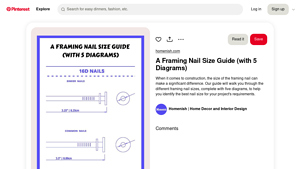
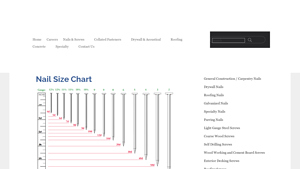
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for framing nail size chart
In the competitive landscape of construction materials, sourcing the right framing nail size chart can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With a multitude of nail types, lengths, and coatings available, making an informed decision is crucial to ensuring structural integrity and project efficiency. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of framing nails, including various types such as 16d, 10d, and 8d nails, their specific applications in different framing scenarios, and the importance of selecting nails based on the type of lumber used.
Furthermore, we will explore the nuances of supplier vetting, allowing you to identify reliable manufacturers and distributors that meet international standards. Cost considerations will also be addressed, helping you navigate the financial implications of sourcing nails in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key economies such as Brazil and Germany. By equipping you with the knowledge to evaluate nail specifications and supplier offerings, this guide empowers you to make strategic purchasing decisions that enhance the quality and safety of your construction projects. Whether you’re framing residential buildings or commercial structures, understanding the intricacies of framing nails is vital for success in today’s global market.
Understanding framing nail size chart Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common Nails | Smooth shank, wider diameter (0.162 inches) | General framing and construction | Pros: Economical; Cons: Not suitable for high moisture areas, prone to rust. |
| Sinker Nails | Textured head, thinner diameter (0.148 inches) | Framing 2x lumber, sheathing | Pros: Better grip, less splitting; Cons: More expensive than common nails. |
| Ring-Shank Nails | Grooved shank for enhanced holding power | Roof decking, sheathing | Pros: Superior holding strength; Cons: More difficult to remove. |
| Galvanized Nails | Coated to resist corrosion | Exterior applications, high humidity | Pros: Long-lasting in wet conditions; Cons: Higher cost due to coating process. |
| Duplex Nails | Double-headed for easy removal | Temporary structures and scaffolding | Pros: Easily removable; Cons: Not suitable for permanent applications. |
What Are the Characteristics and Applications of Common Nails?
Common nails are widely used in framing and construction due to their smooth shank and wider diameter, which provides good holding power for various lumber types. Their primary application includes general framing where moisture exposure is minimal. However, they are not recommended for high-humidity environments, as they are susceptible to rust, which can compromise structural integrity over time. B2B buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of common nails, especially for projects where moisture is not a concern.
Why Choose Sinker Nails for Framing Projects?
Sinker nails are characterized by their textured heads and thinner diameter, making them ideal for driving into 2x lumber without causing splits. Their vinyl or epoxy coatings enhance driving ease and grip, which is particularly beneficial in framing applications. While they are slightly more expensive than common nails, their superior performance in preventing wood splitting justifies the investment. B2B purchasers should prioritize sinker nails for projects that require a reliable hold and where the quality of finish is critical.
How Do Ring-Shank Nails Enhance Structural Integrity?
Ring-shank nails feature a grooved shank that significantly increases their holding power, making them particularly suitable for applications like roof decking and sheathing. Their design minimizes the risk of pull-out, which is essential for maintaining structural integrity in demanding environments. However, their removal can be challenging, which may impact labor costs during deconstruction or renovations. For B2B buyers, investing in ring-shank nails is advisable for projects requiring robust holding strength.
What Are the Benefits of Using Galvanized Nails?
Galvanized nails are coated to resist corrosion, making them the preferred choice for exterior applications, especially in regions with high humidity or exposure to the elements. Their durability ensures long-lasting performance, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of structures over time. However, the additional cost associated with galvanized nails may deter some buyers. For B2B customers, the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and replacement costs can justify the initial investment.
When Should Duplex Nails Be Utilized?
Duplex nails are uniquely designed with two heads, allowing for easy removal, making them ideal for temporary applications such as scaffolding or concrete forms. Their design facilitates quick assembly and disassembly, which can significantly enhance project efficiency. However, they are not suitable for permanent structures due to their temporary nature. B2B buyers should consider duplex nails for projects requiring flexibility and ease of access, particularly in construction environments where changes are frequent.
Key Industrial Applications of framing nail size chart
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of framing nail size chart | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Framing residential and commercial buildings | Ensures structural integrity and compliance with building codes | Local availability of specific nail sizes and types |
| Furniture Manufacturing | Assembling wooden furniture frames | Enhances durability and aesthetics of furniture products | Quality of materials and coatings for long-lasting use |
| Roofing | Attaching roof decking and sheathing | Increases resistance to weather-related damage | Corrosion resistance of nails, especially in humid climates |
| DIY Home Improvement | General framing projects in renovations | Cost-effective solutions for home upgrades | Compatibility with nail guns and ease of use |
| Industrial Fabrication | Temporary structures and scaffolding | Facilitates quick assembly and disassembly of structures | Strength and durability of nails for heavy-duty applications |
How is the Framing Nail Size Chart Used in the Construction Industry?
