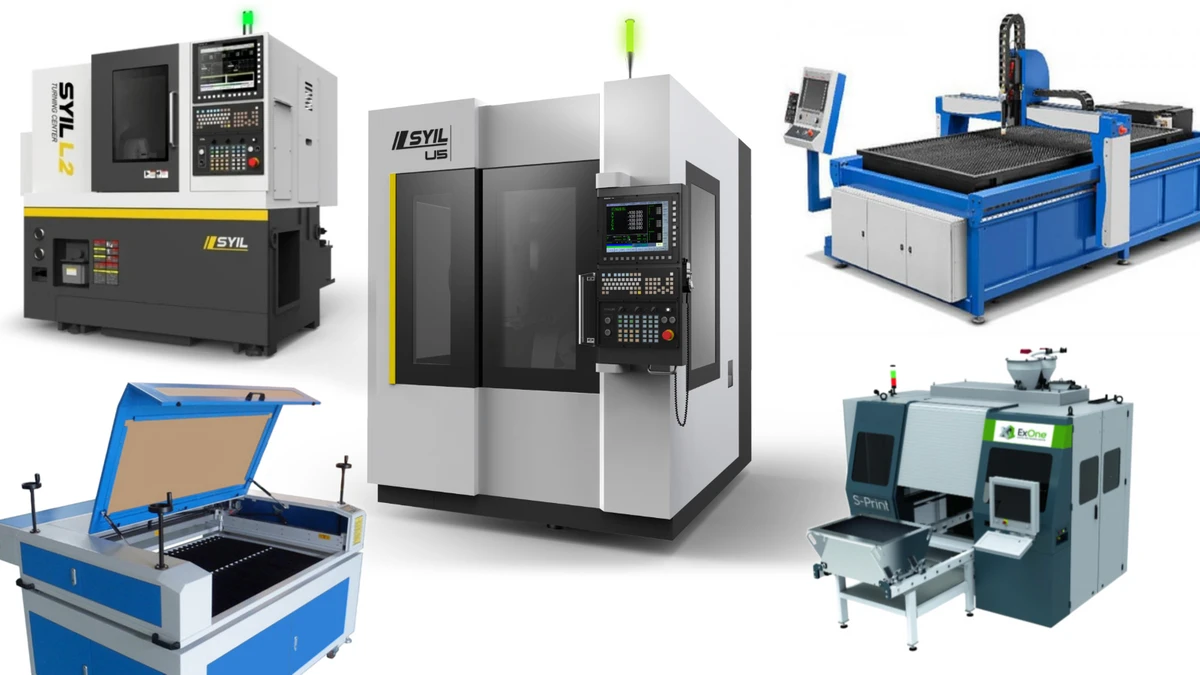
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for different types of cnc machines
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right CNC machines can be a pivotal challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As manufacturers increasingly turn to automation for efficiency and precision, understanding the diverse types of CNC machines and their specific applications becomes essential. This guide delves into the various CNC machine types—from CNC lathes and milling machines to advanced laser and plasma cutters—illuminating their functionalities, strengths, and ideal use cases.
Beyond just identifying machine types, this comprehensive resource provides critical insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and market trends that can influence purchasing decisions. By equipping buyers with the knowledge to evaluate their options effectively, this guide empowers them to make informed choices that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Navigating the global market for CNC machines doesn’t have to be daunting. With the right information at your fingertips, you can streamline your procurement processes, enhance production capabilities, and ultimately drive your business’s success in an increasingly automated world. Whether you’re a seasoned industry player or a newcomer exploring CNC technology, this guide serves as your roadmap to unlocking the potential of CNC machining in your operations.
Understanding different types of cnc machines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Milling Machine | Utilizes rotating multi-point cutting tools; available in 3-6 axes | Automotive parts, aerospace components, custom tooling | Pros: High precision, versatile; Cons: Higher initial investment, larger footprint. |
| CNC Lathe Machine | Rotates workpieces against single-point cutting tools | Shaft production, cylindrical components | Pros: Excellent for round shapes, efficient; Cons: Limited to rotational parts, less versatile than mills. |
| CNC Laser Cutting Machine | Employs focused laser beams for cutting; versatile material compatibility | Sign-making, sheet metal fabrication, intricate designs | Pros: Clean cuts, minimal material waste; Cons: Limited thickness capabilities, can be costly. |
| CNC Plasma Cutting Machine | Uses plasma to cut electrically conductive materials | Metal fabrication, automotive, and construction industries | Pros: Fast cutting speed, effective on thick materials; Cons: Requires ventilation, limited to conductive materials. |
| CNC 3D Printer | Builds parts layer-by-layer using additive manufacturing techniques | Prototyping, custom parts, small-scale production | Pros: Flexible designs, quick prototyping; Cons: Slower for mass production, material limitations. |
What are the Key Characteristics of CNC Milling Machines?
