Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fr4 vs carbon fiber plate
Navigating the complexities of sourcing FR4 vs. carbon fiber plates can be a formidable challenge for international B2B buyers. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, understanding the unique properties, applications, and costs associated with these materials becomes crucial. This guide delves deep into the distinctions between FR4 and carbon fiber plates, providing insights into their mechanical properties, electrical insulation capabilities, and weight considerations.
Buyers will discover a comprehensive analysis of various types of plates, their specific applications in diverse sectors such as electronics, aerospace, and automotive, and strategies for vetting suppliers effectively. Additionally, we will address cost factors, helping businesses make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
With this guide, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the global market, ensuring they select the right material for their projects. By empowering decision-makers with knowledge and actionable insights, we aim to foster successful procurement strategies that enhance product performance and operational efficiency. Whether you’re based in Nigeria, Vietnam, or anywhere in between, understanding the nuances of FR4 and carbon fiber plates will enable you to thrive in a competitive landscape.
Understanding fr4 vs carbon fiber plate Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR4 Standard | Glass-reinforced epoxy laminate, flame-resistant | Electronics (PCBs), industrial components | Pros: Excellent electrical insulation, high mechanical strength. Cons: Heavier than carbon fiber. |
| FR4 High-Temperature | Enhanced thermal resistance, suitable for extreme conditions | Aerospace, automotive, and military sectors | Pros: Maintains properties at high temperatures. Cons: More expensive than standard FR4. |
| Carbon Fiber Standard | Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, and rigidity | Aerospace, automotive, sports equipment | Pros: Exceptional strength with minimal weight. Cons: Higher cost, less electrical insulation. |
| Carbon Fiber Reinforced | Incorporates additional materials for improved properties | High-performance applications, automotive | Pros: Tailored properties for specific applications. Cons: Can be complex to source and manufacture. |
| FR4 Composite | Combination of FR4 with other materials for enhanced features | Electronics, structural components | Pros: Versatile applications, customizable properties. Cons: May compromise on specific properties. |
What Are the Characteristics of FR4 Standard Plates?
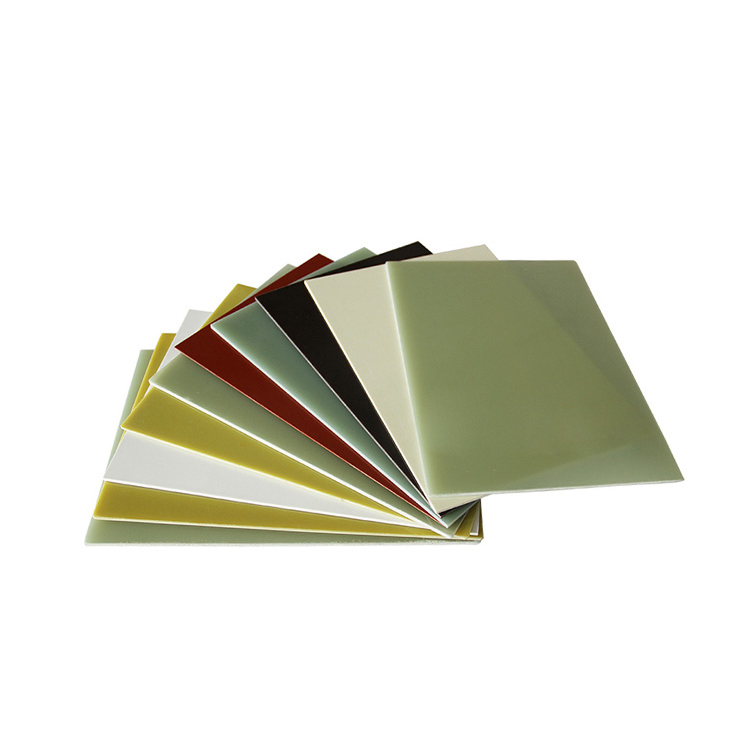
FR4 Standard plates are composed of woven fiberglass fabric impregnated with epoxy resin, providing excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength. These plates are widely used in the electronics industry for printed circuit boards (PCBs) and in various industrial components. B2B buyers should consider the weight of FR4, as it is denser compared to carbon fiber, which may be a critical factor in applications where weight savings are essential.
How Do High-Temperature FR4 Plates Differ?
High-Temperature FR4 plates are specifically designed to withstand extreme thermal conditions, making them suitable for aerospace, automotive, and military applications. Their enhanced thermal resistance allows them to maintain structural integrity under high heat, which is crucial in demanding environments. Buyers should be aware that these plates typically come at a higher price point due to their specialized properties, but they offer significant long-term value in critical applications.
What Makes Carbon Fiber Standard Plates Unique?
