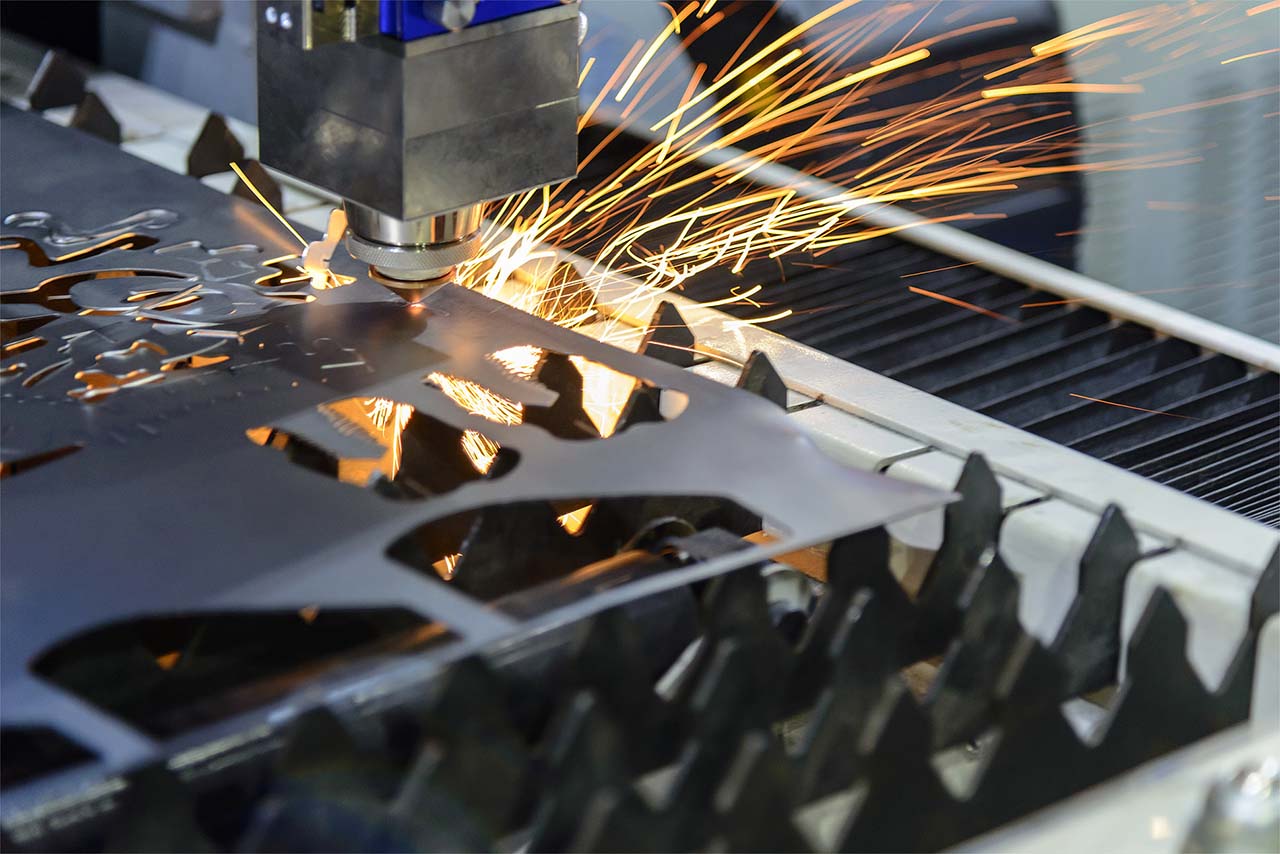
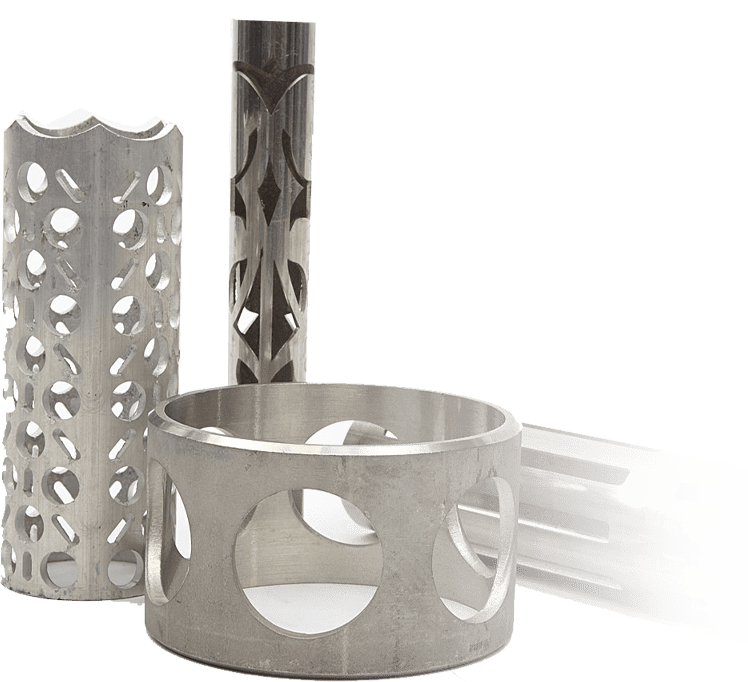
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fiber laser cut metal
Navigating the complex landscape of fiber laser cut metal can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the rising demand for precision metal fabrication, sourcing the right fiber laser cutting technology is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. This guide addresses the key challenges faced by organizations in sourcing fiber laser cut metal, including understanding the various machine types, evaluating applications, and assessing the total cost of ownership.
