Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dfm guidelines
In today’s competitive global marketplace, navigating the complexities of Design for Manufacturing (DFM) guidelines is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The challenge lies in balancing product functionality with manufacturability, particularly when sourcing components that meet stringent quality and cost requirements. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of DFM principles, including types of guidelines, practical applications across various industries, and effective strategies for supplier vetting.
By delving into the intricacies of DFM, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—will gain valuable insights into how to streamline their purchasing processes. The guide outlines actionable steps to evaluate potential suppliers, assess cost implications, and ultimately make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
With a focus on enhancing product quality, reducing lead times, and fostering innovation, this resource serves as an authoritative tool for manufacturers looking to thrive in an increasingly demanding environment. Empowering B2B buyers with the knowledge to implement effective DFM practices will not only facilitate smoother product development but also position them for long-term success in the global market.
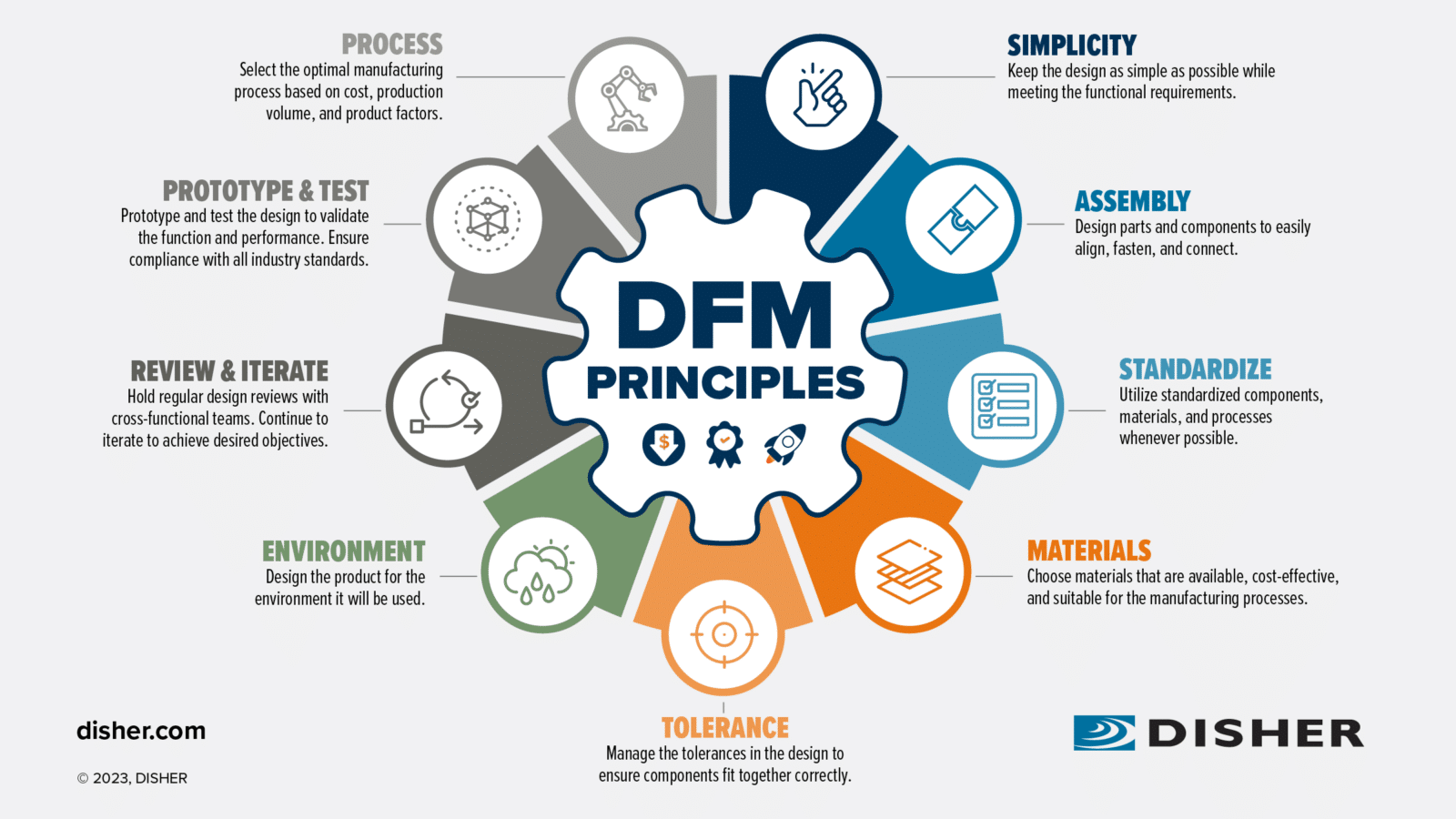
Understanding dfm guidelines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design for Manufacturing (DFM) | Focuses on optimizing product design for efficient manufacturing. | Automotive, Electronics, Consumer Goods | Pros: Cost reduction, improved quality. Cons: Requires upfront investment in design processes. |
| Design for Assembly (DFA) | Simplifies the assembly process by reducing part count and complexity. | Aerospace, Machinery, Electronics | Pros: Faster assembly, lower labor costs. Cons: May limit design flexibility. |
| Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) | Combines DFM and DFA principles to optimize both manufacturing and assembly processes. | Complex products like Medical Devices, Automotive | Pros: Comprehensive efficiency gains. Cons: More complex to implement. |
| Design for Sustainability (DFS) | Integrates environmental considerations into product design and manufacturing. | Consumer Products, Packaging, Electronics | Pros: Enhances brand reputation, regulatory compliance. Cons: Potentially higher initial costs. |
| Design for Cost (DFC) | Focuses primarily on minimizing production costs through design choices. | Mass Production, Consumer Electronics | Pros: Direct cost savings, competitive pricing. Cons: May compromise quality or functionality. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Design for Manufacturing (DFM)?
