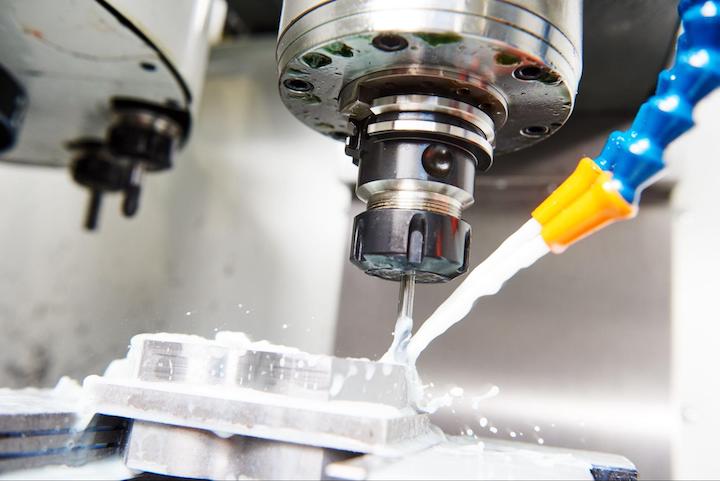
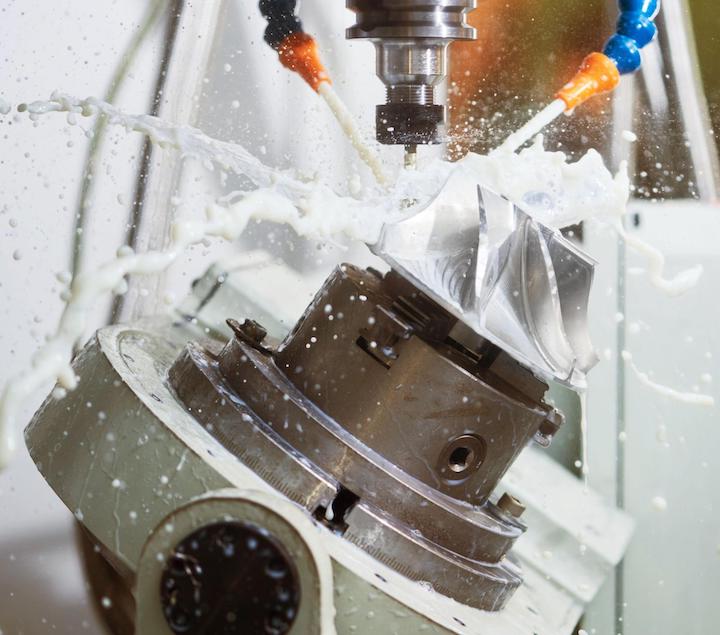
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for coolant for cnc machines
In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing, sourcing the right coolant for CNC machines is critical to enhancing operational efficiency and extending tool life. With diverse applications across various materials—from aluminum to exotic alloys—B2B buyers face the challenge of navigating an increasingly complex global market. This comprehensive guide addresses these challenges by exploring the different types of coolants, including soluble oils, semi-synthetics, and full synthetics, as well as their specific applications in machining processes.
International buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, will find valuable insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and performance metrics. By examining key factors such as compatibility with various machining operations and environmental regulations, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, it highlights the importance of selecting high-performance products that not only meet operational needs but also comply with industry standards.
Whether you are a seasoned procurement professional or new to the world of CNC machining, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the global market effectively, ensuring that your operations run smoothly and competitively.
Understanding coolant for cnc machines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Soluble Coolants | Easily mixed with water, offering good cooling and lubrication. | General machining, grinding, and cutting. | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Can lead to corrosion if not properly maintained. |
| Semi-Synthetic Coolants | Blend of synthetic and mineral oils, offering enhanced lubrication and cooling. | Versatile applications across various metals. | Pros: Extended tool life; Cons: Higher initial cost compared to water-soluble options. |
| Full Synthetic Coolants | Composed entirely of synthetic materials, providing superior cooling and lubrication. | Aerospace, automotive, and high-precision machining. | Pros: Excellent performance and low maintenance; Cons: Higher cost and potential disposal regulations. |
| Neat Oils | Non-water-based oils designed for specific machining applications. | Heavy-duty machining and grinding operations. | Pros: High lubricity; Cons: More expensive and can create a mess if not managed properly. |
| Vegetable-Based Coolants | Eco-friendly option derived from natural sources, often biodegradable. | Green manufacturing, food processing equipment. | Pros: Environmentally friendly; Cons: May not perform as well in extreme conditions compared to synthetic options. |
What Are Water Soluble Coolants and Their Applications?
Water soluble coolants are designed to be mixed with water, creating a milky emulsion that enhances cooling during machining. They are commonly used in general machining and grinding applications due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of use. However, it’s crucial for businesses to maintain proper concentrations to prevent corrosion and ensure optimal performance. Buyers should consider the local water quality, as hard water can negatively impact the coolant’s effectiveness.