In this comprehensive resource, we delve into the intricacies of fiber laser cutting, exploring the diverse types of machines available—from entry-level models to high-powered systems—and their specific applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. We also provide actionable insights on vetting suppliers, ensuring that buyers can identify reputable manufacturers and service providers.
Furthermore, we analyze cost factors, including initial investments, operational expenses, and potential return on investment, enabling informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are in Brazil looking to enhance your production capabilities or in Vietnam aiming to optimize your metal fabrication processes, this guide empowers you with the knowledge needed to make strategic investments in fiber laser technology. By understanding the global market dynamics, you can confidently navigate your sourcing journey and achieve significant business growth.
Understanding fiber laser cut metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutters | Fully enclosed design for safety; reduced noise; enhanced dust control | Industrial manufacturing, automotive parts | Pros: Safety, reduced contamination. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Open Bed Fiber Laser Cutters | Open design for larger materials; easier loading/unloading | Sign making, artwork, large components | Pros: Flexibility, lower cost. Cons: Less safety, more noise. |
| High-Power Fiber Lasers | Power range from 1kW to 20kW; suitable for thick materials | Heavy machinery, structural components | Pros: Efficiency in cutting thick metals. Cons: Higher operating costs. |
| Flatbed Fiber Laser Cutters | Ability to handle large sheets (up to 5’x10′); low running costs | Sheet metal fabrication, signage | Pros: Quick ROI, versatility. Cons: Requires significant floor space. |
| Portable Fiber Laser Cutters | Compact and lightweight; ideal for on-site jobs | Construction, maintenance, custom work | Pros: Mobility, ease of use. Cons: Limited cutting capacity and power. |
What Are Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutters and Their Benefits for B2B Buyers?
Enclosed fiber laser cutters are designed with a fully enclosed structure, enhancing safety and reducing noise levels. They are ideal for industries where contamination and worker safety are critical, such as automotive manufacturing and industrial fabrication. Buyers should consider the higher initial investment but can benefit from a cleaner working environment and lower maintenance costs due to reduced exposure to dust and debris.
How Do Open Bed Fiber Laser Cutters Cater to Diverse Applications?
Open bed fiber laser cutters offer flexibility in handling larger materials, making them suitable for sign making and creative applications. Their open design allows for easy loading and unloading of materials, which can be a significant time-saver. While they tend to be more cost-effective, buyers must weigh the trade-off in safety and noise levels, as the open design exposes operators to potential hazards.
Why Are High-Power Fiber Lasers Essential for Heavy Industries?
High-power fiber lasers, ranging from 1kW to 20kW, are essential for cutting thick materials like heavy machinery components and structural steel. Their efficiency and speed can drastically reduce production times, making them a valuable investment for companies in heavy industries. However, buyers should anticipate higher operating costs associated with power consumption and maintenance.
What Advantages Do Flatbed Fiber Laser Cutters Offer for Large Sheet Fabrication?
Flatbed fiber laser cutters are designed to handle large sheets of metal, making them ideal for sheet metal fabrication and signage. Their ability to deliver a quick return on investment (ROI) is enhanced by low running costs, as they typically consume less energy and require fewer consumables. However, businesses must ensure they have adequate floor space to accommodate these larger machines.
How Do Portable Fiber Laser Cutters Facilitate On-Site Jobs?
Portable fiber laser cutters are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for on-site applications such as construction, maintenance, and custom work. Their mobility allows businesses to respond quickly to customer needs without the requirement for transporting materials back to a central facility. However, buyers should be aware of the limitations in cutting capacity and power compared to larger, stationary machines.
Key Industrial Applications of fiber laser cut metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fiber laser cut metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Manufacturing of automotive panels and components | Reduces production costs and increases precision | Power capacity, cutting speed, and material compatibility |
| Electrical & Electronics | Fabrication of electrical enclosures and components | Enhanced design flexibility and reduced lead times | Customization options and machine durability |
| Construction & Architecture | Creation of metal structures and frameworks | Improved structural integrity and design accuracy | Cutting area size, material thickness capabilities |
| Jewelry & Fashion | Production of intricate jewelry designs | High detail precision and reduced waste material | Compact machine designs and specific cutting capabilities |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of lightweight components | Weight reduction and enhanced performance | Compliance with industry standards and material types |
How is Fiber Laser Cut Metal Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, fiber laser cutting is essential for producing panels and components with high precision. This technology enables manufacturers to achieve complex geometries and tight tolerances, which are critical for vehicle safety and performance. Fiber lasers can cut through various metals, including high-strength steel and aluminum, making them suitable for diverse applications. Buyers in this sector should consider the power capacity and cutting speed of the machines, as these factors directly impact production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
What Role Does Fiber Laser Cutting Play in Electrical & Electronics Fabrication?
