Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for feature of size
In today’s competitive global market, sourcing components with precise dimensions, such as features of size, presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the intricacies of features of size—such as regular and irregular types, their applications, and the implications of geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T)—is crucial for ensuring product quality and operational efficiency. This guide aims to demystify the concept of features of size, providing an in-depth exploration of their classifications, measurement techniques, and how they integrate into various manufacturing processes.
Moreover, we will delve into practical considerations for vetting suppliers, evaluating cost factors, and ensuring compliance with international standards. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights, this comprehensive resource empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are sourcing precision machined parts in Brazil or evaluating suppliers in Vietnam, understanding features of size will enhance your procurement strategy, reduce risks, and foster successful partnerships in the global marketplace. The following sections will guide you through the essential aspects of features of size, enabling you to navigate this critical element of engineering and manufacturing with confidence.
Understanding feature of size Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Features of Size | Have opposing surfaces; measurable dimensions like diameter or thickness | Manufacturing, Engineering, Quality Control | Pros: High accuracy, standardized measurements. Cons: Limited to geometries with opposing surfaces. |
| Irregular Features of Size A | Fit within a circle or between parallel planes; non-standard shapes | Custom Part Design, Prototyping | Pros: Flexibility in design, accommodates unique shapes. Cons: More complex tolerancing requirements. |
| Irregular Features of Size B | Do not fit into standard geometric constraints; complex shapes | Aerospace, Automotive, Specialized Equipment | Pros: Enables intricate designs, custom solutions. Cons: Increased difficulty in measurement and verification. |
| Internal Features of Size | Features like holes and slots; can be cylindrical or rectangular | Assembly, Machining, Fabrication | Pros: Critical for component fit, functionality. Cons: Often requires specialized tools for measurement. |
| External Features of Size | Features like pegs and plates; measurable from the outside | Structural Components, Tooling | Pros: Easier to measure, commonly used. Cons: May require specific tolerances to ensure compatibility. |
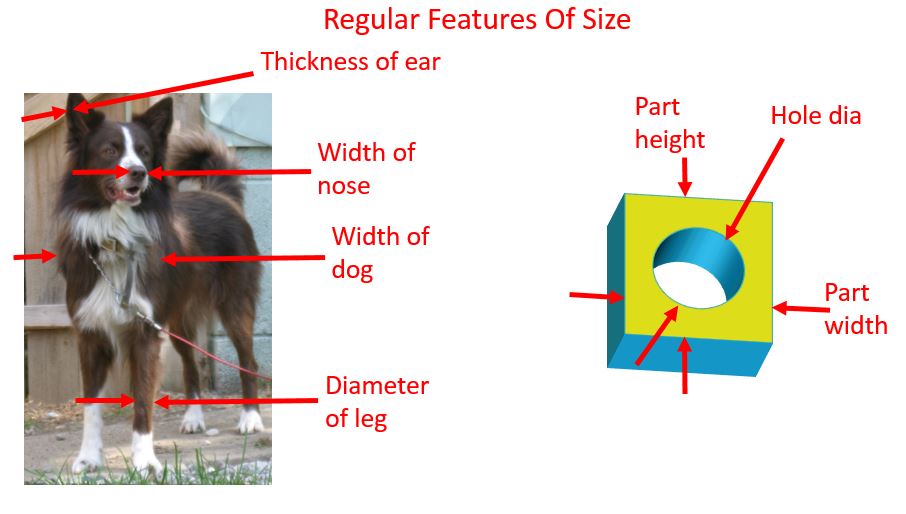
What Are the Characteristics of Regular Features of Size?
Regular Features of Size are characterized by having two opposing surfaces that can be accurately measured, such as a hole’s diameter or a plate’s thickness. They are commonly found in manufacturing and engineering applications, where precision is critical. B2B buyers should consider their need for standardized measurements and the ease of applying geometric controls, as these features simplify quality assurance processes. However, they are limited to geometries that possess opposing surfaces, which may not suit all design requirements.
How Do Irregular Features of Size A Differ From Regular Features?
Irregular Features of Size A can fit within a defined geometric boundary, like a circle or parallel planes, but do not conform to standard dimensions. They are particularly useful in custom part design and prototyping, where unique shapes are required. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of design flexibility against the potential complexities in tolerancing and measurement. While these features allow for innovative designs, they may complicate the manufacturing process due to their non-standard nature.
What Defines Irregular Features of Size B?
Irregular Features of Size B are complex shapes that cannot be neatly fitted into standard geometric forms. These features are prevalent in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where custom solutions are often necessary. When considering these features, B2B buyers should focus on the potential for intricate designs that meet specific functional requirements. However, the challenges in measurement and verification may increase costs and lead times, necessitating careful evaluation of supplier capabilities.
