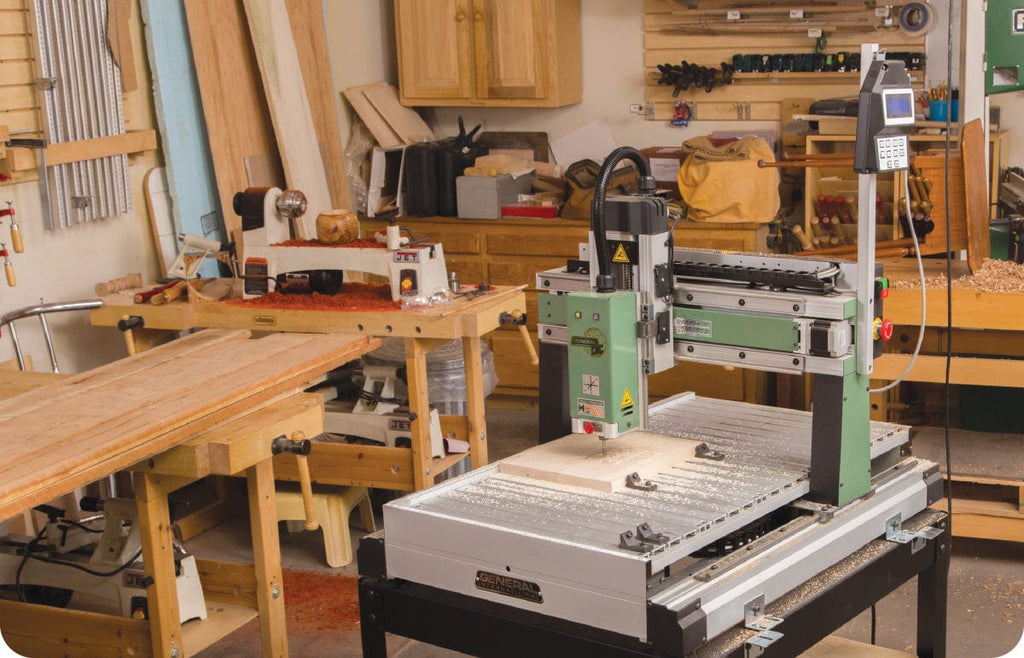
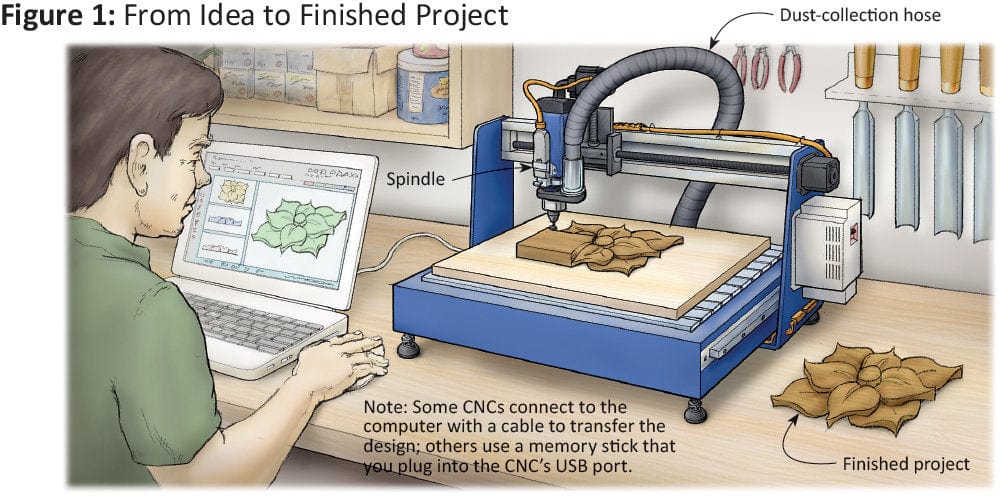
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for computer wood cutter
The global market for computer wood cutters presents a myriad of opportunities for B2B buyers seeking to enhance their woodworking capabilities. As companies strive to meet rising customer demands for precision and efficiency, sourcing the right CNC wood router can be a pivotal challenge. This guide is designed to navigate the complexities of the computer wood cutter landscape, providing insights into various types of machines, their applications, and the essential factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
In this comprehensive resource, you will find detailed analyses of CNC wood routers, including entry-level models suitable for hobbyists and high-end machines designed for industrial applications. We will also explore customization options, cost considerations, and essential features that can significantly impact productivity and profitability.
For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—this guide serves as an invaluable tool. It empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions by equipping you with the knowledge needed to identify the right equipment for your specific needs. By understanding the nuances of the computer wood cutter market, you can enhance your operational efficiency, boost your competitive edge, and ultimately drive your business forward.
