Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for co2 laser cutter metal
Navigating the complexities of sourcing a CO2 laser cutter for metal can be daunting for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the growing demand for precision cutting and engraving capabilities, selecting the right equipment is crucial not only for enhancing operational efficiency but also for maintaining a competitive edge in the market. This guide comprehensively addresses key challenges faced by businesses, including the types of CO2 laser cutters available, their various applications across industries, and essential criteria for vetting suppliers.
Buyers will also gain insights into cost considerations and financing options, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their budget and operational needs. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable knowledge and a clear understanding of the global market landscape, this guide empowers them to confidently navigate their purchasing journey. Whether you are a manufacturer in Germany looking to optimize production or a startup in Brazil aiming to break into the metal fabrication industry, this resource will serve as your roadmap to successful procurement of CO2 laser cutters tailored for metal applications. Embrace the potential of advanced laser technology to elevate your business to new heights.
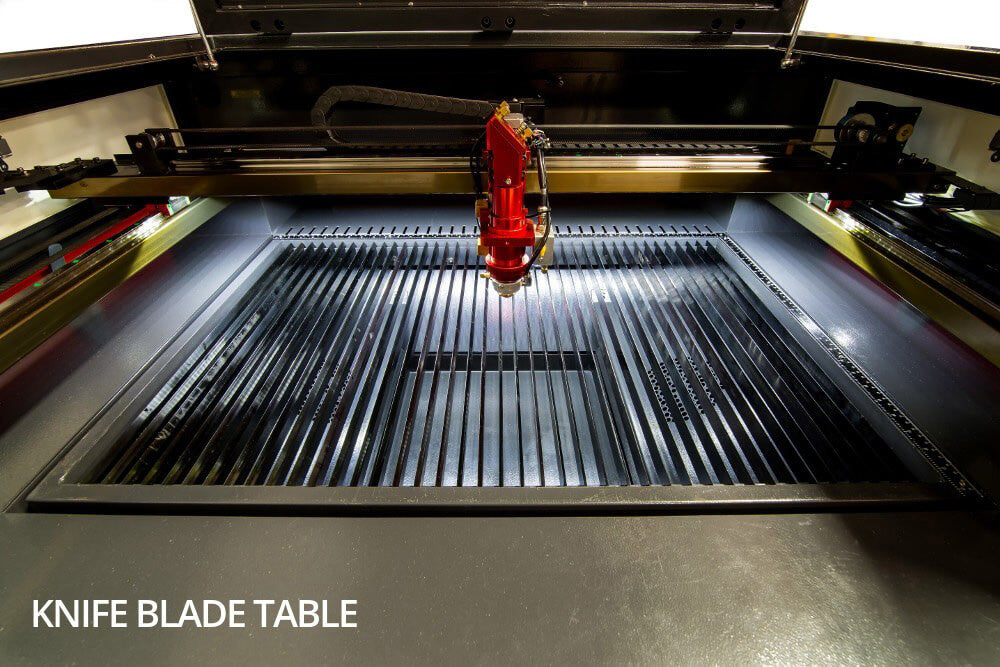
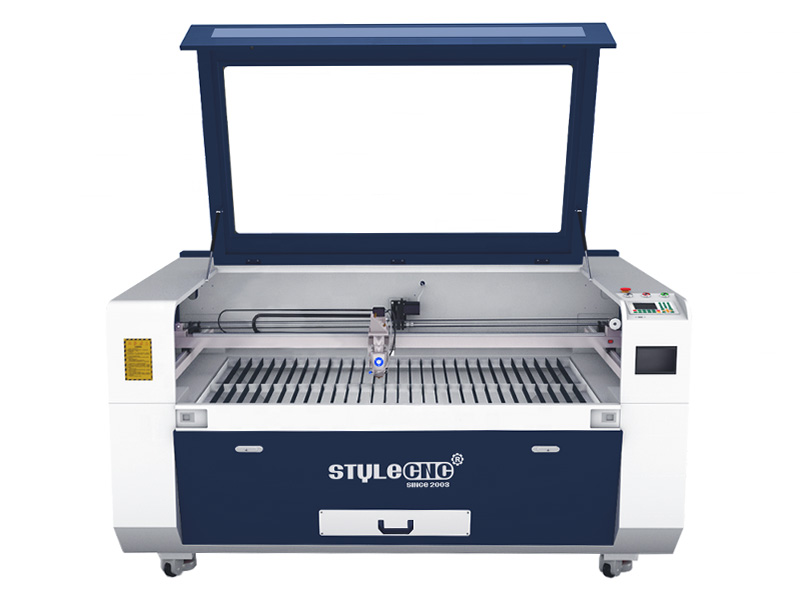
Understanding co2 laser cutter metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard CO2 Laser Cutters | Versatile, suitable for various materials, typically 30-120W | Signage, crafting, prototyping | Pros: Affordable, easy to use. Cons: Limited metal cutting capability compared to fiber lasers. |
| High-Power CO2 Laser Cutters | Higher wattage (150W+), capable of cutting thicker metals | Industrial applications, heavy fabrication | Pros: Cuts through thicker materials. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Hybrid CO2 Laser Systems | Combines CO2 and fiber laser technology for versatility | Multi-material processing | Pros: Can handle a wide range of materials effectively. Cons: More complex setup and maintenance. |
| Desktop CO2 Laser Cutters | Compact size, user-friendly interface, lower power (up to 55W) | Small-scale businesses, hobbyists | Pros: Space-efficient, affordable. Cons: Limited to thinner materials. |
| Enclosed CO2 Laser Cutters | Safety features, enclosed design to reduce hazards | Educational institutions, small workshops | Pros: Enhanced safety, quieter operation. Cons: Generally more expensive than open models. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Standard CO2 Laser Cutters?
