Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for co2 laser materials
As international B2B buyers seek to enhance their production capabilities, sourcing high-quality CO₂ laser materials can pose significant challenges. With the diverse range of materials available for laser cutting and engraving, understanding which options best suit specific applications is crucial for optimizing both performance and cost-effectiveness. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of CO₂ laser materials, including wood, acrylic, leather, and more, while examining their unique properties, processing techniques, and safety considerations.
In addition to material selection, the guide provides actionable insights on supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can identify reliable sources that meet their quality and compliance standards. It also covers cost implications, helping businesses make informed financial decisions while maximizing their return on investment.
By equipping B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Germany—with the knowledge needed to navigate the global market for CO₂ laser materials, this guide empowers them to enhance their production processes. Whether you’re a manufacturer, designer, or craftsman, understanding the nuances of CO₂ laser materials will enable you to make strategic purchasing decisions that drive efficiency and innovation in your operations.
Understanding co2 laser materials Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Versatile, available in various types and thicknesses | Furniture, signage, prototypes | Pros: Clean cuts, intricate designs. Cons: Thickness limits based on power; may require multiple passes. |
| Acrylic | Smooth, flame-polished edges; varies in type (cast vs. extruded) | Signage, displays, awards | Pros: Excellent finish, easy to work with. Cons: Requires specific types for best results; can be costly. |
| Leather | Natural material with unique textures and finishes | Fashion, accessories, custom products | Pros: High-quality finishes, detail retention. Cons: Odor during cutting; requires fume extraction. |
| Fabric/Textiles | Soft, flexible material; available in various weights | Fashion, home decor, promotional items | Pros: Fast processing, minimal fraying. Cons: Limited thickness; may require air assist for best results. |
| Paper/Cardboard | Lightweight and easily available | Packaging, prototypes, crafts | Pros: Low cost, quick cutting. Cons: High flammability; needs careful power settings. |
What Are the Characteristics of Wood for CO₂ Laser Cutting?
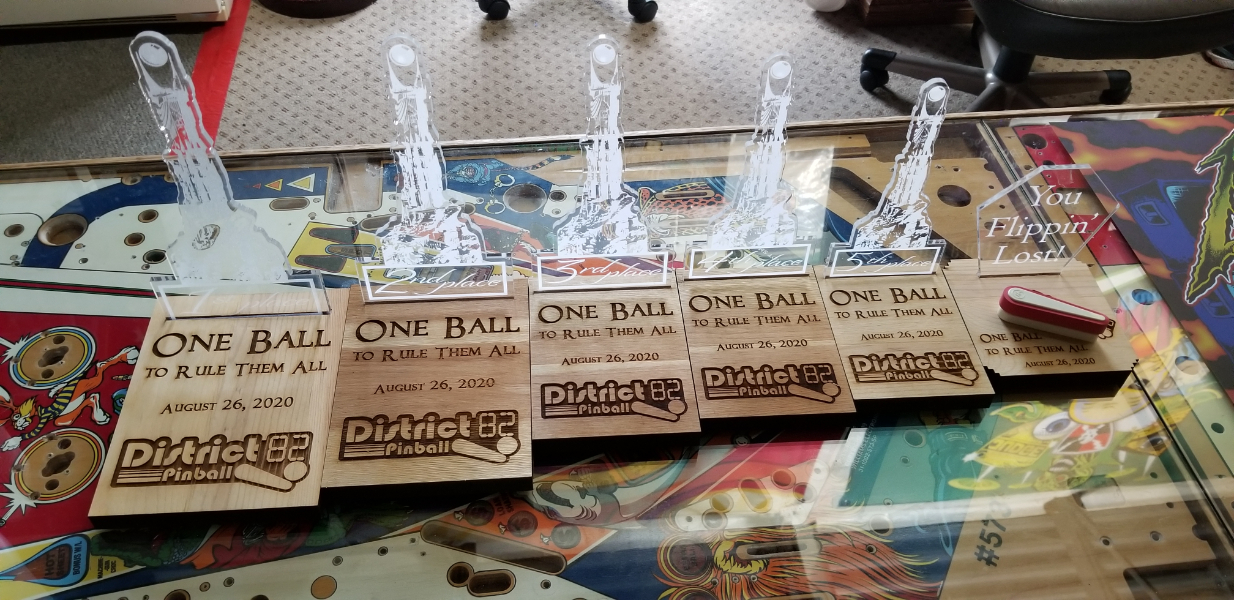
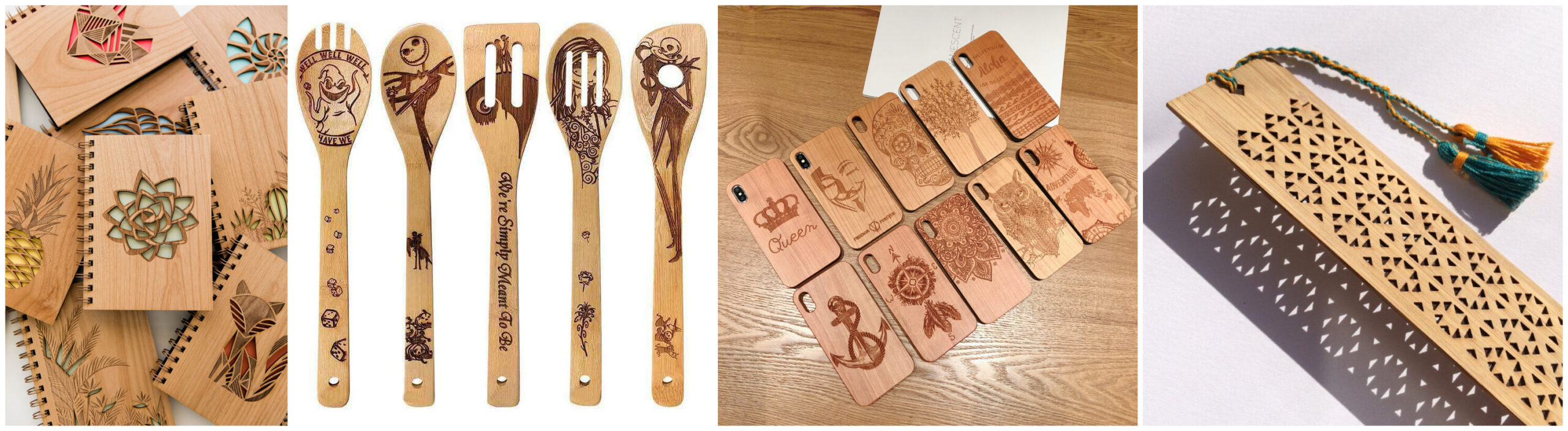
Wood is a favored choice for CO₂ laser cutting due to its versatility and aesthetic appeal. It can be sourced in various types, such as hardwoods and softwoods, allowing for a range of finishes and applications. B2B buyers should consider the material’s thickness, as thicker pieces may require more power and multiple passes. The ability to create intricate designs with high precision makes wood ideal for furniture, signage, and prototypes. However, buyers must also be mindful of potential scorching and the need for air assist to minimize smoke and debris.
How Does Acrylic Stand Out in CO₂ Laser Applications?
Acrylic is renowned for its smooth, flame-polished edges, particularly when using cast acrylic, which is ideal for signage and display applications. This material is available in various colors and thicknesses, making it suitable for a wide range of creative projects. B2B buyers should note that while acrylic can be easily processed, the choice between cast and extruded types can significantly affect the outcome. Cast acrylic is preferred for deeper engravings, while extruded acrylic offers a clearer finish. Buyers must evaluate their specific needs and budget, as acrylic can be more expensive than other materials.
