Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for failed to save document solidworks
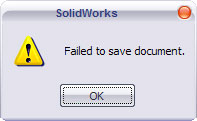
In the fast-paced world of design and engineering, encountering the “failed to save document” error in SOLIDWORKS can be a significant hurdle for businesses. This issue not only jeopardizes valuable project time but also leads to potential losses in productivity and revenue. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of this challenge is crucial. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the “failed to save document” problem, delving into its causes, implications, and effective solutions.
Throughout this guide, readers will find insights into various types of errors associated with document saving, practical applications of troubleshooting methods, and a thorough examination of supplier vetting processes for SOLIDWORKS support. We also explore cost implications and the potential return on investment when seeking reliable solutions. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable knowledge and expert recommendations, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and project outcomes.
Navigating the complexities of the SOLIDWORKS environment can be daunting, but with the right information and strategies, businesses can mitigate risks and enhance productivity. Whether you’re in Brazil or Saudi Arabia, the solutions provided here will serve as essential tools in overcoming the challenges posed by the “failed to save document” error, ensuring smoother workflows and greater success in your design projects.
Understanding failed to save document solidworks Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network-Related Issues | Occurs when saving files over a network; may lose connection | Collaborative engineering projects | Pros: Enables teamwork; Cons: Risk of data loss and interruptions. |
| File Corruption | Results from minor corruption in parts or assemblies | Complex assembly design | Pros: Identifies issues; Cons: Time-consuming to resolve. |
| Software Add-in Conflicts | Caused by conflicts with third-party add-ins | Custom software integrations | Pros: Enhances functionality; Cons: Potential for instability. |
| Large Assembly Challenges | Happens with extensive assemblies due to system limitations | Heavy-duty mechanical design | Pros: Facilitates intricate designs; Cons: Requires robust hardware. |
| Configuration Errors | Arises from errors in part configurations | Customization and variant design | Pros: Supports diverse product lines; Cons: May complicate saving. |
What Are Network-Related Issues in SolidWorks Save Failures?
Network-related issues typically arise when users attempt to save files stored on a network drive. This can lead to disconnections that hinder the saving process, resulting in the dreaded “failed to save document” error. Businesses that rely on collaborative engineering projects may find this particularly problematic, as it can disrupt team workflows and lead to potential data loss. Buyers should consider robust network solutions to minimize downtime and ensure reliable access to shared files.
How Does File Corruption Affect SolidWorks Document Saving?
File corruption is a common cause of save failures in SolidWorks, often stemming from minor issues within parts or assemblies. This type of error can significantly impact complex assembly designs, making it crucial for engineering teams to have protocols in place for regular file backups and integrity checks. While identifying and resolving file corruption can be tedious, it is vital for maintaining the quality and reliability of engineering projects.
Why Are Software Add-in Conflicts a Concern for SolidWorks Users?
Conflicts with third-party add-ins can lead to save errors in SolidWorks, affecting the software’s overall performance. These add-ins are often integrated to enhance functionality, but they can introduce instability, especially if they are not regularly updated or are incompatible with the current version of SolidWorks. Businesses should evaluate the necessity of each add-in and consider their impact on system performance to mitigate risks.
What Challenges Do Large Assemblies Present in SolidWorks?
Large assemblies in SolidWorks can pose significant challenges, primarily due to the limitations of the hardware being used. As assembly sizes increase, so does the likelihood of encountering save errors. This is particularly relevant for businesses engaged in heavy-duty mechanical design, where complex assemblies are the norm. Investing in high-performance computing resources is essential for companies looking to handle large-scale projects without interruptions.
How Do Configuration Errors Lead to Save Failures?
Configuration errors can impede the saving process in SolidWorks, often occurring when users attempt to save designs with multiple configurations. This issue can complicate the design process, particularly for companies focused on customization and variant design. To mitigate these risks, organizations should implement thorough testing and validation of configurations before finalizing designs, ensuring that all variations can be saved without errors.
Key Industrial Applications of failed to save document solidworks
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of failed to save document solidworks | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Design and simulation of aircraft components using SolidWorks. | Prevents loss of critical design data, ensuring project timelines are met. | Look for reliable IT infrastructure and support services. |
| Automotive | Development of vehicle parts and assemblies within SolidWorks. | Enhances productivity by minimizing downtime due to save errors. | Ensure compatibility with existing software and hardware. |
| Industrial Equipment | Creation and modification of complex machinery designs. | Reduces operational disruptions by ensuring secure data management. | Prioritize vendors with robust backup and data recovery solutions. |
| Construction | Modeling of building components and structural designs. | Safeguards architectural integrity by preserving design iterations. | Assess the reliability of network storage solutions. |
| Consumer Electronics | Prototyping and testing of electronic devices using SolidWorks. | Supports innovation by allowing rapid design changes without data loss. | Consider local support availability for troubleshooting. |
How is ‘failed to save document solidworks’ Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, SolidWorks is pivotal for designing and simulating components like wings and fuselages. The “failed to save document” error can lead to significant setbacks, especially when intricate designs are being developed. By implementing robust data management solutions, companies can mitigate risks associated with data loss, ensuring that engineers can focus on innovation rather than troubleshooting. International buyers should seek vendors with proven IT support and backup systems to maintain workflow efficiency.