In the construction industry, the framing nail size chart is crucial for selecting the appropriate nail sizes for various framing tasks, such as building walls and roofs. For instance, 16d nails are predominantly used for 2×4 framing, ensuring that structures adhere to safety standards and building codes. For international buyers, understanding local regulations regarding nail specifications is vital, as it can impact project timelines and costs. Additionally, sourcing nails that are resistant to corrosion is essential in regions with high humidity or exposure to the elements.
What Role Does the Framing Nail Size Chart Play in Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing sector, the framing nail size chart helps manufacturers determine the right nail sizes for assembling wooden furniture frames. Choosing the correct size and type, such as 8d sinker nails, ensures that the furniture is not only sturdy but also visually appealing. For B2B buyers, sourcing nails with high-quality coatings can enhance product longevity and reduce returns due to structural failures. Additionally, manufacturers must consider lead times and shipping costs when sourcing nails from international suppliers.
How is the Framing Nail Size Chart Relevant to Roofing Applications?
Roofing professionals rely on the framing nail size chart for selecting nails suited to various decking materials, such as plywood or OSB. The chart provides guidelines on using 8d or 10d nails based on the thickness of the decking, ensuring secure attachment and preventing issues like uplift during storms. Buyers in regions with harsh weather conditions, such as the Middle East or parts of South America, must prioritize sourcing galvanized nails to prevent rust and corrosion, which can lead to costly repairs.
Why is the Framing Nail Size Chart Important for DIY Home Improvement Projects?
For DIY enthusiasts engaged in home improvement, the framing nail size chart serves as a guide to select the right nails for framing projects, ensuring structural integrity. Utilizing the correct nail size can prevent issues like wood splitting and improve the overall quality of the renovation. B2B buyers in retail or hardware sectors should consider the ease of use of the nails and their compatibility with various nail guns, as this can significantly affect customer satisfaction and repeat business.
How Does the Framing Nail Size Chart Assist in Industrial Fabrication?
In industrial fabrication, the framing nail size chart is instrumental in applications involving temporary structures and scaffolding. The chart guides users in selecting nails that provide the necessary strength for heavy-duty applications while allowing for easy disassembly. Buyers must focus on sourcing nails that meet specific load requirements and consider local availability to minimize downtime on projects. Ensuring that nails are compliant with safety standards is also crucial in protecting workers and maintaining operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘framing nail size chart’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding Nail Sizes and Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face confusion regarding the various sizes and types of nails available for framing. A common pain point arises when contractors select the wrong nail size for a specific application, leading to structural weaknesses or costly rework. For example, using 8d nails instead of the required 16d nails for framing walls can compromise the integrity of the structure, resulting in safety risks and potential project delays. This misunderstanding can be particularly acute in international markets, where local terminology and standards may vary.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this issue, it’s essential for buyers to familiarize themselves with the nail size chart, which outlines the appropriate sizes for different framing applications. A detailed comparison of nail types—such as common vs. sinker nails—and their respective lengths, diameters, and coatings should be a priority. Buyers can create a standardized reference guide for their teams, emphasizing the specific applications for each nail size. Additionally, engaging with local suppliers for training sessions can help ensure that everyone involved in the project understands the proper specifications. Implementing a system for double-checking nail sizes against project plans before procurement can further mitigate this risk.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Corrosion Resistance in Framing Nails
The Problem: In regions with high humidity or exposure to weather elements—common in many areas across Africa and South America—buyers often encounter issues with nail corrosion. Using non-galvanized nails in these environments can lead to rust and degradation, ultimately jeopardizing the structural integrity of the building. Many buyers may not be aware of the importance of selecting the right type of galvanized nails, which can lead to significant long-term maintenance costs and safety concerns.
The Solution: B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing hot-dip galvanized nails for framing projects that will be exposed to harsh weather conditions. It’s critical to educate procurement teams on the differences between hot-dip and electro-galvanized nails, as the former provides superior corrosion resistance. Buyers can collaborate with manufacturers to ensure that their supply chains include a robust stock of appropriately coated nails. Additionally, incorporating corrosion resistance specifications into project planning documents can help enforce the use of durable materials. Establishing partnerships with suppliers who can provide reliable information on nail coatings and their suitability for specific applications will also enhance decision-making.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing the Right Nail Types
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing specific nail types due to regional supply limitations. For instance, while 16d sinker nails are commonly used in the United States, buyers in Europe or the Middle East might find these nails are not readily available or are offered at a premium price. This situation can lead to project delays and increased costs as buyers scramble to find alternative solutions that may not meet the necessary specifications.