CNC milling machines are among the most versatile and widely used CNC machines in industrial settings. They utilize rotating multi-point cutting tools to shape a workpiece, making them suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. Their ability to operate on multiple axes (from 3 to 6) allows for complex designs and precision machining. When considering a CNC milling machine, B2B buyers should evaluate factors such as machine size, axis capabilities, and the types of tooling available to ensure it meets their specific production needs.
How Do CNC Lathe Machines Operate and What Are Their Advantages?
CNC lathe machines are designed for turning operations, where a rotating workpiece is shaped using single-point cutting tools. This makes them ideal for producing cylindrical components, such as shafts and fittings, with high accuracy. The compact design of CNC lathes often allows for faster setups and easier operation compared to larger CNC milling machines. Buyers should consider the machine’s axis configuration, speed, and tooling compatibility when selecting a CNC lathe to align with their production requirements.
What Makes CNC Laser Cutting Machines Ideal for Precision Work?
CNC laser cutting machines utilize highly focused laser beams to cut through a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. They are particularly favored for applications requiring intricate designs and high precision, such as signage and decorative elements. The clean cuts produced by laser technology minimize post-processing work and material waste. When purchasing a CNC laser cutter, B2B buyers should assess the laser type, cutting speed, and material thickness capabilities to ensure it meets their production standards.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of CNC Plasma Cutting Machines?
CNC plasma cutting machines operate by using a plasma torch to cut through electrically conductive materials, making them well-suited for heavy-duty applications in the metal fabrication industry. Their high cutting speeds make them an attractive option for projects requiring quick turnaround times. However, buyers should be aware of the limitations, such as the need for proper ventilation and the inability to cut non-conductive materials. Evaluating the thickness of materials to be cut and the required precision can help buyers choose the right plasma cutting solution for their needs.
How Do CNC 3D Printers Support Modern Manufacturing Needs?
CNC 3D printers represent a shift towards additive manufacturing, building parts layer-by-layer from digital models. They are particularly advantageous for prototyping and creating complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional subtractive methods. While they offer flexibility and speed in small-scale production, buyers should consider the materials used, production speed, and scalability for larger runs when integrating 3D printing into their manufacturing processes.
Key Industrial Applications of different types of cnc machines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of different types of cnc machines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | CNC milling and turning for precision components | High precision and repeatability, essential for safety standards | Certification of machines, material compatibility, lead times |
| Automotive | CNC machining for prototyping and production of parts | Increased efficiency, reduced production costs | Supplier reliability, after-sales support, customization options |
| Electronics | CNC pick and place machines for PCB assembly | Improved assembly speed and accuracy | Equipment scalability, integration with existing systems |
| Metal Fabrication | CNC plasma and laser cutting for sheet metal processing | Enhanced cutting precision and reduced waste | Material types, machine power, and maintenance requirements |
| Furniture Manufacturing | CNC routers for custom furniture design and production | Greater design flexibility and faster production times | Software compatibility, training for operators, size constraints |
How Are Different Types of CNC Machines Applied in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, CNC milling and turning machines are crucial for manufacturing precision components such as turbine blades and structural parts. The high precision offered by CNC technology ensures that components meet strict safety and quality standards, which is vital in this highly regulated industry. International buyers should consider sourcing machines that are certified for aerospace applications, ensuring they can handle specific materials like titanium and aluminum alloys. Furthermore, understanding lead times for machine delivery can significantly impact production schedules.
What Role Do CNC Machines Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
CNC machines are extensively used in the automotive industry for both prototyping and the mass production of parts, including engine components and body panels. The automation provided by CNC technology leads to increased efficiency and reduced costs, allowing manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands. Buyers must assess the reliability of suppliers and their ability to provide after-sales support, which is essential for maintaining production continuity. Additionally, customization options for specific automotive applications can enhance operational efficiency.
How Do Electronics Manufacturers Benefit from CNC Technology?
In the electronics industry, CNC pick and place machines are employed for the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs). These machines significantly improve assembly speed and accuracy, which is critical as electronic devices become more compact and complex. For international buyers, it is important to evaluate the scalability of the equipment, ensuring it can adapt to varying production volumes. Integration with existing manufacturing systems is another key consideration, as it can enhance overall production efficiency.
What Are the Advantages of CNC Machines in Metal Fabrication?
