Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cost laser cutting machine
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing the right cost laser cutting machine can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a multitude of options available, including CO2 and fiber laser technologies, understanding the nuances of each type is crucial for making an informed investment. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various laser cutting machines on the market, their applications across industries, and key factors to consider when selecting a supplier.
Buyers will gain insights into the cost structures associated with different models and features, helping them navigate pricing strategies effectively. We’ll delve into the specifics of machine capabilities, from precision cutting of intricate designs to robust performance for heavy-duty applications. Furthermore, this guide emphasizes the importance of thorough supplier vetting, ensuring that international buyers can trust the reliability and quality of their chosen equipment.
By empowering B2B buyers with essential knowledge, this guide aims to facilitate smarter purchasing decisions, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and competitiveness in their respective markets. Whether you are in manufacturing, craft production, or any industry that requires precise cutting solutions, understanding the landscape of laser cutting machines will be invaluable in your quest for the right technology.
Understanding cost laser cutting machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser Cutting Machines | Best for non-metal materials; uses CO2 gas for laser generation | Sign making, engraving, woodworking | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile for various materials. Cons: Limited to thinner metals. |
| Fiber Laser Cutting Machines | High precision; ideal for metals; uses fiber optics for laser delivery | Sheet metal fabrication, automotive parts | Pros: Fast cutting speeds, low maintenance. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Handheld Laser Cutting Machines | Portable; multifunctional (cutting, welding, cleaning) | Construction, repair work, small workshops | Pros: Versatile, easy to transport. Cons: Limited cutting thickness compared to fixed machines. |
| Mini Laser Cutting Machines | Compact size; suitable for intricate designs | Jewelry making, small crafts | Pros: Space-efficient, ideal for small businesses. Cons: Limited work area and power. |
| Industrial Laser Cutting Machines | High power and large work area; designed for mass production | Heavy manufacturing, aerospace, large-scale fabrication | Pros: High throughput, robust and durable. Cons: Requires significant space and investment. |
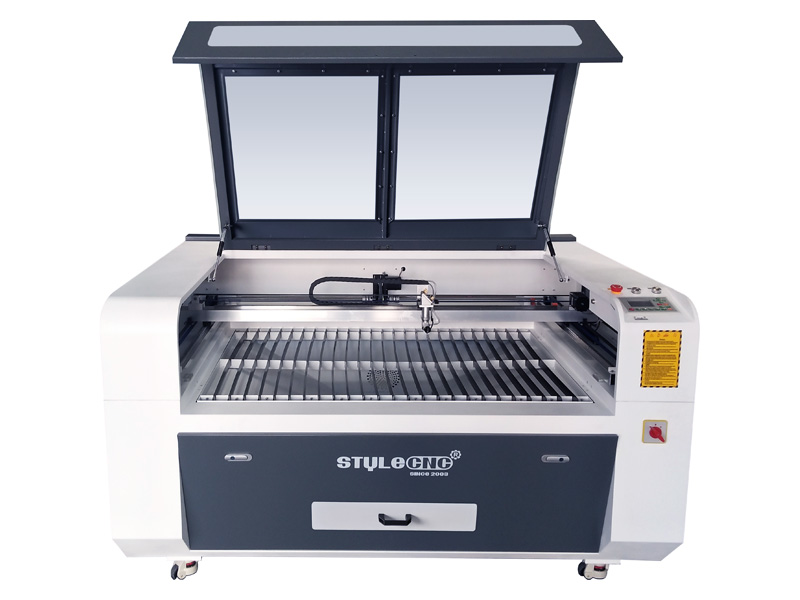
What Are the Key Characteristics of CO2 Laser Cutting Machines?
CO2 laser cutting machines are renowned for their ability to cut and engrave a variety of non-metal materials such as wood, acrylic, and leather. They utilize a CO2 gas laser, which is less effective on metals but highly efficient for softer materials. B2B buyers should consider the types of materials they will predominantly work with, as CO2 lasers excel in applications like signage and decorative items. The affordability of these machines makes them ideal for small businesses and startups looking to enter the laser cutting market without a heavy upfront investment.