The Solution: To address sourcing challenges, buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify reliable suppliers in their region who stock a comprehensive range of framing nails. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can provide backup options and ensure consistent availability. It may also be beneficial to explore bulk purchasing agreements or partnerships with local manufacturers who can produce specific nail types tailored to regional needs. Implementing a tracking system for nail availability and demand forecasts can help buyers anticipate shortages and adapt their purchasing strategies accordingly. Additionally, sharing insights with other industry stakeholders about sourcing experiences can foster a collaborative environment that leads to better purchasing decisions across the board.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for framing nail size chart
What Are the Key Materials for Framing Nails and Their Properties?
When selecting framing nails, understanding the materials used is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in framing nails, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Steel
Key Properties: Steel nails are known for their high tensile strength and durability. They can withstand significant pressure and are generally resistant to bending. However, standard steel is susceptible to corrosion, particularly in humid or wet environments.
Pros & Cons: Steel nails are relatively inexpensive and widely available, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications. They offer excellent holding power, especially when used in structural framing. However, their susceptibility to rust means they are not suitable for outdoor applications unless they are coated or treated.
Impact on Application: Steel nails are ideal for indoor framing where moisture exposure is minimal. They are commonly used in residential construction, but their use in regions with high humidity or rain should be avoided unless treated.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that steel nails comply with local standards, such as ASTM or JIS, particularly for construction in coastal areas where corrosion is a concern.
2. Galvanized Steel
Key Properties: Galvanized nails are coated with a layer of zinc, providing enhanced corrosion resistance. This makes them suitable for outdoor applications and areas exposed to moisture.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of galvanized nails is their durability in harsh environments, which can significantly extend the lifespan of the framing. However, they tend to be more expensive than standard steel nails due to the additional manufacturing process.
Impact on Application: Galvanized nails are preferred for framing in regions with high humidity or where the structure may be exposed to rain or snow. They are commonly used in roofing and exterior wall applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should verify the type of galvanization (e.g., hot-dip vs. electro-galvanized) to ensure compliance with local building codes and standards.
3. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel nails are highly resistant to rust and corrosion, thanks to their alloy composition, which includes chromium. They maintain their strength and integrity even in extreme conditions.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel nails is their longevity and reliability in corrosive environments. However, they are significantly more expensive than both standard and galvanized steel nails, which may deter some buyers.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel nails are ideal for coastal construction or areas with high salinity, where other types of nails would fail. They are often used in high-end residential projects and marine applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Germany and Brazil should consider the specific grades of stainless steel (e.g., 304 vs. 316) to meet local standards and ensure appropriate performance for their applications.
4. Ring-Shank Nails
Key Properties: Made from various materials, including steel and galvanized steel, ring-shank nails feature a series of ridges along the shaft that enhance holding power.
Pros & Cons: The design of ring-shank nails provides superior grip compared to smooth-shank nails, making them ideal for applications where pull-out resistance is critical. However, they can be more challenging to drive into harder materials and may require specialized tools.
Impact on Application: Ring-shank nails are commonly used in framing, roofing, and sheathing applications where strong connections are necessary. They are particularly effective in areas prone to high winds.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that ring-shank nails meet local building codes, particularly in regions prone to severe weather conditions.
Summary Table of Framing Nail Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for framing nail size chart | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Indoor framing | Cost-effective and strong | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Galvanized Steel | Outdoor framing, roofing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost than standard steel | Med |
| Stainless Steel | Coastal and high-salinity applications | Long-lasting and corrosion-resistant | Significantly more expensive | High |
| Ring-Shank Nails | Framing, roofing, sheathing | Superior grip and holding power | Difficult to drive into hard materials | Med |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in framing nails, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for framing nail size chart
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Framing Nails?
The manufacturing process of framing nails involves several critical stages, each aimed at ensuring the final product meets the necessary specifications for strength, durability, and application. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Framing Nails?
The first step in manufacturing framing nails is material preparation. This typically involves selecting high-quality steel wire, which is the primary raw material. The wire is sourced based on specific tensile strength and ductility requirements, ensuring that the nails can withstand the stress they will encounter in framing applications. After selection, the wire undergoes processes such as cleaning and straightening to remove any surface impurities and ensure uniformity in diameter.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Nail Production?
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves several methods, including cold heading and forging. In cold heading, the wire is cut to length and then shaped into a nail through a series of high-speed mechanical presses. This method allows for precise control over the nail’s dimensions and is crucial for producing the different sizes and types of framing nails, such as common and sinker nails.
Forging may also be used, particularly for nails requiring additional strength. In this process, heated metal is shaped under pressure to create a denser and more robust nail. The choice of technique often depends on the specific requirements of the nail type being produced.
How Is the Assembly Process Managed?
The assembly stage in framing nail manufacturing is relatively straightforward, as nails are typically produced as single pieces. However, assembly can refer to the packaging process where nails are collated into strips or boxes for distribution. This is an essential step that ensures ease of use for contractors and builders. Automated machines often handle this packaging, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in the number of nails per package.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Durability?