What Role Does ‘failed to save document solidworks’ Play in Automotive Development?
Automotive manufacturers rely on SolidWorks for the design of vehicle parts, which often involves complex assemblies. The “failed to save document” error can disrupt production timelines and lead to costly delays. To combat this, businesses should invest in reliable data management systems that facilitate smooth saving processes. Buyers from regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia should prioritize software solutions that integrate seamlessly with their existing infrastructure to minimize compatibility issues.
How is ‘failed to save document solidworks’ Relevant in Industrial Equipment Design?
In the industrial equipment sector, SolidWorks is used to create detailed machinery designs. The risk of encountering a “failed to save document” error can jeopardize project timelines and lead to lost work. Companies can enhance their operational efficiency by implementing robust data recovery solutions and ensuring frequent backups. Buyers should evaluate potential suppliers based on their ability to provide comprehensive support and reliable network storage solutions.
What Impact Does ‘failed to save document solidworks’ Have on Construction Projects?
The construction industry utilizes SolidWorks for modeling building components and structural designs. A “failed to save document” error can threaten the integrity of a project, leading to costly revisions. By investing in reliable data management practices, companies can safeguard their designs and maintain project integrity. International buyers should assess the reliability of their network storage solutions and ensure they have adequate support for troubleshooting to minimize disruptions.
How Can ‘failed to save document solidworks’ Influence Consumer Electronics Innovation?
In consumer electronics, SolidWorks is essential for prototyping and testing new devices. The “failed to save document” error can hinder the pace of innovation by causing data loss during critical design phases. By implementing effective backup strategies, companies can protect their intellectual property and expedite the design process. Buyers should consider local support availability to ensure quick resolution of any issues that arise during design iterations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘failed to save document solidworks’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Lost Work Due to Network Issues
The Problem: A common issue faced by B2B buyers using SOLIDWORKS is the frustration of encountering the “failed to save document” error, especially when working on large assemblies saved on a network drive. This scenario often unfolds when an engineer has invested several hours into a project, only to find that they cannot save their progress due to network connectivity problems. As they attempt to save, they may experience disconnections from the server, leading to not only potential loss of work but also increased downtime as they reboot their systems or log back onto the network.
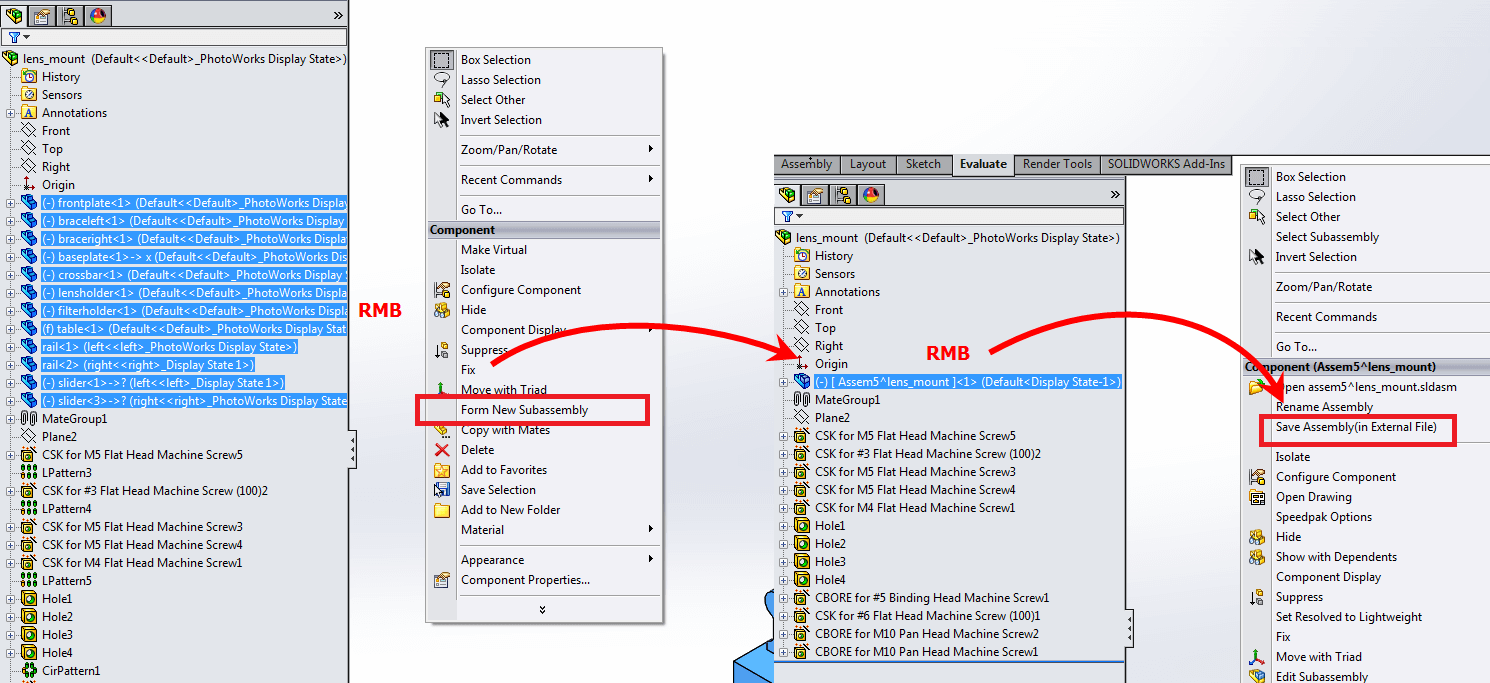
The Solution: To address this issue, companies should consider implementing a more reliable local file management strategy. One effective approach is to work on files locally and then transfer them to the network drive upon completion. This can be achieved by using the “Pack and Go” feature to bundle all related files and save them to a local drive before uploading them to the server. Additionally, ensuring that the network infrastructure is robust, with minimal downtime and high-speed connections, can prevent such disruptions. Regular backups and a clear version control system can also help mitigate the loss of work.
Scenario 2: Document Corruption During Saving Process
The Problem: Document corruption is another prevalent pain point that can arise when users attempt to save their SOLIDWORKS files. This often happens when users make extensive modifications to complex assemblies, leading to minor corruptions that prevent successful saving. Engineers may find themselves stuck in a cycle of attempting to save, only to receive repeated error messages, resulting in increased stress and potential project delays.
