Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for custom foam molding
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing custom foam molding solutions can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As companies seek to enhance their product offerings—ranging from protective packaging to consumer goods—the demand for tailored foam solutions continues to grow. This guide is designed to equip you with the insights necessary to navigate the complexities of the custom foam molding market, offering a comprehensive overview of available materials, diverse applications, and the critical factors to consider when evaluating potential suppliers.
Throughout this guide, you will discover the various types of custom foam materials—such as expanded polystyrene, polyurethane, and innovative composites—each with unique properties that cater to specific industry needs. We delve into the applications of custom foam molding, highlighting its significance across sectors like automotive, electronics, and consumer products. Additionally, we provide practical advice on supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the importance of prototyping to ensure that your final product meets both design specifications and market expectations.
By leveraging the insights provided in this guide, you will be empowered to make informed purchasing decisions, streamline your sourcing process, and ultimately enhance your competitive edge in a global marketplace. Whether you’re looking to innovate or optimize existing products, understanding the landscape of custom foam molding is crucial for your business’s success.
Understanding custom foam molding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) | Lightweight, rigid, excellent insulation properties | Packaging, insulation, construction | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Less durable, can be brittle. |
| Expanded Polyethylene (EPE) | Flexible, durable, shock-absorbing | Protective packaging, automotive | Pros: Resistant to moisture, good cushioning; Cons: Higher cost than EPS. |
| Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) | Lightweight, resilient, and recyclable | Automotive parts, sports equipment | Pros: Superior energy absorption, long lifespan; Cons: More expensive than EPE and EPS. |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Versatile, can be rigid or flexible, high resilience | Furniture, mattresses, industrial | Pros: Excellent durability and comfort; Cons: Can be costly, varies in density. |
| EVA Foam | Soft, lightweight, chemical-resistant | Footwear, sporting goods, toys | Pros: Safe, easy to clean; Cons: Limited structural integrity compared to others. |
What are the characteristics of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and its suitability for B2B applications?
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a lightweight and rigid foam material known for its excellent insulation properties. It is particularly suitable for packaging fragile items and thermal insulation in construction. B2B buyers often prefer EPS due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility in various applications. However, its brittleness can be a drawback, especially in environments where durability is essential. Buyers should consider the balance between cost and the specific performance needs of their applications.
How does Expanded Polyethylene (EPE) differ in terms of flexibility and durability?
Expanded Polyethylene (EPE) is characterized by its flexibility and durability, making it an ideal choice for applications that require shock absorption, such as protective packaging for electronics and automotive parts. Its resistance to moisture and chemicals enhances its appeal for industries needing reliable packaging solutions. While EPE tends to be more expensive than EPS, its superior cushioning properties justify the investment for many B2B buyers, especially in high-value sectors.
What advantages does Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) offer for industrial applications?
Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) stands out for its lightweight, resilient nature, and recyclability, making it a popular choice in automotive parts and sports equipment. Its superior energy absorption capabilities provide excellent protection for sensitive components during transport. Although EPP is generally more costly than both EPE and EPS, its long lifespan and performance make it a worthwhile investment for businesses looking to enhance product durability and reduce long-term costs.
In what scenarios is Polyurethane (PU) the preferred foam material?
Polyurethane (PU) foam is highly versatile, available in both rigid and flexible forms, and is renowned for its durability and comfort. Commonly used in furniture and mattresses, PU is also prevalent in industrial applications requiring high resilience. While its cost can be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers, the long-term benefits of durability and comfort often outweigh the initial investment, particularly in industries focused on quality and customer satisfaction.
Why choose EVA Foam for specific product applications?
EVA foam is recognized for its softness, lightweight nature, and chemical resistance, making it a favorite in the footwear and sporting goods industries. Its safety and ease of cleaning are significant advantages for products intended for consumer use. However, EVA foam’s limited structural integrity compared to other foam types may restrict its use in applications requiring high strength. Buyers should assess the specific needs of their products and consider EVA foam’s unique benefits when making their selection.
