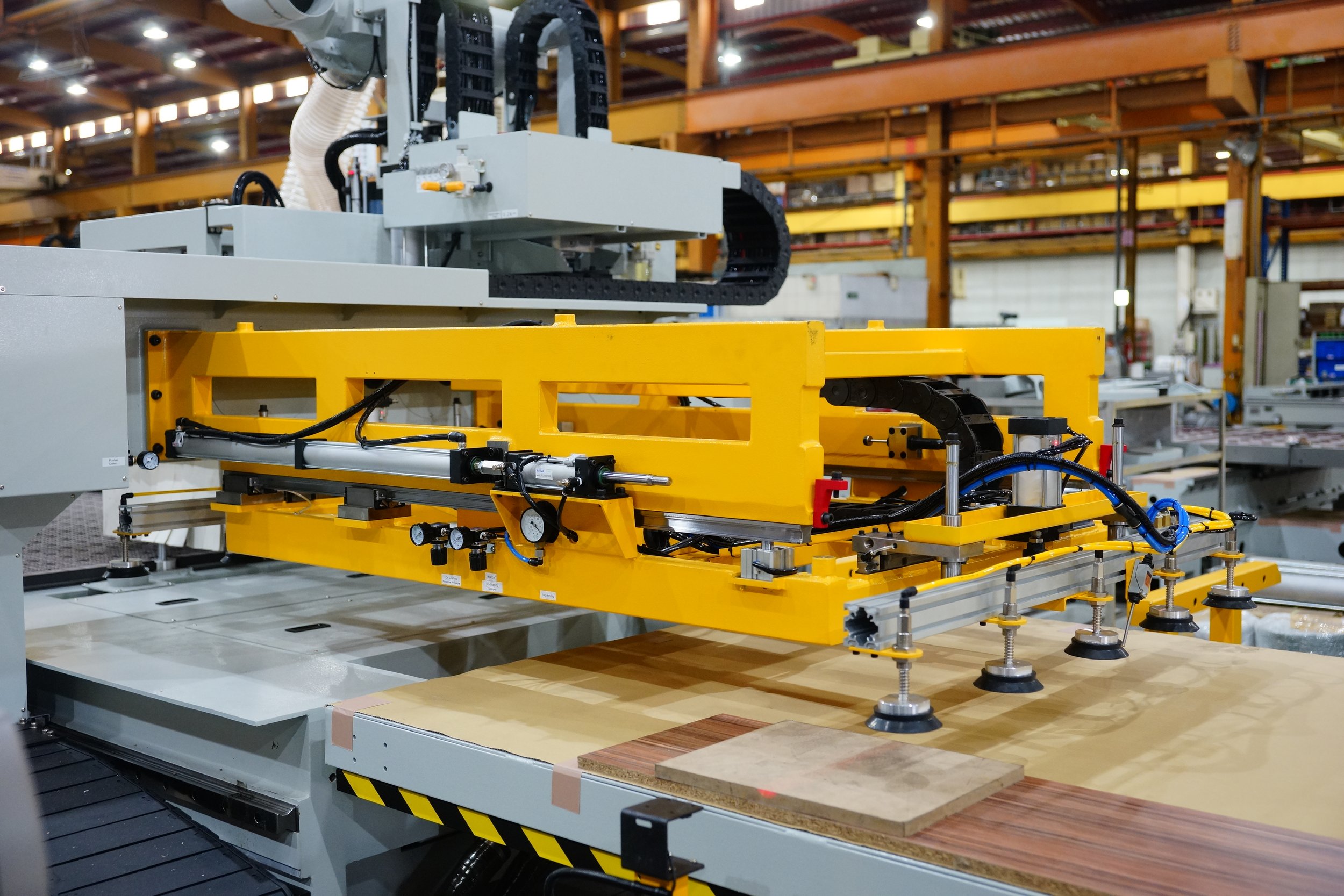
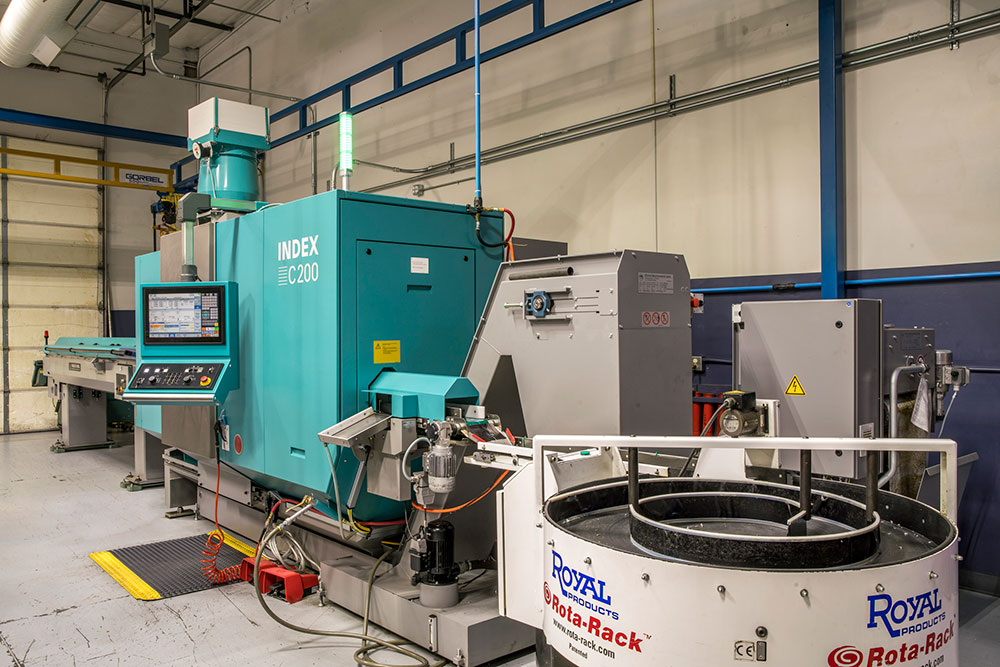
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for commercial cnc machine
The global market for commercial CNC machines presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers seeking the right equipment to enhance their manufacturing capabilities. Sourcing the ideal CNC machine involves understanding various factors, including types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations. With an array of options available, from high-precision CNC routers to robust lathes, navigating this landscape can be daunting, especially for businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Germany and Nigeria.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower B2B buyers by providing in-depth insights into the diverse range of CNC machines and their applications across various industries. It covers essential topics such as identifying reputable suppliers, assessing quality and performance standards, and understanding pricing structures to facilitate informed purchasing decisions. By equipping decision-makers with actionable knowledge, this guide not only simplifies the sourcing process but also enhances the potential for maximizing return on investment.
