Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for easy to use cad software
In today’s fast-paced global marketplace, sourcing easy-to-use CAD software is crucial for businesses looking to streamline their design processes and enhance productivity. However, with numerous options available, B2B buyers often face challenges in identifying the right solutions that meet their specific needs, especially in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This comprehensive guide aims to empower international buyers by exploring various types of CAD software, their applications across industries, and essential factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
From sophisticated 3D modeling tools to intuitive 2D drafting solutions, the guide delves into the functionalities and unique advantages of popular CAD software options, ensuring you find the ideal fit for your organization. It also addresses critical aspects such as cost considerations, licensing models, and support services, providing you with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers from regions like Nigeria and Brazil can navigate the complexities of the CAD software landscape, ensuring they select solutions that not only enhance design capabilities but also align with their business goals. Whether you are a small startup or an established enterprise, understanding the nuances of CAD software will position your organization for success in an increasingly competitive environment.
Understanding easy to use cad software Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2D CAD Software | Focus on 2D drafting, easy interface, often less expensive | Architectural drawings, schematics | Pros: Affordable, quick learning curve. Cons: Limited 3D capabilities. |
| 3D CAD Software | Advanced modeling tools, simulation capabilities | Product design, prototyping | Pros: Detailed visualization, robust features. Cons: Steeper learning curve, higher cost. |
| Cloud-Based CAD | Accessible from anywhere, real-time collaboration | Remote teamwork, flexible project management | Pros: Enhanced collaboration, no installation required. Cons: Reliant on internet connectivity. |
| BIM Software | Integrated design and construction management tools | Large-scale construction projects | Pros: Streamlined workflows, improved accuracy. Cons: Complexity, higher initial investment. |
| Educational CAD Tools | Free or discounted software for students and educators | Training, skill development | Pros: Cost-effective for institutions, fosters learning. Cons: May lack advanced features. |
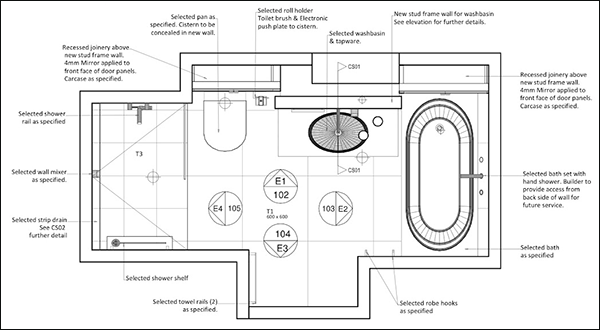
What Characteristics Define 2D CAD Software for B2B Buyers?
2D CAD software is designed primarily for creating detailed drawings and schematics. Its user-friendly interface allows even novice users to produce professional-quality drafts quickly. This type of software is particularly suitable for industries like architecture and engineering, where precise 2D representations are essential. When considering a purchase, businesses should evaluate the software’s compatibility with existing systems and the cost-effectiveness of licensing options.
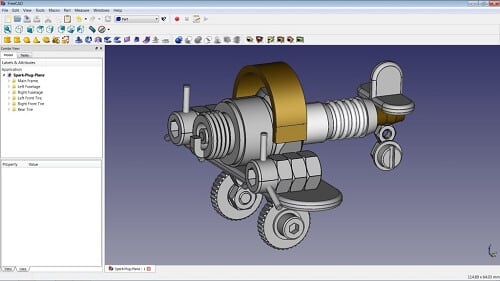
How Does 3D CAD Software Meet Advanced Design Needs?
3D CAD software offers comprehensive tools for creating complex models, simulations, and prototypes. This software is ideal for product design and manufacturing sectors, where visualizing a product before production can save time and costs. B2B buyers should consider their team’s expertise, as the learning curve can be significant. Additionally, the investment required for robust 3D solutions is often higher, necessitating careful budgeting.
What Advantages Does Cloud-Based CAD Provide for Collaboration?
Cloud-based CAD solutions allow teams to access design files from any location, promoting real-time collaboration among remote teams. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in today’s globalized work environment, where teams may be spread across different regions. However, businesses should assess the reliability of their internet connections, as these tools require stable access to function effectively. The ability to collaborate seamlessly can justify the investment for many organizations.
Why is BIM Software Essential for Large-Scale Projects?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) software integrates design and construction management, making it invaluable for large projects. It enhances collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned throughout the project lifecycle. While BIM software can be complex and require a higher initial investment, its ability to streamline workflows and improve project outcomes can lead to significant long-term savings for businesses.
How Can Educational CAD Tools Benefit Institutions?
Educational CAD tools provide free or discounted access to software for students and educators, making them an attractive option for institutions looking to foster learning and skill development. These tools often come with essential features that allow users to learn foundational design principles. However, businesses and educational institutions must consider whether these tools meet their advanced needs, as they may lack some functionalities found in professional-grade software.