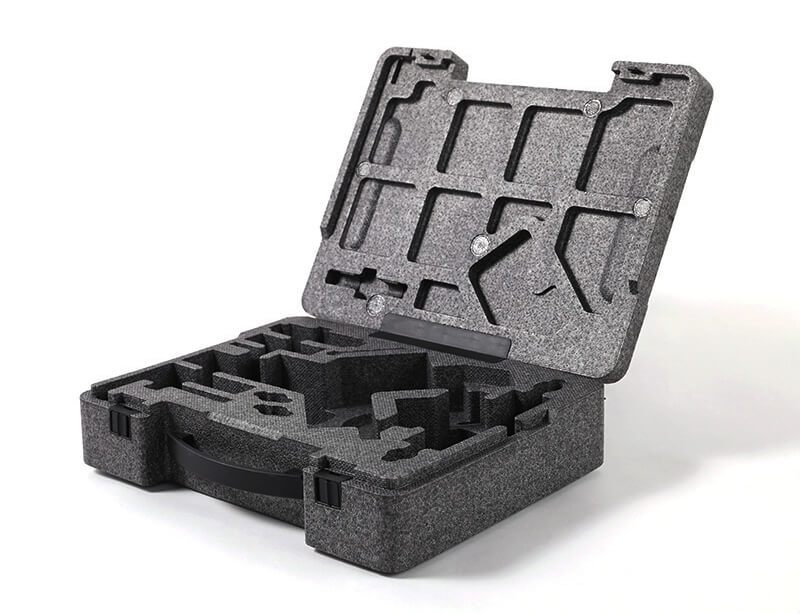
Key Industrial Applications of custom foam molding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of custom foam molding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Interior cushioning and soundproofing | Enhances passenger comfort and reduces noise pollution | Material durability, weight reduction, and compliance with safety standards |
| Packaging | Protective packaging for fragile goods | Minimizes damage during transportation and storage | Customization options, sustainability of materials, and cost-effectiveness |
| Consumer Electronics | Custom foam inserts for electronic devices | Provides secure fit, reduces movement, and protects devices | Precision in dimensions, anti-static properties, and compatibility with various shapes |
| Medical Equipment | Foam padding for hospital beds and surgical equipment | Improves patient comfort and safety during medical procedures | Biocompatibility, ease of cleaning, and compliance with healthcare regulations |
| Sports and Recreation | Custom foam for sporting goods and protective gear | Enhances performance and safety for athletes | Lightweight materials, moisture resistance, and customization capabilities |
How is Custom Foam Molding Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, custom foam molding is essential for creating interior cushioning and soundproofing materials. These foams are designed to absorb vibrations and noise, significantly enhancing passenger comfort. Buyers in this sector must prioritize materials that meet safety standards, are lightweight for fuel efficiency, and provide long-lasting durability. Sourcing from manufacturers who can deliver high-quality, compliant products is crucial, especially for international buyers in regions with strict automotive regulations.
What Role Does Custom Foam Molding Play in Packaging Solutions?
Custom foam molding is widely used in packaging applications to create protective inserts for fragile goods, such as electronics and glass products. By providing tailored cushioning, these foams minimize damage during transit and storage, reducing costs related to product returns and replacements. For B2B buyers, sourcing considerations include the ability to customize foam shapes to fit specific products, the sustainability of the materials used, and the overall cost-effectiveness of the packaging solutions.
How Does Custom Foam Molding Enhance Consumer Electronics?
In the consumer electronics industry, custom foam inserts are crucial for securing devices during shipping and handling. These foams are designed to fit the exact dimensions of the products, preventing movement and protecting against impacts. Buyers should consider the precision of the foam dimensions, anti-static properties to safeguard electronic components, and the flexibility of manufacturers to accommodate various device shapes. This is particularly important for international buyers looking for reliable packaging solutions that comply with local regulations.
In What Ways is Custom Foam Molding Applied in Medical Equipment?
Custom foam molding is utilized in medical equipment for padding hospital beds and surgical tools. The foams used in these applications enhance patient comfort and safety, which are paramount in healthcare settings. Buyers must ensure that the materials are biocompatible, easy to clean, and compliant with healthcare regulations. For international buyers, understanding local healthcare standards and sourcing from manufacturers with a strong compliance record is essential to ensure the safety and effectiveness of medical products.
How is Custom Foam Molding Beneficial in Sports and Recreation?
In the sports and recreation industry, custom foam is used to manufacture protective gear and sporting goods, such as helmets and pads. These foams are designed to enhance performance while ensuring the safety of athletes. When sourcing, buyers should focus on lightweight materials that offer moisture resistance and durability. Customization capabilities are also vital, as different sports may require specific foam properties to meet unique performance demands.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘custom foam molding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Material Selection Challenges in Custom Foam Molding
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the right material for their custom foam molding projects. With a variety of options available—such as Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), Polyurethane (PU), and EVA foam—making an informed choice can be daunting. The implications of this decision are significant; the wrong material can lead to product failure, increased costs, or even safety compliance issues, especially when dealing with international regulations.
The Solution: To address material selection challenges, buyers should first conduct thorough research on the properties and applications of each foam type. Engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive material data sheets and expert consultations can provide valuable insights tailored to specific needs. For instance, if a product requires moisture resistance and durability, Polyurethane might be more suitable than EPS. Additionally, buyers should request samples or prototypes for testing to evaluate performance under real-world conditions. Establishing a collaborative relationship with manufacturers can ensure that material choices align with both functional requirements and budget constraints.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Prototyping Delays in the Custom Foam Molding Process
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face delays in the prototyping phase of custom foam molding projects, which can significantly impact timelines and market launch schedules. Complications arise from unclear design specifications or a lack of efficient communication with manufacturers. Delays in receiving prototypes can lead to extended lead times, increased costs, and lost competitive advantage.