How Do Semi-Synthetic Coolants Differ from Other Options?
Semi-synthetic coolants combine synthetic and mineral oils, providing a balanced approach to cooling and lubrication. They are suitable for a wide range of applications across various metals, making them a versatile choice for many manufacturers. Businesses may find that while semi-synthetic coolants have a higher initial cost, their ability to extend tool life and improve machining efficiency can lead to significant long-term savings.
What Advantages Do Full Synthetic Coolants Offer?
Full synthetic coolants consist entirely of synthetic materials, offering superior cooling and lubrication properties. They are particularly beneficial in high-precision machining and industries such as aerospace and automotive, where performance is critical. While these coolants can be more expensive, their low maintenance requirements and excellent performance make them a wise investment for businesses focused on efficiency and quality.
When Should Neat Oils Be Considered for Machining?
Neat oils are non-water-based lubricants specifically designed for heavy-duty machining and grinding operations. They provide high lubricity, making them ideal for tough materials and demanding applications. However, they tend to be more expensive than other coolant options and can create challenges regarding cleanup and disposal. Companies should evaluate their machining processes to determine if the benefits of neat oils justify the additional costs.
Why Choose Vegetable-Based Coolants for Your CNC Machines?
Vegetable-based coolants are an eco-friendly alternative derived from natural sources, making them suitable for green manufacturing initiatives. They are often used in food processing equipment due to their biodegradable nature. While these coolants are environmentally friendly, businesses must assess their performance in extreme conditions, as they may not match the effectiveness of synthetic options in high-stress applications. Buyers should weigh the benefits of sustainability against performance needs.
Key Industrial Applications of coolant for cnc machines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of coolant for cnc machines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision machining of aircraft components | Enhances tool life, reduces thermal distortion | Certification (e.g., Boeing approved), viscosity, and compatibility with various materials |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Machining of engine parts and transmission components | Increases production efficiency and reduces downtime | Performance under high pressure, cooling capacity, and environmental compliance |
| Metal Fabrication | Grinding and milling of various metals | Improves surface finish and reduces wear on tools | Concentration levels, compatibility with cutting tools, and local availability |
| Electronics | Machining of circuit boards and electronic housings | Ensures precision and minimizes thermal damage | Non-conductive properties, biodegradability, and cooling efficiency |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling and machining of downhole tools | Extends tool life and improves operational safety | High lubricity, resistance to extreme temperatures, and local sourcing options |
How is Coolant Used in the Aerospace Industry for CNC Machines?
In the aerospace sector, CNC machines are essential for precision machining of aircraft components, such as turbine blades and structural parts. The use of high-performance coolants reduces thermal distortion, which is critical for maintaining tight tolerances. Buyers in this sector must consider certifications like Boeing approval and ensure the coolant’s viscosity suits the specific machining processes. Additionally, compatibility with various materials, including titanium and aluminum alloys, is crucial for optimal performance.
What Role Does Coolant Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Automotive manufacturing relies heavily on CNC machining for producing engine parts and transmission components. Effective coolant usage enhances tool life and significantly reduces downtime during production. Coolants must perform well under high pressure and provide excellent cooling capacity to manage the heat generated during machining. Buyers should prioritize sourcing coolants that comply with environmental regulations while ensuring high performance to maintain production efficiency.
How is Coolant Beneficial in Metal Fabrication?
In metal fabrication, CNC machines are used for grinding and milling various metals, where the right coolant can improve surface finish and prolong tool life. The choice of coolant affects the wear on cutting tools, making it essential for buyers to consider concentration levels and compatibility with their specific cutting tools. Additionally, local availability of these coolants can influence sourcing decisions, especially for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America.
Why is Coolant Important in Electronics Manufacturing?
Electronics manufacturing involves machining circuit boards and electronic housings, where precision is paramount. The right coolant minimizes thermal damage during machining, ensuring high-quality outputs. Buyers need to focus on non-conductive properties and biodegradability for safety and environmental considerations. Cooling efficiency is also vital, particularly when working with delicate components that require careful handling.
How Does Coolant Enhance Operations in the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, CNC machining is crucial for the production of downhole tools. Using high-quality coolants extends tool life and enhances operational safety by managing the extreme temperatures and pressures encountered during drilling. Buyers should seek coolants with high lubricity and resistance to extreme conditions, while also considering the availability of local suppliers to ensure timely procurement.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘coolant for cnc machines’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Cooling Leading to Tool Wear
The Problem: One of the most pressing challenges for B2B buyers of CNC coolant is the inconsistency in cooling performance, which can lead to accelerated tool wear. In many cases, the coolant may not effectively dissipate heat during machining operations, especially when working with tough materials like titanium or high-strength alloys. This can result in frequent tool replacements, increased downtime, and ultimately, a negative impact on production efficiency. Buyers may find themselves caught between the need for high-performance coolants and the reality of using subpar products that fail to deliver consistent results.
