Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fiber laser metal cutter
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing a fiber laser metal cutter that meets specific production needs can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With the rapid advancements in technology and the increasing demand for precision in metal fabrication, understanding the diverse range of options available is critical. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, exploring various types of fiber laser cutters, their applications across industries, and essential insights for vetting suppliers.
Buyers will learn about key factors influencing cost, including power capabilities, operational efficiency, and maintenance requirements. The guide also highlights how to navigate the complexities of international shipping and compliance, particularly for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Saudi Arabia and Germany.
By providing actionable insights and practical tips, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to enhance in-house capabilities or seeking reliable partnerships for outsourced services, understanding the fiber laser metal cutter market can significantly impact your operational efficiency and return on investment. Dive into the details and equip yourself with the knowledge needed to thrive in the global marketplace.
Understanding fiber laser metal cutter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
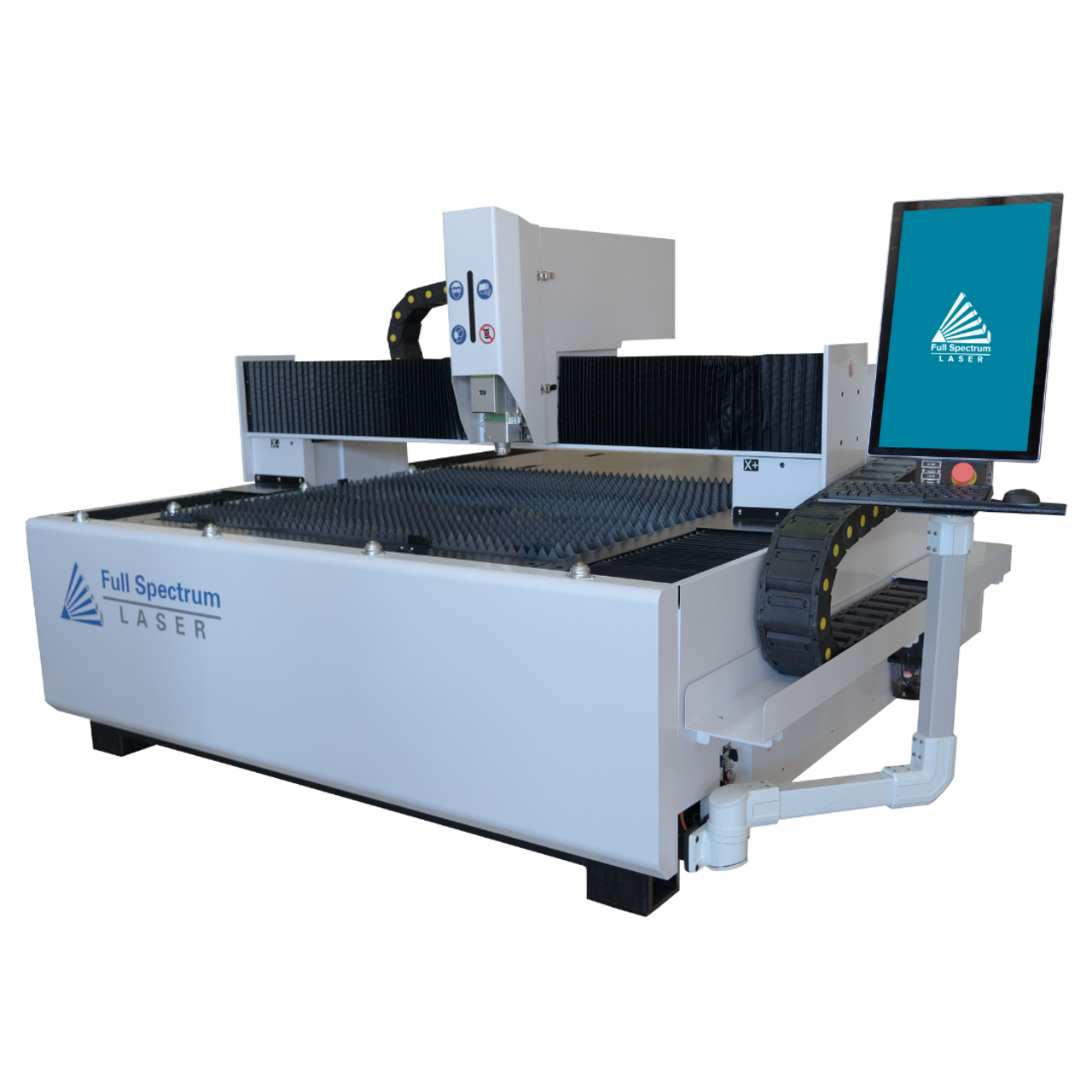
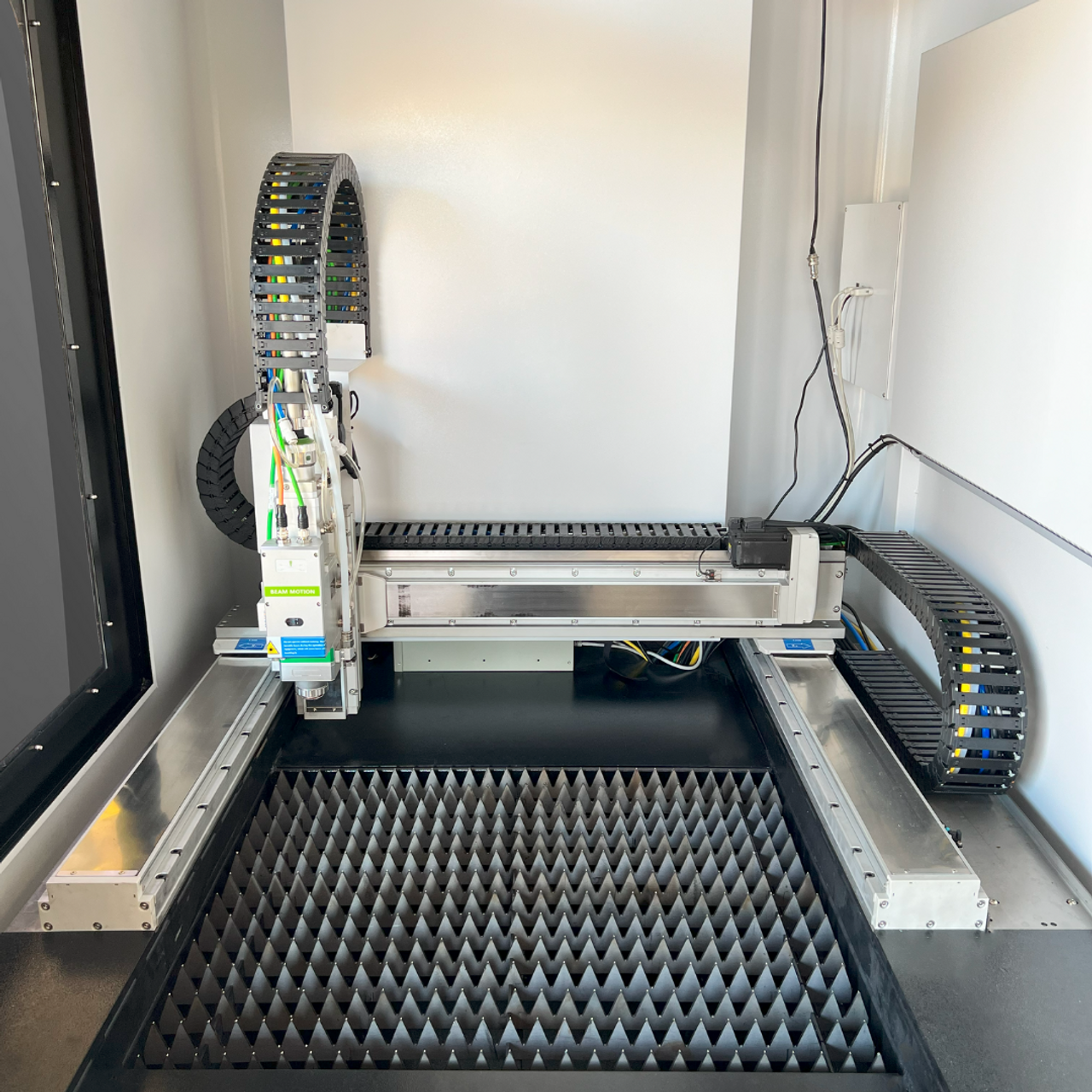
| Flatbed Fiber Laser Cutter | Large cutting area, typically 4×8 or 5×10 feet, high efficiency | Sheet metal fabrication, automotive parts | Pros: High throughput, versatile materials. Cons: Requires significant space. |
| Tube Fiber Laser Cutter | Specialized for cutting metal tubes and profiles | Structural components, furniture design | Pros: Precision cutting of complex shapes. Cons: Limited to tubular materials. |
| High-Power Fiber Laser Cutter | Power range from 10kW to 30kW for cutting thick materials | Heavy-duty industrial applications | Pros: Excellent for thick metals, fast cutting. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Compact Fiber Laser Cutter | Smaller footprint, ideal for limited workspace | Custom parts, small batch production | Pros: Space-saving, often lower cost. Cons: Limited cutting area and capacity. |