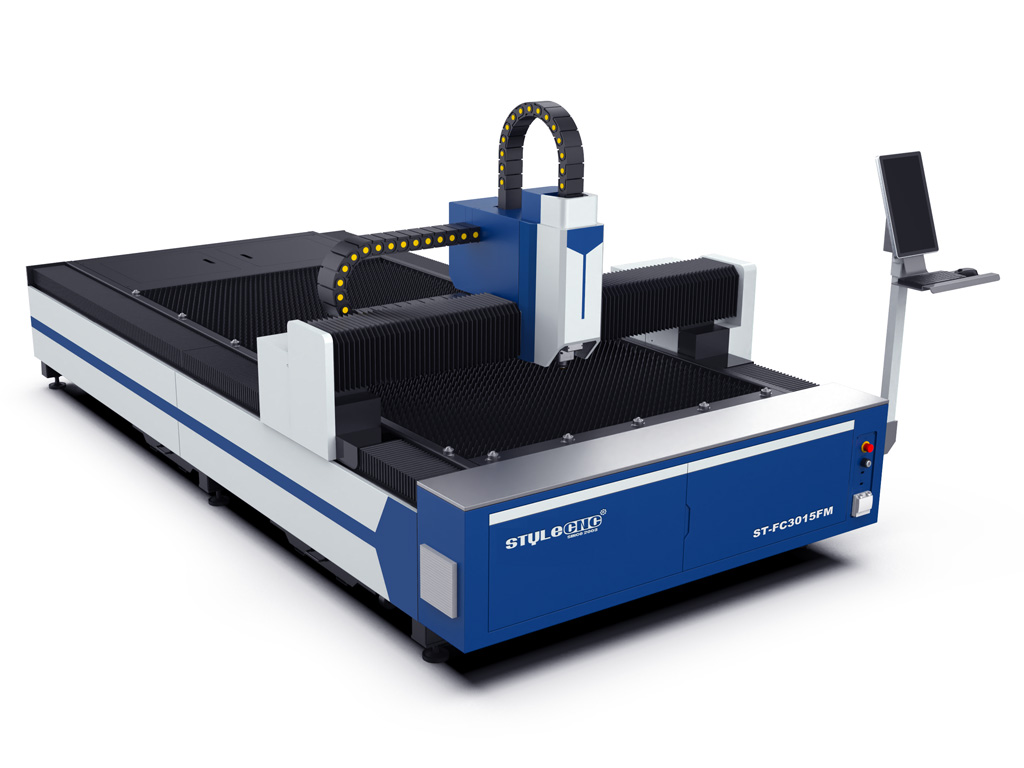
How Do Fiber Laser Cutting Machines Stand Out in Metal Fabrication?
Fiber laser cutting machines are designed for precision cutting of metals, leveraging fiber optics to generate high-intensity laser beams. These machines can handle a wide range of metals, including stainless steel and aluminum, making them essential for industries such as automotive and aerospace. When purchasing, businesses should evaluate their production volume needs, as fiber lasers offer rapid cutting speeds and lower operating costs over time, despite a higher initial purchase price. Their durability and low maintenance requirements also enhance their appeal for industrial applications.
What Advantages Do Handheld Laser Cutting Machines Provide for Small Operations?
Handheld laser cutting machines offer a unique blend of portability and multifunctionality, capable of cutting, welding, and cleaning. This versatility makes them particularly useful in construction and repair sectors, where mobility and ease of use are crucial. B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements, as these machines are ideal for smaller workshops or on-site work. While they provide flexibility, potential buyers should be aware of their limitations in cutting thickness compared to stationary machines, making them suitable for lighter tasks.
Why Choose Mini Laser Cutting Machines for Jewelry and Crafts?
Mini laser cutting machines are compact and designed for precision work, making them ideal for applications in jewelry making and intricate craft projects. Their small footprint is perfect for businesses with limited space, allowing them to operate in tighter environments. However, buyers must consider their production scale, as these machines typically have a smaller work area and lower power output. For artisans and small businesses focused on custom designs, mini machines offer an affordable entry point into the laser cutting market.
What Are the Benefits of Industrial Laser Cutting Machines for Large-Scale Production?
Industrial laser cutting machines are built for high-volume production, featuring larger work areas and powerful laser capabilities. They are essential in sectors that require mass fabrication, such as manufacturing and aerospace. When considering these machines, businesses should evaluate their facility’s space and the scale of their operations, as these machines require significant investment and infrastructure. While they provide high throughput and durability, the initial costs and operational complexity can be substantial, making them more suitable for established companies with ongoing production needs.
Key Industrial Applications of cost laser cutting machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cost laser cutting machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision cutting of metal parts for machinery | Increases production efficiency and reduces waste | Assess power capacity and cutting speed for materials used |
| Automotive | Custom parts fabrication and prototyping | Enhances innovation and rapid prototyping capabilities | Evaluate machine compatibility with various metals |
| Aerospace | Lightweight structural components production | Meets stringent safety and performance standards | Consider certifications and quality assurance processes |
| Jewelry & Fashion | Intricate designs and patterns for jewelry and apparel | Allows for unique, personalized products | Focus on precision capabilities and material versatility |
| Signage & Advertising | Creation of custom signage and promotional materials | Improves brand visibility and customization options | Investigate engraving and cutting capabilities together |
How is the ‘cost laser cutting machine’ utilized in manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, cost laser cutting machines are instrumental in precision cutting of metal parts used in various machinery. These machines streamline production processes by providing high-speed and accurate cuts, which significantly reduce material waste. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing machines that can handle diverse materials and thicknesses is crucial. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding machinery imports can facilitate smoother transactions.