The Solution: To mitigate prototyping delays, it’s crucial for buyers to provide clear and detailed design specifications upfront. Utilizing 3D modeling software can help visualize the final product and reduce misunderstandings. Additionally, selecting a supplier that offers rapid prototyping services can expedite the process. Some manufacturers provide CNC cut prototypes that allow for quick iterations based on feedback. Establishing a direct line of communication with the design team can also streamline adjustments and ensure that the final product meets expectations. Regular updates and check-ins throughout the prototyping phase can help maintain momentum and keep the project on track.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with International Standards for Custom Foam Products
The Problem: B2B buyers, especially those in international markets, often encounter compliance issues related to safety and environmental standards when sourcing custom foam products. Regulations can vary significantly between regions, such as the EU’s REACH or the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA). Non-compliance can result in costly recalls, legal challenges, and damage to brand reputation.
The Solution: To navigate compliance complexities, buyers should prioritize working with manufacturers who are well-versed in international standards and can provide necessary certifications for their products. Conducting due diligence on potential suppliers, including reviewing their compliance history and certifications, is essential. Buyers should also seek manufacturers that offer documentation detailing material safety, environmental impact, and compliance with relevant standards. Furthermore, staying informed about regulatory changes in target markets can empower buyers to make proactive adjustments to their sourcing strategies. Engaging legal or compliance consultants may also be beneficial for larger projects to ensure that all aspects of the supply chain adhere to necessary regulations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for custom foam molding
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Custom Foam Molding?
When selecting materials for custom foam molding, it is essential to consider the specific properties and performance characteristics that align with your product requirements. Below, we analyze four common materials used in custom foam molding: Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), Polyurethane (PU), Expanded Polyethylene (EPE), and XL EXTRALIGHT® foam.
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
EPS is a lightweight, rigid foam material known for its excellent thermal insulation properties. It has a temperature rating of up to 75°C and is resistant to moisture, making it suitable for various applications, including packaging and insulation.
Pros: EPS is cost-effective and easy to mold, which simplifies manufacturing processes. It is also recyclable, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
Cons: Its structural integrity can be compromised under high pressure, and it is not suitable for applications requiring high durability. Additionally, EPS can be sensitive to certain solvents.
Impact on Application: EPS is ideal for packaging fragile items and insulation in construction. However, it may not be suitable for outdoor applications where UV exposure is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations regarding recyclability and environmental impact is crucial, especially in Europe where sustainability standards are stringent.
Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane foam is highly versatile and can be formulated to be either flexible or rigid. It has excellent resilience and can withstand a wide range of temperatures, typically between -30°C to 90°C.
Pros: PU offers superior durability and can be tailored for specific applications, such as cushioning or insulation. It also has good chemical resistance.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex and more expensive compared to other materials. Additionally, PU can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production.
Impact on Application: Its adaptability makes PU suitable for automotive, furniture, and medical applications. However, its VOC emissions may require compliance with health and safety regulations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding VOC emissions and seek materials that meet standards such as ASTM or DIN.
Expanded Polyethylene (EPE)
EPE is a closed-cell foam that is lightweight and offers excellent shock absorption. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 80°C and is resistant to moisture and chemicals.
Pros: EPE is durable and flexible, making it suitable for various applications, including protective packaging and insulation. It is also recyclable.
Cons: While EPE is resistant to many chemicals, it is less effective against certain solvents. Additionally, it may not provide the same level of insulation as EPS or PU.
Impact on Application: EPE is commonly used in packaging fragile items and in the construction industry for insulation. Its moisture resistance makes it a good choice for outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of recycling facilities in their region and ensure compliance with any local environmental regulations.
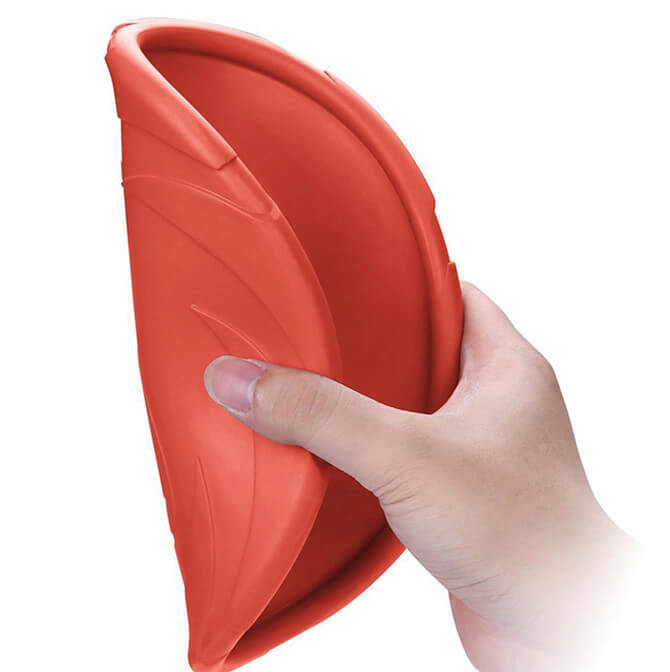
XL EXTRALIGHT® Foam
XL EXTRALIGHT® foam is a proprietary material known for its lightweight, waterproof, and chemical-resistant properties. It is suitable for temperatures up to 80°C and is free from harmful substances like phthalates and heavy metals.