Standard CO2 laser cutters are known for their versatility and ability to handle a variety of materials, including wood, acrylic, and some metals. Typically ranging from 30 to 120 watts, they are ideal for signage, crafting, and prototyping. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the wattage needed for their specific applications, as this will affect cutting speed and material thickness capabilities. Additionally, the affordability of these machines makes them a popular choice for businesses just starting in laser cutting.
How Do High-Power CO2 Laser Cutters Differ From Standard Models?
High-power CO2 laser cutters, often exceeding 150 watts, are designed for industrial applications where thicker materials are involved. These machines excel in heavy fabrication settings, making them suitable for industries such as automotive and aerospace. Buyers should consider the initial investment required for high-power models, as they offer greater cutting capabilities but come with a higher price tag. This type of cutter is ideal for businesses that require robust performance and durability.
What Advantages Do Hybrid CO2 Laser Systems Offer?
Hybrid CO2 laser systems integrate both CO2 and fiber laser technologies, allowing for a broader range of material processing capabilities. These systems are particularly advantageous for businesses that need to work with multiple materials, from metals to plastics. While they offer versatility, buyers should be aware that the complexity of these systems may require additional training for effective operation and maintenance. This investment can be justified for companies looking to streamline production processes across diverse materials.
What Are the Benefits of Desktop CO2 Laser Cutters?
Desktop CO2 laser cutters are compact and user-friendly, making them suitable for small-scale businesses and hobbyists. With power outputs typically up to 55 watts, they are perfect for cutting thinner materials. Buyers should consider their workspace limitations and budget, as these machines are generally more affordable and space-efficient. However, the limited cutting capacity may restrict their use in larger industrial applications, making them best suited for smaller projects.
How Do Enclosed CO2 Laser Cutters Enhance Safety?
Enclosed CO2 laser cutters feature a protective design that minimizes hazards, making them ideal for educational institutions and small workshops. These machines often come equipped with advanced safety features, reducing the risk of accidents during operation. While the added safety measures may lead to a higher price, the peace of mind they provide can be invaluable for businesses prioritizing worker safety. Buyers should assess their specific safety needs and the potential benefits of investing in enclosed systems.
Key Industrial Applications of co2 laser cutter metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CO2 Laser Cutter Metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Precision cutting of metal components for vehicles | Enhanced accuracy and reduced waste in production processes | Supplier reliability, machine power, and cutting speed capabilities |
| Aerospace Engineering | Fabrication of intricate metal parts for aircraft | Improved safety and performance through precise component design | Compliance with industry standards, machine versatility |
| Electronics Industry | Cutting and engraving of metal housings and components | Streamlined production and enhanced product aesthetics | Material compatibility, customization options |
| Metal Fabrication | Custom signage and metal art creation | Unique branding opportunities and increased customer engagement | Design flexibility, machine size, and material thickness capabilities |
| Construction | Manufacturing of metal frameworks and support structures | Cost-effective solutions with high durability | Structural integrity, machine precision, and after-sales support |
How is CO2 Laser Cutter Metal Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, CO2 laser cutters are employed for precision cutting of metal components such as brackets, frames, and panels. This technology allows manufacturers to achieve intricate designs while minimizing waste and maximizing material efficiency. For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America, sourcing machines that can accommodate various metal thicknesses and ensure high-speed cutting is crucial for meeting production demands.
What Role Does CO2 Laser Cutting Play in Aerospace Engineering?
Aerospace engineering utilizes CO2 laser cutters for fabricating complex metal parts that require high precision, such as turbine blades and structural components. The accuracy of laser cutting enhances the safety and performance of aircraft. Buyers in Europe, especially in countries like Germany, must consider machines that comply with stringent aviation industry standards, ensuring reliability and durability in high-stakes applications.
How Does CO2 Laser Cutting Benefit the Electronics Industry?
In the electronics industry, CO2 laser cutters are vital for producing metal housings and components that require detailed engravings and precise cuts. This technology enables manufacturers to streamline production while enhancing the aesthetic appeal of their products. International buyers should focus on sourcing machines that support a range of materials and thicknesses, as well as those that offer customization capabilities to meet specific design needs.
What Are the Applications of CO2 Laser Cutters in Metal Fabrication?
Metal fabrication companies leverage CO2 laser cutters to create custom signage and intricate metal art. This application not only allows for unique branding opportunities but also fosters customer engagement through personalized designs. For businesses in regions like the Middle East, sourcing laser cutters that provide flexibility in design and the ability to work with various metal types can significantly enhance their service offerings.
