Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fiberglass pieces
Navigating the complexities of sourcing fiberglass pieces for a diverse array of applications can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re managing supply chains in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—countries like Vietnam and Brazil require effective solutions that deliver not only quality, but also value. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the global fiberglass market, helping you understand the wide range of fiberglass products available, their specific applications, and the decision-making factors involved in choosing reliable suppliers.
From lightweight composite parts ideal for automotive manufacturing to robust insulation materials for the electrical industry, fiberglass is a versatile material that combines strength, moldability, and cost-effectiveness. This guide covers essential topics such as identifying and vetting suppliers, understanding pricing structures, and recognizing the different types of products—like fiberglass tape, woven roving, and custom fabrications—available for your specific needs.
Empowering you with critical insights and actionable strategies, this guide aims to enhance your purchasing decisions in sourcing fiberglass pieces. It’s designed to equip you with the knowledge and confidence necessary to navigate a competitive market and ultimately, succeed in your operational goals.
Understanding fiberglass pieces Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiberglass Fabric | Versatile and strong; available in various weaves and weights | Automotive, aerospace, marine, construction | Pros: Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio. Cons: UV exposure can degrade over time. |
| Chop Strand Mat | Composed of randomly oriented fibers; excellent for bulk reinforcement | Boat hulls, automotive parts, molds | Pros: Good chemical durability, easy application. Cons: Limited strength in specific orientations. |
| Woven Roving | Thick layers of woven glass fibers; high tensile and compressive strength | Structural components, automotive bodies | Pros: High strength, suitable for large parts. Cons: Heavier than other fiberglass types. |
| Biaxial Fabric | Fibers oriented in two directions; high impact resistance | Wind turbine blades, automotive components | Pros: Excellent mechanical properties, better load distribution. Cons: More complex to handle. |
| Epoxy Resin-Fiberglass | Combination of epoxy resin and fiberglass; superior bonding and durability | Electronics, appliances, high-performance parts | Pros: High chemical resistance, better dimensional stability. Cons: Higher cost than standard resins. |
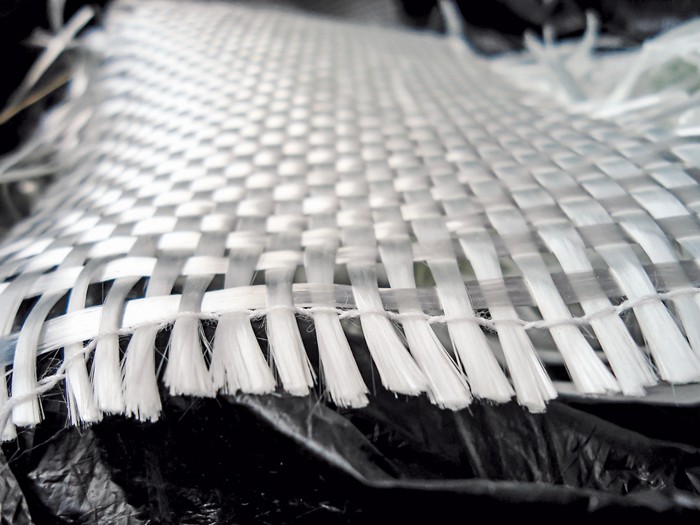
What Are the Characteristics of Fiberglass Fabric?
Fiberglass fabric is widely recognized for its versatility and strength, available in multiple weaves and weights tailored to meet various industrial needs. Its adaptability makes it suitable for a range of applications, including automotive, aerospace, and marine industries. When purchasing fiberglass fabric, buyers should consider the fabric’s weight, weave style, and the specific environmental conditions it will face, including exposure to UV light which can degrade the material over time.
How Does Chop Strand Mat Differ from Other Fiberglass Types?
Chop strand mat consists of randomly oriented fiberglass strands, making it ideal for bulk reinforcement in many applications, particularly in boat hulls and automotive parts. Its simplicity in application and good chemical resistance are key advantages. When considering chop strand mat, businesses should evaluate the required thickness and density to ensure optimal performance in their intended use without compromising structural integrity.
Why Choose Woven Roving for Your Project?
Woven roving is characterized by thick layers of woven glass fibers, providing exceptional tensile and compressive strength, essential for structural components in automotive and industrial applications. Companies looking for strong yet lightweight solutions should consider woven roving, especially for large parts. However, it is heavier than other options, which may impact overall design choices and logistics.
What Are the Advantages of Biaxial Fabric in Industrial Applications?
Biaxial fabric, with fibers oriented in two different directions, offers superior impact resistance and mechanical properties. This fabric is particularly valuable in applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios, such as wind turbine blades and automotive components. When sourcing biaxial fabric, it’s crucial for B2B buyers to assess its handling complexity and to ensure that their fabrication processes can accommodate this sophisticated material.
How Does Epoxy Resin-Fiberglass Enhance Performance?
The integration of epoxy resin with fiberglass creates a robust composite known for its high chemical resistance and dimensional stability. This type of fiberglass is often sought after for electronics and high-performance applications due to its superior bonding qualities. B2B buyers should weigh the cost against the performance advantages, as epoxy resin products can be more expensive but often provide better long-term ROI through durability and reliability in demanding environments.