What Unique Benefits Does Leather Offer for Laser Cutting?
Leather is a premium material that adds value to products through its natural textures and durability. It is widely used in fashion and accessories, allowing for high-quality finishes and personalization through engraving. Buyers should consider the thickness and type of leather, as these factors can affect processing ease and quality. While laser cutting leather can produce stunning results, it does generate odors that necessitate proper ventilation and fume extraction systems. Understanding the specific requirements for leather processing is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to deliver high-end products.
Why Choose Fabric/Textiles for CO₂ Laser Processing?
Fabric and textiles are increasingly popular choices for CO₂ laser cutting due to their flexibility and diverse applications in fashion and home decor. The material is lightweight and can be cut quickly, making it suitable for high-volume production. B2B buyers should consider the weight and type of fabric, as these factors impact the cutting process and finish quality. While laser cutting fabric minimizes fraying, using low-pressure air assist can enhance results. Buyers should also keep in mind that thicker textiles may require more powerful lasers, influencing their purchasing decisions.
How Does Paper/Cardboard Fit into the CO₂ Laser Material Landscape?
Paper and cardboard are cost-effective materials ideal for rapid prototyping and packaging solutions. Their lightweight nature allows for quick cuts, making them suitable for various applications, including crafts and promotional items. However, B2B buyers must be cautious about the high flammability of these materials; thus, careful management of power settings is essential to avoid fire hazards. The ease of sourcing paper and cardboard further enhances their appeal, but buyers should ensure they select appropriate grades to meet their project’s requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of co2 laser materials
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CO₂ Laser Materials | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signage and Advertising | Cutting and engraving acrylic for signs | High precision and aesthetic appeal, enhancing brand visibility | Source from suppliers that provide high-quality cast acrylic for optimal results |
| Woodworking | Laser cutting intricate designs in wood | Clean cuts with minimal waste, allowing for complex shapes and designs | Ensure the wood is laser-safe and check for moisture content to prevent warping |
| Textile and Fashion | Engraving and cutting fabrics for apparel | Customization options that enhance product uniqueness, increasing market appeal | Look for suppliers that offer a variety of fabric types compatible with laser processing |
| Packaging | Cutting cardboard and paper for packaging solutions | Efficient production of custom packaging, reducing costs and improving turnaround time | Prioritize sourcing from vendors that provide eco-friendly materials to align with sustainability goals |
| Leather Goods | Cutting and engraving leather for accessories | Precision and detail in product design, improving product quality and customer satisfaction | Verify that the leather is suitable for laser processing to avoid excessive fume generation |
What Are the Key Applications of CO₂ Laser Materials in Signage and Advertising?
In the signage and advertising sector, CO₂ lasers are extensively used for cutting and engraving acrylic materials. This method allows businesses to produce high-precision signs that are visually appealing and durable. The laser cutting process minimizes waste while enabling intricate designs that traditional methods cannot achieve. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality cast acrylic is crucial to ensure optimal engraving results and brand visibility.