| Multi-Function Fiber Laser Cutter | Combines sheet and tube cutting capabilities | Versatile manufacturing, prototyping | Pros: Flexibility in applications. Cons: May compromise speed for versatility. |
What are the Characteristics of Flatbed Fiber Laser Cutters?
Flatbed fiber laser cutters are designed for high-volume production with a large cutting area, typically accommodating sheets of metal measuring 4×8 or 5×10 feet. They offer rapid cutting speeds and are capable of handling a variety of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. For businesses involved in sheet metal fabrication or automotive components, these machines provide a significant return on investment by reducing reliance on third-party services. Buyers should consider the required space and potential energy costs when evaluating these machines.
How Do Tube Fiber Laser Cutters Differ?
Tube fiber laser cutters are specifically engineered to cut metal tubes and profiles with precision. These machines excel in applications where intricate designs and complex geometries are required, making them ideal for structural components in construction and furniture design. The ability to cut various tube diameters and wall thicknesses adds to their appeal. However, businesses should note that these machines are limited to tubular materials, which may not suit all manufacturing needs.
What are the Advantages of High-Power Fiber Laser Cutters?
High-power fiber laser cutters, ranging from 10kW to 30kW, are ideal for industries requiring the cutting of thick metals, such as aerospace and heavy machinery manufacturing. Their ability to maintain speed and precision while cutting through tough materials makes them invaluable in high-demand settings. While they deliver exceptional performance and efficiency, buyers should consider the higher initial investment and operational costs associated with these powerful machines.
Why Choose Compact Fiber Laser Cutters?
Compact fiber laser cutters are perfect for businesses with limited workspace or those just starting in metal fabrication. These machines maintain a balance between performance and space efficiency, making them suitable for custom parts and small batch production. While they often come at a lower price point, potential buyers should be aware of the limitations in cutting area and overall capacity compared to larger models.
What Makes Multi-Function Fiber Laser Cutters Versatile?