As you explore the content, you will gain valuable strategies for evaluating machine specifications, understanding technological advancements, and ultimately selecting the right CNC solution tailored to your operational needs. In a competitive global market, informed choices can lead to improved productivity, efficiency, and profitability for your business.
Understanding commercial cnc machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Router | Uses computer controls to guide cutting tools; versatile | Woodworking, sign making, aerospace | Pros: High precision, flexible materials; Cons: Initial cost can be high. |
| CNC Lathe | Rotates workpiece against stationary cutting tool | Metal fabrication, automotive parts | Pros: Exceptional accuracy for cylindrical shapes; Cons: Limited to round parts. |
| Vertical Machining Center | Vertical spindle orientation for machining; high rigidity | Aerospace, automotive, complex parts | Pros: Efficient for detailed work; Cons: Requires skilled operators. |
| CNC Plasma Cutter | Uses plasma to cut through metals; ideal for thick materials | Metal fabrication, construction | Pros: Fast cutting speed; Cons: Limited to conductive materials. |
| CNC Waterjet Cutter | Uses high-pressure water to cut; minimal heat distortion | Aerospace, architecture, automotive | Pros: Cuts a wide range of materials; Cons: Slower than plasma cutting. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of CNC Routers for B2B Buyers?
CNC routers are distinguished by their ability to handle various materials, including wood, plastics, and composites. They are widely utilized in woodworking, sign-making, and even aerospace applications due to their precision and versatility. For B2B buyers, the ability to customize designs and produce intricate cuts efficiently is a significant advantage. However, the initial investment can be considerable, and ongoing maintenance and training may be required to maximize operational efficiency.
How Do CNC Lathes Serve Specific Industry Needs?
CNC lathes excel in machining cylindrical parts with high precision. They are predominantly used in metal fabrication and automotive industries, where components require exact specifications. Buyers should consider the lathe’s capacity, tooling options, and software compatibility when purchasing. While CNC lathes offer exceptional accuracy, they are limited to round parts, which could restrict their utility in more diverse manufacturing settings.
What Advantages Do Vertical Machining Centers Offer for Complex Parts?
Vertical machining centers (VMCs) are designed for high precision and are ideal for producing complex geometries in various industries, including aerospace and automotive. With a vertical spindle orientation, VMCs can achieve detailed work efficiently. B2B buyers should evaluate the machine’s rigidity, tooling options, and software integration. Although VMCs can be more expensive and require skilled operators, their efficiency in handling intricate designs makes them a valuable investment.
Why Choose CNC Plasma Cutters for Metal Fabrication?
CNC plasma cutters are known for their rapid cutting capabilities and are primarily used in metal fabrication and construction. These machines utilize plasma to cut through metals, making them suitable for thick materials. B2B buyers benefit from the speed and efficiency of plasma cutters, but they should note that these machines are limited to conductive materials. The initial cost and operational requirements should also be factored into purchasing decisions.
What Makes CNC Waterjet Cutters Unique for Diverse Materials?
CNC waterjet cutters utilize high-pressure water to slice through materials, offering the unique advantage of minimal heat distortion. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, including aerospace and architecture. For B2B buyers, the versatility in cutting various materials, including metals, glass, and ceramics, is a significant benefit. However, waterjet cutters tend to operate at a slower pace compared to plasma cutters, which may affect production timelines.