Understanding computer wood cutter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Wood Router | 3, 4, or 5 axes for 2D, 2.5D, and 3D cutting | Cabinet making, sign making, furniture production | Pros: Versatile, high precision. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Desktop CNC Router | Compact size, suitable for hobbyists and small businesses | Prototyping, small-scale production | Pros: Affordable, easy to use. Cons: Limited work area. |
| ATC CNC Router | Automatic tool changer, suitable for high-volume production | Industrial woodworking, custom furniture | Pros: Increased efficiency, reduced downtime. Cons: More complex setup. |
| Nesting CNC Machine | Optimized for space-saving cuts, often used in furniture | Custom furniture making, cabinetry | Pros: Material savings, streamlined production. Cons: Requires skilled operation. |
| Laser Wood Cutter | Uses laser technology for precision cutting | Detailed engraving, intricate designs | Pros: High detail, minimal waste. Cons: Slower for bulk cutting. |
What are the Characteristics of CNC Wood Routers?
CNC wood routers are highly versatile machines capable of handling various woodworking tasks, from intricate carvings to large-scale furniture production. They come equipped with multiple axes, typically ranging from three to five, allowing for complex 2D, 2.5D, and 3D designs. These machines are ideal for B2B applications such as cabinet making and signage, where precision and customization are critical. When purchasing, businesses should consider the machine’s axis configuration, software compatibility, and support services.
How Do Desktop CNC Routers Fit into Small Business Needs?
Desktop CNC routers are compact machines designed for hobbyists and small businesses. They offer an affordable entry point into CNC woodworking, making them suitable for prototyping and small-scale production. Their user-friendly design allows operators with minimal experience to produce quality results. However, potential buyers should keep in mind their limited working area and lower power compared to industrial models, which may restrict larger projects.
What Advantages Do ATC CNC Routers Provide for Industrial Applications?
Automatic Tool Change (ATC) CNC routers are specifically designed for high-volume production environments. They feature an automatic tool changer that allows for quick transitions between different cutting tasks, significantly increasing operational efficiency. This is particularly beneficial for industries focused on custom furniture and cabinetry. However, businesses must be prepared for a more complex setup and higher upfront costs, making it essential to assess long-term production needs before investing.
Why Choose a Nesting CNC Machine for Custom Furniture?
Nesting CNC machines are engineered to optimize material usage, making them a preferred choice for custom furniture makers. By nesting parts closely together on the material sheet, these machines minimize waste and reduce costs. They are ideal for cabinetry and modern furniture designs that require precise cuts. However, operating a nesting CNC machine often requires skilled personnel to maximize its potential, which is a crucial consideration for businesses looking to enhance production efficiency.
What are the Key Benefits of Laser Wood Cutters in Woodworking?
Laser wood cutters offer exceptional precision and detail, making them suitable for intricate designs and engravings. They are particularly effective for applications that require minimal material waste and high-quality finishes. While laser cutters can be slower for bulk cutting tasks, their ability to produce fine details makes them invaluable in markets such as custom signage and artistic woodworking. Buyers should evaluate their specific needs regarding speed and detail to ensure the right fit for their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of computer wood cutter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of computer wood cutter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furniture Manufacturing | Precision cutting and shaping of wood components for furniture | Enhanced production efficiency and reduced material waste | Machine size, cutting precision, and automation features |
| Signage and Display | Custom sign creation with intricate designs and lettering | Ability to produce unique, high-quality signage quickly | Software compatibility, ease of use, and design capabilities |
| Cabinetry and Millwork | Automated cabinetry production including doors and frames | Increased throughput and consistent quality in cabinet making | Size of the work area, tooling options, and material types |
| Arts and Crafts | Detailed carving and engraving for decorative items | Unique product offerings and customization potential | Versatility in design, user-friendly operation, and support |
| Construction and Renovation | Custom wood fittings and fixtures for residential and commercial use | Tailored solutions for specific projects, improving client satisfaction | Durability, maintenance requirements, and after-sales support |
How Are Computer Wood Cutters Used in Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing sector, computer wood cutters are employed for precision cutting and shaping of various wood components. This technology allows manufacturers to produce intricate designs and complex shapes that would be difficult or time-consuming to achieve manually. By automating the cutting process, businesses can significantly enhance production efficiency and minimize material waste, which is crucial for cost management. International buyers should consider machine size, cutting precision, and available automation features when sourcing equipment to ensure it meets their production needs.
What Role Do Computer Wood Cutters Play in Signage and Display?
Computer wood cutters are essential for the signage and display industry, where they facilitate the rapid production of custom signs featuring intricate designs and lettering. This capability enables businesses to create high-quality, unique signage that stands out in a competitive market. The ability to produce signs quickly without sacrificing quality is a key advantage, particularly for businesses that require fast turnaround times. Buyers should prioritize software compatibility, ease of use, and advanced design capabilities when sourcing these machines.