Multi-function fiber laser cutters offer the unique advantage of combining both sheet and tube cutting capabilities within a single machine. This versatility allows manufacturers to streamline their operations and reduce the need for multiple machines. They are particularly beneficial for prototyping and versatile manufacturing environments. However, businesses should assess whether the trade-off in speed and specialization aligns with their production goals.
Key Industrial Applications of fiber laser metal cutter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fiber laser metal cutter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Cutting automotive panels and components | Enhanced precision and reduced waste, leading to cost savings | Power requirements, cutting speed, and maintenance support |
| Aerospace | Fabrication of lightweight structural components | High accuracy and minimal thermal distortion, ensuring safety and compliance | Material compatibility and certifications needed |
| Electronics | Production of enclosures and heat sinks | Improved design flexibility and faster prototyping cycles | Size of the cutting bed and software compatibility |
| Jewelry | Custom jewelry designs and intricate patterns | Ability to create detailed, unique pieces with minimal labor | Precision settings and the ability to work with precious metals |
| Construction | Fabrication of metal frameworks and fittings | Streamlined production processes and reduced lead times | Machine durability and service availability in remote locations |
How is Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Beneficial in the Automotive Manufacturing Sector?
In the automotive manufacturing industry, fiber laser metal cutters are extensively used for cutting automotive panels and components. These machines provide enhanced precision that significantly reduces material waste, resulting in substantial cost savings for manufacturers. Furthermore, the ability to cut various materials, including high-strength steels and aluminum, allows for the production of lightweight components that improve vehicle efficiency. Buyers in this sector should consider factors such as the power requirements of the laser, cutting speed, and the availability of maintenance support to ensure operational continuity.
What Role Does Fiber Laser Cutting Play in Aerospace Fabrication?
In aerospace, fiber laser metal cutters are vital for fabricating lightweight structural components. The high accuracy of these machines minimizes thermal distortion during the cutting process, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of safety-critical components. Additionally, fiber lasers can efficiently cut through advanced materials like titanium and carbon fiber composites. Buyers must prioritize material compatibility and ensure that the equipment meets industry-specific certifications to comply with stringent aerospace standards.
How Does Fiber Laser Cutting Enhance Electronics Production?
The electronics industry leverages fiber laser metal cutters for producing enclosures and heat sinks that require intricate designs and precision. These machines allow manufacturers to rapidly prototype and produce components, significantly speeding up the design-to-production cycle. The flexibility to work with various metals and thicknesses enhances the design possibilities for electronic devices. Buyers should evaluate the size of the cutting bed and the software compatibility with their existing systems to ensure seamless integration into their production lines.
In What Ways Does Fiber Laser Cutting Benefit the Jewelry Sector?
In the jewelry industry, fiber laser cutters are employed to create custom designs and intricate patterns on various metals. The precision offered by these machines allows artisans to produce detailed pieces with minimal manual labor, enhancing productivity and creativity. This capability is particularly valuable for businesses looking to differentiate themselves through unique offerings. Buyers should focus on precision settings and the machine’s ability to work with precious metals to maintain quality standards.
Why is Fiber Laser Cutting Important in Construction?
Fiber laser metal cutters play a significant role in the construction sector by fabricating metal frameworks and fittings. These machines enable streamlined production processes, leading to reduced lead times and improved project timelines. Their ability to handle large sheets of metal with precision ensures that components fit together correctly, minimizing installation issues. Buyers should consider the durability of the machine and the availability of service support, especially in remote locations where construction projects may take place.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fiber laser metal cutter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Operating Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience sticker shock when evaluating the operational costs associated with fiber laser metal cutters. This concern is particularly pronounced in regions where energy prices are high, such as parts of Europe and the Middle East. Buyers often find that ongoing expenses for electricity, gas, and maintenance can quickly erode their profit margins, especially when outsourcing cutting jobs to third-party services could be more cost-effective in the short term.
The Solution: To mitigate high operational costs, businesses should invest in energy-efficient fiber laser models. For instance, selecting machines that utilize low-cost nitrogen or oxygen for cutting can reduce gas expenses significantly—potentially to less than $0.25 per hour. Additionally, buyers should focus on models that offer a quick return on investment (ROI), such as those designed for high-speed cutting with minimal energy consumption. Researching and comparing the energy usage metrics of different models can help buyers identify machines that balance power and efficiency. Engaging with manufacturers who provide robust warranties and maintenance support can also alleviate long-term cost concerns, ensuring that the equipment remains in optimal working condition without incurring excessive repair costs.
Scenario 2: Limited Versatility in Material Cutting
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the limited versatility of their cutting machines. Many businesses need to work with a variety of materials—including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper—but some fiber laser cutters are optimized for specific metals only. This limitation can hinder production capabilities and force companies to invest in multiple machines, complicating logistics and increasing overhead costs.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize fiber laser metal cutters that offer a broad cutting range for different materials and thicknesses. When sourcing equipment, they should look for machines that can handle various metals with adjustable power settings, allowing for seamless transitions between materials. For instance, a fiber laser cutter with power options ranging from 1 kW to 30 kW can accommodate everything from thin aluminum sheets to thicker stainless steel. Additionally, potential buyers should inquire about customizable features and add-ons that enhance versatility, such as automatic material detection systems and programmable cutting parameters. This will ensure that the machine can adapt to different jobs without requiring extensive recalibration or downtime, ultimately maximizing productivity and minimizing the need for multiple machines.
Scenario 3: Technical Skill Gaps Among Operators
The Problem: As technology advances, many companies find that their workforce lacks the necessary technical skills to operate sophisticated fiber laser cutters effectively. This skill gap can lead to inefficient operations, increased error rates, and even safety hazards, particularly in regions where there is a shortage of trained technicians. B2B buyers may feel pressured to either invest in training programs or hire specialized personnel, both of which can be costly and time-consuming.