How Do Woodworking Businesses Benefit from CO₂ Laser Materials?
Woodworking industries leverage CO₂ laser technology for cutting intricate designs in various types of wood. This process produces clean cuts with sealed edges, which reduces the need for post-processing. It also allows for the creation of complex shapes that enhance product offerings. Buyers should ensure that the wood sourced is laser-safe and check moisture levels to avoid warping during processing, especially in humid climates prevalent in some regions of Africa and South America.
What Role Do CO₂ Lasers Play in the Textile and Fashion Industry?
In the textile and fashion industry, CO₂ lasers are used for both engraving and cutting fabrics, which helps in creating customized apparel and accessories. This capability not only enhances product uniqueness but also increases market appeal. For international buyers, it’s essential to source fabrics that are compatible with laser processing, as some materials may fray or warp. Suppliers should provide a range of fabric types to cater to diverse design needs.
Why Are CO₂ Lasers Important for Packaging Solutions?
The packaging industry benefits significantly from CO₂ laser cutting technology, particularly in producing custom cardboard and paper packaging. This method allows for efficient production processes, reducing costs and improving turnaround times for businesses. International buyers should prioritize eco-friendly materials when sourcing packaging solutions, as sustainability is becoming increasingly important in global markets, particularly in Europe and South America.
How Do Leather Goods Manufacturers Utilize CO₂ Laser Technology?
Leather goods manufacturers use CO₂ lasers for cutting and engraving leather, which ensures precision and detail in product design. This technology enhances the quality of the final products, leading to higher customer satisfaction. Buyers should verify that the leather sourced is suitable for laser processing to minimize fume generation, which can be a concern in certain manufacturing environments. Additionally, suppliers should be able to provide various leather types to meet diverse design requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘co2 laser materials’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Compatible CO2 Laser Materials
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to find materials that are not only compatible with CO2 laser cutting but also meet their specific project requirements. For instance, a company in Brazil may need acrylic sheets for signage but finds that local suppliers offer only extruded acrylic, which does not engrave as well as cast acrylic. This mismatch can lead to increased costs and project delays, ultimately affecting their competitiveness in the market. Furthermore, buyers may encounter hazardous materials that are inappropriate for laser processing, leading to safety concerns and potential machine damage.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, buyers should establish relationships with specialized suppliers who understand laser-compatible materials. Conducting thorough research on local and international suppliers can reveal those that specifically offer materials designed for laser applications. It’s beneficial to create a checklist of required material properties—such as thickness, type (cast vs. extruded), and safety characteristics—before making a purchase. Additionally, consider using online marketplaces or dedicated laser material suppliers who provide detailed specifications and safety notes for their products. This proactive approach will help ensure that you receive the right materials for your laser projects, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Cutting and Engraving Quality
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers using CO2 lasers is the inconsistency in cutting and engraving quality across different materials or even batches of the same material. For example, a company in Germany may find that its laser cutter produces clean cuts on one batch of wood but struggles with scorching or uneven edges on another. This inconsistency can arise from variations in material quality, thickness, or even environmental factors such as humidity, leading to frustration and increased production costs.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, it is essential to implement standardized testing procedures for each new material batch. Buyers should establish a quality control process that includes testing small samples of materials before full-scale production. Documenting the settings—such as power, speed, and frequency—used during successful cuts or engravings will create a reference guide for future projects. Additionally, investing in a laser cutter with adjustable settings can help tailor the machine’s performance to specific materials, allowing for more consistent results. Regular maintenance of the laser cutter, including lens cleaning and calibration, will also enhance cutting precision and prolong the machine’s lifespan.
Scenario 3: Health and Safety Concerns with Laser Processing
The Problem: Health and safety issues are paramount when it comes to using CO2 lasers, particularly with materials that may release hazardous fumes during cutting or engraving. A company in South Africa might be using PVC for custom signage, unaware that it emits toxic chlorine gas when laser cut. Such oversights not only endanger the health of operators but can also lead to costly equipment repairs due to corrosion from harmful fumes.
The Solution: To address these health and safety concerns, it is crucial for buyers to conduct thorough material safety assessments before initiating any laser processing. Familiarizing oneself with the properties of materials—especially those that are known to be hazardous—will prevent costly mistakes. Buyers should maintain an updated list of safe and unsafe materials for laser cutting, and always consult safety data sheets (SDS) for any new materials being considered. Implementing effective ventilation and fume extraction systems in the workspace will further protect employees from harmful emissions. Regular training sessions on material safety and proper handling of the laser cutter can cultivate a culture of safety within the organization, ultimately leading to more efficient and responsible production practices.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for co2 laser materials
What Are the Key Properties of Wood for CO₂ Laser Applications?
Wood is a highly versatile material favored for CO₂ laser cutting and engraving due to its natural aesthetic and ease of processing. Its key properties include a wide range of thicknesses (typically 1-20 mm) and a low thermal conductivity, which allows for clean cuts without significant charring when proper settings are used. Wood is generally cost-effective, making it a popular choice for small to medium-sized businesses looking to produce custom items like signage, furniture, and decorative pieces.
Pros: Wood offers excellent engraving detail and can produce intricate designs with high repeatability. It is widely available and can be sourced locally in many regions, reducing shipping costs.
