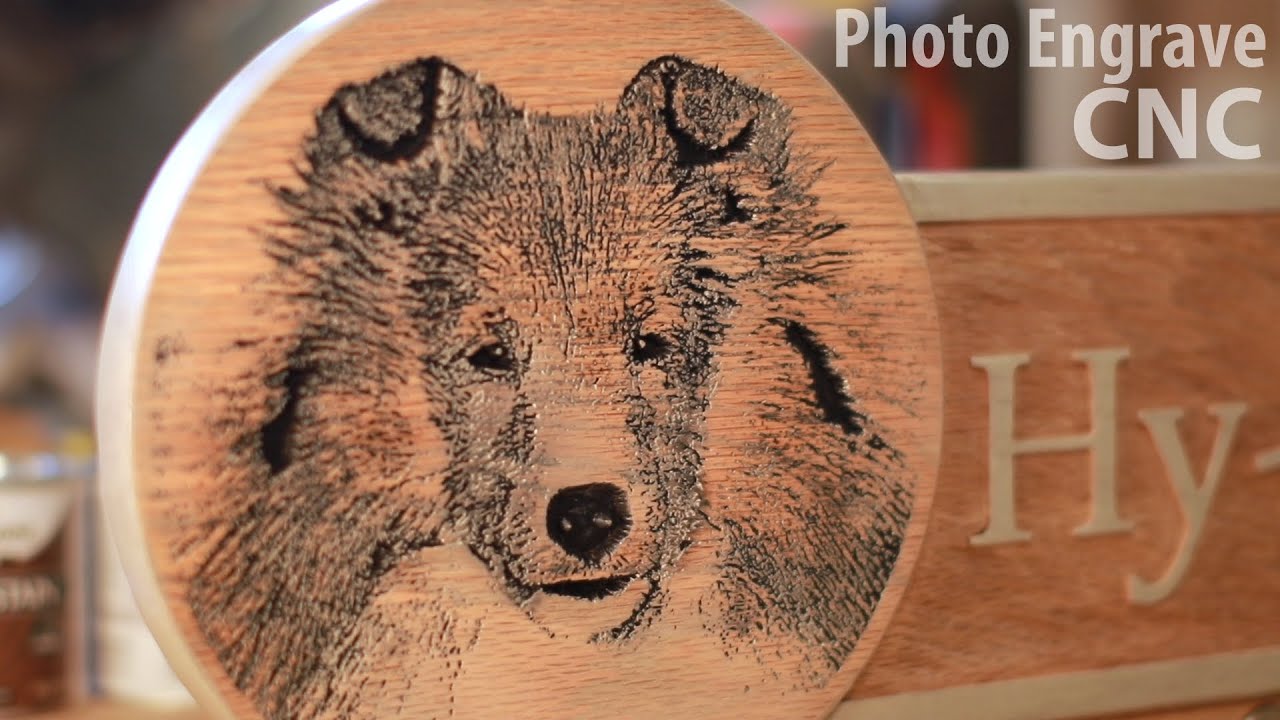
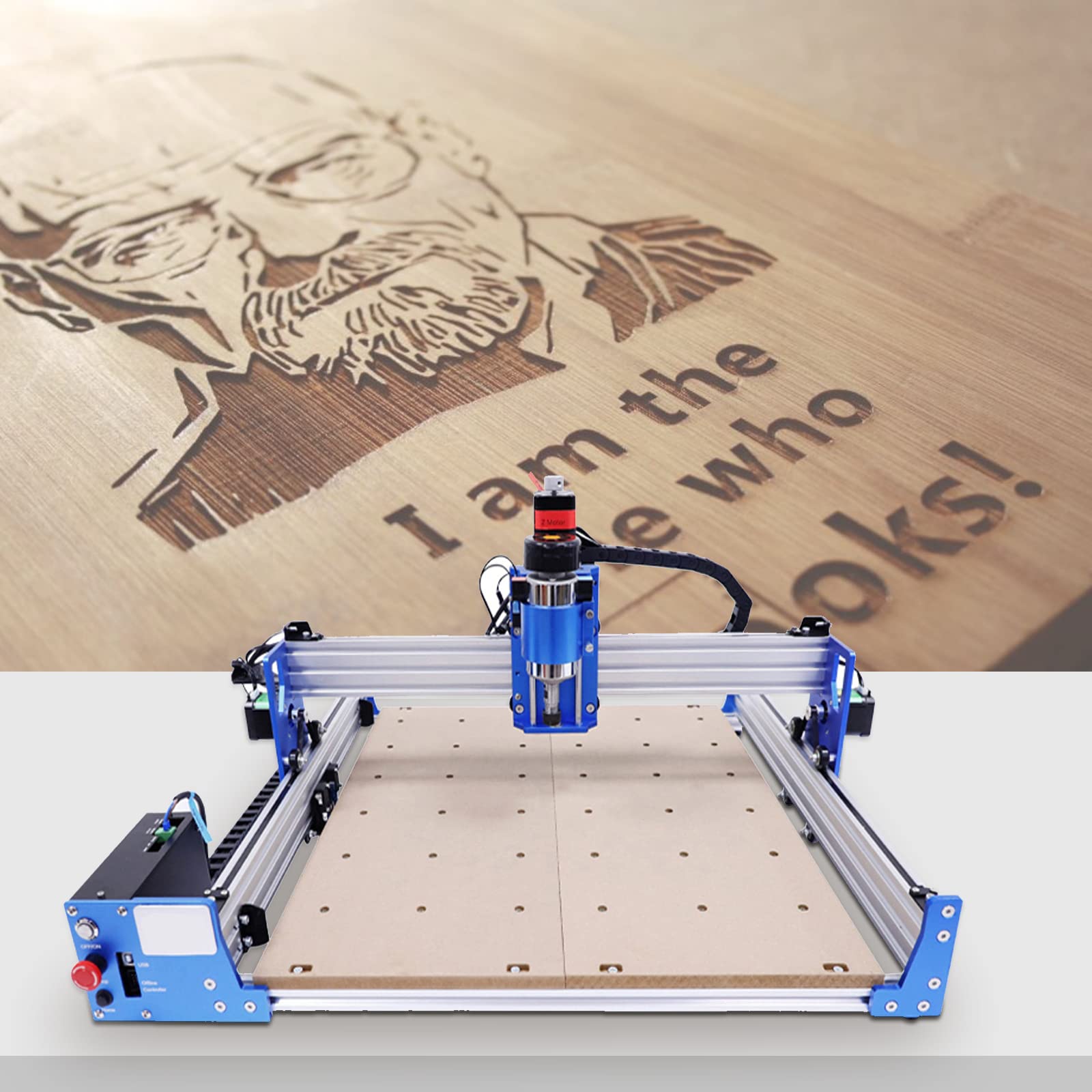
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for engraving with cnc router
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing the right CNC router for engraving can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With a diverse array of machines, materials, and applications available, making informed decisions is crucial to ensure that investments yield maximum returns. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of engraving with CNC routers, covering essential topics such as types of machines, suitable materials, application areas, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By exploring these aspects, this guide serves as an invaluable resource for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia. It aims to equip decision-makers with actionable insights and practical knowledge to navigate the complexities of sourcing CNC engraving solutions. Whether you are looking to personalize products, enhance branding, or create intricate designs, understanding the nuances of CNC engraving technology will empower you to make strategic purchasing decisions that align with your business objectives.
As you embark on this journey, let this guide illuminate the path towards selecting the ideal CNC router, ensuring that your engraving projects not only meet quality standards but also drive business growth in an evolving marketplace.
Understanding engraving with cnc router Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-Carving | Utilizes a V-bit for sharp, detailed engraving; ideal for text and intricate designs. | Signage, trophies, personalized gifts | Pros: High detail; versatile. Cons: Slower process for large areas. |
| Raster Engraving | Follows a path similar to a printer, ideal for images and complex patterns. | Decorative items, custom artwork | Pros: Great for images; high detail. Cons: More time-consuming; requires precision. |
| 3D Engraving | Creates depth and relief by varying cutter depth; best for three-dimensional designs. | Sculptures, custom molds, prototypes | Pros: Unique designs; high impact. Cons: Requires advanced software and setup. |
| Deep Engraving | Involves deeper cuts for bold designs; often uses larger bits. | Industrial parts, tools, and mechanical items | Pros: Durable markings; strong visibility. Cons: Limited detail; higher material wear. |
| Laser Engraving | Uses laser technology for precision; can engrave on a wide variety of materials. | Promotional items, electronics, jewelry | Pros: Extremely precise; fast. Cons: Higher initial investment; may require additional safety measures. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of V-Carving in CNC Router Engraving?