How Are Computer Wood Cutters Transforming Cabinetry and Millwork?
In cabinetry and millwork, computer wood cutters automate the production of cabinets, doors, and frames, ensuring consistent quality and increased throughput. This technology allows for precise cuts that fit together seamlessly, reducing the need for manual adjustments. As a result, manufacturers can deliver high-quality products more efficiently, meeting customer demands for customization and speed. Buyers should focus on the size of the work area, tooling options, and the types of materials the machine can handle when sourcing equipment.
What Advantages Do Computer Wood Cutters Offer in Arts and Crafts?
For the arts and crafts sector, computer wood cutters enable detailed carving and engraving, allowing artisans to create unique decorative items. This technology opens up new avenues for creativity, enabling the production of personalized items that can command higher prices in the market. The versatility of these machines allows for a wide range of designs, making them an attractive investment for craft businesses. Buyers should look for machines that offer versatility in design, user-friendly operation, and comprehensive support services.
How Are Computer Wood Cutters Beneficial in Construction and Renovation?
In construction and renovation, computer wood cutters are utilized to create custom wood fittings and fixtures tailored to specific projects. This capability allows contractors to provide tailored solutions that enhance client satisfaction and project outcomes. By utilizing precise cutting technology, businesses can ensure that every piece fits perfectly, minimizing installation time and costs. When sourcing machines, buyers should consider durability, maintenance requirements, and the availability of after-sales support to ensure long-term operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘computer wood cutter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complexity in Software Integration
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties when integrating computer wood cutters with existing software systems for design and production management. This can lead to inefficiencies, increased operational costs, and frustration among staff who may not be trained to handle the technical intricacies. Particularly for businesses transitioning from traditional methods to CNC technology, the lack of seamless integration can hinder productivity and delay project timelines.
The Solution: To tackle this challenge, buyers should prioritize CNC machines that offer robust compatibility with widely-used design software such as AutoCAD or Vectric. When sourcing a computer wood cutter, inquire about the machine’s software capabilities and ask for demonstrations that showcase its integration with popular CAD/CAM systems. It’s advisable to choose suppliers who provide comprehensive training sessions for staff to ensure they are comfortable with the software. Additionally, consider investing in a machine with a user-friendly interface and customer support that can assist with any technical issues that arise post-purchase. This proactive approach not only streamlines operations but also enhances the overall user experience for your team.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Limitations in Material Handling
The Problem: B2B companies often face challenges related to material handling, especially when working with large sheets of wood or complex designs. Inadequate handling systems can lead to misalignment during cutting, resulting in wasted materials and increased costs. This problem is particularly pronounced in regions where labor is scarce or expensive, making efficient material management crucial for profitability.
The Solution: To resolve material handling issues, buyers should look for CNC wood cutters equipped with advanced features such as automatic material loading systems, vacuum tables, or nesting software that optimizes material usage. During the purchasing process, it’s beneficial to consult with the supplier to understand how their machine addresses material handling. Additionally, investing in an auxiliary material handling system—like a conveyor belt or lift system—can significantly enhance efficiency. Regular training for operators on best practices for loading and unloading materials can also help minimize errors and material waste. By prioritizing these features, businesses can not only improve production efficiency but also reduce costs associated with material waste.
Scenario 3: Addressing Skill Gaps in Workforce Training
The Problem: A significant barrier for many B2B buyers is the existing skill gap within their workforce when it comes to operating advanced computer wood cutters. As technology evolves, workers may feel overwhelmed by the complexity of operating CNC machinery, which can lead to lower morale, increased errors, and higher turnover rates. This challenge is particularly relevant in regions where training resources are limited or where the workforce may not have a strong background in technology.
The Solution: To bridge the skill gap, companies should invest in comprehensive training programs provided by the CNC machine suppliers. Many reputable suppliers offer free or low-cost training sessions, both online and in-person, to help operators become proficient with the machinery. In addition, consider establishing a mentorship program within your organization where more experienced employees can guide newer operators. Implementing a structured training schedule that includes hands-on practice can help build confidence and competence. Furthermore, creating a supportive environment where employees can share tips and troubleshoot issues collectively fosters a culture of continuous learning. By equipping your workforce with the necessary skills, you not only enhance productivity but also create a more engaged and satisfied team.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for computer wood cutter
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Computer Wood Cutters?
When selecting materials for computer wood cutters, understanding the properties of commonly used materials is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring compatibility with various applications. Here, we analyze four prevalent materials: aluminum, steel, composite materials, and high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
Aluminum: A Lightweight and Versatile Option
Aluminum is widely favored in CNC wood cutting machines due to its lightweight nature and excellent machinability. Its thermal conductivity allows for effective heat dissipation during operations. Key properties include a temperature rating of up to 600°F and good corrosion resistance, which is essential for longevity in humid environments.
