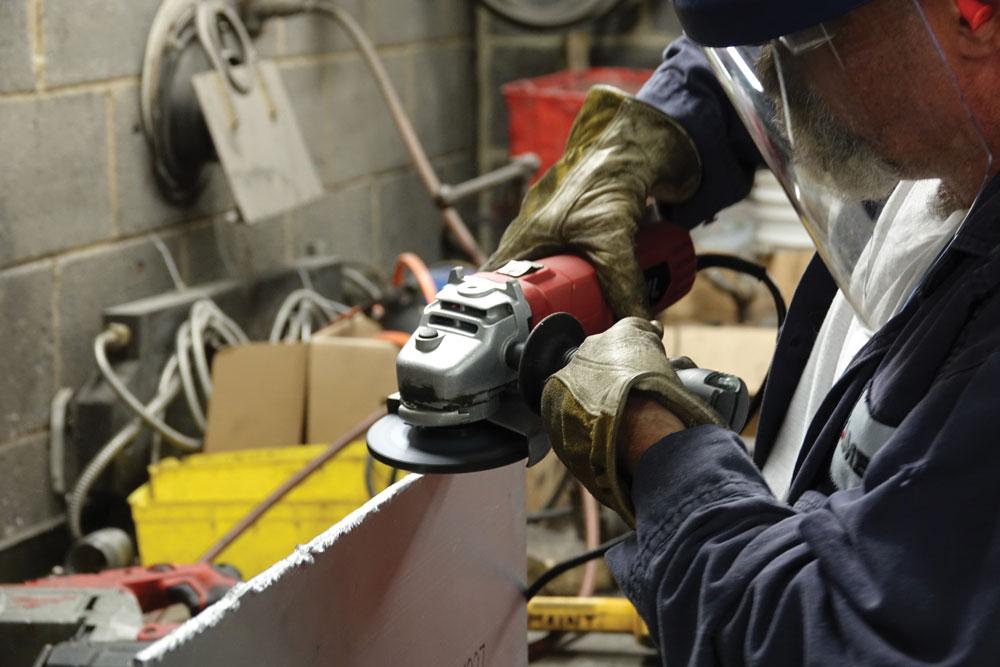
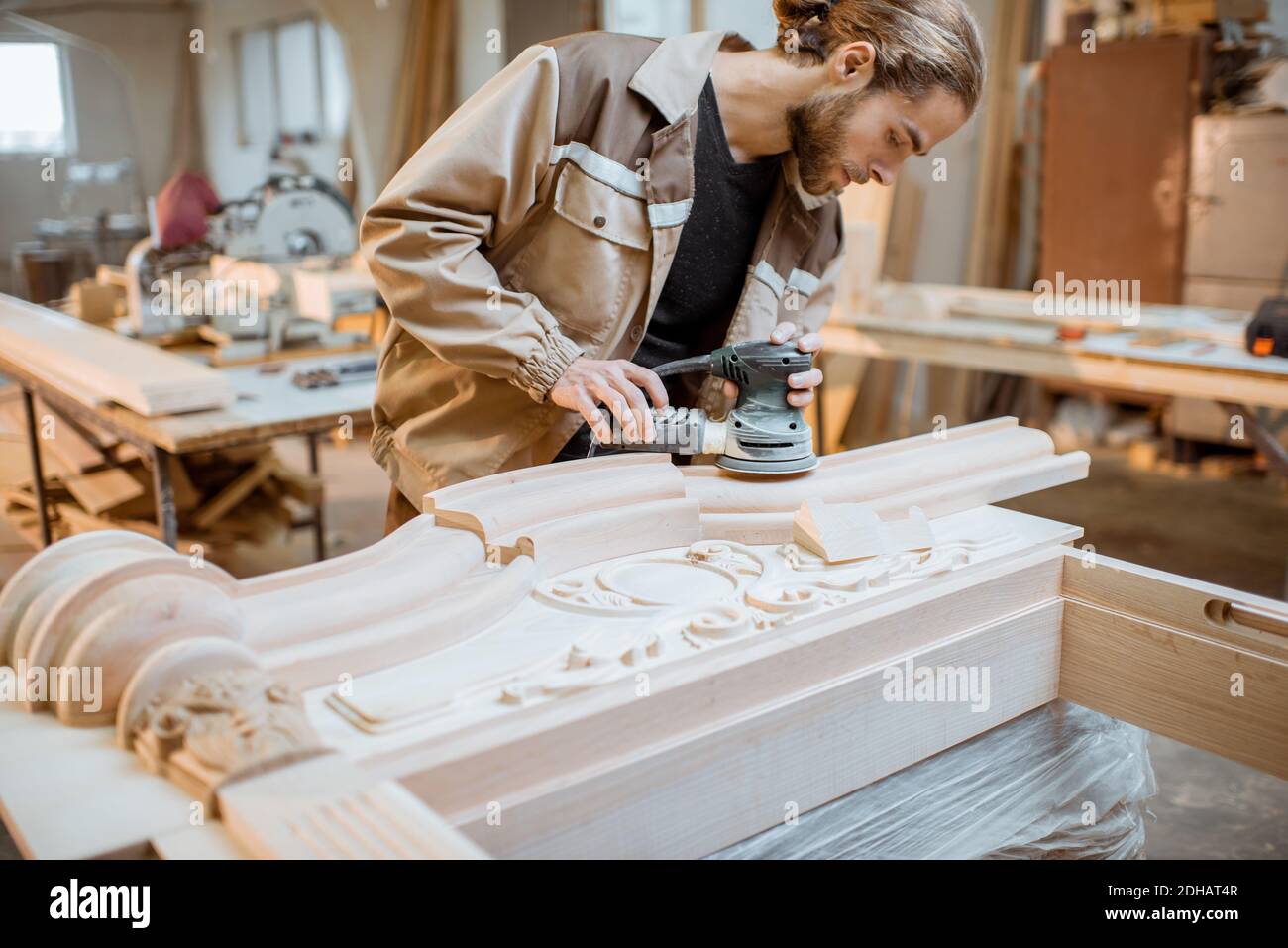
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for finishing grinding
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing the right finishing grinding solutions can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Whether you are looking to enhance surface finishes for aerospace components or require precision grinding for automotive parts, understanding the complexities of this specialized market is essential. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource that addresses the various types of finishing grinding processes, their applications across industries, and the critical factors to consider when selecting suppliers.