Why Are Internal Features of Size Important in B2B Transactions?
Internal Features of Size, such as holes and slots, are crucial for ensuring that components fit together correctly during assembly. These features can be cylindrical or rectangular and require precise measurements to maintain functionality. Buyers must consider the need for specialized measurement tools, as internal features often present unique challenges. While they are essential for the performance of assembled products, the complexity of measuring these features can lead to increased costs if not managed effectively.
What Advantages Do External Features of Size Offer?
External Features of Size, including pegs and plates, are easily measurable from the outside, making them simpler to work with in most manufacturing processes. They are commonly used in structural components and tooling applications. B2B buyers appreciate the ease of measurement and the standardization associated with these features, which can streamline production and quality control. However, specific tolerances are often necessary to ensure compatibility with other components, which may add another layer of complexity to the purchasing decision.
Key Industrial Applications of feature of size
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of feature of size | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision manufacturing of aircraft components | Ensures safety and performance in flight | Compliance with stringent aerospace standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Engine component production | Enhances engine efficiency and durability | Need for high precision and quality control in manufacturing |
| Consumer Electronics | Production of electronic enclosures | Protects sensitive components and improves aesthetics | Sourcing of materials that support complex geometries |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments | Guarantees reliability and patient safety | Strict adherence to regulatory requirements and quality assurance |
| Construction | Structural steel fabrication | Ensures structural integrity and longevity | Availability of high-strength materials and precise tolerances |
How is ‘feature of size’ utilized in the aerospace industry?
In the aerospace sector, the application of feature of size is critical for the precision manufacturing of aircraft components, such as turbine blades and fuselage sections. These components require exact dimensions to ensure safety and performance during flight. Buyers must consider suppliers who comply with stringent aerospace standards and certifications, as any deviation can lead to catastrophic failures. Furthermore, the ability to measure and maintain tight tolerances is essential, making sourcing precision measurement tools and materials that can withstand high stress crucial.
What role does ‘feature of size’ play in automotive manufacturing?
The automotive industry relies heavily on feature of size for the production of engine components, where precision is paramount. Features such as hole diameters and plate thicknesses directly impact engine efficiency and durability. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers that can consistently deliver high-quality components with precise dimensions, as variations can lead to performance issues or increased wear. Additionally, understanding the specific tolerances required for different engine designs is vital for successful sourcing.
How is ‘feature of size’ applied in consumer electronics?
In the consumer electronics sector, feature of size is employed in the production of electronic enclosures, which must protect sensitive components while also being aesthetically pleasing. Features such as the thickness of materials and the diameter of mounting holes are critical for ensuring that devices function correctly and are user-friendly. International buyers should focus on sourcing materials that not only meet dimensional specifications but also support complex geometries and finishes, as this can enhance product appeal and user experience.
What is the importance of ‘feature of size’ in medical device manufacturing?
The medical device industry uses feature of size extensively in the fabrication of surgical instruments, where precision and reliability are non-negotiable. Features such as the dimensions of blades and handles must meet stringent regulatory requirements to ensure patient safety. Buyers in this field need to work with suppliers who have a robust quality assurance process and can demonstrate compliance with industry standards, as the consequences of failure can be severe. Moreover, understanding the specific tolerances and material properties required for different applications is essential for effective sourcing.
How does ‘feature of size’ impact construction projects?
In the construction sector, feature of size is pivotal in structural steel fabrication, where precise dimensions are necessary to ensure structural integrity and longevity. Components like beams and columns must be manufactured to exact specifications to support loads safely. Buyers should consider sourcing high-strength materials that can withstand the demands of construction while also ensuring that suppliers can maintain the required tolerances. Additionally, understanding local building codes and regulations is critical for successful project execution.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘feature of size’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misalignment Between Design Specifications and Manufacturing Tolerances
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter significant challenges when the design specifications for features of size do not align with the manufacturing tolerances. This misalignment can lead to the production of components that do not meet the required specifications, resulting in costly rework or delays. For instance, a buyer may specify a hole diameter of 10mm with a tolerance of ±0.1mm, but the manufacturing facility may only be equipped to achieve a tolerance of ±0.5mm. This discrepancy can create frustration and impact project timelines, especially in industries like aerospace or automotive, where precision is paramount.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research on their manufacturing partners’ capabilities before finalizing design specifications. Engaging in early communication with manufacturers can help establish a clear understanding of what tolerances can realistically be achieved. Buyers should also consider using tools such as CAD software to simulate manufacturing processes and identify potential discrepancies in tolerances. Implementing a robust quality assurance program that includes regular tolerance checks during production can further ensure that the features of size remain within specified limits, thus minimizing the risk of misalignment and associated costs.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Measurement Techniques Across Suppliers
The Problem: B2B buyers often face difficulties when sourcing components from multiple suppliers, especially when each supplier employs different measurement techniques for features of size. For example, one supplier may use calipers, while another uses laser measurement systems. This inconsistency can lead to confusion and quality issues, as the same feature may be interpreted and measured differently across suppliers. Such scenarios can result in disputes over quality, potential returns, and damage to supplier relationships.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should establish clear measurement standards that all suppliers must adhere to. This can include specifying the use of standardized measurement tools and techniques, such as the ASME Y14.5 guidelines for geometric dimensioning and tolerancing. Additionally, implementing a supplier training program to educate them on the agreed-upon standards can foster consistency. Regular audits and inspections can help verify compliance with these standards, ensuring that all parties are aligned on measurement practices. By standardizing measurement techniques, buyers can enhance quality control and streamline communications with suppliers.