Cons: Variability in wood species can lead to inconsistent results; harder woods may require more power and slower speeds. Additionally, the risk of burning or scorching increases with thicker cuts.
Impact on Application: Wood is suitable for a variety of applications, including personalized gifts, architectural models, and art pieces. Its compatibility with various finishes also enhances its appeal for end products.
How Does Acrylic Perform in CO₂ Laser Cutting?
Acrylic, also known as PMMA, is another preferred material for CO₂ laser applications. It boasts excellent optical clarity and can be cut in thicknesses ranging from 1-15 mm. The material melts rather than burns when cut, resulting in smooth, flame-polished edges, which is crucial for high-quality display products.
Pros: Acrylic is lightweight, durable, and available in various colors and finishes. It is particularly effective for signage, awards, and decorative items due to its aesthetic appeal.
Cons: While acrylic is generally easy to work with, it can be more expensive than wood and may require specific types (cast versus extruded) for optimal results.
Impact on Application: Acrylic is widely used in the signage and display industries, where clarity and finish are paramount. Its versatility allows for both cutting and engraving, making it suitable for a range of creative applications.
What Are the Considerations for Laser-Cutting Leather?
Leather is a unique material that poses specific challenges and advantages for CO₂ laser cutting. It typically ranges from 0.5 to 3 mm in thickness and has a high tensile strength, which allows for detailed cutting and engraving.
Pros: Laser cutting leather produces clean edges and intricate designs without fraying, making it ideal for high-quality fashion items, accessories, and personalized gifts.
Cons: Leather can produce strong fumes during cutting, necessitating effective ventilation systems. Additionally, the cost of high-quality leather can be significant.
Impact on Application: Leather’s tactile quality and aesthetic appeal make it desirable for luxury products. However, international buyers must consider sourcing and compliance with environmental regulations regarding leather processing.
What Are the Implications of Using Paper and Cardboard in CO₂ Laser Cutting?
Paper and cardboard are among the most accessible materials for CO₂ laser applications, with typical thicknesses of less than 5 mm. These materials are highly flammable, which requires careful management of laser settings to prevent ignition.
Pros: They are inexpensive and widely available, making them ideal for prototyping and small-scale production. Laser cutting paper allows for intricate designs, making it suitable for packaging, crafts, and educational materials.
Cons: The risk of fire is a significant concern, and users must employ low power settings and air assist to mitigate this hazard.
Impact on Application: Paper and cardboard are often used in packaging and promotional materials, where cost-effectiveness and design flexibility are crucial. International buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding the use of recycled materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CO₂ Laser Applications
| Material | Typical Use Case for CO₂ Laser Materials | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Signage, furniture, decorative items | Excellent engraving detail and availability | Variability in species affects consistency | Low |
| Acrylic | Signage, awards, decorative items | Smooth, polished edges and aesthetic appeal | Higher cost compared to wood | Med |
| Leather | Fashion items, accessories | Clean cuts and luxury appeal | Strong fumes and high material cost | High |
| Paper/Cardboard | Prototyping, packaging | Cost-effective and widely available | High flammability risk | Low |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for co2 laser materials
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for CO₂ Laser Materials?
The manufacturing of CO₂ laser materials involves several critical stages that ensure optimal performance and quality. Understanding these stages can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing materials from suppliers, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of CO₂ Laser Materials?
-
Material Preparation
The first step involves selecting and preparing the raw materials. This stage includes sourcing materials such as acrylic, wood, leather, and paper, which are commonly used in laser applications. Suppliers often utilize advanced technology to ensure that materials meet specific thickness and quality standards. This preparation may involve cutting raw sheets to manageable sizes and treating them to enhance performance, such as applying coatings to certain plastics for better engraving results. -
Forming Techniques
Forming techniques vary based on the type of material being processed. For instance, acrylic sheets may be formed using methods like thermoforming, where heat is applied to mold the material into desired shapes. In contrast, wood may undergo processes like laser cutting or CNC routing to achieve intricate designs. Ensuring that these techniques are optimized for CO₂ laser compatibility is crucial for maintaining material integrity and performance during laser operations. -
Assembly
In cases where products are composed of multiple components (e.g., signage or display stands), assembly is a vital stage. This may involve using adhesives or mechanical fasteners that are compatible with laser materials. During assembly, attention must be given to the alignment and fit of the components to ensure that they can withstand operational stresses, especially if they are to be used in demanding environments. -
Finishing Processes
Finishing techniques enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of the materials. This can include sanding, polishing, or applying protective coatings. For laser-cut materials, achieving a clean edge is essential, and suppliers may employ techniques like flame polishing for acrylics or using air assist during cutting to minimize burning on wood. Finishing processes directly impact the final product’s quality and marketability, making them a critical focus area for manufacturers.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of CO₂ Laser Materials?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to ensuring that CO₂ laser materials meet international standards and client specifications. A robust QA process can significantly reduce the risk of defects and enhance customer satisfaction.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for CO₂ Laser Material Quality?