V-Carving is distinguished by its use of a V-bit cutter, which allows for sharp, detailed engravings, making it an excellent choice for text, logos, and intricate designs. This technique is particularly suitable for applications like signage, trophies, and personalized gifts, where aesthetic detail is paramount. For B2B buyers, considerations include the machine’s spindle speed and the need for a flat work surface to ensure consistent engraving depth.
How Does Raster Engraving Differ from Other Techniques?
Raster engraving operates by following a path similar to that of a printer, making it ideal for reproducing images and complex patterns on various materials. This method is commonly used for decorative items and custom artwork. Buyers should consider the required precision and time investment, as raster engraving can be slower and more intricate than other methods. Ensuring the CNC router is capable of handling the desired materials is also crucial.
What Advantages Does 3D Engraving Offer for Custom Designs?
3D engraving is notable for its ability to create depth and relief in designs, allowing for unique three-dimensional outputs. It is particularly useful for applications like sculptures, custom molds, and prototypes. B2B buyers should be aware that this method requires advanced software and precise setup, which may increase initial costs. However, the ability to produce striking, custom designs can justify the investment for businesses focused on differentiation.
What is the Role of Deep Engraving in Industrial Applications?
Deep engraving involves making deeper cuts to create bold designs, often utilizing larger bits. This technique is frequently employed in industrial settings for marking tools, parts, and mechanical items, where durability and visibility are essential. Buyers should weigh the benefits of strong, long-lasting markings against the potential loss of detail and increased wear on materials. Equipment capable of handling the necessary depth and speed is vital for successful deep engraving.
How Does Laser Engraving Compare to Traditional CNC Methods?
Laser engraving employs laser technology to achieve precision engravings on a wide variety of materials, from wood to metal. It is favored for promotional items, electronics, and jewelry due to its speed and accuracy. However, B2B buyers should consider the higher initial investment and the need for safety measures when using lasers. This method’s efficiency and precision can provide a significant return on investment, particularly for businesses with high-volume engraving needs.