The Solution: To address this issue, companies should seek out fiber laser cutting machines that come with user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive training resources. When evaluating potential purchases, buyers should ask about training programs offered by manufacturers, including online tutorials, on-site training sessions, and access to technical support. Investing in machines that incorporate intuitive software can also simplify the learning curve for operators, allowing them to gain proficiency more quickly. Furthermore, forming partnerships with local technical schools or vocational training programs can provide ongoing education for employees, ensuring they remain up-to-date with the latest advancements in laser technology. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters employee retention by investing in their professional development.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fiber laser metal cutter
What Are the Key Materials for Fiber Laser Metal Cutting?
When selecting materials for fiber laser metal cutting, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness in various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in fiber laser cutting: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Fiber Laser Cutting?
Carbon steel is widely used in various industries due to its strength and versatility. It has excellent machinability and can be cut with high precision using fiber lasers. The key properties of carbon steel include high tensile strength and good weldability, making it suitable for structural applications.
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively low-cost compared to other metals, making it an economical choice for large-scale production. It is durable and can withstand high loads.
Cons: However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which may limit its use in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is ideal for applications like automotive parts, construction materials, and industrial equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 is crucial. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that the steel meets local regulations regarding quality and environmental impact.
What About Stainless Steel in Fiber Laser Cutting?
Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Its key properties include high strength, ductility, and resistance to oxidation and staining.
Pros: The durability of stainless steel makes it suitable for applications in harsh environments, such as food processing and chemical industries. It also offers a longer lifespan compared to carbon steel.
Cons: The cost of stainless steel is higher than that of carbon steel, and its cutting can be more complex due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is commonly used in the manufacturing of kitchenware, medical devices, and architectural components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM A240 and EN 10088 for stainless steel. In regions like South America, where corrosion can be a significant issue, selecting the right grade is essential.
How Does Aluminum Fare in Fiber Laser Cutting?
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent thermal conductivity, making it a popular choice in various industries, including aerospace and automotive. Its key properties include low density and high corrosion resistance.
Pros: Aluminum is easy to cut and shape, allowing for complex designs and lightweight structures. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
Cons: However, aluminum can be more expensive than carbon steel and may require specialized cutting techniques to achieve optimal results.
Impact on Application: It is widely used for manufacturing aircraft components, automotive parts, and consumer electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 is important. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should consider local availability and cost fluctuations of aluminum.
What Are the Considerations for Copper in Fiber Laser Cutting?
Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. Its key properties include high ductility and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: Copper is ideal for electrical applications and is often used in wiring and electronic components due to its conductivity.
Cons: The main drawback is its high cost and the complexity of cutting due to its thermal properties, which can lead to warping if not managed properly.
Impact on Application: Copper is extensively used in electrical and electronic applications, plumbing, and roofing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B152 is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of copper in their respective regions, as it can vary significantly.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Fiber Laser Metal Cutters
| Material | Typical Use Case for fiber laser metal cutter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Automotive parts, construction materials | Low cost, high strength | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Kitchenware, medical devices | Corrosion resistance, durability | Higher cost, complex cutting | Med |
| Aluminum | Aircraft components, consumer electronics | Lightweight, easy to shape | Higher cost, specialized cutting needed | Med |
| Copper | Electrical wiring, plumbing | Excellent conductivity | High cost, cutting complexity | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in fiber laser cutting, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fiber laser metal cutter
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Fiber Laser Metal Cutters?
The manufacturing process of fiber laser metal cutters involves several critical stages that ensure both performance and reliability. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers seeking to invest in high-quality cutting machines.
Material Preparation: What Are the Initial Steps?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, where high-quality raw materials are selected. Typically, manufacturers use high-grade stainless steel or aluminum for the frame and housing, ensuring durability and stability. The choice of materials significantly affects the performance and longevity of the machine.
In this stage, materials are subjected to various treatments, such as annealing or surface hardening, to enhance their properties. Once prepared, materials are cut to size using preliminary cutting techniques, ensuring they meet the specific dimensions required for the machine’s components.
Forming: How Are the Components Shaped?
Following material preparation, the forming stage involves shaping the components using techniques like laser cutting, CNC machining, or bending. Laser cutting is particularly relevant, as it offers precision and efficiency, reducing waste and ensuring accurate dimensions.
CNC machining is also employed for components that require intricate designs or tight tolerances, such as the cutting head and mirrors. The use of advanced forming techniques ensures that each part meets the exact specifications necessary for optimal performance.
Assembly: What Is Involved in the Assembly Process?
Once the components are formed, they are assembled in a clean and controlled environment. This stage includes the installation of critical systems such as the laser source, optics, and the cooling system. Each assembly step is performed with precision, as even minor misalignments can affect the machine’s performance and cutting quality.
Manufacturers often employ a modular assembly approach, allowing for easier upgrades and maintenance. This is particularly advantageous for B2B buyers, as it enhances the machine’s longevity and adaptability to evolving production needs.
Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared?
The finishing stage focuses on quality and aesthetics. This includes surface treatments like powder coating or anodizing to protect against corrosion and wear, as well as to enhance the machine’s appearance.
Additionally, thorough cleaning processes are implemented to remove any contaminants that could affect performance. Final adjustments, calibration, and testing are conducted to ensure that the machine operates at peak efficiency before it is shipped to the buyer.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Commonly Implemented?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of fiber laser metal cutters, ensuring that each machine meets international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Fiber Laser Metal Cutters?