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) emphasizes the importance of integrating manufacturing considerations early in the product design phase. This approach is particularly suitable for industries with high production volumes, such as automotive and consumer goods. Buyers should consider DFM when looking to reduce costs and improve product quality, as it enables manufacturers to streamline processes and minimize waste. However, the initial investment in design improvements may be a barrier for some companies.
How Does Design for Assembly (DFA) Enhance Efficiency?
Design for Assembly (DFA) focuses on simplifying the assembly process by reducing the number of parts and optimizing their arrangement. This methodology is ideal for sectors like aerospace and machinery, where assembly speed and accuracy are critical. B2B buyers should prioritize DFA when seeking to lower labor costs and improve assembly efficiency. However, the trade-off may involve limitations on design creativity, which could affect product differentiation.
What is the Value of Combining DFM and DFA in DFMA?
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) merges the principles of DFM and DFA to create a holistic approach to product design. This method is particularly beneficial for complex products, such as medical devices and automotive components, where both manufacturing and assembly efficiency are crucial. Buyers should consider DFMA for its potential to deliver significant cost savings and quality improvements. However, implementing this approach can be more complex and may require advanced collaboration between design and manufacturing teams.
How Does Design for Sustainability (DFS) Impact Purchasing Decisions?
Design for Sustainability (DFS) incorporates environmental considerations into the product design process, making it increasingly relevant for companies looking to enhance their brand reputation and meet regulatory requirements. Industries such as consumer products and packaging can greatly benefit from DFS. B2B buyers should evaluate the long-term advantages of sustainability, despite potential higher initial costs, as this approach can lead to reduced waste and improved compliance with environmental standards.
What are the Key Considerations for Design for Cost (DFC)?
Design for Cost (DFC) prioritizes minimizing production costs through strategic design choices, making it particularly applicable in mass production environments like consumer electronics. B2B buyers focused on competitive pricing should consider DFC, as it can lead to direct cost savings. However, this approach may come at the expense of product quality or functionality, making it essential for buyers to balance cost with overall product value.
Key Industrial Applications of dfm guidelines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of dfm guidelines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Streamlining component design for vehicle assembly | Reduced production costs and improved time-to-market | Availability of standardized parts and local manufacturing capabilities |
| Electronics | Designing circuit boards for ease of assembly | Enhanced product quality and reduced manufacturing defects | Sourcing reliable suppliers for high-quality materials and components |
| Consumer Goods | Simplifying packaging designs for mass production | Lower material costs and faster production cycles | Compliance with regional packaging regulations and sustainability standards |
| Aerospace | Optimizing parts for weight reduction without compromising safety | Increased fuel efficiency and lower operational costs | Ensuring compliance with stringent industry safety standards and certifications |
| Medical Devices | Designing user-friendly interfaces for devices | Improved patient outcomes and reduced training costs | Sourcing biocompatible materials and adhering to regulatory requirements |
How Are DFM Guidelines Applied in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, DFM guidelines are crucial for streamlining component design, particularly for complex assemblies like engines and transmissions. By simplifying designs and utilizing standardized components, manufacturers can significantly reduce production costs and enhance the speed of assembly. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate local manufacturing capabilities to mitigate long lead times and customs issues.
What Role Does DFM Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics, DFM is applied by focusing on the design of circuit boards that facilitate easier assembly and minimize defects. This approach leads to enhanced product quality and reliability, which is essential in a highly competitive market. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider sourcing from suppliers who can provide high-quality materials and components that meet international standards, ensuring performance and compliance.
How Can DFM Improve Consumer Goods Packaging?
For consumer goods, DFM guidelines can simplify packaging designs to optimize for mass production. This not only lowers material costs but also accelerates production cycles. B2B buyers, particularly in Europe, must ensure that their packaging suppliers comply with regional regulations and sustainability standards to avoid potential fines and enhance brand reputation in environmentally conscious markets.
Why Is DFM Essential in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, DFM focuses on optimizing parts for weight reduction while maintaining safety standards. This leads to increased fuel efficiency and lower operational costs, crucial for airlines striving to improve profitability. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with stringent industry safety standards and certifications, which are critical for maintaining operational integrity.
How Does DFM Enhance Medical Device Design?
DFM guidelines are instrumental in designing medical devices with user-friendly interfaces, which can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce training costs for healthcare professionals. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing biocompatible materials and ensure that their suppliers adhere to regulatory requirements, which is vital for the safety and effectiveness of medical devices in diverse markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘dfm guidelines’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Product Designs
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter intricate product designs that complicate the manufacturing process, leading to increased costs and extended lead times. This complexity arises when multiple components are involved, requiring specialized assembly techniques. Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, where skilled labor may be limited, find it particularly challenging to manage these complex designs, resulting in higher production errors, wasted materials, and ultimately, reduced profitability.
The Solution:
To address this challenge, B2B buyers should prioritize simplification in their design approach by adhering to DFM guidelines. Begin by conducting a thorough review of the product’s design and identifying components that can be eliminated or combined. Use standardized parts wherever possible to minimize the variety of components needed. Engaging cross-functional teams during the design phase can also foster innovative ideas for simplification. For instance, employing 3D modeling tools can help visualize potential manufacturing challenges early on, enabling teams to iterate designs that are easier to assemble. This proactive approach can significantly reduce complexity and enhance efficiency, ultimately leading to lower production costs and faster time-to-market.