-
ISO 9001
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Adhering to this standard helps manufacturers ensure consistent quality, improve customer satisfaction, and facilitate continuous improvement. B2B buyers should inquire whether their suppliers have ISO 9001 certification, which indicates a commitment to quality. -
CE Marking
For materials sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking demonstrates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Suppliers that provide CE-marked products reassure buyers of the material’s suitability for their intended use. -
Industry-Specific Certifications
Depending on the material’s application, additional certifications such as API (American Petroleum Institute) for industrial applications or specific safety standards for materials used in consumer products may be relevant. Understanding these certifications can aid buyers in selecting materials that align with regulatory requirements in their respective markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that materials meet specified standards. Here are the common checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
This initial checkpoint focuses on inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. IQC verifies that materials meet predefined specifications and standards before they enter the production process. This step is crucial for preventing defects that could arise from substandard materials. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, IPQC involves monitoring various parameters such as temperature, laser power settings, and cutting speeds. This ensures that all processes are executed within specified limits, thus maintaining product quality throughout the production cycle. Regular checks during forming and assembly can catch deviations early, preventing costly rework. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
The FQC stage involves a thorough inspection of the final products. This includes visual inspections for defects, dimensional checks, and performance testing to ensure that the materials perform as intended. For laser-cut materials, FQC may also involve testing for edge quality and finish to meet customer specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
Ensuring that suppliers adhere to rigorous quality control measures is essential for B2B buyers. Here are several approaches to verify supplier QC practices:
-
Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. These audits can evaluate adherence to international standards and identify areas for improvement. B2B buyers should establish a systematic audit schedule to maintain oversight of their suppliers. -
Requesting Quality Reports
Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including test results and compliance certifications. These reports serve as evidence of a supplier’s commitment to maintaining high standards and can help buyers make informed decisions. -
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. These services can perform checks at various stages of production, offering buyers additional assurance regarding the quality of materials.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially those from regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East, may face unique challenges in verifying quality control. Here are some considerations:
-
Understanding Regional Standards
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations regarding material quality. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these standards to ensure compliance and avoid potential issues with importation or usage. -
Cultural and Language Barriers
Engaging with suppliers in different countries may involve navigating cultural and language differences. Establishing clear communication channels is vital to ensure that quality expectations are understood and met. -
Shipping and Handling Risks
The transportation of materials across international borders introduces risks such as damage or degradation. Buyers should discuss packaging and handling procedures with suppliers to minimize these risks and ensure that materials arrive in optimal condition.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for CO₂ laser materials equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed sourcing decisions. By focusing on supplier capabilities, adherence to international standards, and robust quality control practices, buyers can ensure that they procure materials that meet their operational and safety requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘co2 laser materials’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure materials suitable for CO₂ laser cutting and engraving. By following these steps, you can ensure that you select the right materials that meet your project requirements while aligning with safety and operational standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before sourcing materials, it’s essential to clarify the technical specifications required for your projects. Determine the material types you need (e.g., wood, acrylic, leather) and the thickness ranges compatible with your CO₂ laser cutter. Knowing these details will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure compatibility with your equipment.
Step 2: Research Material Compatibility
Not all materials are suitable for CO₂ laser processing. Conduct thorough research on the materials that can be effectively cut or engraved by your specific laser machine. Pay attention to material properties such as reflectivity and flammability, as these can impact cutting quality and safety.
- Key Considerations:
- Avoid materials like PVC or ABS, which can release hazardous fumes.
- Prioritize materials like wood, acrylic, and certain textiles that offer optimal results.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This due diligence will help you assess the supplier’s reliability and their ability to meet your specific needs.
- Specific Checks:
- Verify their experience with your desired materials.
- Look for customer testimonials or reviews that speak to their service quality.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications for quality and safety standards. Certifications can indicate that the materials are tested and meet industry regulations, which is critical for maintaining compliance in your operations.
- Important Certifications:
- ISO certifications for quality management.
- Environmental certifications if sustainability is a priority for your business.
Step 5: Request Sample Materials
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the materials you are considering. Testing samples will allow you to evaluate their compatibility with your laser machine and assess the cut quality and engraving detail.
- Testing Criteria:
- Check for edge finish and clarity of engravings.
- Evaluate the material’s response to your specific laser settings.
Step 6: Discuss Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions with suppliers about pricing structures, minimum order quantities, and payment terms. Understanding these aspects upfront can help you budget effectively and avoid unexpected costs later in the procurement process.
- Negotiation Tips:
- Inquire about discounts for bulk orders.
- Clarify shipping costs and delivery timelines to ensure timely project execution.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Protocol
Once you select a supplier, create a quality assurance protocol to ensure that all materials received meet your specifications. Regularly inspect the materials upon arrival and maintain communication with the supplier to address any discrepancies immediately.
- Quality Control Measures:
- Conduct periodic reviews of material performance in your projects.
- Keep a record of supplier performance to inform future sourcing decisions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for CO₂ laser materials, ensuring that they source high-quality products that enhance their operational efficiency and project outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for co2 laser materials Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of CO₂ laser materials is essential for B2B buyers seeking to make informed purchasing decisions. This analysis covers the key components of costs, influences on pricing, and practical tips for negotiating better deals, particularly tailored for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in CO₂ Laser Materials?