Manufacturers typically adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
Moreover, specific industry certifications, such as CE marking in Europe or API standards for industrial applications, may also be required. These certifications indicate that the products meet safety and performance standards, which is crucial for B2B buyers in regulated markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that standards are met. The following checkpoints are commonly used:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, processes are monitored to ensure they adhere to predefined parameters. This includes checking the accuracy of laser cuts and assembly tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the finished product undergoes comprehensive testing and inspection. This may involve functional testing, performance evaluations, and safety checks to validate that the machine operates correctly.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should actively seek verification of a supplier’s QC processes to ensure they are investing in high-quality machines. Here are several methods:
-
Audits: Conducting supplier audits can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and QC measures. This can be done through on-site visits or by reviewing audit reports.
-
Certification Verification: Buyers should request copies of relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking, to confirm compliance with quality standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the machine’s quality and performance before purchase.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the performance and reliability of fiber laser metal cutters:
-
Laser Performance Tests: These tests measure the laser’s cutting speed, precision, and kerf width, ensuring that it meets operational specifications.
-
Durability Testing: Machines are often subjected to stress tests to evaluate their performance under extreme conditions, simulating real-world usage.
-
Safety Tests: Compliance with safety standards is assessed through tests that check for electrical safety, laser radiation containment, and overall machine stability.
How Do International Standards and Quality Nuances Affect Buyers from Different Regions?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality certifications and standards is essential. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe may encounter varying regulations and standards that can influence their purchasing decisions.
-
Regional Compliance: Buyers should be aware of region-specific regulations, such as the EU’s RoHS directives, which restrict certain hazardous substances in electronic equipment.
-
Cultural Expectations: Different markets may have varying expectations regarding machine performance and durability. Understanding these cultural nuances can aid in selecting a supplier who aligns with specific regional needs.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in fiber laser metal cutters, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and compliance needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fiber laser metal cutter’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure fiber laser metal cutters. With the rapid advancements in laser technology and varying supplier capabilities, making informed decisions is crucial. This checklist will help you identify your needs, evaluate potential suppliers, and ensure a successful purchase.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. Determine the materials you will be cutting (e.g., carbon steel, aluminum, titanium) and the thickness ranges you expect to work with. Additionally, assess the desired cutting area dimensions and power output (measured in watts) based on your production needs.
- Key Considerations:
- Identify whether you need a flatbed or tube cutter.
- Consider the production volume to select the appropriate power capacity.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of fiber laser metal cutters. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your region or industry. Utilize online resources, trade shows, and industry publications to gather a list of candidates.
- Tips:
- Check online reviews and testimonials from previous clients.
- Explore industry forums and networks for recommendations.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that the suppliers you are considering have relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking. Certifications ensure that the manufacturer adheres to international quality standards, which is critical for the reliability and safety of the equipment.
- Important Aspects:
- Request documentation of certifications.
- Ensure compliance with local regulations in your region.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Reach out to multiple suppliers for quotes tailored to your specifications. Analyze the pricing structures, including any additional costs for shipping, installation, and training. Comparing quotes will help you identify the best value for your investment.
- Considerations:
- Look for transparency in pricing and avoid hidden fees.
- Assess the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs.
Step 5: Inquire About After-Sales Support
After-sales support is a critical factor in your purchasing decision. Confirm what kind of warranty and technical support the supplier provides. A solid support system can greatly reduce downtime in your operations.
- Questions to Ask:
- What is the duration and coverage of the warranty?
- Are spare parts readily available, and what are the response times for service requests?
Step 6: Schedule Product Demonstrations
Whenever possible, schedule live demonstrations or virtual showcases of the fiber laser cutter. Observing the machine in action can provide insights into its capabilities and performance, helping you make a more informed decision.
- Follow-Up:
- Ask for samples of materials cut with the machine.
- Evaluate the ease of use and setup during the demonstration.
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision and Negotiate Terms
After thorough evaluation, select the supplier that best meets your needs. Engage in negotiations to finalize terms, including payment plans, delivery timelines, and any customization options. Clear agreements will set the foundation for a successful partnership.
- Final Checks:
- Ensure all terms are documented in a formal contract.
- Confirm the timeline for delivery and installation to align with your operational schedule.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for fiber laser metal cutters, ensuring they select the best option for their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fiber laser metal cutter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Fiber Laser Metal Cutters?
When considering the acquisition of fiber laser metal cutters, it’s essential to understand the underlying cost structure. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s margin.
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used in constructing the fiber laser cutter significantly influence costs. High-quality components, such as solid-state lasers and precision optics, can increase the initial outlay but enhance performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for both manufacturing and assembly. Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the region and the expertise required, which is particularly relevant for international buyers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling and fixtures required for the production of fiber laser cutters contribute to the overall cost. Custom tooling may be necessary for specific applications, adding to the expense.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the machines meet industry standards and function correctly. Investing in quality assurance can prevent costly returns and repairs down the line.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international transactions. These can include freight charges, customs duties, and insurance, which vary based on the destination and Incoterms.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can differ based on brand reputation, market demand, and the exclusivity of technology. Understanding these margins can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Fiber Laser Cutter Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of fiber laser metal cutters, including volume of purchase, specifications, material quality, certifications, supplier factors, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often lead to significant discounts, making it crucial for buyers to assess their needs and negotiate accordingly.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized machines tailored to specific applications can incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against their budget and operational requirements.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: The choice of materials directly affects performance and durability. Additionally, certifications (such as ISO) can enhance a supplier’s credibility but may also increase costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and service offerings impact pricing. Suppliers with robust after-sales support and warranties may justify higher prices.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This knowledge can help avoid unexpected costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing fiber laser metal cutters, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations with multiple suppliers to secure the best price. Presenting competitive quotes from other vendors can strengthen your bargaining position.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes initial purchase price, operating costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher long-term expenses, making it crucial to assess the complete picture.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should factor in currency fluctuations, import duties, and compliance with local regulations. Understanding these nuances can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Supplier Relationships: Cultivating strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms, reliable support, and early access to new technologies or pricing structures.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough research on market prices and trends. Benchmarking against industry standards can provide insights into fair pricing and quality expectations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for fiber laser metal cutters can vary widely based on numerous factors, including specifications, supplier, and regional market conditions. The indicative prices mentioned in various sources serve as a reference point but should not be considered fixed or absolute. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing tailored to your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fiber laser metal cutter With Other Solutions
When considering the optimal solution for metal cutting in a B2B context, it is essential to evaluate various technologies. Fiber laser metal cutters have become a popular choice due to their efficiency and precision. However, other alternatives also exist that may better suit specific operational needs or budget constraints. This analysis compares fiber laser metal cutters with two viable alternatives: CO2 laser cutters and plasma cutting machines.