Scenario 2: Managing Material Selection and Costs
The Problem:
Another prevalent pain point for B2B buyers is the challenge of selecting appropriate materials that balance cost, availability, and manufacturability. Companies in South America and Europe often face fluctuating material prices and availability, which can derail budgets and production timelines. A lack of understanding regarding the implications of material choices can lead to subpar product quality or even compliance issues with local regulations.
The Solution:
B2B buyers should adopt a systematic approach to material selection by leveraging DFM principles. Begin by conducting market research to identify reliable suppliers that offer materials meeting both quality and cost requirements. Collaborate with design engineers to assess material properties and ensure they align with the product’s functional needs. Utilize tools such as material selection software to compare different options based on criteria such as cost, availability, and manufacturability. Furthermore, consider engaging in long-term contracts with suppliers to stabilize costs and ensure consistent material availability. This strategic approach not only optimizes material usage but also supports better budgeting and compliance with industry standards.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Assembly Challenges
The Problem:
Assembly challenges are a significant concern for B2B buyers, particularly when dealing with products that require intricate assembly processes. Buyers in regions like the Middle East may struggle with labor shortages or a lack of training among assembly workers, leading to increased errors and inefficiencies during production. This can cause delays, higher operational costs, and dissatisfaction among end customers.
The Solution:
To mitigate assembly issues, B2B buyers should integrate DFM guidelines that emphasize design for assembly (DFA). Begin by analyzing the current assembly process to identify bottlenecks or areas of complexity. Simplify assembly steps by designing components that can be easily aligned, fastened, and connected without requiring extensive manual labor. Implementing modular design principles can also facilitate easier assembly and disassembly. Additionally, investing in training programs for assembly workers can enhance their skills and reduce the likelihood of errors. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and regularly reviewing assembly processes, companies can significantly enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve overall product quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for dfm guidelines
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for DFM Guidelines?
Aluminum: A Lightweight Champion
Aluminum is renowned for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it a preferred choice in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace. Its temperature rating can reach up to 600°F (315°C), and it exhibits good corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized. However, while aluminum is durable, it can be more expensive than other metals, and its manufacturing processes can be complex, especially when intricate designs are involved. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, understanding the local availability of aluminum and compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial for ensuring consistent quality and performance.
Stainless Steel: The Corrosion-Resistant Workhorse
Stainless steel is celebrated for its exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as the oil and gas industry. It can withstand temperatures up to 1600°F (870°C) and is available in various grades, each suited for specific applications. While it offers excellent longevity, the higher cost and complexity of machining can be drawbacks. International buyers should consider the common standards applicable in their regions, such as JIS for Japan or ASTM for the U.S., to ensure compliance and compatibility in their supply chains.
Polycarbonate: The Versatile Plastic
Polycarbonate is a robust plastic known for its high impact resistance and transparency, making it a popular choice for safety equipment and electronic housings. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°F to 240°F (-40°C to 115°C) and has good dimensional stability. However, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications and can be more expensive than other plastics. For B2B buyers in regions like South America and Europe, understanding the material’s compliance with environmental regulations and its recyclability can be essential for sustainable practices.
Carbon Fiber: The Lightweight Innovator
Carbon fiber is a high-performance material known for its incredible strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness. It can handle temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) and is often used in high-end applications like aerospace and automotive. However, its high cost and complex manufacturing processes can limit its use in more budget-sensitive projects. International buyers should be aware of the specific certifications and standards required for carbon fiber products in their respective markets, particularly in Europe where regulations can be stringent.