Key Industrial Applications of engraving with cnc router
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of engraving with CNC router | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Custom part labeling and serial number engraving | Enhances traceability and compliance with industry standards | Precision of engraving, material compatibility, machine speed |
| Signage and Branding | Production of promotional and decorative signage | Increases brand visibility and customer engagement | Material choices, durability of the engraving, design flexibility |
| Aerospace and Automotive | Component identification and marking | Ensures safety and quality control through clear markings | Compliance with industry regulations, engraving depth, material type |
| Jewelry and Fashion | Personalization of jewelry and accessories | Adds unique value and customer appeal | Precision tooling, material handling, design software integration |
| Electronics | Circuit board and component engraving | Facilitates assembly and reduces errors in production | Compatibility with various materials, engraving speed, precision requirements |
How is CNC Router Engraving Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, CNC router engraving is crucial for custom part labeling and serial number engraving. This application enhances traceability, ensuring that products comply with industry standards and regulations. Buyers in this sector, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize precision in engraving and compatibility with various materials, as these factors directly affect the quality and compliance of the final products.
What Role Does Engraving Play in Signage and Branding?
Engraving with CNC routers is widely used in the signage and branding industry for creating promotional and decorative signage. This process allows businesses to produce high-quality, visually appealing signs that enhance brand visibility and customer engagement. For international buyers, especially from Europe and the Middle East, considerations such as material durability and design flexibility are essential to ensure the signage withstands environmental factors while effectively communicating the brand message.
How Do Aerospace and Automotive Industries Utilize Engraving?
In the aerospace and automotive industries, engraving is employed for component identification and marking. This application plays a vital role in ensuring safety and quality control by providing clear markings that facilitate maintenance and compliance checks. Buyers in these sectors must focus on compliance with stringent industry regulations, alongside the engraving depth and the types of materials being used, to ensure that markings are both durable and legible.
Why is Personalization Important in Jewelry and Fashion?
CNC router engraving is key in the jewelry and fashion industries for personalizing items such as jewelry and accessories. This customization adds unique value, making products more appealing to consumers. For B2B buyers, especially in regions like Europe, sourcing considerations should include precision tooling and effective material handling to achieve the desired intricate designs without compromising quality.
How is Engraving Beneficial in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics sector, engraving is used for marking circuit boards and components, which aids in assembly and reduces production errors. This application is vital for maintaining efficiency and quality in manufacturing processes. International buyers should consider the compatibility of engraving tools with various materials, alongside precision requirements and engraving speed, to optimize production workflows and minimize waste.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘engraving with cnc router’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Engraving Depth Across Materials
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter issues with inconsistent engraving depth when working with different materials. For instance, while engraving wood, the depth may vary due to the material’s density or grain pattern. This inconsistency can lead to poor-quality products that fail to meet customer expectations, especially in industries like signage or custom gifts where precision is paramount. When the engraving depth is not uniform, it can result in a lack of detail, and the overall aesthetic appeal is compromised, leading to customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, it is crucial to invest in a high-quality CNC router that features a robust Z-axis control. This allows for precise depth adjustments and ensures that the cutter maintains a consistent distance from the workpiece. Additionally, conducting material-specific tests before the actual engraving job can help identify the optimal settings for speed and feed rate. Implementing a toolpath simulation software can also provide insights into how the engraving will appear, allowing for adjustments before the final run. For buyers, sourcing reliable suppliers that offer a variety of bits designed for specific materials—like V-bits for wood and engraving cutters for plastics—can significantly enhance engraving quality and consistency.
Scenario 2: Software Compatibility Issues with CNC Routers
The Problem: Many international B2B buyers face challenges with software compatibility when integrating CNC routers into their production lines. Different CNC machines often use proprietary software, which can lead to difficulties in creating or importing designs. This fragmentation can cause delays in production schedules, as teams spend unnecessary time troubleshooting software issues instead of focusing on actual engraving tasks. Moreover, the learning curve associated with new software can further hinder productivity, especially if the workforce is not adequately trained.
The Solution: To mitigate software compatibility issues, buyers should prioritize CNC routers that support open-source software or widely used CAD/CAM applications. Utilizing software like Inkscape or Fusion 360, which can export files in various formats, can streamline the design process and improve compatibility across different machines. Furthermore, investing in training programs for staff on these platforms can enhance overall operational efficiency. Engaging with suppliers that offer comprehensive support and resources—such as tutorials and community forums—can also assist in overcoming initial learning barriers, ensuring that businesses can maximize their engraving capabilities without frequent disruptions.
Scenario 3: High Tool Wear and Maintenance Costs
The Problem: A significant pain point for B2B buyers in the engraving industry is the rapid wear and tear of cutting tools, which can lead to increased maintenance costs and downtime. For instance, using subpar bits can result in frequent replacements, impacting profitability. Additionally, poorly maintained machines can lead to inconsistent engraving quality, forcing buyers to rework projects and delay delivery timelines. This scenario can be particularly detrimental for businesses that rely on quick turnaround times for custom orders.
The Solution: To reduce tool wear and associated costs, buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality, durable cutting tools specifically designed for the materials they frequently use. For example, investing in carbide-tipped bits can significantly enhance longevity and performance compared to standard steel bits. Regular maintenance checks on the CNC router, including cleaning and lubrication, can also extend the lifespan of both the machine and the tools. Implementing a scheduled tool replacement strategy based on usage metrics can help businesses optimize their operations. Lastly, working closely with suppliers who offer warranties or tool performance guarantees can provide an extra layer of financial protection, ensuring that buyers receive value for their investment while minimizing unexpected expenses.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for engraving with cnc router
What Are the Key Properties of Wood for CNC Router Engraving?