The Solution: To address this issue, it’s crucial to select a coolant specifically designed for high-performance machining. Buyers should look for semi-synthetic or full synthetic coolants that offer superior heat transfer capabilities. When sourcing these products, consider conducting a thorough analysis of the machining operations to determine the specific requirements such as viscosity, concentration, and compatibility with the materials being machined. Testing a few different formulations in small batches can also provide valuable insights into which coolant performs best under actual working conditions. Additionally, regular monitoring and maintenance of the coolant system can help ensure that the coolant is mixed at the correct ratio and that the system is free from contaminants that can impair performance.
Scenario 2: Environmental Compliance and Safety Concerns
The Problem: B2B buyers are increasingly faced with stringent environmental regulations and safety standards that impact their choice of coolant. Many traditional coolants contain harmful chemicals that can pose health risks to workers and lead to environmental violations. Buyers in regions with strict compliance standards, such as Europe and parts of South America, must navigate the complexities of selecting a coolant that not only meets operational needs but also adheres to legal requirements. Failing to do so can result in costly fines and damage to the company’s reputation.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize environmentally friendly and non-toxic coolant options. Look for water-soluble coolants that are free from chlorine, formaldehyde, and other hazardous substances. Engaging with suppliers who provide detailed safety data sheets (SDS) and compliance certifications can help buyers make informed decisions. Additionally, consider implementing a regular review of coolant usage and disposal practices to ensure ongoing compliance. Investing in training for employees on the safe handling and disposal of coolants can further enhance workplace safety and reduce liability.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Maintaining Coolant Quality Over Time
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the challenge of maintaining coolant quality over time. As coolants are used, they can become contaminated with metal shavings, bacteria, and other particulates that compromise their effectiveness. This degradation can lead to poor machining results, increased wear on tools, and even machine damage. Buyers often struggle with finding the right balance between coolant longevity and performance, leading to increased costs and operational inefficiencies.
The Solution: To combat coolant degradation, buyers should implement a comprehensive coolant management program. This includes regularly testing coolant concentration and quality using refractometers and pH meters to ensure optimal performance. Establishing a routine for coolant replacement and filtration can also help maintain quality. Consider investing in high-quality filtration systems that can remove contaminants while preserving the coolant’s properties. Additionally, educating staff on best practices for coolant maintenance, such as regularly cleaning the coolant tanks and monitoring for signs of contamination, can prolong coolant life and improve overall machining outcomes. By taking these proactive steps, buyers can enhance productivity and reduce waste associated with coolant disposal and replacement.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for coolant for cnc machines
When selecting coolant for CNC machines, understanding the properties and performance of various materials is crucial for optimizing machining processes. Here, we analyze four common coolant materials: water-soluble oils, semi-synthetic coolants, full synthetic coolants, and vegetable-based coolants. Each material has distinct characteristics that can significantly impact machining efficiency and product quality.
What are the Key Properties of Water-Soluble Oils for CNC Coolants?
Water-soluble oils are a blend of mineral oils and emulsifiers, allowing them to mix with water. They are known for their excellent lubrication and cooling properties, making them suitable for various machining operations. Key properties include a temperature rating of up to 50°C and moderate corrosion resistance, which is essential for protecting machine components.
Pros: Water-soluble oils are cost-effective and provide good cooling performance. They are widely available and compatible with many materials, including aluminum and steel.
Cons: They can be prone to bacterial growth if not maintained properly, leading to odor issues and potential health hazards. Additionally, they may require more frequent changes compared to synthetic options.
How Do Semi-Synthetic Coolants Perform in CNC Machining?
Semi-synthetic coolants combine both oil and water, offering a balance between the benefits of water-soluble oils and full synthetics. They typically have a higher temperature rating, often exceeding 60°C, and provide excellent lubrication and cooling.
Pros: These coolants are versatile and can be used across a wide range of materials, including exotic metals. They also offer better stability and lower maintenance needs than water-soluble oils.
Cons: The cost can be higher than traditional water-soluble oils, and they may not be suitable for all machining applications, particularly those requiring extreme pressure lubrication.
What Advantages Do Full Synthetic Coolants Offer for CNC Applications?
Full synthetic coolants are formulated entirely from synthetic compounds, providing superior performance in high-temperature environments. They often have a temperature rating above 70°C and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-speed machining operations.
Pros: Full synthetics offer the best cooling and lubrication properties, leading to extended tool life and improved surface finishes. They are also less likely to cause skin irritation and are more environmentally friendly.
Cons: The primary drawback is their higher cost, which can be a significant consideration for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, they may require specific handling and disposal methods due to their chemical composition.
What are the Benefits of Using Vegetable-Based Coolants in CNC Machining?