With insights into supplier vetting, cost analysis, and best practices, this guide empowers decision-makers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Brazil and Nigeria—to make informed purchasing choices. By highlighting the latest technologies and innovations in finishing grinding, as well as the potential for optimizing production processes, we aim to facilitate strategic partnerships that drive efficiency and quality in your operations.
Navigating the global market for finishing grinding requires not only knowledge of the available solutions but also an understanding of the specific needs of your industry. This guide will equip you with the tools necessary to elevate your sourcing strategy, ensuring you achieve the highest standards in precision and performance.
Understanding finishing grinding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Grinding | Utilizes rotating cylindrical workpieces; high precision. | Automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. | Pros: High precision, excellent surface finish. Cons: Longer setup time, may require specialized machinery. |
| Surface Grinding | Flat surfaces are ground using a rotating wheel; versatile. | Tool making, metal fabrication, and machining. | Pros: Effective for large surfaces, adaptable. Cons: Limited to flat surfaces, may not achieve the finest finishes. |
| Centerless Grinding | Workpieces are ground without a spindle; allows for continuous production. | Bar stock, automotive parts, and fasteners. | Pros: High efficiency, suitable for mass production. Cons: Limited to cylindrical parts, setup complexity. |
| Gear Grinding | Specialized for finishing gears; uses specific grinding wheels. | Automotive and machinery manufacturing. | Pros: Precision for gear teeth, enhances performance. Cons: Equipment can be costly, requires skilled operators. |
| Microfinishing | Achieves ultra-fine finishes using superabrasives; often a secondary process. | Aerospace, medical devices, and high-precision components. | Pros: Exceptional surface quality, reduces friction. Cons: Higher operational costs, may require specialized abrasives. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Cylindrical Grinding?
Cylindrical grinding is characterized by its ability to handle cylindrical workpieces, enabling high precision and excellent surface finishes. This method is particularly suitable for industries such as automotive and aerospace, where tight tolerances are essential. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the required precision levels and the type of materials being processed, as these factors will influence the choice of grinding equipment and abrasives.
How Does Surface Grinding Meet Diverse B2B Needs?
Surface grinding is a versatile finishing method that focuses on producing flat surfaces. It is widely used in tool making and metal fabrication due to its adaptability to various materials. Buyers should consider the dimensions of the workpieces and the desired finish quality when selecting surface grinding machines. The ability to grind large areas efficiently makes this method appealing, but it may not achieve the same fine finishes as other methods.
What Advantages Does Centerless Grinding Offer for Mass Production?
Centerless grinding stands out for its efficiency in producing cylindrical components without the need for a spindle. This method is ideal for mass production applications such as bar stock and automotive parts. B2B buyers should assess the production volume and the complexity of the parts being produced, as while it offers high throughput, it may present challenges in setup and alignment.
Why is Gear Grinding Critical in Manufacturing?
Gear grinding is specifically designed to finish gears with precision, utilizing specialized grinding wheels. This method is crucial in automotive and machinery manufacturing, where the performance of gears is vital. Buyers need to consider the costs associated with gear grinding equipment and the expertise required to operate it effectively. The precision achieved through this method can significantly impact the performance and longevity of gear systems.
How Does Microfinishing Enhance Product Quality?
Microfinishing employs superabrasives to achieve ultra-fine surface finishes, often as a secondary process after initial grinding. This technique is essential in industries like aerospace and medical devices, where component performance is critical. B2B buyers should evaluate the overall cost implications and the specific requirements for surface finishes when investing in microfinishing solutions, as the quality achieved can reduce friction and enhance product performance.