Wood is one of the most commonly used materials for engraving with CNC routers. Its key properties include a relatively low density, which makes it easy to cut and engrave, and a natural aesthetic appeal that enhances the final product’s visual quality. However, wood can vary significantly in hardness and grain structure, affecting engraving detail and depth.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of using wood include its availability, cost-effectiveness, and the ease with which it can be sourced in various types (e.g., pine, oak, mahogany). However, softer woods may not hold intricate details well, requiring larger bits for engraving, which can limit design complexity. Additionally, the potential for warping and splitting during machining can pose challenges for manufacturers.
Impact on Application: Wood is compatible with a wide range of engraving techniques, making it suitable for decorative items, signage, and personalized gifts. B2B buyers should consider the specific type of wood to ensure it meets their design requirements.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America may face challenges regarding the availability of specific wood types due to local regulations on logging and sustainability. Compliance with international standards for wood treatment (such as ISPM 15) is crucial for export purposes.
How Do Metals Perform in CNC Router Engraving?
Metals such as aluminum, brass, and stainless steel are popular choices for CNC engraving due to their durability and ability to hold fine details. Key properties include high strength, resistance to wear and corrosion, and the ability to withstand high temperatures without deforming.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of engraving metals is their longevity and aesthetic appeal, particularly for branding and industrial applications. However, the cost of metal materials can be significantly higher than wood or plastic, and the manufacturing complexity increases due to the need for specialized tools and higher spindle speeds.
Impact on Application: Metals are ideal for applications requiring durability, such as nameplates, industrial components, and decorative items. The choice of metal can impact the engraving depth and detail achievable, with softer metals allowing for finer detail.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN for metal quality. Additionally, understanding local sourcing options and import regulations is essential for cost management.
What Advantages Do Plastics Offer for CNC Router Engraving?
Plastics, including acrylic, polycarbonate, and ABS, are increasingly used for CNC engraving due to their versatility and range of colors. Key properties include lightweight, resistance to moisture, and the ability to be easily molded or shaped.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of using plastics include lower costs and ease of machining compared to metals. However, softer plastics may melt or deform during engraving, requiring careful control of speed and tool sharpness. Additionally, the aesthetic finish may not match that of metal or wood.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for a variety of applications, including signage, promotional items, and custom parts. The choice of plastic can significantly affect the engraving’s clarity and detail.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of specific plastics in their region and any environmental regulations concerning plastic use. Compliance with standards such as ISO for plastic quality can also be a concern.
Summary Table for Material Selection in CNC Router Engraving
| Material | Typical Use Case for engraving with cnc router | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Decorative items, signage, personalized gifts | Cost-effective and widely available | Limited detail retention in softwoods | Low |
| Metal | Nameplates, industrial components, decorative items | High durability and aesthetic appeal | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Plastic | Signage, promotional items, custom parts | Lightweight and versatile | Potential for melting or deformation | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding the materials best suited for their CNC engraving projects, ensuring compliance with regional standards and preferences while maximizing product performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for engraving with cnc router
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for CNC Router Engraving?
Engraving with CNC routers involves several critical manufacturing stages that ensure precision and quality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers effectively.
1. Material Preparation: How Is the Material Chosen and Processed?
The first step in the engraving process is material selection, which is crucial for achieving the desired results. Common materials include wood, metals (such as aluminum and stainless steel), and various plastics. Once selected, materials are cut to size and surface-prepared to ensure they are flat and free from defects, as even minor inconsistencies can lead to poor engraving quality.
After cutting, materials may undergo a treatment process, such as sanding or chemical cleaning, to enhance adhesion and finish quality. This preparation stage is essential for ensuring that the engraving tool interacts optimally with the material.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Achieve Accurate Engraving?
The forming stage is where the actual engraving occurs. CNC routers utilize a high-speed spindle (typically exceeding 12,000 RPM) combined with various cutting tools, such as V-bits, engraving cutters, or ball end mills, to create precise engravings.
During this stage, the CNC machine follows a programmed toolpath, which is generated using CAD/CAM software. The software determines the depth and speed of the engraving based on the material and desired finish. Real-time monitoring of the engraving process is often employed to ensure accuracy and adjust parameters as necessary.
3. Assembly: How Are Engraved Parts Processed Further?
In many cases, engraved parts may require additional assembly steps, especially if they are components of a larger product. This can involve combining engraved pieces with other manufactured parts, which may include fastening, soldering, or additional machining.
Quality at this stage is paramount, as any misalignment or inconsistency can affect the overall functionality and aesthetics of the final product. Therefore, precise measurements and alignment techniques are employed to ensure that all components fit together seamlessly.
4. Finishing: What Techniques Enhance the Final Appearance of Engraved Products?
Finishing processes are critical in enhancing the aesthetic appeal of engraved items. Techniques may include polishing, coating, or applying treatments to prevent corrosion, especially for metal engravings.
For wood, finishing might involve staining or sealing to protect the engraved surface while enhancing its visual impact. The choice of finishing technique depends on the material and the intended use of the product. This stage not only improves the look but also adds durability, making the final product more market-ready.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in CNC Router Engraving?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital for ensuring that the engraving process meets both international standards and client specifications. Various QA techniques and standards apply at different stages of manufacturing.
