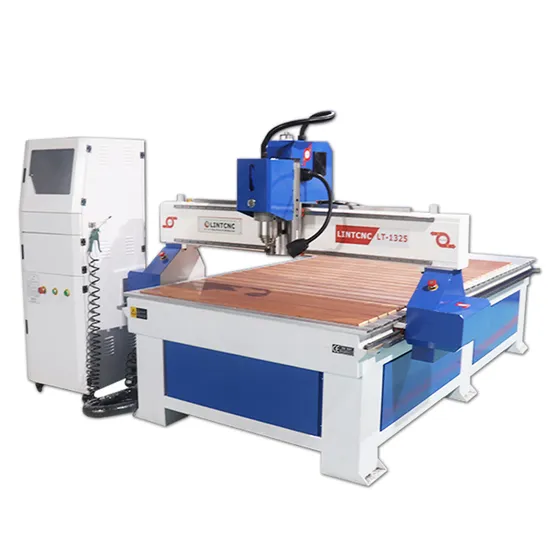
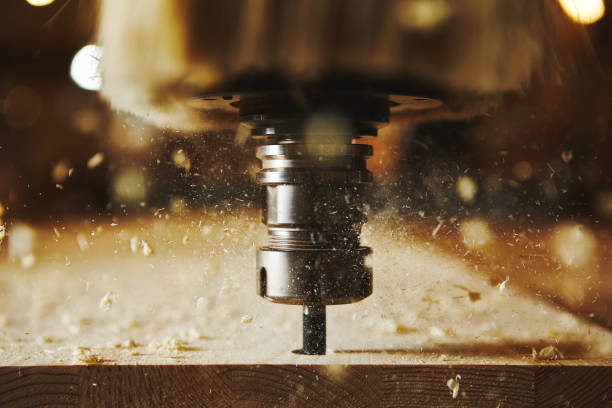
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for computer controlled router
Navigating the global market for computer-controlled routers can be daunting, especially for B2B buyers who seek to balance quality, functionality, and cost. With an increasing demand for precision machining across various industries, understanding the nuances of sourcing the right CNC router is essential for optimizing production processes. This guide is designed to demystify the complexities surrounding computer-controlled routers, covering essential topics such as types of machines available, their applications in diverse sectors, and how to effectively vet suppliers.
As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Vietnam and Saudi Arabia) expand their operations, they face unique challenges in identifying reliable suppliers and making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive resource empowers international buyers by providing actionable insights into the specifications that matter most, from spindle power and working area to software compatibility and after-sales support.
Moreover, we delve into cost considerations, helping you understand the price ranges associated with various router models, ensuring you get the best value for your investment. By equipping you with the knowledge needed to navigate the global landscape of computer-controlled routers, this guide aims to enhance your purchasing strategy and ultimately drive your business success.
Understanding computer controlled router Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hobbyist CNC Routers | Compact size, user-friendly, lower power (typically < 2kW) | Small-scale woodworking, craft projects | Pros: Affordable, easy to use; Cons: Limited material capacity and speed. |
| Professional CNC Routers | Larger work area, higher spindle power (2.2kW or more), advanced software options | Furniture making, signage, intricate designs | Pros: Precision and versatility; Cons: Higher investment required. |
| Commercial CNC Routers | Heavy-duty construction, large format capabilities, high-speed performance | Mass production, industrial applications | Pros: Designed for high volume; Cons: Requires significant space and investment. |
| Laser-Cutting CNC Routers | Integrated laser capabilities, multi-functional for cutting and engraving | Prototyping, intricate designs, signage | Pros: High precision, versatile; Cons: Higher maintenance costs. |
| Desktop CNC Routers | Small footprint, typically under 3ft x 3ft, user-friendly software | Prototyping, small batch production | Pros: Space-efficient, good for small businesses; Cons: Limited material handling capabilities. |
What are the Characteristics of Hobbyist CNC Routers?
Hobbyist CNC routers are ideal for individuals or small businesses venturing into CNC machining. Typically compact and easy to operate, these machines are designed for low-power use, often under 2kW. They are perfect for small-scale woodworking and craft projects, allowing users with little to no prior experience to create intricate designs. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the machine’s ease of use and software compatibility, as well as the range of materials it can handle.
How Do Professional CNC Routers Stand Out?
Professional CNC routers offer larger work areas and higher spindle power, usually around 2.2kW or more, making them suitable for more demanding applications like furniture making and signage. These machines come equipped with advanced software options that enhance design capabilities and precision. For B2B buyers, investing in a professional CNC router means ensuring robust performance and versatility, but it also requires a higher initial investment and ongoing operational costs.