Key Industrial Applications of easy to use cad software
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of easy to use cad software | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | 2D drafting and 3D modeling for building designs | Streamlined design processes and enhanced collaboration | User-friendly interface, integration with BIM tools |
| Manufacturing | Product design and prototyping | Faster time-to-market and reduced design errors | Compatibility with existing manufacturing tools and systems |
| Civil Engineering | Infrastructure design and planning | Improved project accuracy and compliance with regulations | Support for civil engineering standards and local codes |
| Media & Entertainment | Animation and 3D modeling for visual effects | Enhanced creativity and efficiency in content creation | Support for collaborative workflows and rendering capabilities |
| Education | Teaching CAD principles through accessible tools | Increased engagement and skill development among students | Availability of educational licenses and training resources |
How is Easy-to-Use CAD Software Transforming Architecture?
In the architecture sector, easy-to-use CAD software facilitates both 2D drafting and 3D modeling, allowing architects to visualize their designs more effectively. This software streamlines the design process, enabling quick iterations and real-time collaboration among team members. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, the ability to integrate these tools with Building Information Modeling (BIM) systems is crucial. This integration ensures compliance with local building codes and standards, ultimately leading to enhanced project accuracy and efficiency.
What Role Does CAD Software Play in Manufacturing?
Manufacturers leverage easy-to-use CAD software for product design and prototyping, which accelerates the development cycle. The intuitive nature of these tools minimizes design errors, leading to faster time-to-market for new products. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it’s essential to consider compatibility with existing manufacturing systems and tools. This ensures that the CAD software can seamlessly integrate into the production workflow, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
How is CAD Software Beneficial in Civil Engineering?
In civil engineering, easy-to-use CAD software is instrumental in infrastructure design and planning. It allows engineers to create detailed plans that comply with local regulations, improving project accuracy and minimizing risks associated with design errors. Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Brazil should prioritize software that supports local civil engineering standards, as this can significantly impact project approval and execution timelines.
In What Ways Does CAD Software Enhance Media and Entertainment?
The media and entertainment industry utilizes easy-to-use CAD software for animation and 3D modeling, which enhances the creative process. These tools enable artists to produce high-quality visual effects more efficiently. For international B2B buyers, especially in Europe, the ability to support collaborative workflows and advanced rendering capabilities is a key consideration. This ensures that teams can work together effectively, regardless of geographical barriers, ultimately leading to more innovative content creation.
How Does CAD Software Impact Education?
In the educational sector, easy-to-use CAD software plays a vital role in teaching CAD principles to students. The accessibility of these tools increases engagement and skill development among learners. For institutions in Africa and South America, sourcing software that offers educational licenses and comprehensive training resources is critical. This enables schools to provide students with hands-on experience using industry-standard tools, preparing them for future careers in design and engineering.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘easy to use cad software’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming Resistance to New Technology Adoption
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when integrating new CAD software into their existing workflows. Employees may resist adopting new tools due to fear of the learning curve or concern that it will disrupt their established processes. This resistance can be especially pronounced in organizations with a long history of using traditional methods or legacy software. For instance, a construction firm in Nigeria may have a team accustomed to manual drafting techniques, making it difficult to transition to a more advanced, yet user-friendly, CAD software like AutoCAD or DraftSight. This reluctance can lead to inefficiencies, wasted resources, and ultimately, a failure to realize the potential benefits of modern design tools.
The Solution:
To facilitate a smoother transition, it’s vital to implement a comprehensive training program that emphasizes the ease of use and advantages of the new software. Start by identifying “champions” within the team—individuals who are tech-savvy and can advocate for the new system. Pair these champions with those who are less comfortable with technology. Offering hands-on workshops that demonstrate the software’s capabilities in real-world scenarios can alleviate fears and showcase its intuitive features. Additionally, consider providing access to online tutorials, webinars, and community forums where users can seek support and share experiences. Highlighting success stories from similar industries can also motivate users to embrace the change.
Scenario 2: Managing Collaboration Across Diverse Teams
The Problem:
In global projects, especially in regions like South America and the Middle East, teams often face difficulties in collaboration due to varying software capabilities and file compatibility issues. For example, an engineering firm in Brazil may work with partners in Europe who use different CAD tools, leading to frustration over file formats and project alignment. This disjointed collaboration can slow down project timelines and increase costs, as teams spend time troubleshooting compatibility rather than focusing on design innovation.
The Solution:
To enhance collaboration, select CAD software that supports a wide range of file formats and offers cloud-based solutions. Tools like Autodesk Fusion and DraftSight facilitate seamless sharing of designs, allowing teams to work on the same files in real time, regardless of their geographic location. Establish clear guidelines on file management and version control to prevent confusion. Moreover, utilizing integrated communication tools within the software can streamline feedback and discussions, ensuring all team members are aligned. Encourage regular check-ins and collaborative sessions to build rapport among team members and foster a unified project approach.