In the electrical and electronics industry, fiber laser cutting is used to fabricate enclosures and components that require precise dimensions and intricate designs. This method allows for faster production cycles and reduced lead times, which are vital in a fast-paced market. The ability to customize designs easily and adapt to changing specifications is a significant advantage. Buyers should focus on the customization options available, as well as the durability and maintenance of the machines, to ensure long-term operational efficiency.
How is Fiber Laser Cutting Transforming Construction & Architecture?
Fiber laser cutting is revolutionizing the construction and architecture sectors by enabling the creation of complex metal structures and frameworks. The precision of fiber lasers ensures that components fit together seamlessly, enhancing structural integrity and reducing the need for rework. This technology also allows for the efficient cutting of large metal sheets, which can be crucial for large-scale projects. Buyers should consider the cutting area size and material thickness capabilities when sourcing machines for construction applications.
What Benefits Does Fiber Laser Cutting Provide to the Jewelry & Fashion Industry?
In the jewelry and fashion sectors, fiber laser cutting is utilized to produce intricate designs and patterns with minimal material waste. The high precision of fiber lasers allows artisans to create detailed pieces that would be challenging to achieve with traditional methods. This technology not only enhances creativity but also speeds up production. Buyers should look for compact machine designs that can fit into smaller workshop spaces while ensuring they have the specific cutting capabilities needed for various materials.
How Does Fiber Laser Cutting Support the Aerospace Industry?
The aerospace industry relies on fiber laser cutting for manufacturing lightweight components that are crucial for performance and fuel efficiency. The ability to cut through advanced materials while maintaining precision ensures that components meet stringent industry standards. Additionally, fiber lasers can reduce the overall weight of components, contributing to improved aircraft performance. Buyers in this sector must ensure compliance with industry standards and consider the types of materials that can be processed by the machines they source.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fiber laser cut metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Operational Costs of Outsourcing Metal Cutting Services
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in sectors like automotive and manufacturing, face the challenge of high operational costs when relying on third-party metal cutting services. Outsourcing can lead to expenses exceeding $300 per hour, which not only strains budgets but also impacts project timelines. These costs can be particularly burdensome for companies in regions with limited access to affordable fabrication services, such as parts of Africa and South America. As a result, businesses may find themselves compromising on quality or facing delays due to scheduling conflicts with external providers.
The Solution: To mitigate these costs, businesses should consider investing in a fiber laser cutting machine for in-house operations. The initial investment can be offset by the reduced long-term expenses associated with outsourcing. For instance, machines like the Atlas Alloy Flatbed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser, which can handle full-size sheets and operate with minimal running costs (less than $0.25 per hour for gas and electricity), offer a rapid return on investment. Companies should consult with manufacturers to customize machines that fit their specific cutting needs, whether for alloy, carbon, or stainless steel. By bringing the cutting process in-house, businesses gain greater control over production schedules, quality, and costs.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Achieving Precision and Quality Standards
The Problem: In industries where precision is paramount—such as aerospace, medical devices, and high-end automotive manufacturing—B2B buyers often struggle to achieve the necessary quality standards with conventional cutting methods. Variability in cutting quality can lead to increased waste, rework, and ultimately, customer dissatisfaction. Buyers may find themselves questioning the reliability of their current processes, particularly when dealing with complex designs or when working with materials like aluminum or titanium that require precise cuts.
The Solution: Investing in a high-quality fiber laser cutting system can significantly enhance cutting precision and reduce variability. Machines equipped with features like capacitive auto-height adjusting cutting heads and closed-loop servo motors ensure that the cutting process is consistently accurate. Buyers should prioritize machines that offer programmable cutting parameters tailored to different materials and thicknesses. For example, selecting a machine with a power range of 1 kW to 22 kW allows for versatility in cutting various metals effectively. Regular maintenance and calibration of the equipment will further ensure that precision is maintained over time. By adopting these advanced technologies, companies can meet or exceed industry quality standards while minimizing waste and rework.
Scenario 3: Limited Expertise and Training in Fiber Laser Technology
The Problem: A common pain point for businesses venturing into fiber laser cutting is the lack of expertise and training among their staff. Many companies find it challenging to recruit skilled technicians or provide adequate training for existing employees, which can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, and increased downtime. This issue is particularly prominent in emerging markets where access to specialized training programs may be limited.
The Solution: To address this challenge, companies should seek out suppliers who offer comprehensive training and support as part of their fiber laser cutting machine purchase. Many manufacturers provide on-site training, online resources, and ongoing technical support to ensure that employees are well-equipped to operate the machines safely and efficiently. Additionally, investing in user-friendly software interfaces can help minimize the learning curve for new users. Companies can also consider forming partnerships with local vocational schools or technical colleges to create customized training programs that align with their specific operational needs. By prioritizing training and skill development, businesses can enhance their workforce’s capability, improve productivity, and ensure safe operations in their cutting processes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fiber laser cut metal
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Fiber Laser Cutting?