Summary of Material Selection for DFM Guidelines
| Material | Typical Use Case for DFM Guidelines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight with excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas equipment | Exceptional corrosion resistance and durability | High cost and machining complexity | High |
| Polycarbonate | Safety equipment and electronic housings | High impact resistance and transparency | Limited high-temperature suitability | Medium |
| Carbon Fiber | Aerospace and high-performance automotive | Incredible strength-to-weight ratio | Very high cost and complex processes | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with DFM principles while considering regional standards and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dfm guidelines
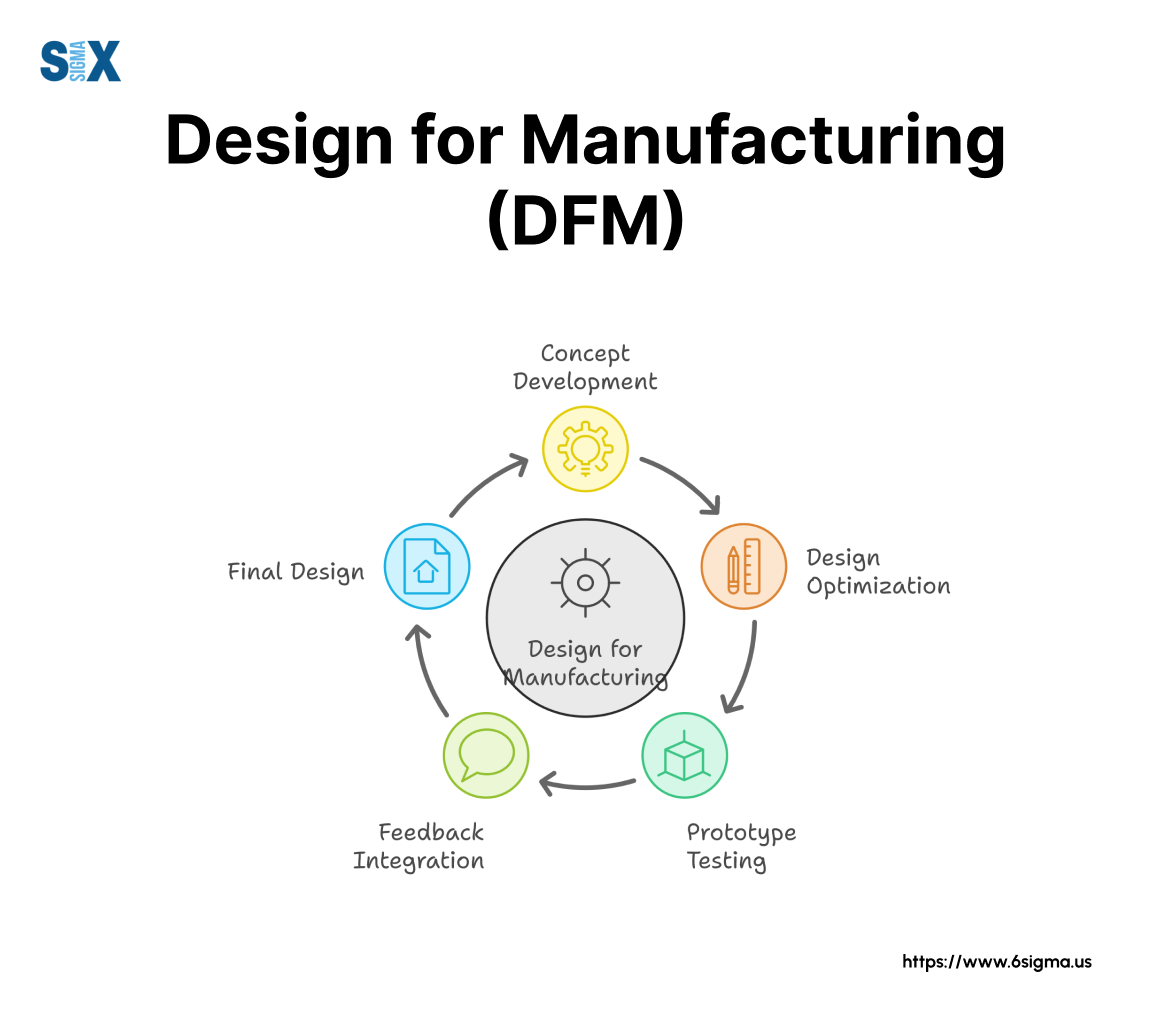
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes in DFM?
In the context of Design for Manufacturing (DFM), understanding the manufacturing processes is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize product development and production efficiency. The typical manufacturing process can be divided into four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Does Material Preparation Impact Manufacturing Efficiency?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process and involves selecting the right materials and preparing them for production. This stage includes activities like cutting, shaping, and treating raw materials to ensure they meet specific requirements. For B2B buyers, the choice of materials can significantly influence both cost and quality. Utilizing standardized materials can reduce lead times and costs, while ensuring compliance with international standards.
Additionally, incorporating DFM principles during material preparation allows manufacturers to assess the suitability of materials for the intended manufacturing processes, leading to better outcomes. For example, using lighter materials may simplify the forming and assembly processes, ultimately reducing production costs.
What Techniques Are Commonly Used in the Forming Stage?
Forming is the second stage of the manufacturing process, where raw materials are shaped into desired forms. Common techniques include:
- Casting: Pouring molten material into a mold to create complex shapes.
- Machining: Removing material from a workpiece using cutting tools to achieve precise dimensions.
- Stamping: Using a die to cut or shape metal sheets into specific designs.
- Molding: Shaping materials (like plastics) by heating and then cooling them in molds.
Each technique has its advantages and limitations, and selecting the appropriate method is vital for meeting design specifications while controlling costs. B2B buyers should engage with suppliers to understand the capabilities and limitations of their forming techniques, ensuring alignment with DFM guidelines.
How Does Assembly Influence the Quality of the Final Product?
Assembly refers to the process of combining different components to create a finished product. Effective assembly processes minimize errors and improve efficiency. Key considerations include:
- Simplicity of Design: Reducing the number of parts can streamline assembly, making it easier to produce and maintain high quality.
- Ergonomics: Designing components that fit together intuitively can decrease assembly time and reduce the potential for errors.
- Standardization: Utilizing standardized components can simplify the assembly process and enhance quality control.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who implement DFM principles in their assembly processes, as this can lead to higher quality products and lower overall costs.
What Finishing Techniques Are Essential for High-Quality Products?
The finishing stage involves processes that enhance the appearance and durability of the product. Common finishing techniques include:
- Coating: Applying a layer of paint, varnish, or other materials to protect and enhance the product’s surface.
- Polishing: Smoothing the surface of a product to improve aesthetics and reduce friction.
- Heat Treatment: Strengthening materials through controlled heating and cooling processes.
Quality finishing can significantly impact the perceived value of a product. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to finishing quality standards that align with their market requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for DFM?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the DFM process. International standards, such as ISO 9001, provide frameworks for ensuring quality management systems are in place. These standards emphasize continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance, which are essential for maintaining quality throughout the manufacturing process.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific standards may apply, such as:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for manufacturers in the oil and gas industry to ensure quality in products and services.