What role does laser cutting play in the automotive industry?
The automotive industry leverages cost laser cutting machines for custom parts fabrication and prototyping. These machines enable manufacturers to create complex shapes and designs that are essential for modern vehicles, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it’s vital to consider the machine’s ability to work with high-strength materials and its adaptability to evolving design specifications to stay competitive in a fast-paced market.
How does aerospace benefit from laser cutting technology?
In aerospace, cost laser cutting machines are used to produce lightweight structural components that meet rigorous safety and performance standards. The precision offered by these machines ensures that parts fit together perfectly, which is critical in aircraft assembly. Buyers from regions like Germany should prioritize machines that comply with international aerospace quality standards and certifications to ensure reliability and safety in their production processes.
Why is laser cutting important for the jewelry and fashion industry?
The jewelry and fashion sectors utilize cost laser cutting machines for creating intricate designs and patterns that set their products apart. These machines allow for the customization of items, catering to unique customer preferences and trends. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, it’s essential to evaluate the machine’s precision capabilities and its ability to work with various materials, including metals and fabrics, to meet diverse design needs.
How does signage and advertising benefit from laser cutting machines?
In the signage and advertising industry, cost laser cutting machines are employed to create custom signage and promotional materials that enhance brand visibility. These machines allow for intricate designs and high-quality finishes that attract customers. B2B buyers should focus on machines that offer both cutting and engraving functionalities, ensuring versatility for different projects. Additionally, understanding local market trends can help in selecting machines that meet specific regional demands.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cost laser cutting machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Budget Constraints on Laser Cutting Equipment
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets like Africa and South America, grapple with limited budgets for purchasing laser cutting machines. These buyers may be under pressure to optimize costs while meeting the demands of their growing businesses. The challenge lies in finding a cost-effective solution that still offers the necessary functionality and precision for their applications. This often leads to frustration as they encounter machines that are either too expensive or lack the capabilities required for their specific projects.
The Solution: To navigate budget constraints effectively, buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify a range of laser cutting machines that fit their financial parameters. Utilizing online platforms that aggregate reviews and specifications can help in comparing features across different models. Consider opting for refurbished machines or entry-level models that still provide the necessary cutting power but at a lower cost. Additionally, reaching out to manufacturers for bulk purchasing discounts or financing options can help alleviate upfront expenses. Engaging with local suppliers may also uncover hidden costs associated with shipping and installation that could affect overall pricing.
Scenario 2: Technical Expertise and Machine Usability
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the technical expertise required to operate advanced laser cutting machines. Companies in various regions may find that their workforce lacks the necessary skills to operate, maintain, or troubleshoot these machines effectively. This gap can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased downtime, and ultimately a decline in productivity, as employees struggle to maximize the capabilities of the equipment they have invested in.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize machines that come with comprehensive training and support from the manufacturer. Many reputable suppliers offer hands-on training sessions and detailed user manuals that can help staff quickly learn to operate the machinery. Moreover, investing in machines with user-friendly interfaces can significantly reduce the learning curve. Another option is to consider leasing equipment that includes training as part of the package. This allows businesses to test the technology with minimal commitment while ensuring their employees gain the necessary skills to use it effectively.
Scenario 3: Compatibility with Diverse Materials
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring their laser cutting machine can handle a variety of materials, from metals to plastics and textiles. This is particularly relevant for industries that require versatility in their production processes. Buyers may find that many machines are limited to specific materials, which can force them to invest in multiple machines, complicating their operations and increasing costs.
The Solution: When selecting a laser cutting machine, it is crucial to assess its material compatibility thoroughly. Buyers should look for machines that offer adjustable settings or come equipped with different lens options to handle a wide range of materials. Engaging with suppliers to clarify what materials can be cut and what configurations are necessary will help buyers make informed decisions. Additionally, attending trade shows or demonstrations can provide hands-on experience with different machines and their capabilities. Investing in a versatile machine not only streamlines operations but also positions businesses to adapt to changing market demands without incurring additional expenses for new equipment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cost laser cutting machine
What Are the Key Materials for Cost Laser Cutting Machines?
When selecting materials for laser cutting machines, it’s essential to consider not only the properties of the materials but also their suitability for specific applications and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in laser cutting, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Steel: The Backbone of Industrial Applications
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and has excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Corrosion resistance can vary depending on the steel grade.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its robustness, making it ideal for structural components. However, its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where lightweight materials are preferred. The manufacturing complexity can increase with thicker gauges, leading to higher costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is widely used in automotive, construction, and manufacturing sectors. Its compatibility with various media, including high-stress environments, makes it a go-to choice for many industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as EN 10025 for structural steel. In Africa and South America, local sourcing of steel may also impact costs and availability.