When selecting materials for fiber laser cutting, it is essential to consider their properties, manufacturing complexities, and suitability for specific applications. Below are analyses of four common metals used in fiber laser cutting, focusing on their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Fiber Laser Cutting?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and versatility. It has excellent weldability and machinability, making it a popular choice in various industries. Its temperature rating can exceed 500°C, and it has moderate corrosion resistance, which can be enhanced with coatings.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is durable and cost-effective, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive to construction. However, it may require additional treatments to improve corrosion resistance, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is compatible with various media, including automotive parts and structural components. Its ability to withstand high pressures makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel. Compliance with these standards ensures quality and safety in applications.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Fiber Laser Cutting?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It maintains its strength at elevated temperatures and is non-reactive, making it suitable for food and medical applications.
Pros & Cons: While stainless steel is highly durable and requires minimal maintenance, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel. The cutting process can be more complex due to its toughness, which may require higher-powered lasers.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is commonly used in kitchen equipment, medical devices, and architectural applications. Its resistance to corrosion and staining makes it ideal for environments where hygiene is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. Understanding local preferences and standards in regions like the Middle East and Europe can also influence material selection.
How Does Aluminum Compare in Fiber Laser Cutting Applications?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance. It has a good strength-to-weight ratio and can be easily formed and machined. Its thermal and electrical conductivity also make it a preferred choice in various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern, such as aerospace and automotive. However, it can be more costly than carbon steel and may require specialized cutting techniques due to its thermal properties.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is widely used in the manufacturing of components for electronics, automotive parts, and packaging. Its compatibility with various media is enhanced by its non-reactive nature.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. Understanding the local market dynamics in regions like Brazil can help in selecting the right aluminum grade.
What Role Does Copper Play in Fiber Laser Cutting?
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. It is ductile and malleable, allowing for complex designs. However, it has a lower melting point compared to other metals, which can impact the cutting process.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of copper is its conductivity, making it ideal for electrical applications. However, it is more expensive than other metals and can be challenging to cut due to its thermal properties, which may lead to warping.
Impact on Application: Copper is commonly used in electrical components, plumbing, and heat exchangers. Its properties make it suitable for applications requiring efficient thermal management.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 for copper is crucial. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should also consider local preferences for specific copper alloys.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Fiber Laser Cutting
| Material | Typical Use Case for fiber laser cut metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Automotive parts, structural components | Cost-effective and durable | Requires corrosion treatments | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Kitchen equipment, medical devices | Corrosion resistance and durability | Higher cost and complex cutting process | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, packaging | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | More expensive and requires specialized cutting | Med |
| Copper | Electrical components, plumbing | Excellent conductivity | Expensive and challenging to cut | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fiber laser cut metal
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Fiber Laser Cut Metal?
The manufacturing process of fiber laser cut metal encompasses several critical stages that ensure precision, efficiency, and quality. Each stage is integral to achieving the final product that meets the specifications required by B2B buyers.
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Selected and Prepared?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. This phase involves selecting the appropriate type of metal, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or carbon steel, based on the intended application. The metal is typically procured in sheets or rolls and must undergo thorough inspection to ensure it meets specified standards for thickness and quality.
Once selected, the material is cleaned to remove any contaminants that could affect the cutting process. This may involve degreasing or using other cleaning agents to ensure a pristine surface. Accurate measurement and cutting of the raw material into manageable sizes also occur during this stage, ensuring that the dimensions align with the design specifications.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Metal?
After material preparation, the next stage involves forming the metal. This typically includes the fiber laser cutting process, where high-powered lasers are used to cut the material with exceptional precision. The fiber laser cutting technique is favored for its ability to achieve intricate designs with minimal kerf loss, reducing waste and optimizing material usage.
In addition to cutting, other forming techniques may be employed, such as bending or punching, depending on the complexity of the final product. The combination of laser cutting with these additional techniques allows manufacturers to create components that meet specific design requirements.
Assembly: How Are Components Joined Together?
Once the metal components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This stage can involve welding, bolting, or riveting, depending on the product’s design and the required strength of the joints. Quality control during assembly is crucial to ensure that all parts fit together correctly and function as intended.
B2B buyers should be aware that some manufacturers might offer modular designs that facilitate easier assembly and disassembly, which can be advantageous for shipping and maintenance. Understanding the assembly process can help buyers assess the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of the final product.
Finishing: What Processes Enhance the Final Appearance and Durability?
The finishing stage is essential for enhancing the appearance and durability of fiber laser cut metal products. This may include surface treatments like powder coating, anodizing, or plating, which not only improve aesthetics but also provide corrosion resistance and increased wearability.
Manufacturers often apply finishing techniques based on the end-use environment of the product. For instance, products intended for outdoor use may undergo more rigorous treatments to withstand harsh conditions. B2B buyers should inquire about the finishing options available and their implications for longevity and maintenance.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Commonly Used in Fiber Laser Cutting?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for fiber laser cut metal. It ensures that products meet international standards and customer specifications. Various QA measures are employed at different checkpoints throughout the production cycle.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers of fiber laser cut metal often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management principles. Compliance with these standards indicates a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe or API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications may also be relevant.
B2B buyers should check for these certifications when evaluating potential suppliers. These standards not only enhance product reliability but also facilitate smoother international trade by ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to monitor and verify product quality. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough examination of the finished product before it is shipped to ensure it meets all specifications and standards.