Scenario 3: Misunderstanding of Feature of Size Terminology
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the misunderstanding of the terminology associated with features of size, which can lead to errors in specifications and production. For instance, a buyer may refer to a cylindrical feature without clearly stating whether it is an internal or external feature of size. This lack of clarity can result in misinterpretations during the manufacturing process, leading to the production of incorrect components that do not fit their intended applications.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should invest time in understanding the terminology and concepts related to features of size. Participating in training sessions or workshops focused on geometric dimensioning and tolerancing can significantly enhance their knowledge. Moreover, buyers should ensure that all specifications are accompanied by clear diagrams and annotations that illustrate the intended features. Utilizing software tools that incorporate GD&T principles can also help in generating precise specifications. By fostering a culture of clarity and education around feature of size terminology, buyers can significantly reduce the likelihood of errors and improve overall project outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for feature of size
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Features of Size?
When selecting materials for features of size in engineering applications, it’s essential to consider properties that impact product performance, including temperature and pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, stainless steel, engineering plastics, and titanium.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Versatile
Aluminum is a popular choice for features of size due to its lightweight nature and good corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 150°C and can withstand moderate pressure levels. The material is easy to machine and can be anodized for enhanced surface protection.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. Its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication also contribute to its widespread use.
Cons: However, aluminum may not be suitable for high-temperature applications beyond its rating, and it can be less durable than other metals under certain conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and mild chemicals, making it suitable for a range of applications. However, care should be taken in environments with strong acids or bases.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO. Aluminum alloys are often specified in these standards, so understanding local regulations is key.
Stainless Steel: Strength and Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel is known for its excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for many engineering applications. It can handle temperatures up to 800°C and is suitable for high-pressure environments.
Pros: Its durability and resistance to rust and corrosion make stainless steel ideal for harsh environments, such as chemical processing and marine applications.
Cons: The primary drawbacks include higher costs compared to aluminum and challenges in machining, which can increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including aggressive chemicals, making it suitable for food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel grades is crucial. Buyers should also be aware of the varying grades available and their specific applications.
Engineering Plastics: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Engineering plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, offer a lightweight alternative to metals for features of size. They can withstand temperatures up to 120°C and provide good chemical resistance.
Pros: These materials are generally lower in cost and easier to process than metals, allowing for complex shapes and designs.
Cons: However, engineering plastics may not have the same strength or durability as metals, making them less suitable for high-load applications.
Impact on Application: Engineering plastics are ideal for applications involving low to moderate stress and exposure to chemicals, such as in consumer goods and electronic housings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastics comply with relevant standards, such as ISO 1043 for plastic materials. Understanding the local market for these materials is also important for cost-effectiveness.
Titanium: Superior Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Titanium is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it an excellent choice for demanding applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and is suitable for high-pressure environments.
Pros: Its durability and lightweight properties make titanium ideal for aerospace and medical applications where performance is critical.
Cons: The main limitations are its high cost and difficulty in machining, which can lead to increased production times and expenses.
Impact on Application: Titanium is compatible with a variety of media, including seawater and aggressive chemicals, making it suitable for marine and chemical processing applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B348 for titanium is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of titanium in their region, as it may not be as readily accessible as other materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Features of Size
| Material | Typical Use Case for feature of size | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Engineering Plastics | Consumer goods and electronics | Easy to process and lower cost | Lower strength and durability | Low |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical applications | Superior strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and machining complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on material properties, application impacts, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for feature of size
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Features of Size?