Key Industrial Applications of commercial cnc machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of commercial cnc machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furniture Manufacturing | Custom furniture design and production | Enhances precision and reduces waste in material usage | Consider the machine’s size, tooling options, and software compatibility. |
| Aerospace | Component manufacturing for aircraft | Increases safety and compliance with stringent standards | Evaluate the machine’s ability to handle specialized materials and its precision capabilities. |
| Automotive | Prototyping and production of parts | Accelerates product development cycles and reduces costs | Look for machines with high-speed capabilities and robust support for CAD/CAM software. |
| Electronics | PCB manufacturing and housing fabrication | Improves production efficiency and product reliability | Ensure compatibility with various materials and consider after-sales support. |
| Signage and Graphics | Custom signage production | Allows for intricate designs and faster turnaround times | Assess the machine’s versatility in handling different substrates and its ease of use. |
How is Commercial CNC Machinery Used in Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing sector, commercial CNC machines are pivotal for creating custom designs and producing high-quality components. These machines enable manufacturers to achieve precise cuts and intricate patterns, significantly reducing material waste and labor costs. Buyers in this industry, particularly from regions like Africa and Europe, should prioritize machines that offer customizable tooling options and software compatibility to streamline their production processes.
What Role Does CNC Machinery Play in Aerospace Component Manufacturing?
The aerospace industry relies heavily on commercial CNC machines for the manufacturing of critical components, including brackets, panels, and structural elements. These machines ensure that parts meet stringent safety and regulatory standards, which is paramount in this sector. International buyers must consider sourcing machines that can handle specialized materials, such as titanium and composites, while also providing high precision and reliability to ensure compliance with aerospace regulations.
How is CNC Technology Transforming Automotive Prototyping and Production?
In the automotive sector, commercial CNC machines facilitate rapid prototyping and the production of various parts, from engine components to interior fixtures. These machines enhance the speed of production cycles, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands and reduce overall costs. When sourcing CNC machinery, automotive companies should look for models that offer high-speed capabilities and robust support for CAD/CAM software, which are essential for maintaining competitive advantage.
What are the Applications of CNC Machines in Electronics Manufacturing?
CNC machines are increasingly utilized in the electronics industry for tasks such as PCB manufacturing and the fabrication of enclosures. Their precision allows for the production of intricate designs that are vital for modern electronic devices. Buyers in this sector should prioritize machines that can work with various materials and provide excellent after-sales support to address any technical challenges that may arise during production.
How Do CNC Machines Enhance Custom Signage Production?
In the signage and graphics industry, commercial CNC machines are essential for producing custom signs with intricate designs and high-quality finishes. These machines allow businesses to deliver unique products quickly, improving turnaround times and customer satisfaction. When sourcing CNC equipment for signage, companies should evaluate the machine’s versatility to handle different substrates and its user-friendliness, ensuring that staff can operate it efficiently.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘commercial cnc machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the Complexity of CNC Machine Specifications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face the daunting task of selecting the right CNC machine from an overwhelming variety of options. With numerous specifications—such as work area size, spindle speed, and compatible materials—making an informed decision can be challenging. For instance, a manufacturer in Nigeria may require a CNC router that can handle both wood and metal, but with limited local expertise and resources, they may struggle to identify which model meets their needs effectively. The fear of investing in a machine that doesn’t deliver on performance or versatility can lead to hesitation and potential losses.
The Solution:
To mitigate these challenges, it is crucial for buyers to engage in thorough research and leverage expert consultations. Start by defining the specific applications and materials your business will use. Create a checklist of essential features based on production needs, such as maximum cutting depth, material compatibility, and automation capabilities.
Engage with reputable suppliers and request detailed product demonstrations or case studies that highlight how similar businesses have successfully integrated the machine into their operations. Additionally, consider utilizing online forums or industry groups to solicit feedback from other users who have faced similar challenges. This collaborative approach ensures that you are informed by real-world applications, thus making a more confident purchasing decision.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Technical Support Gaps in Remote Locations
The Problem:
Many regions, particularly in Africa and South America, face significant challenges regarding access to technical support for CNC machines. A company in Brazil might invest heavily in a high-end CNC router, only to encounter operational issues due to a lack of immediate assistance. This situation can lead to downtime, production delays, and ultimately, a loss of revenue—all critical pain points for any manufacturing business that relies on timely outputs.
The Solution:
To address this issue, buyers should prioritize manufacturers and suppliers that offer robust technical support services, including remote assistance and comprehensive training programs. Before making a purchase, inquire about the availability of a dedicated support team that can provide troubleshooting help via video calls or chat.
Investing in online training resources or workshops can also equip your staff with the necessary skills to handle minor issues independently. Furthermore, consider establishing a relationship with local service providers who specialize in CNC machinery maintenance. This proactive approach ensures that your operations remain smooth and minimizes the risk of prolonged downtimes.
Scenario 3: Managing Integration with Existing Manufacturing Processes
The Problem:
Integrating a new CNC machine into an existing manufacturing setup can be fraught with complications. For instance, a manufacturer in Germany may face operational disruptions as they try to synchronize the new CNC router with outdated machinery and workflows. This lack of compatibility can lead to inefficiencies, increased costs, and frustration among staff who must adapt to new systems while still managing older equipment.
The Solution:
To streamline integration, start with a comprehensive assessment of your current manufacturing processes. Map out workflows and identify potential bottlenecks that the new CNC machine could alleviate. Collaborate closely with the machine supplier to ensure they understand your existing setup and can recommend the best solutions for integration.