Pros: This foam is exceptionally soft and easy to clean, making it ideal for consumer products like footwear and sports equipment. Its unique properties enhance product performance.
Cons: The cost of XL EXTRALIGHT® foam can be higher than traditional materials, which may impact budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, specialized manufacturing techniques may be required.
Impact on Application: XL EXTRALIGHT® foam is perfect for applications requiring high comfort and durability, such as in the footwear industry.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the material meets international safety standards, particularly when used in consumer products, to avoid compliance issues.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Custom Foam Molding
| Material | Typical Use Case for custom foam molding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) | Packaging, insulation | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Low structural integrity under pressure | Low |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Automotive, furniture, medical applications | Superior durability and chemical resistance | Complex manufacturing process | High |
| Expanded Polyethylene (EPE) | Protective packaging, insulation | Excellent shock absorption and moisture resistance | Less effective insulation than EPS | Medium |
| XL EXTRALIGHT® Foam | Footwear, sports equipment | Lightweight, waterproof, and easy to clean | Higher cost and specialized manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with crucial insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various foam materials, helping them make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for custom foam molding
The manufacturing processes for custom foam molding and the associated quality assurance protocols are crucial for B2B buyers aiming to procure high-quality foam products. This guide outlines the typical manufacturing stages, key techniques, and international quality assurance standards that B2B buyers should be aware of when selecting a supplier.
What Are the Main Stages in the Custom Foam Molding Manufacturing Process?
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used?
The first step in the manufacturing process involves selecting the appropriate foam material based on the product requirements. Common materials include:
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS): Lightweight and cost-effective, ideal for packaging and insulation.
- Expanded Polyethylene (EPE): Known for its flexibility and durability, often used in protective packaging.
- Polyurethane (PU): Offers excellent cushioning properties, commonly used in furniture and automotive applications.
Once the material is selected, it is prepped through processes like compounding or blending, ensuring uniformity and quality before molding.
How Is Foam Formed During the Custom Molding Process?
The forming stage is where the prepared materials are transformed into the desired shapes. This typically involves:
- Foam Injection Molding: A method where foam is injected into a mold under pressure, allowing for intricate designs and uniform density. This technique is effective for high-volume production and provides consistent quality.
- CNC Cutting: For prototypes or smaller runs, CNC machines can cut foam into precise shapes based on 3D drawings provided by design engineers. This flexibility allows for rapid adjustments during the development phase.
What Happens During the Assembly Phase?
Once the foam components are formed, they often need to be assembled into final products. This can include:
- Adhesive Bonding: Using strong adhesives to bond different foam pieces together or to attach foam to other materials.
- Mechanical Fastening: Depending on the application, mechanical fasteners may be used to ensure durability and strength in the assembly.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied in Custom Foam Molding?
The finishing stage involves refining the product to meet specific customer requirements. Techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: This may involve coating or laminating the foam to enhance durability or aesthetic appeal.
- Trimming and Shaping: Excess material is trimmed away, and final shapes are refined to meet exact specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Custom Foam Molding Process?
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance in foam manufacturing is vital for ensuring that products meet safety and performance standards. B2B buyers should look for suppliers that comply with:
- ISO 9001: This international standard outlines criteria for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA), indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify any deviations from quality standards in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished products undergo rigorous testing and inspection to ensure they meet client specifications and regulatory requirements.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Foam Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods used to verify foam quality include:
- Compression Testing: Evaluates the foam’s ability to withstand compressive forces, important for applications requiring cushioning.
- Flammability Testing: Ensures compliance with safety standards, especially critical for products used in public spaces or transportation.
- Durability Testing: Assesses the foam’s resistance to wear and tear over time, essential for products intended for long-term use.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to ensure their suppliers maintain high-quality standards. This can include:
- Conducting Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify their adherence to quality standards and operational procedures.
- Requesting Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality assurance processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC tests.
- Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Independent verification from third-party organizations can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific considerations:
- Understanding Local Regulations: Buyers must be aware of the regulatory requirements in their region that may affect product standards and safety.
- Cultural Sensitivity in Communication: Clear and respectful communication can help mitigate misunderstandings related to quality expectations.