Implementing these checkpoints allows manufacturers to catch and correct issues early, reducing the likelihood of defects in the final product.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. Conducting audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their processes and adherence to quality standards. Buyers should also request quality assurance reports that detail testing methods, results, and compliance with relevant standards.
Additionally, involving third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality assurance processes. This is particularly important for international transactions, where buyers may not have direct oversight of manufacturing practices.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Product Quality?
Various testing methods are utilized to ensure the integrity and functionality of fiber laser cut metal products. These methods may include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Verifying that the dimensions of the finished product match the specifications.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing the material properties, such as tensile strength and hardness, to ensure they meet required standards.
- Visual Inspection: Conducting a thorough visual examination for surface defects or inconsistencies.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle testing are employed to detect internal flaws without damaging the product.
Understanding these testing methods can help B2B buyers gauge the reliability and quality of the products they are purchasing.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, navigating quality control nuances is essential to ensure product reliability and compliance with local regulations. Different regions may have varying standards and certifications, making it crucial for buyers to understand these differences.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear specifications and maintaining open lines of communication with suppliers can mitigate misunderstandings.
B2B buyers should also consider the logistics of shipping and delivery, as these factors can influence product condition upon arrival. It is advisable to clarify return policies and warranty conditions to ensure protection against defective products.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with fiber laser cut metal is vital for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, along with robust quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fiber laser cut metal’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of fiber laser cut metal can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a clear, actionable checklist to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clarify your technical requirements. Consider factors such as the types of metals you need to cut (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum), thickness ranges, and the required precision levels. This clarity will help suppliers provide tailored solutions that meet your specific needs.
Step 2: Research Supplier Capabilities
Investigate potential suppliers to understand their production capabilities. Look for companies that specialize in fiber laser cutting and can handle your specific materials and volumes. Pay attention to their machinery specifications, including power capacity (1.5 kW to 22 kW options) and cutting speeds, as these directly impact your project’s efficiency and quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers before making commitments. Request company profiles, production capacity details, and case studies demonstrating their experience with similar projects. It’s also beneficial to seek references from other businesses in your industry or region to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that potential suppliers adhere to international quality standards and certifications (e.g., ISO 9001). Compliance with safety and environmental regulations is also crucial, especially if you operate in regions with strict guidelines. This not only protects your business but also ensures the quality and safety of the materials you receive.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before placing a large order, ask for samples or prototypes of your specific cuts. This step is essential to evaluate the quality of the cuts, precision, and overall craftsmanship. A well-executed sample can provide insight into the supplier’s capabilities and help you make an informed decision.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Consider the total cost of ownership, including operational costs like gas and electricity, to ensure you’re getting the best deal. Establish clear terms to avoid misunderstandings later.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Lastly, set up a communication plan to ensure ongoing dialogue with your supplier. Regular updates on production status, potential delays, and quality checks can help mitigate issues. Clear communication channels foster a better partnership, ultimately leading to smoother transactions and enhanced cooperation.
By following these steps, you can effectively navigate the procurement of fiber laser cut metal, ensuring quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in your sourcing efforts.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fiber laser cut metal Sourcing
When navigating the landscape of fiber laser cut metal sourcing, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for B2B buyers. The costs associated with fiber laser cutting encompass various components, each influencing the overall price.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Fiber Laser Cutting?
-
Materials: The type and quality of metals being cut significantly affect costs. Common materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum vary in price, with additional factors such as thickness and alloy composition impacting the final expense. Buyers should seek bulk purchasing options to capitalize on volume discounts.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for operating fiber laser cutting machines. Labor costs can vary by region, with higher wages in developed markets like Europe compared to South America or Africa. Investing in training for operators can enhance efficiency and reduce error rates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs for utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility expenses. Efficient machine operation can reduce overhead; for instance, machines with lower power consumption, like those utilizing fiber lasers, often yield lower running costs.
-
Tooling: The investment in high-quality tooling is crucial for maintaining precision and reducing material waste. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn-out tools can help optimize production efficiency and minimize costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that products meet required specifications and certifications, which can prevent costly reworks and enhance customer satisfaction. The costs associated with QC should be factored into the overall pricing structure.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling of materials and finished products can add significant costs, especially for international shipping. Understanding Incoterms is essential to determine who bears these costs and their impact on pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market positioning. This margin can vary widely based on supplier reputation, service level, and market demand.
What Influences Pricing in Fiber Laser Cutting Services?
Several factors can influence pricing strategies in fiber laser cutting, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized tooling and setups. Clear communication regarding requirements can help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
-
Quality Certifications: Suppliers with recognized quality certifications may charge a premium, but this can be justified by the assurance of consistent quality and reliability in the end product.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and operational capacity can significantly affect pricing. Buyers should evaluate multiple suppliers to find the best balance between cost and service.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Effectively for Fiber Laser Cutting Services?
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the upfront costs, consider the long-term implications of maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. A higher initial investment in quality equipment may yield lower TCO over time.