Consider investing in software solutions that facilitate seamless communication between different machines and systems. For example, adopting a centralized CAD/CAM software can help unify design and production processes, thus enhancing overall efficiency. Additionally, involving your team in the transition process and providing adequate training on the new equipment can foster a smoother adaptation and minimize resistance to change.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for commercial cnc machine
When selecting materials for commercial CNC machines, it’s crucial to consider the properties and suitability of various materials based on the intended applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in CNC machining: aluminum, steel, plastics, and composites. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact performance, cost, and application compatibility.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in CNC Machining?
Aluminum is favored for its lightweight nature and excellent machinability. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°F and is known for its corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized. This property makes aluminum ideal for applications requiring durability and aesthetic appeal.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively inexpensive, easy to machine, and offers a good strength-to-weight ratio. It is suitable for various applications, including automotive parts, aerospace components, and consumer products.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it may not withstand extreme temperatures or heavy loads as effectively as steel. Additionally, it can be prone to scratching and denting.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a wide range of media, including plastics and other metals, making it versatile for various industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN, especially when sourcing from different regions. In markets like Germany and Nigeria, understanding local regulations regarding aluminum alloys is essential.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for CNC Machines?
Steel, particularly stainless steel, is known for its high strength and durability. It can handle high-pressure environments and has excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: Steel is incredibly strong and can withstand significant wear and tear, making it ideal for industrial applications. It is also readily available and can be sourced globally.
Cons: The downside is that steel can be more expensive than aluminum and may require more complex machining processes, which can increase production time and costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and construction applications, where strength and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with standards such as JIS and ASTM for steel grades and ensure that the material meets local regulations, particularly in the Middle East and Europe.
What Role Do Plastics Play in CNC Machining?
Plastics, including acrylic, polycarbonate, and nylon, are increasingly popular in CNC machining due to their lightweight and versatile properties. They typically have lower temperature ratings but can be engineered for specific applications.
Pros: Plastics are generally less expensive than metals and offer good chemical resistance. They are also easier to machine and can be produced in various colors and finishes.
Cons: The main limitation is their lower strength compared to metals, making them unsuitable for high-stress applications. They can also deform under high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for prototypes, consumer goods, and components that require intricate designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety and environmental regulations, such as REACH in Europe, is critical when sourcing plastics. Buyers should also consider local preferences for specific plastic types.
How Do Composites Enhance CNC Machining Applications?
Composites, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, offer unique properties that combine lightweight characteristics with high strength. They are engineered materials that can withstand various environmental conditions.
Pros: Composites are incredibly strong and lightweight, making them ideal for applications in aerospace and automotive industries. They also provide excellent corrosion resistance.
Cons: The complexity of machining composites can lead to higher costs and longer production times. Additionally, they require specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical without sacrificing strength, such as in aerospace components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific machining requirements for composites and ensure compliance with international standards for material specifications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Machining
| Material | Typical Use Case for commercial cnc machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive parts, consumer products | Lightweight and easy to machine | Less durable under extreme conditions | Low |
| Steel | Industrial machinery, construction | High strength and durability | More expensive and complex to machine | Medium |
| Plastics | Prototypes, consumer goods | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower strength and heat resistance | Low |
| Composites | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Strong and lightweight | Higher machining complexity | High |
This guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in diverse markets, emphasizing the importance of material selection based on application needs, cost considerations, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for commercial cnc machine
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Commercial CNC Machine?
The manufacturing process of commercial CNC machines involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the high standards of precision and reliability expected by B2B buyers. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The first step is the selection and preparation of raw materials, typically high-grade metals such as aluminum, steel, or composite materials. These materials are sourced from certified suppliers to ensure quality. The preparation involves cutting, shaping, and machining the raw materials into usable components. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting or waterjet cutting may be employed to achieve the necessary dimensions and tolerances.
-
Forming: In this stage, the prepared materials undergo forming processes, which may include bending, forging, or milling. CNC machining plays a significant role here, as computer-controlled tools precisely shape the components according to design specifications. This stage is crucial for creating parts that require high accuracy, such as frames, bases, and moving components.
-
Assembly: The assembly process involves fitting together the various components of the CNC machine. This may include integrating electronic systems, motors, and control panels. Skilled technicians work meticulously to ensure that all parts are aligned and connected properly. The use of jigs and fixtures can enhance precision during assembly, minimizing the risk of errors.
-
Finishing: After assembly, the CNC machines undergo finishing processes, such as painting, anodizing, or coating. These not only improve the aesthetic appeal of the machines but also enhance their durability and resistance to corrosion. Finishing is crucial for machines that will operate in demanding environments, ensuring longevity and reliability.
What Quality Control Measures Are Involved in CNC Machine Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an essential aspect of the manufacturing process for CNC machines. Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations.
-
International Standards Compliance: Many manufacturers adhere to internationally recognized standards, such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, certifications like CE (European Conformity) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be relevant depending on the specific industry and application of the CNC machines.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process help maintain quality. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) checks the quality of raw materials upon delivery. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) monitors the production process, ensuring that components are manufactured within specified tolerances. Final Quality Control (FQC) evaluates the completed machines before they leave the factory, ensuring they function correctly and meet all specifications.