Manufacturing features of size involves several critical stages that ensure precision and quality. The main processes include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage has its unique requirements and techniques, tailored to achieve the desired specifications.
How Does Material Preparation Impact Feature of Size?
The first step in manufacturing is material preparation, which includes selecting appropriate materials based on mechanical properties, cost, and application requirements. Common materials include metals, plastics, and composites. Techniques such as cutting, shearing, or machining are employed to create raw shapes that approximate the final design. This initial phase is vital because the quality of the material directly influences the final feature of size.
What Forming Techniques Are Utilized in Producing Features of Size?
Forming processes convert raw materials into desired shapes and sizes. Techniques such as machining, casting, forging, and additive manufacturing are prevalent.
- Machining involves removing material through processes like turning, milling, or drilling to achieve precise dimensions. This method is ideal for achieving tight tolerances and complex geometries.
- Casting allows for the creation of intricate shapes by pouring molten material into molds, which can be particularly useful for larger features of size.
- Forging improves the strength of the material through deformation, often used for components requiring enhanced durability.
- Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is becoming increasingly popular, especially for prototypes and custom features of size, as it allows for rapid production with complex geometries.
Why Is Assembly Important in the Manufacturing Process?
The assembly stage is where multiple components are brought together to form a complete product. For features of size, ensuring that each part fits together correctly is crucial for overall functionality. Techniques such as welding, fastening, and adhesive bonding are commonly used. Attention to detail in this phase can prevent misalignment and ensure that the assembled feature meets specified tolerances.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Features of Size?
Finishing processes enhance the surface quality and performance of features of size. Techniques such as polishing, coating, or heat treatment are employed to meet specific requirements. For instance, coatings can provide corrosion resistance, while heat treatments can alter the material properties to improve strength or flexibility. These processes are essential for ensuring that the final product not only meets aesthetic standards but also performs well in its intended application.
What Are the Key Quality Control Practices for Features of Size?
Quality control (QC) is integral to ensuring that features of size meet international standards and customer specifications. B2B buyers must understand the various QC checkpoints and methods used in the manufacturing process.
How Do International Standards Influence Quality Control?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. These standards guide manufacturers in establishing consistent processes and documentation practices. Industry-specific standards, like CE marking for products sold in Europe or API standards for oil and gas components, also play a crucial role in defining quality expectations.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control can be broken down into several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC) ensures that raw materials meet specified requirements before production begins. This step includes verifying material certificates and conducting initial inspections.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) involves monitoring the manufacturing process itself. Regular checks during machining or assembly help identify deviations from specifications early in the production cycle.
- Final Quality Control (FQC) is performed on completed products to verify they meet all specifications before shipment. This includes dimensional checks, functional testing, and visual inspections.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Various testing methods are employed to verify features of size:
- Dimensional Inspection involves measuring features using tools like calipers, micrometers, or coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to ensure they meet specified tolerances.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle testing, are used to detect internal defects without damaging the product.
- Functional Testing assesses whether the product performs its intended function under real-world conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should adopt proactive measures to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. This can include:
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Supplier Quality Verification?
Conducting supplier audits is crucial for assessing compliance with quality standards. These audits can be scheduled or unannounced and should evaluate the entire quality management system, from material sourcing to finished product inspection. Buyers should also request quality reports that detail the results of inspections and testing, providing transparency and accountability.
Why Is Third-Party Inspection Important for Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These organizations often have specialized expertise and can perform detailed inspections and testing, ensuring that products meet both local and international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control across different regions is essential.
- Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality assurance. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local practices and expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Import regulations and standards can differ significantly from one country to another. For example, products sold in the EU must comply with CE marking requirements, while those in the U.S. may need to meet FDA or other regulatory standards.
By understanding these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish strong partnerships with suppliers, ensuring that the features of size produced meet their quality expectations and functional requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘feature of size’
To assist international B2B buyers in effectively sourcing features of size, this guide provides a concise checklist. Understanding features of size is crucial for ensuring product quality, compliance, and functionality in various industries, especially in manufacturing and engineering. This step-by-step approach will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing these critical components.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining your technical requirements for the feature of size. This includes dimensions, tolerances, and any specific material requirements. Establishing precise specifications ensures that all parties involved have a clear understanding of the product, reducing the risk of miscommunication and potential errors during production.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in features of size relevant to your industry. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record and expertise in your specific application. Utilize online directories, industry associations, and trade shows to create a list of potential partners who can meet your needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities and Certifications
Before committing, assess each supplier’s capabilities and certifications. Verify that they have the necessary quality management systems in place, such as ISO 9001, and check for industry-specific certifications that may apply. This step is vital as it demonstrates the supplier’s commitment to quality and regulatory compliance, ensuring that they can deliver reliable products.