Pros: Aluminum is durable yet lightweight, making it easier to handle and install. It offers good strength-to-weight ratios and is relatively cost-effective compared to other metals.
Cons: While it is resistant to corrosion, aluminum can be prone to scratching and denting. It may also require more frequent maintenance to preserve its appearance and functionality.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for various media, including softwoods and hardwoods, and is commonly used in the frames and components of CNC routers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers meet local quality standards to avoid issues with durability and performance.
Steel: The Heavy-Duty Workhorse
Steel is another common material used in CNC wood cutting machinery, particularly for structural components. Its high tensile strength and durability make it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Steel’s temperature rating can exceed 1,500°F, providing excellent performance under high-stress conditions.
Pros: Steel is incredibly strong and resistant to wear, making it ideal for high-volume production environments. Its robustness ensures longevity, even under rigorous use.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its weight, which can complicate transportation and installation. It is also more expensive than aluminum and may require additional treatments to prevent rust and corrosion.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in the construction of machine frames and bases, ensuring stability during operation. It is compatible with a wide range of wood types.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for compliance with safety and environmental regulations regarding steel production and treatment, especially in the Middle East and Europe.
Composite Materials: A Modern Approach
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are increasingly being used in CNC wood cutters. These materials offer unique properties, including high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent resistance to environmental factors.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and provide good thermal stability, making them suitable for high-speed applications. They also resist corrosion and are less prone to warping.
Cons: The main limitation is the higher cost of composite materials compared to traditional metals. Additionally, manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly effective for intricate designs and high-precision applications, making them ideal for artistic woodworking and detailed carvings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that composites meet relevant international standards for safety and performance, especially in regions with stringent regulations like Europe.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): The Flexible Choice
HDPE is a thermoplastic known for its durability and chemical resistance. It is often used in CNC applications where moisture resistance is essential. Its temperature rating is typically around 120°F, making it suitable for less demanding applications.
Pros: HDPE is lightweight, easy to machine, and resistant to impact and moisture. It is also cost-effective and has a low friction coefficient, making it ideal for moving parts.
Cons: While it is durable, HDPE may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads as effectively as metals. Its use is generally limited to non-structural components.
Impact on Application: HDPE is commonly used for jigs, fixtures, and protective covers in CNC wood cutting applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that HDPE materials comply with local regulations concerning plastic usage and recycling, especially in regions like South America and Africa where environmental standards are evolving.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Computer Wood Cutters
| Material | Typical Use Case for computer wood cutter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Frames and components | Lightweight and easy to handle | Prone to scratching and denting | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components | High strength and durability | Heavy and more expensive | High |
| Composite Materials | Artistic woodworking and precision cuts | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Jigs, fixtures, protective covers | Cost-effective and moisture-resistant | Limited load-bearing capacity | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for computer wood cutters, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for computer wood cutter
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Computer Wood Cutter?
The manufacturing process of a computer wood cutter involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets the high standards required by B2B buyers. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The process begins with the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials for CNC wood cutters include high-grade steel for structural components, aluminum for lighter sections, and various plastics for non-structural parts. Quality control at this stage is crucial; materials must meet specific standards regarding strength, durability, and compatibility with the intended application. Suppliers often perform tests such as tensile strength analysis and dimensional checks to ensure compliance.
Forming: How Are Components Shaped?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves various techniques such as CNC machining, laser cutting, and plasma cutting. Each method is chosen based on the precision required and the material characteristics. For instance, CNC machining is favored for its accuracy in producing intricate designs, while laser cutting is often employed for faster, cleaner cuts in thinner materials. It is essential that manufacturers utilize advanced technologies and skilled operators to minimize errors during this phase.
Assembly: How Are Components Brought Together?
After forming, the individual components are assembled. This step may involve welding, bolting, or using adhesives, depending on the design specifications. During assembly, quality control checkpoints are implemented to ensure that all components fit together correctly and function as intended. This may include checks for alignment, tension, and electrical connections, especially in machines that incorporate sophisticated electronics for control systems.
Finishing: What Techniques Ensure a Quality Surface?
The final stage of manufacturing is finishing, which may include painting, coating, or polishing to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal. Finishing techniques not only protect the machine from corrosion and wear but also contribute to its overall performance. Manufacturers often apply surface treatments such as anodizing for aluminum parts or powder coating for steel structures, which can significantly improve resistance to environmental factors.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Computer Wood Cutters?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, particularly for machines that must perform reliably under heavy use. B2B buyers should be aware of the various QA practices and standards that manufacturers adhere to.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Consider?