Key Industrial Applications of fiberglass pieces
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fiberglass pieces | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Production of lightweight structural components for aircraft | Enhances aircraft efficiency through weight reduction | Ensure compliance with aviation safety standards and quality certifications |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of fiberglass body parts and interiors | Reduces vehicle weight, improves fuel efficiency | Look for suppliers with advanced molding capabilities and quick turnaround times |
| Construction | Creation of fiberglass reinforcement materials for building structures | Provides strength and durability to constructions | Sourcing from local suppliers can reduce lead time and logistics costs |
| Marine | Development of boats and marine accessories | Offers corrosion resistance and durability in a harsh environment | Verify the supplier’s experience with marine-grade materials |
| Electrical & Electronics | Fabrication of insulating components for circuit boards | Ensures safety and functionality of electronic devices | Consider suppliers with expertise in electrical insulation and flame-resistant materials |
How is Fiberglass Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, fiberglass pieces are essential for manufacturing lightweight structural components such as wing skins, fuselages, and interiors. The use of fiberglass helps to significantly reduce the overall weight of the aircraft, which, in turn, enhances fuel efficiency and payload capacity. International buyers must seek suppliers who comply with stringent aviation standards and possess quality certifications to ensure the reliability and safety of fiberglass components.
Why is Fiberglass Important in Automotive Manufacturing?
Automotive manufacturers utilize fiberglass for body panels, internal structures, and various aesthetic components. This application not only contributes to reduced vehicle weight but also improves fuel economy and performance. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing fiberglass from suppliers that possess advanced molding techniques and can deliver products within tight timelines to meet production schedules.
In What Ways Does Fiberglass Benefit Construction Projects?
Fiberglass pieces are increasingly used in construction for reinforcement in various structures, from buildings to bridges. These materials provide significant strength and durability while being lighter than traditional materials, which aids in reducing structural load. Buyers from the construction industry should prioritize sourcing fiberglass that meets local building codes and regulations, as well as considering local suppliers to minimize shipping costs and delays.
How is Fiberglass Used in Marine Applications?
In marine manufacturing, fiberglass is a go-to material for constructing boats, hulls, and various marine accessories due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and longevity. The ability to withstand harsh marine environments makes fiberglass a reliable choice for these applications. International buyers should assess suppliers who specialize in marine-grade fiberglass to ensure that products meet the necessary resilience and safety standards.
What Role Does Fiberglass Play in Electrical and Electronic Applications?
Fiberglass is critical in the electrical and electronics industry, particularly for creating insulating components for circuit boards and other electronic devices. Its non-conductive properties help safeguard against electrical hazards, ensuring device functionality and safety. Buyers in this field should engage suppliers that have proven expertise in producing high-quality, flame-resistant fiberglass materials suitable for electronic applications to ensure compliance and reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fiberglass pieces’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing High-Quality Fiberglass Components
The Problem: In the international B2B market, sourcing fiberglass components that meet specific quality and performance standards can pose a significant challenge. Buyers often struggle to distinguish between low and high-quality products, especially when suppliers are spread across different regions, such as Africa or South America. This can lead to costly mistakes, including the purchase of subpar materials that underperform, thereby affecting product durability and increasing long-term expenses.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of sourcing high-quality fiberglass pieces, international buyers should develop a robust supplier evaluation process. Start by conducting thorough research on potential suppliers, focusing on their manufacturing practices and certifications. Establish criteria such as ISO certifications or industry-specific quality standards that ensure the fiberglass products meet rigorous performance benchmarks. Furthermore, consider requesting samples for initial assessments before placing bulk orders. Create a shortlist of suppliers who consistently provide high-quality products, and maintain open lines of communication to clarify any specifications, such as resin types or fiber weights, which are critical to desired performance attributes.
Scenario 2: Managing Lead Times and Delivery Challenges
The Problem: Efficient logistics and timely delivery of fiberglass materials can be a major pain point, especially for businesses operating on tight manufacturing schedules. Delays in acquiring fiberglass parts due to transportation issues or supply chain disruptions can halt production lines, resulting in lost revenue and disgruntled clients. This is particularly prevalent in developing markets where infrastructure may be lacking.
The Solution: To mitigate risks associated with lead times, buyers should implement a comprehensive supply chain management strategy. Start by collaborating with suppliers who offer realistic lead time estimates, and maintain a buffer stock of critical materials to cushion against unexpected delays. Utilize a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory system that aligns orders closely with production needs, which can help reduce costs associated with storing excess materials. For urgent projects, consider suppliers located closer to your manufacturing facilities to provide quicker access to fiberglass supplies. Building long-term, strategic partnerships with suppliers can also enhance communication and reliability in meeting delivery timelines.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Technical Suitability for Specific Applications
The Problem: Buyers often encounter difficulties in ensuring that the fiberglass products they select are technically suitable for their intended applications. Specific projects may require materials with precise mechanical properties, such as impact resistance or thermal stability, which can vary widely among different fiberglass products. If these specifications are not met, it can lead to product failure and subsequent financial loss.