Aluminum: The Lightweight Champion
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal and electrical conductivity. It can be easily shaped and formed, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which is beneficial for applications requiring portability. However, it is generally more expensive than steel and can be less durable under high-stress conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and packaging industries. Its compatibility with laser cutting allows for intricate designs and lightweight structures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions is crucial. Buyers in regions like Germany may prefer high-grade aluminum alloys, impacting sourcing decisions.
Acrylic: The Versatile Plastic
Key Properties: Acrylic, also known as PMMA, is a transparent thermoplastic with excellent optical clarity and UV resistance. It is lightweight and can be easily cut and shaped.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of acrylic is its versatility and aesthetic appeal, making it popular for signage and displays. However, it can be prone to scratching and may not withstand high temperatures, limiting its use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Acrylic is widely used in advertising, retail displays, and decorative items. Its compatibility with laser cutting allows for precise shapes and designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with safety standards, especially in regions with strict regulations on plastics. In Europe, REACH compliance may be a consideration.
Wood: The Traditional Choice
Key Properties: Wood is a natural material with excellent machinability and aesthetic qualities. It is available in various species, each with unique properties, including hardness and grain patterns.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of wood is its sustainability and the warmth it brings to products. However, wood can be susceptible to moisture and pests, which may limit its durability in some applications.
Impact on Application: Wood is commonly used in furniture, crafts, and decorative items. Its compatibility with laser cutting allows for intricate designs and personalized products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations regarding sustainable sourcing is crucial, especially in Europe where FSC certification may be preferred. Buyers in Africa and South America should consider local wood species and their availability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Cost Laser Cutting Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for cost laser cutting machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components in automotive and construction | High strength and durability | Heavier, higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and lightweight automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | More expensive, less durable under stress | High |
| Acrylic | Signage and decorative displays | Versatile with aesthetic appeal | Prone to scratching, limited temperature resistance | Medium |
| Wood | Furniture and crafts | Sustainable and aesthetically pleasing | Susceptible to moisture and pests | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of materials commonly used in laser cutting, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cost laser cutting machine
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Cost Laser Cutting Machines?
The manufacturing of cost laser cutting machines involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the necessary performance and quality standards. Understanding these processes can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared in the Manufacturing Process?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting high-quality raw materials, typically metals or composites, that can withstand the precision cutting required by laser technology. Suppliers often utilize materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and various alloys.
Once the materials are chosen, they undergo cutting and shaping into manageable sizes. This may involve initial machining to create sheets or tubes that fit within the laser cutting machine’s operational parameters. Proper material preparation ensures that the end product will have the durability and strength necessary for industrial applications.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming and Assembly?
Following material preparation, the forming stage begins. This involves using advanced techniques such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining to create the machine’s components. Key components include the laser source, optics, and the cutting bed.
The assembly process is critical and requires skilled technicians to ensure that all parts are accurately fitted and aligned. It’s common for manufacturers to use automated assembly lines to enhance efficiency and precision. This stage often includes integrating software that controls the laser cutting process, ensuring that the machine can execute complex cutting patterns as designed in CAD software.
How Do Manufacturers Finish Laser Cutting Machines?
Finishing processes are vital for enhancing the aesthetics and performance of laser cutting machines. This stage may involve surface treatments such as anodizing or powder coating, which provide corrosion resistance and improve visual appeal.
Additionally, manufacturers conduct thorough cleaning processes to remove any contaminants that could affect the machine’s performance. Each machine is typically tested for functionality after finishing, ensuring that all components operate seamlessly.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Laser Cutting Machines?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process, especially for laser cutting machines that are used in precision applications. Adhering to international standards and implementing rigorous QC checkpoints can significantly impact the reliability of the machines.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Laser Cutting Machines?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are critical for ensuring that manufacturers maintain high-quality management systems. This certification indicates that a company has established effective processes for managing quality and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) are often required, depending on the machine’s intended use. These standards assure buyers that the machines comply with safety, health, and environmental protection regulations.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. The typical QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting the raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, components are regularly tested for alignment, tolerance, and functionality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the entire machine undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance specifications. This may include operating the laser under various conditions to verify cutting speed and precision.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality assurance practices of potential suppliers. Here are some effective strategies:
What Are the Best Practices for Supplier Audits and Reports?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Buyers should look for manufacturers that are open to audits, as this transparency indicates confidence in their operations.
Requesting detailed quality assurance reports can also provide insights into the supplier’s performance history, including defect rates and compliance with international standards. This information can be invaluable in making a purchasing decision.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Verification?