Finishing is a critical stage that enhances the performance of framing nails. This may involve various treatments, such as galvanization, to prevent rust and corrosion. Hot-dip galvanization is commonly used for nails that will be exposed to moisture, providing a thick, protective zinc coating. Alternatively, electro-galvanization offers a thinner layer suitable for interior applications.
Additionally, nails may undergo surface treatments like epoxy or vinyl coating to enhance driving ease and holding power. These finishes are crucial for ensuring that nails perform well in different environmental conditions, which is particularly relevant for international markets where humidity and temperature can vary significantly.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Framing Nails?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of framing nails is paramount, especially for international B2B buyers. Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential, as it outlines the requirements for a quality management system that can enhance customer satisfaction and ensure continuous improvement.
How Do International Standards Impact Nail Manufacturing?
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific standards may apply. For instance, nails used in construction may need to comply with CE marking requirements in Europe, indicating that they meet safety and environmental protection standards. Similarly, in certain regions, adherence to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards might be necessary for nails used in oil and gas applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is integrated into various stages of the manufacturing process through systematic checkpoints. Key QC stages include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet predefined specifications. Steel wire is often tested for tensile strength and diameter.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, random samples may be tested for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and mechanical properties. This step is crucial for identifying defects early in the production process.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the nails are manufactured, a final inspection is conducted to ensure that the finished products meet all specifications. This may involve testing the nails for strength and corrosion resistance.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Nail Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to validate the quality of framing nails:
-
Tensile Testing: This assesses the strength of the nails under tension and ensures they can withstand the forces they will encounter in use.
-
Corrosion Resistance Testing: Nails are subjected to environmental conditions that simulate real-world exposure to moisture and humidity, ensuring that protective coatings perform as expected.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Automated systems often conduct dimensional checks to ensure that each nail meets the specified length and diameter requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is crucial. Here are actionable steps to ensure quality:
-
Request Certification Documents: Suppliers should provide proof of compliance with relevant international standards like ISO 9001 and CE marking. These documents should be current and verifiable.
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify their adherence to quality control processes. These audits can include facility inspections and reviews of production practices.
-
Seek Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent quality assurance firms to conduct inspections can provide unbiased assessments of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and product quality.
-
Review Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to furnish detailed reports on their QC processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results. These reports offer insight into the consistency and reliability of their products.
-
Understand Regional Variations: Different regions may have specific standards or expectations for framing nails. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these nuances to ensure compliance and suitability for their specific applications.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of the nuances in quality control and certification that may vary by region. For example, in Europe, nails must comply with the EN 14592 standard for structural use, while in the Americas, different codes may apply based on local building regulations.
Additionally, buyers should consider the logistics of certification processes. Some suppliers may have certifications that are more recognized in one region than another. Understanding these differences can help buyers make informed decisions and ensure compliance with local regulations.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for framing nails are critical components that directly impact the performance and reliability of these products in construction applications. For international B2B buyers, diligence in verifying supplier practices and understanding the relevant standards is essential to ensure quality and compliance in their projects.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘framing nail size chart’
Introduction
This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers aiming to procure a comprehensive framing nail size chart. Understanding the specifications and application of framing nails is essential for ensuring structural integrity in construction projects. By following these steps, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and regional standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the specific requirements for your framing project. Consider factors such as the types of materials being used, the size of the structures, and environmental conditions that may affect nail performance.
– Material Type: Identify whether you will use softwood or hardwood, as this influences the nail size and type.
– Environmental Factors: Determine if the project is indoors or outdoors, as this will dictate whether you need galvanized nails for rust resistance.
Step 2: Research Common Nail Sizes for Framing
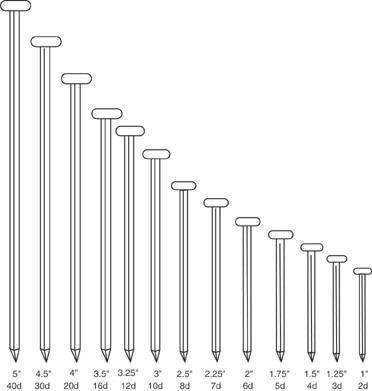
Familiarize yourself with the standard nail sizes used in framing, such as 8d and 16d nails. Each size corresponds to specific applications and materials, impacting the overall strength of the structure.
– 8d Nails: Typically used for subflooring and sheathing, measuring 2.5 inches in length.
– 16d Nails: Commonly employed for framing walls, measuring 3.5 inches, with options for common and sinker types.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers to ensure they meet your requirements. Look for suppliers with a solid reputation in the industry and a track record of quality products.
– Request Documentation: Ask for product specifications, certifications, and safety data sheets to verify compliance with international standards.