Scenario 3: Budget Constraints Limiting Software Options
The Problem:
Budget constraints are a significant concern for many B2B buyers, particularly in developing regions such as Africa and South America. Companies may struggle to justify the costs associated with high-end CAD software, fearing that it will strain their financial resources. For instance, a small architecture firm in Nigeria may be hesitant to invest in premium software when free or low-cost alternatives are available, even if those alternatives lack essential features. This dilemma can hinder their ability to compete effectively in the market.
The Solution:
Buyers should carefully evaluate their specific needs against the features offered by different software solutions. Consider starting with free or low-cost options like Tinkercad or Autodesk’s educational licenses, which provide robust tools for beginners and can be upgraded as the firm grows. Additionally, explore licensing models that offer flexibility, such as subscription plans, which can help manage cash flow better than one-time purchases. Engage with vendors to discuss potential discounts or bundled offerings that may be available for startups or small businesses. By strategically assessing software needs and exploring various pricing options, firms can find a solution that fits their budget while still enabling them to produce high-quality work.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for easy to use cad software
What Are the Key Materials for Easy to Use CAD Software?
When selecting easy-to-use CAD software, understanding the materials that can impact product performance is crucial for B2B buyers. This analysis focuses on four common materials—plastic, aluminum, steel, and composite materials—highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international markets.
How Does Plastic Impact CAD Software Usability?
Key Properties: Plastics are lightweight and offer good resistance to corrosion and chemicals. They typically have a lower temperature rating compared to metals, but advancements have improved their thermal stability.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic is its low cost and ease of manufacturing, making it suitable for rapid prototyping and small-scale production. However, plastics can be less durable than metals and may not withstand high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: CAD software that supports plastic design often includes features for simulating injection molding and other manufacturing processes. This is particularly relevant for industries like consumer goods and automotive.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM D638 for tensile properties is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America may prefer CAD solutions that facilitate local manufacturing processes and materials.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in CAD Software Development?
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It typically has a higher temperature rating than plastics, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of aluminum is its versatility and durability, which make it ideal for structural applications. However, it is more expensive than plastic and can be more complex to machine, requiring specialized tools.
Impact on Application: CAD software that includes features for aluminum design can help in optimizing weight and strength, particularly in aerospace and automotive sectors. This is crucial for projects requiring precise engineering calculations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the CAD software complies with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. Understanding local market preferences for lightweight materials can also influence purchasing decisions.
Why Choose Steel for CAD Software Projects?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high strength and durability, making it suitable for applications requiring high pressure and temperature ratings. It is also resistant to wear and tear.
Pros & Cons: The major advantage of steel is its robustness, which makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications in construction and manufacturing. However, it is heavier and more expensive than both plastic and aluminum, and its machining can be complex.
Impact on Application: CAD software that supports steel design often includes features for stress analysis and structural integrity assessments, which are critical in construction and industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A36 for structural steel is vital. Buyers from Europe may also need to consider EN standards, while those in the Middle East may focus on local building codes.
How Do Composites Enhance CAD Software Functionality?
Key Properties: Composite materials combine two or more constituents to achieve superior properties, such as high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance. They can be tailored for specific applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their lightweight and customizable nature, making them suitable for advanced applications in aerospace and automotive industries. However, they can be costly and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: CAD software that supports composite design often includes features for simulating material behavior under various conditions, which is essential for high-performance applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding local regulations and standards for composite materials, such as ASTM D3039 for tensile properties, is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America may need to consider the availability of composite materials locally.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Easy to Use CAD Software
| Material | Typical Use Case for easy to use CAD software | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Rapid prototyping, consumer goods | Low cost and easy to manufacture | Less durable, lower temperature rating | Low |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive components | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive, complex to machine | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty construction, industrial applications | High strength and durability | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Composite | Aerospace, high-performance automotive | Lightweight and customizable | Costly and requires specialized processes | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for CAD software, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their specific industry needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for easy to use cad software
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for Easy-to-Use CAD Software?
When it comes to easy-to-use CAD software, the manufacturing processes typically encompass several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers who seek reliable software solutions that can meet their specific needs.
How Does Material Preparation Impact CAD Software Development?
Material preparation in CAD software development involves the selection and optimization of software components and libraries. Developers often utilize advanced programming languages and frameworks to create a robust architecture that supports user-friendly interfaces. The choice of materials, in this context, refers to the underlying technology stack, which can include cloud-based solutions for better accessibility and collaboration.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in CAD Software Creation?
Forming techniques in CAD software development refer to the methodologies employed to create the software’s core functionalities. Agile development methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, are commonly used to ensure that the software can adapt to evolving user needs. This iterative approach allows for continuous integration and testing, making it easier to implement user feedback and improve the software’s usability.