For B2B buyers, understanding these standards is crucial in evaluating potential suppliers and ensuring product quality.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Integrated into the DFM Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential for maintaining product quality throughout the manufacturing process. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring production processes to detect and rectify issues as they arise.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting a thorough inspection of finished products before shipment.
Implementing these checkpoints allows manufacturers to identify defects early, reducing waste and ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market. B2B buyers should inquire about the QC processes employed by suppliers to ensure alignment with their quality standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in DFM?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality and performance of products designed with DFM principles. Common testing methods include:
- Functional Testing: Assessing whether the product performs as intended under various conditions.
- Material Testing: Evaluating the properties of materials used in production to ensure they meet specifications.
- Durability Testing: Simulating long-term use to identify potential failure points.
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers utilize appropriate testing methods and maintain detailed reports of testing outcomes. This transparency helps buyers assess product quality and reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential. Buyers can implement several strategies:
- Audits: Conducting on-site audits of suppliers to evaluate their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to standards.
- Reports: Requesting regular quality control reports detailing inspection results, testing outcomes, and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to verify that suppliers meet specified quality standards.
Understanding the nuances of QC and certifications can provide B2B buyers with confidence in their supply chain, ensuring that products meet both international and local standards.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider in Quality Control?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances when it comes to quality control. These include:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations is vital, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarizing themselves with local regulations and standards is crucial for ensuring product acceptance in different markets.
- Logistical Challenges: Considering the impact of transportation and storage on product quality during international shipping.
By acknowledging these nuances, B2B buyers can foster stronger relationships with suppliers and ensure that their quality expectations are met consistently.
In conclusion, incorporating DFM principles into manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices not only enhances product quality but also drives cost efficiency and competitive advantage. B2B buyers should prioritize these aspects when selecting suppliers to ensure successful product development and market performance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘dfm guidelines’
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Design for Manufacturing (DFM) guidelines is essential for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their product development processes. This checklist serves as a practical guide to ensure you effectively source DFM principles, which can significantly enhance manufacturing efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
Step 1: Identify Your Product Requirements
Before diving into DFM guidelines, clearly define your product’s functional and technical specifications. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for all subsequent sourcing activities. Consider factors like performance expectations, target market, and regulatory requirements.
- Functional Specifications: Outline what the product must accomplish.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure alignment with local and international standards.
Step 2: Research DFM Frameworks and Standards
Understanding the various DFM frameworks available is vital for informed decision-making. Investigate established guidelines that are relevant to your industry, as these can provide a structured approach to designing for manufacturability.
- Industry-Specific Guidelines: Look for standards published by organizations relevant to your sector.
- Global Standards: Familiarize yourself with ISO or ASTM standards that might impact your product.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thorough vetting of suppliers is essential before making commitments. Request comprehensive profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients in similar markets to validate their expertise in DFM.
- Supplier Experience: Check their history in implementing DFM principles.
- Client Testimonials: Seek feedback from businesses that have collaborated with them.
Step 4: Verify Technical Capabilities
Assess whether potential suppliers possess the necessary technical capabilities to implement DFM effectively. This includes evaluating their manufacturing processes, technology, and workforce skills.
- Manufacturing Technology: Confirm they utilize advanced machinery that supports DFM practices.
- Skilled Labor: Ensure they have a workforce trained in modern manufacturing techniques.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples or prototypes to evaluate their DFM application. This practical insight can help you gauge the supplier’s ability to meet your design requirements effectively.
- Quality Assessment: Analyze the samples for adherence to your specifications.
- Feedback Loop: Use this opportunity to assess their responsiveness to design iterations.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is key to successful DFM implementation. Set up regular meetings or updates to discuss progress, challenges, and any necessary adjustments to the design or manufacturing processes.
- Project Management Tools: Utilize collaborative platforms for real-time updates.
- Design Reviews: Schedule periodic reviews to address potential issues early.
Step 7: Monitor and Evaluate Performance
After selecting a supplier, continuously monitor their performance against established metrics. Evaluate their ability to deliver on time, maintain quality, and adapt to any changes in design requirements.
- Performance Metrics: Track lead times, defect rates, and overall quality.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement regular feedback sessions to improve the partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can strategically source DFM guidelines that align with their organizational goals, ensuring a smoother transition from design to production and ultimately leading to enhanced product success in the marketplace.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dfm guidelines Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in DFM Guidelines Sourcing?
When assessing the cost structure of sourcing DFM guidelines, several components play a crucial role. The primary cost factors include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts overall costs. Opting for readily available and cost-effective materials can lead to substantial savings. Additionally, sourcing local materials may reduce shipping costs and lead times, particularly relevant for international buyers.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and skill level. In regions like Africa and South America, labor may be more affordable, but it’s essential to ensure that the workforce is adequately trained in DFM principles to avoid costly mistakes during production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Understanding the overhead structure of your suppliers can provide insights into the overall pricing strategy.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider whether the tooling can be reused for future production runs, which can amortize costs over time.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures can lead to higher upfront costs but ultimately saves money by reducing defects and rework. Investing in quality assurance is particularly critical for international markets where regulatory compliance is stringent.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary dramatically based on distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms. Understanding these factors can help buyers negotiate better terms and optimize their supply chain.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin that reflects their costs and market conditions. This margin can vary significantly depending on the supplier’s location and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Impact DFM Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of DFM guidelines, affecting the total cost of ownership for buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can enable buyers to negotiate better terms based on projected volumes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs can increase costs due to additional engineering and tooling requirements. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential for higher expenses.