What Makes Commercial CNC Routers Suitable for Industrial Use?
Commercial CNC routers are built for heavy-duty applications, featuring large format capabilities and high-speed performance. They are designed to handle mass production and industrial applications, making them essential for businesses looking to scale operations. While they offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency and output, potential buyers must consider the required space and capital investment, as these machines can be substantial in size and cost.
Why Choose Laser-Cutting CNC Routers?
Laser-cutting CNC routers integrate laser capabilities, allowing for both cutting and engraving functions. This versatility makes them valuable for prototyping, intricate designs, and signage production. The precision of laser cutting can significantly enhance product quality, but buyers should be mindful of the higher maintenance costs associated with these advanced machines. Additionally, understanding the specific materials that can be processed is crucial for maximizing their utility.
What are the Benefits of Desktop CNC Routers?
Desktop CNC routers are compact machines that fit well in small workspaces, making them ideal for startups and small businesses focused on prototyping or small batch production. With user-friendly software and a manageable size, these routers are accessible for beginners. However, buyers should be aware of their limited material handling capabilities and ensure that the machine aligns with their production needs before making a purchase.
Key Industrial Applications of computer controlled router
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Computer Controlled Router | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Woodworking | Custom furniture production | High precision and repeatability in design | Ensure machine compatibility with various wood types |
| Signage | Manufacturing of custom signs | Quick turnaround times and cost-effectiveness | Look for routers with large working areas |
| Aerospace | Component fabrication for aircraft | Exceptional accuracy and compliance with standards | Consider advanced software integration for design |
| Automotive | Production of prototypes and parts | Increased efficiency in design iterations | Evaluate machine speed and material versatility |
| Arts and Crafts | Artistic engraving and decorative items | Ability to create intricate designs with ease | Check for customization options and support services |
How is Computer Controlled Router Used in Woodworking?
In the woodworking industry, computer-controlled routers are employed for custom furniture production, enabling artisans to create intricate designs with high precision. These machines automate the cutting, carving, and engraving processes, significantly reducing manual labor while enhancing repeatability. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing routers that can handle various wood types and thicknesses is crucial. Additionally, compatibility with design software can streamline the workflow, allowing businesses to quickly adapt to market demands.
What Role Do Computer Controlled Routers Play in Signage Manufacturing?
In signage manufacturing, computer-controlled routers facilitate the production of custom signs with complex shapes and designs. The ability to cut and engrave materials like wood, plastic, and metal quickly allows businesses to offer rapid turnaround times, which is essential in competitive markets. B2B buyers, especially from the Middle East and Europe, should prioritize sourcing routers with larger working areas to accommodate various sign sizes. Furthermore, reliable customer support and training resources can enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
How Are Computer Controlled Routers Utilized in Aerospace Component Fabrication?
Aerospace companies leverage computer-controlled routers for the fabrication of components that require exceptional accuracy and adherence to strict regulatory standards. These machines can cut intricate designs in lightweight materials, ensuring that parts meet the necessary specifications for safety and performance. Buyers in this sector must consider sourcing routers with advanced software capabilities that integrate seamlessly with CAD systems. Additionally, the machinery should be capable of handling specialized materials used in aerospace applications.
In What Ways Do Computer Controlled Routers Benefit the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry utilizes computer-controlled routers for the production of prototypes and parts, significantly enhancing design efficiency. These routers allow for rapid iterations and modifications, which are critical in the fast-paced automotive market. For B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Saudi Arabia and Europe, it is essential to evaluate the machine’s speed and versatility in handling different materials. Investing in routers that offer advanced features, such as multi-axis capabilities, can further improve production outcomes.
How Do Computer Controlled Routers Enhance Artistic and Craft Production?