Step 4: Request Samples and Perform Quality Checks
Always request samples of the features of size you intend to procure. Conduct quality checks using appropriate measurement tools, such as calipers or micrometers, to ensure that the samples meet your specifications. This step allows you to assess the supplier’s quality control processes and the accuracy of their products before making a larger commitment.
Step 5: Assess Lead Times and Logistics
Inquire about the supplier’s lead times and logistics capabilities. Understanding their production schedules and delivery times is crucial for planning your project timelines effectively. Evaluate whether the supplier can meet your deadlines and discuss any potential logistical challenges that may arise in shipping, especially for international transactions.
Step 6: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Compare pricing structures among different suppliers while considering the quality of the features of size they offer. Request detailed quotes that outline costs, including any additional fees for tooling or customizations. Additionally, clarify payment terms and conditions to avoid any surprises later in the procurement process.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Finally, ensure that you have clear communication channels established with your chosen supplier. Determine who your point of contact will be and how issues will be addressed should they arise. Effective communication is essential for maintaining a good relationship and resolving any potential problems quickly.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for features of size, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who meet their technical and quality requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for feature of size Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Feature of Size?
When sourcing features of size, several cost components must be considered to ensure an accurate budget and effective pricing strategy. The primary costs include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. For example, metals may be more expensive than plastics, and high-grade materials that meet specific certifications can further increase costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is often required for precision manufacturing processes, particularly for complex features of size. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region and the expertise needed.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these costs, benefiting buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost, particularly for unique or complex features. Understanding the tooling needs upfront can help in negotiating better pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that features of size meet required specifications often necessitates rigorous QC processes, which can add to costs. Certifications and testing can further impact pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on distance, mode of transportation, and the urgency of delivery. Incorporating logistics into the total cost of ownership is essential for accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding industry standards for margins can help buyers gauge whether they are receiving a fair offer.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Feature of Size Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of features of size, which B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger order quantities often lead to lower per-unit costs. Negotiating MOQ can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features typically incur higher costs due to the additional design and production efforts required. Clear communication of specifications can help avoid costly revisions.
-
Material Selection: The choice of material affects not only the cost but also the performance of the feature. High-performance materials may justify higher prices if they lead to reduced failure rates.
-
Quality and Certifications: Features that require specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ASME) will often come at a premium. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications based on their application.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and history can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer consistent quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can significantly affect pricing. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers manage costs related to freight and insurance.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Pricing for Features of Size?
B2B buyers can employ several strategies to negotiate favorable terms when sourcing features of size:
-
Emphasize Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than focusing solely on the initial price, consider long-term costs associated with quality, maintenance, and logistics. This broader perspective can justify a higher initial price if it leads to lower overall costs.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If you anticipate repeat orders or have a long-term need, use this as leverage in negotiations. Suppliers often prefer guaranteed business over uncertain single orders.
-
Research Market Prices: Conducting market research to understand average pricing can provide a strong basis for negotiations. Being informed can help you recognize unreasonable pricing.
-
Be Flexible with Specifications: If you can adjust your requirements without compromising functionality, you may unlock cost savings by allowing suppliers to propose alternative solutions or materials.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Trust and communication often result in more favorable negotiations.
Conclusion
Navigating the sourcing of features of size requires a thorough understanding of cost components, pricing influencers, and negotiation strategies. By leveraging these insights, international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can make informed decisions that optimize their procurement processes. While indicative prices may vary based on specific circumstances, a strategic approach will help achieve cost-effective sourcing outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing feature of size With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing and design, the concept of ‘feature of size’ (FOS) plays a crucial role in ensuring precision and quality. However, various alternative methods and technologies can achieve similar goals. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
| Comparison Aspect | Feature Of Size | Alternative 1 Name | Alternative 2 Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in measurement of features with opposing elements, essential for quality control. | Moderate precision, suitable for less complex geometries. | High precision, but requires advanced technology and expertise. |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective for standard applications. | Lower initial investment but may incur higher long-term costs due to inefficiencies. | Higher upfront costs, but potential for long-term savings through reduced errors. |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward to implement with standard measurement tools. | Simple implementation with minimal training required. | Requires specialized training and advanced equipment. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, as traditional tools are reliable and durable. | Low maintenance, but may require occasional recalibration. | High maintenance, as advanced technologies need regular servicing. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for complex parts where precision is critical, such as aerospace and automotive. | Best for simpler parts where high precision is not critical, such as basic consumer products. | Best for high-volume production where precision and automation are essential, such as electronics. |
What are the Pros and Cons of Using Conventional Measurement Tools Compared to Feature of Size?