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials can dramatically alter costs. Buyers should explore alternatives that meet quality standards while being more cost-effective.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific certifications may incur additional costs. Understanding the certification requirements in the target market is essential for accurate budgeting.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge a premium, but their reliability can offset potential risks.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping costs, insurance, and liability. Understanding these terms can lead to more favorable negotiations and lower overall expenses.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize DFM Sourcing Costs?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can benefit from several strategic approaches:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about payment terms, delivery schedules, and pricing structures. Building a good rapport can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. This approach includes considering maintenance, logistics, and potential defects.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences and how local economic conditions can affect supplier pricing strategies. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Leverage Long-Term Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more flexible terms. Consider establishing contracts for recurring orders to secure favorable rates.
-
Perform Due Diligence: Thoroughly research potential suppliers to understand their capabilities, financial stability, and reputation in the market. This insight can prevent costly mistakes and ensure a smooth sourcing process.
Disclaimer
Prices and cost structures mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough research and consult with suppliers to obtain the most accurate pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing dfm guidelines With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to DFM Guidelines for Manufacturing Optimization
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, companies continuously seek methods to optimize their processes. Design for Manufacturing (DFM) is a prominent approach that emphasizes the integration of manufacturing considerations into the product design phase. However, there are other viable methodologies that can be considered for enhancing production efficiency and product quality. This analysis compares DFM guidelines with two notable alternatives: Design for Assembly (DFA) and Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA).
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | DFM Guidelines | Design for Assembly (DFA) | Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in manufacturing | Reduces assembly time and errors | Combines DFM and DFA for optimized efficiency |
| Cost | Potentially lowers production costs | May require initial investment | Moderate costs with high ROI |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires cross-functional collaboration | Simpler than DFM, focused on assembly | More complex due to integration of two methods |
| Maintenance | Continuous improvement needed | Low maintenance once established | Requires ongoing assessment and adjustment |
| Best Use Case | Complex products needing manufacturing optimization | Products with high assembly complexity | Products where both manufacturing and assembly are critical |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Design for Assembly (DFA)?
Design for Assembly (DFA) focuses specifically on simplifying the assembly process of products. This method is particularly beneficial for products with numerous components, as it aims to minimize the number of parts and streamline assembly steps. The main advantage of DFA is its ability to significantly reduce assembly time and minimize errors, leading to improved product quality. However, its limitations include a narrower focus that may overlook some critical manufacturing aspects, making it less effective for complex manufacturing environments.
How Does Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) Enhance Production Efficiency?
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) merges the principles of DFM and DFA, creating a comprehensive approach that addresses both manufacturing and assembly processes. This methodology is particularly effective for products requiring careful consideration of both design and assembly efficiency. The primary benefit of DFMA is its holistic view, which allows manufacturers to optimize the entire product lifecycle, reducing costs and enhancing product performance. However, the complexity of implementing DFMA can be a drawback, as it requires thorough training and collaboration across various departments.
How Can B2B Buyers Make the Right Choice Among These Solutions?
When evaluating the right solution for manufacturing optimization, B2B buyers should consider their specific product requirements and operational capabilities. For companies producing complex products that require extensive manufacturing processes, DFM may be the most beneficial approach. Conversely, those focusing on streamlining assembly may find DFA more suitable. DFMA serves as a middle ground, ideal for organizations needing a balanced focus on both manufacturing and assembly. Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s strategic goals, budget constraints, and the nature of their products to ensure maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dfm guidelines
What Are the Key Technical Properties Essential for DFM Guidelines?
When engaging in Design for Manufacturing (DFM), understanding critical technical properties is vital for optimizing production processes and ensuring product quality. Here are several key specifications that play a crucial role in DFM:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of materials based on their mechanical and chemical properties. In DFM, selecting the right material grade is essential for ensuring that the product can withstand intended use while remaining cost-effective. For B2B buyers, understanding material grades helps in negotiating prices and ensuring compliance with industry standards. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in manufacturing. It is crucial in ensuring that parts fit together correctly during assembly. Tight tolerances can lead to increased production costs and complexity, while loose tolerances may compromise product quality. B2B buyers must grasp the balance between cost and precision to avoid costly reworks or defects. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of a manufactured surface. It affects not only the aesthetic appeal of a product but also its functionality, such as friction and wear resistance. Buyers should consider surface finish requirements early in the design phase to avoid additional processing costs later. -
Dimensional Stability
Dimensional stability is the ability of a material to maintain its dimensions under varying environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, etc.). This property is crucial for products that will be used in diverse climates, especially for international markets. Ensuring dimensional stability can prevent costly failures and enhance customer satisfaction. -
Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties such as tensile strength, ductility, and hardness are fundamental in determining how a material behaves under stress. Understanding these properties allows B2B buyers to select materials that not only meet performance requirements but also align with budget constraints.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to DFM?
In the realm of DFM, familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and decision-making. Here are several commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the role of OEMs is crucial for B2B buyers as it can influence sourcing strategies and partnerships. Buyers often seek OEMs for high-quality components that can enhance their product offerings. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it impacts inventory levels, cash flow, and overall purchasing strategy. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better terms and avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This term is essential for B2B transactions, as it helps buyers compare costs and make informed purchasing decisions. A well-crafted RFQ can streamline procurement and ensure competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding Incoterms is critical for B2B buyers to manage shipping costs, risk, and liability effectively. -
DFA (Design for Assembly)
DFA is a methodology focused on simplifying the assembly process. While closely related to DFM, it emphasizes the ease of putting parts together. B2B buyers should be aware of DFA principles to ensure that their products not only are manufacturable but also can be assembled efficiently, reducing labor costs and time to market. -
DFMA (Design for Manufacturing and Assembly)
DFMA combines both DFM and DFA principles to optimize the entire product lifecycle. This holistic approach ensures that products are designed with both manufacturing and assembly in mind, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. B2B buyers should advocate for DFMA practices to maximize production effectiveness.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance product quality, streamline manufacturing processes, and improve overall competitiveness in the marketplace.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the dfm guidelines Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing DFM Guidelines in B2B Markets?