In the arts and crafts sector, computer-controlled routers are invaluable for creating decorative items and intricate engravings. Artists and craftspeople can use these machines to bring their creative visions to life with high precision and minimal effort. International buyers should focus on sourcing routers that offer customization options, such as varying spindle speeds and engraving capabilities, to cater to diverse artistic styles. Additionally, robust customer support is vital for troubleshooting and maximizing the router’s potential in artistic applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘computer controlled router’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Software Integration for CNC Routers
The Problem: Many businesses transitioning to computer-controlled routers face significant challenges with software integration. Users often find themselves overwhelmed by the complexity of different design and control software options. This is particularly daunting for companies in regions like Africa or South America, where access to comprehensive training resources may be limited. The fear of investing in a machine that may not seamlessly integrate with existing systems can lead to hesitation in purchasing decisions.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize CNC routers that come with comprehensive software packages tailored for their specific needs. When evaluating potential purchases, inquire about the availability of user-friendly design software that includes tutorials and customer support. It’s advisable to choose routers that offer compatibility with popular design software, such as Vectric or Fusion 360, which are widely recognized for their robust features and ease of use. Additionally, consider reaching out to suppliers for demonstrations or trial versions of the software before committing to a purchase. This proactive approach will ensure that the integration process is smooth and that the team can quickly get up to speed.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Reliable Maintenance and Support for CNC Machines
The Problem: A common concern among B2B buyers is the reliability of after-sales support and maintenance services for CNC routers. In regions with emerging markets, such as parts of the Middle East and South America, access to skilled technicians can be limited. This can lead to prolonged downtimes in case of machine failure, significantly impacting production schedules and profitability.
The Solution: When selecting a computer-controlled router, it’s essential to thoroughly vet the manufacturer’s service capabilities. Look for suppliers that offer comprehensive maintenance packages, including regular check-ups and emergency repair services. Establish a relationship with local distributors who can provide on-site support and training, ensuring that your team can perform basic troubleshooting and maintenance. Additionally, investing in machines that come with extensive warranties and readily available spare parts will provide peace of mind and minimize operational disruptions. Consider setting up a service-level agreement (SLA) with the supplier to guarantee timely responses to maintenance requests.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Material Versatility Challenges with CNC Routers
The Problem: Businesses often struggle with the versatility of materials that can be processed with a computer-controlled router. This challenge is particularly prevalent in diverse markets where customers may demand a variety of products made from different materials, such as wood, plastic, and metal. Buyers may fear that a single router will not meet all their production needs, leading to the potential for missed sales opportunities.
The Solution: To address this pain point, companies should invest in CNC routers that are specifically designed for multi-material capabilities. When evaluating options, look for machines with adjustable spindle speeds and compatible tooling that can handle a variety of materials efficiently. It’s also beneficial to select routers that provide flexibility in terms of setup and configuration, allowing for quick changes between material types. Additionally, training your team on the nuances of working with different materials can significantly enhance productivity. Consider sourcing materials that are commonly used in your target markets to test the machine’s capabilities before full-scale production begins. This approach will not only ensure that the router meets current demands but also position the business to capitalize on future opportunities.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for computer controlled router
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Computer Controlled Routers?
When selecting materials for computer-controlled routers, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with various applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in CNC routers: wood, aluminum, MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard), and plastics.
Wood: A Traditional Choice for CNC Routers
Key Properties: Wood is a natural material known for its workability and aesthetic appeal. It has a variable density, which can affect its machining characteristics. The temperature and pressure ratings depend on the type of wood, but generally, it exhibits good dimensional stability when properly dried.
Pros & Cons: Wood is relatively inexpensive and readily available, making it a popular choice for various applications. However, it can be prone to warping and splitting, especially under moisture or temperature changes. Additionally, different wood types may require specific tooling and machining strategies.
Impact on Application: Wood is ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and decorative items. Its compatibility with various finishes enhances its appeal in consumer markets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding sustainable sourcing and treatment of wood products. Standards like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) certification may be important in regions like Europe.
Aluminum: The Durable and Lightweight Option
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, with excellent corrosion resistance. It has a high thermal conductivity and can withstand moderate temperature variations, making it suitable for various machining environments.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum is durable and can be machined to high tolerances, making it suitable for precision applications. However, it is more expensive than wood and may require specialized tooling to achieve the desired finish.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications where strength-to-weight ratios are critical. Its compatibility with anodizing and other surface treatments adds to its versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of international standards such as ASTM for material specifications. Additionally, sourcing aluminum from reputable suppliers ensures compliance with quality standards.
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard): The Versatile Composite
Key Properties: MDF is made from wood fibers bonded with resin under heat and pressure, resulting in a uniform density and smooth surface. It has good machinability and is less prone to warping compared to solid wood.
Pros & Cons: MDF is cost-effective and provides a smooth finish, making it ideal for intricate designs. However, it is less durable than solid wood and can be susceptible to moisture damage if not properly sealed.
Impact on Application: MDF is widely used in cabinetry, moldings, and decorative applications due to its ease of machining and finishing capabilities.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding formaldehyde emissions is crucial, especially in regions like Europe, where standards are stringent.