Alternative 1: Conventional Measurement Tools
Conventional measurement tools, such as calipers and micrometers, provide a straightforward approach to gauging dimensions. They are easy to use, require minimal training, and have low initial costs. However, their effectiveness diminishes with complex geometries, where precision becomes paramount. In such cases, the lack of opposing elements in certain features can lead to inaccuracies, making them less suitable for high-stakes applications. Over time, the cumulative errors in measurement can result in costly rework or scrap.
Alternative 2: Advanced Measurement Technologies (e.g., Laser Scanning, CMM)
Advanced measurement technologies, such as laser scanning and coordinate measuring machines (CMM), offer unparalleled precision and the ability to measure complex geometries. They are particularly beneficial in high-volume production environments where automation is a priority. However, these technologies come with significant upfront costs and require specialized training for effective use. Additionally, they have higher maintenance demands due to the complexity of the equipment. While they can save costs related to errors and rework in the long run, the initial investment may be a barrier for some businesses.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between ‘feature of size’ and its alternatives, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements, including the complexity of parts, production volume, and budget constraints. If precision is critical and the parts are complex, investing in FOS or advanced technologies may be justified. Conversely, for simpler applications or lower production volumes, conventional measurement tools might suffice. Ultimately, the right choice hinges on balancing performance, cost, and ease of implementation to align with the organization’s strategic goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for feature of size
What Are the Key Technical Properties Related to Feature of Size?
Understanding the essential technical properties associated with features of size is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in manufacturing and engineering sectors. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material grade determines the strength, durability, and suitability of the feature of size for specific applications. For instance, stainless steel may be required for corrosion resistance in the automotive industry, while aluminum is often chosen for its lightweight properties. Selecting the appropriate material grade can significantly affect the performance and longevity of the final product. -
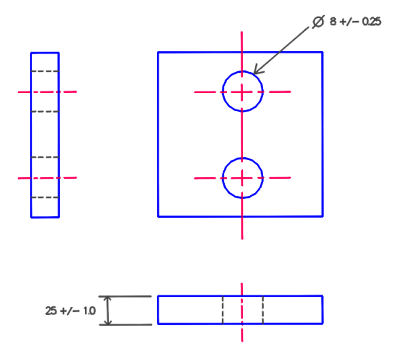
Tolerance
Tolerance specifies the allowable variations in the dimensions of a feature of size. This is vital for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assemblies. Tight tolerances may be necessary for precision engineering applications, while looser tolerances might suffice for less critical components. Understanding tolerances helps in minimizing defects and reducing production costs. -
Feature Type
Features can be categorized into regular and irregular types. Regular features of size, such as holes or plates with opposing surfaces, have dimensions that can be easily measured. Irregular features, like complex geometries, require specific consideration for manufacturing and tolerancing. Knowing the type of feature helps in selecting the right measurement tools and methods. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of a feature of size affects not only aesthetic qualities but also functional aspects such as wear resistance and friction. Different applications may require specific surface finishes, such as polished, matte, or anodized. A clear understanding of surface finish specifications can enhance product performance and customer satisfaction. -
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T)
GD&T is a system that communicates engineering tolerances using symbols and annotations. It helps in defining the allowable variations in the geometry of features of size. Implementing GD&T can streamline the manufacturing process and improve the interchangeability of parts, which is crucial for international trade. -
Virtual Condition
This concept refers to the worst-case scenario of a feature of size when considering its maximum material condition and geometric tolerances. Understanding virtual condition is essential for ensuring that parts will assemble correctly in their operational environment. It provides a more comprehensive view of how features will interact in practice.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Feature of Size?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of features of size, OEMs often specify particular dimensions and tolerances that suppliers must meet to ensure compatibility with their products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory costs and production schedules effectively. This term can significantly influence purchasing decisions and supplier relationships. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. When dealing with features of size, including detailed specifications and tolerances in an RFQ ensures that suppliers provide accurate pricing and feasibility assessments. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Knowledge of Incoterms is vital for understanding shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities related to features of size in cross-border trade. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the goods. In industries where features of size are critical, understanding lead times helps in planning production schedules and meeting project deadlines. -
BOM (Bill of Materials)
A BOM is a comprehensive list of all components, including features of size, needed to manufacture a product. It helps in inventory management and cost estimation, providing a clear overview of the materials required for production.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, enhance supplier relationships, and streamline their manufacturing processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the feature of size Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Feature of Size Sector?