In the current landscape, several global drivers are shaping the Design for Manufacturing (DFM) sector, particularly for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Rapid technological advancements, such as the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, are enabling manufacturers to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. The demand for customized solutions is also on the rise, pushing manufacturers to adopt DFM principles to streamline production processes and improve product quality.
Emerging B2B tech trends, including automation and artificial intelligence, are transforming how companies approach manufacturing. These technologies facilitate real-time data analysis, allowing for better decision-making and resource allocation. Additionally, the shift towards digital platforms for sourcing and procurement is changing market dynamics, making it easier for buyers to find suppliers who adhere to DFM guidelines.
Furthermore, geopolitical factors and trade agreements are influencing sourcing strategies. For instance, businesses in regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria are increasingly looking for reliable partners who can meet DFM standards while navigating local regulatory landscapes. The emphasis on reducing lead times and optimizing supply chains is paramount, making DFM not just a design consideration but a strategic advantage in a competitive global market.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting DFM Guidelines?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing practices, influencing B2B buyers to prioritize ethical sourcing and environmentally friendly materials. The environmental impact of production processes cannot be overlooked, as companies face increasing pressure from consumers and regulators to minimize their carbon footprints. This shift is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations on emissions and waste management drive the adoption of sustainable practices.
Ethical supply chains are vital for building brand reputation and customer loyalty. Companies that implement DFM principles often focus on using ‘green’ certifications and materials to enhance their product offerings. This not only helps reduce waste during manufacturing but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses. By selecting sustainable materials and optimizing designs for minimal environmental impact, manufacturers can achieve significant cost savings while enhancing product quality.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and LEED for sustainable building practices are increasingly important in the DFM space. These certifications signal to buyers that a manufacturer is committed to ethical practices, thus influencing purchasing decisions. As the global market evolves, integrating sustainability into DFM guidelines will be essential for long-term success.
What Is the Evolution of DFM Guidelines and Their Relevance in Today’s B2B Context?
The concept of Design for Manufacturing (DFM) has evolved significantly over the years, adapting to the changing needs of the manufacturing industry. Initially focused on simplifying production processes, DFM has expanded to encompass a broader range of considerations, including sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and quality enhancement. The integration of methodologies such as Lean and Six Sigma has further refined DFM principles, emphasizing waste reduction and continuous improvement.
In today’s B2B context, the relevance of DFM cannot be overstated. As companies face increasing competition and demand for rapid innovation, adopting DFM guidelines is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. By prioritizing manufacturability from the outset, organizations can reduce costs, improve product quality, and accelerate time-to-market. The evolution of DFM reflects a shift towards a more holistic approach to product development, making it an indispensable strategy for international buyers seeking reliable, high-quality manufacturing partners.
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of the DFM guidelines sector requires a keen understanding of market dynamics, a commitment to sustainability, and a recognition of the evolving landscape of manufacturing practices. International B2B buyers must leverage these insights to make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dfm guidelines
-
How do I solve issues related to high manufacturing costs when sourcing products?
To address high manufacturing costs, consider implementing Design for Manufacturing (DFM) principles. Begin by simplifying your product design to minimize complexity and reduce the number of components. Standardizing parts can also lead to cost savings. Collaborate with suppliers early in the design process to identify potential production challenges and optimize manufacturing methods. Additionally, sourcing materials that are locally available in your region can help lower costs and improve efficiency. -
What is the best approach to vet suppliers for DFM compliance?
When vetting suppliers for DFM compliance, prioritize those with a proven track record in adopting DFM principles. Request case studies or references showcasing their previous projects. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, technology, and certifications, particularly in quality management systems like ISO 9001. Conduct site visits if possible to assess their facilities and processes. Additionally, ensure that they have a collaborative approach to design, allowing for iterative feedback during the development phase. -
How can I customize products while adhering to DFM guidelines?
Customizing products within DFM guidelines requires a balance between flexibility and manufacturability. Start by clearly defining your customization needs and ensure they align with DFM principles such as simplification and standardization. Work closely with your supplier to explore modular designs that allow for customization without complicating manufacturing processes. This can include using interchangeable parts or designing for easy assembly. Regular communication throughout the design phase will help ensure that modifications do not compromise production efficiency. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for DFM-compliant products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for DFM-compliant products can vary significantly based on factors such as the supplier’s capabilities, the complexity of the product, and the materials used. Generally, suppliers may set MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness in production. For custom or specialized items, MOQs might be higher due to setup costs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your business requirements while ensuring adherence to DFM principles. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing DFM-compliant products?
Payment terms when sourcing DFM-compliant products can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include partial upfront payments, progress payments during production, and final payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. In international transactions, consider factors such as currency fluctuations and transaction fees. Establishing a transparent payment schedule that aligns with production milestones can foster a stronger partnership and ensure a smooth procurement process. -
How do quality assurance (QA) processes impact DFM in manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) processes are critical in ensuring that DFM principles are effectively implemented during manufacturing. A robust QA framework helps identify potential defects early in the production cycle, reducing waste and rework. Incorporating QA checks at various stages, such as design reviews and prototype testing, ensures that the final product meets both functional and quality standards. Engaging in regular communication with your supplier about QA processes can enhance product reliability and compliance with DFM guidelines. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing DFM products internationally?