How Is the Assembly Stage Critical for CAD Software Functionality?
The assembly stage in CAD software development involves integrating various components, such as user interfaces, design tools, and collaboration features. Effective integration is essential to ensure that all elements work seamlessly together. This stage often includes rigorous testing to identify any potential bugs or usability issues. A well-assembled CAD software not only enhances the user experience but also ensures that the software meets industry standards.
What Finishing Techniques Enhance the User Experience in CAD Software?
Finishing techniques in CAD software development focus on polishing the user interface and optimizing performance. This may involve refining graphics, improving load times, and ensuring compatibility across different devices and operating systems. In addition, user experience (UX) design plays a pivotal role in this stage, as intuitive navigation and clear functionalities are crucial for user satisfaction.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Easy-to-Use CAD Software?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component in the manufacturing process of easy-to-use CAD software. It ensures that the final product meets both user expectations and industry standards. B2B buyers should be aware of the various QA practices that software developers implement.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for CAD Software Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. For CAD software, adherence to such standards can enhance credibility and trust among international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CAD Software Development?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the QA process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase ensures that all incoming software components and libraries meet predefined quality standards before they are integrated into the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the development phase, IPQC involves continuous monitoring and testing to catch defects early in the process. This can include unit testing and integration testing.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the software is developed, FQC focuses on comprehensive testing of the final product to ensure that it meets all specifications and quality standards before release.
How Are Common Testing Methods Applied in CAD Software Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of CAD software:
-
Functional Testing: Verifying that each feature works as intended.
-
Performance Testing: Assessing how the software performs under various conditions, including load and stress tests.
-
Usability Testing: Gathering feedback from actual users to identify any usability issues and improve the user experience.
-
Security Testing: Ensuring that the software is secure against potential vulnerabilities.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those from international markets, verifying the quality control processes of CAD software suppliers is paramount. Here are some strategies to consider:
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Supplier Quality Verification?
Conducting audits and reviewing quality reports are effective ways for buyers to assess a supplier’s commitment to quality assurance. Regular audits can reveal compliance with international standards and internal quality processes. Buyers should request documentation that outlines the supplier’s quality management practices, including any certifications they hold.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence in Software Quality?
Engaging third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can validate the effectiveness of the supplier’s QA practices and ensure adherence to industry standards. For international buyers, this added layer of scrutiny can significantly reduce risks associated with software procurement.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control.
How Do Regional Regulations Influence Quality Standards?
Different regions may have varying regulations and standards that impact quality assurance processes. For instance, software used in industries such as healthcare or construction might be subject to stringent regulations. Understanding these regional standards is crucial for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential legal challenges.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding Localization and Cultural Differences?
Localization is another critical factor for international buyers. CAD software should not only function well technically but also accommodate local languages and cultural nuances. Buyers should inquire whether the supplier has considered these aspects in their software development and QA processes.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for easy-to-use CAD software is essential for B2B buyers. By evaluating how suppliers approach material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, as well as their commitment to quality control through international standards and testing methods, buyers can make informed decisions. Moreover, recognizing the regional nuances and implementing thorough verification strategies can enhance the likelihood of acquiring high-quality CAD software tailored to their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘easy to use cad software’
The following guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure easy-to-use CAD software. This guide outlines essential steps to ensure an informed and efficient purchasing process.
Step 1: Identify Your Business Needs
Understanding your specific requirements is the foundation of any successful software procurement. Consider the types of projects you will be working on—whether architectural, engineering, or product design—and the features necessary for those tasks. Make a list of must-have functionalities such as 2D drafting, 3D modeling, simulation capabilities, and collaboration tools.
Step 2: Set a Budget
Establishing a clear budget is crucial in determining the range of software options available to you. Research the pricing models of various CAD software solutions, including subscription-based and one-time purchase options. Be aware of additional costs, such as training, support, and potential upgrades that may impact your overall investment.
Step 3: Evaluate User-Friendliness
The ease of use of the CAD software should be a priority, especially for teams with varying levels of expertise. Look for software that offers an intuitive interface and comprehensive tutorials or training resources. Consider trial versions to assess how quickly your team can adapt to the software and whether it meets their needs without extensive training.
Step 4: Check Compatibility and Integration
Ensure that the CAD software is compatible with your existing systems and workflows. This includes evaluating file formats supported (like DWG or DXF) and the ability to integrate with other tools your team uses, such as project management or BIM software. Compatibility minimizes disruptions and enhances productivity.
Step 5: Review Customer Support and Training Options
Reliable customer support can significantly influence the success of your CAD implementation. Investigate the level of support offered, such as live chat, phone assistance, and online resources. Additionally, look for training programs to help your team get the most out of the software, ensuring they can leverage all available features effectively.
