What is the Historical Context of the Fundición de Metales Sector?
The fundición de metales process boasts a rich history that dates back over 7,000 years, originating in ancient civilizations where metal casting was employed for both functional and artistic purposes. The earliest known example of metal casting is a copper frog from 3200 B.C. in modern-day Iraq. Over the centuries, techniques have evolved significantly, with the introduction of various methods such as lost-wax casting and sand casting, which laid the foundation for contemporary practices.
By the 20th century, technological advancements propelled the sector forward, introducing methods that enhanced precision and efficiency. The integration of digital technologies, particularly 3D printing, into traditional casting processes is a recent development that illustrates the sector’s adaptability to modern manufacturing demands. Understanding this historical context provides B2B buyers with valuable insights into the evolution of practices that can influence their sourcing strategies today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fundicion de metales
-
1. How can I ensure the quality of metal castings from suppliers?
To guarantee quality in metal castings, establish clear quality assurance (QA) standards before engaging with suppliers. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 to confirm adherence to international quality management systems. Conduct on-site audits or request samples for testing. Additionally, consider suppliers with a proven track record of delivering high-quality products and customer testimonials. Regular communication and feedback loops with the supplier can also help in maintaining standards throughout the production process. -
2. What are the typical payment terms for international metal casting suppliers?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers, but common practices include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining 70% upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms based on your business relationship and order volume. Always clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, letters of credit, or PayPal. Ensure that you also understand any associated fees and currency conversion rates, especially when dealing with international transactions. -
3. What factors should I consider when vetting metal casting suppliers?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience in the industry, production capacity, and technological capabilities. Check for certifications and compliance with international standards. Evaluate their ability to meet your specific requirements, including customization options and minimum order quantities (MOQs). Additionally, assess their reputation through reviews and references. Proximity to your location can also influence lead times and shipping costs, making it a critical factor in your decision. -
4. How can I customize metal castings to fit my specific needs?
Customization of metal castings typically begins with a detailed design specification. Collaborate with your supplier to discuss material choices, dimensions, and finishes that meet your requirements. Advanced technologies like 3D printing can facilitate the creation of complex patterns and molds, enabling more intricate designs. Be prepared to share prototypes or CAD models to ensure alignment with your vision. Understand the implications of customization on lead times and costs, as these may vary based on complexity. -
5. What are the common types of metal casting processes available?
Common metal casting processes include sand casting, investment casting (lost wax), die casting, and ceramic mold casting. Each method has its advantages depending on the application: sand casting is ideal for large parts, investment casting offers precision for complex shapes, and die casting is efficient for high-volume production of small components. Discuss your specific needs with suppliers to determine the most suitable casting process for your project, considering factors such as material type and production volume. -
6. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for metal castings?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for metal castings vary by supplier and are influenced by factors such as production capabilities and material costs. Typically, MOQs can range from a few pieces for custom orders to hundreds or thousands for standard products. Discuss your project requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that fit your business model. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for new clients or smaller projects, so it’s worth exploring options based on your needs. -
7. How do logistics and shipping impact the sourcing of metal castings?
Logistics and shipping play a crucial role in the sourcing process. Factors such as the supplier’s location, shipping methods, and delivery times can affect your overall costs and timelines. Ensure that your supplier has a reliable logistics partner to avoid delays. Understand the incoterms applicable to your order, as these define responsibilities for shipping costs and risk. It’s also wise to factor in customs regulations and duties when importing metal castings to avoid unexpected fees. -