Carbon Fiber Standard plates are known for their remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for industries like aerospace and automotive. Their lightweight nature allows for significant weight savings in high-performance applications, such as aircraft components and sports equipment. While they provide exceptional mechanical properties, buyers should factor in the higher costs associated with carbon fiber materials and consider their specific application needs, particularly in terms of electrical insulation.
What Are the Advantages of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plates?
Carbon Fiber Reinforced plates combine carbon fiber with other materials to enhance specific properties, making them suitable for high-performance applications. These plates are often tailored to meet the unique requirements of various industries, including automotive and aerospace. B2B buyers should consider the complexity of sourcing and manufacturing these customized solutions, as well as the potential for improved performance in specific applications, despite the higher costs.
How Do FR4 Composites Offer Versatility?
FR4 Composites are engineered by combining FR4 with other materials to create a product that meets diverse application needs. This versatility allows for a balance of properties, making them suitable for both electronic and structural applications. Buyers should evaluate the specific enhancements that the composite offers, as well as any trade-offs in terms of performance characteristics, to ensure that they select the right material for their projects.
Key Industrial Applications of fr4 vs carbon fiber plate
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fr4 vs carbon fiber plate | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) | FR4 provides excellent electrical insulation and mechanical support, crucial for reliable electronic performance. | Ensure compliance with international standards for electrical insulation and flame resistance. |
| Aerospace | Structural Components | Carbon fiber’s lightweight and high-strength properties reduce overall aircraft weight, enhancing fuel efficiency. | Verify certification for aerospace-grade materials and consider local sourcing for reduced lead times. |
| Automotive | High-Performance Vehicle Parts | Carbon fiber components enhance performance while minimizing weight, leading to better fuel economy and handling. | Assess the supplier’s ability to meet stringent automotive safety standards and quality assurance processes. |
| Construction | Structural Insulation Panels | FR4 offers robust structural integrity and flame resistance, making it suitable for various construction applications. | Evaluate the fire safety ratings and thermal properties of the material for specific building regulations. |
| Sports Equipment | Equipment Frames and Components | Carbon fiber’s lightweight nature and strength improve performance in high-end sporting goods, appealing to professional athletes. | Consider the supplier’s experience in producing high-performance materials tailored for sports applications. |
How is FR4 Used in Electronics for International Buyers?
In the electronics sector, FR4 is predominantly utilized in the manufacturing of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). This composite material’s superior electrical insulation properties prevent electrical interference and ensure the reliability of electronic devices. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing FR4 requires an understanding of local regulatory standards to ensure compliance with safety and performance specifications. Buyers must also consider the availability of high-quality FR4 to avoid issues with durability and functionality in their products.
What Role Does Carbon Fiber Play in Aerospace Applications?
Carbon fiber is extensively used in aerospace for structural components due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. This material helps reduce the overall weight of aircraft, leading to improved fuel efficiency and enhanced performance. For international B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it is crucial to source aerospace-grade carbon fiber that meets specific certifications. Understanding the supply chain dynamics, including lead times and local sourcing options, can significantly impact project timelines and costs.
How is Carbon Fiber Beneficial in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, carbon fiber is favored for high-performance vehicle parts, such as chassis and body panels. Its lightweight nature contributes to improved fuel economy and handling characteristics. For buyers in regions like Nigeria and Vietnam, the challenge lies in sourcing carbon fiber materials that meet rigorous automotive safety standards. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers who have proven quality assurance processes is essential to ensure the integrity and performance of automotive components.
What Advantages Does FR4 Offer in Construction?
In construction, FR4 is used for structural insulation panels, providing both mechanical strength and flame resistance. This makes it an ideal choice for various applications, including electrical enclosures and support structures. International buyers must assess the fire safety ratings and thermal properties of FR4 to ensure compliance with local building regulations, particularly in regions with strict safety codes. Additionally, sourcing from reputable suppliers can mitigate risks associated with material performance in demanding environments.
How is Carbon Fiber Transforming Sports Equipment Manufacturing?
Carbon fiber is revolutionizing the sports equipment industry by allowing manufacturers to create lighter and stronger products, such as bicycle frames and tennis rackets. This material appeals to professional athletes who seek performance enhancements. For international buyers, understanding the supplier’s expertise in producing tailored carbon fiber solutions is vital. Buyers should also consider the supplier’s ability to innovate and adapt to the evolving demands of the sports equipment market, ensuring they remain competitive.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fr4 vs carbon fiber plate’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Material Selection for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate material between FR4 and carbon fiber for their specific applications. For instance, a buyer in the electronics sector may require a material for a printed circuit board (PCB) but is unsure whether FR4’s excellent electrical insulation or carbon fiber’s lightweight properties would be more beneficial. This indecision can lead to project delays, increased costs, or even product failures if the wrong material is chosen.