Plastics: The Modern Material for Diverse Applications
Key Properties: Plastics, such as acrylic and polycarbonate, offer excellent machinability and a wide range of properties, including transparency, flexibility, and chemical resistance. They can withstand moderate temperatures but may deform under excessive heat.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are lightweight and available in various colors and finishes, making them suitable for creative applications. However, they can be more expensive than wood and may require specific machining techniques to avoid melting or chipping.
Impact on Application: Plastics are used in signage, prototypes, and consumer products where aesthetics and functionality are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific plastic grades and their compliance with international standards such as ISO for quality assurance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Computer Controlled Routers
| Material | Typical Use Case for computer controlled router | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Furniture and cabinetry | Readily available and inexpensive | Prone to warping and splitting | Low |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive applications | Lightweight and durable | Higher cost and requires specialized tooling | High |
| MDF | Cabinetry and decorative applications | Smooth finish and easy to machine | Susceptible to moisture damage | Medium |
| Plastics | Signage and prototypes | Lightweight and versatile | Can deform under high temperatures | Medium |
This guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions regarding material selection for computer-controlled routers.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for computer controlled router
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Computer Controlled Routers?
The manufacturing of computer-controlled routers involves a series of intricate processes that ensure high-quality output tailored to the specific needs of B2B buyers. Understanding these processes is vital for international buyers seeking reliable and durable machinery.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used?
The first stage of manufacturing CNC routers is material preparation, where manufacturers select high-grade materials such as aluminum, steel, and composite materials for structural components. The choice of materials directly affects the machine’s durability, weight, and performance. For instance, aluminum is often favored for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, while steel is used for its strength and rigidity.
Cutting and machining processes are employed to shape these materials into the required components, such as frames, bases, and housings. Advanced techniques like laser cutting and CNC machining ensure precision and reduce waste, which is crucial for maintaining cost-effectiveness in production.
How Is the Forming Process Executed?
Once materials are prepared, the next phase is forming, where components are shaped into their final forms. This may include processes like extrusion, forging, and machining, depending on the component’s requirements. For example, CNC machining is employed to create intricate designs on the router’s body, ensuring that all parts fit together seamlessly.
The use of automated machinery during this stage enhances precision and consistency, which are essential for high-quality performance. Manufacturers may also implement techniques like anodizing or powder coating to enhance the surface finish of aluminum components, providing additional protection against wear and corrosion.
What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
Assembly is a critical stage where all the pre-manufactured components come together to create a functional CNC router. Skilled technicians or automated systems carefully fit parts such as the spindle, motors, control systems, and frame. This stage often includes integrating electronic components, such as the CNC controller and software, which are crucial for the router’s operation.
Quality checks during assembly are vital. Manufacturers may employ jigs and fixtures to ensure that components are aligned correctly. This minimizes the risk of operational issues and enhances the overall reliability of the machine.
How Is Finishing Performed to Ensure Quality?
The finishing process includes several steps aimed at enhancing both the aesthetic and functional qualities of the CNC router. This may involve polishing, painting, or applying protective coatings. The goal is to ensure that the router is not only visually appealing but also resistant to environmental factors that could affect its performance.
Additionally, final inspections are conducted to ensure that each machine meets the required specifications before it is shipped to customers. This is a vital step in maintaining the brand’s reputation and ensuring customer satisfaction.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for CNC Router Manufacturers?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process that ensures the finished product meets international standards and customer expectations. For international B2B buyers, understanding these practices is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers of CNC routers typically adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with this standard indicates that the manufacturer has established processes to ensure consistent quality in their products and services.
In addition to ISO standards, products may also need to meet specific certifications relevant to the industry, such as CE marking for compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For markets in the Middle East, buyers should look for compliance with GSO (Gulf Standards Organization) standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Effective quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This involves ongoing inspections during the manufacturing stages, ensuring that any deviations from quality standards are addressed immediately.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the completed CNC router to verify that it meets all specifications before it is shipped.
Each of these checkpoints plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process and ensuring that the final product is reliable and durable.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are some effective strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing facility’s adherence to quality standards and practices firsthand.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for documentation related to quality control processes, including inspection reports and compliance certificates.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the product’s quality and compliance with standards.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
When sourcing CNC routers, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of potential nuances in quality control and certification. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations, which can impact the importation process.