CNC plasma and laser cutting machines are widely used in metal fabrication for processing sheet metal into intricate designs. These machines provide enhanced cutting precision and minimize waste, which translates to cost savings. Buyers in this sector should carefully consider the types of materials they will be working with, as different machines are optimized for various metals. Additionally, understanding the power requirements and maintenance needs of these machines can help ensure long-term operational efficiency.
How Do CNC Routers Transform Furniture Manufacturing?
In furniture manufacturing, CNC routers are utilized to create custom designs with high precision and speed. This technology allows manufacturers to produce intricate patterns and shapes that would be challenging to achieve manually. For B2B buyers, it’s essential to evaluate the software compatibility of CNC routers, as this can impact design capabilities. Training for operators is also crucial, as skilled personnel can maximize the potential of CNC technology, leading to faster production times and enhanced design flexibility.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘different types of cnc machines’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right CNC Machine for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when trying to determine which type of CNC machine is best suited for their specific production needs. With various options available, such as CNC milling machines, lathes, and laser cutters, the decision-making process can become overwhelming. This complexity is exacerbated by the need for precision in production, the variety of materials being processed, and the different capabilities each machine offers. Buyers may worry about making the wrong investment, leading to subpar production quality or inefficiencies in operations.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment before making a purchase. Start by analyzing the specific components or products you intend to manufacture. Consider factors such as material type, required tolerances, and production volume. Once these criteria are established, engage with suppliers to request detailed specifications and case studies that demonstrate the performance of various CNC machines in similar applications. It may also be beneficial to visit manufacturing facilities or attend industry trade shows to see the machines in action. This hands-on approach will provide valuable insights into how different machines can meet your operational demands, ensuring you make an informed and strategic investment.
Scenario 2: Managing Downtime Due to CNC Machine Malfunctions
The Problem: CNC machines are critical to production efficiency, and any downtime caused by malfunctions can significantly impact a business’s bottom line. For many B2B buyers, the challenge lies in the unanticipated breakdowns of CNC equipment, which can lead to delays in fulfilling orders and increased operational costs. Additionally, identifying the root cause of machine failures can be time-consuming and may require specialized knowledge that the in-house team lacks.
The Solution: To mitigate downtime, implementing a proactive maintenance strategy is essential. Buyers should work with suppliers to develop a maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections, software updates, and parts replacement based on usage metrics. Investing in training for operators can also empower them to conduct basic troubleshooting and maintenance, allowing for quicker resolutions to minor issues before they escalate. Furthermore, establishing a relationship with a reliable service provider for rapid response repairs will ensure that any significant issues are addressed promptly, minimizing production interruptions and maintaining efficiency in operations.
Scenario 3: Integration Challenges with Existing Manufacturing Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter integration issues when incorporating new CNC machines into their existing manufacturing processes. This can stem from outdated software, compatibility issues with legacy systems, or a lack of technical expertise within the team. Such challenges can hinder the seamless flow of production data, resulting in inefficiencies and potential errors in the manufacturing process.
The Solution: To address integration challenges, buyers should prioritize compatibility when selecting CNC machines. Before making a purchase, it is crucial to discuss integration capabilities with suppliers and ensure that the machines can interface with existing software systems. Additionally, investing in comprehensive training for staff on the new equipment and software can help ease the transition. Employing a phased implementation approach, where new machines are introduced gradually, allows for adjustments to be made based on feedback from operators. This method not only smooths the integration process but also enables the team to become proficient in using the new technology, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and productivity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for different types of cnc machines
What Are the Key Materials for CNC Machines?
When selecting materials for CNC machining, it is essential to consider their properties and how they align with specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in CNC machining, focusing on their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: A Versatile Choice for CNC Applications
Aluminum is widely used in CNC machining due to its excellent machinability and lightweight properties. It typically has a temperature rating up to 400°F (204°C) and exhibits good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros: Aluminum is durable yet lightweight, which enhances product performance without adding unnecessary weight. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to other metals, making it a cost-effective option for many applications.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it is softer than steel, which can lead to wear in high-friction applications. Furthermore, its lower melting point can limit its use in high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a wide range of media, making it ideal for components in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing aluminum from local suppliers can reduce costs and lead times.
Steel: The Backbone of Industrial CNC Machining
Steel, particularly high-carbon and stainless varieties, is a staple in CNC machining due to its strength and versatility. Steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros: Steel offers exceptional durability and strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty components. It also has excellent wear resistance, which enhances the longevity of machined parts.
Cons: The higher cost of steel compared to aluminum can be a drawback, especially for large-scale production. Additionally, machining steel requires more complex tooling and longer machining times.