The feature of size sector is experiencing significant shifts driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving customer expectations. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly focusing on precision engineering and high-quality manufacturing processes. This demand is largely fueled by the rise of Industry 4.0, which incorporates automation, data exchange, and smart manufacturing. These technologies allow for better measurement and tolerance control, enhancing the reliability of features of size in complex components.
Emerging trends indicate a growing emphasis on digital twin technologies and advanced analytics, enabling manufacturers to simulate and optimize the design and production processes. Additionally, the integration of cloud-based solutions is facilitating improved collaboration among global supply chains, allowing B2B buyers to manage sourcing processes more effectively. As sustainability becomes a non-negotiable aspect of business operations, there’s a marked shift towards sourcing from suppliers who prioritize environmentally friendly practices, particularly in the feature of size sector, where precision can significantly impact material usage and waste.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Practices in the Feature of Size Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers in the feature of size sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of resource consumption and waste generation, is prompting companies to seek suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. This includes using ‘green’ materials and certifications that verify the environmental credentials of products.
Buyers are increasingly looking for manufacturers who can demonstrate compliance with international environmental standards and who utilize renewable resources in their production processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the use of recycled materials are becoming key factors in supplier selection. Furthermore, companies are adopting circular economy principles, which emphasize the reuse and recycling of materials, thereby minimizing waste and promoting sustainability throughout the supply chain. Ethical sourcing practices not only enhance brand reputation but also mitigate risks associated with regulatory compliance and consumer backlash.
What Is the Historical Evolution of Features of Size in B2B Manufacturing?
The concept of features of size has evolved significantly over the past few decades, primarily influenced by advancements in engineering and manufacturing technologies. Initially, the focus was primarily on traditional measuring techniques, which relied heavily on manual inspections. However, as precision engineering gained prominence, the need for standardized measurements and tolerances became essential.
The introduction of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) in the late 20th century revolutionized how features of size were defined and measured. GD&T provided a systematic approach to communicating the allowable variations in part geometry, thus enhancing the clarity and efficiency of manufacturing processes. This framework has continued to evolve with the integration of digital tools, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustments in production. As the industry moves towards more advanced technologies, the historical context of features of size is crucial for understanding current trends and future directions in B2B sourcing and manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of feature of size
-
How do I ensure the accuracy of feature of size measurements?
Accurate measurements of features of size are critical in ensuring product quality. Utilize calibrated measuring tools, such as micrometers or calipers, that can provide precise readings. Additionally, implement a rigorous quality assurance process that includes regular calibration of equipment and training for personnel on measurement techniques. Consider employing statistical process control (SPC) to monitor measurements over time, allowing for early detection of deviations from specifications. -
What is the best method for sourcing feature of size components internationally?
When sourcing feature of size components internationally, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers with certifications such as ISO 9001 or those specializing in GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing). Request samples to evaluate quality and precision. Attend trade shows and industry events to network with suppliers. Utilizing platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources can also provide a wide range of options, but always vet suppliers through references and reviews. -
What are the common customization options for feature of size products?
Customization options for feature of size products typically include variations in dimensions, tolerances, materials, and surface finishes. Suppliers often offer tailored solutions to meet specific project requirements. When requesting customization, clearly communicate your specifications and expected outcomes. It’s advisable to collaborate closely with the supplier during the design phase to ensure feasibility and to avoid costly changes later in production. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for feature of size components?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the feature of size component. Generally, MOQs may range from a few dozen to several hundred units. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their MOQ policies and whether they can accommodate lower quantities for initial orders or prototypes. Many suppliers are willing to negotiate MOQs for long-term partnerships or repeat orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing feature of size components?
Payment terms for sourcing feature of size components can vary widely based on supplier policies and your negotiation skills. Common terms include advance payment, net 30, net 60, or even letters of credit for larger orders. It’s crucial to establish clear payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Always assess the supplier’s financial stability and reputation, as this can impact their willingness to offer favorable payment terms. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing feature of size parts?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing feature of size parts, implement a robust quality control process. This includes requiring detailed inspection reports and certifications from suppliers, conducting on-site audits, and establishing clear quality standards before production begins. Consider third-party inspections or tests to validate compliance with specifications. Building strong relationships with suppliers can also encourage adherence to quality standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international shipments of feature of size products?
Logistics considerations for international shipments include understanding shipping regulations, tariffs, and customs procedures in both the exporting and importing countries. Opt for reliable logistics partners who specialize in international freight to navigate these complexities. Additionally, ensure that the packaging of feature of size components protects them during transit. Tracking shipments and having contingency plans for delays can also help mitigate risks associated with international logistics. -
How do I evaluate a supplier’s capability in producing feature of size components?