| Comparison Aspect | Fiber Laser Metal Cutter | CO2 Laser Cutter | Plasma Cutter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and speed; ideal for thin metals and intricate designs. | Good for thicker materials; less precise than fiber lasers. | Fast cutting speed, effective on thick materials, but lower precision. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment ($72,000 – $475,000), but low operating costs. | Moderate cost ($4,497 – $22,497); higher consumable costs. | Lower upfront cost ($2,000 – $20,000), but higher operating costs and maintenance. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; setup can be complex. | Easier to set up and operate; widely used in various industries. | Straightforward installation; requires safety measures due to high temperatures. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance needs; long lifespan (50,000+ hours). | Moderate maintenance; requires periodic replacement of tubes. | Higher maintenance demands due to wear and tear on consumables. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for precision cutting of metals such as stainless steel and aluminum. | Suitable for thicker materials and general cutting applications. | Best for heavy-duty cutting tasks in manufacturing and construction. |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of CO2 Laser Cutters Compared to Fiber Lasers?
CO2 laser cutters are a common alternative to fiber lasers, particularly valued for their versatility in cutting a range of materials, including non-metals. They typically have a lower initial cost, making them accessible for smaller operations. However, CO2 lasers are generally less efficient in cutting metals compared to fiber lasers, with a larger kerf and slower cutting speeds. They also incur higher ongoing costs due to the need for regular tube replacements and their energy consumption.
How Do Plasma Cutters Stack Up Against Fiber Laser Metal Cutters?
Plasma cutters are known for their ability to cut through thick materials at high speeds, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. They have a lower upfront cost than fiber lasers, which can be appealing for businesses on a budget. However, they lack the precision of fiber lasers, leading to rougher edges and a wider kerf. Additionally, plasma cutting can be less energy-efficient and may involve higher operating costs due to consumable wear.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Metal Cutting Solution?
When selecting the right metal cutting solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements, including the types of materials they need to cut, the desired precision, and budget constraints. For businesses focused on high-precision tasks and working with thinner metals, fiber laser cutters are likely the best option despite their higher initial costs. Conversely, for those needing to cut thicker materials quickly and economically, plasma cutters may be more suitable. CO2 lasers serve as a versatile middle ground, ideal for those seeking a balance of cost and functionality across various materials. Ultimately, understanding the unique needs of your business will guide you to the most effective metal cutting solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fiber laser metal cutter
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Fiber Laser Metal Cutters?
When evaluating fiber laser metal cutters, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are essential properties that highlight their capabilities and impact on production efficiency.
1. Laser Power (Wattage)
The laser power of a fiber cutter typically ranges from 1,000W to 30,000W. Higher wattage allows for faster cutting speeds and the ability to process thicker materials. For B2B buyers, selecting the right power is essential as it directly affects productivity and the types of materials that can be efficiently cut, such as stainless steel, aluminum, and brass.
2. Cutting Speed
Measured in meters per minute (m/min), cutting speed indicates how quickly the machine can process materials. A high cutting speed is vital for maximizing output and minimizing production time. For businesses with high-volume orders, investing in a machine with superior cutting speed can lead to significant cost savings and improved turnaround times.
3. Kerf Width
Kerf width refers to the width of the cut made by the laser. A narrower kerf (often less than 0.1 mm) minimizes material wastage and enhances accuracy, making it a critical factor for precision applications. Businesses focused on reducing costs through efficient material use will benefit from a cutter that offers fine kerf capabilities.
4. Material Capability
Different fiber lasers can cut various materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. Understanding the material capabilities of a laser cutter is essential for businesses that work with multiple types of metals. Selecting a machine that can accommodate a range of materials ensures versatility and can cater to diverse project requirements.
5. Positioning Accuracy
Positioning accuracy defines how precisely the machine can position the laser beam relative to the material. High accuracy (typically ≤±0.03 mm) is critical for intricate designs and tight tolerances in manufacturing. Companies specializing in detailed fabrication or requiring high-quality finishes must prioritize this specification to maintain their competitive edge.
6. Cooling System
Fiber laser cutters require efficient cooling systems to maintain operational integrity. Refrigerated water chillers are common and help prevent overheating, which can affect performance and longevity. Understanding the cooling requirements is essential for maintaining uptime and ensuring the machine operates within optimal temperature ranges.
What Trade Terms Are Commonly Used in Fiber Laser Metal Cutting?