Step 6: Assess Scalability and Future-Proofing
Choose software that can grow with your business. Assess whether the software can handle increased workloads or additional users without compromising performance. Future-proofing is critical; look for vendors that regularly update their software with new features and improvements to stay relevant in the evolving CAD landscape.
Step 7: Read Reviews and Case Studies
Finally, gather insights from current users through reviews and case studies. Look for testimonials from companies in similar industries or regions, focusing on their experiences with the software. This feedback can provide valuable information regarding software reliability, performance, and overall satisfaction.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting easy-to-use CAD software that aligns with their business objectives and enhances productivity.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for easy to use cad software Sourcing
When sourcing easy-to-use CAD software, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the components of cost, factors influencing pricing, and essential tips for buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components of CAD Software?
The cost of CAD software can be broken down into several critical components:
-
Materials: This primarily pertains to the software itself, which may include licenses and subscriptions. Some software options offer free trials or educational versions, which can be beneficial for organizations looking to minimize initial costs.
-
Labor: Development and maintenance of CAD software require skilled professionals. The cost of labor is typically reflected in the pricing of the software, especially for complex solutions that offer extensive features.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: While not directly applicable to software, overhead costs related to support services, server maintenance, and cloud services can influence pricing. Companies often pass these costs onto customers.
-
Tooling: In the context of CAD software, tooling costs can include the investment in software tools and frameworks that enhance functionality, such as plugins or extensions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Software testing and quality assurance are essential for ensuring reliability. This aspect adds to the overall cost structure but is critical for maintaining customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: For cloud-based software, logistics primarily involve the infrastructure needed to deliver the software to users, including bandwidth and server capacity.
-
Margin: Software companies typically apply a profit margin to cover their costs and generate revenue, which varies based on the company’s business model and market positioning.
What Influences the Pricing of CAD Software?
Several factors can significantly impact the pricing of CAD software:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing can lead to discounts. Buyers should consider negotiating for volume pricing if they plan to deploy software across multiple users or departments.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored solutions or additional features often come at a premium. Buyers should assess their specific needs to avoid overpaying for unnecessary functionalities.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality or certified software (e.g., compliance with industry standards) may command higher prices. It’s essential to evaluate the long-term benefits of investing in certified solutions.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the software provider can influence pricing. Established brands may charge more due to their proven track record and customer support.
-
Incoterms: For international transactions, understanding Incoterms is crucial. They define responsibilities related to shipping and logistics, which can impact the total cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing CAD Software?
-
Negotiate Pricing: Always negotiate with suppliers. Many software providers offer flexible pricing or discounts for long-term commitments.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront costs but also ongoing expenses such as maintenance, updates, and support. A lower initial price may lead to higher costs down the line if the software requires frequent updates or lacks adequate support.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes can affect the final cost of software. Buyers from regions like Africa or South America should consider these factors when budgeting.
-
Leverage Free Trials and Educational Licenses: Take advantage of free trials or educational versions to assess the software’s fit for your organization before making a financial commitment.
-
Research and Compare Options: With numerous CAD software options available, conducting thorough research and comparing features, costs, and customer reviews can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of easy-to-use CAD software is essential for B2B buyers. By considering the key cost components, pricing influencers, and effective sourcing strategies, organizations can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Buyers are encouraged to remain vigilant and proactive in their negotiations and assessments to maximize value from their investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing easy to use cad software With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Easy-to-Use CAD Software
In the rapidly evolving landscape of design and engineering, businesses are often faced with a multitude of software solutions. While easy-to-use CAD software is designed to simplify design processes, there are alternative technologies and methods available that cater to various needs. This analysis will compare easy-to-use CAD software with two prominent alternatives: Drafting Software and 3D Modeling Tools. By examining key aspects such as performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases, businesses can make informed decisions tailored to their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Easy To Use CAD Software | Drafting Software | 3D Modeling Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and reliability for 2D/3D design | Reliable for 2D designs but limited 3D capabilities | Excellent for complex 3D designs and simulations |
| Cost | Subscription-based pricing; free options for students | Generally lower cost; often one-time purchase | Can be expensive; may require additional plugins |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly interfaces; quick onboarding | Moderate; familiar to those with traditional drafting background | Steeper learning curve; may require training |
| Maintenance | Regular updates and support available | Limited support; dependent on the vendor | Frequent updates; can be resource-intensive |
| Best Use Case | Versatile for architecture, engineering, and manufacturing | Best for architectural plans and simple mechanical designs | Ideal for product design, animation, and prototyping |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Drafting Software as an Alternative?
Drafting software, such as DraftSight, is a robust solution primarily focused on 2D design. It is particularly advantageous for businesses that prioritize cost-effectiveness and simplicity. The software offers a familiar interface for users with traditional drafting experience, allowing for quick adoption. However, it lacks advanced 3D capabilities, making it less suitable for projects requiring intricate modeling or simulations. Additionally, while it generally incurs lower costs, ongoing support and updates may not be as comprehensive as those provided by more specialized CAD solutions.