A key international standard relevant to the manufacturing of computer wood cutters is ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established processes to ensure consistent quality, which is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. Additionally, certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may be relevant, depending on the application of the wood cutters.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control within the manufacturing process typically includes several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections ensure that components are being produced according to specifications. This might include monitoring machine settings and conducting dimensional checks.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the final product undergoes comprehensive testing to ensure it operates correctly and meets all performance criteria. This may include functional tests, safety checks, and performance evaluations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive measures to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. This can be achieved through:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of the manufacturing facility can help buyers assess compliance with quality standards and identify areas for improvement.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline inspection results and testing methodologies provides transparency into the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and product quality, ensuring adherence to international standards.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be mindful of specific nuances in quality control and certification.
Are There Regional Standards to Consider?
Different regions may have unique certification requirements. For example, products sold within the European Union must comply with CE marking regulations, while North American buyers may look for UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification. Understanding these regional requirements is critical for ensuring that products are compliant with local laws and market expectations.
How Do Cultural Differences Impact Quality Expectations?
Cultural differences may also influence quality expectations. For instance, buyers in Europe may prioritize sustainability and eco-friendliness in manufacturing processes, while buyers in the Middle East may focus more on durability and performance. It is essential for international buyers to communicate their quality expectations clearly to suppliers to avoid misunderstandings and ensure satisfaction with the final product.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Computer Wood Cutter Manufacturing
The manufacturing and quality assurance processes for computer wood cutters are complex but crucial for delivering reliable, high-performance machines. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, relevant quality standards, and how to verify supplier practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that will enhance their operations and profitability. A focus on quality not only ensures the longevity of the equipment but also fosters trust and reliability in supplier relationships, paving the way for successful international business endeavors.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘computer wood cutter’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure a computer wood cutter, specifically CNC wood routers. With the growing demand for precision and efficiency in woodworking, selecting the right machine is critical for enhancing productivity and maintaining quality standards. This guide will walk you through essential steps to ensure a successful procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the specific requirements of your woodworking projects. Consider factors such as the types of materials you will be cutting, the complexity of designs, and the desired cutting speed.
– Material Compatibility: Ensure the machine can handle the wood types you plan to work with.
– Axis Configuration: Decide between 3, 4, or 5 axes based on the intricacy of your projects.
Step 2: Establish Your Budget
Determine a realistic budget that includes not only the cost of the machine but also installation, maintenance, and potential training.
– Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Value: While cheaper models may save money upfront, assess their durability and efficiency to avoid higher costs in the long run.
– Financing Options: Explore financing or leasing options that can ease the initial financial burden.
Step 3: Research and Shortlist Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers. Look for manufacturers that specialize in CNC wood routers and have a track record of quality and reliability.
– Industry Reputation: Seek reviews and testimonials from other businesses in similar sectors.
– Certifications: Verify that suppliers meet international standards and certifications, which can indicate quality assurance.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it is crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Visit Facilities: If possible, visit the supplier’s manufacturing facility to assess quality control processes.
– Ask for Demonstrations: Request live demonstrations of the machinery to evaluate performance and ease of use.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support
After-sales service is critical for minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal machine performance.
– Training and Resources: Confirm whether the supplier offers training for your staff and access to user manuals or online resources.
– Maintenance and Warranty: Inquire about warranty terms and the availability of maintenance services to keep your machine in peak condition.
Step 6: Review Contract Terms
Carefully examine the contract terms before finalizing your purchase. Ensure all details, including payment schedules, delivery timelines, and service agreements, are clearly outlined.
– Transparency: Look for any hidden fees or clauses that could affect your budget or service.
– Dispute Resolution: Ensure there are clear terms regarding dispute resolution should issues arise post-purchase.
Step 7: Make an Informed Decision
After gathering all necessary information, weigh the pros and cons of each option. Consider not only the technical aspects but also the overall partnership potential with the supplier.
– Long-Term Partnership: Choose a supplier that aligns with your business goals and can adapt to future needs as your operations grow.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process for computer wood cutters more effectively, ensuring they invest in machinery that meets their operational demands and enhances their business capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for computer wood cutter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Computer Wood Cutters?