Familiarizing yourself with trade terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B market. Here are some key terms related to fiber laser metal cutters:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of fiber laser cutters, buyers often engage with OEMs to ensure they are sourcing high-quality machines that meet specific industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for businesses looking to manage inventory effectively while ensuring they meet production demands without overcommitting financially.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It includes specifications and quantities for the required products. This process allows businesses to compare offers and select the best supplier based on price and terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Knowing these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is crucial for effective logistics management.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is critical for businesses to plan their production schedules and manage customer expectations effectively.
6. Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the performance and longevity of the equipment. Knowing the warranty terms is essential for assessing the risk of investment in fiber laser cutters and ensuring long-term support for maintenance and repairs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals in the metal fabrication industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fiber laser metal cutter Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting the Fiber Laser Metal Cutter Industry?
The fiber laser metal cutter market is experiencing significant growth, driven by several global factors including technological advancements, increasing demand for precision manufacturing, and the need for cost-effective production solutions. The rise of Industry 4.0 has fueled the adoption of automation and smart technologies in manufacturing processes, making fiber laser cutters an essential tool for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency and precision. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize their manufacturing capabilities, the demand for high-performance fiber laser machines is expected to rise.
Current sourcing trends reveal a shift toward customizable solutions that cater to specific industrial needs. For instance, manufacturers are increasingly offering machines with varying power capacities and optional features, allowing buyers to tailor their purchases to fit their operational requirements. Additionally, the emphasis on quick return on investment (ROI) is becoming a central theme, with many suppliers promoting the cost-effectiveness of in-house cutting versus outsourcing. This trend is particularly relevant for markets in developing regions where manufacturing costs can significantly impact overall business sustainability.
Moreover, the market dynamics are influenced by regional factors, such as the rapid industrialization in Africa and South America, alongside the robust manufacturing sectors in Europe and the Middle East. As these regions evolve, the demand for reliable and efficient cutting technologies will continue to shape sourcing strategies, with buyers prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a strong commitment to innovation and customer support.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Fiber Laser Metal Cutter Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the fiber laser metal cutter industry, particularly as global environmental regulations tighten and businesses seek to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles. The production and operation of fiber laser cutters can significantly impact the environment, with energy consumption and waste generation being critical factors. Therefore, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing energy-efficient machines that minimize power usage and reduce carbon footprints. For instance, fiber laser technology typically offers lower operational costs and energy consumption compared to traditional CO2 laser systems, making them more environmentally friendly.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining traction among B2B buyers, who are now more inclined to partner with suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices in their supply chains. This includes sourcing raw materials from certified suppliers that adhere to environmental standards, as well as implementing recycling programs for metal waste produced during cutting processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are becoming essential in establishing credibility and ensuring compliance with sustainability objectives.
In addition, the demand for ‘green’ materials is on the rise, with buyers increasingly looking for equipment made from recyclable or sustainably sourced components. This trend not only supports environmental goals but also aligns with consumer preferences for responsible manufacturing practices, thereby enhancing brand reputation and market competitiveness.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Fiber Laser Metal Cutters?
The evolution of fiber laser metal cutters has been marked by significant technological advancements since their introduction in the late 20th century. Initially, laser cutting technology relied heavily on CO2 lasers, which, while effective, faced limitations in efficiency and operational costs. The development of fiber lasers in the early 2000s revolutionized the industry, offering higher power density and better absorption rates for metal cutting applications.
This transition has allowed manufacturers to achieve greater precision and speed while reducing energy consumption. As the technology matured, fiber laser cutters became more accessible to a wider range of industries, from automotive to aerospace and beyond. Today, the market is characterized by continuous innovation, with manufacturers striving to enhance capabilities through automation, AI integration, and advanced software solutions. This ongoing evolution is crucial for B2B buyers looking to remain competitive in an increasingly demanding manufacturing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fiber laser metal cutter
-
How do I choose the right fiber laser metal cutter for my business needs?
Selecting the right fiber laser cutter involves evaluating several factors, including the materials you will be cutting, thickness requirements, and production volume. Consider machines with customizable power options to suit various materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and brass. Additionally, assess the machine’s cutting area dimensions and speed capabilities, ensuring they align with your operational needs. Consulting with suppliers for recommendations based on your specific applications can also provide valuable insights. -
What is the best power rating for a fiber laser cutter for sheet metal?
The ideal power rating for a fiber laser cutter largely depends on the thickness and type of sheet metal you intend to work with. For cutting thinner sheets (up to 3 mm), a 1 kW to 2 kW laser is typically sufficient. For thicker materials, such as 6 mm carbon steel or 3 mm stainless steel, a power rating between 3 kW and 6 kW is recommended. It’s crucial to match the power rating with your cutting requirements to ensure efficiency and cost-effectiveness. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering a fiber laser cutter internationally?
Lead times for international orders of fiber laser cutters can vary based on the supplier, machine specifications, and shipping logistics. Generally, you can expect lead times ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. It’s advisable to communicate with the supplier for precise timelines, especially if customization is required. Consider potential delays due to customs clearance and ensure that you have a clear agreement on delivery schedules. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a fiber laser cutter?
Payment terms for fiber laser cutters can differ significantly by supplier and region. Common terms include a deposit upon order confirmation, followed by the balance before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or installment plans. Always clarify payment conditions in the contract to avoid misunderstandings, and consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment. -
How do I vet suppliers of fiber laser cutters?