Utilizing third-party inspection services can further enhance quality verification. Independent inspectors can conduct thorough evaluations of the manufacturing processes and finished products, providing unbiased assessments. This is particularly important for international buyers who may not have the resources to visit manufacturing facilities directly.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control.
How Do Cultural and Regulatory Differences Impact Quality Standards?
Cultural differences can affect how quality is perceived and managed. For instance, manufacturers in Europe may adhere to stricter environmental regulations compared to those in other regions. Understanding these differences can help buyers set appropriate expectations regarding machine performance and compliance.
Furthermore, international shipping and logistics can introduce additional challenges, such as damage during transport. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and handling practices to mitigate these risks.
What Role Do Certifications Play in International Transactions?
Certifications can facilitate smoother transactions between international buyers and suppliers. Buyers should seek manufacturers with relevant certifications that demonstrate adherence to quality and safety standards recognized in their regions. This not only ensures compliance but also builds trust between trading partners.
Conclusion
In-depth knowledge of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for cost laser cutting machines is essential for B2B buyers. By understanding the stages of production, the importance of quality control, and strategies for verifying supplier capabilities, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cost laser cutting machine’
In this guide, we aim to provide a practical checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring cost-effective laser cutting machines. This step-by-step approach will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing, ensuring that you make informed decisions tailored to your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is crucial before initiating the purchasing process. This includes determining the types of materials you will be cutting, the thicknesses involved, and the desired precision.
– Material Types: Consider whether you need a machine for metals, plastics, or wood.
– Cutting Speed and Power: Higher wattage generally means faster cutting, which can impact your production efficiency.
Step 2: Establish Your Budget
Setting a clear budget will guide your options and help narrow down your choices effectively. Determine not just the upfront cost of the machine but also account for maintenance, operational costs, and potential training for staff.
– Initial Investment vs. Long-term Costs: Balance your desire for high-quality equipment with what your company can afford in the long run.
– Financing Options: Explore leasing or financing opportunities if upfront costs are a concern.
Step 3: Research Available Models
Conduct thorough research on the various models available in the market. Compare specifications, features, and prices of different brands to identify machines that fit your criteria.
– Brand Reputation: Look for established brands known for reliability and customer service.
– User Reviews: Read testimonials and reviews from other businesses that have used the machines you’re considering.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Certifications and Compliance: Ensure that the suppliers meet international standards and have the necessary certifications for safety and performance.
– After-sales Support: Investigate what kind of support and maintenance services are offered post-purchase.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Samples
Whenever possible, request a demonstration of the laser cutting machine to assess its performance firsthand. This will allow you to evaluate the quality of cuts and the machine’s operational ease.
– Trial Periods: Some suppliers may offer a trial period, enabling you to test the machine in your working environment.
– Technical Support: Ensure that technical assistance is available during the demonstration to address any immediate questions.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, it’s time to negotiate the terms of purchase. This includes price, warranty, delivery timeframes, and payment terms.
– Warranty and Service Agreements: Understand the warranty coverage and any service agreements that may be included.
– Delivery and Installation: Confirm who will handle installation and whether there are additional costs involved.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Plan for Integration
After negotiations, finalize the purchase and prepare for integration into your workflow. This includes training staff and adjusting operational processes to accommodate the new equipment.
– Training Programs: Ensure that the supplier provides adequate training for your team.
– Integration Strategy: Plan how the new machine will fit into your existing production processes to maximize efficiency.
Following this checklist will not only streamline your procurement process but also enhance the likelihood of selecting a laser cutting machine that meets your operational needs and budget.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cost laser cutting machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Laser Cutting Machines?
When analyzing the cost structure of laser cutting machines, several key components come into play:
-
Materials: The primary cost component is the materials used in manufacturing laser cutting machines. This includes high-quality metals for the frame and laser components, as well as electronic parts. The choice of materials significantly affects durability, performance, and ultimately the price.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in the assembly and quality control processes. The labor cost varies depending on the region of sourcing. For example, labor in Europe may be more expensive compared to Africa or South America, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and administrative expenses related to production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and equipment required for production can represent a significant upfront investment. The depreciation of these tools is factored into the pricing of the machines.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each machine meets safety and performance standards incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes can increase the price but are crucial for maintaining brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: The cost of shipping and handling is influenced by the machine’s size and weight. International shipping may also involve tariffs and customs fees that must be factored into the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their costs and generate profit. This margin can vary widely based on market conditions and supplier reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Laser Cutting Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of laser cutting machines:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders often lead to discounts, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs carefully. Ordering in larger quantities can lower the per-unit cost significantly.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom-built machines tailored to specific industry needs may attract higher prices. The more unique the specifications, the more expensive the machine will be due to increased manufacturing complexity.