Key Industrial Applications of finishing grinding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Finishing Grinding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Surface finishing of turbine blades and engine components | Enhances performance, reliability, and longevity of parts | Precision requirements, material compatibility, certification standards |
| Automotive | Gear grinding for transmission systems | Improves efficiency and reduces noise in vehicle operations | Tolerances, material specifications, and production volume |
| Medical Devices | Finishing of surgical instruments and implants | Ensures high standards of hygiene and biocompatibility | Compliance with medical standards, surface finish quality, and traceability |
| Oil & Gas | Finishing of drilling tools and pipeline components | Increases durability and resistance to harsh environments | Material selection, corrosion resistance, and certification requirements |
| Tool Manufacturing | Grinding of cutting tools and molds | Enhances tool longevity and precision, reducing operational costs | Customization options, tooling materials, and lead times |
How Is Finishing Grinding Applied in the Aerospace Sector?
In the aerospace industry, finishing grinding is crucial for achieving the precise surface finishes required for turbine blades and engine components. These components must endure extreme conditions, and a smooth finish reduces friction and improves efficiency. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers who meet strict certification standards and can provide detailed documentation of their grinding processes to ensure compliance with aerospace regulations.
What Role Does Finishing Grinding Play in Automotive Gear Systems?
For the automotive industry, finishing grinding is essential in the production of gears used in transmission systems. This process enhances the efficiency and noise characteristics of vehicles, directly impacting customer satisfaction. B2B buyers should consider the specific tolerances and material specifications required for their gear systems, as well as the supplier’s ability to handle high production volumes while maintaining quality.
Why Is Finishing Grinding Important for Medical Devices?
In the medical devices sector, finishing grinding is applied to surgical instruments and implants to achieve the highest hygiene standards and biocompatibility. This process ensures that surfaces are smooth and free from contaminants, which is critical for patient safety. Buyers must source materials that comply with medical standards and require detailed traceability of manufacturing processes to guarantee product integrity.
How Does Finishing Grinding Enhance Oil & Gas Equipment Durability?
In the oil and gas industry, finishing grinding is used to enhance the durability of drilling tools and pipeline components. These tools must withstand extreme conditions, making effective surface finishing essential for resistance to wear and corrosion. Buyers should focus on sourcing materials that offer the best corrosion resistance and verify that suppliers can meet the necessary certification requirements for safety and quality.
What Benefits Does Finishing Grinding Provide in Tool Manufacturing?
Finishing grinding is vital in tool manufacturing, particularly for cutting tools and molds, as it improves precision and extends tool life. This leads to reduced operational costs and increased productivity. When sourcing for this application, buyers should look for suppliers who can offer customization options tailored to specific tooling needs and who have proven capabilities in using high-quality materials.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘finishing grinding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Surface Quality Leading to Product Rejections
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as aerospace and automotive often face the challenge of inconsistent surface quality in their finishing grinding processes. This inconsistency can lead to product rejections during quality control checks, resulting in costly delays and rework. For companies operating in competitive markets, even minor deviations in surface finish can lead to significant financial losses and damage to reputation. Buyers may struggle with identifying the root cause of these inconsistencies, which can stem from inadequate equipment, poor abrasive selection, or ineffective operator training.
The Solution: To address surface quality issues, buyers should invest in high-quality, industry-specific abrasives tailored to their specific materials and surface finish requirements. Conducting a thorough analysis of the grinding process is essential; this includes evaluating the equipment’s capabilities, the types of abrasives used, and the grinding parameters. Collaborating with suppliers who offer technical expertise can provide insights into optimizing grinding wheels or belts for specific applications. Additionally, implementing regular training programs for operators can enhance their understanding of the equipment and the importance of maintaining consistent operational parameters. By establishing a feedback loop that includes both quality control data and operator insights, companies can continuously refine their processes and achieve the desired surface finishes.
Scenario 2: Equipment Downtime and Maintenance Costs
The Problem: Many B2B manufacturers experience frequent equipment downtime due to the wear and tear associated with finishing grinding operations. This can be particularly problematic in regions where access to maintenance services is limited, such as in parts of Africa and South America. The costs associated with unplanned maintenance can quickly escalate, leading to budget overruns and reduced production capacity. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the complexity of maintaining various types of grinding machinery and may lack the resources to implement a comprehensive maintenance strategy.
The Solution: To mitigate equipment downtime, B2B buyers should adopt a proactive maintenance approach, focusing on predictive maintenance techniques that leverage technology. Investing in sensors and monitoring systems can help track the performance of grinding machines and predict potential failures before they occur. Furthermore, partnering with equipment manufacturers for scheduled maintenance and service agreements can ensure that machines are kept in optimal condition. Buyers should also consider standardizing equipment across their operations to simplify maintenance procedures and reduce training costs. By fostering a culture of preventive care and investing in the right technology, manufacturers can extend the lifespan of their equipment and reduce overall maintenance costs.
Scenario 3: Navigating Regulatory Compliance and Quality Standards
The Problem: International buyers often face the challenge of navigating complex regulatory compliance and quality standards, particularly in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. Ensuring that finishing grinding processes meet strict standards can be daunting, especially when sourcing materials and equipment from different regions. Buyers may find themselves struggling to align their operations with local and international regulations, risking penalties and damage to their market reputation.