What International Standards Are Relevant for CNC Engraving?
Many companies adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards ensures that companies maintain consistent quality and continually improve their processes.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may apply, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe, which indicates compliance with health and safety standards. Companies operating in specialized sectors, like aerospace or oil and gas, may also need to comply with API standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Engraving?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to monitor and verify quality at each stage. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they are processed. Suppliers must provide certification for materials, and samples may be tested for compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the engraving process, regular checks are performed to ensure that the CNC machine operates within set parameters. This can include monitoring spindle speed, engraving depth, and tool wear.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After engraving and finishing, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to assess the quality of the finished product. This may involve visual inspections, dimensional checks, and functional tests to confirm that the product meets client specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in CNC Engraving Quality Control?
Testing methods used in QC can vary based on the material and the complexity of the engraving. Common methods include:
-
Dimensional Measurement: Tools such as calipers and gauges are used to verify that engraved dimensions match specifications.
-
Surface Finish Testing: Techniques such as roughness testers assess the smoothness and quality of the engraving.
-
Durability Testing: For products subject to wear, tests may simulate environmental conditions to assess long-term performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes, QC practices, and compliance with international standards firsthand.
-
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed QA reports, including documentation of inspections, testing results, and certifications. This transparency helps buyers assess the reliability of the supplier.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes and product compliance.
What Are the Specific QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider various certification requirements that may differ by region. For instance, products imported into the EU must meet CE marking requirements, while products in the U.S. may need to comply with FDA regulations if they are food-related.
Additionally, cultural and regulatory differences can impact supplier practices. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards applicable in their target market to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for CNC router engraving is essential for B2B buyers. This knowledge equips them to make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their specifications and international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘engraving with cnc router’
To support B2B buyers in the procurement of CNC engraving services, this guide offers a practical checklist that outlines critical steps to follow. By adhering to this checklist, buyers can ensure they select the right equipment and partners to meet their engraving needs efficiently.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for ensuring that the CNC router meets your specific engraving requirements. Consider factors such as the materials to be engraved (wood, metal, or plastic), the desired engraving depth, and the precision needed for your projects. Defining these parameters will guide your equipment selection and supplier discussions.
Step 2: Research Suitable CNC Router Models
Not all CNC routers are created equal; some are better suited for engraving than others. Focus on routers with high-speed spindles (over 12,000 RPM) and a reputation for accuracy and stability. Look for models that can handle your material types effectively, as this will influence the quality and efficiency of the engraving process.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, it is crucial to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in your industry or geographical region. This not only helps in assessing their capabilities but also provides insights into their reliability and customer service.
Step 4: Check for Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your selected suppliers have the necessary certifications that demonstrate adherence to international quality and safety standards. Certifications like ISO 9001 can be indicators of a supplier’s commitment to quality management. Compliance with local regulations is also essential, particularly in regions with stringent manufacturing laws.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing your supplier, request samples or prototypes of their engraving work. This step allows you to assess the quality of their engraving firsthand and ensures that their output meets your expectations. It’s an opportunity to evaluate their attention to detail and the overall finish of the engraved products.
Step 6: Evaluate Software Compatibility
Consider the software solutions that your suppliers use for CNC engraving. A compatible software system will streamline the engraving process and facilitate easier communication regarding design specifications. Ensure that they utilize efficient CAD/CAM software that can handle your design files without complications.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Establish clear lines of communication with your supplier, including regular updates on project status and responsiveness to inquiries. This will help in addressing any issues that may arise promptly and ensure that projects stay on track.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing CNC engraving services more effectively, ensuring that they choose the right partners and technologies to meet their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for engraving with cnc router Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Router Engraving?
When considering CNC router engraving, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials—wood, metal, or plastic—directly affects costs. High-quality materials typically lead to better engraving results but can increase initial expenditure. For instance, engraving metals like aluminum and brass tends to be more expensive than wood due to the material’s hardness and the need for specialized tooling.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for operating CNC machines effectively. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region, expertise level, and the complexity of the engraving project. In many regions, the labor force may require training or certification, which adds to the overall labor cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Overhead costs can fluctuate based on the operational efficiency of the engraving facility.
-
Tooling: The type and quality of cutting tools, such as V-bits or engraving cutters, directly influence engraving precision and durability. Investing in high-quality tooling can enhance productivity but requires a higher upfront investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the engraving meets specified quality standards incurs additional costs. Implementing stringent QC measures is essential, especially for international buyers who may need to comply with various certification standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling fees can vary widely, particularly for international transactions. These costs should be factored into the overall budget, especially when dealing with bulky machinery or large quantities of engraved products.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a margin to cover risks and ensure profitability. Understanding the margin expectations of suppliers can aid in negotiation efforts.
What Influences Pricing in CNC Router Engraving?
Several factors can significantly affect pricing in CNC router engraving:
-
Volume/MOQ: Buyers often benefit from lower unit costs when ordering in bulk. Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary by supplier, influencing the overall price structure.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized engraving projects may require additional setup or specialized tools, impacting costs. Clear communication of specifications can help manage expectations and pricing.
-
Material Choices: As mentioned earlier, the choice of material plays a pivotal role in cost. Harder materials typically require more robust tooling and can increase labor time.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers that offer certified materials or processes may charge a premium. Certifications can be essential for international buyers who need to comply with local regulations.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their reputation, reliability, and service offerings. However, newer suppliers might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, risk, and costs, which can significantly impact pricing.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs in CNC Router Engraving?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can help optimize costs:
-
Negotiation: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices and terms. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially for large orders or long-term contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, replacement, and operational costs when assessing the value of a supplier.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and economic factors that may affect costs. For example, currency fluctuations can impact pricing for international buyers.