– Seek References: Obtain testimonials or case studies from previous clients to gauge the supplier’s reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Assess Quality and Coating Options
When selecting nails, consider the quality and type of coatings available. The right coating can enhance durability, especially in adverse weather conditions.
– Hot-Dip Galvanized vs. Electro-Galvanized: Understand the differences in corrosion resistance and application suitability.
– Coating Types: Evaluate options like vinyl or epoxy coatings that improve driving ease and holding power.
Step 5: Establish Bulk Purchase Agreements
Negotiate bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers to secure better pricing and consistent supply. This is particularly important for large projects where demand may fluctuate.
– Volume Discounts: Inquire about discounts based on order size to optimize costs.
– Long-Term Partnerships: Consider establishing long-term relationships with suppliers to streamline procurement processes and enhance reliability.
Step 6: Verify Shipping and Delivery Capabilities
Confirm the supplier’s ability to meet your shipping and delivery needs, especially for international orders. Timely delivery is crucial for maintaining project timelines.
– Lead Times: Ask about typical lead times for various quantities to plan your inventory accordingly.
– Shipping Options: Evaluate their shipping methods and costs to ensure they align with your budget and timeline.
Step 7: Monitor and Review Supplier Performance
Once you start sourcing nails, regularly monitor supplier performance based on delivery, quality, and responsiveness. This ongoing evaluation will help you make adjustments as needed.
– Feedback Loop: Establish a system for providing feedback to suppliers to foster continuous improvement.
– Regular Audits: Schedule periodic reviews of supplier practices to ensure they continue to meet your standards.
By following this structured approach, B2B buyers can effectively source a framing nail size chart that meets their specific project needs and regional requirements, ensuring successful construction outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for framing nail size chart Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Framing Nail Sourcing?
When sourcing framing nails, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of steel or other materials used significantly impacts the cost. Galvanized nails, which are coated to resist corrosion, tend to be more expensive than standard steel nails due to the additional processing required.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in manufacturing the nails. These costs can vary based on location, skill levels, and labor laws in different countries, impacting the overall pricing strategy.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses such as utilities, rent, and machinery maintenance. Efficient production processes and economies of scale can help reduce these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized machinery for nail production can be substantial. Tooling costs are often amortized over large production runs, making them a critical consideration for pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that nails meet specific standards requires investment in quality assurance processes, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, play a significant role, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and local tariffs must be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary significantly based on market competition and demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Framing Nail Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of framing nails:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases can significantly lower the per-unit cost. Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized nails that meet specific industry standards or unique buyer requirements can lead to higher costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential savings from standard products.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of materials and the presence of certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can affect pricing. Higher-quality nails often come at a premium but can provide long-term savings through enhanced durability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a strong track record may command higher prices but offer better service, consistency, and quality.
-
Incoterms: The chosen shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can impact total costs. Understanding these terms helps buyers manage logistics expenses and negotiate better deals.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost Efficiency in Sourcing Framing Nails?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing framing nails, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Leverage relationships with suppliers to negotiate better pricing, especially for larger orders. Building long-term partnerships can lead to favorable terms and discounts.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the long-term costs associated with the nails, such as maintenance, replacement, and potential structural issues due to inferior products. This holistic view can lead to better purchasing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Different regions may have varying cost structures due to labor, material availability, and market demand. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should research local suppliers and market conditions to identify the best sourcing options.
-
Monitor Market Trends: Stay informed about fluctuations in raw material prices and market demand. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations and help in timing purchases for optimal pricing.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough research and consult with multiple suppliers before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing framing nail size chart With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to the Framing Nail Size Chart
In the construction industry, selecting the appropriate fastening solution is critical for ensuring structural integrity and efficiency. While the framing nail size chart provides essential guidance on nail selection for various applications, there are alternative methods and technologies that can achieve similar goals. This analysis compares the traditional framing nail size chart with two viable alternatives: the use of screws and adhesive bonding. Each alternative presents unique advantages and considerations, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their project requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Framing Nail Size Chart | Screws | Adhesive Bonding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High holding strength; reliable for framing applications. | Excellent tensile strength; suitable for many materials. | Strong bond; effective for non-structural applications. |
| Cost | Generally low cost for nails; bulk purchasing can reduce expenses. | Moderate to high; costs can vary based on type and material. | Variable; depends on adhesive type and application method. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to use with a hammer or nail gun; requires minimal training. | Requires pre-drilling in some materials; may need specialized tools. | Requires surface preparation and curing time; can be complex. |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance; nails remain in place unless removed. | Low maintenance; screws can be removed and reused. | May require reapplication over time; less durable in wet conditions. |
| Best Use Case | Framing, sheathing, roofing in wood construction. | General construction, cabinetry, and metal fastening. | Ideal for bonding materials like wood, plastics, and composites. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
How Do Screws Compare to Framing Nails?