The Solution: To combat this issue, it is crucial to adopt a proactive approach toward file management and error prevention. Users should regularly utilize the “Save As” function to create incremental backups of their files, which can help avoid data loss if corruption occurs. Additionally, employing the “Ctrl + Q” command can force a rebuild of the assembly, potentially resolving any underlying issues before attempting to save. Encouraging team members to validate their assemblies regularly by checking for rebuild errors and ensuring all components are in good standing can further reduce the risk of corruption.
Scenario 3: Incompatibility with Add-Ins or Third-Party Software
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the interference caused by incompatible add-ins or third-party software while using SOLIDWORKS. Users may experience the “failed to save document” error when these extensions conflict with the software’s operations, particularly during critical moments in their workflow. Such conflicts can lead to wasted time as users troubleshoot the issue, often leading to frustration and delays in project timelines.
The Solution: To alleviate this problem, it is advisable for companies to implement a standardized environment where only vetted add-ins and software are used in conjunction with SOLIDWORKS. Users should be encouraged to disable unnecessary add-ins, especially during high-stakes projects, to minimize the risk of conflicts. Regularly updating SOLIDWORKS and any associated software can also help ensure compatibility. Furthermore, conducting training sessions on best practices for managing add-ins and troubleshooting techniques can empower users to resolve these issues more efficiently, ultimately leading to smoother project execution.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for failed to save document solidworks
What are the Key Properties of Common Materials Relevant to SOLIDWORKS Document Saving Issues?
When dealing with the “failed to save document” error in SOLIDWORKS, understanding the materials used in the design and engineering processes can significantly impact performance and reliability. Here, we analyze four common materials that are frequently encountered in B2B applications, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Aluminum Alloys
Key Properties:
Aluminum alloys are known for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. They typically withstand temperatures up to 150°C and pressures relevant to most engineering applications.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is lightweight and easy to machine, making it suitable for complex designs. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may not be as durable under high-stress conditions.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and chemicals, making it a versatile choice for different applications. However, its lower strength compared to steel may limit its use in high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Aluminum alloys must comply with international standards such as ASTM and EN. Buyers should consider local availability and cost fluctuations, especially in regions with less developed supply chains.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers exceptional corrosion resistance and can endure high temperatures (up to 800°C) and pressures. Its durability makes it a preferred choice for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons:
While stainless steel is highly durable and resistant to rust, it is heavier and more expensive than aluminum. Manufacturing processes can also be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is ideal for applications involving exposure to corrosive environments, such as marine or chemical processing. Its compatibility with various media enhances its utility across sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS is crucial. Buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia should ensure that their suppliers can meet these standards to avoid regulatory issues.