-
Build Relationships: Developing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and priority service. Trust can often translate into better terms and conditions.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures mentioned herein are indicative and can vary widely based on specific project requirements, supplier agreements, and market conditions. Always conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes before making sourcing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing engraving with cnc router With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternative Engraving Solutions
In the realm of engraving, businesses are often faced with various technological options that can meet their specific needs. While engraving with CNC routers has gained popularity due to its precision and versatility, it is essential to explore alternative solutions that may offer unique advantages. This analysis compares engraving with CNC routers against laser engraving and manual engraving methods, providing B2B buyers with insights into each option’s performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Engraving With CNC Router | Laser Engraving | Manual Engraving |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; suitable for various materials | Extremely high precision; quick for detailed designs | Variable precision; dependent on skill level |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower operational costs | Higher initial investment; operational costs vary | Low initial cost; high labor cost over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup and programming; user-friendly software available | Simple setup; requires skilled operators | Requires no machinery; skill-based |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular calibration needed | Low; minimal maintenance required | High; frequent tool replacement needed |
| Best Use Case | Custom parts, signage, and 3D designs | High-detail designs, engraving on metals and plastics | Artistic projects and one-off designs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Pros and Cons of Laser Engraving?
Laser engraving technology utilizes a focused beam of light to engrave materials, offering exceptional precision and speed. One of the significant advantages of laser engraving is its ability to handle intricate designs and detailed patterns with ease, making it ideal for branding and fine art applications. However, the initial investment for laser engraving machines can be substantial, and operational costs, including maintenance and consumables, may add up. Additionally, while laser engravers can work with a variety of materials, they may struggle with thicker substrates compared to CNC routers.
How Does Manual Engraving Compare?
Manual engraving involves the use of hand tools to create designs on materials. This method is often employed for bespoke projects or artistic endeavors, where the human touch is essential. The primary advantage of manual engraving is its low initial cost and the ability to produce unique, one-of-a-kind pieces. However, the precision and consistency of manual engraving can vary significantly based on the engraver’s skill level. Furthermore, the time required to complete projects can lead to higher labor costs, making it less efficient for large-scale production compared to automated methods like CNC and laser engraving.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Engraving Solution
When selecting an engraving solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific requirements, including the type of materials they work with, the desired precision, and budget constraints. CNC routers offer a balanced approach with moderate investment and operational costs, making them suitable for various applications. Laser engraving provides unmatched detail and speed but may require a higher initial investment. In contrast, manual engraving can be a cost-effective choice for unique projects, although it lacks the efficiency of automated methods. Ultimately, the decision should align with the buyer’s production goals, material needs, and long-term business strategy.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for engraving with cnc router
When engaging in CNC router engraving, understanding the essential technical properties and industry terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This section outlines critical specifications and common jargon that international B2B buyers should be aware of.
What Are the Key Technical Properties for CNC Router Engraving?
-
Material Compatibility
– CNC routers can engrave a variety of materials, including wood, plastics, and metals. Understanding the material compatibility is essential for selecting the right machine and cutters. For example, softer woods may require deeper engravings, while harder metals like stainless steel may need specialized cutters to achieve fine detail. -
Spindle Speed (RPM)
– The spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), is vital for engraving efficiency. A high-speed spindle (typically over 12,000 RPM) is crucial when using small cutters, as it allows for quicker and cleaner cuts. Buyers should prioritize machines with adjustable RPM settings to accommodate various materials and engraving styles. -
Tolerance Levels
– Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In engraving, tighter tolerances lead to better detail and finish quality. Understanding tolerance levels is important for industries requiring precise engravings, such as aerospace or medical applications. -
Cutting Depth
– The cutting depth determines how deep the engraving will be. Shallow engravings are often preferred for decorative purposes, while deeper cuts may be necessary for functional items like measurements or alignment points. Buyers should evaluate the machine’s capability to adjust cutting depth according to project requirements. -
Cutter Types and Specifications
– Different cutters, such as V-bits, engraving cutters, and ball end mills, are designed for specific engraving tasks. Each type has unique specifications, such as tip angles and flute count, which impact the engraving’s precision and finish. Selecting the appropriate cutter is vital for achieving the desired outcome. -
Flatness and Rigidity of the Machine
– A CNC router must have a flat and rigid structure to ensure that the cutter remains parallel to the engraving surface. Any deviations can lead to inconsistent engraving depth, affecting the overall quality. Buyers should assess the machine’s build quality and stability before purchase.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Router Engraving?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In the context of CNC routers, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reputable suppliers and ensure quality components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially when considering bulk purchases of CNC machines or engraving tools. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This term is critical for buyers looking to compare prices and negotiate terms before making a purchasing decision. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk during the transportation of CNC equipment. -
CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
– CAD/CAM refers to software used for designing and manufacturing processes. In CNC engraving, CAD software is used to create designs, while CAM software generates the toolpaths for the engraving process. Understanding CAD/CAM systems is crucial for integrating design and manufacturing workflows. -
Toolpath
– The toolpath is the trajectory that the cutter follows during the engraving process. Knowledge of toolpaths is essential for optimizing engraving speed and accuracy, ensuring efficient use of materials and minimizing waste.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making process and ensure successful CNC router engraving projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the engraving with cnc router Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends Influencing CNC Router Engraving?