Screws offer a robust fastening solution that provides excellent tensile strength, making them suitable for a variety of construction applications. They are particularly effective in joining dissimilar materials or when a tighter connection is needed. However, the installation process can be more labor-intensive, often requiring pre-drilling in harder materials. Additionally, while screws are generally more expensive than nails, their reusability and strong holding power can justify the cost in certain scenarios.
Are Adhesive Bonding Solutions Effective Alternatives?
Adhesive bonding presents a unique alternative, particularly for non-structural applications. Adhesives can bond a wide range of materials, including wood, plastics, and metals, which makes them versatile in construction. However, they require careful surface preparation and can be time-consuming to apply, as many adhesives need to cure for a certain period before achieving their full strength. Additionally, adhesives may not be suitable for applications exposed to moisture unless specifically designed for such environments. The effectiveness and durability of adhesive bonds can vary significantly based on the product used and environmental conditions.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting fastening solutions, B2B buyers should carefully consider the specific requirements of their projects. The framing nail size chart remains a reliable resource for traditional framing applications, ensuring structural integrity with minimal effort and cost. However, screws and adhesive bonding offer valuable alternatives that can enhance performance in particular situations. Buyers should evaluate factors such as material compatibility, cost implications, and application methods to determine the most appropriate solution for their needs. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their project goals and operational efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for framing nail size chart
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Framing Nails?
When selecting framing nails, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and suitability for specific applications. Here are the essential properties that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
Framing nails are typically made from steel, with variations in grade affecting strength and corrosion resistance. Common grades include carbon steel for general use and stainless steel or galvanized options for enhanced durability in harsh environments. Buyers should evaluate material grades based on the project’s exposure to moisture or corrosive elements, especially in outdoor or humid conditions. -
Length and Diameter
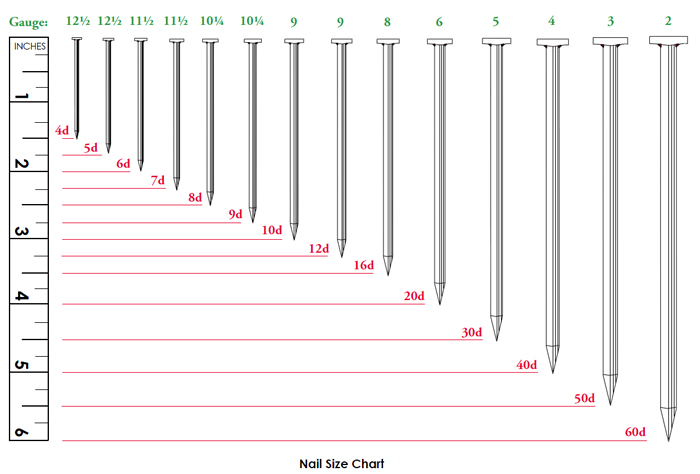
The length (often denoted in “pennies” or “d”) and diameter of the nail are critical for achieving the required holding power. For instance, 16d nails are 3.5 inches long, while 8d nails measure 2.5 inches. The diameter influences the nail’s ability to penetrate and hold wood without splitting it. Selecting the correct size based on the lumber thickness and application type is vital for structural stability. -
Coating Type
Nails can come with various coatings, such as vinyl, epoxy, or galvanized finishes. Each coating serves a specific purpose; for example, galvanized nails resist rust and corrosion, making them suitable for exterior applications. Understanding the benefits of different coatings can help buyers choose the right nail for their framing needs, ensuring longevity and performance. -
Head Style
The head style of a nail—common, sinker, or ring-shank—affects its holding capacity and ease of use. Ring-shank nails, for instance, have ridges that provide superior grip, making them ideal for high-stress applications like roof decking. Knowing the differences in head styles can guide buyers in selecting nails that meet specific project requirements. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions of the nails. High tolerance levels ensure that nails fit properly within the intended applications, reducing the risk of structural failures. B2B buyers should verify that suppliers meet industry standards for tolerance to ensure quality and reliability in their framing projects.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Framing Nails?
Understanding industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and better decision-making for B2B buyers. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When sourcing framing nails, knowing whether a supplier is an OEM can indicate the quality and reliability of the products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers who need to manage inventory costs. Understanding MOQ can help in negotiating better terms and ensuring that bulk purchases align with business needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quotation for specific products, such as framing nails. This process helps buyers compare prices and terms from different suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities, which is crucial when sourcing framing nails from international suppliers. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning, as delays can impact construction schedules. Buyers should inquire about lead times when sourcing framing nails to avoid project disruptions. -
Certification Standards
Certification standards ensure that products meet specific safety and quality benchmarks. Common certifications for framing nails include ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization). Buyers should seek suppliers who comply with these standards to ensure the reliability of their framing materials.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing framing nails, ultimately enhancing project outcomes and ensuring structural integrity.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the framing nail size chart Sector
How Are Global Market Dynamics Shaping the Framing Nail Size Chart Sector?