When sourcing DFM products internationally, logistics considerations include shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose shipping methods that align with your delivery timelines and budget, considering air freight for faster delivery or ocean freight for cost savings. Understand the import/export regulations in your region and work with suppliers who have experience in international logistics. Additionally, plan for potential delays in customs clearance by allowing buffer time in your project schedules. -
How can I ensure regulatory compliance when implementing DFM in my products?
To ensure regulatory compliance when implementing DFM, familiarize yourself with the relevant industry standards and regulations applicable to your products. Collaborate with your supplier to integrate compliance checks throughout the design and manufacturing processes. This includes adhering to safety, environmental, and quality standards. Regular audits and documentation can help maintain compliance and provide transparency to stakeholders. Engaging legal or compliance experts may also be beneficial to navigate complex regulatory landscapes effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Dfm Guidelines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. 6Sigma – Design for Manufacturing
Domain: 6sigma.us
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Design for Manufacturing (DFM) is a comprehensive methodology that integrates manufacturing considerations into the product design process from the very beginning. Key principles of DFM include: 1. Simplification – reducing complexity of design, leading to fewer components and lower assembly costs. 2. Standardization – using standard components to reduce inventory costs and simplify assembly. 3. M…
2. ProtoExpress – DFM Rules for PCB Design
Domain: protoexpress.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: DFM rules for PCB design ensure manufacturability by adhering to fabricator capabilities such as trace width, drill size, and via types. Ignoring these rules can lead to costly redesigns. DFM analysis evaluates PCB layouts to minimize manufacturing issues, utilizing CAD tools to set constraints. Key files required for fabrication include Gerber/ODB++ files, NC drill files, IPC 356A netlists, and c…
3. Protolabs – Advanced Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Protolabs offers a range of manufacturing services including Injection Molding (plastic and liquid silicone rubber), CNC Machining (milling and turning), 3D Printing (metal and various additive manufacturing methods), and Sheet Metal Fabrication (laser cutting, punching, forming, and bending). They provide rapid prototyping and production capabilities, with a focus on quality and efficiency. New m…
4. Alpha Circuit – PCB Manufacturing Excellence
Domain: alphacircuit.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Alpha Circuit I LLC specializes in high-quality printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing. They emphasize the importance of Design for Manufacturing (DFM) principles to ensure smooth transitions from design to production, reduce costs, improve manufacturability, and minimize errors. Key DFM rules include maintaining design clearance, optimizing trace widths, minimizing layer counts, using standard…
5. Fractory – Design for Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: fractory.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Design for Manufacturing (DFM) is a product design ideology that optimizes product design by selecting suitable materials and manufacturing processes for easier and cost-effective production. Key principles include optimizing manufacturing processes, product design, product material, service environment, and testing compliance with standards. DFM aims to minimize manufacturability issues, reduce r…
6. Five Flute – Engineering Design Review Platform
Domain: fiveflute.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Five Flute offers an engineering design review platform focused on sheet metal design for manufacturability (DFM) for formed and punched parts. The platform emphasizes the importance of understanding various cutting processes such as waterjet, laser cutting, and punch pressing, which are essential for preparing sheet metal blanks. Key considerations include cut quality, kerf width, and tolerances …
7. Altium – DFM and DFA Essentials
Domain: resources.altium.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: DFM (Design for Manufacturability) and DFA (Design for Assembly) are essential processes in PCB design that ensure a circuit can be manufactured and assembled using current technologies. DFM focuses on the rules and guidelines for manufacturability, while DFA addresses assembly requirements. Key considerations include trace widths, spacing, drilling, masks, and component placement. The IPC standar…
8. aPriori – Design for Manufacturability Guide
Domain: apriori.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: A Guide to Design for Manufacturability (DFM) by aPriori provides an overview of DFM methodology, emphasizing its importance in avoiding costly mistakes during product modeling that can complicate manufacturing and sustainability goals. It defines manufacturability, which is the degree to which a product can be effectively manufactured based on design, cost, and distribution requirements. The guid…
9. Titoma – DFM Solutions
Domain: titoma.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: DFM (Design For Manufacturing) is the process of designing parts, components, or products for a smooth transition into mass manufacturing, focusing on maintaining quality and reducing costs. Key advantages include a smooth transition from prototyping to mass manufacturing, lower production costs while maintaining quality, faster time to market, and minimal mistakes during assembly. There are speci…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dfm guidelines
How Can DFM Transform Your Strategic Sourcing Approach?
Incorporating Design for Manufacturing (DFM) principles into your strategic sourcing strategy is paramount for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. DFM not only simplifies production processes but also reduces costs, improves product reliability, and accelerates time-to-market. By prioritizing DFM during the early stages of product development, companies can proactively address manufacturing challenges, ensuring a smoother transition from design to production.
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, embracing DFM can lead to significant competitive advantages. It fosters collaboration between design and manufacturing teams, promoting innovation and responsiveness to market demands. As global supply chains become increasingly complex, leveraging DFM principles will enable businesses to mitigate risks and optimize resource allocation.
As you consider your next sourcing decisions, remember that adopting DFM is not merely a technical adjustment but a strategic imperative. Engage with suppliers who prioritize DFM, and explore how these guidelines can drive your product development to new heights. The future of manufacturing is here—make it work for you.