-
Leverage Negotiation Tactics: Buyers should be prepared to negotiate terms, including payment schedules and delivery timelines. Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can result in better rates and priority service.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers from regions like Africa or South America, fluctuations in currency exchange rates and local tariffs can affect overall costs. It’s prudent to factor in these elements when evaluating quotes.
-
Request Indicative Pricing: Always ask for indicative prices and detailed breakdowns to understand the cost structure better. This transparency can aid in making informed decisions.
Conclusion
Navigating the cost landscape of fiber laser cut metal sourcing requires careful consideration of various components and pricing influences. By understanding these elements, B2B buyers can make strategic purchasing decisions, negotiate effectively, and achieve cost efficiencies that align with their operational goals.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fiber laser cut metal With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Fiber Laser Cutting for Metal
When considering metal cutting solutions, fiber laser cutting stands out for its efficiency and precision. However, there are various alternatives that businesses can explore depending on their specific needs, budget, and operational capabilities. Below, we provide a detailed comparison of fiber laser cutting against other viable methods, including CO2 laser cutting and plasma cutting.
| Comparison Aspect | Fiber Laser Cut Metal | CO2 Laser Cutting | Plasma Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, fast cutting speeds, minimal kerf | Good for thicker materials, slower than fiber lasers | Suitable for thick materials, faster than CO2 lasers but less precision |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, low operational costs | Lower initial investment, moderate operational costs | Moderate initial investment, higher operational costs due to consumables |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators and setup | Easier to implement, more common technology | Requires training for effective operation and safety |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, long lifespan of components | Moderate maintenance, CO2 tubes may need replacement | Higher maintenance due to consumable parts and equipment wear |
| Best Use Case | Precision cutting of thin to medium metals | Cutting thicker materials like wood, plastic, and some metals | Heavy-duty cutting, ideal for construction and heavy industries |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of CO2 Laser Cutting?
CO2 laser cutting is a well-established method that uses a gas laser to produce a high-quality beam. Its primary advantage lies in its ability to cut thicker materials effectively, making it suitable for applications involving wood and certain plastics, as well as metals. The initial investment is generally lower compared to fiber lasers, and the technology is more widely available. However, CO2 lasers are slower than fiber lasers and typically have a larger kerf, which may lead to more material waste. Additionally, the maintenance of CO2 systems can be more cumbersome, particularly due to the need for replacing the laser tubes periodically.
How Does Plasma Cutting Compare in Terms of Efficiency?
Plasma cutting is an excellent alternative for those needing to cut thick materials quickly. This method uses ionized gas to create a plasma arc that can slice through metals, making it a preferred choice in construction and heavy industry. Plasma cutting can be faster than both fiber and CO2 laser cutting, particularly for thicker sections. However, it is less precise and can result in a rougher edge finish, which may require additional processing. The operational costs can also be higher due to the need for consumables like electrodes and nozzles. Therefore, while plasma cutting is efficient for heavy-duty applications, it may not be suitable for projects requiring fine detail.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Metal Cutting Solution?
When selecting a metal cutting solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, material types, and volume of production. Fiber laser cutting is ideal for businesses focused on precision and efficiency with thinner materials. CO2 laser cutting may be better suited for those working with a variety of materials, including thicker substrates. Plasma cutting is advantageous for heavy-duty applications where speed is critical, albeit at the expense of precision. Understanding these differences will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their manufacturing goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fiber laser cut metal
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Fiber Laser Cut Metal?
When evaluating fiber laser cut metal, several key technical properties are vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers assess the suitability of materials for specific applications, ensuring they meet operational needs and quality standards.
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of metals based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties. Common grades include stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316), aluminum (e.g., 6061, 7075), and carbon steel (e.g., S235, S275). Selecting the correct material grade is crucial, as it impacts the metal’s strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Buyers should ensure that the chosen grade aligns with the intended application, such as structural components or decorative elements.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. For fiber laser cutting, standard tolerances typically range from ±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm. Maintaining tight tolerances is critical for applications requiring precision, such as aerospace or automotive parts. Buyers must consider the required tolerance levels to avoid costly rework or production delays.
3. Cutting Speed
Cutting speed is the rate at which the laser moves across the material, usually measured in meters per minute (m/min). Higher cutting speeds can lead to increased productivity, but may also affect the quality of the cut. Buyers should balance the need for speed with the desired finish quality, as some materials may require slower speeds for optimal results.
4. Kerf Width
Kerf width is the width of the material removed during cutting, typically measured in micrometers (µm). A narrower kerf results in less material waste and improved efficiency, making it a desirable property for cost-sensitive projects. Understanding kerf width is essential for buyers looking to optimize material usage and reduce costs.
5. Power Output
The power output of a fiber laser cutter, typically ranging from 1 kW to 22 kW, directly influences its cutting capabilities. Higher power outputs allow for cutting thicker materials and achieving faster processing speeds. Buyers should assess their production needs against the power capabilities of available machines to ensure they select equipment that meets their requirements.
6. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency measures the power consumption relative to the output produced during cutting operations. Fiber lasers are generally more energy-efficient than traditional CO2 lasers, often requiring less than 2 kW for operation. B2B buyers should consider energy costs as part of their total cost of ownership, as more efficient machines can lead to significant savings over time.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Fiber Laser Cutting Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the fiber laser cutting market. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should understand.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the fiber laser cutting industry, OEMs often supply specialized components or entire systems to other businesses, making it crucial for buyers to understand the reputation and reliability of these manufacturers.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory costs effectively and ensure they can meet production demands without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. This process helps buyers compare prices and terms from multiple vendors, facilitating better decision-making in procurement.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is critical for B2B buyers to clarify shipping costs, insurance, and risk management throughout the supply chain.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Shorter lead times can be critical for businesses needing to respond quickly to market demands, making this a vital consideration during negotiations.
6. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels denote the specific range of acceptable dimensional variation in manufactured parts. Different industries may have varying tolerance requirements, making it crucial for buyers to communicate their needs clearly to ensure product quality.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the fiber laser cutting market more effectively, leading to informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fiber laser cut metal Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in Fiber Laser Cut Metal?
The fiber laser cutting market is experiencing robust growth driven by the increasing demand for precision and efficiency in metal fabrication. Key global drivers include advancements in laser technology, which offer improved cutting speeds and lower operational costs compared to traditional methods. Additionally, industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics are increasingly relying on fiber laser cutting for its ability to handle various materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and even non-ferrous metals like copper and titanium.
Emerging trends reflect a shift towards automation and integration of smart technologies. Companies are adopting Industry 4.0 principles, where IoT-enabled machines offer real-time monitoring and data analytics, enhancing operational efficiency. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where the push for modernization is strong. Furthermore, as manufacturers seek to optimize production processes, the demand for customizable and scalable laser cutting solutions is on the rise, allowing businesses to tailor machines to their specific needs.
The competitive landscape is also evolving, with more manufacturers entering the market, leading to increased price competition. Buyers are encouraged to explore options from different suppliers to ensure they obtain the best value for their investment. As such, understanding local market conditions and supplier capabilities in regions like Europe and the Middle East is crucial for informed sourcing decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Operations in Fiber Laser Cutting?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming increasingly important considerations for B2B buyers in the fiber laser cut metal sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste production, has prompted a shift towards greener practices. Fiber laser cutting is inherently more efficient than traditional methods, using less energy and producing minimal waste, making it an attractive option for companies looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are gaining traction. Buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers who prioritize sustainable sourcing of materials, such as certified metals and eco-friendly coatings. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to REACH regulations for chemical safety are becoming prerequisites for suppliers to engage in global trade. This not only fosters a responsible image for businesses but also ensures compliance with increasing regulatory demands in many regions.
For companies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in sustainable practices can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. Buyers should look for suppliers who provide transparency in their sourcing processes and demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental impact through innovations such as recycled materials and energy-efficient operations.
What Is the Historical Context of Fiber Laser Cutting Technology?
Fiber laser cutting technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 20th century. Initially, CO2 lasers dominated the market due to their relatively lower costs and simpler technology. However, with advancements in fiber optic technology in the early 2000s, fiber lasers began to gain traction, offering superior efficiency and cutting capabilities.
The introduction of solid-state lasers marked a turning point, as these lasers provided higher power outputs and better beam quality, facilitating the cutting of thicker materials with greater precision. As industries began to recognize the advantages of fiber lasers—such as reduced maintenance costs and lower operational expenses—adoption rates soared.
Today, fiber laser cutting is not only a staple in metal fabrication but also a cornerstone technology for various applications, from intricate designs in jewelry to robust components in the automotive sector. The ongoing innovation in laser technology continues to shape the landscape, providing businesses with new opportunities for efficiency and creativity in metalworking.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fiber laser cut metal
-
1. How do I select the right fiber laser cutting machine for my business needs?
Choosing the right fiber laser cutting machine depends on several factors, including the types of materials you plan to cut, the thickness of those materials, and your production volume. Consider machines with adjustable power capacities ranging from 1.5 kW to 4 kW to accommodate different cutting requirements. Additionally, evaluate features such as cutting area dimensions, speed, and precision. Requesting a consultation with a supplier can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific applications and budget. -
2. What materials can be efficiently cut with fiber laser technology?
Fiber lasers are versatile and can cut a wide range of metals, including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and even precious metals like gold and silver. The efficiency of cutting varies with power settings; for example, a 1 kW laser can cut through 6mm carbon steel and 3mm stainless steel. Understanding the capabilities of your chosen machine will help you maximize productivity and ensure quality cuts for your projects. -
3. What customization options are available for fiber laser cutting machines?
Most suppliers offer extensive customization options for fiber laser cutting machines, allowing you to tailor specifications to meet your business needs. Customizations can include power capacity, cutting head types, bed sizes, and additional features such as automatic height adjustment or enclosed designs for safety. Discussing your unique requirements with a manufacturer can lead to a machine that enhances your operational efficiency and aligns with your production goals. -
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for fiber laser cut metal products?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and the complexity of the parts required. Some manufacturers may have MOQs as low as a few pieces, while others might require larger orders to maintain cost-effectiveness. It’s essential to communicate directly with potential suppliers to understand their policies and find a partner that can accommodate your production needs without compromising your budget. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing fiber laser cut metal?