The framing nail market is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by several global factors, particularly affecting B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. A significant driver is the booming construction industry, which is fueled by urbanization, infrastructure development, and increased housing demand. In Brazil, for instance, government initiatives to promote affordable housing are leading to a surge in framing projects, thereby increasing the demand for specific nail sizes, particularly the 16d and 8d nails. Similarly, Europe is witnessing a shift towards sustainable construction practices, which influence the types of materials and fastening solutions used.
Emerging technologies are also playing a crucial role in sourcing trends. The adoption of e-commerce platforms and digital supply chain management tools allows international buyers to access a broader range of products and suppliers. For example, buyers can now easily compare nail specifications and prices from different manufacturers, improving their procurement efficiency. Additionally, automation in manufacturing processes is enhancing the quality and consistency of nails, catering to precise construction requirements.
As buyers navigate these market dynamics, they must remain vigilant about fluctuating raw material costs and regional supply chain challenges. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains, prompting buyers to consider local sourcing options to mitigate risks. Understanding these trends is crucial for making informed decisions about sourcing framing nails that align with project specifications and budgetary constraints.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions for Framing Nails?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a focal point in the sourcing of framing nails. The environmental impact of construction materials, including fasteners, has led many businesses to prioritize ethical sourcing and green certifications. For framing nails, this means looking for products that minimize ecological footprints, such as those made from recycled materials or produced with energy-efficient processes.
Buyers should consider suppliers that offer galvanized nails, as these are often treated to resist corrosion, thereby enhancing durability and reducing the frequency of replacements. Furthermore, nails coated with eco-friendly substances are gaining popularity, reflecting a growing preference for materials that do not harm the environment.
An ethical supply chain is essential not only for compliance with regulations but also for enhancing brand reputation. Companies that adopt sustainable practices often find themselves more appealing to environmentally-conscious consumers and partners. For instance, certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can signal a commitment to sustainability, making it an attractive selling point for B2B buyers.
What Is the Historical Context of Framing Nails in the Construction Industry?
The evolution of framing nails reflects broader changes in construction practices and materials. Historically, nails were handcrafted from wrought iron, making them expensive and labor-intensive. The introduction of mass production techniques in the late 19th century revolutionized the industry, leading to the widespread availability of nails made from steel and, later, stainless steel.
The terminology surrounding nail sizes, such as the “penny” system, dates back to the early 20th century, where the “d” in nail sizes (e.g., 16d) originally referred to the cost in pennies for a hundred nails. Over the years, advancements in coating technologies, such as galvanization, have significantly enhanced the durability and corrosion resistance of framing nails, aligning them with the evolving needs of construction projects.
Today, framing nails are not only crucial for structural integrity but also represent a critical component in sustainable construction efforts. As the industry continues to evolve, understanding the historical context helps buyers appreciate the importance of selecting the right framing nails for their projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of framing nail size chart
-
How do I choose the right nail size for framing projects?
Choosing the correct nail size for framing depends on several factors, including the type of lumber and the specific application. Commonly, 16d nails (3.5 inches) are used for framing 2x4s, while 8d nails (2.5 inches) are ideal for attaching furring strips or sheathing. Ensure the nail length is appropriate to avoid splitting the wood or compromising structural integrity. Consult local building codes or project specifications, as they may dictate the required nail sizes and types for specific applications. -
What is the best type of nail for framing in different climates?
The best type of nail for framing varies with climate conditions. For humid or wet environments, galvanized nails are recommended as they resist rust and corrosion. Hot-dip galvanized nails offer robust protection for exterior applications, while electro-galvanized nails are suitable for less exposed areas. In dry climates, standard steel nails may suffice, but always consider local weather conditions and potential exposure to moisture when selecting nails. -
How do I verify the quality of framing nails from suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing framing nails, request certifications and test reports from potential suppliers. Look for nails that meet international standards such as ASTM or ISO. It’s also advisable to ask for samples to assess the nail’s material, finish, and coating. Additionally, consider suppliers with positive reviews and a proven track record in the industry, as well as those who offer warranties or guarantees on their products. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for framing nails?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for framing nails can vary significantly by supplier. While some may offer MOQs as low as 500 or 1,000 pieces, others might require larger orders, particularly for bulk pricing. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about flexibility in MOQs, especially if you’re testing a new product or entering a new market. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can often lead to better terms and conditions. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing framing nails internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing typically include options like advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before finalizing any orders. Some suppliers may offer favorable terms such as net 30 or net 60 days, especially for established buyers. Always ensure that the payment method provides adequate security for both parties and is compliant with international trade regulations. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for framing nails?