3. Polycarbonate
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and transparency. It can function effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C.
Pros & Cons:
This material is lightweight and easy to mold, making it suitable for intricate designs. However, it has lower chemical resistance compared to metals and can be prone to scratching.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is often used in applications requiring transparency and toughness, such as safety goggles and protective shields. Its limitations in chemical exposure must be considered in design.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Polycarbonate must meet specific safety and environmental regulations, particularly in Europe. Buyers should verify compliance with REACH regulations to avoid legal complications.
4. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRP)
Key Properties:
CFRP is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness. It can withstand temperatures up to 200°C and is resistant to various chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
CFRP is incredibly strong and lightweight, making it ideal for high-performance applications. However, it is more expensive and requires specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application:
CFRP is suitable for aerospace and automotive applications where weight reduction is critical. Its high cost may limit its use in more budget-sensitive projects.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of CFRP in their region and its compliance with international standards. Countries with developing markets may face challenges in sourcing high-quality CFRP materials.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for failed to save document solidworks | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Lightweight components in automotive and aerospace | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive than steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive environments in chemical processing | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Heavier and more complex to manufacture | High |
| Polycarbonate | Safety equipment and protective shields | Lightweight and impact-resistant | Lower chemical resistance | Medium |
| Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers | High-performance applications in aerospace and automotive | High strength and lightweight | Expensive and complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that can enhance product performance and reliability while navigating regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for failed to save document solidworks
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for SOLIDWORKS Document Management Solutions?
In the realm of SOLIDWORKS document management, ensuring that files are saved without errors is crucial. The manufacturing process for software solutions addressing the “failed to save document” issue involves several stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage focuses on gathering and preparing the necessary software components and libraries that facilitate document management in SOLIDWORKS. This includes ensuring that the software is compatible with various operating systems and hardware configurations. Developers must prepare robust backup and recovery systems to mitigate data loss risks.
-
Forming: In this stage, developers create the core functionalities that allow users to save, retrieve, and manage their files effectively. Techniques such as version control, real-time collaboration tools, and integration with cloud storage solutions are essential. This phase also involves rigorous coding practices to minimize bugs that could lead to saving errors.
-
Assembly: The assembly stage integrates various components developed in the previous steps into a cohesive software solution. This includes the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design, ensuring that users can easily navigate the software. Effective assembly also involves the integration of error-handling protocols that provide users with actionable insights when a “failed to save document” error occurs.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves thorough testing and quality assurance (QA). This includes stress testing under various conditions to simulate potential user scenarios that could lead to saving errors. The finishing stage is critical to ensure that the software not only functions correctly but also provides a seamless user experience.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Software Development for SOLIDWORKS?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process for software solutions. It ensures that the final product meets international standards and performs reliably under various conditions.
-
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Adherence to international standards such as ISO 9001 is vital for establishing credibility. ISO 9001 outlines criteria for a quality management system and emphasizes continuous improvement. B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers implement these standards in their development processes. -
What Are the Industry-Specific Certifications Relevant to SOLIDWORKS?
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications can be significant. These certifications ensure that software solutions comply with regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Software Development?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical for maintaining high standards throughout the software development lifecycle. Here are the main checkpoints that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint assesses the quality of incoming components and libraries used in software development. By verifying that these components meet specified criteria, developers can reduce the likelihood of errors arising from third-party integrations.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the development process, continuous monitoring is essential. IPQC involves regular code reviews, unit testing, and integration testing to catch issues early. This proactive approach helps ensure that the software can handle saving documents without errors.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The FQC stage evaluates the complete software solution before it reaches the market. This includes user acceptance testing (UAT) to ensure that the end product meets user needs and expectations. It is also an opportunity to test the software under various scenarios to confirm that it can handle the “failed to save document” issue effectively.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are actionable steps to ensure that suppliers meet high-quality standards:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems. These audits should assess compliance with international standards and the effectiveness of their QA processes.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation demonstrating their adherence to quality standards. These reports may include metrics on error rates, customer feedback, and corrective actions taken in response to issues.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control processes. This step is particularly valuable for buyers in regions with varying standards and practices.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality management. Understanding local practices and adapting quality assurance strategies accordingly can enhance collaboration and product quality.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with local regulations is paramount. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers understand and adhere to regional standards, which may differ from international norms.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping and communication can introduce additional complexities. Buyers must ensure that quality control measures are maintained throughout the supply chain, from development to delivery.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting software solutions for SOLIDWORKS document management, minimizing the risk of encountering “failed to save document” errors.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘failed to save document solidworks’
In the world of engineering and design, facing the “failed to save document” error in SOLIDWORKS can be a significant setback. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking solutions or services related to this common issue. By following these steps, you can ensure a smoother procurement process and ultimately enhance your organization’s productivity.