The Solution: To effectively navigate material selection, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment that considers mechanical properties, weight, and electrical requirements. For applications where electrical insulation is paramount, such as in PCBs, FR4 is the clear choice due to its superior insulating capabilities and mechanical strength. Conversely, if the application demands a lightweight solution with high strength, such as in aerospace components, carbon fiber would be more suitable. Buyers should also engage with suppliers who can provide technical data sheets and sample materials, allowing for hands-on evaluation of both options before making a decision. Establishing clear specifications and performance criteria will facilitate informed decision-making and minimize the risk of costly errors.
Scenario 2: Understanding Cost Implications in Material Procurement
The Problem: A common pain point for international B2B buyers is the cost disparity between FR4 and carbon fiber plates. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America may find that carbon fiber, while offering superior performance characteristics, comes at a significantly higher price point than FR4. This price difference can complicate budgeting and cost forecasting, especially for startups or businesses operating on tight margins.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis that evaluates the long-term value of each material against its initial procurement costs. While carbon fiber may present a higher upfront cost, its lightweight nature can lead to reduced shipping expenses and improved energy efficiency in applications such as automotive and aerospace. Buyers should also explore bulk purchasing options or long-term contracts with suppliers to secure more favorable pricing. By aligning material selection with the overall project budget and considering the lifecycle costs, businesses can make informed financial decisions that optimize both performance and expenditure.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Manufacturing Compatibility Issues
The Problem: Buyers often encounter compatibility issues when transitioning between FR4 and carbon fiber in manufacturing processes. For example, a company that has traditionally used FR4 may find that their current equipment and processes are not easily adaptable for carbon fiber plates. This can lead to increased downtime, additional training for staff, and the need for new tools or machinery, which can significantly disrupt production schedules.
The Solution: To mitigate these manufacturing compatibility challenges, it is essential for buyers to engage in proactive planning before switching materials. This includes consulting with manufacturers and engineers to assess current processes and identify necessary adjustments. Conducting pilot tests with carbon fiber plates can help determine the compatibility of existing machinery and production lines. Additionally, investing in training programs for staff on the handling and processing of carbon fiber can alleviate transition issues. Buyers should also collaborate with suppliers who offer technical support and resources to facilitate a smoother transition, ensuring that production timelines and quality standards are maintained.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fr4 vs carbon fiber plate
What Are the Key Properties of FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates?
FR4 Plates: Properties and Performance
FR4 is a composite material made of woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with epoxy resin. It is known for its excellent mechanical strength, good rigidity, and impressive electrical insulating properties, making it a staple in the electronics industry, particularly for printed circuit boards (PCBs). FR4 typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 130°C and can withstand moderate pressures. Its corrosion resistance is adequate for most applications, but it may not perform well in highly aggressive chemical environments.
Carbon Fiber Plates: Properties and Performance
Carbon fiber plates consist of thin fibers primarily made of carbon atoms, offering exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and high tensile strength. These plates can handle temperatures up to 200°C, making them suitable for high-performance applications in aerospace and automotive industries. While carbon fiber is lightweight and strong, it can be more brittle than FR4, which may lead to failure under certain stress conditions. Additionally, carbon fiber exhibits electrical conductivity, which can be a disadvantage in applications requiring insulation.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates?
Advantages and Disadvantages of FR4
FR4 is durable and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for a variety of applications. Its manufacturing process is relatively straightforward, allowing for mass production at lower costs. However, its heavier weight compared to carbon fiber can be a disadvantage in applications where weight is critical. Additionally, while FR4 is excellent for electrical insulation, it may not be suitable for environments with extreme temperatures or corrosive substances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Carbon Fiber
The main advantage of carbon fiber is its lightweight nature combined with high strength, making it ideal for applications where performance and weight are crucial. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly, which may deter some buyers. Furthermore, while carbon fiber’s conductivity can be advantageous in certain applications, it poses challenges in environments requiring electrical insulation.
How Do FR4 and Carbon Fiber Impact Application Suitability?
Application Considerations for FR4
FR4 is widely used in electronics, especially for PCBs, due to its excellent insulating properties. It is also suitable for structural applications where a balance of strength and rigidity is needed. However, buyers must consider its limitations in high-temperature or corrosive environments, which could affect long-term performance.
Application Considerations for Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber plates excel in high-performance sectors, including aerospace and automotive, where minimizing weight without sacrificing strength is critical. They are also used in sporting goods and high-end consumer products. However, international buyers should be aware of the material’s brittleness and ensure it meets specific application requirements.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Choosing Between FR4 and Carbon Fiber?
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider compliance with local and international standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS when selecting materials. Different regions may have varying preferences based on application needs and environmental conditions. For instance, buyers in regions with high humidity or temperature fluctuations may prioritize the moisture resistance and thermal stability of FR4. Conversely, those in industries requiring lightweight materials may lean towards carbon fiber despite its higher cost.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for fr4 vs carbon fiber plate | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR4 | Printed circuit boards, structural applications | Excellent electrical insulation | Heavier than carbon fiber | Medium |
| Carbon Fiber | Aerospace components, high-performance vehicles | Lightweight with high strength | More brittle and costly to manufacture | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of FR4 and carbon fiber plates, equipping international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed material selections based on their specific application needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fr4 vs carbon fiber plate
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates?