The Solution: To ensure technical suitability, B2B buyers should first engage in a thorough requirements assessment for their projects. Consult with engineers or materials specialists to establish a detailed specification sheet outlining essential properties, including load-bearing capacities or environmental resistance. When reaching out to potential suppliers, provide this specification to receive tailored recommendations on suitable fiberglass products, including detailed datasheets to support your decision. Additionally, consider utilizing simulation software or prototyping services from suppliers like eMachineShop to validate the performance of selected materials under expected operational conditions. By taking a proactive approach in assessing and validating the technical requirements, buyers can reduce the risk of material incompatibilities and enhance overall project success.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fiberglass pieces
Which Fiberglass Materials Are Best for Your Specific Needs?
When selecting fiberglass materials for applications, it’s crucial to consider their key properties, advantages, and limitations. This not only impacts manufacturing efficiency but also the end-use performance of the final products. Here, we analyze four common fiberglass construction materials, including fiberglass cloth, vinyl ester resin, epoxy resin, and chopped strand mat, from a B2B perspective.
What Are the Key Properties of Fiberglass Cloth?
Fiberglass cloth, made from woven strands of fiberglass, offers exceptional tensile strength and durability. It is resistant to high temperatures, making it suitable for high-performance applications, including automotive and aerospace components. The ability to withstand environmental stressors such as UV radiation and moisture further enhances its usability in outdoor settings.
Pros: High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent dimensional stability, and versatility in applications. The manufacturing process is straightforward, and it can conform easily to complex shapes.
Cons: The cloth can lose some structural integrity when exposed to certain chemicals, and it may require additional sealing or protection from moisture.
Impact on Application: Commonly used for boat hulls and automotive parts, fiberglass cloth proves effective in applications requiring high strength and lightweight performance.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, and consider the product’s intended use in regions vulnerable to harsh weather conditions.
Why Choose Vinyl Ester Resin?
Vinyl ester resin combines the properties of polyester and epoxy resins, offering enhanced corrosion resistance and durability at elevated temperatures. It is particularly effective in environments where chemical resistance is paramount.
Pros: Provides a good balance between cost and performance, exceptional humidity resistance, and thermal stability. Its fast curing time allows for efficient production cycles.
Cons: Although it is more expensive than polyester resin, it can be more complex to handle and requires specific application techniques.
Impact on Application: Ideal for applications in the chemical processing industry, vinyl ester resin is utilized in manufacturing tanks, pipes, and containment vessels.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: When purchasing vinyl ester resin, it’s important to be aware of the specific chemical compatibility of the medium used and to follow compliance guidelines relevant to the materials being produced.
How Does Epoxy Resin Compare?
Epoxy resin is renowned for its superior adhesion and strength properties. It excels under thermal and chemical stress and retains its integrity in adverse conditions.
Pros: Offers excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile and compressive strength, as well as excellent moisture resistance. It’s an ideal choice for high-end applications needing precise dimensions.
Cons: Generally higher in cost and may require specific mix ratios, increasing manufacturing complexity. Cure times can also be longer compared to vinyl ester resins.
Impact on Application: Commonly used in high-performance automotive and aerospace components, progress in epoxy resin technology enhances its performance footprint across variable sectors.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Buyers must prioritize ensuring epoxy formulations comply with international standards and consider the logistics of shipping in terms of handling reactive materials.
What Are the Benefits of Chopped Strand Mat?
Chopped strand mat (CSM) consists of randomly arranged fiberglass strands bonded together, providing uniform thickness and density. It’s often preferred for its simplicity in application and availability.
Pros: CSM is cost-effective, easy to work with, and provides mechanical strength while being lightweight. It quickly adapts to various shapes, making it suitable for molds and repairs.
Cons: While it can offer good tensile strength, it typically lacks the structural properties found in woven cloths. Durability may also present concerns when exposed to specific chemicals.
Impact on Application: Frequently utilized in boat manufacturing and automotive applications, CSM’s ability to bond well with resin enhances overall part strength.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Ensure to review local compliance and certifications, as well as assess how performance in specific environments aligns with intended applications, especially in dynamic markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Summary of Material Properties
| Material | Typical Use Case for fiberglass pieces | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiberglass Cloth | Boat hulls, automotive parts | High strength-to-weight ratio, dimensional stability | Chemical exposure risks | Medium |
| Vinyl Ester Resin | Chemical tanks, pipes | Excellent corrosion and humidity resistance | More expensive, handling complexities | Medium/High |
| Epoxy Resin | Aerospace components, high-performance parts | Superior mechanical properties and adhesion | Higher cost, longer cure times | High |
| Chopped Strand Mat | Boat manufacturing, automotive applications | Cost-effective, easy to manipulate | Lacks structural strength compared to cloth | Low/Mid |
This table and detailed analysis equip B2B buyers with crucial insights to make informed decisions regarding fiberglass materials suitable for their specific application needs, taking into account performance, cost, and compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fiberglass pieces
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Fiberglass Pieces?
Manufacturing fiberglass pieces involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the creation of high-quality components that meet industry standards. The main stages of the manufacturing process include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Fiberglass Manufacturing?