Vegetable-based coolants are derived from natural oils and are gaining popularity due to their eco-friendly properties. They typically have a moderate temperature rating of around 50-60°C and provide good lubricity and cooling.
Pros: These coolants are biodegradable and less harmful to the environment, making them an attractive option for companies focused on sustainability. They also provide good performance across various materials.
Cons: The main limitations include potential higher costs and shorter shelf life compared to synthetic options. They may also require more frequent replenishment due to their natural composition.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers
When sourcing coolant for CNC machines, international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider compliance with local regulations and standards, such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS. Understanding the specific requirements of the target market is essential, as preferences may vary significantly based on local practices and environmental regulations. Additionally, factors such as shipping logistics, availability of products, and local supplier relationships can influence purchasing decisions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for coolant for cnc machines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water-Soluble Oils | General machining of aluminum and steel | Cost-effective and widely available | Prone to bacterial growth | Low |
| Semi-Synthetic Coolants | Versatile use across various materials | Better stability and lower maintenance | Higher cost compared to oils | Medium |
| Full Synthetic Coolants | High-speed machining of exotic metals | Superior cooling and lubrication | Higher cost and specific handling | High |
| Vegetable-Based Coolants | Eco-friendly machining applications | Biodegradable and less harmful | Higher costs and shorter shelf life | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of coolant options for CNC machines, ensuring that B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for coolant for cnc machines
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Coolant for CNC Machines?
The manufacturing process for coolant designed for CNC machines involves several critical stages, each essential for producing high-quality products that meet industry demands.
Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The first step is material preparation, where raw materials such as base oils (mineral or synthetic), emulsifiers, and additives are sourced. Base oils provide the primary lubrication properties, while emulsifiers enable the mixing of oil and water, creating a stable coolant. Additives are included to enhance properties like corrosion resistance, cooling performance, and foam control. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who use high-quality, industry-grade raw materials to ensure optimal performance in diverse machining applications.
Forming: How Is the Coolant Mixture Created?
Once materials are prepared, they undergo the forming stage, where the coolant mixture is created. This typically involves blending base oils with emulsifiers and additives in precise ratios. Advanced mixing techniques, such as high-shear mixing or homogenization, ensure uniform distribution of components, which is vital for the coolant’s performance. Buyers should consider suppliers that employ state-of-the-art blending technology to guarantee consistency and quality.
Assembly: Are There Any Additional Components Involved?
In the assembly stage, the coolant may be subjected to additional processing, such as filtration to remove impurities or the addition of more specialized additives tailored for specific applications. For instance, coolants intended for high-speed machining might require additives that provide enhanced cooling and lubrication. Suppliers should provide detailed information about the formulation process to ensure that B2B buyers understand the properties of the coolant they are sourcing.
Finishing: What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented?
The final stage is finishing, where the product is packaged and labeled according to regulatory standards. Proper labeling is crucial, as it includes safety data and handling instructions. The packaging must be designed to protect the coolant from contamination and degradation during transport and storage. Buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to international packaging standards to ensure product integrity.
How Is Quality Assurance Maintained in Coolant Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of CNC machine coolants is paramount, as it directly impacts performance, safety, and compliance with regulations.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are widely adopted in coolant manufacturing. ISO 9001 provides a framework for establishing a quality management system (QMS) that helps organizations ensure consistent product quality and improve customer satisfaction. B2B buyers should look for suppliers with ISO certification, as this indicates a commitment to quality processes.
What Industry-Specific Certifications Should Be Considered?
In addition to ISO certifications, industry-specific certifications may be required, especially for companies supplying to sectors like aerospace or automotive. For example, compliance with CE marking indicates conformity with European safety standards, while API certifications can be crucial for lubricants used in specific machinery. Buyers should inquire about these certifications to ensure that the coolant meets the necessary industry standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in coolant manufacturing typically includes several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of raw materials before production begins. Suppliers should conduct thorough testing of incoming materials to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks are performed to monitor parameters such as viscosity, pH level, and emulsification stability. Continuous monitoring helps identify any deviations early in the process.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before packaging, the final product undergoes rigorous testing to confirm its adherence to quality specifications. This may include tests for thermal stability, lubricity, and corrosion resistance.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Coolant Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the performance and safety of CNC coolants:
-
Viscosity Testing: Measures the thickness of the coolant, which is crucial for its ability to lubricate and cool effectively.
-
pH Testing: Ensures that the coolant maintains a neutral pH to prevent corrosion and damage to both the machine and the workpiece.
-
Flash Point Testing: Determines the temperature at which the coolant vapors may ignite, ensuring safety during handling and usage.
-
Emulsification Stability Testing: Assesses the ability of the coolant to remain stable and effective when mixed with water.
B2B buyers should request test reports from suppliers to verify the quality of the coolants.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality assurance practices of potential suppliers:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This includes visiting production facilities to observe practices firsthand.