Buyers should ensure that the products they intend to import comply with local regulations and standards. Engaging legal counsel or consulting with local authorities can provide clarity on these requirements and facilitate a smoother procurement process.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in CNC Router Procurement
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for CNC routers is crucial for B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with these elements, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations. This knowledge not only aids in selecting reliable suppliers but also enhances overall procurement strategies in a competitive global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘computer controlled router’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring a computer-controlled router, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business needs. By following this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process, minimize risks, and select the right machine and supplier for your operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline your technical requirements before initiating the procurement process. Consider factors such as the size of the router, material compatibility, spindle power, and the intended applications (e.g., woodworking, metalworking). This step is crucial because it helps narrow down options that meet your specific operational needs.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay updated on the latest advancements in CNC router technology. Understanding current trends can guide your selection process and ensure you choose a machine that incorporates modern features like automation, enhanced speed, and improved precision. Look for innovations that can increase productivity and reduce operational costs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Assess their reputation for quality and customer service by reading reviews and seeking testimonials from existing customers. This evaluation is vital to ensure you partner with a reliable supplier.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications and comply with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can indicate a commitment to quality management. Compliance with safety and environmental regulations is also essential to avoid potential legal issues and ensure the longevity of your equipment.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Samples
Whenever possible, request demonstrations of the CNC routers you are considering. This allows you to see the machine in action and assess its performance, ease of use, and capabilities firsthand. Additionally, inquire about sample materials to test the machine’s functionality in your production environment.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Training
Inquire about the after-sales support provided by the supplier, including warranty terms, maintenance services, and availability of spare parts. Training on the operation and maintenance of the router is also crucial for maximizing your investment. A supplier that offers comprehensive support can significantly enhance your operational efficiency.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Finally, compare pricing among different suppliers, but also consider the total cost of ownership (TCO). TCO includes initial purchase price, installation costs, maintenance expenses, and energy consumption over time. A slightly higher upfront cost may be justified by lower operating costs and better performance in the long run.
By following these steps, you can effectively navigate the sourcing process for a computer-controlled router, ensuring a successful investment for your business.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for computer controlled router Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Computer Controlled Routers?
When sourcing computer-controlled routers, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary components of the cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
Materials typically encompass the cost of raw components such as aluminum frames, motors, spindles, and electronics. High-quality materials can significantly impact the durability and precision of the router, thus affecting the overall price.
Labor costs will vary depending on the manufacturing location and the complexity of assembly. Regions with skilled labor may have higher wages but can offer superior craftsmanship, which is crucial for high-precision equipment.
Manufacturing overhead includes indirect costs like utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. This varies by supplier and can affect pricing competitiveness.
Tooling costs refer to the specialized equipment required to manufacture CNC routers. Suppliers with advanced technology may have higher upfront costs but can deliver better precision and consistency.
Quality Control measures ensure the routers meet specified standards. Investing in robust QC processes can lead to higher initial costs but can reduce long-term issues and warranty claims.
Logistics costs involve shipping and handling, which can be substantial, especially for international orders. Understanding the Incoterms used in the transaction will help buyers anticipate these costs.
Margin is the profit that suppliers build into their pricing, which can vary significantly based on brand reputation, market positioning, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Computer Controlled Routers?
Several factors influence the pricing of computer-controlled routers. Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) are crucial; larger orders often attract discounts, making it essential to assess your needs against your budget.
Specifications and customization can also drive up costs. Custom features such as specific spindle types, larger working areas, or advanced software integration may require additional investments.
Material quality and certifications play a significant role in pricing. Routers built with premium materials and recognized certifications (e.g., CE, ISO) often command higher prices due to their reliability and performance.
Supplier factors such as reputation, location, and support services can impact costs. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their brand, but they often provide better after-sales support and warranty services.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency When Sourcing CNC Routers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency. Negotiation is key; understanding the supplier’s cost structure can empower buyers to negotiate better terms, especially for bulk orders.
Calculating the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is vital. This includes not just the purchase price but also operating costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A lower initial price might lead to higher long-term costs if the router is less reliable or requires frequent repairs.
Buyers should be aware of pricing nuances in international sourcing, such as tariffs, taxes, and currency fluctuations, which can significantly affect the final price. Engaging with suppliers who have experience in international trade can help navigate these complexities.
Lastly, considering Incoterms is crucial for understanding responsibilities for shipping costs, risks, and delivery. Choosing the right Incoterm can lead to substantial savings and a smoother procurement process.