The Solution: To effectively navigate regulatory compliance, B2B buyers should establish a comprehensive compliance framework that includes a clear understanding of the applicable regulations in their target markets. This involves thorough research into local standards, such as the ASME BPE for biopharmaceutical equipment, and maintaining open communication with suppliers to ensure that materials and processes meet these standards. Buyers should also seek certification from recognized bodies to validate their processes and products. Implementing a robust quality management system (QMS) that integrates compliance checks into every stage of production can further enhance assurance. Training staff on compliance requirements and regularly reviewing processes will help maintain adherence to standards, thereby minimizing risk and ensuring quality throughout the supply chain.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for finishing grinding
What Are the Key Materials Used in Finishing Grinding?
When selecting materials for finishing grinding processes, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. This analysis will cover four common materials: aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, ceramic, and diamond abrasives. Each material offers unique benefits and challenges, particularly relevant to international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Aluminum Oxide Perform in Finishing Grinding?
Aluminum oxide is a widely used abrasive material known for its durability and versatility. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various grinding applications. Its corrosion resistance is moderate, which allows it to perform well in environments with minimal moisture.
Pros: Aluminum oxide is cost-effective and readily available, making it a popular choice for many manufacturers. It is suitable for grinding ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Cons: While durable, it may not perform as well on harder materials compared to other abrasives. Its performance can degrade at elevated temperatures, limiting its use in high-speed applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum oxide is compatible with a wide range of grinding media, making it a versatile choice for various industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers should also consider local sourcing options to minimize costs and ensure timely delivery.
What Benefits Does Silicon Carbide Offer for Finishing Grinding?
Silicon carbide is another popular abrasive material, particularly effective for hard materials. It has a high thermal conductivity and is known for its sharpness, allowing for efficient cutting.
Pros: Silicon carbide is excellent for grinding non-ferrous metals and hard materials like ceramics and glass. Its high wear resistance extends tool life, making it a cost-effective option in the long run.
Cons: It is more brittle than aluminum oxide, which may lead to chipping or fracturing during aggressive grinding operations. This brittleness can limit its use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Silicon carbide is particularly effective in applications requiring fine finishes, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of regional preferences for silicon carbide abrasives and ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as JIS in Japan or EN in Europe.
Why Choose Ceramic Abrasives for Finishing Grinding?
Ceramic abrasives are engineered for high-performance applications. They are known for their exceptional durability and ability to maintain sharpness over extended periods.
Pros: The long lifespan of ceramic abrasives results in lower overall costs due to reduced tool changes. They are suitable for high-speed grinding and can handle tough materials effectively.
Cons: The initial cost of ceramic abrasives is higher than that of aluminum oxide or silicon carbide. This can be a deterrent for smaller businesses or those with tight budgets.
Impact on Application: Ceramic abrasives excel in applications requiring high precision and surface finish, making them ideal for industries such as aerospace and medical devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Given their specialized nature, buyers should evaluate the availability of ceramic abrasives in their region and ensure they meet specific industry standards.
What Are the Advantages of Diamond Abrasives in Finishing Grinding?
Diamond abrasives are the hardest known materials and are highly effective for precision grinding applications. They offer unmatched cutting efficiency and longevity.
Pros: Diamond abrasives can grind the hardest materials, including carbide and ceramics, providing superior surface finishes. Their extended lifespan leads to reduced downtime and increased productivity.
Cons: The high cost of diamond abrasives can be a barrier for many businesses. Additionally, they require specific handling and storage conditions to maintain their performance.
Impact on Application: Diamond abrasives are ideal for high-precision applications in industries such as electronics and optics, where surface quality is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the cost-benefit ratio of diamond abrasives and ensure compliance with international standards for safety and performance.
Summary of Material Selection for Finishing Grinding
| Material | Typical Use Case for finishing grinding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide | General metal grinding | Cost-effective and versatile | Performance degrades at high temperatures | Low |
| Silicon Carbide | Grinding hard materials | Excellent for fine finishes | Brittle, may chip under stress | Medium |
| Ceramic Abrasives | High-precision applications | Long lifespan and high performance | Higher initial cost | High |
| Diamond Abrasives | Precision grinding of hard materials | Unmatched cutting efficiency and longevity | Very high cost, requires careful handling | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers looking to optimize their finishing grinding processes. By understanding the properties and applications of these materials, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for finishing grinding
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Finishing Grinding?
Finishing grinding is a crucial operation in the manufacturing sector, ensuring that products meet precise specifications and quality standards. The process typically involves several key stages:
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting the appropriate raw materials and preparing them for grinding. Depending on the application, materials may be metals, plastics, or ceramics. Effective preparation includes cutting the material to size, removing any surface contaminants, and ensuring uniformity in shape and dimensions.
-
Forming: In this phase, the material undergoes shaping processes, which could include turning, milling, or casting. The goal is to achieve a near-net shape that requires minimal finishing. Advanced techniques like CNC machining can be employed for high precision, ensuring that the formed parts are ready for grinding.
-
Grinding: This is the core of the finishing process, where abrasive materials are used to remove excess material and achieve the desired surface finish. Different techniques may be applied, such as cylindrical grinding, surface grinding, or centerless grinding, depending on the shape and finish required. The choice of grinding wheel, speed, and feed rate significantly influences the quality and efficiency of the operation.