The manufacturing processes for FR4 and carbon fiber plates involve several critical stages, each essential to ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions about material selection based on their specific applications.
Material Preparation: How Are FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates Made?
FR4 Manufacturing Process:
-
Material Design: The production of FR4 begins with the careful selection of woven fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin. The glass fibers are arranged in a specific pattern to optimize strength and insulation properties.
-
Impregnation: The fiberglass cloth is then impregnated with epoxy resin. This step requires precision to ensure the resin fully saturates the fibers, which enhances the mechanical and electrical properties of the final product.
-
Lamination: After impregnation, the fiberglass layers are subjected to heat and pressure in a lamination process. This step solidifies the resin, bonding the layers together and creating a solid composite material.
Carbon Fiber Manufacturing Process:
-
Fiber Production: Carbon fiber is produced by spinning polyacrylonitrile (PAN) or other carbon-rich materials into thin fibers. These fibers are then subjected to a series of heating processes, known as carbonization, to remove non-carbon elements.
-
Weaving or Layering: The carbon fibers are woven or layered to form sheets or pre-impregnated materials (prepregs). This process allows for the creation of complex shapes and structures, crucial for high-performance applications.
-
Curing: The final step in carbon fiber plate manufacturing involves curing the material, where it is heated to harden the resin and solidify the structure. This is often done in an autoclave to ensure uniform temperature and pressure.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that both FR4 and carbon fiber plates meet the necessary performance and safety standards. B2B buyers should be aware of the relevant international and industry-specific standards that govern the production of these materials.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates?
Both FR4 and carbon fiber plates are subject to various international quality standards. Here are some key standards to consider:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable across various industries. Suppliers who are ISO 9001 certified demonstrate a commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
-
IEC 61249: This standard specifies the requirements for materials used in printed circuit boards, including FR4. Compliance ensures that the material meets stringent electrical and mechanical performance criteria.
-
ASTM D7264: This standard covers the mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced polymer matrix composites, ensuring that the materials meet the necessary performance specifications for high-stress applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
To maintain high quality, manufacturers implement several quality control (QC) checkpoints throughout the production process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt. For FR4, this may include verifying the quality of fiberglass and resin, while for carbon fiber, it would involve checking the quality of the precursor fibers.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and material consistency. This helps identify any deviations from the production standards early on.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the products are completed, a thorough inspection is performed. This includes dimensional checks, mechanical testing, and electrical testing (for FR4). For carbon fiber, tests may include tensile strength and flexural strength assessments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are some strategies to ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This can help buyers assess compliance with international standards and identify areas for improvement.
-
Quality Control Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports from suppliers can help buyers understand the specific tests conducted and the results achieved. This transparency is essential for building trust and ensuring product reliability.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly valuable for buyers who may not have the resources to conduct their own audits.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
When engaging with suppliers of FR4 and carbon fiber plates, international buyers must consider several nuances that can affect their purchasing decisions:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations in their respective markets.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can enhance communication and negotiation. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better collaboration and quality outcomes.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping and logistics can pose challenges, including delays and increased costs. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to establish clear timelines and expectations for delivery.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for FR4 and carbon fiber plates, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and industry standards. This knowledge not only enhances product quality but also fosters stronger supplier relationships, essential for long-term success in the competitive global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fr4 vs carbon fiber plate’
Introduction
When considering the procurement of FR4 or carbon fiber plates, it is essential for B2B buyers to follow a systematic approach. This guide serves as a practical checklist to navigate the complexities of material selection, ensuring you make informed decisions tailored to your specific application needs. Whether for electronic components or structural applications, understanding the nuances of these materials is crucial for optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your project. This includes mechanical strength, weight constraints, electrical insulation properties, and environmental conditions.
– Considerations: FR4 is ideal for applications requiring good electrical insulation, while carbon fiber excels in lightweight and high-strength applications.
– Documentation: Keep a record of these specifications to streamline the sourcing process.
Step 2: Identify Application Requirements
Assess the specific applications where the plates will be used. Different industries have varying demands that affect material choice.
– Examples: FR4 is commonly used in printed circuit boards due to its electrical insulation, whereas carbon fiber is preferred in aerospace for its high strength-to-weight ratio.
– Performance Metrics: Ensure that you have measurable performance metrics to evaluate material suitability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, conduct a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers. This includes reviewing their company profiles, product offerings, and industry experience.
– References: Request case studies or testimonials from previous clients, particularly those in similar sectors or regions.