- Flexibility in Quality Expectations: Different regions may have varying quality benchmarks; it’s crucial to align expectations with suppliers based on local standards.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for custom foam molding. This comprehensive approach not only enhances product quality but also strengthens supplier relationships, ultimately leading to successful business outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘custom foam molding’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure custom foam molding products. The custom foam molding process involves multiple stages, from defining specifications to selecting the right supplier. By following these steps, you can ensure that your sourcing process is efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with your product requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly articulating your technical specifications is crucial. This includes determining the type of foam material (e.g., EPS, EPE, PU) and the desired physical properties such as density, durability, and insulation capabilities. Understanding these parameters will help you communicate your needs effectively to potential suppliers.
- Consider applications: Identify how the foam will be used in your product to guide material selection.
- Set performance criteria: Specify any certifications or standards the foam must meet (e.g., fire resistance, environmental compliance).
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in custom foam molding. Look for companies that specialize in your required materials and have experience in your industry.
- Check online directories: Utilize platforms like ThomasNet and industry-specific sites to find reputable manufacturers.
- Review case studies: Assess past projects to gauge their expertise and capabilities.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a commitment, verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications. This can include ISO certifications or compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
- Request documentation: Ask suppliers to provide proof of their certifications and quality management systems.
- Assess compliance: Ensure that the supplier’s processes meet your industry’s specific requirements.
Step 4: Request Prototypes
Engage with suppliers to create prototypes based on your specifications. This step is essential for testing and validating the design before mass production.
- Prototype options: Look for suppliers that offer CNC-cut prototypes or 3D modeling services.
- Conduct testing: Use prototypes to evaluate the foam’s performance in real-world conditions relevant to your application.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Minimum Order Quantities
Understanding lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs) is vital for planning your production schedule. Each supplier may have different requirements that can impact your overall timeline.
- Negotiate MOQs: Ensure the MOQ aligns with your budget and production needs.
- Clarify timelines: Confirm production and shipping timelines to avoid delays in your supply chain.
Step 6: Assess Cost Structures
Request detailed quotes from shortlisted suppliers, including a breakdown of costs associated with materials, tooling, and production.
- Compare quotes: Look beyond the base price and consider factors like shipping costs and payment terms.
- Evaluate value: Consider the quality of materials and the supplier’s reliability as part of the overall value proposition.
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Effective communication is key throughout the sourcing process. Set up clear channels for ongoing dialogue with your selected supplier.
- Designate contacts: Identify key personnel on both sides to streamline communication.
- Regular updates: Schedule periodic check-ins to discuss progress and any potential issues that may arise during production.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing custom foam molding products effectively, ensuring they choose a supplier that meets their specific needs while maintaining quality and compliance standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for custom foam molding Sourcing
When sourcing custom foam molding, understanding the cost structure and pricing nuances is essential for international B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here’s a breakdown of the key components influencing costs and pricing strategies for custom foam molding.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Custom Foam Molding?
-
Materials: The choice of foam material significantly impacts the overall cost. Common options include Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), Expanded Polypropylene (EPP), and Polyurethane (PU). Each material offers distinct properties that may suit different applications, but they also come with varying price points. Custom blends, like expanded co-polymers, can further adjust costs depending on the desired characteristics.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the skilled workforce involved in design, production, and quality control. For custom projects, specialized labor may be required, which can increase costs. It’s important to assess the skill level of the workforce and the complexity of the manufacturing processes when evaluating labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Overhead can vary based on the location of the manufacturer and their operational efficiencies. Buyers should consider suppliers with optimized processes to mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Custom foam molding often requires specific tooling for production. The initial investment in tooling can be significant, especially for unique designs. Some suppliers may charge tooling fees upfront, while others might amortize these costs over the production run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is paramount, especially for international shipments. QC processes add to the cost structure but are essential for compliance with industry standards and certifications. Buyers should inquire about the QC measures employed by potential suppliers to ensure their products meet required specifications.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary greatly depending on the distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms agreed upon. These factors can significantly affect the total cost, especially for international buyers. Understanding logistics and potential tariffs can help in budgeting more accurately.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary depending on market conditions and supplier reputation. Understanding typical margins in the industry can aid in negotiating better deals.
What Influences Pricing in Custom Foam Molding?
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) often dictate pricing. Larger orders can lead to economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost. Conversely, small orders may incur higher prices due to setup and production costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Highly customized products or intricate designs generally come with higher costs. Clear communication of specifications can help suppliers provide more accurate quotes and possibly identify cost-saving alternatives.
-
Material Selection and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and required certifications can influence costs. High-quality materials with certifications often come at a premium, but they may also provide long-term cost savings through durability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The experience and reputation of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of reliability and quality, while newer suppliers may offer competitive pricing to build their client base.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can affect the total cost of ownership. Understanding terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for international buyers to avoid unexpected expenses.
How Can Buyers Negotiate and Optimize Costs?