Conclusion: Understanding Pricing Dynamics for Strategic Sourcing
While indicative prices for computer-controlled routers can range widely—from hobbyist models starting around $999 to advanced commercial units exceeding $8,499—buyers should focus on the broader cost structure and pricing influences. By leveraging this knowledge, international B2B buyers can make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing computer controlled router With Other Solutions
Understanding the Alternatives to Computer Controlled Routers
In the realm of manufacturing and woodworking, various technologies can achieve similar outcomes to those offered by computer-controlled routers (CNC routers). While CNC routers are celebrated for their precision and versatility in cutting and engraving materials, it’s essential to explore alternative solutions that can also meet diverse production needs. This analysis focuses on comparing CNC routers with laser cutting machines and traditional woodworking methods, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Computer Controlled Router | Laser Cutting Machine | Traditional Woodworking Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and speed; suitable for various materials | Exceptional detail and speed; ideal for thin materials | Variable; dependent on skill and tools |
| Cost | Moderate to high; starts around $2,799 for entry-level models | Generally higher initial investment; machines can exceed $10,000 | Low to moderate; primarily tool costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires CAD/CAM software knowledge; setup can be complex | Easier setup; often comes with user-friendly software | Requires skilled labor; learning curve for traditional techniques |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular calibration and software updates needed | Lower; infrequent maintenance, mostly lens cleaning | High; requires consistent upkeep of tools and workspace |
| Best Use Case | Versatile applications, including furniture, signage, and prototypes | Best for intricate designs and materials like acrylic and paper | Ideal for artisanal work and custom craftsmanship |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Laser Cutting Machines
Laser cutting machines utilize focused light to cut materials with high precision. They excel in detailed engraving and can handle a variety of materials, including wood, acrylic, and metals. The key advantage of laser cutters is their ability to produce intricate designs quickly, making them ideal for projects requiring fine detail, such as signage and decorative items. However, the initial cost can be significantly higher compared to CNC routers, often exceeding $10,000 for quality machines. Additionally, while laser cutting is efficient for thin materials, it may not be suitable for thicker substrates.
Traditional Woodworking Methods
Traditional woodworking methods encompass hand tools and manual techniques for crafting wood products. This approach allows for a high degree of craftsmanship and customization, which can be appealing for artisanal businesses. The primary benefits of traditional methods include lower initial costs and the ability to create unique, one-of-a-kind pieces. However, the performance can be inconsistent and heavily reliant on the skill of the craftsman. Moreover, traditional woodworking often requires significant time and labor, which may not align with the fast-paced demands of modern production.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business
When selecting the most suitable solution for woodworking or manufacturing needs, B2B buyers must consider multiple factors, including performance, cost, and the specific applications they intend to pursue. Computer-controlled routers offer a balanced approach for various projects, combining precision with versatility. However, for businesses focused on intricate designs, laser cutting may be the better choice, despite the higher cost. Conversely, those who prioritize artisanal craftsmanship might find traditional woodworking methods more aligned with their values and budget. Ultimately, understanding the unique strengths and weaknesses of each option will empower buyers to make strategic decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for computer controlled router
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Computer Controlled Router?
When evaluating computer-controlled routers, understanding their technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Spindle Power
Spindle power, typically measured in kilowatts (KW) or horsepower (HP), indicates the machine’s cutting strength. A higher spindle power allows for the machining of denser materials and faster operation. For businesses that require precision and efficiency, like those in woodworking or metal fabrication, selecting a router with adequate spindle power is vital to meet production demands.
2. Working Area
The working area dimensions (length x width x height) define the maximum size of the materials that can be processed. A larger working area enables the handling of full sheets of material, which is crucial for commercial applications. Companies aiming to maximize productivity should opt for routers that accommodate their largest material sizes to avoid operational bottlenecks.
3. Speed and Feed Rate
Speed is often measured in inches per minute (IPM) and indicates how quickly the router can move across the material. Feed rate refers to the speed at which the material is fed into the cutter. A balance between speed and feed rate is essential for achieving optimal cutting quality and efficiency. Businesses must consider their specific application needs to ensure the chosen router can deliver the desired performance.
4. Material Compatibility
Different routers are designed to work with various materials, including wood, metal, plastic, and composites. Understanding the material compatibility of a router is crucial for ensuring it meets the specific needs of your production. Choosing a router that can handle multiple materials can provide flexibility and reduce the need for additional equipment.
5. Control System
The control system, whether it’s a proprietary or open-source solution, dictates how operators interact with the machine. A user-friendly interface can significantly reduce the learning curve, making it easier for staff to operate the machinery efficiently. Businesses should evaluate the control system’s compatibility with their existing software and workflow to ensure seamless integration.
6. Tolerance and Precision
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified measurement, while precision indicates the router’s ability to consistently reproduce that measurement. High tolerance levels are crucial for industries requiring tight specifications, such as aerospace or automotive manufacturing. Selecting a router with appropriate tolerance and precision levels is essential for maintaining product quality and minimizing waste.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Computer Controlled Routers?