How Do 3D Modeling Tools Compare to Easy-to-Use CAD Software?
3D modeling tools, such as Autodesk Fusion 360, are designed for users who need to create complex three-dimensional designs. These tools excel in performance, especially for simulations and prototyping, making them ideal for product design and engineering applications. However, the cost can be higher, and the software often requires a more substantial investment in training and onboarding due to its sophisticated features. Maintenance can also be resource-intensive, with frequent updates and the need for powerful hardware. Despite these challenges, the capabilities of 3D modeling tools make them invaluable for businesses focusing on innovation and advanced design.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When considering which solution best fits their needs, B2B buyers must assess their specific requirements, including the complexity of their projects, budget constraints, and the technical expertise of their teams. Easy-to-use CAD software is ideal for organizations seeking a balance of functionality and user-friendliness, especially for teams that require versatility across various design disciplines. On the other hand, drafting software is suitable for businesses focused primarily on 2D designs, while 3D modeling tools are better suited for those engaged in intricate product development and simulations. By weighing these factors, organizations can make strategic decisions that align with their long-term goals and operational demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for easy to use cad software
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Easy-to-Use CAD Software?
1. User Interface (UI) Design
The user interface is crucial for any CAD software, especially for non-technical users. A well-designed UI enhances user experience by providing intuitive navigation, clear icons, and easy access to tools. For B2B buyers, investing in software with a user-friendly UI can significantly reduce the learning curve for employees, thereby increasing productivity and minimizing training costs.
2. Compatibility and File Support
Compatibility with various file formats (like DWG, DXF, and DGN) is vital for seamless collaboration across different platforms and software. Easy-to-use CAD software should support both 2D and 3D files to cater to diverse project needs. This property is particularly important for businesses that work with partners or clients using different CAD tools, as it ensures smooth data exchange and reduces the risk of errors.
3. Cloud Integration and Collaboration Tools
With the rise of remote work and global teams, cloud integration has become a critical feature for CAD software. This property allows users to access projects from anywhere and facilitates real-time collaboration. For B2B buyers, investing in cloud-enabled CAD solutions means enhanced teamwork, quicker project turnaround times, and the ability to manage workflows more effectively across geographically dispersed teams.
4. Customization and Automation Features
The ability to customize tools and automate repetitive tasks can significantly improve efficiency. Features such as custom templates, scripts, and macros allow businesses to tailor the software to their specific needs. This is particularly valuable in B2B settings, where operational efficiency can lead to cost savings and a competitive edge in the market.
5. Technical Support and Training Resources
Robust technical support and extensive training resources are essential properties of any CAD software. This includes access to online tutorials, forums, and customer service. For B2B buyers, reliable support ensures that any issues can be resolved quickly, minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity. Comprehensive training resources help new users acclimate faster, which is critical for maintaining project momentum.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand When Choosing CAD Software?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the CAD context, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify software that is compatible with their existing systems or machinery, ensuring smoother integration and functionality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For CAD software, understanding MOQ can help businesses plan their software purchases, especially if they require multiple licenses for a large team. This can also affect budgeting and procurement strategies.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers. When considering CAD software, sending out RFQs can help businesses compare options and negotiate better deals, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. For B2B buyers of CAD software, understanding Incoterms can help clarify shipping, handling, and insurance responsibilities, which is crucial for international procurement.
5. SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS refers to software that is hosted in the cloud and accessed via subscription rather than being purchased outright. Many modern CAD solutions operate on a SaaS model, which can provide flexibility and scalability for businesses. Understanding this model helps B2B buyers evaluate ongoing costs and the potential for future growth.
6. CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
While this term is widely recognized, it’s essential to understand that CAD encompasses a variety of software tools used for design and drafting. In a B2B context, recognizing the specific capabilities of different CAD applications can aid in making informed purchasing decisions that align with project requirements.
In summary, understanding these technical properties and trade terminology is vital for B2B buyers looking to invest in easy-to-use CAD software. This knowledge not only aids in making informed decisions but also enhances the overall efficiency and productivity of design and engineering processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the easy to use cad software Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Easy to Use CAD Software?
The easy to use CAD software market is witnessing a transformation fueled by several global drivers. One of the most significant trends is the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions, which allow for real-time collaboration and accessibility from any location. This trend is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in emerging markets like Nigeria and Brazil, where remote work and distributed teams are becoming more common. Additionally, the rise of educational access programs, such as those offered by Autodesk, is creating a new generation of skilled users who are familiar with these tools, thereby expanding the market.