– Certifications: Verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications (e.g., ISO) to ensure quality and reliability.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Always request material samples before placing a bulk order. This allows you to assess the physical properties and compatibility with your application.
– Testing Criteria: Evaluate the samples based on strength, flexibility, and thermal properties.
– Feedback Loop: Gather feedback from your engineering team to confirm that the samples meet your requirements.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Conduct a comprehensive comparison of pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms among shortlisted suppliers.
– Cost Analysis: Take into account not just the initial purchase price, but also the total cost of ownership, including shipping and potential tariffs.
– Negotiation: Be prepared to negotiate terms to secure the best deal while ensuring quality.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Evaluate the after-sales support and warranty options provided by the suppliers. Reliable support can significantly impact your project’s success.
– Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Look for suppliers that offer clear SLAs for response times and issue resolution.
– Warranty Terms: Understand the warranty coverage for defects or performance issues to safeguard your investment.
Step 7: Finalize and Place Your Order
Once all evaluations are complete and you are confident in your choice, proceed to finalize the contract and place your order.
– Contract Review: Ensure that all terms discussed are documented in the contract, including delivery schedules and payment terms.
– Follow-Up: Maintain communication with the supplier throughout the order process to mitigate any potential issues.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the selection and procurement of FR4 and carbon fiber plates, ensuring their choices align with project requirements and operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fr4 vs carbon fiber plate Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing FR4 and carbon fiber plates, it is essential to dissect the various cost components involved. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials can significantly influence the overall pricing. FR4 is typically less expensive due to its widespread availability and the established manufacturing processes. Conversely, carbon fiber is generally more costly, reflecting its advanced manufacturing techniques and superior properties, such as strength-to-weight ratio.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the complexity of the manufacturing process. Carbon fiber fabrication often requires specialized skills and techniques, which can lead to higher labor costs compared to the more straightforward production of FR4 plates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs encompass utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility expenses. These costs may be higher for carbon fiber due to the specialized equipment needed for its production.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can also differ between the two materials. Carbon fiber plates may require more advanced tooling, increasing initial investment. However, once established, the tooling for FR4 can be equally costly due to the need for precision in PCB applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Both materials necessitate stringent QC processes, but carbon fiber might incur additional testing costs due to its applications in high-performance sectors, such as aerospace and automotive.
-
Logistics: Logistics costs can vary based on the weight and volume of the materials. Carbon fiber, being lighter, may offer advantages in shipping costs, especially for international buyers.
-
Margin: Supplier margins will also influence pricing. As carbon fiber is a premium product, suppliers may maintain higher margins compared to FR4 manufacturers.
How Do Price Influencers Impact FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plate Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of FR4 and carbon fiber plates, including order volume, specifications, material quality, and supplier characteristics.
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often lead to reduced unit costs. Suppliers may offer significant discounts for larger quantities, making it more economical for B2B buyers to purchase in bulk.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses. Carbon fiber plates, due to their manufacturing process, may have higher customization costs compared to FR4.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The presence of industry certifications can elevate costs, particularly for carbon fiber, which is often subject to stringent safety and performance standards in sectors like aerospace.
-
Supplier Factors: The choice of supplier can greatly impact costs. Established suppliers with a good reputation may charge more due to their reliability and quality assurance processes. It’s crucial for buyers to evaluate potential suppliers based on their track record and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international shipping terms is vital. Different Incoterms can affect the total landed cost, influencing decisions for buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates?
To maximize value when sourcing FR4 and carbon fiber plates, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate: Always negotiate prices and terms with suppliers. Establishing a strong relationship can lead to better deals, especially for long-term contracts.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with each material, including maintenance, performance longevity, and potential failure costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and tariffs that may affect pricing for international buyers. For example, buyers from Nigeria or Vietnam should consider local economic conditions and trade agreements.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Gather quotes from various suppliers to compare not just prices, but also quality, lead times, and service offerings. This competitive approach can yield better overall value.
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics of FR4 versus carbon fiber plates allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and market conditions. Always remember that indicative prices can vary based on the factors discussed, necessitating diligent research and negotiation.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fr4 vs carbon fiber plate With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Material Alternatives in Engineering
When selecting materials for industrial applications, B2B buyers often face a myriad of choices that can significantly impact performance, cost, and ease of implementation. In the context of FR4 and carbon fiber plates, it’s essential to assess viable alternatives that could meet specific project requirements. By examining other materials or methods, buyers can make more informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
| Comparison Aspect | Fr4 Vs Carbon Fiber Plate | Alternative 1: Aluminum Plate | Alternative 2: Polycarbonate Plate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good electrical insulation; moderate mechanical strength; flexible | High strength and rigidity; good thermal conductivity | Excellent flexibility; good impact resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost; cost-effective for electronic applications | Moderate cost; varies with thickness and treatment | Lower to moderate cost; highly available |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific handling due to fragility; easier to process than carbon fiber | Easy to machine; widely used in various applications | Simple to work with; lightweight |
| Maintenance | Low; stable under normal conditions | Low; corrosion resistant with proper treatment | Low; resistant to impact but can scratch |
| Best Use Case | PCBs, electronic devices, structural components | Structural applications, automotive, aerospace | Enclosures, safety goggles, lightweight components |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Aluminum Plates?