Step 1: Identify Your Specific Needs
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly define the specific issues you are encountering with the “failed to save document” error. Understanding whether this is a frequent occurrence, linked to network issues, or related to specific file types will help you communicate effectively with potential vendors.
- Document Frequency: Note how often the error occurs and under what circumstances.
- Impact Assessment: Evaluate how this issue affects your team’s workflow and project timelines.
Step 2: Research Reliable Suppliers
Invest time in researching suppliers who specialize in SOLIDWORKS support and data management solutions. Look for companies with a solid reputation in the industry and positive customer feedback.
- Industry Experience: Prioritize suppliers who have a proven track record in resolving SOLIDWORKS-related issues.
- Client Testimonials: Seek out case studies or testimonials that showcase successful interventions in similar scenarios.
Step 3: Request Technical Support Capabilities
Evaluate the technical support capabilities of potential suppliers. This includes their response times, the availability of remote support, and their knowledge of SOLIDWORKS intricacies.
- Support Channels: Ensure they offer multiple support channels such as phone, email, and chat.
- Expertise Level: Confirm that their support team consists of certified SOLIDWORKS professionals.
Step 4: Evaluate Software and Tools Offered
Look into any software or tools offered by suppliers that could help mitigate the “failed to save document” issue. Solutions might include backup systems, file recovery tools, or network optimization software.
- Integration Compatibility: Ensure that the tools are compatible with your current SOLIDWORKS version and IT infrastructure.
- User Training: Inquire whether the supplier provides training on how to effectively use their tools.
Step 5: Assess Customer Support and Maintenance Plans
Consider the customer support and maintenance plans available from the supplier. Ongoing support is crucial for long-term success and quick resolution of any future issues.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Review SLAs to understand response times and support availability.
- Regular Updates: Ensure that the supplier commits to regular software updates and maintenance checks.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Value Propositions
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, compare their pricing structures and the value they offer. Look beyond the initial cost to assess the overall return on investment.
- Cost Transparency: Request detailed quotes that outline all costs associated with services and support.
- Long-Term Benefits: Consider the potential long-term savings from reduced downtime and increased productivity.
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision with a Trial or Pilot Project
Before making a final commitment, consider running a trial or pilot project with the chosen supplier. This will allow you to assess their services in real-time and ensure they meet your needs.
- Performance Metrics: Define clear metrics for success during the trial period.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback mechanism to address any issues promptly during the pilot.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement of solutions related to the “failed to save document” error in SOLIDWORKS more effectively, ensuring they choose the right partner to enhance their operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for failed to save document solidworks Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Addressing ‘Failed to Save Document’ Issues in SolidWorks?
When analyzing the costs associated with addressing the ‘failed to save document’ error in SolidWorks, several key components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: In the context of software issues, “materials” may refer to the hardware and software resources required to run SolidWorks effectively. This includes the cost of high-performance computers, network infrastructure, and backup solutions to prevent data loss.
-
Labor: Technical support teams and IT personnel are often needed to troubleshoot and resolve issues related to the ‘failed to save’ error. Labor costs can vary based on the complexity of the problem and the expertise required, making it essential to factor in the hourly rates of skilled professionals.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the indirect costs associated with maintaining IT infrastructure, software licenses, and administrative support. These costs can accumulate quickly, especially if businesses experience frequent disruptions.
-
Tooling: If custom solutions or upgrades are necessary to enhance performance and mitigate errors, tooling costs will arise. This can include specialized software tools or additional hardware.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that files are saved correctly and data integrity is maintained may require additional QC measures. This might involve implementing a system for regular backups or utilizing version control software.
-
Logistics: For businesses operating in multiple regions, logistics costs related to software deployment, updates, and support can be substantial. Understanding local infrastructure and connectivity can help in planning and budgeting.
-
Margin: Finally, profit margins must be considered when sourcing solutions to these issues. Companies must ensure that their pricing reflects the value of the support and technology they provide.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Cost Structures for SolidWorks Solutions?
Several price influencers can significantly impact the cost structure for solutions aimed at preventing or resolving ‘failed to save document’ errors:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Buying software licenses or support services in bulk can reduce per-unit costs. Companies should negotiate for better pricing based on their needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Tailoring solutions to meet specific operational requirements can increase costs. However, customized solutions may offer better long-term efficiency and reduced error rates.
-
Materials: The choice of hardware and software components can affect overall costs. High-quality, reliable components may have a higher initial investment but can lead to lower operational costs over time.