-
Common Testing Methods: Manufacturers employ various testing methods, including functional testing, load testing, and performance testing. Functional testing assesses the operational capabilities of the CNC machine, while load testing ensures that the machine can handle the intended weight and stresses. Performance testing evaluates the machine’s precision and speed, comparing them against the manufacturer’s specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is vital to ensure reliability and performance. Here are several strategies to achieve this:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide valuable insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. During an audit, buyers can assess the facilities, equipment, and workforce, as well as review quality management documentation and procedures.
-
Quality Control Reports: Requesting detailed quality control reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their QC processes. These reports should include data on testing results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturer’s quality control processes. These inspections can occur at various stages of production, offering reassurance that the machines meet the required specifications and standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, B2B buyers must navigate various nuances related to quality control, especially concerning cultural and regulatory differences.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context of a supplier’s country can impact communication and expectations regarding quality. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local business practices and quality standards to establish effective partnerships.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements for manufacturing and quality assurance. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with both local regulations and international standards, which may affect the machine’s usability in their home markets.
-
Documentation and Certification: Buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide comprehensive documentation and certification for their products. This includes material certifications, quality management system documentation, and compliance certificates. Such documentation is crucial for facilitating customs clearance and ensuring that the machines meet local regulatory requirements.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in commercial CNC machines, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and standards. This knowledge not only aids in supplier selection but also fosters long-term relationships built on trust and quality assurance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘commercial cnc machine’
Introduction
When sourcing a commercial CNC machine, international B2B buyers face a complex landscape of options and considerations. This guide serves as a practical checklist to help you navigate the procurement process effectively, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your CNC machine sourcing process. Consider the materials you will be working with, the complexity of your projects, and the precision required.
– Key factors include:
– Work Area Size: Ensure the machine can accommodate your largest projects.
– Spindle Power: Higher power may be necessary for denser materials.
– Speed and Precision: Look for machines that offer high RPM and precision cutting capabilities.
Step 2: Determine Your Budget and Total Cost of Ownership
Understanding your budget is critical for narrowing down your options. It’s not just about the initial purchase price; consider ongoing costs such as maintenance, tooling, and software updates.
– Consider the following:
– Financing Options: Explore lease or financing options to manage cash flow.
– Operating Costs: Factor in electricity consumption and potential downtime.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Assess their reputation, reliability, and service offerings to ensure they align with your needs.
– What to look for:
– Company History: Research how long they’ve been in the market and their track record with similar clients.
– Customer Testimonials: Seek reviews or case studies from businesses in your industry.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This is particularly crucial for international buyers who may face different regulatory environments.
– Important certifications may include:
– ISO Standards: Demonstrating adherence to quality management principles.
– CE Marking: For compliance with European safety standards.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes and Compare Offerings
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline the specifications, warranties, and service agreements. Comparing these quotes will help you understand the value offered by each supplier.
– Ensure you examine:
– Included Services: Installation, training, and ongoing support should be clearly defined.
– Warranty Terms: A robust warranty can save you significant costs down the line.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Training
After-sales support is vital for the successful operation of your CNC machine. Evaluate what training and technical support are available to ensure your team can operate the machine efficiently.
– Look for:
– Technical Support Availability: Confirm the hours of support and response times.
– Training Programs: Consider whether the supplier offers on-site or remote training options.
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision and Negotiate Terms
After thorough evaluation, finalize your decision and be prepared to negotiate terms. A well-negotiated contract can provide additional benefits such as better pricing or extended warranties.
– Focus on:
– Payment Terms: Flexibility can ease cash flow concerns.
– Delivery Timeline: Ensure that the timeline aligns with your operational needs.
By following this structured checklist, you can confidently navigate the procurement of a commercial CNC machine that meets your business requirements and sets you up for success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for commercial cnc machine Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics for commercial CNC machines is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their sourcing strategies. This analysis will cover the critical components of costs, the factors influencing prices, and practical tips for buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Commercial CNC Machines?
When sourcing CNC machines, several cost components must be considered:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials significantly impacts the overall price. High-quality steel and aluminum are common in CNC construction, and fluctuations in global prices can affect machine costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct labor for assembly and skilled technicians for installation and maintenance. Regions with lower labor costs can offer more competitive pricing, but this may also affect the quality of workmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses such as factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads, enabling suppliers to offer better prices.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling for different CNC applications can add to initial costs. Buyers should consider whether the supplier includes tooling in their quotes or if it will be an additional expense.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures that machines meet performance and safety standards, which can be reflected in the pricing. Certifications and compliance with international standards may also add to costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary based on distance, mode of transport, and import duties. Understanding the logistics involved in getting the machine from the supplier to the end-user is crucial for cost estimation.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding standard margins in the CNC machine industry can help buyers gauge whether a quote is competitive.
What Influences the Pricing of CNC Machines?
Several factors can affect CNC machine pricing, making it vital for buyers to understand these nuances:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to lower per-unit costs. Negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQ) can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can substantially increase costs. Buyers should assess whether they need customized solutions or if standard models suffice.