When sourcing CO₂ laser materials, various cost components contribute to the overall pricing structure:
-
Materials: The type of material significantly affects the cost. For instance, acrylic and wood generally have lower prices compared to specialized plastics or treated materials. Prices can vary widely based on the quality and source of the materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the complexity of processing the materials. Skilled labor may be required for cutting and engraving, especially when dealing with intricate designs, thus impacting the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to machinery operation, maintenance, and facility costs. A well-maintained laser cutter can yield better efficiency, reducing per-unit costs in the long run.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom projects. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the necessary tooling already available or if additional costs will be incurred for new tools.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that materials meet specific standards incurs additional costs. Buyers should look for suppliers with rigorous QC processes, as this can prevent costly errors and wastage later in the production process.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary greatly depending on the supplier’s location and the delivery method. International buyers need to factor in customs duties, shipping fees, and potential delays.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. Understanding market rates for similar materials can help buyers gauge whether a supplier’s pricing is reasonable.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CO₂ Laser Materials Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CO₂ laser materials:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often yield lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for bulk pricing when possible.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses due to miscommunication.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Higher-quality materials or those with specific certifications (e.g., eco-friendly, fire-resistant) typically command higher prices. Buyers should assess whether the additional cost aligns with their project needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery (e.g., FOB, CIF) can help buyers evaluate the total cost of ownership. This includes shipping costs, insurance, and responsibilities associated with the delivery.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating CO₂ Laser Material Prices?
For international buyers, particularly from diverse regions, effective negotiation and cost management strategies can lead to significant savings:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand the average prices for specific materials. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, waste, and potential downtime. This holistic view can lead to better decision-making.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building a strong relationship with suppliers can facilitate better pricing and terms. Regular communication and loyalty can lead to discounts or preferential treatment.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing structures based on local demand, availability, and regulatory environments. Buyers should be mindful of these factors when negotiating.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for CO₂ laser materials can fluctuate based on market conditions, availability, and supplier pricing strategies. It is essential for buyers to obtain updated quotes directly from suppliers to ensure accurate budgeting and procurement planning.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing co2 laser materials With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CO₂ Laser Materials
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial processing, businesses often seek solutions that optimize performance, cost, and efficiency. CO₂ laser materials have established themselves as a leading choice for cutting and engraving a variety of substrates, particularly non-metals. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider alternative technologies that can meet similar needs. This section will compare CO₂ laser materials with other viable options, including traditional cutting methods and fiber laser technologies.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | CO₂ Laser Materials | CNC Routing | Fiber Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; suitable for non-metals | Good precision; slower than lasers | High speed; excellent for metals |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; operational costs vary | Lower initial cost; higher labor costs | Higher initial investment; lower operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training; setup can be complex | User-friendly; minimal training needed | Requires specialized knowledge for setup |
| Maintenance | Moderate; lens cleaning and alignment needed | Low; regular bit replacements | Low; minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Wood, acrylic, leather, textiles | Woodworking, signage, prototyping | Metal fabrication, industrial applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Pros and Cons of CNC Routing?
CNC routing is a traditional method that employs a rotating cutting tool to carve out materials. This technology is known for its user-friendly nature and lower initial investment compared to CO₂ lasers. CNC routers excel in woodworking and can handle larger sheets of material effectively. However, they generally operate at slower speeds and may require more manual labor, which can increase operational costs over time. Additionally, the precision is often not as high as that of CO₂ lasers, particularly for intricate designs.
How Does Fiber Laser Cutting Compare to CO₂ Lasers?
Fiber laser cutting is another alternative that has gained traction, especially in metal fabrication. Fiber lasers are known for their speed and efficiency, making them ideal for high-volume production environments. They provide excellent cutting quality on metals and can be more cost-effective in the long run due to lower operational costs. However, the initial investment for fiber laser systems can be significantly higher than that of CO₂ lasers. Additionally, fiber lasers are not suitable for non-metal materials, which limits their versatility compared to CO₂ laser technologies.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between CO₂ laser materials and alternative cutting solutions, B2B buyers must assess their specific requirements. Considerations such as the types of materials you will be processing, the desired precision, and your budget constraints are crucial. CO₂ lasers are unparalleled for intricate designs on non-metals, while CNC routers may be more appropriate for straightforward woodworking tasks. Conversely, fiber lasers are the go-to choice for those focused on metal applications and high-speed production.
Ultimately, aligning your choice with your operational needs, material types, and budget will ensure that you invest in the most effective technology for your business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for co2 laser materials
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CO₂ Laser Materials?
When sourcing materials suitable for CO₂ laser processing, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and quality. Here are some key specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of a material based on its composition and intended use. For laser applications, materials such as acrylic, wood, and specialized plastics are commonly graded based on their suitability for cutting and engraving. Selecting the right material grade ensures compatibility with laser systems, affecting the quality of cuts and engravings. For buyers, this means enhanced efficiency and reduced waste during production.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a material’s dimensions. In laser cutting, tighter tolerances are essential for applications requiring precision, such as in the manufacturing of parts or intricate designs. For businesses, understanding tolerance levels helps in predicting the accuracy of the final product, which is vital for customer satisfaction and compliance with industry standards.
3. Thickness Range
The thickness of materials plays a significant role in the cutting process. CO₂ lasers have varying capabilities based on their wattage; for instance, an 80W laser may effectively cut materials up to 10mm thick, while a 130W laser can handle thicker substrates. Knowing the thickness range helps buyers select materials that match their equipment’s specifications, ensuring efficient processing without compromising quality.