-
Quality/Certifications: Solutions that come with industry certifications or proven reliability may command a premium price. Buyers should weigh these costs against the potential risks of using less reliable alternatives.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Engaging with established suppliers may provide peace of mind but could also result in higher costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery can affect total costs, especially for international buyers. Properly negotiating Incoterms can help avoid unexpected fees.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Navigating Costs Related to SolidWorks Errors?
International B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips to navigate costs effectively:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. Be prepared to discuss volume discounts, extended warranties, or additional support services.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider long-term savings from reduced errors and downtime.
-
International Pricing Nuances: Be aware of currency fluctuations and how they can affect pricing. Understanding local market conditions can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Seek Local Expertise: Engage with local IT support or consultants who understand regional challenges and can offer tailored solutions to mitigate errors effectively.
-
Regular Training: Investing in training for employees can minimize errors and improve overall efficiency. This proactive approach can save costs associated with troubleshooting and lost productivity.
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics related to SolidWorks errors is crucial for B2B buyers. By considering these factors and implementing the suggested strategies, companies can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing failed to save document solidworks With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Document Saving Issues in SolidWorks
In the realm of CAD software, encountering the “failed to save document” error in SolidWorks can be a significant setback for engineers and designers. This issue often arises due to minor file corruptions, network disruptions, or system limitations, resulting in lost work and productivity. To mitigate such challenges, organizations can explore alternative solutions that enhance file management and improve overall productivity. This section will compare SolidWorks’ saving challenges with alternative solutions that address similar file management needs.
Comparison of Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Failed To Save Document SolidWorks | Autodesk Inventor | Onshape |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate; prone to errors | High; stable with large files | High; cloud-based efficiency |
| Cost | Requires SolidWorks license | Requires Autodesk license | Subscription-based pricing |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires troubleshooting | Moderate; familiar interface | Easy; no installation needed |
| Maintenance | High; frequent updates and support | Moderate; regular updates | Low; managed by provider |
| Best Use Case | Large assemblies and parametric design | Mechanical design projects | Collaborative design in cloud |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Autodesk Inventor
Autodesk Inventor is a robust CAD software widely used for mechanical design. It boasts high performance, particularly with large files, making it suitable for complex assemblies. Users often find the interface familiar and easy to navigate, which can reduce the learning curve. However, it requires a significant investment in licensing, and users may face maintenance challenges due to regular updates and support needs. Inventor is best for companies that focus heavily on mechanical design and require extensive 3D modeling capabilities.
Onshape
Onshape is a cloud-based CAD solution that offers high performance and efficiency in file management. Its architecture allows for real-time collaboration, making it ideal for teams working remotely or across different locations. The ease of implementation is a significant advantage, as no local installation is required; users can access the software from any device with internet connectivity. However, Onshape operates on a subscription model, which can accumulate costs over time. It is best suited for companies looking for collaborative design solutions with minimal maintenance overhead.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting an alternative to address the “failed to save document” issue in SolidWorks, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including performance needs, budget constraints, and the nature of their projects. If high-performance mechanical design is a priority, Autodesk Inventor may be the ideal choice. Conversely, for teams emphasizing collaboration and ease of access, Onshape presents a compelling solution. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the unique context of the organization and its workflow demands, ensuring that productivity remains uncompromised.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for failed to save document solidworks
What Are the Key Technical Properties Related to ‘Failed to Save Document’ in SolidWorks?
Understanding the technical properties associated with the “Failed to Save Document” error in SolidWorks is crucial for businesses that rely on this software for design and engineering tasks. Here are several critical specifications that can significantly impact your workflow:
-
File Size Limitations
SolidWorks has specific file size limitations that can affect saving operations. Large assemblies or parts may exceed system capabilities, leading to save failures. Recognizing these limitations helps businesses manage their projects effectively, ensuring they allocate sufficient resources and optimize file sizes to avoid disruptions. -
Network Performance
Saving files over a network can introduce latency and increase the risk of save errors. High latency or unstable connections can lead to the “Failed to Save Document” error, particularly in collaborative environments. Businesses must invest in robust network infrastructure to ensure reliable access to shared files and minimize disruptions during critical design phases. -
System RAM and Virtual Memory Settings
The amount of RAM and the configuration of virtual memory can directly influence SolidWorks’ performance. Insufficient RAM can hinder the software’s ability to process large assemblies, leading to save failures. Companies should ensure their workstations are equipped with adequate memory and consider optimizing virtual memory settings to enhance performance. -
Add-in Compatibility
Third-party add-ins can sometimes conflict with SolidWorks, resulting in save errors. Understanding which add-ins are essential for your operations and ensuring their compatibility with your SolidWorks version can mitigate these risks. Companies should regularly review and update their add-ins to maintain smooth functionality. -
Backup and Recovery Settings
Proper backup settings can be a lifesaver when encountering a save failure. Configuring SolidWorks to create frequent backups ensures that work is not lost in case of an error. Businesses should prioritize establishing a robust backup protocol to protect their intellectual property and minimize downtime. -
Assembly Complexity
The complexity of assemblies, including the number of components and mating conditions, can lead to increased processing times and potential save errors. Companies should assess the complexity of their designs and consider breaking them into smaller, manageable assemblies to enhance performance and reliability.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand in Relation to SolidWorks Errors?