The process begins with material preparation, wherein raw materials such as fiberglass fabrics, resins, and additives are selected based on the desired properties and application of the final product. Fiberglass fabrics come in various forms—including woven roving, chopped strand mat, and needled mat—each offering different strength and flexibility characteristics. Resins, primarily polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy, play a crucial role in binding fibers and offering thermal resistance.
Careful consideration is given to environmental factors like humidity and temperature, as these can affect the curing process. Advanced suppliers often pre-condition their materials to ensure optimal mixing and application conditions. Also, thorough inspection of raw material quality at this stage reduces the risk of defects in final products, ensuring that only the highest-grade materials are utilized throughout the manufacturing process.
What Are Typical Forming Techniques Used in Fiberglass Production?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This stage typically employs one of several techniques, each suited to specific product requirements:
-
Hand Layup Process: This is a manual technique where layers of fiberglass cloth and resin are laid onto a mold. It allows for flexibility and is often used for custom applications, although it may be more labor-intensive.
-
Vacuum Bag Molding: This method involves placing the layered materials in a vacuum bag to remove air, ensuring even compaction and maximizing bond strength. It is particularly effective for producing high-strength, lightweight parts.
-
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding): This closed-mold technique injects resin into the mold after placing the fiberglass material inside. RTM is efficient for medium to high-volume production, delivering finished parts with superior surface quality.
-
Chopper Gun Technique: Used primarily for larger parts, a chopper gun sprays chopped fiberglass strands mixed with resin onto a mold. This can optimize material usage and speed up production times, making it a favorite for large-scale applications like boat hulls or automotive body parts.
What Finishing Processes Are Critical for Quality?
Finishing is essential to ensure that the fiberglass pieces meet both functional requirements and aesthetic standards. This stage involves trimming excess material, curing (if not already done in the forming process), and applying protective coatings or paint. Techniques include:
-
Sanding and Surface Prep: The surface is often sanded down to achieve a smooth finish, ensuring proper adhesion for any coatings applied afterwards.
-
Gel Coating: A gel coat may be applied for additional protection against environmental factors like UV rays and water damage as well as enhancing the cosmetic appearance.
-
Painting or Lamination: Depending on the application, paint or laminate may be added to enhance performance and longevity. Coatings help resist wear, chemicals, and impacts.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Fiberglass Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) throughout the manufacturing process is crucial for maintaining product integrity and meeting international standards.
What International Standards Should Suppliers Adhere To?
One primary quality standard that many manufacturers adhere to is ISO 9001, which provides a framework for consistent quality management systems and ensures continuous improvement. Additional relevant certifications for specific industries might include:
-
CE Marking: Essential for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: Particularly necessary in the oil and gas industry, ensuring that products meet critical operational standards.
Manufacturers catering to international markets often innovate to meet local regulations, which may differ across continents like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the QC Checkpoints in Fiberglass Production?
Quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves validating the raw materials before they are used in production. Tests may include visual inspections and physical property assessments.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, operators perform regular checks on materials and components to ensure quality standards are maintained. This may also involve visual inspections of the molded parts and testing of adhesive bonds.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Upon completion, the final products undergo rigorous inspections, including dimensional checks, surface finish assessments, and functional testing. Any deviations from specifications are documented and rectified.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
B2B buyers must mitigate risks associated with supplier quality. Here are some effective strategies to ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control practices:
-
Audits: Consider conducting regular audits of your suppliers’ facilities. An on-site assessment allows buyers to verify adherence to quality processes, equipment, and workforce qualifications.
-
Quality Reports: Request comprehensive quality assurance reports. These should detail the results of quality checks at each production stage and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Employing independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased overview of supplier quality. These reports can help validate claims made by suppliers and serve as reliable assessments of product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers may face unique challenges regarding quality control. Different regulatory practices, cultural interpretations of quality, and regional standards necessitate a tailored approach. Understanding local compliance regulations in target markets like Africa or South America will be crucial. Buyers must also familiarize themselves with the logistical constraints often encountered in these regions, which may impact lead times and the supply chain.
Additionally, building relationships with your suppliers can improve communication and transparency concerning quality. Jointly developing quality standards tailored to specific markets can result in more robust supply chains and improved product quality.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of the fiberglass manufacturing process and implementing rigorous quality assurance measures are essential steps for engaging in successful B2B transactions internationally. By doing so, buyers not only secure high-quality products but also establish long-term partnerships that can lead to sustainable growth in the global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fiberglass pieces’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring fiberglass pieces effectively, this guide provides a structured approach for sourcing quality materials that meet specific needs. By following the checklist below, buyers can enhance their procurement processes, ensuring that they choose the right products and suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications for your desired fiberglass components, including dimensions, weight requirements, and performance characteristics. This allows potential suppliers to provide accurate quotes and ensures your needs are effectively met. Consider the specific applications and environments in which the fiberglass pieces will be used—such as exposure to chemicals or high temperatures.