Emerging technologies such as AI and machine learning are also shaping the CAD landscape, enabling automation of routine tasks and enhancing design capabilities. These innovations cater to a diverse range of industries, from architecture and engineering to manufacturing and media. For B2B buyers, understanding these technological advancements is crucial for selecting software that not only meets current needs but also scales with future demands.
Another noteworthy trend is the emphasis on user-friendly interfaces. As the market becomes more competitive, software providers are focusing on simplifying user experiences, making it easier for non-technical users to engage with complex design tasks. This focus on usability is particularly appealing to businesses in developing regions, where training resources may be limited.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Easy to Use CAD Software Sector?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a priority for B2B buyers across all sectors, including CAD software. The environmental impact of software production and usage is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek out solutions that prioritize eco-friendly practices. This includes sourcing materials from ethical supply chains and ensuring that software development processes minimize carbon footprints.
For CAD software providers, obtaining ‘green’ certifications can serve as a valuable differentiator in the market. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems signal to potential buyers that a company is committed to sustainable practices. Furthermore, many organizations are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing, making it essential for CAD software vendors to align with these values.
Moreover, the integration of sustainability features within CAD tools—such as energy analysis capabilities or materials lifecycle assessments—can provide significant value to B2B buyers. By facilitating sustainable design practices, these tools enable companies to not only comply with regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious marketplace.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Easy to Use CAD Software?
The evolution of easy to use CAD software dates back to the late 1960s when the first CAD systems were developed to aid in engineering and architectural design. Initially, these systems were complex and required specialized knowledge, limiting their accessibility. However, as technology advanced, software developers began to prioritize user experience, resulting in more intuitive interfaces and features.
By the 1990s, the advent of Windows-based applications and the introduction of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) marked a significant turning point. This evolution continued with the rise of 3D modeling tools and cloud-based platforms in the 2000s, democratizing access to CAD technology. Today, easy to use CAD software is characterized by its focus on collaborative features, real-time project management, and integration with other design tools, enabling a wider range of users—from students to seasoned professionals—to engage in the design process.
Understanding this historical context allows B2B buyers to appreciate the advancements that have made CAD software more accessible and versatile, ultimately aiding them in making informed purchasing decisions that align with their business needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of easy to use cad software
-
1. How do I choose the right CAD software for my business needs?
Selecting the right CAD software involves assessing your specific design requirements, budget, and team capabilities. Start by identifying the primary functions you need, such as 2D drafting, 3D modeling, or simulation. Consider software that offers a user-friendly interface and robust support resources, especially for teams new to CAD. Additionally, evaluate whether the software integrates well with existing tools and workflows in your organization. Finally, take advantage of free trials to test the software in real-world scenarios before making a commitment. -
2. What are the key features to look for in easy-to-use CAD software?
When sourcing easy-to-use CAD software, focus on features such as an intuitive interface, comprehensive toolsets for both 2D and 3D design, and strong collaboration capabilities. Look for cloud-based options that allow remote access and real-time updates, which can enhance team productivity. User support and training resources are also critical, as they help onboard new users quickly. Additionally, ensure the software supports industry-standard file formats to facilitate seamless integration with other tools and platforms. -
3. How do I evaluate the reliability of a CAD software supplier?
To evaluate a CAD software supplier’s reliability, research their reputation within the industry by reading customer reviews and case studies. Check for any industry certifications or partnerships that indicate credibility, such as collaborations with recognized organizations or educational institutions. Additionally, assess their customer support services, including responsiveness and availability of resources like tutorials and forums. It’s also beneficial to engage with current users to gain insights into their experiences with the software and supplier. -
4. What are the common payment terms for CAD software in international trade?
Payment terms for CAD software can vary widely depending on the supplier and the region. Common arrangements include upfront payments, subscription-based models, or installment plans. For international transactions, consider factors such as currency exchange rates, potential import taxes, and the payment methods accepted by the supplier. Always clarify the payment schedule and any additional fees during the negotiation process to avoid unexpected costs. Establishing a clear agreement can help ensure a smooth transaction. -
5. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CAD software licenses?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CAD software licenses typically depends on the supplier’s licensing model. Some companies offer individual licenses, while others may have a minimum requirement for bulk purchases, especially for network or enterprise licenses. It’s essential to communicate with the supplier about your team size and licensing needs to determine the best option. Additionally, inquire if discounts are available for larger orders, which can significantly reduce overall costs. -
6. How can I ensure the quality of the CAD software I am purchasing?
To ensure the quality of CAD software, start by reviewing the software’s specifications and features to confirm they align with your needs. Conduct thorough testing through free trials or demos to assess usability and performance. Additionally, seek feedback from current users regarding their experiences, focusing on reliability and support. Checking for regular updates and active community engagement can also indicate a commitment to quality and continuous improvement by the software provider. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing CAD software internationally?