When sourcing computer wood cutters, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The type of materials used in the construction of CNC routers can significantly affect the overall cost. High-quality steel, aluminum, and composite materials generally increase durability and performance, but they also raise the price. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in higher-quality materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary by region and supplier. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, manufacturers may pass these expenses onto buyers. Conversely, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs could provide cost savings, but it may introduce risks related to quality and consistency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Manufacturers with efficient processes and lower overhead costs can offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial setup costs for specialized tooling can be significant, especially for custom designs. These costs should be factored into the total price, as they can vary widely depending on the complexity of the machine and its specifications.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that the CNC routers meet specific standards often involves additional QC costs. Buyers should inquire about the QC processes employed by suppliers to ensure product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can be substantial, especially for large machines. International buyers should consider the costs associated with shipping, customs duties, and insurance.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions and competition. Understanding this margin can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Computer Wood Cutter Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of computer wood cutters, including volume and minimum order quantities (MOQs), specifications and customization, materials used, quality certifications, supplier reputation, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities can lead to significant discounts. Buyers should evaluate their needs carefully to take advantage of these savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features and specifications will increase the price. Buyers should be clear about their requirements and understand how these affect the overall cost.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines made from premium materials and those that meet international quality standards will generally command higher prices. Buyers should ensure that the quality justifies the price increase.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a good reputation may charge more due to their reliability and service levels. However, they often provide better warranties and support.
-
Incoterms: The terms of delivery (Incoterms) can significantly affect the final price. Understanding who bears the shipping costs, insurance, and responsibilities can lead to more favorable pricing.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Computer Wood Cutter Purchases?
International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider several strategies to optimize costs when sourcing computer wood cutters.
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially if you are a repeat customer or are purchasing in bulk. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or improved terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency Analysis: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also operational costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A more expensive machine may offer better performance and lower operating costs in the long run.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and market conditions. For instance, economic fluctuations can influence costs, so staying informed can help in negotiating better deals.
-
Supplier Evaluation: Choose suppliers who offer comprehensive support, including training and after-sales service. This not only impacts productivity but can also reduce long-term costs.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in various sources are indicative and may vary based on factors such as specifications, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Always conduct thorough research and seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing computer wood cutter With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternative Solutions to Computer Wood Cutters
In the realm of woodworking and manufacturing, efficiency and precision are paramount. While computer wood cutters, particularly CNC routers, have revolutionized the industry, various alternatives exist that can also meet diverse business needs. By evaluating these alternatives, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Computer Wood Cutter | Laser Cutter | Manual Woodworking Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in complex designs | Exceptional detail for intricate cuts | Variable precision, heavily skill-dependent |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | High initial cost, but low material waste | Low initial cost, but high labor cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires technical knowledge and training | Requires operator training and safety measures | Minimal setup, but requires skilled labor |
| Maintenance | Regular software and hardware upkeep | Regular lens cleaning and maintenance | Minimal maintenance, but tool replacement needed |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale production with complex designs | Fine detailing and engraving on various materials | Custom, artisanal projects with a personal touch |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Cutters?
Laser cutters are increasingly popular in woodworking for their ability to produce highly detailed designs and clean edges. They excel in applications requiring intricate cuts, making them ideal for custom signage and decorative items. However, they come with a higher initial investment and operational costs, particularly due to their energy consumption and maintenance needs. Additionally, laser cutters can only work with materials that can withstand high temperatures, limiting their versatility compared to CNC routers.
How Do Manual Woodworking Tools Compare?
Manual woodworking tools, such as saws, chisels, and hand planes, offer a low-cost entry into woodworking, making them accessible for small-scale operations or hobbyists. They require minimal investment and maintenance, allowing artisans to create bespoke pieces with a personal touch. However, the reliance on human skill can lead to inconsistencies in precision and quality, especially for larger production runs. Additionally, manual methods can be labor-intensive, which might not be feasible for businesses aiming for higher efficiency.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Woodworking Solution for Your Business
When selecting the right woodworking solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and production goals. Computer wood cutters offer unmatched precision and efficiency for large-scale projects, while laser cutters excel in detailed work but come with higher costs. Alternatively, manual woodworking tools provide a cost-effective solution for artisanal craftsmanship but may lack the consistency required for larger productions. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of each alternative, businesses can align their choice with their strategic objectives, ensuring they invest in the most suitable technology for their woodworking operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for computer wood cutter
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Computer Wood Cutter?