-
Materials and Quality: Higher-grade materials and advanced technology typically increase machine prices. Buyers should balance their need for quality with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong reputation may command higher prices due to perceived reliability and service quality. Researching supplier backgrounds can help in making informed decisions.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (Incoterms) is crucial for international buyers. These terms determine who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risks, impacting the total landed cost.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing CNC Machines?
To maximize value when sourcing CNC machines, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate: Always negotiate pricing and payment terms. Suppliers may have room for flexibility, especially for bulk orders or long-term contracts.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operation costs, and potential downtime. A cheaper machine may lead to higher TCO if it requires frequent repairs or has lower efficiency.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of potential additional costs, such as tariffs and import duties. Engaging a local expert can help navigate these complexities.
-
Conduct Market Research: Regularly review market prices and technological advancements. This helps in identifying fair pricing and making informed purchasing decisions.
In conclusion, understanding the cost structure, price influencers, and effective sourcing strategies can empower B2B buyers in their quest for commercial CNC machines. By focusing on key components and negotiating wisely, buyers can optimize their investments and enhance operational efficiency. Always remember that prices may vary, and obtaining multiple quotes can provide a clearer picture of the market landscape.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing commercial cnc machine With Other Solutions
When considering manufacturing solutions, B2B buyers often seek alternatives to commercial CNC machines that can fulfill similar operational needs. This section compares commercial CNC machines with two viable alternatives: laser cutting machines and traditional manual machining. Each solution has unique attributes that may suit different business requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Commercial CNC Machine | Laser Cutting Machine | Traditional Manual Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, suitable for complex designs | Very high precision for cutting thin materials | Variable precision, depends on operator skill |
| Cost | Medium to high initial investment, long-term savings | Lower initial cost, but operational costs can add up | Low initial investment, but higher labor costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training, integration into existing systems | Easier setup and operation, less training required | No technology required, but skilled labor needed |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance needs, parts can be costly | Generally low maintenance, but lens replacement is needed | High maintenance due to wear and tear on tools |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for mass production and complex geometries | Best for cutting metals and plastics, especially in thin sheets | Suitable for low-volume, custom jobs requiring craftsmanship |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Cutting Machines?
Laser cutting machines offer significant advantages in terms of precision and operational efficiency, particularly for cutting thin materials like metals and plastics. They excel in speed and accuracy, making them ideal for industries requiring intricate designs. However, their operational costs can be higher due to energy consumption and the need for regular lens replacements. Moreover, laser cutting is less effective for thicker materials, which may limit its application in certain manufacturing scenarios.
How Does Traditional Manual Machining Compare?
Traditional manual machining relies heavily on skilled labor and offers a lower initial investment compared to CNC and laser cutting machines. This method is particularly effective for low-volume production and custom jobs where intricate craftsmanship is required. However, the precision and efficiency of manual machining can be inconsistent, as it largely depends on the operator’s skill level. Additionally, manual machining can incur higher labor costs over time, especially if production scales up.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate manufacturing solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, production volume, and budget constraints. For businesses prioritizing precision and the ability to handle complex geometries, commercial CNC machines stand out as a robust option. Conversely, laser cutting machines are advantageous for those focused on speed and efficiency in cutting thin materials. Traditional manual machining may suit smaller operations or specialized custom work where craftsmanship is paramount. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each alternative will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their production goals and financial objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for commercial cnc machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Commercial CNC Machines?
When evaluating commercial CNC machines, understanding essential technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
This specification indicates the type and quality of materials used in the construction of the CNC machine, such as steel or aluminum. High-grade materials enhance durability and performance, especially in demanding environments. B2B buyers should prioritize machines with robust material grades to ensure longevity and reliability, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified measurement. In CNC machining, tighter tolerances lead to higher precision in the final product. For businesses that require intricate designs or components, such as in aerospace or medical industries, understanding the machine’s tolerance capabilities is vital for meeting strict quality standards and customer expectations. -
Axis Configuration
The axis configuration indicates how many axes the CNC machine operates on, such as 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis systems. More axes allow for complex cuts and shapes, which can increase production capabilities. B2B buyers should assess their specific needs and consider machines that offer the necessary axis configurations to achieve desired production outcomes. -
Spindle Speed
Spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), indicates how fast the cutting tool can rotate. Higher spindle speeds can lead to faster machining times and improved surface finish quality. When selecting a CNC machine, businesses should evaluate the spindle speed to match their production speed requirements and material types. -
Work Area Size
This refers to the maximum dimensions of the material the CNC machine can accommodate. A larger work area allows for processing bigger sheets or multiple parts simultaneously, which can enhance efficiency. Buyers must consider their production scale and choose machines with appropriate work area sizes to optimize workflow. -
Power Consumption
The energy efficiency of a CNC machine is increasingly important for B2B buyers concerned about operational costs and environmental impact. Understanding a machine’s power consumption can help businesses budget accurately and choose equipment that aligns with sustainability goals.
Which Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand When Purchasing CNC Machines?