-
Engage in Open Negotiation: Discussing pricing transparently with suppliers can lead to better deals. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts on larger orders or inquire about potential cost-saving measures.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO rather than just the upfront costs. This includes maintenance, durability, and logistics. A higher-quality product may yield lower long-term costs.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about trends in the foam molding industry, as this knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Comparing quotes from various suppliers can help identify competitive pricing and uncover hidden costs that may not be immediately apparent.
Understanding these cost components, pricing influences, and negotiation strategies will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing custom foam molding, ultimately leading to more successful purchasing outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing custom foam molding With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Custom Foam Molding
In the realm of product design and packaging, custom foam molding stands out as a versatile solution. However, various alternatives can achieve similar objectives, offering different benefits and trade-offs. This analysis will compare custom foam molding against two viable alternatives: injection molding and vacuum forming. Understanding these options will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Custom Foam Molding | Injection Molding | Vacuum Forming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent cushioning, insulation, and lightweight | High precision and durability | Good for lightweight, simple shapes |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; low material costs | High tooling costs; economical for large runs | Lower tooling costs; economical for medium runs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires design expertise; relatively quick setup | Complex setup; longer lead times | Simple design; quick to implement |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable under various conditions | Moderate; depends on material used | Low; easy to clean |
| Best Use Case | Packaging, protective cases, custom applications | High-volume production of precise parts | Large sheets for simple shapes, signage |
How Does Injection Molding Compare to Custom Foam Molding?
Injection molding is a widely adopted manufacturing process that creates parts by injecting molten material into a mold. It excels in producing high-precision components, making it ideal for industries requiring exact specifications, such as automotive and electronics. While the initial tooling costs are high, the per-unit cost decreases significantly at high volumes, making it economically viable for mass production. However, the complexity of setup and longer lead times can be drawbacks for businesses needing rapid prototyping or small production runs.
What Are the Benefits of Vacuum Forming Over Custom Foam Molding?
Vacuum forming involves heating a plastic sheet until pliable, then forming it over a mold using vacuum pressure. This method is particularly advantageous for producing lightweight products and is cost-effective for medium production runs. The tooling costs are lower than injection molding, making it accessible for businesses with smaller budgets. However, vacuum forming is less suited for intricate designs and does not offer the same level of durability or insulation properties as custom foam molding, which may limit its application in protective packaging.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right manufacturing method requires a thorough understanding of your project’s specific needs, including volume, precision, and material properties. Custom foam molding is ideal for applications demanding excellent cushioning and insulation, while injection molding is best for high-volume, precision-driven projects. Vacuum forming serves well for simpler designs at a lower cost. By carefully evaluating these alternatives against your operational requirements, you can make an informed decision that balances performance, cost, and practicality, ultimately driving your project’s success.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for custom foam molding
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Custom Foam Molding?
In the realm of custom foam molding, understanding the critical properties of materials and manufacturing processes is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of foam used in the molding process. Common materials include Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), Expanded Polyethylene (EPE), and Polyurethane (PU). Each material has distinct characteristics such as density, flexibility, and resistance to moisture, which influence the end product’s performance. Choosing the right material grade is vital as it impacts durability, weight, and application suitability, ensuring the final product meets specific operational needs.
2. Density
Density is a measure of mass per unit volume and is a crucial property in foam manufacturing. It affects the foam’s strength, cushioning ability, and insulation properties. Higher density foams generally provide better durability and support, making them ideal for applications requiring longevity. For buyers, understanding density helps in selecting the appropriate foam for specific applications, balancing cost and performance effectively.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions during the manufacturing process. It is critical in ensuring that the molded foam fits precisely within its intended application, whether it be for packaging, cushioning, or structural support. Tight tolerances may be necessary for intricate designs or where the foam interacts with other components. A clear understanding of tolerance requirements aids in minimizing errors and ensuring product quality.
4. Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance indicates how well a foam material can withstand exposure to various substances without degrading. This property is particularly important for applications in industries such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, and food packaging, where exposure to oils, solvents, or cleaning agents is common. Buyers should assess chemical resistance based on the intended environment of use to avoid premature failure of the foam products.
5. Thermal Insulation Properties
Thermal insulation properties define a foam’s ability to resist the transfer of heat. This is crucial for applications requiring temperature control, such as refrigerated transport or thermal packaging. Understanding the insulation capabilities of different foam types allows buyers to select materials that meet their thermal management needs, enhancing energy efficiency and product safety.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Custom Foam Molding?
Navigating the custom foam molding industry involves understanding key terminology that facilitates communication and negotiations. Here are several essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or products that are sold by another company under its brand name. In the context of foam molding, an OEM may contract a foam manufacturer to produce custom molded components that fit within their larger product line. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking to establish partnerships for product development.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly significant for custom foam orders, as it can affect pricing and production schedules. Buyers should be aware of MOQ requirements to optimize their inventory management and cost-efficiency when placing orders.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process in which a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. When dealing with custom foam molding, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to obtain detailed information on pricing, lead times, and material options, facilitating better decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping and delivery. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaging with international suppliers, as it clarifies aspects like shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer during the transportation of molded foam products.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the finished product. In custom foam molding, lead times can vary based on material availability, complexity of the mold, and production capacity. Understanding lead times is vital for buyers to plan their projects and manage their supply chains effectively.