Payment terms can differ based on supplier policies and your negotiation outcomes. Common options include upfront payments, deposits followed by balance payments upon delivery, or extended credit terms for established business relationships. Ensure you clarify payment structures, currency preferences, and any potential financing options, especially when dealing with international suppliers, to avoid misunderstandings. -
6. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for fiber laser cut metal products?
To maintain high-quality standards, establish a quality assurance process with your supplier that includes inspection protocols, material certifications, and adherence to industry standards. Request samples or prototypes before placing large orders to assess the cutting quality and finish. Additionally, consider suppliers who implement rigorous QA measures and provide documentation to support their claims of quality and precision. -
7. What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing fiber laser cut metal?
When importing fiber laser cut metal, logistics considerations include shipping methods, lead times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties applicable in your region. Work with your supplier to understand their shipping practices and timelines. Additionally, consider partnering with a logistics provider experienced in international trade to streamline the process and ensure compliance with local regulations. -
8. How do I vet suppliers for fiber laser cutting services in international markets?
Vetting suppliers in international markets involves researching their reputation, certifications, and industry experience. Request references and case studies from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality of work. Attend industry trade shows or utilize platforms that connect buyers with suppliers to establish direct communication. Additionally, consider conducting factory visits or virtual assessments to evaluate their capabilities firsthand before committing to a partnership.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Fiber Laser Cut Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. OMTech – Fiber Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Best Fiber Laser Cutting Machine for Metal Fabrication, OMTech Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machines, Models include: FC22 1500W Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutting Machine, FC22-C 1500W Open Metal Laser Cutting Machine, FC-105 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine, FC-44 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine, FC-510 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine, FC-105SA Fiber Laser Cutting Machine, FC-105T Fiber Laser Cutting Machine, FC-105S…
2. Atlas Alloy – Flatbed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser
Domain: fslaser.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Atlas Alloy Flatbed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser up to 20kW
– Model Options: 4’x8′ 1000W, 4’x8′ 1500W, 4’x8′ 2000W, 5’x10′ 3000W, 5’x10′ 6000W
– MSRP: $55,000.00
– Cutting Area: 47″ x 95″ (1100 mm x 2400 mm) or 59″ x 118″ (1500 mm x 3000 mm)
– Machine Dimensions: 4’x8′: 173″ x 90″ x 55″ (4.4m x 2.3m x 1.4m); 5’x10′: 197″ x 89″ x 75″ (5010 mm x 2260 mm x 1900 mm)
– Weight: 4’x8′: 6024 lbs (2732 kg); …
3. Boss Laser – 2kw AccuCut
Domain: shop.bosslaser.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Laser Machines – Boss Laser offers a variety of laser cutting, engraving, and marking machines including CO2 lasers, UV lasers, and fiber laser markers. Key products include the 2kw AccuCut priced at $57,997, and various models across different series such as LS-Series, HP-Series, FC-Series, FM-Series, and UV-Series. The machines are capable of cutting and engraving a wide range of materials inclu…
4. LightBurn Software – Small-Scale Laser Cutters
Domain: forum.lightburnsoftware.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: This company, LightBurn Software – Small-Scale Laser Cutters, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Oshcut – Laser Cutting & Sheet Metal Services
Domain: oshcut.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Laser Cutting and Sheet Metal Services, 2-day delivery throughout the US, Online DFM/Ordering, Laser Metal Cutting, Laser Tube Cutting, Flat Finishing, Bending, Metal Tapping, Bead Blasting, Centrifugal Tumbling, Powder Coating, ISO 9001:2015 Certified, Supported Files: DXF, SVG, AI, STEP, SLDPRT, CATPART, IPT, IGS, PAR, IGES, NX, SolidEdge, JT, Rhino (3DM), Parasolid (x_t), ACIS (SAT, SAB), Insta…
6. Kern – Metal Cutting Laser System
Domain: kernlasers.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Kern’s metal cutting laser system allows for accurate cutting of sheet metal including stainless steel, mild steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. Key features include an Automatic Focusing Height Follower for optimal cutting, a protective cover lens (K-Lens for CO2 machines, F-Lens for fiber systems), and a durable steel grid work cutting table. The KCAM Laser Software offers advanced features such…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fiber laser cut metal
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of fiber laser cut metal is not just a cost-saving measure but a pathway to operational excellence and innovation. By investing in advanced fiber laser cutting technologies, businesses can enhance precision, reduce waste, and significantly lower operational costs, particularly when compared to outsourcing. The ability to customize equipment to meet specific needs—ranging from varying power capacities to machine configurations—empowers companies to tailor their operations for maximum efficiency.
Furthermore, the rapid return on investment associated with in-house fiber laser cutting capabilities underscores its importance for businesses in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries evolve and demand for high-quality metal fabrication grows, the strategic sourcing of fiber laser technology will be crucial in maintaining a competitive edge.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers should leverage the advancements in fiber laser technology to not only meet current demands but also to anticipate future trends in metal fabrication. Engage with experts to explore customized solutions that align with your business objectives. Embrace this opportunity to transform your metal cutting processes and drive growth in your market.