Navigating the purchase of CNC machines involves familiarizing oneself with specific industry jargon. Here are some common trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for buyers to ensure they are getting quality components and support from reputable sources. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and overall purchasing strategy. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses negotiate better terms and avoid excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is vital for buyers to gather competitive quotes and make informed decisions based on cost and service offerings. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to manage shipping, costs, and risk during transportation effectively. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time that elapses from placing an order until it is fulfilled. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times helps in planning production schedules and managing inventory levels, ensuring that operations run smoothly without delays. -
Turnkey Solutions
This term refers to a complete product or service that is ready for immediate use upon delivery. B2B buyers should consider turnkey solutions when looking for CNC machines, as they often include installation, training, and support, simplifying the integration process into existing operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that optimize their CNC machine investments, ultimately enhancing their production capabilities and profitability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the commercial cnc machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Commercial CNC Machine Sector?
The commercial CNC machine sector is experiencing a robust transformation driven by several global factors. The rise of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is revolutionizing manufacturing processes, making CNC machines more integral to production efficiency and precision. International B2B buyers, especially in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking advanced CNC solutions that enhance productivity while reducing operational costs. Key trends include the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities in CNC machines, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring consistent output.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on customization and flexibility. Buyers are increasingly looking for machines that can handle a variety of materials and production sizes, reflecting a shift towards more bespoke manufacturing solutions. The demand for used or refurbished CNC machines is also on the rise, particularly in emerging markets where budget constraints are common. This trend allows businesses to access high-quality equipment at lower costs, making it an attractive option for small to mid-sized enterprises.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Commercial CNC Machine Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a paramount concern for B2B buyers in the CNC machine sector. Environmental impacts associated with manufacturing processes, including waste generation and energy consumption, are prompting companies to seek machines that are designed with eco-friendly practices in mind. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable or produced from sustainable sources, as well as investing in energy-efficient machines that lower carbon footprints.
Furthermore, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly demanding transparency in sourcing practices, looking for suppliers who adhere to ethical standards and can provide certifications for their materials. ‘Green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, and adherence to international environmental standards are becoming essential criteria in supplier selection. This shift towards sustainability not only enhances brand reputation but also meets the growing consumer demand for responsible manufacturing practices.
What Is the Evolution of CNC Machines and Its Significance for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of CNC machines dates back to the 1950s when the first numerical control systems were developed. Initially, these machines were limited in capability and primarily used for simple tasks. However, advancements in computer technology and software have transformed CNC machines into sophisticated tools capable of executing complex designs with unparalleled precision.
This evolution is significant for B2B buyers as it has led to the proliferation of diverse CNC machine types, such as routers, lathes, and milling machines, each tailored for specific applications. The introduction of user-friendly software and automation has also democratized access to CNC technology, enabling even smaller manufacturers to leverage these powerful tools. As a result, businesses can now achieve higher production rates, improved quality control, and greater customization, positioning them competitively in the global market.
In summary, understanding market dynamics, embracing sustainability, and recognizing the historical context of CNC machines will empower international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and market presence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of commercial cnc machine
-
How do I ensure the quality of the CNC machine before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of a CNC machine, it is essential to conduct thorough research on the manufacturer. Look for established brands with positive reviews and a track record of reliability. Request detailed specifications and certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards. If possible, visit the supplier’s facility or request a video demonstration of the machine in operation. Additionally, consider asking for references from previous clients to gain insights into their experiences with the product and the supplier’s customer service. -
What is the best CNC machine for small to medium-sized businesses?
The best CNC machine for small to medium-sized businesses often depends on the specific applications and materials being used. For general-purpose machining, a mid-range CNC router, such as the 4′ x 8′ models, strikes a balance between capability and affordability. These machines can handle a variety of materials, including wood, plastics, and light metals, making them versatile for different projects. It’s advisable to evaluate the machine’s precision, ease of use, and the availability of technical support when making a choice. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing a CNC machine?
When sourcing a CNC machine, consider customization options such as size, spindle power, and specific tooling capabilities. Depending on your production needs, you may require specialized attachments for unique tasks, like engraving or 3D milling. Additionally, software compatibility is crucial; ensure the machine can integrate with your existing CAD/CAM systems. Discussing these options with suppliers can help you find a machine tailored to your operational requirements and improve efficiency. -
What are the common payment terms when purchasing CNC machines internationally?
Common payment terms for international CNC machine purchases can vary, but they often include options such as wire transfers, letters of credit, or payment in installments. Many suppliers may require an upfront deposit (typically 30-50%) before production, with the balance due upon completion or prior to shipping. It’s crucial to clearly outline payment terms in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection for added security. -
How do I vet suppliers for CNC machines in international markets?
Vetting suppliers for CNC machines in international markets involves several steps. Start by researching the supplier’s reputation through online reviews, industry forums, and trade associations. Request documentation such as business licenses, certifications, and references from previous clients. Consider conducting a background check or using third-party services that specialize in supplier verification. Establish communication to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to support your needs, as effective communication is critical for successful international transactions. -
What are the typical lead times for CNC machine orders?
Typical lead times for CNC machine orders can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on factors such as the machine’s complexity, customization requirements, and supplier location. For standard models, lead times are generally shorter, while customized machines may require additional time for engineering and production. It’s advisable to discuss lead times upfront with the supplier and factor in potential delays due to shipping or customs procedures, especially for international orders. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC machines?