-
Request Documentation: Buyers should ask for quality control documentation, including inspection reports, testing results, and certifications. This transparency helps build trust and ensures compliance with standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly beneficial for international transactions, where buyers may have limited access to supplier facilities.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding quality control nuances is vital:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding chemical products. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local laws, which may involve specific labeling, safety data sheets (SDS), and handling instructions.
-
Cultural Considerations: Communication styles and business practices can vary by region. Building strong relationships with suppliers through regular communication can facilitate better quality control and understanding.
-
Logistics and Transport: The quality of coolant can be affected by transport conditions. Buyers should verify that suppliers have appropriate logistics strategies to prevent contamination and degradation during shipping.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing coolant for CNC machines, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘coolant for cnc machines’
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing the right coolant for CNC machines is essential for optimizing performance, extending tool life, and ensuring quality finishes. This guide provides a practical checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific machining needs is the first step in sourcing coolant. Consider factors such as the types of materials you will be cutting (e.g., aluminum, stainless steel, exotic materials) and the machining processes involved. Each material may require a different coolant formulation for optimal results.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the coolant is suitable for all materials you intend to work with.
- Application Type: Different processes (turning, milling, grinding) may require distinct coolant properties.
Step 2: Research Coolant Types and Formulations
Familiarize yourself with the various types of coolants available, such as soluble oils, semi-synthetics, and full synthetics. Each type has unique properties that affect cooling performance, lubrication, and environmental impact.
- Cooling Efficiency: Consider coolants with high thermal conductivity for better heat dissipation.
- Lubrication Properties: Look for formulations that enhance tool life and surface finish.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your requirements. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and references from similar industries.
- Supplier Reputation: Research customer reviews and industry testimonials to gauge reliability.
- Production Capacity: Ensure the supplier can meet your volume needs, especially during peak demand.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
It’s crucial to check that your chosen coolant and supplier comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. This includes safety certifications and environmental compliance.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Request SDS for all coolant products to understand health and safety implications.
- ISO Certifications: Look for ISO certifications to ensure quality management practices.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the coolants you’re considering. Testing samples in your actual machining processes will provide valuable insights into their performance.
- Performance Evaluation: Test for cooling efficiency, lubrication, and overall effectiveness on different materials.
- Compatibility Testing: Ensure the coolant does not adversely affect your machinery or work environment.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and product, negotiate the terms of purchase. This includes pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms.
- Bulk Pricing: Inquire about discounts for bulk orders to optimize your budget.
- Delivery Logistics: Discuss shipping options, lead times, and any potential customs implications for international suppliers.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Building a strong relationship with your coolant supplier can lead to better service and support. Regular communication can help address issues quickly and adapt to changing needs.
- Feedback Loop: Provide feedback on product performance to foster improvements.
- Partnership Opportunities: Explore opportunities for joint development of customized coolant solutions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they procure the most suitable coolant for their CNC machining operations, enhancing productivity and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for coolant for cnc machines Sourcing
When sourcing coolant for CNC machines, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The cost of coolant is influenced by various components, price influencers, and strategic buyer tips that can lead to more effective procurement decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components for CNC Machine Coolant?
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the quality and type of base oils and additives used in coolant formulation. Semi-synthetic and fully synthetic coolants generally command higher prices due to their superior performance characteristics, including better lubrication and heat dissipation.
-
Labor: Labor costs are associated with the manufacturing process, including formulation, mixing, and quality control. Skilled labor is often required to ensure that the coolant meets specific performance standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Manufacturers with advanced production technologies might have higher overhead but can produce more consistent and higher-quality products.
-
Tooling: The development of specialized tooling for certain formulations can add to costs. Custom formulations may require unique production processes, impacting the overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are essential, particularly for products meant for high-precision applications in industries such as aerospace and automotive. This adds another layer to the cost structure.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, especially for bulk orders, can significantly affect pricing. The geographical location of suppliers and buyers plays a critical role in determining these logistics costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins vary based on brand reputation, product quality, and market positioning. Premium brands may have higher margins due to perceived value.
What Influences Prices for CNC Machine Coolant?
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit prices. Many suppliers offer tiered pricing structures based on minimum order quantities (MOQs), incentivizing bulk purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom formulations to meet specific machining requirements can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether standard products meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: The choice between mineral-based, semi-synthetic, and synthetic coolants will influence price points. Synthetic options typically cost more but may offer better performance and longevity.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM) or industry-specific certifications (e.g., aerospace) may come at a premium. Buyers should evaluate whether these certifications are necessary for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and service offerings can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a strong track record may charge more but offer better support and product consistency.
-
Incoterms: The chosen shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) impact the total cost. Buyers should negotiate these terms to optimize logistics costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts. Building a relationship can lead to better terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the longevity and performance of the coolant. A higher initial cost may be justified by reduced downtime and longer tool life.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and regional market conditions that can affect pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate some risks.