-
Materials: The choice between CO2 and fiber lasers, as well as other material options, can impact the overall cost. Fiber lasers, for instance, tend to be more expensive but offer better efficiency and speed.
-
Quality/Certifications: Machines that meet international quality standards and certifications may have higher prices due to the assurance of quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can influence costs. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The shipping terms can significantly affect the final price. Buyers should be aware of whether costs include insurance, freight, and duties, as these can add up considerably.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help International B2B Buyers Optimize Costs?
-
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should evaluate not just the purchase price but also operational costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A lower initial cost may not always lead to savings in the long term.
-
Leverage Multiple Quotes: Soliciting multiple quotes from different suppliers can create competition, leading to better pricing.
-
Negotiate on Volume: If planning to order multiple machines, use this as leverage to negotiate better pricing or additional services such as extended warranties or free training.
-
Be Aware of Regional Variations: Prices can vary significantly between regions. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider local suppliers or those with experience in exporting to their region to mitigate costs associated with logistics and customs.
-
Explore Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can ease cash flow and may even allow for better pricing if suppliers are willing to negotiate based on payment timelines.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of laser cutting machines is essential for international B2B buyers. By considering the various cost components, price influencers, and negotiation strategies, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints. Always remember to request indicative prices as these can fluctuate based on market conditions and specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cost laser cutting machine With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Cost Laser Cutting Machines
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing and fabrication, businesses often seek solutions that optimize costs while maintaining performance. While cost laser cutting machines are a popular choice for precision cutting, several alternative technologies offer viable options for various applications. This analysis provides a comparative overview of cost laser cutting machines against other methods, assisting B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Cost Laser Cutting Machine | Plasma Cutting Machine | Waterjet Cutting Machine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, minimal kerf | Good for thick materials, lower precision | Excellent for intricate shapes, no heat-affected zone |
| Cost | $3,600 – $60,000 depending on specs | $20,000 – $50,000 | $50,000 – $150,000 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires CAD/CAM software, training | Easier setup, less training needed | Complex setup, requires skilled operators |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular lens cleaning | Low; infrequent consumable replacement | High; requires water management and pump maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Metal fabrication, signage, arts | Heavy-duty cutting of metals, construction | Complex designs, non-metal materials |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Plasma Cutting Machines?
Plasma cutting machines utilize a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to cut through electrically conductive materials. One of the main advantages of plasma cutting is its ability to handle thick materials efficiently, making it an excellent choice for heavy-duty applications such as construction and metal fabrication. However, plasma cutting generally offers lower precision than laser cutting, resulting in a wider kerf and less intricate detailing. Additionally, while the initial investment is lower than that of a laser cutter, operational costs can rise due to the need for consumables and potential waste generated during the cutting process.
How Does Waterjet Cutting Compare?
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure jet of water, often mixed with abrasive substances, to slice through materials. This method is particularly advantageous for intricate designs and can cut a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. The primary benefit of waterjet cutting is that it does not introduce heat into the material, preventing warping or altering the properties of the material. However, the complexity of the setup and the higher initial costs make it less appealing for smaller operations. Maintenance requirements are also significant, as the system must be carefully managed to ensure proper water flow and pressure.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Cutting Solution?
When selecting the appropriate cutting solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific needs, including the types of materials they will be working with, the complexity of designs, and budget constraints. Cost laser cutting machines provide high precision and versatility, making them ideal for detailed work in industries such as signage and jewelry. Plasma cutting machines are suitable for heavy-duty applications where thickness is a priority, while waterjet cutting is best for intricate designs and a variety of materials without thermal effects. Ultimately, the decision should align with the operational goals, production scale, and financial considerations of the business. By carefully evaluating each option, buyers can invest in a solution that enhances their capabilities and supports their growth.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cost laser cutting machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cost Laser Cutting Machines?
Understanding the technical specifications of laser cutting machines is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Laser Type (CO2 vs. Fiber)
– Definition: CO2 lasers utilize a gas mixture for cutting non-metal materials, while fiber lasers are solid-state lasers suitable for metals.
– B2B Importance: Fiber lasers are more efficient for metal cutting, providing faster processing speeds and lower operational costs. Choosing the right laser type can significantly impact production efficiency and material compatibility. -
Cutting Thickness
– Definition: The maximum thickness of material that a laser cutting machine can effectively cut.
– B2B Importance: Machines capable of cutting thicker materials allow businesses to diversify their product offerings. For instance, a machine that cuts up to 25mm can handle a wider range of applications, from intricate designs to industrial parts. -
Power Rating (Wattage)
– Definition: The power output of the laser, typically measured in watts (e.g., 1,500W to 60,000W).