Aluminum plates are a popular alternative due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent thermal conductivity. They are commonly used in aerospace and automotive applications where structural integrity and weight savings are critical. However, while aluminum provides robustness, it lacks the electrical insulation properties of FR4, which may limit its use in electronic applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more costly than FR4, depending on the thickness and treatment required, which could affect budget-conscious projects.
How Do Polycarbonate Plates Compare to FR4 and Carbon Fiber?
Polycarbonate plates are known for their excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making them a suitable choice for applications requiring durability without significant weight. They are often used in safety equipment and lightweight structural components. However, while polycarbonate offers good performance in terms of flexibility, it does not match the electrical insulating capabilities of FR4. Furthermore, polycarbonate can be more susceptible to scratches compared to the rigidity of carbon fiber and aluminum, which may affect long-term aesthetic performance.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Material for Your Application
When selecting between FR4, carbon fiber plates, and their alternatives, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and application context. FR4 is ideal for electronic applications due to its electrical insulating properties, while carbon fiber excels in high-performance environments where weight is a critical factor. Alternatives like aluminum and polycarbonate offer unique benefits but come with trade-offs in terms of cost and specific application suitability. Ultimately, understanding the specific needs of your project will guide you in making the most effective choice.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fr4 vs carbon fiber plate
What Are the Key Technical Properties of FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates?
When selecting between FR4 and carbon fiber plates, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key properties that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Definition: Material grade refers to the classification of a material based on its composition and performance characteristics. For FR4, it indicates its flame resistance and electrical insulation capabilities. Carbon fiber grades are determined by the tensile strength and modulus of elasticity.
B2B Importance: Selecting the appropriate material grade is essential for ensuring that the product meets industry standards and performs reliably in its intended application. For example, FR4 is often used in electronics where flame resistance is critical, while high-grade carbon fiber is preferred in aerospace for its strength-to-weight ratio.
2. Tolerance
Definition: Tolerance specifies the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension or property of a material. This includes measurements like thickness, width, and length.
B2B Importance: Tighter tolerances are essential in applications where precision is critical, such as in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs) or in aerospace components. Understanding tolerance levels helps in maintaining quality control and ensuring compatibility with other components.
3. Mechanical Strength
Definition: Mechanical strength refers to a material’s ability to withstand applied forces without failure. For FR4, this is characterized by tensile and compressive strength, while carbon fiber is known for its superior tensile strength.
B2B Importance: The right mechanical strength is vital for applications requiring durability and reliability. For instance, carbon fiber is ideal for high-performance automotive parts, while FR4 is suitable for structural supports in electronic devices.
4. Electrical Insulation
Definition: This property indicates a material’s ability to resist the flow of electric current. FR4 is recognized for its excellent electrical insulating properties, whereas carbon fiber can exhibit varying levels of conductivity.
B2B Importance: Choosing the right material based on its electrical insulation properties is crucial for preventing electrical interference in electronic applications. For example, FR4 is a standard choice for PCBs, while carbon fiber may be used in specialized applications where conductivity is advantageous.
5. Weight
Definition: Weight refers to the mass of the material per unit volume. FR4 is heavier than carbon fiber, which is known for its lightweight characteristics.
B2B Importance: In industries like aerospace and automotive, minimizing weight is often a critical design parameter. Carbon fiber’s lightweight nature allows for better fuel efficiency and performance, making it a preferred choice in these sectors.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to FR4 and Carbon Fiber?
Understanding industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some common terms relevant to FR4 and carbon fiber plates:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Definition: An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
Relevance: Buyers may need to ensure that suppliers are OEM-certified to guarantee the quality and compatibility of the components being procured.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
Definition: MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
Relevance: Understanding MOQ is essential for budget management and inventory planning. For instance, if a buyer needs a small batch of FR4 plates but the MOQ is high, it may lead to excess inventory costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products.
Relevance: Sending an RFQ can help buyers compare prices, terms, and conditions across different suppliers, aiding in informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Definition: Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for understanding shipping, liability, and risk management in international trade, especially when sourcing materials like FR4 and carbon fiber from global suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Definition: Lead time refers to the amount of time between the initiation of an order and its completion.
Relevance: Knowing the lead time is critical for project planning and delivery schedules, especially in industries where timely product availability can impact production timelines.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing FR4 and carbon fiber plates more effectively, ensuring that they select the right materials for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fr4 vs carbon fiber plate Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers for FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates?