-
Research and Compare: Utilize available resources to compare prices and formulations across different suppliers. Leverage industry forums and expert recommendations to identify the best products for your specific needs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for CNC machine coolant can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing coolant for cnc machines With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Coolant for CNC Machines
When considering the most effective solutions for optimizing CNC machining processes, it’s crucial to evaluate various alternatives to traditional coolant. Each solution has its unique advantages and drawbacks, making it essential for B2B buyers to understand how these options compare in terms of performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications.
| Comparison Aspect | Coolant For CNC Machines | Alternative 1: Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) | Alternative 2: Air Cooling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent lubrication and cooling; enhances tool life and surface finish | Good for light machining; reduces coolant usage significantly | Limited cooling; best for low-speed operations |
| Cost | Moderate to high ongoing costs due to replenishment and disposal | Lower overall cost; less product needed | Very low cost; requires no consumables |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup of coolant systems and regular maintenance | Simple installation; often retrofittable | Very easy; usually just requires air lines |
| Maintenance | Regular monitoring and disposal needed; can be complex | Minimal maintenance; filter changes may be needed | Very low maintenance; air systems are generally maintenance-free |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty machining with diverse materials | Precision machining of metals with minimal waste | Low-speed machining or operations where heat generation is minimal |
Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL)
Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) is a technique that delivers a minimal amount of lubricant directly to the cutting edge of the tool. This method significantly reduces the volume of fluid used, leading to lower operational costs and less waste. MQL is particularly effective for precision machining of metals, providing enough lubrication while minimizing coolant-related issues such as disposal and contamination. However, it may not be suitable for heavy-duty machining or when cutting tougher materials, as the reduced lubrication can lead to increased wear and heat generation.
Air Cooling
Air cooling is a method that relies solely on compressed air to cool the cutting tools during machining operations. This approach is highly cost-effective, as it eliminates the need for any consumable fluids. While air cooling can be effective in low-speed operations or for materials that do not generate excessive heat, it falls short in high-performance applications where heat management is critical. Its simplicity and ease of maintenance make it an attractive option for specific machining scenarios, but buyers should be cautious about its limitations in more demanding environments.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right cooling solution for CNC machining, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, including the types of materials being machined, the scale of production, and the associated costs. Coolant for CNC machines remains the go-to option for heavy-duty applications due to its superior performance and heat management capabilities. However, for operations focused on precision and minimizing waste, alternatives like MQL or air cooling may provide a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly approach. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each solution will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for coolant for cnc machines
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Machine Coolants?
When selecting coolant for CNC machines, understanding the technical properties is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring machine longevity. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Viscosity
Viscosity refers to the thickness or resistance to flow of the coolant. It is typically measured in centipoise (cP). High viscosity coolants provide better lubrication, reducing friction and wear on cutting tools. This property is vital in high-speed machining processes where excessive heat generation can lead to tool failure. A coolant with appropriate viscosity enhances the efficiency of operations, especially in machining complex materials. -
pH Level
The pH level of a coolant indicates its acidity or alkalinity, which can significantly affect the performance and longevity of both the coolant and the machine. A neutral pH (around 7) is generally preferred to minimize corrosion and oxidation of machine components. Coolants with a high pH can help prevent rust formation, making them suitable for ferrous metals. Selecting the right pH-balanced coolant is crucial for maintaining equipment integrity and reducing maintenance costs. -
Concentration Ratio
This property indicates the dilution level of the coolant when mixed with water. A proper concentration ratio ensures optimal cooling and lubrication during machining. Too diluted a mixture may lead to insufficient cooling, while a high concentration could cause foam formation and reduce effectiveness. Understanding the required concentration for specific materials and machining operations is essential for maximizing performance and cost-effectiveness. -
Additives
The presence of additives in coolants can significantly enhance performance. Common additives include anti-corrosion agents, biocides to prevent microbial growth, and extreme pressure additives that improve lubrication under high-stress conditions. For B2B buyers, selecting a coolant with the right additives tailored to specific machining tasks ensures better tool life and surface finish, ultimately leading to increased productivity. -
Emulsibility
Emulsibility refers to the ability of a coolant to mix with water, forming a stable emulsion. This property is crucial for water-soluble coolants, as it affects their cooling efficiency and lubrication characteristics. A well-emulsified coolant provides consistent performance and reduces the risk of separation, which can lead to ineffective cooling and increased tool wear. Understanding emulsibility helps buyers select the right coolant for their specific machining operations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to CNC Coolants?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CNC machine coolants, understanding OEM specifications ensures that the chosen coolant is compatible with the machinery in use, thereby optimizing performance and reducing downtime. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant in B2B transactions where bulk purchasing is common. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and manage costs effectively, ensuring they meet production demands without overstocking. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a detailed quote for specific products or services. For coolant procurement, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, terms, and conditions from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to clarify logistics and avoid unexpected costs when sourcing CNC machine coolants from global suppliers. -
SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
An SDS provides detailed information about the properties of a chemical product, including hazards, handling, and safety precautions. For CNC coolant buyers, reviewing the SDS is essential for ensuring compliance with safety regulations and protecting workers’ health.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their machining processes and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the coolant for cnc machines Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global coolant market for CNC machines is witnessing significant growth driven by several factors, including the rising demand for precision machining and the increasing complexity of manufacturing processes. As industries continue to advance technologically, there is a growing requirement for high-performance coolants that not only enhance machining efficiency but also extend tool life. Emerging trends such as the adoption of semi-synthetic and fully synthetic coolants are becoming prominent, as they offer superior lubrication and heat dissipation properties compared to traditional soluble oils.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics is crucial. Factors such as fluctuating raw material prices, regulatory changes regarding chemical compositions, and the push towards environmentally friendly solutions are shaping sourcing strategies. Additionally, the integration of digital technologies, such as IoT and AI, in monitoring coolant effectiveness and optimizing usage, is gaining traction. Buyers should look for suppliers that not only provide diverse coolant options but also embrace technological advancements to enhance operational efficiency.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As global awareness of environmental issues intensifies, the demand for sustainable and ethically sourced products is becoming a priority for B2B buyers in the coolant sector. The environmental impact of traditional coolant formulations, which often include harmful chemicals, has prompted many manufacturers to innovate and provide greener alternatives. This includes the development of bio-based and water-soluble coolants that minimize ecological footprints while maintaining performance.
Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining importance. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and adhere to environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and various eco-labels can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By choosing products that are environmentally friendly, businesses can not only reduce their ecological impact but also enhance their brand reputation among increasingly environmentally conscious customers.
Brief Evolution/History
The coolant industry has evolved significantly over the decades, transitioning from simple mineral oils to complex formulations designed for specific machining needs. Initially, coolants were primarily used for lubrication to reduce friction and heat generation during machining processes. However, with advancements in materials and machining techniques, the industry has shifted towards developing specialized coolants, including semi-synthetic and fully synthetic options, which offer improved performance, safety, and environmental benefits. This evolution reflects the industry’s response to the growing demands for efficiency, sustainability, and technological integration in modern manufacturing environments.
Understanding these trends and dynamics can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions in sourcing the right coolant solutions for their CNC machining operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of coolant for cnc machines
-
How do I choose the right coolant for CNC machining?
Choosing the right coolant involves understanding the materials you will be machining and the specific operations you will be performing. Consider factors such as the coolant type (synthetic, semi-synthetic, or soluble), its viscosity, and its compatibility with various materials like aluminum, stainless steel, or exotic alloys. Additionally, evaluate the coolant’s performance in terms of lubrication, cooling capacity, and its ability to prevent corrosion. Consulting with suppliers and reviewing technical data sheets can help you make an informed decision tailored to your specific needs. -
What is the best coolant for machining aluminum?
For machining aluminum, a water-soluble coolant with high lubricity is often recommended. Semi-synthetic coolants are popular as they provide excellent cooling and lubrication while minimizing residue. Look for products specifically designed for aluminum machining that prevent oxidation and enhance surface finish. Additionally, consider the coolant’s pH level and stability, as these can impact tool life and workpiece quality. Brands like Castrol and Hangsterfer offer well-regarded options that have been proven effective in this application. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing coolant suppliers internationally?
When sourcing coolant suppliers internationally, key factors include the supplier’s reputation, product quality, and compliance with international regulations. It’s important to assess their manufacturing processes and certifications, such as ISO standards. Additionally, consider their ability to customize products based on your specific machining needs and materials. Logistics capabilities, including shipping times and costs, as well as their responsiveness to inquiries, can significantly influence your decision. Establishing clear communication channels is essential for a successful partnership. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC coolants?
The MOQ for CNC coolants can vary significantly among suppliers and may range from a few gallons to multiple drums. Many manufacturers offer flexible MOQs to accommodate different business sizes and requirements. For international buyers, it’s advisable to discuss your anticipated usage and order frequency with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Some suppliers may provide trial quantities for new customers to evaluate product performance before committing to larger orders. -
How do payment terms typically work for international coolant purchases?
Payment terms for international coolant purchases often depend on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s relationship with them. Common options include upfront payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms before placing an order. Consider using escrow services for added security during initial transactions. Establishing a reliable payment history can lead to more favorable terms in future dealings, such as extended payment periods or volume discounts. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from coolant suppliers?
Reputable coolant suppliers should provide quality assurance measures that include product testing and certification. Look for suppliers that perform regular quality checks and have detailed documentation of their testing processes. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, inquire about their policies on product recalls and customer feedback mechanisms. A reliable supplier will be transparent about their quality assurance practices and willing to address any concerns that arise. -
How can I ensure the coolant is compatible with my CNC machine?