The CNC router engraving sector is experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. The increasing demand for customization in products—from promotional materials to intricate designs in furniture—has propelled the need for efficient engraving solutions. With advancements in technology, CNC routers have become more accessible and affordable, allowing small to medium enterprises (SMEs) in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East to leverage these tools for competitive advantage. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has amplified the need for unique, branded items, further stimulating demand for engraving services.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the integration of AI and machine learning into CNC operations, enhancing precision and reducing waste. These technologies facilitate real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, ensuring optimal performance. Furthermore, open-source software solutions for CNC programming are gaining traction, enabling businesses to customize their engraving processes without incurring high software licensing costs. International buyers should also note the growing significance of multi-material capabilities in CNC routers, as versatility in engraving different substrates—from metals to plastics—becomes a sought-after feature.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the CNC Router Engraving Sector?
Sustainability is increasingly shaping the landscape of the CNC router engraving industry. International buyers are becoming more conscious of their environmental impact, prompting a shift towards sustainable practices. The use of eco-friendly materials, such as responsibly sourced wood and recyclable plastics, is gaining traction. Additionally, suppliers are expected to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability through certifications like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and ISO 14001, which validate ethical sourcing and environmental management practices.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, especially in regions prone to resource exploitation. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who prioritize transparency and social responsibility, ensuring that their engraving processes do not contribute to environmental degradation or violate labor rights. This approach not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty. As the market evolves, businesses that prioritize sustainability in their sourcing strategies will likely gain a competitive edge.
What Is the Historical Context Behind CNC Router Engraving?
The evolution of CNC router engraving can be traced back to the early days of computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing (CAM) technologies in the late 20th century. Initially, these machines were primarily utilized in large-scale industrial applications, but as technology advanced, they became more compact and affordable, opening doors for smaller enterprises and hobbyists. The introduction of user-friendly software further democratized access to CNC engraving, allowing a broader range of businesses to incorporate these machines into their operations.
In the past decade, the surge in demand for personalized products and rapid prototyping has transformed the engraving landscape. Today, CNC routers are not only essential tools in manufacturing but also key players in creative industries, enabling artisans and designers to produce intricate designs with precision. This historical context highlights the shift from traditional engraving methods to modern, technology-driven solutions, illustrating the significant role CNC routers play in today’s marketplace.
Conclusion
In summary, international B2B buyers must stay attuned to the dynamic trends and market drivers in the CNC router engraving sector. With a focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can position themselves favorably in a competitive landscape. Understanding the historical evolution of this technology also offers valuable insights into its future trajectory, ensuring that companies are well-equipped to meet the demands of an increasingly personalized and environmentally-conscious market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of engraving with cnc router
-
How do I choose the right CNC router for engraving?
Choosing the right CNC router for engraving involves evaluating factors such as spindle speed, accuracy, and material compatibility. Look for machines with a high-speed spindle (over 12,000 RPM) to handle small engraving bits efficiently. Additionally, ensure the machine has a flat working surface to maintain consistent engraving depth. Consider the materials you plan to engrave—some routers excel with wood, while others are better for metals or plastics. Research and compare different brands and models to find one that meets your specific engraving needs. -
What materials can I engrave with a CNC router?
CNC routers can engrave a variety of materials, including wood, plastics, and metals. For wood, softer varieties may require deeper cuts to achieve detail, while harder woods can hold finer engravings. Common metals suitable for engraving include aluminum, stainless steel, and brass. When working with plastics, opt for harder types like acrylic or polycarbonate for best results. Always consider the material’s properties to select the appropriate cutter and settings for optimal engraving quality. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC engraving services?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC engraving services can vary significantly between suppliers. Some manufacturers may accept small batches, while others may set higher MOQs to justify production costs. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and understand their capabilities. If you require a small order, consider looking for suppliers who specialize in prototyping or custom projects, as they may be more flexible with MOQs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in CNC engraving?
To ensure quality assurance in CNC engraving, request samples from potential suppliers before placing a large order. This allows you to assess their engraving precision, material handling, and finishing quality. Additionally, inquire about their quality control processes, such as inspection methods and compliance with international standards. Establish clear specifications for your project, including tolerances and finishes, to avoid misunderstandings and ensure the final product meets your expectations. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing CNC engraving services?
Payment terms for CNC engraving services can vary widely, depending on the supplier and the scale of your order. Common arrangements include upfront deposits (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer payment upon receipt of goods or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). Always clarify payment terms during negotiations, and consider using escrow services for large orders to protect your investment. -
What software do I need for CNC engraving, and is it user-friendly?
For CNC engraving, software like Carbide Create or open-source options like Inkscape and PyCAM are commonly used. These programs are designed to create 2D designs and toolpaths for engraving. Most of these software options come with user-friendly interfaces, making them accessible even for beginners. Ensure that your chosen software is compatible with your CNC machine and provides the features you need for your specific engraving projects. -
How do I vet potential suppliers for CNC engraving services?
Vetting potential suppliers involves assessing their experience, capabilities, and reputation. Start by checking their portfolio and client testimonials to gauge their quality of work. Request references and conduct background checks on their business practices. Additionally, inquire about their production capacity, lead times, and responsiveness to ensure they can meet your needs. A site visit or virtual tour can also provide insights into their operations and quality control processes. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing CNC engraving internationally?