4. Cut Quality
Cut quality encompasses the smoothness and precision of the cut edges produced by laser processing. Factors such as the material type, thickness, and laser settings influence cut quality. For B2B buyers, understanding cut quality is essential when selecting materials, as it directly impacts the aesthetic and functional attributes of the final product, influencing marketability and brand reputation.
5. Safety Ratings
Certain materials may release harmful fumes or pose fire hazards when processed with lasers. Safety ratings provide critical information regarding the health risks associated with specific materials. Buyers should prioritize materials with favorable safety profiles to protect their workforce and comply with regulatory requirements, thereby minimizing liability and potential disruptions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to CO₂ Laser Materials?
Understanding trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B environment. Here are some commonly used terms relevant to CO₂ laser materials:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of laser materials, it often pertains to suppliers who provide raw materials specifically designed for laser processing. For buyers, engaging with OEMs can ensure compatibility and performance, resulting in more reliable outcomes.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important in B2B transactions where bulk purchasing is common. Understanding MOQ helps buyers manage inventory costs and ensures they meet supplier requirements, facilitating smoother procurement processes.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific materials or services. In the context of CO₂ laser materials, an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms, ensuring they receive the best value for their investments.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. They outline who is responsible for transportation, insurance, and duties, which is crucial for international trade. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers mitigate risks and manage logistics more effectively when sourcing materials across borders.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the materials. In the laser processing industry, understanding lead times is essential for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should consider lead times when sourcing materials to ensure timely delivery and avoid production delays.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, optimize their procurement strategies, and enhance their overall operational efficiency in the CO₂ laser materials market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the co2 laser materials Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the CO2 Laser Materials Market?
The CO2 laser materials market is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and increasing demand for precision cutting across various industries. Key sectors such as woodworking, signage, packaging, and textiles are increasingly adopting CO2 laser cutting due to its efficiency, versatility, and ability to produce high-quality finishes. Emerging markets in Africa and South America are particularly noteworthy, as businesses in these regions seek innovative solutions to enhance production capabilities and meet the rising expectations of consumers for quality and customization.
In Europe, particularly in countries like Germany, there is a strong emphasis on automation and Industry 4.0, which is further propelling the adoption of CO2 lasers. Additionally, the increasing trend toward personalized products is creating opportunities for manufacturers to leverage laser technology for custom designs. The integration of digital tools and software in the sourcing process has also simplified procurement for international buyers, allowing for better tracking of material availability and pricing trends.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the CO2 Laser Materials Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the CO2 laser materials sector. As global awareness of environmental issues grows, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical sourcing practices and provide eco-friendly materials. This includes sourcing wood from sustainably managed forests and using recyclable materials like acrylic and paper that have a lower environmental footprint.
The importance of certifications cannot be overstated. Materials with ‘green’ certifications, such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for wood or ISO certifications for manufacturing processes, are gaining traction among buyers focused on reducing their ecological impact. Furthermore, suppliers that demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and commitment to reducing waste are more likely to attract international buyers who recognize the value of sustainability in their procurement strategies.
How Has the CO2 Laser Materials Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the CO2 laser materials market has been marked by technological advancements that have significantly enhanced cutting and engraving capabilities. Initially, laser cutting was primarily limited to industrial applications; however, over the past two decades, it has expanded to various sectors, including crafts, education, and small-scale manufacturing. The introduction of more affordable and user-friendly CO2 laser machines has democratized access to this technology, enabling small businesses and startups to leverage laser cutting for innovative product development.
As industries adapt to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements, the market is likely to continue evolving. The focus is shifting toward automation, efficiency, and sustainability, aligning with broader trends in global manufacturing. International B2B buyers should remain vigilant to these changes, as they present both challenges and opportunities in sourcing CO2 laser materials.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of co2 laser materials
-
1. How do I choose the right material for CO₂ laser cutting?
Choosing the appropriate material for CO₂ laser cutting involves evaluating several factors: the material’s compatibility with laser technology, the desired finish, and the project’s specific requirements. Common materials like wood, acrylic, and leather are often favored due to their cutting and engraving qualities. It’s crucial to consider the thickness, as thicker materials may need higher power settings and longer cutting times. Always consult with material suppliers to understand their recommendations and conduct tests to ensure optimal results. -
2. What is the best CO₂ laser material for engraving detailed designs?
Acrylic (PMMA) is one of the best materials for engraving detailed designs with CO₂ lasers. It allows for sharp, intricate engravings and yields a polished finish, especially when using cast acrylic. Wood is also a popular choice, offering a range of engraving depths and textures depending on the type of wood used. For projects requiring high detail, selecting high-quality materials and fine-tuning your laser settings will enhance the engraving’s clarity and precision. -
3. How can I ensure the safety of materials used with CO₂ lasers?
Safety is paramount when using CO₂ lasers. It is essential to verify that the materials are laser-compatible and do not emit hazardous fumes when processed. Avoid materials like PVC and ABS, which can release toxic gases. Always consult material safety data sheets (MSDS) and perform risk assessments before starting any project. Implementing adequate ventilation systems and using fume extraction devices can further enhance safety in the workspace. -
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CO₂ laser materials?