Impact on Application: Steel is widely used in industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing, where strength and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with regional standards such as DIN in Europe or JIS in Japan is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific steel grades in their region.
Plastics: Lightweight and Cost-Effective Solutions
Plastics, such as ABS and polycarbonate, are increasingly popular in CNC machining due to their lightweight nature and ease of machining. They typically have lower temperature resistance but offer good chemical resistance.
Pros: Plastics are often more affordable than metals and can be machined quickly. Their lightweight nature makes them suitable for applications where weight is a concern.
Cons: Plastics generally lack the strength and durability of metals, which can limit their application in high-stress environments. Additionally, they may not perform well under high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastics are commonly used in consumer goods, electronic housings, and prototypes, where weight and cost are critical factors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of plastics that meet their application needs and ensure compliance with relevant standards. Sourcing from local suppliers can also mitigate shipping costs.
Composites: Advanced Materials for Specialized Applications
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, are gaining traction in CNC machining due to their unique properties. They offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros: Composites are incredibly lightweight while offering high strength, making them ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. They also resist corrosion and fatigue, enhancing product longevity.
Cons: The cost of composites can be significantly higher than metals and plastics, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, machining composites can require specialized tooling and techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly suited for high-performance applications in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with industry-specific standards is essential, especially in regulated sectors. Buyers should also consider the availability of composite materials in their region and the associated machining capabilities.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for different types of cnc machines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and cost-effective | Softer than steel, lower melting point | Low |
| Steel | Heavy-duty machinery, construction equipment | Exceptional strength and durability | Higher cost, complex machining | High |
| Plastics | Consumer goods, electronic housings | Affordable and quick to machine | Lacks strength, limited high-temperature use | Low |
| Composites | Aerospace, automotive, marine applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost, requires specialized tooling | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding material selection for CNC machining, considering performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for different types of cnc machines
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for Different Types of CNC Machines?
Understanding the manufacturing processes involved in producing CNC machines is crucial for B2B buyers. The processes generally encompass four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specific techniques and machinery tailored to the type of CNC machine being manufactured.
What Is Material Preparation for CNC Machine Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process and involves selecting the right raw materials, such as metals, plastics, or composites. This stage may include cutting materials to size, deburring edges, and ensuring they meet the required specifications.
For CNC milling machines, for instance, aluminum and steel are common materials. They are often pre-processed using techniques like shearing or laser cutting to achieve the desired dimensions. In the case of CNC routers, softer materials like wood or foam are prepared in a similar manner but may require different handling techniques to prevent damage.
How Is the Forming Stage Conducted in CNC Machine Production?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into components that will be assembled into the final CNC machine. Techniques vary widely depending on the type of machine. For example, CNC lathes and milling machines utilize subtractive manufacturing processes, where material is removed from a workpiece using cutting tools.
In contrast, CNC 3D printers employ additive manufacturing, building parts layer by layer from a digital model. Each type of CNC machine requires different forming techniques, such as forging for metal parts or molding for plastic components, ensuring precision and quality are maintained throughout the process.
What Assembly Techniques Are Used for CNC Machines?
Assembly is a critical stage where individual components are brought together to create the final product. This process can be highly automated or manual, depending on the complexity and scale of production. For CNC milling machines, assembly involves integrating the spindle, motor, and control systems.
Quality assurance is paramount during this phase. Automated assembly lines often use robotic arms for precision, while manual assembly may involve skilled technicians to ensure that parts fit together correctly.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied in CNC Machine Manufacturing?
Finishing techniques are employed to enhance the aesthetics and functionality of the CNC machines. This may include surface treatment processes like anodizing for aluminum parts, painting, or applying protective coatings.
Additionally, precision machining may take place to ensure tight tolerances are met, especially for components that require high accuracy, such as those used in CNC laser cutting machines. Finishing not only improves the machine’s appearance but also extends its lifespan by providing resistance against wear and corrosion.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Practices for CNC Machine Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is an integral part of CNC machine manufacturing. It ensures that the machines meet both international and industry-specific standards. Key practices include implementing quality checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for CNC Machine Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in ensuring quality management systems are in place. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer follows globally recognized quality management principles, including customer focus and continual improvement.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for machinery sold in the European market or API standards for oil and gas equipment are critical for demonstrating compliance and quality assurance. B2B buyers should verify that suppliers possess the necessary certifications relevant to their market.
What Are the Critical Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Machine Production?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are crucial throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring production processes and conducting inspections at various stages to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting a comprehensive inspection of the finished product before it leaves the factory.