Navigating the technical landscape of SolidWorks and its associated challenges requires familiarity with certain industry-specific terminology. Here are some essential trade terms that can enhance understanding and communication among B2B buyers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for businesses sourcing components or software solutions, as it affects quality, compatibility, and support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Recognizing MOQs is essential for businesses to plan their purchasing strategies, especially when dealing with custom parts or components necessary for SolidWorks projects. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. This term is crucial for B2B transactions, as it facilitates the procurement process and helps buyers compare options based on price, quality, and delivery times. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of international sales terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with these terms is essential for businesses engaged in global trade, as they clarify shipping, insurance, and risk management responsibilities. -
PDM (Product Data Management)
PDM refers to the process of managing design data and engineering workflows. Understanding PDM is critical for companies that use SolidWorks, as it helps streamline collaboration and version control, reducing the likelihood of errors like failed saves. -
SP (Service Pack)
A service pack is a collection of updates and fixes for software. Awareness of the latest SolidWorks service packs is crucial for businesses to ensure they are using the most stable and secure version, reducing the likelihood of encountering errors during design processes.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and mitigate risks associated with using SolidWorks.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the failed to save document solidworks Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing the ‘Failed to Save Document’ Issue in SolidWorks?
The global engineering and design software market, particularly within sectors utilizing SolidWorks, is witnessing significant shifts driven by digital transformation and the increasing complexity of design projects. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the challenges associated with software errors—such as the ‘failed to save document’ issue—underscore the need for robust IT infrastructure and support systems. As businesses increasingly adopt cloud-based solutions and collaborative design environments, the interdependence on stable network connections and efficient file management becomes critical. Companies are now focusing on comprehensive training and support to mitigate such risks, ensuring that employees are well-versed in troubleshooting and data recovery methods.
Moreover, the rise of remote work has amplified the demand for reliable software performance. As teams operate across various geographies, the ability to save and manage design files without interruptions is vital. Emerging trends also indicate a growing emphasis on integrated solutions that combine design software with project management tools to streamline workflows. This integration not only enhances productivity but also minimizes the likelihood of encountering save errors by allowing for real-time collaboration and version control.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affect the SolidWorks Software Sector?
In the context of the ‘failed to save document’ issue, sustainability and ethical sourcing are increasingly important considerations for B2B buyers. As companies become more environmentally conscious, the impact of software on sustainable practices is under scrutiny. The use of software solutions like SolidWorks can significantly influence design efficiency and material usage, which in turn affects waste generation. Buyers are now prioritizing vendors that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through eco-friendly practices and materials.
Furthermore, ethical supply chains are gaining traction as businesses seek to align with suppliers that adhere to responsible sourcing standards. This trend is particularly relevant for companies operating in markets such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia, where regulatory frameworks are evolving to promote environmental responsibility. As part of this shift, certifications for green materials and sustainable practices are becoming essential criteria for vendor selection. By investing in software that supports sustainable design practices, B2B buyers can enhance their reputation while contributing to a circular economy.
What Is the Historical Context of SolidWorks and Its Issues?
The evolution of SolidWorks has been marked by significant advancements in CAD (Computer-Aided Design) technology since its inception in 1995. Initially designed to cater to small and medium-sized enterprises, SolidWorks quickly gained traction in various industries due to its user-friendly interface and robust features. Over the years, the software has undergone numerous updates to improve functionality, including enhancements to file management and error resolution processes.
Despite these advancements, issues such as the ‘failed to save document’ error have persisted, reflecting the complexities of modern design environments. As SolidWorks has adapted to incorporate more sophisticated features, the challenges associated with network dependencies and large assemblies have become more pronounced. Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of ongoing training, support, and proactive measures to mitigate potential disruptions in their design processes. By recognizing the evolution of SolidWorks and its associated challenges, businesses can make informed decisions about their software investments and operational strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of failed to save document solidworks
-
1. How do I resolve the “Failed to save document” error in SolidWorks?
To resolve the “Failed to save document” error in SolidWorks, start with simple troubleshooting steps. First, try using the “Save All” function or the Ctrl+Q command for a force regeneration. If that fails, check for any configuration issues, and correct any errors in the part or assembly tree. Disabling all add-ins may also help. If you’re working over a network, attempt to save the file locally to your desktop. Finally, consider using the Pack and Go feature to save the entire assembly to a new location. -