When sourcing CNC engraving services internationally, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery times. Ensure that your supplier is familiar with international shipping and can provide reliable logistics solutions. Discuss packaging requirements to prevent damage during transport, and confirm that the supplier can handle necessary documentation for customs clearance. Establish clear communication channels to track your order’s progress and address any potential issues promptly.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Engraving With Cnc Router Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carbide 3D – Nomad Desktop CNC
Domain: carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: CNC engraving is a process that creates shallow cuts for fine detail, often used for personalization, branding, or adding markers. Ideal CNC machines for engraving include high-speed spindles (over 12,000 RPM) and accurate, flat setups. Carbide 3D offers the Nomad Desktop CNC for small items and the Shapeoko CNC Router for larger items. Materials suitable for engraving include wood, plastics (like…
2. Instructables – CNC Router Solutions
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC Router, Open Source Software, CAELinux 2013, Inkscape 0.91, Hershey Text, PyCAM 0.5.1, CAMotics 1.0.6, LinuxCNC, V-bit
3. CNC Routers vs. Laser Engravers – Key Capabilities
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the capabilities of CNC routers versus laser engravers. Key points include: CNC routers are more versatile and can perform deep relief work, while lasers primarily do surface engraving. CO2 and fiber lasers can engrave metals but may require high investment for industrial-grade machines. The current engraving operation includes award plaques, trophies, and signage, p…
4. Monoprice – Benchtop CNC Router Kit
Domain: monoprice.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: This company, Monoprice – Benchtop CNC Router Kit, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. OpenBuilds – 3 Flutes V Groove & 3D Sign Maker CNC Bit Kit
Domain: us.openbuilds.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: 1. 3 Flutes V Groove Solid Carbide 60 Degree 1/4″ SharkBits – Price: $17.99 (MSRP: $29.99) – Ideal for creating signs and decorative lettering with V carving software.
2. 3D Sign Maker 4 Pc CNC Bit Kit V2 SharkBits – Price: $80.99 (MSRP: $134.99) – Includes essential bits for CNC sign making with polished cutting edges for longer tool life.
3. Wood V-Cutting/Carving/Engraving 3 Pc CNC Bit Kit V2 S…
6. CNC Cookbook – CNC Engraving Machines
Domain: cnccookbook.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: CNC Engraving is the process of carving designs into hard surfaces using CNC machines. There are various types of CNC engraving machines, including laser engravers, milling machines, and CNC routers. Laser engravers can cut materials or discolor them through laser marking. Common materials for laser engraving include wood, leather, plastic, and metals. The most common laser types are CO2 lasers, w…
7. OMNI – CNC Router
Domain: omni-cnc.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: OMNI CNC Router is a versatile engraving machine designed for woodworking, drilling, and engraving. It allows for intricate designs on plaques, trophies, and medals. The CNC router operates on CAD files, enabling precise engraving on various materials including brass, copper, wood, aluminum, stainless steel, glass, and anodized aluminum. It engraves in three dimensions (X, Y, Z) for detailed desig…
8. CNC-STEP – High-Z S-Serie Engraving Machines
Domain: cnc-step.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC Engraving Machines: High-Z S-Serie (up to 1000x600mm), GranitoGrav Module (photo engraving), applications for deep 2D and 3D engravings in materials like stainless steel, aluminium, granite, marble, and wood. Capabilities include engraving signs, nameplates, jewelry, round surfaces, and glass. Methods include VCarving and 2D scratch engravings. CNC engraving machines utilize CAD-CAM software f…
9. SainSmart – Genmitsu CNC Routers & Laser Engravers
Domain: sainsmart.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Genmitsu CNC & Engraving products include various CNC routers and laser engravers such as Cubiko 4040-PRO, MAX PROVerXL 4×4, Kiosk 2.5W~10W, Falcon A1 10W, and L8 40W/20W. The collection also features parts and accessories like laser upgrade parts, spindle and stepper motors, extension kits, spoilboard clamps, controllers, and dust collection replacements. Additional offerings include milling bits…
10. Zoytek – Minimillr 4015PRO CNC Router
Domain: minimillr.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Minimillr 4015PRO CNC Router; designed and manufactured in the UK by Zoytek Ltd; suitable for engraving images using LaserGRBL software; uses 0.1mm tip 20 degree 3mm carbide engraving bits; recommended engraving speed of 125mm/min; supports various materials including aluminium; requires clamping of workpiece on the router bed; Z-axis movements for engraving; finished pieces may require cleaning w…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for engraving with cnc router
In conclusion, strategic sourcing in the CNC engraving sector offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the nuances of CNC router engraving—including machine capabilities, material compatibility, and cutter selection—companies can optimize their procurement processes to achieve higher efficiency and quality in production.
Investing in high-speed spindles, accurate machinery, and suitable software solutions not only enhances engraving precision but also supports the scalability of operations. Furthermore, the ability to work with diverse materials such as wood, metals, and plastics opens up new avenues for customization and branding, essential for gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.
As the global demand for personalized products continues to rise, now is the time for B2B buyers to leverage strategic sourcing to refine their CNC engraving capabilities. By collaborating with trusted suppliers and investing in advanced technologies, businesses can position themselves for growth and innovation in this dynamic industry. Embrace the future of engraving with CNC routers, and explore the limitless possibilities it offers for your business.