These checkpoints help to minimize defects and ensure that the final product adheres to quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should be proactive in verifying supplier quality control measures. One effective method is to conduct audits of potential suppliers, assessing their manufacturing processes and quality management systems. This can include reviewing documentation, inspecting facilities, and meeting with quality assurance personnel.
Additionally, requesting detailed QC reports and certifications can provide insight into a supplier’s quality practices. Engaging third-party inspection services is another viable option, especially for buyers in regions with varying quality standards. These services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance processes.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential. Different regions may have varying standards and expectations. For instance, buyers in Africa may face challenges related to inconsistent quality assurance practices among local suppliers, while those in Europe often have stringent regulations to comply with.
Buyers should also consider language barriers and cultural differences when engaging with suppliers. Clear communication regarding quality expectations and standards is crucial for successful partnerships. Utilizing local representatives or consultants familiar with regional practices can help navigate these challenges effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for CNC machines are complex and multifaceted. By understanding these processes and implementing rigorous quality control measures, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that they acquire high-quality CNC machines that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘different types of cnc machines’
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, sourcing the right CNC machines is critical for optimizing production efficiency and product quality. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers, ensuring a comprehensive approach to procurement that aligns with technical requirements and business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by outlining the specific technical needs of your project. Consider the types of materials you will be working with, the complexity of the designs, and the required precision levels. Each type of CNC machine—whether it’s a milling machine, lathe, or laser cutter—has distinct capabilities.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the machine can handle the materials you intend to use, such as metals, plastics, or composites.
- Precision Requirements: Identify the tolerances needed for your products to meet industry standards.
Step 2: Research Different Types of CNC Machines
Understanding the various types of CNC machines available is essential for making an informed decision. Each machine type serves unique purposes and is suited for different applications.
- CNC Milling Machines: Great for complex shapes and high precision.
- CNC Lathes: Ideal for cylindrical parts and quick production runs.
- Laser Cutters and Plasma Cutters: Best for high-speed cutting of various materials.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from similar industries or regions to gauge their reliability and expertise.
- Supplier Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the CNC market.
- Customer Reviews: Seek testimonials and feedback from other buyers to understand the supplier’s service quality.
Step 4: Check for Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the CNC machines and suppliers meet international quality standards and certifications. This step is crucial for ensuring product reliability and compliance with local regulations.
- ISO Certifications: Look for suppliers with ISO 9001 or similar certifications to guarantee quality management practices.
- Safety Standards: Confirm compliance with safety standards relevant to your industry.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Trials
Whenever possible, request demonstrations or trials of the CNC machines. This hands-on experience allows you to assess the machine’s functionality and performance in real-time.
- Production Capability: Evaluate how well the machine can handle your specific tasks.
- User Interface: Consider the ease of use and the software compatibility with your existing systems.
Step 6: Analyze Total Cost of Ownership
Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO) associated with each machine. This includes not only the initial purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
- Maintenance Costs: Investigate the availability of spare parts and service support.
- Operational Efficiency: Assess how the machine contributes to productivity and cost savings over time.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms. Clear agreements on pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty conditions can help mitigate risks.
- Payment Terms: Discuss flexible payment options that suit your cash flow.
- Warranty and Support: Ensure the warranty covers essential parts and that support services are readily available.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can strategically approach the procurement of CNC machines, ensuring that the selected equipment meets their operational needs while fostering long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for different types of cnc machines Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Different Types of CNC Machines?
When sourcing CNC machines, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. For instance, CNC milling machines often require high-quality steel or aluminum, while CNC laser cutters might use specialized optics and higher-grade metals. The material’s properties can influence machining speeds and tool wear, ultimately affecting long-term operational costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can significantly influence the overall price of CNC machines. In regions like Africa and South America, labor might be less expensive, but skilled labor shortages can drive up costs. Conversely, in Europe, labor is typically higher but may bring greater expertise and quality assurance.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the facility, utilities, and indirect labor. A well-optimized manufacturing process can lower overhead, which can be a competitive advantage in pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs encompass the tools and equipment needed for machine operation. High-quality tooling can improve precision and reduce material waste but may increase initial costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes can add to costs but is essential for ensuring product reliability. Certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) can also affect pricing, as they often require additional processes and documentation.
-
Logistics: Shipping and transportation costs can be significant, especially for heavy machinery. Incoterms will dictate who bears these costs and can influence final pricing.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary widely based on market conditions and competition. Understanding the typical margins for different types of CNC machines can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC machines, making it vital for buyers to understand these dynamics:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often have minimum order quantities (MOQs), which can affect pricing structures.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom machines tailored to specific applications typically cost more due to the additional engineering and manufacturing processes involved. Standard machines are generally more cost-effective.