Understanding industry jargon can facilitate smoother negotiations and clearer communications in B2B transactions. Here are several common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CNC routers, it can denote the manufacturer of the router components. Knowing the OEM can provide insights into the quality and reliability of the equipment.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly important for businesses looking to purchase CNC routers, as understanding MOQ can impact budgeting and inventory management. Companies should clarify MOQ with suppliers to avoid unexpected costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products. For B2B buyers, submitting an RFQ can help compare options and negotiate better deals. A well-structured RFQ can streamline procurement processes and ensure that all necessary specifications are addressed.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to clarify shipping costs, risk, and delivery responsibilities. Proper knowledge of Incoterms can prevent misunderstandings and disputes during the shipping process.
5. CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
CAD refers to software used for designing products, while CAM is used for manufacturing them. These technologies are integral to the operation of CNC routers, as they help streamline the design-to-production workflow. Familiarity with CAD/CAM can enhance a company’s efficiency and product development capabilities.
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the computer controlled router Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Computer Controlled Router Sector?
The computer-controlled router market is experiencing a dynamic shift fueled by several global drivers. The rise in automation and Industry 4.0 initiatives has increased the demand for precision engineering tools across various sectors, including woodworking, metalworking, and prototyping. This demand is particularly pronounced in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where local manufacturing capabilities are being enhanced through the adoption of advanced technologies.
In addition to automation, the growing trend towards customization in manufacturing is pushing businesses to seek CNC routers that offer flexibility and adaptability. International buyers are increasingly prioritizing machines that can handle a range of materials and are equipped with user-friendly software. Companies are also investing in hybrid models that combine CNC routing with laser engraving capabilities, thus expanding their service offerings without significant capital expenditure.
Furthermore, the ongoing digital transformation has led to a rise in the use of cloud-based software solutions for design and production management. This trend enables real-time collaboration and data analysis, which are essential for optimizing production processes. B2B buyers should be aware of these technological advancements to ensure they are selecting equipment that will remain relevant and efficient in the long term.
How Is Sustainability Reshaping Sourcing Practices in the Computer Controlled Router Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the sourcing of computer-controlled routers. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, and businesses are increasingly held accountable for their carbon footprints. As a result, buyers are looking for suppliers who adhere to ethical sourcing practices and can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
One significant aspect of this trend is the importance of sourcing materials that are environmentally friendly. Manufacturers are now offering routers made from sustainable materials and components that minimize waste during production. Additionally, many companies are pursuing certifications such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems, as a way to reassure buyers of their commitment to sustainable practices.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications into procurement strategies not only enhances brand reputation but also opens up new markets that prioritize sustainability. B2B buyers should actively seek suppliers who can provide documentation of sustainable practices and materials, ensuring that their investments align with their corporate social responsibility goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Computer Controlled Routers in B2B Markets?
The evolution of computer-controlled routers can be traced back to the early days of CNC technology in the 1950s and 1960s. Initially, these machines were primarily used in industrial settings for high-precision applications. Over the decades, advancements in computer technology and software have significantly transformed the capabilities of CNC routers, making them more accessible and versatile.
By the late 20th century, the introduction of user-friendly interfaces and affordable models led to a boom in the hobbyist and small business markets. Today, CNC routers are essential tools for a wide range of applications, from intricate woodworking to metal fabrication, catering to both large manufacturers and individual creators. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the advancements that have shaped the current landscape and guides them in making informed purchasing decisions that meet modern production needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of computer controlled router
-
1. How do I choose the right CNC router for my business needs?
Selecting the right CNC router involves assessing your specific application requirements, such as material type, size, and complexity of the projects you will undertake. Consider the working area dimensions, spindle power, and speed capabilities. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s compatibility with design software and ease of use, especially if your team has varying levels of CNC experience. Researching supplier reputations and customer reviews can also provide insights into reliability and performance. -
2. What are the key features to look for in a CNC router?
When evaluating CNC routers, prioritize features such as spindle power (measured in watts or horsepower), working area size, and precision (resolution and repeatability). Look for machines that offer versatility, such as the ability to handle multiple materials and include options for laser attachments or additional axes. User-friendly controls, robust construction for durability, and included software packages can significantly enhance productivity and ease of operation. -
3. What are the common payment terms for international CNC router purchases?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier and the buyer’s location. Common options include upfront payments, payment on delivery, or letters of credit for larger transactions. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring security for both parties. Confirm if the supplier accepts multiple currencies and payment methods, including wire transfers or online payment platforms, which can streamline the process. -