By familiarizing themselves with these essential properties and terms, B2B buyers can navigate the custom foam molding landscape more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the custom foam molding Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Custom Foam Molding?
The custom foam molding sector is witnessing robust growth driven by several global factors. As industries increasingly prioritize lightweight, durable materials, the demand for custom molded foam solutions continues to surge. Key markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly active, with buyers seeking innovative packaging solutions, insulation materials, and cushioning products. The rise of e-commerce has further intensified the need for protective packaging, compelling manufacturers to innovate in foam designs that enhance product safety during transit.
Emerging B2B tech trends, such as advanced manufacturing techniques and automation, are reshaping the sourcing landscape. Technologies like 3D printing and CNC machining enable manufacturers to offer rapid prototyping and customization, allowing buyers to receive tailored solutions with shorter lead times. The integration of IoT in supply chains is also enhancing transparency, giving buyers real-time insights into production processes and material sourcing. This is particularly vital for international buyers who must navigate varying regulations and standards across regions, such as those in Brazil and Vietnam.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Trends in Custom Foam Molding?
Sustainability is a critical concern for B2B buyers in the custom foam molding sector. The environmental impact of foam materials, particularly in terms of production and disposal, has led to a growing demand for eco-friendly alternatives. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who offer sustainable materials, such as biodegradable or recyclable foam options. This shift is not merely a trend; it reflects a broader commitment to reducing carbon footprints and adhering to global sustainability standards.
Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining prominence. Buyers are more inclined to partner with manufacturers that maintain transparent supply chains and uphold ethical labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for sustainable sourcing are becoming essential criteria in supplier selection. By aligning with suppliers that prioritize sustainability, companies can enhance their brand reputation while meeting the growing consumer demand for eco-conscious products.
What Is the Historical Context of Custom Foam Molding That Buyers Should Be Aware Of?
The custom foam molding industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially dominated by traditional materials like expanded polystyrene (EPS), the sector has seen a diversification of materials and techniques, including the advent of closed-cell foam technologies. Innovations in foam injection molding, such as the development of XL EXTRALIGHT® foam, have expanded the application possibilities, offering benefits like enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and lightweight characteristics.
This evolution has been marked by a shift from simple cushioning applications to complex designs used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Buyers today benefit from a wealth of options tailored to specific needs, supported by advanced design capabilities that ensure precision and efficiency in manufacturing. Understanding this historical context helps international buyers appreciate the breadth of solutions available and the ongoing innovations that continue to shape the market landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of custom foam molding
-
How do I ensure the quality of custom foam molding products?
To ensure quality in custom foam molding, establish a clear communication channel with your supplier. Request detailed specifications and samples before full production. Look for suppliers with ISO certifications, as these indicate adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including testing methods and production monitoring. Regular audits and evaluations can also help maintain quality throughout the manufacturing process. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for custom foam molding?
The MOQ for custom foam molding can vary significantly between suppliers and depends on factors such as material type and complexity of design. Typically, MOQs can range from 100 to 500 units. It is crucial to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and flexibility. Some manufacturers may offer lower MOQs for specific products or during promotional periods, so it’s worth inquiring. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing custom foam products internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of custom foam products often include a deposit upfront (usually 30-50%) and the balance upon delivery or before shipment. Some suppliers may offer payment through letters of credit or escrow services to enhance security. It is advisable to negotiate favorable terms that work for your cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s confidence in the transaction. Always confirm payment methods accepted, as these may vary by region. -
How can I customize my foam molding order?
Customization of foam molding orders involves collaborating closely with your supplier to define the product specifications. This includes material selection, density, color, and dimensions. Suppliers often provide design support, including 3D modeling and prototypes, to help visualize the final product. Be clear about your requirements and any industry-specific standards that need to be met, as this will facilitate a smoother customization process. -
What are the benefits of using closed-cell foam in custom molding?
Closed-cell foam offers several advantages, including excellent insulation properties, resistance to moisture, and durability. This type of foam is lightweight yet strong, making it ideal for various applications, from packaging to automotive parts. Its chemical resistance also ensures longevity, particularly in harsh environments. When discussing options with suppliers, highlight your application needs to identify the best closed-cell foam solutions. -
How do I vet potential suppliers for custom foam molding?
When vetting suppliers, start by researching their reputation through online reviews and industry references. Request information about their manufacturing processes, capabilities, and certifications. It’s beneficial to ask for case studies or examples of similar projects they have completed. Additionally, consider visiting their facility if possible or using virtual tours to assess their operational standards. Establishing a good rapport and clear communication is also essential for long-term partnerships. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international foam orders?