-
Materials and Quality: The choice of materials directly influences the machine’s performance and longevity. Machines built from higher-grade materials tend to have a higher upfront cost but lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) due to reduced maintenance and longer lifespans.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, location, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more, but this can be offset by better quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. They determine the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and customs, which can significantly impact total costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for CNC Machine Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective sourcing strategies are essential:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Always aim to negotiate terms and pricing. Leverage multiple quotes to understand the market and establish a baseline for negotiations.
-
Prioritize Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider the TCO, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional differences in pricing and supply chain factors. For example, tariffs, taxes, and local regulations can impact costs for machines imported from different countries.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the purchase price but the long-term costs associated with operation, maintenance, and potential upgrades.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost components and price influencers related to CNC machines is essential for B2B buyers. By leveraging this knowledge, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints. It’s advisable to seek multiple quotations and engage in thorough negotiations to achieve the best value. Keep in mind that indicative prices may vary based on market conditions and specific supplier circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing different types of cnc machines With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to CNC Machines
In the realm of manufacturing and machining, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines have revolutionized how businesses produce components and products. However, various alternative technologies and methods can achieve similar objectives, offering different advantages and limitations. This section compares CNC machines against two viable alternatives: manual machining and additive manufacturing (3D printing). By exploring these options, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs and budget.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Different Types of CNC Machines | Manual Machining | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and repeatability | Lower precision; skilled labor required | High precision for complex geometries |
| Cost | High initial investment; lower long-term costs | Lower initial costs; higher labor costs | Moderate initial costs; material costs vary |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires trained personnel and programming | Requires skilled machinists; longer setup | User-friendly software; less skilled labor needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance | Less frequent maintenance; depends on machinery | Minimal maintenance; focus on material management |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production and complex parts | Custom one-off parts and repairs | Prototyping and complex shapes with less waste |
Pros and Cons of Manual Machining
Manual machining involves using traditional tools operated by skilled machinists. This method can be advantageous for small batch production or unique custom parts where precision is less critical. Manual machines often have lower initial costs, but labor expenses can accumulate due to the need for skilled operators. Additionally, manual machining may result in longer production times and variability in output quality, making it less suitable for high-volume applications.
Pros and Cons of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, builds objects layer by layer based on digital models. This technology excels in creating complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with CNC machines. It is particularly valuable for prototyping and small production runs, offering flexibility and reducing material waste. However, the material costs can vary significantly, and the speed of production may not match the efficiency of CNC machines for larger volumes. Additionally, while 3D printing is becoming more accessible, it still requires an understanding of software and design principles.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate manufacturing solution involves assessing your specific production requirements, budget, and available resources. If your operations demand high precision and repeatability for large-scale production, CNC machines are likely the best choice. On the other hand, if you require flexibility for custom jobs or prototyping, manual machining or additive manufacturing may be more suitable. By carefully evaluating the pros and cons of each alternative, B2B buyers can align their manufacturing processes with their strategic goals, ensuring efficient production and optimal resource utilization.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for different types of cnc machines
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Different Types of CNC Machines?
Understanding the technical properties of CNC machines is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are several essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Compatibility
CNC machines can work with a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, composites, and wood. Knowing the compatibility of a machine with specific materials is vital for businesses that require versatility in production. For instance, a CNC router is ideal for softer materials like wood, while a CNC plasma cutter excels with metals. This affects not only the choice of machine but also operational costs and output quality. -
Precision and Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in a manufactured part’s dimensions. CNC machines are known for their precision, often achieving tolerances as tight as 0.001 mm. This is particularly important for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where even minor deviations can lead to significant performance issues. Selecting a machine with the appropriate tolerance level can enhance product quality and reduce waste. -
Axis Configuration
The number of axes a CNC machine operates on (typically ranging from 3 to 5 or even more) dictates its capability to perform complex cuts and shapes. A 3-axis CNC machine can handle basic tasks, while a 5-axis machine offers greater flexibility by allowing cuts from multiple angles without repositioning the workpiece. This can significantly speed up the production process and improve the efficiency of complex manufacturing tasks. -
Speed and Feed Rate
Speed (the spindle speed) and feed rate (the speed at which the tool moves through the material) are critical for determining production efficiency. Higher speeds and feed rates can lead to faster production times but may compromise surface finish or tool life. Understanding the optimal speed and feed settings for specific materials can help businesses balance efficiency with quality. -
Power Consumption
The power requirements of CNC machines can impact operational costs. Machines with higher power ratings may offer faster processing but will also incur higher energy costs. For businesses focused on sustainability or operating within budget constraints, evaluating power consumption is essential for long-term operational planning. -
Software Compatibility
CNC machines typically require specific software for programming and operation, such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) systems. Compatibility with industry-standard software can ease integration into existing workflows and reduce training time for operators.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in CNC Machining?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiation with suppliers. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the role of OEMs can help buyers identify quality suppliers and ensure that they are receiving genuine parts. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for budgeting and inventory management, as it can affect cash flow and storage requirements. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific goods or services. Issuing an RFQ can help businesses compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms can help businesses navigate logistics and reduce the risk of misunderstandings in cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is essential for production planning and inventory management, especially for businesses with tight schedules. -
CNC Machining Cycle Time
This term refers to the total time required to complete a machining operation. Reducing cycle time is often a key focus for manufacturers looking to enhance efficiency and productivity, making it a critical consideration for buyers evaluating CNC machines.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make better-informed decisions that align with their operational goals and manufacturing requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the different types of cnc machines Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the CNC Machine Sector?