-
Finishing: After grinding, additional finishing processes may be necessary to enhance the surface quality. Techniques like buffing, polishing, or microfinishing can create a mirror-like finish that meets stringent specifications. This stage is vital for applications in industries such as aerospace and medical devices, where surface integrity is critical.
-
Assembly: In cases where multiple components are involved, assembly follows finishing. This stage requires precision to ensure that all parts fit together seamlessly, maintaining the integrity of the finished product.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Finishing Grinding?
Quality assurance in finishing grinding is essential for ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. Here are some key components of an effective quality assurance program:
-
International Standards Compliance: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001 standards, which emphasize a quality management system focused on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Compliance with these standards is often a prerequisite for doing business internationally, particularly for buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East.
-
Industry-Specific Standards: In addition to ISO certifications, some industries require adherence to specific standards such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications. Understanding these requirements is critical for B2B buyers to ensure that suppliers can meet their specific needs.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, ongoing checks are performed to monitor parameters such as dimensions, surface finish, and tooling wear.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): This final checkpoint involves comprehensive testing of finished products against specifications before they are shipped. Testing methods may include dimensional inspections, surface roughness measurements, and non-destructive testing techniques.
What Testing Methods are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance for Finishing Grinding?
To ensure the highest quality, various testing methods are employed during the quality assurance process:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing precision measuring tools such as calipers and coordinate measuring machines (CMM), manufacturers assess the dimensions of finished components to ensure they meet tolerances.
-
Surface Roughness Testing: Specialized instruments like profilometers measure surface roughness, providing insights into the effectiveness of the grinding process and ensuring that it meets customer specifications.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection help identify internal defects without damaging the components, which is crucial for high-stakes applications in aerospace and medical fields.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is critical for mitigating risks. Here are several strategies to ensure supplier compliance with quality standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate a supplier’s quality management practices firsthand. During these audits, buyers can review documentation, observe processes, and assess adherence to standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide regular quality reports that outline inspection results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken. These reports are vital for buyers to gauge ongoing supplier performance.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These agencies can conduct independent evaluations and testing, offering an added layer of assurance.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of quality control and certification can be challenging for international B2B buyers. Here are some nuances to consider:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Buyers must be aware that quality standards and practices may vary significantly between regions. Understanding local regulations and cultural attitudes toward quality can help in selecting the right suppliers.
-
Documentation and Traceability: Ensure that suppliers maintain thorough documentation for all quality control processes. This includes records of inspections, certifications, and compliance with international standards, which can be crucial for audits and product traceability.
-
Communication: Establishing clear lines of communication with suppliers regarding quality expectations and standards is essential. Buyers should feel comfortable discussing quality issues and expectations to foster a collaborative relationship focused on continuous improvement.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for finishing grinding, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘finishing grinding’
In the highly competitive landscape of manufacturing and metalworking, sourcing the right finishing grinding solutions can significantly impact your production efficiency and product quality. This guide provides a practical checklist to assist B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets, in navigating the procurement process for finishing grinding services and equipment.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of a successful sourcing process. Identify the materials you will be grinding, the required surface finish, tolerances, and any special processing needs. This clarity will not only streamline your search but also enable suppliers to provide tailored solutions that meet your exact requirements.
- Considerations: Material types (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum), desired finish (e.g., mirror-like, matte), and tolerances (e.g., ±0.001 mm).
Step 2: Research Suppliers and Their Capabilities
Once specifications are defined, begin researching potential suppliers. Focus on those with a proven track record in finishing grinding, particularly in your industry. Look for suppliers that offer advanced technology and equipment, such as CNC grinding machines and superabrasives, which can enhance precision and efficiency.
- Where to find suppliers: Industry trade shows, online directories, and professional networks.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; engage directly with their past clients to understand their performance and reliability.
- Key questions to ask: What are their lead times? Can they meet your volume requirements? What quality assurance processes do they have in place?
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. This verification is essential for maintaining high standards and compliance with international regulations, particularly if you operate in regulated industries like aerospace or pharmaceuticals.
- Checklist of certifications: ISO 9001, AS9100, or any specific local certifications relevant to your region.
Step 5: Request Samples and Trial Runs
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples or conduct trial runs to assess the quality of the grinding services or equipment. This step is crucial for evaluating the supplier’s capability to meet your specifications and quality standards in real-world conditions.
- What to evaluate: Surface finish quality, consistency, and adherence to specified tolerances.
Step 6: Discuss Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have narrowed down your options, engage in discussions about pricing and payment terms. Ensure that the pricing reflects the quality of service provided, and clarify any additional costs, such as shipping or handling fees. Establishing favorable payment terms can also improve cash flow management.
- Tips for negotiation: Consider long-term contracts for better pricing, and be clear about your budget constraints upfront.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Establish a clear communication plan that includes regular updates on production progress, any potential issues, and feedback loops. This proactive approach can help mitigate risks and enhance collaboration.
- Best practices: Schedule regular check-ins, utilize project management tools, and ensure all stakeholders are informed of any changes.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing finishing grinding solutions, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and product quality.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for finishing grinding Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing for finishing grinding sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding these components can lead to better decision-making and more favorable procurement outcomes.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Finishing Grinding?