When sourcing CAD software internationally, consider logistics factors such as software delivery methods, licensing restrictions, and support availability in your region. Ensure that the supplier can provide digital downloads or cloud access to avoid shipping delays. Additionally, be aware of any regional compliance issues or localization needs, such as language support and system compatibility. It’s also wise to clarify the time zone differences to manage communication and support requests effectively. -
8. Can CAD software be customized to fit specific industry needs?
Yes, many CAD software solutions offer customization options to cater to specific industry requirements. This can include tailored toolsets, workflows, and templates that align with unique design processes. Some suppliers also provide APIs or plugins that allow further enhancements and integrations with other software systems. When evaluating options, inquire about the level of customization available and whether the supplier offers support for implementing these modifications to ensure that the software can effectively meet your business needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Easy To Use Cad Software Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Autodesk – Free CAD Software
Domain: autodesk.com
Registered: 1989 (36 years)
Introduction: Free CAD Software for Students & Teachers, and Personal Use. Key products include AutoCAD, Revit, Civil 3D, AutoCAD LT, BIM Collaborate Pro, Inventor, Fusion, Fusion extensions, Navisworks, 3ds Max, Maya, Arnold, Flow Capture, and Flow Production Tracking. Autodesk offers free access to CAD tools for students and educators through the Education plan, allowing use of popular software like AutoCAD a…
2. Bambu Lab – X1 Series 3D Printer
Domain: forum.bambulab.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Bambu Lab X1 Series 3D printer; user experience with CAD software; challenges with Fusion 360; comparison with Carbide Create and Creative Space; suggestions for CAD software including Tinkercad, Onshape, SolidWorks, and SketchUp; emphasis on the importance of intuitive design software for beginners; mention of hobbyist licenses for SolidWorks; concerns about cloud-based solutions and project priv…
3. V1E – 3D Design Software Overview
Domain: forum.v1e.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: 1. Tinkercad: Recommended for beginners, easy to use, allows export to STL files. 2. Fusion 360: Suitable for more advanced users, good for assembly drawings, offers cloud storage, requires a purchase for CAM features. 3. Onshape: Web-based, free with public domain work, great tutorials, allows export to DXF files, ideal for beginners but has limitations for commercial use.
4. DraftSight – 2D CAD and 3D Design Software
Domain: draftsight.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: DraftSight is a 2D CAD drafting and 3D design software developed by the makers of SOLIDWORKS. It allows users to create, edit, view, and share 2D and 3D DWG files. The software is designed for various industries including architecture, engineering, construction, and manufacturing. DraftSight offers several licensing options: Premium ($599 USD/yr), Network Starting ($399 USD/yr), and Professional (…
5. Model Engineer – Essential CAD Tools
Domain: model-engineer.co.uk
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: 1. Open Office Draw: Free drawing package, part of the OpenOffice suite, suitable for simple engineering drawings. 2. Alibre Atom: Paid CAD software with a 30-day free trial, includes tutorials on the forum. 3. FreeCAD: Free software, requires effort to learn, suitable for various projects. 4. Designspark Mechanical: Good for basic 3D parts, user-friendly controls. 5. QCAD: Free community edition …
6. Prusa3D – 3D Printing Solutions
Domain: forum.prusa3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: 1. Prusa i3 MK3S+: A 3D printer that users are looking to design parts for.
2. Tinkercad: A beginner-friendly CAD software that some users found difficult to use.
3. FreeCAD: Recommended for its ease of learning and functionality; runs on multiple platforms.
4. Fusion 360: A popular choice for engineering CAD, available for free under a non-commercial license; offers advanced features like a timel…
7. ZWCAD – 2D Drafting & 3D Modeling Software
Domain: 3dnatives.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: ZWCAD: Beginner to Professional, unconditional 30-day free trial, one-time purchases starting from $899, yearly subscriptions, easy-to-use, user-friendly, 2D drafting and 3D modeling, lightweight (requires 2 GB RAM), advanced features (Smart Mouse, Smart Select), excellent 3D rendering, high compatibility with DWG and STL formats. TinkerCAD: Beginner level, free, online 3D design application, bloc…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for easy to use cad software
In navigating the world of easy-to-use CAD software, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to maximize value and efficiency. Key takeaways highlight the importance of selecting software that not only meets immediate design needs but also supports long-term growth and collaboration. Tools like AutoCAD, Fusion, and DraftSight provide intuitive interfaces and robust capabilities, enabling teams across diverse sectors—from architecture to manufacturing—to enhance productivity and innovation.
Strategic sourcing goes beyond just software acquisition; it involves understanding the licensing models, support options, and integration capabilities that align with your business objectives. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for accessible and powerful design tools will only grow.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage these insights to make informed decisions that foster collaboration and drive success. Embrace the opportunity to explore various CAD solutions tailored to your specific industry needs, ensuring your organization remains competitive in an increasingly digital landscape. Engage with software providers today to unlock the full potential of your design processes and set the foundation for future innovation.