Logistics and shipping for framing nails involve coordinating with freight forwarders and ensuring compliance with customs regulations. When sourcing internationally, consider the shipping methods (air freight vs. sea freight) based on cost and urgency. Always clarify shipping costs, delivery times, and insurance options with your supplier. Additionally, ensure that your supplier provides the necessary documentation for customs clearance to avoid delays. -
Can framing nails be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for framing nails, including variations in size, coating, and packaging. If your project requires specific nail dimensions or unique coatings for added corrosion resistance, discuss these needs with potential suppliers. Customization can also extend to branding or labeling for easy identification on job sites. However, be aware that custom orders may have higher MOQs and longer lead times. -
What are the best practices for storing framing nails?
To maintain the integrity of framing nails, store them in a cool, dry environment to prevent rust and corrosion. Use sealed containers or original packaging to keep nails organized and protected from moisture. It’s also advisable to keep nails away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Regularly check stored nails for signs of damage or rust, and rotate stock to ensure older inventory is used first. Proper storage practices can prolong the life of your nails and maintain their performance in framing applications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Framing Nail Size Chart Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. MCSW – Framing Nails
Domain: mcswusa.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: The most common sizes for framing nails are 16d, 10d, and 8d. 16d nails (3 ½ inches) are used for 2×4 framing, with two varieties: Common nails (0.162 inches diameter) and Sinker nails (0.148 inches diameter, textured head). 8d nails (2 ½ inches) are used for attachments like furring strips and subfloors, available in common and sinker varieties. For roof decking, 8d common or ring-shank nails are…
2. Build My Own Cabin – Nail Size Chart for Framing
Domain: buildmyowncabin.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Nail Size Chart: The guide helps in selecting proper nail sizes for framing projects. The ‘d’ denotes ‘penny’. Nail Measurements: 2d (1 inch), 3d (1.25 inches), 4d (1.5 inches), 5d (1.75 inches), 6d (2 inches), 8d (2.5 inches), 12d (3.25 inches), 16d (3.5 inches). Recommended Nails for Framing: 8d and 16d coated sinkers cover 95% of framing needs. 16d nails are preferred for 2x lumber framing. Typ…
3. Engineers Edge – Nail Size Gauge Chart
Domain: engineersedge.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Nail Size Gauge Chart: 2D (15 gauge, 0.072″ diameter, 1″ length, 3/16″ head), 14 (0.083″, 1″, 13/64″), 3D (14, 0.083″, 1.25″, 13/64″), 4D (12, 0.109″, 1.5″, 1/4″), 5D (12, 0.109″, 1.75″, 1/4″), 6D (11, 0.12″, 2″, 17/64″), 8D (10, 0.134″, 2.5″, 9/32″), 10D (9, 0.148″, 3″, 5/16″), 12D (9, 0.148″, 3.25″, 5/16″), 16D (8, 0.165″, 3.5″, 11/32″), 20D (6, 0.203″, 4″, 13/32″), 30D (5, 0.22″, 4.5″, 7/16″), …
4. HP Eng – Framing Nails
Domain: hp-eng.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Framing nails are essential for fastening structural components in building construction. Key details include: 1. 16d Nail: Length – 3 1/2 inches; Diameter – 0.162 inches. 2. .131 Framing Nail: Diameter – 0.131 inches (length varies by manufacturer). 3. Strength: 16d nails have greater holding power due to their larger diameter, making them suitable for larger structures. 4. Cost: 16d nails are mo…
5. Pinterest – Framing Nail Size Guide
Domain: ca.pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: A Framing Nail Size Guide with 5 Diagrams, includes information on different framing nail sizes to help identify the best nail size for construction projects.
6. Accent Build – Fasteners and Screws
Domain: accentbuild.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Nail Size Chart, General Construction / Carpentry Nails, Drywall Nails, Roofing Nails, Galvanized Nails, Specialty Nails, Furring Nails, Light Gauge Steel Screws, Coarse Wood Screws, Self Drilling Screws, Wood Working and Cement Board Screws, Exterior Decking Screws, Roofing Screws, Collated Fasteners, Framing Nails, Coil Roofing Nails, Staples, Brads and Finish, Siding Coil Nails, Drywall & Acous…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for framing nail size chart
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of framing nail sizes is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their sourcing strategies. Selecting the right nails—such as the widely used 16d and 8d options—ensures structural integrity and minimizes the risk of material failure. Additionally, considering factors like nail coatings and types can enhance durability, particularly in varied climates across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Strategic sourcing not only involves identifying the right products but also establishing reliable supplier relationships that can provide high-quality materials tailored to specific regional needs. By prioritizing these practices, businesses can reduce costs, improve project timelines, and maintain competitive advantages in their respective markets.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for B2B buyers to stay informed about evolving standards and innovations in the fastener industry. Engaging with trusted suppliers and leveraging insights from this guide can facilitate more informed purchasing decisions. We encourage you to explore your options and consider establishing partnerships that align with your strategic goals for successful framing projects in the future.