-
Materials: The choice of abrasives significantly affects the overall cost. High-quality materials, such as diamond or ceramic abrasives, will typically come at a premium. Additionally, the type of metal or alloy being processed influences material costs, with harder materials requiring more durable and often more expensive abrasives.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for precision grinding operations. Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location, labor laws, and the skill level required. In regions with higher labor costs, it may be beneficial to invest in automation technologies to offset these expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Companies that invest in modern, energy-efficient grinding machines may find reduced overhead costs over time, thus improving their pricing flexibility.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling, including the purchase and maintenance of grinding wheels and other accessories, should not be overlooked. Advanced tooling can enhance precision and efficiency but may require a higher initial investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the finished products meet specific quality standards incurs additional costs. Implementing rigorous QC processes is critical, especially in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where adherence to certifications can be a major price influencer.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs, especially for international transactions, can significantly affect the final price. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for anticipating these expenses and negotiating favorable shipping terms.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure viability. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Finishing Grinding Costs?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to discounts, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their purchasing. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized grinding solutions that meet specific requirements may come at a higher price. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential cost savings from standard solutions.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certified processes can elevate prices. However, investing in quality can reduce long-term costs associated with rework and product failures.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and quality assurance, while new entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for Buyers in International Markets?
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the initial purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. This holistic view can guide better purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Local Market Knowledge: Buyers from regions like Brazil or Nigeria should leverage local market conditions, such as currency fluctuations and regional demand, to negotiate better terms.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Engaging with multiple suppliers can provide leverage during negotiations. It allows buyers to compare offers comprehensively and choose the best value.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should recognize that prices can vary widely based on local economic conditions, tariffs, and trade regulations. Conducting thorough market research can help buyers avoid unexpected costs.
Conclusion
In the realm of finishing grinding, understanding the intricate cost components and pricing influencers is vital for informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on strategic negotiation and a comprehensive understanding of total costs, international B2B buyers can secure advantageous deals while ensuring high-quality outcomes. While indicative prices are essential for budgeting, always consult with suppliers for the most accurate quotes tailored to specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing finishing grinding With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Finishing Grinding
When assessing the optimal approach for achieving high-quality surface finishes, it’s essential to consider various alternatives to finishing grinding. Each method offers distinct advantages and limitations that can significantly impact production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and the final quality of the product. This analysis focuses on comparing finishing grinding with two viable alternatives: buffing and electropolishing.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Finishing Grinding | Buffing | Electropolishing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, excellent surface finish | Moderate precision, good for aesthetics | High purity, smooth finish |
| Cost | Moderate to high investment | Low to moderate investment | Higher initial cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators | Easier to implement, less training needed | Requires specialized equipment |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for machines | Low maintenance | Regular checks needed |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive components | Decorative finishes on metals | Biopharmaceuticals, high-purity applications |
Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
Buffing
Buffing is a finishing process that utilizes abrasives or compounds on a flexible backing to achieve a highly reflective, mirror-like surface. This method is particularly effective for non-critical applications where aesthetics are paramount, such as in decorative metalwork.
Pros:
– Cost-Effective: Buffing is generally less expensive than finishing grinding, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to minimize costs.
– Ease of Use: The process requires less technical skill compared to grinding, allowing for quicker training of operators.
Cons:
– Lower Precision: While buffing can produce shiny surfaces, it may not achieve the same level of precision and durability required in industrial applications.
– Not Suitable for High Purity Needs: Buffed surfaces may not meet the stringent cleanliness standards required in sectors like pharmaceuticals.
Electropolishing
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes material from a metallic surface to enhance its finish. This method is particularly advantageous in industries requiring high-purity surfaces, such as biopharmaceuticals.
Pros:
– Superior Cleanliness: Electropolishing significantly reduces surface roughness, making it ideal for applications that demand high purity and non-contaminating surfaces.
– Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: This process improves the longevity of components by reducing the potential for corrosion.
Cons:
– Higher Costs: The initial investment in electropolishing equipment and technology can be substantial, which might deter some businesses.
– Complex Implementation: The process requires specialized knowledge and equipment, making it less accessible for smaller operations.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between finishing grinding, buffing, and electropolishing, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific requirements. If precision and durability are paramount, finishing grinding may be the best choice. Conversely, for projects where aesthetics are crucial and budgets are tighter, buffing can be a suitable alternative. For applications where cleanliness and corrosion resistance are critical, electropolishing stands out despite its higher costs and complexity. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each method will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their production goals and industry standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for finishing grinding
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Finishing Grinding?