Vetting suppliers involves researching their reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Check for certifications and industry affiliations that demonstrate quality assurance. Request references from previous clients and inquire about their after-sales support, warranty policies, and service options. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility or arranging a virtual tour to assess their manufacturing capabilities and commitment to quality. -
Can fiber laser cutters be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for fiber laser cutters to meet specific operational requirements. This can include adjustments in power ratings, cutting bed sizes, and additional features like automated loading systems or specialized cutting heads. Engaging in a detailed consultation with the supplier can help ensure that the machine is tailored to your unique needs, enhancing productivity and precision in your applications. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing a fiber laser cutter?
When importing a fiber laser cutter, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs duties, and local regulations. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger machines but takes longer. Ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation for customs clearance. It’s also advisable to work with a reliable freight forwarder who understands the specifics of importing heavy machinery to streamline the process. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in a fiber laser cutter?
Quality assurance measures can include certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to international quality management standards. Inquire about the manufacturer’s testing protocols for their machines, including pre-shipment inspections and performance guarantees. Additionally, consider the availability of after-sales support and maintenance services, as these can significantly impact the longevity and reliability of your investment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Fiber Laser Metal Cutter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Hytek Tools – Fiber Laser Cutters
Domain: hytektools.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“model”:”2025 FIBERTEK™ Model DE”,”size”:”5×10″,”power”:”2000w-30,000w”,”price”:”from $145,650.00″},{“model”:”ROBOTUBE™ MODEL RT2″,”type”:”Fiber Laser Metal Tube Cutter”,”price”:”from $182,000.00″},{“model”:”2025 FIBERTEK™ MODEL SE”,”size”:”5×10″,”power”:”2000W-12000W”,”price”:”from $122,000.00″,”original_price”:”$144,000.00″},{“model”:”2025 FIBERTEK™ MODEL D”,”size”:”5×10″,”power”:”…
2. FSLaser – Atlas Alloy Flatbed Fiber Laser
Domain: fslaser.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Atlas Alloy Flatbed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser up to 20kW
– Model Options: 4’x8′ 1000W, 4’x8′ 1500W, 4’x8′ 2000W, 5’x10′ 3000W, 5’x10′ 6000W
– MSRP: $55,000.00
– Cutting Area: 47″ x 95″ (1100 mm x 2400 mm) or 59″ x 118″ (1500 mm x 3000 mm)
– Machine Dimensions: 4’x8′: 173″ x 90″ x 55″ (4.4m x 2.3m x 1.4m); 5’x10′: 197″ x 89″ x 75″ (5010 mm x 2260 mm x 1900 mm)
– Weight: 4’x8′: 6024 lbs (2732 kg); 5…
3. OMTech – Fiber Laser Cutter
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: {“title”: “Fiber Laser Cutter”, “features”: [“High precision cutting”, “Versatile material compatibility”, “Fast processing speeds”, “User-friendly interface”, “Durable construction”], “applications”: [“Metal cutting”, “Acrylic cutting”, “Wood cutting”, “Plastic cutting”], “warranty”: “2 years”, “power_options”: [“500W”, “1000W”, “1500W”, “2000W”], “price_range”: “$5,000 – $20,000”}
4. Boss Laser – 2kw AccuCut
Domain: shop.bosslaser.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: {“products”: [{“name”: “2kw AccuCut”, “price”: “$57,997”, “type”: “CO2 Laser”, “applications”: [“Metal Cutting”, “Wood Cutting”, “Glass Etching”, “Acrylic Cutting”, “Leather Engraving”], “series”: “AccuCut”}, {“name”: “HP-2440”, “sale”: “On Sale!”, “type”: “CO2 Laser”, “applications”: [“Metal Marking”, “Wood Engraving”, “Plastic Cutting”], “series”: “HP-Series”}, {“name”: “LS-Series”, “type”: “CO2…
5. LaserCut Pro – Precision Laser Cutter for Home Use
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Looking to purchase a home/small business laser cutter for cutting thin metals (max 3mm), specifically brass and aluminum, with high accuracy. Budget is £7k. Size is a major limiting factor due to home use (upstairs). Research indicates that cutting 3mm is generally not feasible with home machines, with most capable of cutting only up to 1mm. Recommendations include fiber lasers for metal cutting,…
6. BES Cutter – Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
7. Cloudray – Raytools Laser Systems
Domain: cloudraylaser.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Cloudray Raytools BT210S”,”power_range”:”0-1.5kW”,”price”:”$985.00 USD”},{“name”:”Cloudray Raytools BT240S”,”power_range”:”0-3kW”,”price”:”$1,125.00 USD”},{“name”:”Cloudray Raytools BM111″,”power_range”:”0-3.3kW”,”price”:”From $2,645.00 USD”},{“name”:”Cloudray Raytools BM06K”,”power_range”:”0-6kW”,”price”:”From $3,370.00 USD”},{“name”:”Cloudray Raytools BS06K”,”power_range”:”…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fiber laser metal cutter
As the demand for precision and efficiency in metal fabrication continues to rise globally, the strategic sourcing of fiber laser metal cutters is becoming increasingly vital for businesses across various sectors. Key takeaways highlight the importance of selecting equipment that not only meets specific operational needs but also aligns with budgetary constraints. With options ranging from powerful, high-capacity machines to customizable models, buyers can find solutions tailored to their unique requirements, ensuring optimal performance and a rapid return on investment.
Investing in fiber laser technology provides manufacturers with significant advantages, including reduced operational costs and enhanced production capabilities. This is particularly crucial for businesses in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where the ability to cut and fabricate materials in-house can lead to competitive differentiation and improved profitability.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with reputable suppliers who understand the nuances of their regional markets. By leveraging advancements in fiber laser technology, businesses can position themselves for future growth and innovation. Take the next step towards transforming your metal fabrication processes—invest in a fiber laser metal cutter that aligns with your strategic goals today.