Logistics for international foam orders involve understanding shipping methods, costs, and timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling foam products to navigate customs regulations effectively. Discuss with your supplier about packaging methods to prevent damage during transit. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to customs clearance, especially in regions with strict import regulations. Planning ahead will help mitigate risks related to delivery. -
How can I address potential environmental concerns with custom foam products?
To address environmental concerns, opt for suppliers that use eco-friendly materials and sustainable manufacturing practices. Inquire about the chemical composition of the foam and whether it meets relevant environmental standards, such as being free from harmful substances. Many suppliers are moving towards recyclable or biodegradable foam options. Engaging with manufacturers who prioritize sustainability will not only enhance your brand image but also contribute positively to the environment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Custom Foam Molding Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Marko Foam – Custom Molded Foam Products
Domain: markofoam.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Custom Molded Foam Products including Insulated Containers, Foam Edge Protectors, Corner Blocks, Medical Packaging, Custom Molded Foam, Fabricated Packaging, Sporting Goods and Toys. Services offered include CNC Cutting, Custom Corrugated Boxes, Die Cutting, Hot Wire Cutting, Lamination, Mold Making, Prototyping, Woodshop and Crating. Foam types available are Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), Expanded P…
2. Foam Creations – XL EXTRALIGHT® Foam Solutions
Domain: foamcreations.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Foam Creations specializes in closed-cell foam injection molding, particularly using their proprietary XL EXTRALIGHT® technology. This foam is phthalate, heavy metal, and latex-free, making it safe, soft, lightweight, 100% waterproof, and chemical-resistant. The company offers end-to-end product development services, including foam product design, prototyping, mold manufacturing, and custom foam p…
3. General Plastics – Custom Molded Foam Solutions
Domain: generalplastics.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: General Plastics fabricates and machines custom molded foam parts using high-density flexible and semi-flexible polyurethane LAST-A-FOAM® materials. They offer capabilities for part design, tool design, mold tooling manufacture, and production support. Their molded foam parts are used in various applications including aerospace, defense, nuclear, marine, and medical sectors. Key features include: …
4. Roarockit – High Density Mold Foam Pack
5. RCO Engineering – Custom-Molded Foam Solutions
Domain: rcoeng.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: RCO Engineering specializes in custom-molded foam and tooling for various applications, including automotive and aerospace seating, low volume production programs, one-off prototypes, and large scale foam projects. They offer molded polyurethane foam tooling and parts for seating components, with quick turnaround times to meet specifications. Key offerings include: molded foam prototypes, custom f…
6. Polymer Molded Products – POLYFORM ® High-Density Molded Foam
Domain: polytechinc.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Custom Molded Foam Solutions by Polymer Molded Products (PMP) include a range of polyurethane foam products designed for various applications. Key product details include: 1. POLYFORM ® High-Density Molded Foam – Integral Skin (PHDM-IS): 10 – 20 lb/ft³, flexible, self-skinning open cell foam, excellent abrasion resistance, high tear strength, suitable for noise barrier material, ideal for branding…
7. Decorative Ceiling Tiles – Foam Crown Molding
Domain: decorativeceilingtiles.net
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Foam Crown Molding | Easy to install Styrofoam Crown Molding
8. GRFT – Custom Polyurethane Foam Manufacturing
Domain: grft.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Custom polyurethane molded foam manufacturing services including:
– Fully Automated 64 Position Molding Lines
– Tooling Materials: Cast Aluminum, High Resin Epoxy, REN Board
– Flexible Tooling with Temperature Controls: Water Heated, Jacketed, External Heated
– Flexible Run Volume Requirements
– Fully Automated Pour/Paint Robots
– Extensive IFD Range Capabilities
– Extensive Variation Control Capa…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for custom foam molding
What Are the Key Takeaways for Strategic Sourcing in Custom Foam Molding?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of custom foam molding, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers. It enables companies to select suppliers that not only meet their specific material and design requirements but also align with their sustainability goals and cost efficiency. By engaging with experienced manufacturers, buyers can leverage advanced technologies like foam injection molding to create innovative products that resonate with their target markets.
Furthermore, understanding the diverse range of moldable materials—such as Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), Polyurethane (PU), and proprietary blends—allows companies to optimize their product designs for performance and durability. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to collaborative product development, ensuring that your offerings stand out in competitive markets.
How Can International Buyers Leverage Custom Foam Molding for Future Growth?
Looking ahead, the opportunity for growth in custom foam molding is significant, particularly for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As market demands evolve, investing in strategic partnerships with reliable foam manufacturers can enhance product innovation and responsiveness.
Now is the time to act—explore potential collaborations and invest in custom foam solutions that can elevate your brand’s market presence. Embrace the future of foam molding to drive your business forward, ensuring you remain at the forefront of industry advancements.