When evaluating computer wood cutters, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Axis Configuration
The number of axes (typically 3, 4, or 5) indicates the machine’s capability for complex cuts. A 3-axis router can perform basic cutting and engraving, while 4-axis and 5-axis machines offer advanced capabilities for intricate designs and 3D modeling. For businesses aiming for precision and versatility in woodworking, investing in a multi-axis machine can significantly enhance productivity and creative possibilities. -
Working Area Dimensions
The size of the working area directly impacts the scale of projects that can be undertaken. Common dimensions include 4’x8’ or 5’x10’, which are suitable for large sheets of plywood or multiple smaller projects. For B2B buyers, selecting a machine with the right working area is critical to ensure it meets production needs without requiring frequent material changes. -
Spindle Power
Spindle power, measured in kilowatts (KW), affects the cutting speed and efficiency of the machine. A higher spindle power allows for faster cutting of denser materials, which can lead to increased throughput and reduced operational costs. Businesses should assess their material requirements to choose a spindle that aligns with their production goals. -
Material Compatibility
Understanding the types of materials a CNC wood router can handle is vital. Many machines can cut not only wood but also composites, plastics, and even metals. This versatility allows businesses to diversify their offerings and cater to various market demands, making it a key specification to consider. -
Precision and Tolerance
Precision refers to the machine’s ability to produce consistent, accurate cuts, often measured in millimeters. Tolerance indicates the acceptable deviation from a specified measurement. High precision and tight tolerances are essential for ensuring quality in finished products, especially in industries like furniture manufacturing and cabinetry where detail is paramount.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Computer Wood Cutters?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations in the B2B sector. Here are some key terms to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers who want to ensure they are sourcing high-quality components and equipment for their production processes. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is an important consideration for businesses to evaluate their purchasing strategies and cash flow management, as higher MOQs may require larger upfront investments. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and availability for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ can help compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they make cost-effective purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international trade, as they clarify the costs and risks associated with shipping and logistics, helping businesses avoid unexpected expenses. -
Lead Time
This refers to the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the product. For businesses, understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and managing inventory effectively. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the technology that automates the control of machining tools via a computer. This term is fundamental in the industry, as it represents the core technology behind computer wood cutters, emphasizing the importance of precision and automation in modern woodworking.
By comprehending these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of purchasing computer wood cutters more effectively, ensuring they select the right equipment for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the computer wood cutter Sector
What are the Global Drivers and Key Trends in the Computer Wood Cutter Market?
The computer wood cutter market is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for precision and efficiency in woodworking processes is a primary catalyst. Businesses are adopting CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology to streamline operations, reduce waste, and enhance product quality. As industries such as furniture manufacturing, cabinetry, and sign-making expand, the need for advanced wood-cutting solutions becomes paramount.
Emerging trends also highlight a shift towards automation and smart technology integration. The rise of Industry 4.0 and IoT (Internet of Things) has led to the development of smarter CNC machines capable of real-time monitoring and analytics. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in such technologies can enhance productivity and provide a competitive edge. Additionally, manufacturers are increasingly offering customization options, allowing businesses to tailor machines to specific operational needs.
Market dynamics are influenced by regional factors as well. In emerging markets, the availability of affordable CNC machines is making technology more accessible to small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Conversely, in mature markets, there is a growing emphasis on high-end machines with advanced features like multi-axis capabilities and automatic tool changers, appealing to professional woodworkers and large-scale operations.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Computer Wood Cutter Sector?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the sourcing of computer wood cutters, as environmental concerns gain traction globally. The wood industry is inherently tied to forestry practices, and the environmental impact of sourcing materials can significantly affect a company’s reputation and operational viability. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using certified wood from responsibly managed forests.
Ethical sourcing is not just about environmental impact; it also encompasses fair labor practices and transparency in supply chains. Certifications like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC) are becoming essential criteria for B2B buyers. These certifications assure buyers that the wood used in their CNC machines is sourced sustainably and that the production processes adhere to ethical labor practices.
Moreover, as consumers become more environmentally conscious, businesses that prioritize sustainability in their operations can leverage this as a unique selling proposition. Incorporating ‘green’ materials and technologies into the production of computer wood cutters can enhance brand loyalty and open new market opportunities.
What is the Evolution and Historical Context of Computer Wood Cutters?
The evolution of computer wood cutters can be traced back to the advent of CNC technology in the late 20th century. Initially, CNC machines were primarily used in industrial settings for mass production, but their application has expanded significantly. As technology has advanced, CNC wood cutters have become more sophisticated, offering multi-axis capabilities that allow for intricate designs and cuts.
In the early 2000s, the introduction of more user-friendly interfaces and software made CNC technology accessible to a broader audience, including hobbyists and small businesses. Today, the market features a diverse range of products from entry-level models to high-end industrial machines, catering to various skill levels and operational needs. This evolution has not only transformed woodworking practices but has also paved the way for innovative applications in design, prototyping, and custom furniture manufacturing, making computer wood cutters indispensable in the modern woodworking landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of computer wood cutter
-
How do I choose the right computer wood cutter for my business needs?
Selecting the right computer wood cutter involves assessing your specific woodworking applications, production volume, and budget. Determine whether you need a 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis machine based on the complexity of the projects you plan to undertake. Additionally, consider the machine’s table size, power, and compatibility with software. Research different models and read reviews from other businesses in your industry to find a machine that aligns with your operational goals. -
What is the best CNC wood router for small to medium-scale production?