When importing CNC machines, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Determine whether you will use air or sea freight, as each has different cost and speed implications. Ensure that all necessary import documentation is prepared, including invoices, bills of lading, and customs declarations. Collaborating with a freight forwarder can help streamline the process, as they are experienced in handling international shipments and can assist with compliance and logistics management. -
How can I ensure proper installation and training for my new CNC machine?
To ensure proper installation and training for your new CNC machine, request that the supplier includes these services in your purchase agreement. Many reputable manufacturers offer installation support and on-site training as part of the package. Alternatively, consider hiring a third-party technician with expertise in CNC machinery. Ensure that training covers operational best practices, maintenance procedures, and troubleshooting techniques to empower your team to effectively utilize the machine from day one.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Commercial Cnc Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. C.R. Onsrud – BIESSE ROVER K FT1531
Domain: cncmachines.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Used Industrial CNC Routers available for sale at CNCMachines.com. Key brands include Multicam, Laguna, Industrial CNC, Avid, ShopSabre, C.R. Onsrud, and Vision. Notable models include LAGUNA SMARTSHOP M (2024), INDUSTRIAL CNC ARTISAN 408 (2023), BIESSE ROVER K FT1531 (2023), and AVID PRO 60120 (2023). Various specifications include sizes such as 60″x120″x10.5″, 48″x96″x12″, and 49.5″x98.75″. Opti…
2. Industrial CNC – Pro Series CNC Routers
Domain: industrialcnc.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Industrial CNC offers a range of CNC routers designed for various applications, including sign making, cabinetry, exhibits, schools, furniture, and woodworking. Their Pro Series line includes several models: 1. SHORT CUT 203 – 2′ x 3′ work area, engineered to the specs of larger systems. 2. APPRENTICE 404 – 4′ x 4′ table, suitable for full-size sheet jobs. 3. ARTISAN 408 – 4′ x 8′ CNC router, desi…
3. ShopSabre – IS-A and IS-M Series CNC Routers
Domain: shopsabre.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: IS-A Series CNC Router: Industrial and commercial use, auto unload for high efficiency nested based sheet processing, starting at $99,995.00. IS-M Series CNC Router: World’s fastest and most accurate CNC control, industrial and commercial use, dedicated high production, high accuracy, starting at $57,995.00. Industrial Series (IS): Tool grade CNC at a fraction of the price, industrial and commerci…
4. Laguna Tools – Precision CNC Metalworking Machines
Domain: lagunatools.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Metalworking CNC machines by Laguna Tools are designed for precision engineering and robust performance in the metalworking industry. Key features include:
– Unmatched edge quality and cut precision for materials like steel, aluminum, and copper.
– Advanced cutting technologies including fiber lasers, plasmas, and high-pressure waterjets for smooth, burr-free edges.
– High-speed gantries and po…
5. Carbide 3D – Nomad 3
Domain: shop.carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: CNC Machines – Carbide 3D offers a collection of high-quality desktop CNC machines and CNC routers designed for hobbyists, professionals, woodworkers, and small businesses. Key products include: Nomad 3 – Desktop CNC Mill ($2,800.00), Shapeoko 4 CNC Router (from $1,800.00), Shapeoko Pro CNC Router (from $2,400.00), Shapeoko 5 Pro CNC Router (from $3,250.00), Shapeoko HDM ($5,700.00). All machines …
6. Hendrick Manufacturing – CNC Routers
Domain: hendrickmanufacturing.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Hendrick CNC Routers include 3-axis and 5-axis machines designed for heavy-duty production. 3-axis models include the HHD Series, known for 24/7 uptime and high-speed cutting of corrugated, aluminum, plastic, and wood; the HSR Series, which maximizes power and productivity; and the HLD Series, an entry-level option with top-tier machining capabilities. 5-axis models include the HSR-V Series, suita…
7. C.R. Onsrud – Industrial CNC Machines
Domain: cronsrud.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: C.R. Onsrud offers a range of industrial CNC machines designed for high-precision work and heavy-duty production. Key product categories include: 3-Axis Routers (M-Series, T-Series, G-Series, S-Series, RH-Series, C-Series, E-Series), 5-Axis Routers (G-Series, S-Series, C-Series, E-Series), Honeycomb Processing Cell, 5-Axis Mills (Q-Series, HM-Series, CH-Series, HR-Series, X-Series, EX-Series), Mul…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for commercial cnc machine
As global industries increasingly adopt advanced manufacturing techniques, the strategic sourcing of commercial CNC machines has become paramount for companies aiming to enhance productivity and maintain competitiveness. Key takeaways for B2B buyers include the importance of evaluating supplier reliability, understanding the technical specifications of machinery, and considering the total cost of ownership, which encompasses not only the purchase price but also maintenance and operational costs.
Investing in quality CNC equipment can lead to significant improvements in precision, efficiency, and production capacity. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging strategic sourcing allows for the identification of suppliers who can offer tailored solutions, robust support, and competitive pricing.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced CNC technology is expected to grow, driven by increased automation and customization needs across various sectors. Now is the time to engage with reputable manufacturers and suppliers to secure the right machines that align with your operational goals. By doing so, you position your business not just to survive but to thrive in an increasingly digital and automated manufacturing landscape.