Minimum order quantities for CO₂ laser materials vary by supplier and material type. Generally, larger manufacturers might have higher MOQs, while smaller suppliers could accommodate smaller orders. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to find flexibility in MOQs. For international buyers, consider the logistics and shipping costs associated with smaller orders, which may impact overall profitability. -
5. How do I vet suppliers for CO₂ laser materials in international trade?
Vetting suppliers is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability. Start by researching potential suppliers through industry directories and trade shows. Request samples to evaluate material quality, and check for certifications that indicate compliance with international standards. Engaging in direct communication can provide insights into their production processes and customer service. Additionally, seeking reviews or references from other B2B buyers can help assess a supplier’s reputation. -
6. What payment terms should I negotiate with CO₂ laser material suppliers?
Payment terms can significantly impact cash flow and project timelines. Common terms include upfront payments, net 30/60/90 days, or a letter of credit, especially in international transactions. Negotiating favorable terms, such as partial upfront payment followed by the balance upon delivery, can protect your interests while ensuring supplier commitment. Always clarify currency, payment methods, and any potential fees involved in international transactions. -
7. How do logistics affect the sourcing of CO₂ laser materials?
Logistics play a vital role in sourcing CO₂ laser materials, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as shipping times, customs regulations, and transportation costs can influence your supply chain efficiency. It is essential to work with suppliers who have reliable logistics partners and understand the import/export regulations of your country. Establishing clear timelines and communication channels with both suppliers and logistics providers can help mitigate delays and ensure timely delivery. -
8. What quality assurance (QA) measures should I expect from suppliers?
Quality assurance is critical when sourcing CO₂ laser materials. Expect suppliers to implement standardized QA processes, such as material testing, inspections, and compliance with industry standards. Request documentation that outlines their QA protocols, such as certificates of conformity or quality control reports. Regular audits and the ability to track material batches can also provide assurance of consistent quality, which is essential for maintaining production standards in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Co2 Laser Materials Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Thunder Laser – CO₂ Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: thunderlaser.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: CO₂ laser cutting machines are suitable for precision processing of non-metal materials. Common materials include: 1. Wood: Cut Quality ★★★★☆, Engraving Detail ★★★★★, Typical Thickness Range 1–20 mm, Easy processing, Minimal smoke with air assist. 2. Acrylic (PMMA): Cut Quality ★★★★★, Engraving Detail ★★★★☆, Typical Thickness Range 1–15 mm, Easy processing, Use cast acrylic for best engraving. 3. …
2. FabCreator – CO2 Laser Cutters
Domain: fabcreator.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: FabCreator CO2 laser cutters can work with a wide range of materials for cutting and engraving. Recommended materials include: 1. Poplar Plywood – Low cost, ideal for education; best if high grade interior plywood (B/BB) is used. 2. Birch Plywood – Harder than poplar, produces durable products and cleaner engravings; also best if high grade interior plywood (B/BB) is used. 3. MDF (Medium Density F…
3. Laguna Tools – CO2 Laser Engraving Materials
Domain: info.lagunatools.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Common materials for CO2 laser engraving and cutting include wood and plastic. Key considerations for wood include the species, moisture content, and glue type. Solid woods like cedar and pine are commonly used, with pine being easier to cut through. Baltic birch plywood is preferred for projects requiring tight tolerances. Particle board is generally avoided due to excessive glue and burning issu…
4. Elen Laser – CO2 Laser Cutting Solutions
Domain: elenlaser.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: CO2 lasers can cut a wide range of materials including: Wood, paper, cardboard, plastic, PMMA (acrylic), rubber, leather, metals, and ceramics. Specific applications include cutting cardboard boxes, stencils, decorations, various types of wood (especially plywood and MDF), engravings on wood, leather goods, textiles, electronic components, anodized aluminum, glass, marble, and stones. CO2 lasers a…
5. Reddit – CO2 Laser Cutters
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CO2 laser cutters (up to 150W) can cut a variety of materials:
1. **Organics**:
– Acceptable: Wood, Plywood, Paper, Cardboard, Cork, Suede
– Take Care: MDF, Food Products, Fabrics, Leather
– Avoid: Flesh, Pleather
2. **Plastics**:
– Acceptable: PMMA (Acrylic), PES, POM, PP, PE
– Take Care: PETG, PUR, Polyimide, Rubber, EPS, Foams
– Avoid: PVC, PTFE (Teflon), PC, ABS, HD…
6. OmTech – Walnut Plywood 1/8 6PCS 12×12
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Walnut Plywood 1/8 – 6PCS 12″x12″; Price: $28.99; Regular Price: $59.99; Save: $31.00
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for co2 laser materials
As the demand for CO₂ laser materials continues to grow across diverse industries, strategic sourcing becomes essential for international B2B buyers. Understanding the unique properties of various materials—such as wood, acrylic, leather, and textiles—enables businesses to select the right options that align with their cutting and engraving needs. Prioritizing materials that offer optimal performance while ensuring safety and compliance can significantly enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
Moreover, sourcing from reliable suppliers not only guarantees material consistency but also fosters innovation through access to advanced technologies and support. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe expand, the potential for collaboration and investment in laser technologies will only increase.
Looking ahead, businesses should embrace a proactive approach to sourcing CO₂ laser materials, considering not only the immediate requirements but also future trends in customization and sustainability. By aligning with trusted partners and staying informed about material advancements, international buyers can position themselves at the forefront of the laser processing industry. Engage with your suppliers today to explore new opportunities and drive your business forward.