To ensure coolant compatibility with your CNC machine, start by reviewing the machine manufacturer’s recommendations. Consult the technical specifications of both the machine and the coolant. Factors such as the coolant’s chemical composition, viscosity, and pH level are crucial for compatibility. It’s also beneficial to test a small batch of coolant in your operation to monitor any adverse effects on machine performance or workpiece quality. Engaging with the supplier for expert advice can further mitigate compatibility issues. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing coolant?
When importing coolant, consider logistics such as shipping regulations, customs duties, and transportation costs. Ensure that the coolant complies with the importing country’s environmental regulations and safety standards. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to streamline the process. Additionally, plan for lead times that account for potential delays in customs clearance. Having a reliable logistics partner can help mitigate risks and ensure timely delivery of your coolant supplies.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Coolant For Cnc Machines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Redline Tools – RC3500P Semi Synthetic Coolant
Domain: redlinetools.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘RC3500P Semi Synthetic Coolant’, ‘quantity’: ‘5 Gal Pail’, ‘price’: ‘$32.40’, ‘made_in’: ‘USA’}, {‘name’: ‘RC2000P Multi Material High Perf Coolant’, ‘quantity’: ‘5 Gal Pail’, ‘price’: ‘$40.71’, ‘made_in’: ‘USA’}, {‘name’: ‘RC2500D High Perf Coolant’, ‘quantity’: ’55 Gal Drum’, ‘price’: ‘$43.58’, ‘made_in’: ‘USA’}, {‘name’: ‘RC3500D Semi Synthetic Coolant’, ‘quantity’: ’55 Gal Drum’, ‘p…
2. Trim Microsol – 585XT
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1. Trim Microsol 585XT: Recommended for cutting a variety of materials including aluminum and exotic metals. 2. Rustlick WS-5050: Works well but can cause rust if not wiped off; users are looking to try Qualichem 251C. 3. Zurn Aquasol DX-1000: Highly regarded for its performance over 40 years of use. 4. Trim E206: Users report it resolves rust issues associated with Rustlick WS-5050. 5. Trim Micro…
3. WayKen – CNC Coolant
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: CNC coolant, also known as cutting fluid, is an industrial fluid used in metal cutting operations to improve efficiency. It contains chemical additives such as animal fat, water, petroleum distillate, and vegetable oil. CNC coolants serve as lubricants and cooling mechanisms, aiding in chip removal and reducing overheating during machining. There are various types of CNC machining coolants, includ…
4. Metal Fluids – BOSSE LUBRICANTS™ BLADE AID
Domain: metalfluids.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Machine Coolants – Soluble Oils, Semi-Synthetics and Full Synthetics available for various applications. Key products include: 1. BOSSE LUBRICANTS™ BLADE AID – Synthetic band-saw fluid for medium to heavy-duty operations. 2. BOSSE LUBRICANTS™ BOS-SOL 31 – Concentrated water soluble oil with high-grade lubricity additives. 3. BOSSE LUBRICANTS™ PRO-SOL 451 HD – Non-toxic, non-irritating, non-corrosi…
5. Pandora – Premium Spindle Oil
Domain: coolantcontrol.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, Pandora – Premium Spindle Oil, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Haas CNC – Cutting Fluid Solutions
Domain: haascnc.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Haas CNC – Cutting Fluid Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Zebra Skimmers – ZVA8 Tube Skimmer
Domain: zebraskimmers.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Zebra Skimmers offers a variety of products for CNC coolant management, including tramp oil skimmers, tube skimmers, belt skimmers, disk skimmers, coalescers, coolant mixers, proportioning pumps, and various testing equipment. Key products include the ZVA8 Tube Skimmer, Poly Belt Skimmers, FZ17 Coalescer, Dazzle™ Sump Level Controller, and optical/digital BRIX refractometers. The company emphasize…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for coolant for cnc machines
In navigating the competitive landscape of CNC machining, strategic sourcing of coolant is paramount. The variety of coolants available—ranging from semi-synthetic to fully synthetic—offers distinct advantages tailored to specific machining needs. Buyers should prioritize products that enhance tool life, improve machining efficiency, and ensure superior heat transfer, as these factors significantly impact operational costs and productivity.
Understanding regional differences in coolant performance and regulations is critical for international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Selecting the right coolant not only optimizes machine performance but also supports sustainability initiatives, aligning with global trends toward environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
As we look to the future, the demand for high-performance coolants will continue to grow, driven by advancements in materials and machining technologies. International buyers are encouraged to leverage strategic partnerships with reputable suppliers, ensuring access to innovative coolant solutions that meet evolving industry standards. By prioritizing informed sourcing strategies, businesses can enhance their competitive edge, reduce operational risks, and drive sustained growth in their respective markets. Embrace the opportunity to refine your sourcing strategies today, and position your business for success in the dynamic world of CNC machining.