The global market for FR4 and carbon fiber plates is being shaped by several pivotal drivers. As industries strive for lighter, stronger materials, carbon fiber’s exceptional strength-to-weight ratio positions it as a preferred choice in sectors like aerospace and automotive. Conversely, FR4 remains indispensable in electronics due to its excellent electrical insulating properties. The increasing demand for electronic devices and the growth of renewable energy technologies, such as wind and solar, are bolstering the FR4 market. Emerging trends such as automation, IoT, and smart manufacturing are also influencing material choices, with FR4 being favored for PCB applications.
Moreover, geographical dynamics play a significant role in sourcing strategies. For instance, international B2B buyers from Africa and South America are increasingly seeking high-performance materials at competitive prices. In contrast, buyers in Europe and the Middle East are emphasizing the need for compliance with stringent regulations and sustainability criteria. The rise of e-commerce and digital procurement platforms is facilitating easier access to suppliers, enabling buyers to source materials like FR4 and carbon fiber more efficiently.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies for international buyers, especially in the context of FR4 and carbon fiber plates. Both materials have environmental implications, with FR4 being less environmentally friendly due to its epoxy content, which can be challenging to recycle. However, efforts are underway to develop greener alternatives, such as bio-based epoxy resins, which can mitigate environmental impact.
On the other hand, carbon fiber, while lightweight and strong, involves energy-intensive manufacturing processes that raise sustainability concerns. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to ethical sourcing practices and possess certifications like ISO 14001, which focuses on environmental management. Companies are encouraged to engage with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and investing in sustainable production methods. This shift not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with consumer expectations for responsible sourcing.
What Is the Historical Context of FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates in B2B Markets?
The evolution of FR4 and carbon fiber plates traces back to significant advancements in material science. FR4 emerged in the mid-20th century as a reliable electrical insulator, quickly becoming the standard for printed circuit boards (PCBs) due to its mechanical strength and thermal stability. Its adoption in various industries paved the way for innovations in electronics, telecommunications, and automotive sectors.
Carbon fiber, on the other hand, gained prominence in the late 20th century, initially finding applications in aerospace and military sectors due to its unparalleled strength-to-weight ratio. Over the years, its usage has expanded into consumer goods, sports equipment, and automotive components, driven by the demand for lightweight, high-performance materials. As both materials continue to evolve, their historical significance lays the groundwork for future advancements and applications in the B2B landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fr4 vs carbon fiber plate
-
How do I choose between FR4 and carbon fiber plates for my application?
Choosing between FR4 and carbon fiber plates hinges on your specific application requirements. If you need excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength, FR4 is often the better choice, particularly for electronic components and PCBs. Conversely, if your application prioritizes lightweight construction with high tensile strength, carbon fiber is ideal, especially in aerospace or automotive sectors. Evaluate factors like weight, strength, and electrical properties to make an informed decision. -
What are the mechanical properties of FR4 compared to carbon fiber?
FR4 is known for its good rigidity and impact resistance, making it suitable for structural applications. It offers a balance of strength and weight but is denser than carbon fiber. In contrast, carbon fiber boasts an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, providing superior stiffness and tensile strength. While FR4 is robust for electronics and construction, carbon fiber excels in applications requiring minimal mass without sacrificing strength. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for FR4 and carbon fiber plates?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and region. Typically, FR4 plates may have MOQs ranging from 50 to 100 units, while carbon fiber plates often have higher MOQs due to their specialized manufacturing processes. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that suit your project requirements and budget. -
What customization options are available for FR4 and carbon fiber plates?
Customization options for FR4 and carbon fiber plates may include variations in thickness, size, and surface finish. Some suppliers offer additional services like CNC machining, cutting, or layering for specific applications. Discuss your design requirements with suppliers to explore available customization options, ensuring the final product meets your application’s specifications. -
How can I vet suppliers for FR4 and carbon fiber plates?
To effectively vet suppliers, consider their industry experience, certifications, and customer reviews. Request samples to assess material quality and performance. Additionally, inquire about their production capabilities, lead times, and compliance with international standards. Establishing open communication and asking for references can further ensure you partner with a reliable supplier. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing FR4 and carbon fiber plates internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common terms include upfront deposits (20-30%) with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. For larger orders, some suppliers may offer extended credit terms. Always clarify payment methods, currencies accepted, and any potential fees to avoid unexpected costs in international transactions. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in FR4 and carbon fiber plate suppliers?
Quality assurance measures to consider include ISO certification, material testing, and compliance with industry standards. Suppliers should provide documentation proving their products meet specified tolerances and performance criteria. Inquire about their quality control processes, including inspections during manufacturing and post-production testing, to ensure you receive materials that meet your requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing FR4 and carbon fiber plates?