– B2B Importance: Higher wattage allows for quicker cuts and the ability to process thicker materials. Businesses must evaluate their production needs to select a machine with appropriate power to enhance productivity and reduce operational time. -
Speed (Cutting Rate)
– Definition: The rate at which the laser cutting machine can move across the material, usually measured in meters per minute (m/min).
– B2B Importance: Faster cutting speeds lead to increased throughput, which is essential for meeting production deadlines. This is particularly vital for companies in competitive industries where time-to-market can affect profitability. -
Precision and Tolerance
– Definition: The accuracy of the cutting process, often specified in millimeters or microns.
– B2B Importance: High precision is crucial for applications requiring detailed work, such as automotive or aerospace parts. Ensuring tight tolerances can prevent costly rework and improve product quality. -
Material Compatibility
– Definition: The range of materials that can be effectively processed by the laser cutting machine (e.g., metals, plastics, wood).
– B2B Importance: A versatile machine that can cut various materials allows businesses to cater to multiple markets, enhancing their competitive edge.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Cost Laser Cutting Machines?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for navigating the procurement process effectively. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and assess the quality of machine components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for smaller businesses looking to minimize upfront costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ helps businesses compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they get the best value for their investment. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions as they define shipping, insurance, and liability responsibilities, helping to avoid disputes. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time from the placement of an order until it is fulfilled.
– Importance: Knowing the lead time helps businesses plan their production schedules and manage customer expectations effectively. -
Calibration
– Definition: The process of adjusting the precision of the laser cutting machine to ensure accurate cuts.
– Importance: Regular calibration is vital for maintaining cutting quality and achieving the desired tolerances, ultimately affecting production efficiency and product quality.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more strategic decisions when investing in cost laser cutting machines, ensuring they align with their operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cost laser cutting machine Sector
What are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Influencing the Cost Laser Cutting Machine Market?
The cost laser cutting machine market is experiencing significant growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for precision manufacturing across various industries. One of the primary global drivers is the surge in automation and digitalization in manufacturing processes. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics are increasingly adopting laser cutting machines for their ability to deliver high accuracy and efficiency. Emerging trends include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) into laser cutting technology, facilitating smarter production lines that enhance operational efficiency.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics is essential. In regions like Vietnam and Germany, the demand for high-quality, cost-effective laser cutting machines is growing. B2B buyers are leaning towards suppliers that offer a comprehensive range of products, from entry-level models suitable for small businesses to high-powered machines designed for industrial applications. Moreover, the trend of online sourcing platforms is gaining traction, enabling buyers to compare features, prices, and reviews easily, thus streamlining the procurement process.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Cost Laser Cutting Machine Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the cost laser cutting machine sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has led to increased scrutiny on supply chains. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, minimizing waste, and reducing energy consumption in their operations. This shift is evident in the rising demand for laser cutting machines that utilize energy-efficient technologies and materials.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with buyers seeking transparency in their supply chains. This includes understanding the origins of raw materials and ensuring that they are sourced responsibly. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of recycled materials are becoming standard requirements for suppliers. By choosing machines from manufacturers committed to sustainability, B2B buyers can enhance their corporate social responsibility initiatives while also appealing to environmentally conscious customers.
What is the Evolution of Laser Cutting Technology in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of laser cutting technology has significantly transformed the B2B landscape over the past few decades. Initially, laser cutting machines were primarily used for industrial applications, but technological advancements have broadened their accessibility. The introduction of more affordable CO2 and fiber laser cutting machines has made it feasible for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to adopt this technology, thus democratizing access to precision manufacturing tools.
As the technology evolved, manufacturers began integrating advanced features such as CNC control systems and CAM software, allowing for more complex designs and higher productivity. This evolution has resulted in laser cutting machines becoming indispensable tools across various sectors, from crafting personalized items to large-scale industrial production. As the market continues to grow, the focus will likely shift towards enhancing machine capabilities while reducing costs, making laser cutting technology an even more appealing option for B2B buyers worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cost laser cutting machine
-
How do I choose the right laser cutting machine for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate laser cutting machine depends on various factors such as the materials you’ll be working with, the thickness of those materials, and the volume of production. For metalworking, consider fiber lasers, which excel at cutting through various metals. If you’re focusing on non-metals like wood or acrylic, a CO2 laser might be more suitable. Also, assess the machine’s power capacity and cutting speed based on your production requirements. Conducting a thorough needs assessment will help you choose a machine that aligns with your operational goals. -
What is the best laser cutting machine for small businesses?
For small businesses, affordability and versatility are key. A compact CO2 laser cutter, such as the LS-1420, provides a good balance of cost and functionality, allowing for both cutting and engraving on various materials. If metal fabrication is a focus, a lower-power fiber laser can be a cost-effective entry point. Prioritize machines that offer user-friendly interfaces and support for various materials, enabling you to expand your service offerings without significant upfront investment. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing laser cutting machines?