The CNC machine sector is witnessing significant global growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation and precision manufacturing across various industries. Key trends include the rise of Industry 4.0, where smart manufacturing integrates IoT and AI technologies, enabling more efficient production processes. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, evaluate their sourcing strategies, they must consider the shift towards advanced CNC technologies, such as multi-axis machines and automated CNC systems that offer improved productivity and versatility.
Emerging markets are increasingly adopting CNC technologies, with countries like Brazil and Vietnam leading the way in manufacturing capabilities. This trend is driven by a surge in investments in infrastructure and industrial development. Furthermore, buyers are prioritizing suppliers that offer not only high-quality machines but also comprehensive after-sales support and training programs. The increasing emphasis on customization and rapid prototyping also means that CNC machines capable of additive manufacturing, such as 3D printers, are becoming more prevalent in the market.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact CNC Machine Procurement?
In today’s market, sustainability and ethical sourcing are critical considerations for B2B buyers in the CNC machine sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. This includes utilizing energy-efficient machines and reducing waste during production. Buyers should look for CNC machine manufacturers that have certifications such as ISO 14001, which indicates a commitment to environmental management.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are becoming increasingly important. B2B buyers are encouraged to partner with suppliers that prioritize responsible sourcing of materials, ensuring that raw materials are obtained without causing harm to the environment or local communities. The use of ‘green’ materials, such as recyclable metals and biodegradable plastics, is gaining traction. By prioritizing sustainability, companies can not only enhance their brand image but also meet the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Machines and Its Relevance to Today’s Market?
The evolution of CNC machines dates back to the 1950s when they were introduced to automate machining processes. Initially, these machines were used primarily in aerospace and automotive industries, but their applications have since expanded significantly. The advent of computer technology and software advancements has transformed CNC machines into sophisticated tools capable of executing complex designs with high precision.
Understanding this historical context is vital for B2B buyers as it highlights the continuous innovation within the sector. Today’s CNC machines are not just tools; they represent a convergence of technology and manufacturing that can drive efficiency and quality. As buyers evaluate their procurement options, recognizing the evolution of CNC technology can inform decisions on which machines will best meet their operational needs and align with future industry trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of different types of cnc machines
-
How do I choose the right CNC machine for my manufacturing needs?
Choosing the right CNC machine involves assessing your specific production requirements, including the types of materials you will work with, the complexity of parts you need to produce, and the required precision. Start by evaluating the types of CNC machines available—such as milling machines, lathes, and laser cutters—and consider their capabilities in terms of axis movement and tooling options. Additionally, consult with suppliers about customization options to ensure the machine aligns with your production goals. -
What factors should I consider when vetting CNC machine suppliers?
When vetting CNC machine suppliers, consider their industry reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Verify their production capabilities and ask for case studies or references from similar businesses. It’s also essential to assess their after-sales support, including training, maintenance, and spare parts availability. Inspecting their manufacturing facility can provide insights into their quality control processes and adherence to international standards. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering a CNC machine internationally?
Lead times for international CNC machine orders can vary significantly based on factors such as the machine type, customization level, and supplier location. Generally, expect a lead time ranging from 6 to 12 weeks. It’s crucial to communicate with your supplier regarding production timelines and shipping methods to ensure timely delivery. Factor in potential delays due to customs clearance and logistics when planning your production schedule. -
Can I customize my CNC machine according to specific production requirements?
Yes, many CNC machine manufacturers offer customization options to meet unique production needs. This may include modifications to machine size, tooling capabilities, software integration, and additional features for enhanced precision. Discuss your requirements in detail with potential suppliers to understand their customization capabilities and ensure that the final machine meets your operational needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC machines?