When importing these materials, be aware of shipping costs, customs duties, and lead times. Ensure you have a clear understanding of the supplier’s shipping policies and the potential for delays in customs clearance. It’s advisable to partner with logistics providers experienced in handling industrial materials to streamline the import process and minimize risks associated with international shipping.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Fr4 Vs Carbon Fiber Plate Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. FR4 Material – High Strength Composite Solutions
Domain: fr4material.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: FR4 is a composite material made of woven fiberglass fabric impregnated with epoxy resin, known for its high mechanical strength, electrical insulating properties, and applications in electronics and construction. Carbon fiber consists of thin fibers primarily made of carbon atoms, offering exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, tensile strength, and stiffness, making it ideal for aerospace, automo…
2. Z Telec Group – FR-4 Glass-Reinforced Epoxy Laminate
Domain: ztelecgroup.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: FR4: FR-4 is a NEMA grade designation for glass-reinforced epoxy laminate material, composed of woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder that is flame resistant. It has high mechanical strength, good rigidity, and impact resistance, making it suitable for applications in electronics and construction. The density of FR4 typically ranges from 1.7 to 1.9 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). I…
3. Akkogear – Ultimate Guide to Keyboard Plates
Domain: en.akkogear.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
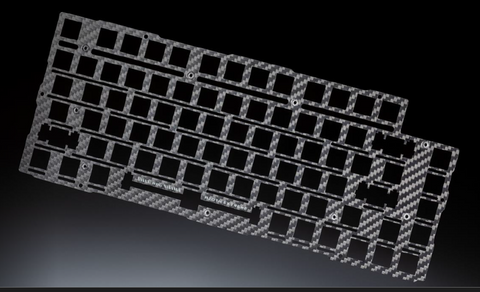
Introduction: The Ultimate Guide to Selecting Keyboard Plates discusses eight common materials used for keyboard plates: PP, PC, POM, FR4, Aluminum, Carbon Fiber, Copper, and Steel. Each material affects the feel and sound of the keyboard.
– **PP**: Soft and bouncy feel; muted sound.
– **PC**: Softer, prone to deformation; soft and muted sound.
– **POM**: Similar to PC; low-pitched sound.
– **FR4**: Medium…
4. KeebTalk – Key Plate Materials
Domain: keebtalk.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: 1. Plate Materials Discussed: Brass, Aluminum, Carbon Fiber, Polycarbonate, POM, Acrylic, FR4, Stainless Steel, Copper, ABS Plastic, Polypropylene. 2. Brass: Preferred for rigidity, sound amplification, and firm bottom-out feel; can be expensive. 3. Aluminum: Safe all-rounder, moderately priced, softer than brass, good sound properties. 4. Carbon Fiber: Lightweight, malleable, sound similar to pol…
5. JHD Materials – FR4 Epoxy Solutions
Domain: blog.jhd-material.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: FR4 is a glass-reinforced epoxy material known for its excellent electrical insulation and mechanical properties, primarily used in the electronics industry for printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electrical components. It is produced by layering fiberglass cloth impregnated with epoxy resin under heat and pressure, resulting in a dense material available in various thicknesses and sizes. FR4 exhibi…
6. Knckeys – Ideal Keyboard Plate Materials
Domain: knckeys.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Selecting the ideal keyboard plate material is crucial for your typing experience. The most popular materials include: Aluminum, Brass, Carbon Fiber, Polypropylene (PP), Polyoxymethylene (POM), Polycarbonate (PC), and Flame Retardant-4 (FR4). Each material has unique characteristics: Aluminum is rigid with a moderate sound profile; Brass is heavier with a pronounced sound; Carbon Fiber is lightwei…
7. RC Groups – Carbon Fiber vs G10 Plates
Domain: rcgroups.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 1mm carbon fiber plate: Lighter and stiffer than 1.5mm G10; can be used in thinner layers; blocks radio signals. 1.5mm G10: Heavier (about 40% heavier per unit volume); gives a bit in a crash; easier to cut and drill.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fr4 vs carbon fiber plate
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers Considering FR4 and Carbon Fiber Plates?
In the competitive landscape of material sourcing, understanding the distinct properties of FR4 and carbon fiber plates is crucial for informed decision-making. FR4 offers excellent electrical insulation, robust mechanical strength, and is ideal for applications in electronics and construction. In contrast, carbon fiber stands out for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it a preferred choice in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Important for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing can enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Evaluating the specific requirements of your projects—whether prioritizing weight, mechanical strength, or electrical insulation—will enable you to select the most suitable material.
What’s Next for Your Material Sourcing Strategy?
As industries continue to evolve, embracing innovation in material selection will be vital. Engage with suppliers who can provide insights tailored to your unique needs and foster partnerships that enhance your supply chain resilience. By strategically sourcing FR4 or carbon fiber plates, you position your business for future growth and success. Explore your options today and stay ahead in the dynamic marketplace.