Understanding the technical specifications in finishing grinding is crucial for international buyers to ensure product quality and operational efficiency. Here are some essential properties that should be considered:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the type and quality of the metal or alloy being ground. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum. Selecting the right material grade is vital, as it affects the durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance of the finished product. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can provide materials that meet specific industry standards, such as ASTM or ISO certifications. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension. In finishing grinding, tight tolerances (such as ±0.001 mm) are often critical for components that require precise fitting and function. Understanding tolerances helps buyers assess the capability of their machining partners and guarantees that components will fit correctly in assemblies, reducing the risk of costly rework or failures. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture of the ground surface, which can significantly impact the performance and aesthetics of the final product. It is measured in Ra (Roughness Average) values, with lower values indicating smoother finishes. Different applications require varying surface finishes; for instance, aerospace components often necessitate ultra-smooth finishes for aerodynamic efficiency. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to ensure compliance with application standards. -
Grinding Wheel Specification
This includes the type of abrasive material, grit size, and bond type used in the grinding wheel. Different applications may require specific wheel characteristics to achieve optimal results. For example, diamond wheels are preferred for hard materials, while aluminum oxide wheels are suitable for softer metals. Choosing the correct grinding wheel is essential for efficient material removal and achieving desired surface finishes. -
Feed Rate
Feed rate is the speed at which the workpiece is fed into the grinding wheel. It influences the efficiency of the grinding process and the quality of the surface finish. A higher feed rate can improve productivity but may compromise finish quality. Buyers should discuss feed rate parameters with their suppliers to balance productivity and quality according to their specific requirements.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in Finishing Grinding?
Familiarity with trade terminology can enhance communication and streamline procurement processes. Here are some essential terms relevant to finishing grinding:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In finishing grinding, understanding the role of OEMs can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who meet specific product standards and quality controls. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production schedules and market demands. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In the context of finishing grinding, an RFQ can help buyers compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best value for their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, delivery, and insurance. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations, which is particularly important for international transactions. -
Batch Processing
This term refers to the processing of multiple items simultaneously rather than individually. In finishing grinding, batch processing can enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s capabilities for batch processing to optimize their production runs.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms empowers B2B buyers in the finishing grinding sector to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the finishing grinding Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Finishing Grinding Sector?
The finishing grinding sector is witnessing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer expectations, and market globalization. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly focused on precision and efficiency. Key trends include the adoption of automated grinding solutions, which enhance productivity while minimizing human error. Innovations in abrasive technology, such as superabrasives and advanced coatings, are also making waves, allowing for finer finishes and longer tool life.
Additionally, the shift towards Industry 4.0 is reshaping the landscape, with integrated data analytics and IoT solutions providing real-time insights into grinding processes. This data-driven approach enables companies to optimize their operations, leading to reduced downtime and better resource allocation. Buyers are also prioritizing suppliers who offer customized solutions, reflecting a growing demand for tailored services that meet specific industry needs, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Emerging markets, particularly in Africa and South America, are increasingly investing in local manufacturing capabilities, presenting opportunities for partnerships with international suppliers. Understanding these dynamics is essential for B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing in a rapidly evolving sector.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Finishing Grinding Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of the B2B landscape, especially in the finishing grinding sector. The environmental impact of grinding operations—ranging from waste generation to energy consumption—has prompted a reevaluation of practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly abrasives and minimizing waste through efficient production processes.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies that prioritize transparency and ethical sourcing are not only enhancing their brand reputation but also meeting the expectations of increasingly conscientious consumers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) are becoming critical for suppliers to showcase their commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, the integration of ‘green’ materials—such as recycled abrasives and biodegradable lubricants—into the finishing grinding process is gaining traction. These innovations not only reduce environmental footprints but can also improve the quality and safety of the final products. For international buyers, aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability can lead to long-term benefits, including cost savings, enhanced market competitiveness, and improved compliance with global regulatory standards.
How Has the Finishing Grinding Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the finishing grinding sector reflects broader trends in manufacturing and technology. Originally, grinding processes were labor-intensive and relied heavily on manual intervention. However, as industries began to prioritize precision and efficiency, the introduction of advanced machinery transformed traditional practices. The advent of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology revolutionized the grinding process, enabling higher levels of accuracy and repeatability.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards automation and smart technologies, such as predictive maintenance and AI-driven process optimization. These advancements not only enhance productivity but also facilitate data collection for continuous improvement. Today, the finishing grinding sector is characterized by a blend of traditional craftsmanship and cutting-edge technology, making it essential for international B2B buyers to stay informed about ongoing innovations and market shifts to maintain competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of finishing grinding
-
How do I solve quality inconsistencies in finishing grinding?
To address quality inconsistencies in finishing grinding, first evaluate the grinding process parameters, including wheel selection, feed rates, and coolant application. Implement rigorous quality control measures, such as in-process inspections and using statistical process control (SPC). Partnering with suppliers who provide consistent, high-quality abrasives and machinery is essential. Additionally, consider training your operators on best practices to enhance their skills in identifying and rectifying issues during the grinding process. -
What is the best abrasive material for precision finishing grinding?
The best abrasive material for precision finishing grinding depends on the specific application and the material being processed. Diamond abrasives are ideal for hard materials, while aluminum oxide or silicon carbide are suitable for softer metals. For high-precision applications, consider superabrasives, which offer superior cutting performance and longevity. Collaborate with your supplier to determine the most effective abrasives for your unique needs, ensuring optimal results in surface finish and dimensional accuracy. -
How can I vet suppliers for finishing grinding services?