2. What is the best practice to prevent data loss in SolidWorks?
To prevent data loss in SolidWorks, adopt a disciplined saving routine. Set up frequent auto-backups in the System Options to ensure that changes are regularly saved. Utilize the “Save As” function to create multiple versions of your work. Additionally, regularly check for software updates and patches, as these often contain fixes for known issues. Encourage your team to save their work frequently and consider using version control systems for collaborative projects to minimize risks. -
3. How can I ensure the reliability of my SolidWorks software from international suppliers?
When sourcing SolidWorks software from international suppliers, verify their reputation through reviews and testimonials from previous clients. Ensure they are authorized resellers and check for certifications that validate their expertise. It’s also prudent to request a demo or trial version before purchase to assess compatibility with your existing systems. Additionally, inquire about their support services, including availability for troubleshooting and ongoing maintenance, to ensure you have reliable assistance when needed. -
4. What are the payment terms typically offered by SolidWorks suppliers?
Payment terms for SolidWorks suppliers can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Many suppliers offer standard terms such as net 30 or net 60 days, while others may require upfront payments or deposits. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and operational capabilities. Always clarify any potential fees related to international transactions, and consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment. -
5. How do I evaluate the quality assurance practices of a SolidWorks supplier?
To evaluate a SolidWorks supplier’s quality assurance practices, request documentation outlining their QA processes. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to international quality standards. Ask about their testing protocols for software and any customer feedback mechanisms in place. Additionally, consider conducting a site visit or virtual meeting to discuss their QA practices and review case studies of past projects to assess their commitment to quality. -
6. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing SolidWorks from abroad?
When sourcing SolidWorks software internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping times, customs clearance, and potential tariffs. Ensure that the supplier has a reliable shipping method and can provide tracking information. Additionally, verify that the supplier can handle any necessary documentation for importation. It’s also wise to factor in time zone differences for support and communication, ensuring that you can effectively collaborate with your supplier. -
7. How can I customize my SolidWorks software to fit specific project needs?
Customizing SolidWorks software can enhance its functionality for specific project requirements. Many suppliers offer customization services, including tailored plugins and add-ins that integrate with existing workflows. Before proceeding, clearly outline your project needs and discuss them with potential suppliers. Additionally, consider training sessions to familiarize your team with the new features. Always ensure that any customizations comply with SolidWorks licensing agreements to avoid issues with software updates and support. -
8. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for purchasing SolidWorks licenses?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for SolidWorks licenses can vary by supplier and region. Some suppliers may offer single licenses, while others might require a minimum order of multiple licenses for bulk purchases. It’s advisable to clarify the MOQ during initial discussions with suppliers to align your purchasing strategy with their terms. If you’re part of a larger organization, consider consolidating licenses to meet MOQ requirements, which may also lead to volume discounts.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Failed To Save Document Solidworks Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SOLIDWORKS – 2018 SP2
2. SolidWorks – 2007 SP3.0
Domain: eng-tips.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: SolidWorks 2007 SP2.2, SolidWorks 2007 SP3.0, Intel Pentium D CPU 3.00 GHz, 3.93 GB of RAM, NVIDIA Quadro FX 3400, AutoCAD 06, PDMWorks 07, GeForce FX 5200, 2GB RAM/3GB Switch, Windows XP Pro SP2.0.
3. Hawkridge Systems – SolidWorks File Recovery
Domain: support.hawkridgesys.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, Hawkridge Systems – SolidWorks File Recovery, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. The CAD Forums – SolidWorks Configurations
Domain: thecadforums.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: SolidWorks 2005, Microsoft Office 2000, EcoSqueeze, part document with 19 configurations, design table, ERW box section, file size 13.8 MB unzipped.
5. Visiativ – Corrupted SLDDRW File Forum
6. Solidworks – STEP File Saving Issue
Domain: community.goengineer.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Solidworks – STEP File Saving Issue, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for failed to save document solidworks
In addressing the persistent challenge of the “Failed to Save Document” error in SOLIDWORKS, international B2B buyers must recognize the critical importance of strategic sourcing and robust IT infrastructure. Effective sourcing strategies can mitigate risks associated with data loss, ensuring that companies have access to reliable software solutions and technical support. This is particularly vital for businesses operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where technical support may vary widely.
Investing in advanced training for engineers and technical staff can empower them to navigate these issues efficiently. Encouraging practices such as regular backups, utilizing SOLIDWORKS’ Pack and Go feature, and ensuring that hardware meets system requirements will enhance productivity and reduce frustration.
As we look to the future, it is essential for B2B buyers to foster partnerships with trusted software vendors and service providers who understand the unique challenges faced in diverse markets. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, organizations can not only safeguard their projects but also drive innovation and growth. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and align them with your operational needs to ensure resilience against technical setbacks.