8. What are the environmental considerations in metal casting?
Environmental considerations in metal casting include waste management, emissions control, and energy consumption. Suppliers should comply with local and international environmental regulations. Inquire about their sustainability practices, such as recycling scrap metal and using eco-friendly materials. Additionally, consider suppliers that invest in energy-efficient technologies and processes to reduce their carbon footprint. By choosing environmentally responsible partners, you can enhance your own sustainability efforts and meet regulatory requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Fundicion De Metales Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. 3DS – Fundición y Moldeo de Materiales
Domain: 3ds.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: La fundición es un proceso de moldeo de 6.000 años que consiste en llenar un molde con material líquido que se enfría y solidifica. Se utilizan metales y materiales de fraguado en frío como epoxi, hormigón, yeso o arcilla. Los principales tipos de fundición son metálicos y no metálicos. La fundición de metales implica calentar el metal hasta su estado líquido y verterlo en un molde, mientras que l…
2. SPEE3D – Metal Casting Technologies
Domain: spee3d.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: SPEE3D ofrece productos relacionados con la fundición de metales, incluyendo tecnologías de impresión 3D. Los productos mencionados son: UEM, XSPEE3D, WarpSPEE3D y LightSPEE3D. La fundición de metales es un proceso antiguo que implica verter metal fundido en un molde para crear objetos metálicos. Se utilizan diferentes metales y aleaciones, como metales ferrosos (acero, fundición maleable, fundici…
3. Amelt – Hornos de Fundición de Hierro y de Inducción
Domain: amelt.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Amelt ofrece cuatro tipos de hornos de fundición: 1. Hornos de fundición de hierro: diseñados para fundir y colar hierro, soportan altas temperaturas y son esenciales para producir piezas de fundición de hierro de alta calidad. 2. Hornos de inducción: fáciles de manejar, pueden producir 65 toneladas de acero por carga, utilizan un crisol rodeado por un electroimán de cobre para generar calor sin a…
4. Xometry – Fundición a Presión
Domain: xometry.pro
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: La fundición a presión es un proceso de fabricación que inyecta metal fundido en un molde para crear piezas metálicas precisas y duraderas. Es ideal para la producción en serie de componentes con gran precisión dimensional, utilizado en industrias como la automoción, aeroespacial y electrónica de consumo. Los pasos del proceso incluyen el diseño del molde, preparación del metal, inyección, fundici…
5. Wayken – Fundición de Metales
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: La fundición de metales es un proceso que implica verter metal fundido en moldes para crear piezas brutas. Los procesos de fundición son esenciales en la fabricación de maquinaria, representando una gran proporción de piezas clave, como las de motores de combustión interna. Los principales tipos de fundición incluyen: 1. Fundición en arena: económica y resistente al calor, adecuada para piezas gra…
6. Ielektro – Fundición de Metales
Domain: ielektro.es
Introduction: La fundición de metales se descubrió hace 5000 años, durante la Edad del Cobre (alrededor del 3000 a.C.), permitiendo la producción de objetos útiles a partir de minerales como la malaquita y la calcopirita. La transición a la Edad del Bronce (alrededor del 3300 a.C.) introdujo la aleación de cobre con estaño, creando bronce, que era más duradero y útil. La fundición de hierro, descubierta alreded…
7. Asociación Metal – Fundición de Piezas Metálicas
Domain: asociacionmetal.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: La fundición es un proceso de fabricación de piezas metálicas que implica fundir un material e introducirlo en un molde donde se solidifica. Los metales y aleaciones utilizados incluyen hierro, acero, latón, bronce, aluminio, titanio, cromo, níquel, magnesio, y metales tóxicos como berilio, cadmio y torio. El proceso incluye la construcción de un modelo, fabricación de moldes y machos, y etapas de…
8. EIPP – Forja y Fundición
Domain: eippcb.jrc.ec.europa.eu
Introduction: Forja y fundición: Procesos en forjas y fundiciones, incluyendo forjado con martillos (energía de impacto > 50 kJ, potencia calorífica > 20 MW), fundición de metales ferrosos (> 20 toneladas/día), y fundiciones de metales no ferrosos (> 4 toneladas/día para plomo, > 20 toneladas/día para otros metales). Procesos de forja: tratamiento térmico y metalúrgico, forja/martillado, mecanizado, refrigeraci…
9. Aleaciones y Fundidos – Fundición de Metales para Construcción
Domain: aleacionesyfundidos.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: La fundición de metales contribuye a la innovación en construcción mediante la creación de herramientas, maquinaria, elementos estructurales (vigas y columnas), soportes, componentes de infraestructura (juntas, placas), sistemas de tuberías y alcantarillado (tuberías, válvulas, tapas), y elementos ornamentales (barandillas, balaustradas). Los tipos de metales utilizados incluyen hierro, aluminio, …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fundicion de metales
What Are the Key Takeaways for Strategic Sourcing in Metal Casting?
In the realm of metal casting, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Emphasizing the importance of selecting reliable suppliers who utilize modern techniques—such as 3D printing in pattern creation—can significantly enhance product quality while reducing lead times. Understanding the nuances of different metal casting methods, including pressure die casting and sand casting, allows businesses to align their sourcing strategies with specific project requirements, ensuring tailored solutions that meet diverse market demands.
How Can B2B Buyers Enhance Their Metal Casting Procurement?
By prioritizing partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to innovation and quality control, buyers can secure a competitive edge in their respective industries. The integration of advanced technologies not only streamlines production but also fosters sustainability, a critical consideration for many international markets today.
What Does the Future Hold for Metal Casting Suppliers and Buyers?
As the global landscape for metal casting evolves, international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should remain proactive in exploring emerging trends and technologies. Engaging in strategic sourcing initiatives that embrace innovation will not only enhance operational resilience but also position businesses for long-term growth in an increasingly competitive environment. Embrace the future of metal casting—start building your strategic sourcing framework today!