Evaluate a supplier’s capability in producing feature of size components by reviewing their manufacturing processes, technology, and equipment. Request information on their experience with similar products and ask for case studies or references from previous clients. Assess their quality control measures, including certifications and compliance with industry standards. Visiting the manufacturing facility, if possible, can provide valuable insights into their operational capabilities and commitment to quality.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Feature Of Size Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Dimensional Consulting – Features of Size
Domain: dimensionalconsulting.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Features of Size are divided into Regular Features Of Size and Irregular Features Of Size. Regular Features Of Size have a size associated with them (diameter, width, length, thickness) and are characterized by having Opposed Surfaces. Irregular Features Of Size come in two varieties: Type A, which can fit into a sphere or between parallel planes, and Type B, which cannot. Regular Features Of Size…
2. eMachineShop – Feature of Size (FOS) in GD&T
Domain: emachineshop.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Feature-of-Size (FOS) in GD&T refers to any surface or set of parallel surfaces associated with a size dimension. Examples include: hole diameter (cylindrical surface), plate thickness (two opposed parallel surfaces), peg diameter (cylindrical surface), and ball bearing diameter (spherical surface).
3. Reddit – Features of Size Discussion
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Features of Size Discussion, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
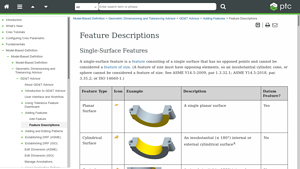
4. GD&T Advisor – Feature Descriptions
Domain: support.ptc.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: Feature Descriptions for Model-Based Definition in GD&T Advisor include various types of features categorized as Single-Surface Features, Features of Size, Multi-Surface Features, and Unsupported Features. Single-Surface Features consist of a single surface without opposing points, while Features of Size have opposing points and size dimensions. Multi-Surface Features involve multiple related CAD …
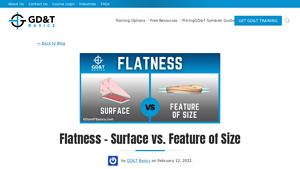
5. GD&T Basics – Understanding Surface Flatness vs. Feature of Size
Domain: gdandtbasics.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: The text discusses the differences between measuring flatness of a surface and flatness of a feature of size (FOS) in the context of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T). It explains that surface flatness is indicated on drawings with a callout that points to the surface, while flatness of a feature of size is indicated directly in line with the size dimension. Both types of flatness have…
6. Eng-Tips – Technical Standards Insights
Domain: eng-tips.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Eng-Tips – Technical Standards Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Tec-Ease – GD&T Training Solutions
Domain: tec-ease.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Tec-Ease, Inc. provides comprehensive GD&T training and coaching for engineers, designers, and inspectors. Their offerings include On-Site Courses, Public Seminars, Webinars, and Computer Based Training. The training is designed to engage participants and is based on the GD&T Hierarchy. They also offer software packages for continued support in the industrial manufacturing field. A specific tip di…
8. Metalcraft Industries – Feature Size Standards
Domain: metalcraftind.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: The text discusses the definitions and classifications of regular and irregular features of size according to ASME Y14.5 standards. A regular feature of size is defined as one cylindrical or spherical surface or two opposed parallel elements associated with a directly toleranced dimension. Irregular features of size are classified into two types: Type (a) includes features that can be contained by…
9. Rob Siegwart – GD&T Basics
Domain: robsiegwart.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Rob Siegwart – GD&T Basics provides foundational knowledge on Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) concepts. Key product details include: 1. Feature of Size (FOS): Defined as a cylindrical or spherical surface or a set of two opposed elements or parallel surfaces associated with a size dimension. 2. Types of FOS: Internal FOS (e.g., holes, slots) and External FOS (e.g., shafts, tabs). 3. …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for feature of size
In the realm of strategic sourcing, understanding the concept of features of size is crucial for international B2B buyers. The differentiation between regular and irregular features of size allows for precise measurements and tolerances, which are essential for ensuring the quality and functionality of components. By leveraging the principles of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T), businesses can enhance their design processes, reduce production costs, and minimize errors in manufacturing.
Moreover, the importance of defining features of size extends beyond engineering; it influences procurement strategies and supplier negotiations. As global markets become increasingly interconnected, the ability to communicate specifications clearly can lead to improved supplier relationships and better quality assurance.
As we look to the future, international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize the adoption of advanced GD&T practices. This proactive approach not only streamlines sourcing processes but also positions businesses to thrive in competitive landscapes. Embrace these insights to elevate your sourcing strategy and drive sustainable growth in your operations. Engage with your suppliers today and leverage the power of features of size to achieve excellence in your product offerings.