Minimum order quantities for CNC machines can vary by supplier and the type of machine. Some manufacturers may have no MOQ for standard models, while others might require orders of multiple units for custom machines. Always clarify MOQ policies upfront and consider your production capacity and budget when deciding how many machines to order. -
What payment terms are typically offered for international CNC machine purchases?
Payment terms for international CNC machine purchases can vary widely. Common terms include a deposit upon order confirmation (usually 30-50%), with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans based on your creditworthiness. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and budget, and ensure that all agreements are documented in your purchase contract. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for my CNC machines?
Ensuring quality assurance for your CNC machines involves working closely with suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Request detailed documentation on the machine’s specifications, testing procedures, and certifications. Additionally, consider conducting pre-shipment inspections to verify that the machine meets your requirements. Establishing a clear communication channel for addressing any concerns post-delivery can also enhance quality assurance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC machines?
When importing CNC machines, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and potential tariffs. Work with logistics providers experienced in heavy machinery transport to ensure safe and compliant delivery. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping fees and taxes, to avoid unexpected expenses. Lastly, ensure that you have the necessary facilities and equipment to receive and install the machine upon arrival.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Different Types Of Cnc Machines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. WayKen – CNC Machine Types
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Types of CNC Machines: 1. Mill CNC Machine – Removes material using high-speed cutting tools; various cutter types (end mills, reamers, face mills). 2. Lathe CNC Machine – Rotates workpiece around a primary axis; used for symmetrical parts (automobile parts, camshafts). 3. Drilling CNC Machine – Uses drill bits for creating holes; applications in automobile manufacturing, shipbuilding. 4. Grinding…
2. CNC Machines – Trusted Brands
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Most trusted CNC machine brands mentioned include Makino, Okuma, Haas, and DMG Mori. Users noted that older Okuma lathes are particularly reliable, while Haas machines are seen as good starting options but may not hold up under heavy use. DMG Mori is recognized for quality, and generally, Japanese brands are considered a safe choice.
3. NS Flamespray – CNC Engraving & Cutting Solutions
Domain: nsflamespray.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 1. Router: Engraves plastic, metal, or wood; operated exclusively by CNC technology; user inputs information via computer.
2. Plasma: Cuts 2D wood and metal; uses a plasma torch; requires less power than CNC routers; flies above the table.
3. Laser: Similar to plasma cutters but uses a laser; suitable for cutting metal, plastic, and wood; different laser strengths for material thickness and hardne…
4. Techniwaterjet – High-Pressure Waterjet Cutting Systems
Domain: techniwaterjet.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Light Series: MAX OUTPUT PRESSURE: 60,000 PSI; Power Series: MAX OUTPUT PRESSURE: 66,000 PSI; Ultimate Series: MAX OUTPUT PRESSURE: 88,000 PSI; i35-G2: Small Cantilever, CUTTING AREA: 915 x 1525 mm; i510-G2: Medium Cantilever, CUTTING AREA: 1525 x 3050 mm; i613-G2: Monoblock, CUTTING AREA: 1700 x 3700 mm; i713-G2: Small Gantry, CUTTING AREA: 2000 x 4000 mm; i815-G2: Medium Gantry, CUTTING AREA: 23…
5. Fadal – CNC Machines
Domain: fadal.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: CNC Machines: 1. CNC Mills: Used for creating complex shapes and profiles, suitable for automotive, aerospace, and mold-making industries. 2. CNC Lathes: Machining cylindrical or conical shapes, used in automotive, aerospace, and medical equipment manufacturing. 3. CNC Plasma Cutters: Cut through metals using a high-temperature plasma torch, used in metal fabrication, construction, and automotive …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for different types of cnc machines
As international B2B buyers navigate the diverse landscape of CNC machines, understanding the unique capabilities and applications of each type is crucial for strategic sourcing. From CNC milling machines that offer precision for complex parts to CNC routers that excel in softer materials, the right choice can significantly enhance production efficiency and product quality.
Strategic sourcing not only involves selecting the right equipment but also considering factors such as supplier reliability, after-sales support, and the availability of spare parts. Establishing long-term partnerships with manufacturers and suppliers can lead to favorable terms and consistent access to the latest technologies, ensuring that your operations remain competitive.
Looking ahead, the CNC machining market is poised for growth, driven by advancements in automation and material science. For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, now is the time to invest in CNC technology that aligns with evolving industry demands. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your production capabilities by sourcing the right CNC machines tailored to your specific needs. Engage with trusted suppliers and stay informed about emerging trends to position your business for future success.