4. How can I ensure quality when sourcing CNC routers internationally?
To guarantee quality, vet potential suppliers by checking their certifications, such as ISO or CE, which indicate compliance with international standards. Request samples or references from previous clients to assess machine performance and customer service. Engaging in third-party inspections or audits prior to shipment can further ensure the machinery meets your specifications and quality expectations before it arrives. -
5. What is the typical lead time for CNC router delivery internationally?
Lead times can vary based on the supplier, model, and shipping logistics. Generally, expect anywhere from 4 to 12 weeks for manufacturing and delivery. Factors such as customization requests, shipping methods, and customs clearance can also impact delivery times. For more accurate timelines, communicate directly with the supplier regarding production schedules and shipping options. -
6. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC routers?
Many suppliers have MOQs depending on the type of CNC router and the associated costs. For standard models, MOQs can be as low as one unit; however, for customized machines or bulk orders, MOQs may be higher. Discussing your specific needs with the supplier can help determine if they can accommodate smaller orders or if there are benefits to larger purchases, such as discounts. -
7. What are the customs and import duties associated with buying CNC routers?
Import duties and customs regulations vary by country and depend on the router’s classification and value. It’s crucial to research the specific tariffs applicable in your region, as well as any necessary documentation required for importation. Engaging a customs broker can streamline the process and help avoid unexpected costs or delays. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary shipping documents to facilitate smooth customs clearance. -
8. How can I customize a CNC router to fit my specific operational needs?
Most manufacturers offer customization options, such as varying spindle types, additional axes, or specific software packages tailored to your application. When discussing customization, clearly outline your operational requirements and desired features. Collaborating closely with the supplier during the design phase can help ensure the final product meets your unique specifications and enhances your production capabilities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Computer Controlled Router Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SainSmart – Genmitsu CNC Router
Domain: sainsmart.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Genmitsu CNC Router, Affordable Beginner-Friendly | SainSmart
2. ShopSabre – IS-A & IS-M Series CNC Routers
Domain: shopsabre.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: IS-A Series CNC Router: Industrial and commercial use, auto unload for high efficiency nested based sheet processing, starting at $99,995.00. IS-M Series CNC Router: World’s fastest and most accurate CNC control, industrial and commercial use, dedicated high production, high accuracy, starting at $57,995.00. Industrial Series (IS): Tool grade CNC at a fraction of the price, industrial and commerci…
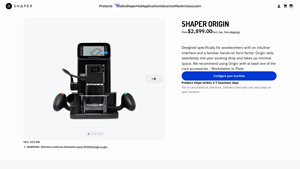
3. Shaper – Shaper Origin
Domain: shapertools.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Shaper Origin
SKU: SO2-NN
Price: From $2,899.00 (Excl. tax, free shipping)
Type: Handheld CNC Router
Weight: ~21 lbs (9.75 Kg)
Dimensions: 306 mm Height, 227 mm Depth, 339 mm Width
Motor: Brushed Motor Spindle (produced with Festool to Shaper specifications)
Touch Screen: Capacitive multi-touch full-color LCD
Connectivity: WiFi & USB (over the air software updates, USB port for offli…
4. Style CNC – Automatic Wood Routers
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Automatic CNC wood routers with 3, 4, or 5 axes for 2D, 2.5D, and 3D cutting, milling, carving, drilling, and grooving. Popular woodworking applications include cabinet making, sign making, furniture making, and home decorations. Available table sizes: 2ft x 3ft, 2ft x 4ft, 4ft x 4ft, 4ft x 6ft, 4ft x 8ft, 5ft x 10ft, and 6ft x 12ft. Models range from entry-level to high-end ATC series, with custo…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for computer controlled router
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of computer-controlled routers is essential for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. By carefully selecting suppliers that offer advanced technology, robust performance, and reliable customer support, companies can significantly improve their manufacturing capabilities. It is crucial for international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to consider not only the upfront costs but also the long-term value these machines bring to their operations.
Investing in high-quality CNC routers can lead to reduced production times, increased precision, and the ability to handle diverse materials, ultimately driving innovation and growth. As the demand for custom and intricate designs continues to rise, businesses that leverage advanced CNC technology will be better positioned to meet market needs and customer expectations.
Looking ahead, international buyers should stay informed about emerging trends and advancements in CNC technology. Embracing these innovations will not only enhance competitiveness but also open new avenues for expansion. Take the next step in your sourcing journey—explore the diverse options available and choose a CNC router that aligns with your business goals and vision for the future.