Step 2: Identify Suitable Applications for Fiberglass
Understanding the various applications of fiberglass can guide your sourcing decisions. Fiberglass is versatile, used in sectors ranging from automotive to aerospace to consumer goods. Define whether you need structural components, molded parts, or custom designs to align your requests with the appropriate suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, rigorously assess suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from businesses in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers who demonstrate expertise in manufacturing fiberglass pieces and show a track record of quality and reliability. Consider their capacity to meet your volume and delivery timelines.
- Check for certifications: Ensure that suppliers hold relevant industry certifications, indicating compliance with international standards.
- Review technical competencies: Suppliers should have advanced manufacturing capabilities and a range of fiberglass materials available.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
It’s crucial to evaluate the quality of fiberglass pieces before making bulk purchases. Request samples or prototypes to assess the material’s performance, durability, and fit for your specific application. This step is essential to avoid costly errors in material selection after a large order.
Step 5: Analyze Cost and Shipping Options
Examine the total cost of procurement, including material, labor, and shipping expenses. Look for suppliers that offer transparent pricing structures and consider the impact of shipping costs on your overall budget. Choosing regional suppliers can reduce lead times and shipping fees, making your procurement process more economical.
Step 6: Review Terms and Conditions
Ensure you fully understand the terms and conditions associated with your supplier agreement. This includes payment terms, warranties, return policies, and timelines for delivery. A clear contract can mitigate risks and establish expectations between you and the supplier, fostering a smoother business relationship.
Step 7: Build a Long-Term Relationship
Finally, consider developing a long-term partnership with your chosen supplier. Continuous collaboration can lead to better pricing, priority on orders, and shared innovations. Engage regularly for feedback and potential improvements in your supply chain, ensuring that both parties benefit and adapt to changing market demands.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can efficiently navigate the sourcing process for fiberglass pieces, ensuring they acquire high-quality materials that meet their operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fiberglass pieces Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Fiberglass Pieces?
Understanding the cost structure for sourcing fiberglass pieces is critical for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The total cost includes multiple components:
-
Materials: Fiberglass itself is sourced in various forms, including chopped strands, fabrics, and mats. The specific type of fiberglass selected impacts pricing significantly. Additional costs arise from resins (polyester, epoxy), which can vary based on performance specifications.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on geography and the complexity of manufacturing processes. In regions with high labor costs, such as parts of Europe, the overall price point may increase.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs related to production, including utilities, facility costs, and machinery maintenance. High-tech processes, like vacuum bag molding or automated systems, may further amplify these overheads.
-
Tooling: Customization often necessitates specific tooling, which represents a significant upfront investment. Buyers should ask suppliers about tooling charges and amortization across order quantities.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring products meet international standards necessitates robust QC processes, which can add to costs. Certifications like ISO or material testing certifications can also impact pricing.
-
Logistics and Transportation: This includes shipping costs, which vary by destination and the method of transportation. Buyers must account for international duties, taxes, and any logistics fees incurred when importing fiberglass.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically apply a markup to cover their operational expenses and profit. Understanding typical industry margins can facilitate better negotiation outcomes.
What Influences the Pricing of Fiberglass Pieces?
Several factors can affect the pricing of fiberglass components:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs): Higher order volumes often lead to discounts, making bulk purchases attractive. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Unique designs or specific material requirements can lead to increased manufacturing costs. Always clarify specifications upfront to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The quality of the fiberglass and whether it meets certain standards significantly influences cost. Products certified for specific applications, such as fire resistance or electrical insulation, typically command higher prices.
-
Supplier Reputation and Reliability: Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge premium rates, but their reliability can reduce the risk of delays and quality issues.
-
Incoterms: Terms of shipping and delivery can greatly affect the overall cost. Buyers should understand the implications of different Incoterms, such as FOB (Free on Board) versus CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), to manage expenses efficiently.
What Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Optimize Pricing for Fiberglass Pieces?
-
Effective Negotiation Strategies: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially regarding volume discounts. Be clear about your budget constraints while emphasizing potential for future orders.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of solely concentrating on immediate purchasing costs, consider long-term expenses related to durability, maintenance, and performance. High-quality fiberglass may have a higher upfront cost but can save money over time by reducing replacements and repairs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: The cost structure can differ dramatically based on regional market conditions, tariffs, and exchange rates. Familiarize yourself with the specific market dynamics of the countries you’re sourcing from, particularly in regions like Vietnam and Brazil, where local production costs can be competitive.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Pricing for fiberglass can be influenced by fluctuations in raw material costs. Keeping abreast of industry developments ensures buyers are well-prepared to make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Always obtain quotes from various suppliers to establish a competitive baseline for pricing. This not only aids in understanding the market rate but also provides leverage in negotiations.
Disclaimer
The pricing outlined is indicative and subject to market fluctuations. Buyers are encouraged to directly consult suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date cost information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fiberglass pieces With Other Solutions
Understanding the Importance of Alternatives in Material Selection
When selecting the right materials for manufacturing or construction, it is critical for businesses to consider various alternatives to fiberglass pieces. Fiberglass is recognized for its lightweight, strength, and adaptability, but other materials may offer improved performance or cost savings for specific applications. Below, we compare fiberglass pieces with two viable alternatives: carbon fiber and aluminum.