When vetting suppliers for finishing grinding services, consider their industry experience, certifications (like ISO 9001), and customer reviews. Request samples of their work to assess quality and consistency. Evaluate their production capabilities, equipment, and technology used in the grinding process. It’s also beneficial to inquire about their quality assurance processes and any adherence to international standards, especially if you are sourcing from different regions like Africa or South America. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for finishing grinding services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for finishing grinding services can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific services required. Generally, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s advisable to communicate your specific needs and production schedules with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Understanding the supplier’s capacity and willingness to accommodate smaller orders can help facilitate a successful partnership. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing finishing grinding?
Payment terms for sourcing finishing grinding services typically include options like net 30, net 60, or even upfront payments, depending on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or larger orders. Ensure you discuss payment methods (bank transfer, credit card, etc.) and any potential fees associated with international transactions. Establishing clear payment terms upfront helps prevent misunderstandings and fosters a more reliable partnership. -
How do logistics impact my sourcing of finishing grinding services?
Logistics play a crucial role in sourcing finishing grinding services, particularly when dealing with international suppliers. Consider factors like shipping times, customs clearance, and transportation costs. Ensure your supplier has a reliable logistics partner to minimize delays. Additionally, factor in lead times for production and shipping when planning your inventory. Effective communication about logistics can help align production schedules and ensure timely delivery of finished products. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from finishing grinding suppliers?
Quality assurance measures from finishing grinding suppliers should include regular inspections, adherence to international standards, and documented processes for each stage of production. Look for suppliers that utilize advanced technologies for measurement and testing, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMM) or surface roughness testers. Inquire about their capability to provide certifications or reports that demonstrate compliance with your specific quality requirements. -
How can I customize finishing grinding services to meet my specific needs?
Customizing finishing grinding services involves clear communication of your specific requirements, including dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes. Collaborate closely with your supplier to develop tailored solutions that may involve unique abrasive materials or specialized grinding techniques. Many suppliers are equipped to handle custom orders and can suggest innovations that enhance efficiency and quality. Providing detailed specifications and samples can also help ensure the final product meets your expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Finishing Grinding Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Surface Grinding Tips
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Surface Grinding Tips, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Grindsurf – Key Grinding and Tooling Solutions
Domain: grindsurf.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: DAWN DN Vertical Grinding Series, OptiForm CNC Press Brake, Sinto AGTOS GmbH wheel blast machines, WALTER VISION LASER for brazed diamond tools, Absolent technology for dust and fume extraction, Leopard Cub from Vapormatt for aerospace surface finishing, ANCA EPX-SF for superior tool performance, Top-Work Machinery Truing and Dressing Machine, HOLROYD HG500 Helical profile grinding machine.
3. 3M – Precision Grinding Solutions
Domain: 3m.com
Registered: 1988 (37 years)
Introduction: 3M offers a range of products for precision grinding and microfinishing, including:
– Conventional and superabrasive wheels
– Microfinishing films
– Dressing equipment
– Tools for precision grinding applications
– 3M™ Cubitron™ II Threaded Gear Grinding Wheels featuring 3M Precision-Shaped Grain
– Solutions for round tool grinding with custom optimization
These products are designed for specializ…
4. Lissmac – SMD 123 RE
Domain: lissmac.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Functional surface grinding and high-quality surface finishing for aluminum and stainless steel parts. Key products include: SMD 123 RE – Dry grinding machine for deburring, consistent edge rounding and surface finishing; SMD 3 S – EDITION – Outstanding results on the edge and on surface; SMW 1 – Wet grinding machine for perfect surface finish; SMW 5 – Wet grinding machine for perfect surface fini…
5. More SuperHard – Grinding Wheels & Tools
Domain: moresuperhard.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: More SuperHard Products Co., Ltd offers various grinding wheels and tools including Diamond Grinding Wheel, CBN Wheel, PCD Cutting Tools, and PCBN Inserts. Key features of mirror finish grinding include achieving a surface roughness of Ra< 0.01μm and flatness not greater than 3μm/1000mm. Essential conditions for the grinder include high precision, spindle rotation accuracy higher than 1μm, and pre…
6. Studio JSD – Level Best Grinding and Finishing System
Domain: studiojsd.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Level Best Grinding and Finishing System”, “price”: “$125.00”, “description”: “Low tech grinding and finishing system for stone, metal, glass and chip inlay materials. A Studio JSD exclusive developed by Julie Sanford, this easy-to-use kit will give you professional results without investing in expensive lapidary equipment.”, “sku”: “”, “weight”: “896”, “currency”: “USD”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for finishing grinding
In the evolving landscape of finishing grinding, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal component for enhancing operational efficiency and product quality. By aligning with reliable suppliers and leveraging advanced technologies, businesses can significantly reduce costs while optimizing their production processes. Key takeaways include the importance of investing in high-quality abrasives, staying updated on industry innovations, and understanding the specific needs of your manufacturing sector.
For international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the value of strategic partnerships cannot be overstated. Engaging with suppliers who offer tailored solutions will not only improve your competitive edge but also ensure compliance with regional standards and practices.
Looking ahead, the demand for precision and sustainability will continue to shape the finishing grinding market. By proactively adapting to these trends and forging strong supplier relationships, businesses can position themselves for long-term success. Now is the time to explore new sourcing opportunities and elevate your finishing grinding capabilities to meet the challenges of tomorrow’s market.