For small to medium-scale production, the 4×8 CNC router is often considered the best option. It provides a balance of size and functionality, allowing you to tackle various projects, from furniture making to sign crafting. Look for models with an automatic tool changer for efficiency and versatility. Additionally, ensure that the machine has a robust customer support system and training resources, which can be invaluable for businesses new to CNC technology. -
How can I verify the credibility of a computer wood cutter supplier?
To verify a supplier’s credibility, check for industry certifications, customer testimonials, and case studies. Request references from previous clients and investigate their reputation within your industry. Additionally, assess their after-sales support, warranty policies, and availability of spare parts. Attending trade shows or exhibitions can also provide insights into their standing in the market and allow you to evaluate their machines firsthand. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC wood routers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC wood routers can vary significantly between suppliers. Some manufacturers may have an MOQ of one unit, especially for standard models, while others may require larger orders to accommodate customizations or special features. Always discuss your needs with the supplier to understand their MOQ policies, as negotiating terms may be possible depending on your business relationship and order size. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a CNC wood cutter internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the country of origin. Commonly, suppliers may request a deposit (typically 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due before shipping or upon delivery. Some may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods (e.g., bank transfer, letter of credit) and ensure they are secure and protect both parties in the transaction. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my CNC wood cutter?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications for the CNC wood cutter before purchase. Many reputable suppliers will conduct factory audits and quality control checks throughout the manufacturing process. Ask for a demonstration of the machine’s capabilities and a sample of its output. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and after-sales support, which can be indicative of the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC wood cutters?
When importing CNC wood cutters, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties specific to your country. Ensure that the supplier provides appropriate documentation for customs clearance. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping and duties, to understand the financial implications. Partnering with a freight forwarder can help streamline the logistics process and ensure that your equipment arrives safely and on time. -
Are there customization options available for CNC wood routers?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for CNC wood routers, allowing you to tailor the machine to your specific needs. Customizations can include modifications to the spindle, additional tool holders, software packages, or unique table sizes. When discussing your requirements with suppliers, be clear about your desired features and any specific applications you plan to pursue. This will help ensure that the machine meets your operational expectations and enhances productivity.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Computer Wood Cutter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Woodcraft – CNC Machines
Domain: woodcraft.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Woodcraft – CNC Machines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Wattsan – CNC Router Machines
Domain: wattsan.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: CNC Router Machines:
– Work Area Sizes: 400 x 400 mm, 900 x 600 mm, 1300 x 1300 mm, 1300 x 2500 mm, 1600 x 1600 mm, 2000 x 3000 mm, 2000 x 4000 mm
– Materials: Plywood, plexiglass, soft metals, aluminum, foam rubber, wood, etc.
– Applications: Doors, frames, handles, staircases, furniture, machinery parts, souvenirs, toys, advertisement elements, decor, organizers, gaskets, mats.
Specific Models:…
3. EagleTec – ET-1500HW CNC Wood Cutting Machine
Domain: eagletec-cnc.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: This company, EagleTec – ET-1500HW CNC Wood Cutting Machine, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Creality – Falcon2 Laser Engraver & Cutter
Domain: walmart.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Creality – Falcon2 Laser Engraver & Cutter, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Omni CNC – CNC Wood Router
Domain: omni-cnc.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: CNC wood router is a computer numerically controlled machine that cuts wood in various shapes and sizes without human interference. It operates on the Cartesian system (X, Y, Z) for 3D motion and features cutting, routing, carving, drilling, grinding, and etching capabilities. Suitable for woodworking projects like cabinet making, furniture making, and wooden toys, it serves multiple industries in…
6. All3DP – CNC Wood Machines Guide
Domain: all3dp.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: This company, All3DP – CNC Wood Machines Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for computer wood cutter
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Computer Wood Cutting?
In the rapidly evolving market of computer wood cutters, strategic sourcing remains a critical component for maximizing operational efficiency and ensuring a competitive edge. By investing in high-quality CNC wood routers tailored to specific business needs—whether for small-scale artisanal projects or large-scale industrial applications—buyers can significantly enhance productivity and output quality. Understanding machine specifications, user-friendliness, and the availability of support services can aid in making informed purchasing decisions that align with business goals.
How Can B2B Buyers Prepare for Future Opportunities in Woodworking?
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe expand, the demand for innovative woodworking solutions will only grow. Buyers should focus on establishing strong supplier relationships and exploring customization options that cater to local market preferences. Additionally, embracing new technologies, such as automated tool changers and advanced software, will be essential for staying ahead in this competitive landscape.
What Is the Next Step for International B2B Buyers?
We encourage you to evaluate your current woodworking operations and consider how investing in a computer wood cutter can streamline processes and enhance your product offerings. Engage with suppliers to explore the latest models and technologies that meet your specific needs. By doing so, you position your business for sustained growth and success in the dynamic world of woodworking.