Comparison of Fiberglass Pieces with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Fiberglass Pieces | Carbon Fiber | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good tensile strength, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, higher stiffness | Moderate strength, heavy, lower corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Cost-effective, especially in bulk | High initial costs | Moderate cost, widely available |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate complexity in fabrication | Requires advanced techniques and equipment | Easy to work with, requires basic machining |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable | Low maintenance; susceptible to UV degradation if uncoated | Moderate; can corrode if not treated |
| Best Use Case | Molds, automotive parts, and consumer products | Aerospace, high-performance automotive applications | General construction and structural applications |
Exploring Carbon Fiber as an Alternative Solution
Carbon fiber provides unique advantages that may be appealing for specific projects, particularly where high strength and lightweight properties are paramount. Its impressive strength-to-weight ratio makes it the go-to material in aviation and sports technology. However, the cost of carbon fiber is significantly higher than fiberglass, which could lead to increased production costs in large-scale applications. Furthermore, manufacturing with carbon fiber often requires specialized equipment and skills, making it less accessible than fiberglass.
Evaluating Aluminum Compared to Fiberglass
Aluminum is a widely utilized alternative that offers a favorable blend of strength and weight. It is easier to fabricate and manipulate compared to either fiberglass or carbon fiber, which can simplify production processes. However, while aluminum has many practical benefits, including its recyclability and availability, it is generally heavier and less durable compared to fiberglass under certain conditions. Additionally, untreated aluminum can suffer from corrosion, which could impact its longevity in specific environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating materials, international B2B buyers must closely analyze the specific application and industry requirements. Fiberglass pieces excel in versatility, affordability, and ease of use, making them an attractive choice for a wide range of applications. However, for projects demanding extreme performance, carbon fiber may justify its higher cost. Similarly, aluminum holds its ground in terms of accessibility and fabricating simplicity, although it may not match fiberglass’s performance in certain scenarios. Ultimately, choosing the right solution hinges on understanding each material’s strengths, weaknesses, and specific use case, allowing businesses to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fiberglass pieces
Fiberglass has become a preferred material in various industries due to its exceptional properties and versatility. Understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology related to fiberglass pieces can significantly influence purchasing decisions for B2B buyers globally.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Fiberglass Pieces?
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Fiberglass combines high tensile strength with a lightweight structure, making it an ideal choice for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in automotive and aerospace components. This property enables manufacturers to produce durable parts without the drawbacks of heavier materials like metals.
Chemical Resistance
Fiberglass is known for its resistance to many chemicals, ensuring that parts maintain their integrity even in harsh environments. This characteristic is vital for industries such as chemical processing and wastewater management, where exposure to corrosive substances is common.
Dimensional Stability
Fiberglass materials are dimensionally stable, meaning they retain their shape and size under varying temperature and humidity conditions. For B2B applications, this translates into reliability and consistency in manufacturing, minimizing the need for frequent adjustments or replacements.
Thermal Insulation
Many fiberglass formulations offer excellent thermal insulation properties, making them suitable for electrical insulation applications and parts that require temperature stability. This quality is especially important in industries such as electronics, where thermal management is crucial.
Customization Flexibility
Fiberglass can be molded into complex shapes and finished in various ways, offering fabrication versatility. This capability allows B2B buyers to request tailored solutions that meet specific requirements, enhancing the performance and appearance of their products.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Fiberglass Procurement?
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For fiberglass pieces, understanding your supplier’s OEM capabilities can help ensure compatibility with existing parts and systems.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ defines the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the fiberglass industry, MOQs vary by supplier and product type, impacting purchasing decisions, especially for smaller businesses that may not need large quantities.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process for soliciting pricing and terms from suppliers. Submitting an RFQ for fiberglass products allows buyers to compare prices, lead times, and payment conditions, making it easier to make informed purchasing decisions.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are predefined commercial terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and logistics. Understanding these terms is essential for international B2B transactions involving fiberglass pieces, as they dictate who bears the risk at different points in the supply chain.
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the product. For fiberglass manufacturing, understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management, as it directly affects the ability to meet production schedules.
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension of a product. In fiberglass manufacturing, specifying tolerance levels ensures that parts fit together correctly and perform as expected. This is particularly important in high-precision applications such as aerospace and automotive industries.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms related to fiberglass pieces, you can enhance your decision-making process, making it easier to procure the right products for your specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fiberglass pieces Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Global Fiberglass Pieces Market?
As the fiberglass industry expands globally, significant market drivers are influencing sourcing trends, especially among B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Vietnam and Brazil. A primary driving force is the increasing demand for lightweight materials in various applications, from automotive to construction, due to heightened fuel efficiency standards and sustainability goals. This shift towards lightweight alternatives is prompting innovation within the fiberglass sector, capitalizing on advanced manufacturing techniques such as vacuum infusion and automated layup processes, which enhance production efficiency while reducing labor costs. Additionally, the rise of composite materials designed specifically for complex applications is encouraging fabricators to explore innovative solutions, further fostering collaboration between manufacturers and clients.