Payment terms for laser cutting machines can vary widely by supplier but generally include options like upfront payment, deposits followed by balance payments, or financing arrangements. Many suppliers may require a 30% deposit at the time of order, with the remaining balance due before shipment. It’s essential to clarify these terms early in negotiations and check for any potential discounts for upfront payments, as well as the implications of financing options if cash flow is a concern. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) when sourcing laser cutting machines?
The MOQ for laser cutting machines can differ significantly depending on the manufacturer and the specific model. Some suppliers may allow single-unit purchases, while others might set a minimum of five or more units, particularly for custom machines. It’s advisable to inquire about MOQs early in the sourcing process, especially if you’re considering bulk purchases for better pricing. Additionally, consider how MOQ aligns with your business capacity and market demand. -
How can I ensure the quality of the laser cutting machine I am purchasing?
To ensure the quality of a laser cutting machine, request detailed specifications, certifications, and performance testing data from suppliers. Look for machines that comply with international quality standards such as ISO 9001. It’s also beneficial to read customer reviews and case studies, and to verify the supplier’s reputation through industry forums or trade associations. If possible, arrange for a factory visit or virtual demonstration to assess the machine’s performance firsthand. -
What should I consider when importing laser cutting machines internationally?
When importing laser cutting machines, consider factors such as shipping costs, import duties, and compliance with local regulations. Understanding the total landed cost is crucial to avoid unexpected expenses. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation, including certificates of origin and compliance. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in handling industrial equipment can facilitate smoother customs clearance and delivery processes. -
Can I customize a laser cutting machine to fit my specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for laser cutting machines to meet unique business needs. Customization can include adjustments in power output, work area size, or additional features such as automatic loading systems or integrated software solutions. When discussing customization, be clear about your specific requirements and ensure that the supplier can accommodate these changes without significantly increasing lead times or costs. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing laser cutting machines?
Logistics is a critical aspect of sourcing laser cutting machines. Consider the shipping methods, timelines, and packaging required to protect the equipment during transit. Ensure that the supplier has a reliable logistics partner and can provide tracking information. It’s also essential to plan for any installation and setup requirements upon arrival, including the availability of skilled personnel and any necessary tools or infrastructure modifications at your facility.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Cost Laser Cutting Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. STYLECNC – Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: 2025 Best Laser Cutting Machines for Every Need – STYLECNC offers a range of laser cutting machines suitable for both beginners and professionals. Key features include:
– Automatic slitting tool using DSP or CNC controller with CAM software.
– CO2 and Fiber laser options for cutting metals, metalloids, and nonmetals.
– Capable of creating precision parts, signs, tags, decorations, and more.
– …
2. Boss Laser – Laser Machines
Domain: shop.bosslaser.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Laser Machines – Boss Laser offers a variety of laser cutting, engraving, and marking machines including CO2 lasers, UV lasers, and industrial fiber cutters. Key product series include LS-Series (4 products), HP-Series (3 products), FC-Series (8 products), FM-Series (3 products), and UV-Series (1 product). The machines can cut and engrave various materials such as acrylic, aluminum, brass, cardboa…
3. AMADA – ENSIS 3015
Domain: cncmachines.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Used CNC Laser Cutters available from various brands including AMADA, MITSUBISHI, MAZAK, TRUMPF, BYSTRONIC, and more. Types of CNC laser cutters include gas laser cutting, crystal laser cutting, and fiber laser cutting. Key models include ENSIS 3015, FM-D, FO3015NT, LAP4836-1808W, ML3015LVPS, SPEEDYII, and others. Year of manufacture ranges from 2015 to 2024. Sizes vary, with examples like 3000″x1…
4. Wattsan – Laser Machines
Domain: wattsan.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: This company, Wattsan – Laser Machines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cost laser cutting machine
As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe consider investing in cost laser cutting machines, strategic sourcing becomes an essential element for success. By understanding the diverse range of options available—from affordable CO2 cutters suitable for hobbyists to advanced fiber laser systems designed for industrial applications—buyers can align their choices with operational needs and budget constraints.
Prioritizing factors such as machine versatility, cutting speed, and material compatibility can greatly enhance productivity while minimizing overhead costs. The importance of supplier relationships cannot be overstated; establishing connections with reputable manufacturers ensures access to quality products and ongoing support, which is critical for maintaining operational efficiency.
Looking ahead, the demand for laser cutting technology is projected to rise, driven by advancements in automation and increasing customization needs across industries. B2B buyers are encouraged to evaluate their specific requirements and proactively engage with suppliers to explore the latest innovations. Embracing this technology can unlock new opportunities for growth and competitive advantage in an ever-evolving market landscape. Take the next step—invest wisely in laser cutting solutions that will propel your business forward.