Emerging technologies, particularly in CAD and 3D printing, are redefining how fiberglass products are designed and produced, enabling rapid prototyping and minimizing time-to-market. These digital tools also facilitate customization, allowing businesses to respond nimbly to customer needs and market demands. In parallel, supply chains are becoming increasingly globalized, with firms sourcing materials and components internationally to reduce costs and expand their market reach. Such dynamics imply that B2B buyers must stay vigilant in their sourcing strategies, emphasizing adaptability and responsiveness in their procurement processes.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Fiberglass Sector?
Sustainability has transitioned from being a competitive advantage to an essential aspect of sourcing and supply chain management in the fiberglass pieces sector. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that champion ethical sourcing and demonstrate environmental stewardship. This shift is encouraging the development of ‘green’ fiberglass materials derived from sustainable sources, alongside innovative production methods that reduce waste and energy consumption.
Moreover, the environmental impact of fiberglass production is under scrutiny, with organizations actively addressing concerns related to emissions and resource usage. Buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers that hold certifications such as ISO 14001 or use sustainable raw materials like bio-based resins. These certifications instill confidence that the suppliers are committed to minimizing their carbon footprint and reducing environmental effects.
Sourcing from companies that integrate sustainability into their business practices not only aligns with global environmental standards but also enhances brand reputation, offering competitive differentiation in the marketplace. Consequently, buyers should thoroughly vet their suppliers regarding their sustainability credentials and practices, fostering long-term partnerships that reflect shared values.
How Has the Fiberglass Industry Evolved to Meet Modern B2B Needs?
The fiberglass industry has undergone significant evolution over the past decades, transitioning from traditional methods to sophisticated manufacturing processes that cater to modern B2B demands. Initially, fiberglass was primarily used for boat hulls and automotive components due to its superior strength and lightweight properties. Over time, as technology advanced, the range of applications expanded to include sectors such as aerospace, renewable energy, and construction.
The introduction of advanced fiberglass compositions such as vacuum-molded pieces and hybrid combinations with other materials has further diversified its use. This evolution has been propelled by the growing need for materials that not only demonstrate durability and resistance but also comply with increasingly stringent regulatory standards across various industries.
Furthermore, the non-conductive and fire-resistant properties of specialized fiberglass versions have opened new avenues in electrical and thermal insulation applications. As industries evolve, the fiberglass sector continues to adapt, underlining its foundational role in the composites market by meeting complex engineering requirements and supporting the ongoing drive for innovation and enhanced performance.
In conclusion, the fiberglass pieces sector is uniquely positioned at the intersection of technology, sustainability, and evolving market demands. B2B buyers must remain informed and adaptable, ensuring their sourcing strategies align with these transformative trends to secure a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fiberglass pieces
-
How do I select the right type of fiberglass for my project?
When selecting fiberglass for your project, consider the end-use requirements such as strength, weight, chemical resistance, and environmental exposure. For structural applications, woven fiberglass cloth offers strength and dimension stability, while chop strand mats provide versatility in complex shapes. Also, evaluate specific products like FR-4 fiberglass laminate for electrical insulation or various resin types (polyester, vinyl ester) based on your application. Conducting preliminary tests with samples can also help you decide. -
What are the benefits of using fiberglass pieces in my manufacturing process?
Fiberglass pieces provide exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for various applications, from automotive to aerospace. Their corrosion resistance ensures durability in hostile environments, while their dimensional stability helps maintain product integrity over time. Additionally, incorporating fiberglass can reduce manufacturing costs compared to metals or carbon fiber alternatives, making it a cost-effective choice for complex designs. Its flexibility in fabrication processes enables customization to meet specific project needs. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for fiberglass pieces?
Minimum order quantities for fiberglass pieces can vary significantly based on the manufacturer, complexity of the parts, and material costs. Generally, B2B suppliers may impose MOQs ranging from as low as 1-5 units for standard items to larger quantities for custom fabrications. It’s essential to communicate your specific requirements with suppliers to understand their policies and explore options that best fit your needs. -
How can I ensure the quality of fiberglass pieces I purchase?
To ensure the quality of fiberglass pieces, work with reputable suppliers who offer ISO-certified manufacturing processes. Request samples and inspect material specifications, including tensile strength, thermal resistance, and chemical properties, before placing large orders. Additionally, consider suppliers that provide quality assurance programs, such as third-party testing or detailed certifications, to confirm compliance with industry standards. Regular communication with your supplier throughout the production process can also mitigate risks. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing fiberglass pieces internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of fiberglass pieces may include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60) depending on the supplier’s policy. It’s crucial to negotiate clear terms that outline deposit requirements, final payment deadlines, and currency considerations. Additionally, consider transaction fees and fluctuations that may arise due to international currency exchanges, and ensure that the payment method protects against potential disputes. -
What are the typical lead times for custom fiberglass products?
Lead times for custom fiberglass products can vary greatly based on order complexity, quantity, and supplier capabilities. Generally, expect lead times ranging from 2 to 8 weeks from design approval to delivery. Factors such as material availability and production scheduling can impact these timelines. Building a strong relationship with your supplier and communicating your deadlines early can facilitate smoother project execution. -
What logistics challenges should I anticipate when importing fiberglass pieces?
When importing fiberglass pieces, potential logistics challenges could include customs clearance delays, import tariffs, and shipping cost fluctuations. Understanding import regulations, specific to your region (e.g., South America or Europe), and ensuring all required documentation is in order can minimize setbacks. Collaborating with experienced freight forwarders who understand the intricacies of fiberglass transport can help you navigate these challenges effectively. -
How can I vet a fiberglass supplier before making a purchase?
To vet a fiberglass supplier, start by assessing their industry experience and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients and verify their production capabilities and quality certifications. Investigate their manufacturing processes, sourcing of materials, and adherence to safety standards. Conducting a factory visit, if possible, can provide valuable insights into their operations and commitment to quality. Engaging in clear communication about your specific needs and expectations is also essential.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Fiberglass Pieces Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Fibreglast – Fiberglass Fabrics
Domain: fibreglast.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Fiberglass Cloth, Fiberglass Fabrics, Certified & Traceable Products, Same-Day Shipping, Same-Day Quotes, Fiberglass Chopper Gun & Roving, Fiberglass Fabric, Fiberglass Mat, Fiberglass Tapes & Sleeve, Stitched Fiberglass, Sample Packs.
2. Sika® – Key Product
Domain: fiberglasssupplydepot.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: {“categories”: [“Abrasives”, “Brushes/Rollers/Pans”, “Boat Parts And Accessories”, “Clothing”, “Epoxy Resin and Glue”, “Fiberglass”, “Foam/Core Material”, “Gel Coat”, “Hardware”, “Paint”, “Putty/Fillers”, “Safety”, “Solvents”, “Tools”, “Vinyl Ester Products”], “featured_products”: [{“name”: “Sika® Primer-207 AGR– Pigmented, Solvent-Based Adhesion Primer (250ml)”, “price”: “$79.99”}, {“name”: “Sika…
3. eMachineShop – Custom Fiberglass Laminate Parts
Domain: emachineshop.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Custom Fiberglass Laminate Parts manufactured by eMachineShop for over a decade. Benefits include free CAD software for design, affordable pricing compared to carbon fiber and metals, and free shipping in the USA. No minimum order quantity with a 100% quality guarantee. Key specifications: FR-4 Fiberglass Laminate made from epoxy resin reinforced woven fiberglass cloth, known for electrical insula…
4. TP Tools – Fiberglass Repair Kit
Domain: tptools.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, TP Tools – Fiberglass Repair Kit, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Instructables – Sailboat Rain Cover
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This guide details the process of making small fiberglass parts, specifically focusing on creating a cover to prevent rain leaks in a sailboat. The key components include: 1. Mold creation using a soda bottle filled with water. 2. West System epoxy for wetting out fiberglass cloth. 3. Glass cloth layers for structuring the part. 4. Use of plastic wrap to prevent sticking during curing. 5. Tools li…
6. US Body – Fiberglass Auto Body Parts
Domain: usbody.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Manufactured locally in Lakeland, FL, USA. The product line includes various fiberglass auto body parts such as hoods, bumpers, trunks, and more, suitable for a wide range of vehicle makes and models from 1923 to 2005. Categories include Car, Truck/SUV; Performance options available; Heavy Duty, Race Weight, and Bolt-On styles are common features. Some specific products include: 1968-1969 Dodge Co…
7. Trick Race Parts – Cowling V.W
Domain: trickraceparts.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: [{“name”:”Cowling V.W”,”price”:”115.79 USD”},{“name”:”VINTAGE GREMLIN ROOF”,”price”:”217.31 USD”},{“name”:”SHORT ROOF”,”price”:”201.45 USD”},{“name”:”MISCELLANEOUS PARTS”,”price”:”0.00 USD”},{“name”:”Dirt Modified Wheel Well”,”price”:”79.31 USD”},{“name”:”LATE MODEL – FAN SHROUD”,”price”:”107.86 USD”},{“name”:”LATE MODEL – AIR BOX SYSTEM”,”price”:”169.72 USD”},{“name”:”FIBERGLASS CAP FOR LMRO2″,”p…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fiberglass pieces
When considering the strategic sourcing of fiberglass pieces, various factors come into play that underline the material’s versatility and cost-effectiveness. Fiberglass serves not just as a robust reinforcement option but also as a practical solution for diverse applications across industries. From automotive to marine, its capability to conform to complex shapes and endure harsh environmental conditions holds significant appeal for fabricators and manufacturers.
Understanding suppliers’ capabilities—from custom fabrication to availability of various fiberglass forms—is crucial for maintaining high-quality output while managing costs. Engaging with reputable suppliers that prioritize customer service and quality assurance can elevate your sourcing strategy, ensuring product reliability and satisfaction.
As global markets evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage strategic sourcing partnerships. The trend toward sustainable manufacturing offers opportunities to embrace fiberglass and its composites, which can be pivotal in reducing costs and enhancing performance.
Looking ahead, organizations must adapt and innovate within the sourcing ecosystem to remain competitive. Invest time in evaluating your fiberglass needs and explore potential partnerships that align with your strategic goals for success in an increasingly interconnected world. The future looks bright for fiberglass sourcing; prioritize it today.