How is CO2 Laser Cutting Used in Construction?
In the construction industry, CO2 laser cutters are used to manufacture metal frameworks and support structures. This method ensures cost-effective solutions with high durability, essential for building integrity. Buyers, particularly in developing regions, should prioritize machines that provide precision cutting capabilities and robust after-sales support to maintain operational efficiency in demanding environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘co2 laser cutter metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Initial Investment Costs for CO2 Laser Cutters
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant initial investment costs when acquiring CO2 laser cutters for metal applications. The high price tag associated with advanced laser cutting technology can be daunting, especially for small to medium enterprises (SMEs) operating in regions with limited budgets, such as parts of Africa and South America. Buyers may struggle with justifying the expense when weighing it against potential returns, leading to hesitation in making a purchasing decision. Additionally, concerns about ongoing maintenance costs and the need for skilled personnel to operate these machines can further complicate the decision-making process.
The Solution:
To navigate these financial hurdles, B2B buyers should consider a phased investment approach. Begin by thoroughly assessing the specific cutting needs and anticipated production volumes to select a CO2 laser cutter that matches those requirements without overspending. Many manufacturers offer financing options or leasing agreements that can spread out the cost over time, making the initial investment more manageable. Furthermore, buyers can explore second-hand or refurbished machines, which often come at a fraction of the cost but still provide reliable performance. Conducting a detailed ROI analysis can also help in illustrating the long-term savings and productivity gains associated with the investment, thereby justifying the upfront costs.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Achieving Precision Cutting on Different Metals
The Problem:
Precision is paramount in metal fabrication, and many B2B buyers encounter challenges in achieving the desired cutting quality across various types of metals using CO2 laser cutters. For example, materials like stainless steel and aluminum require different settings to avoid issues such as excessive heat, warping, or incomplete cuts. Buyers may feel frustrated when their machines underperform, leading to wasted materials and increased production times, which can ultimately impact their competitiveness in the market.
The Solution:
To enhance cutting precision, buyers should invest time in understanding the technical specifications and operational parameters of their CO2 laser cutter. This includes familiarizing themselves with the recommended settings for different metals, such as power levels, speed, and focus adjustments. Manufacturers often provide detailed user manuals or online resources that outline optimal settings for various materials. Additionally, utilizing software that allows for real-time adjustments during cutting can help achieve better results. Conducting test cuts on scrap material before commencing full production runs can also help in fine-tuning the settings, thus ensuring high-quality outcomes and minimizing material waste.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Maintenance and Downtime of CO2 Laser Cutters
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face unexpected downtime due to maintenance issues with their CO2 laser cutters. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance, but many operators may not have the expertise or resources to conduct thorough upkeep. This can lead to prolonged downtimes, affecting production schedules and customer delivery commitments. Additionally, the lack of accessible support and replacement parts can exacerbate these challenges, particularly in regions where such resources are scarce.
The Solution:
To mitigate maintenance-related issues, businesses should establish a comprehensive maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations. This includes routine inspections, cleaning, and timely replacement of wear parts to prevent larger issues from arising. Buyers should also consider investing in training programs for their operators to empower them with the necessary skills to perform basic maintenance tasks. Partnering with reliable suppliers who can offer timely support and readily available replacement parts is essential to minimize downtimes. Furthermore, investing in a service contract with a reputable provider can ensure that professional assistance is available when needed, helping to keep the production running smoothly.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for co2 laser cutter metal
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for CO2 Laser Cutting Metal?
When selecting materials for CO2 laser cutting in a B2B context, it is essential to consider the properties that influence performance, durability, and application suitability. Below are analyses of four common materials used in CO2 laser cutting metal applications.
How Does Steel Perform in CO2 Laser Cutting Applications?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in industrial applications due to its strength and versatility. Key properties include high tensile strength and resistance to deformation under pressure. However, its performance can vary based on the type of steel, such as carbon steel or stainless steel.
Pros: Steel offers excellent durability and is relatively cost-effective, making it suitable for a wide range of applications from structural components to intricate designs.
Cons: The main drawback is its susceptibility to rust and corrosion, especially in humid environments, which can lead to increased maintenance costs. Additionally, cutting thicker sections may require higher power settings, which can increase operational costs.
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum in CO2 Laser Cutting?
Aluminum is known for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making it a popular choice for various applications, including automotive and aerospace industries. It has a lower melting point compared to steel, which allows for faster cutting speeds.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it easier to handle and transport. It also offers excellent corrosion resistance, which is beneficial for applications exposed to moisture.
Cons: The primary limitation is its cost, which can be higher than that of steel. Additionally, its thermal conductivity can lead to issues with heat dissipation during cutting, requiring careful management to avoid warping.
Why Is Copper a Challenging Material for CO2 Laser Cutting?
Copper is valued for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it a preferred choice in electrical applications. However, its properties pose unique challenges during laser cutting.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity allows for efficient energy transfer, making it ideal for electrical components. It also has good corrosion resistance.
Cons: The main disadvantage is its high reflectivity, which can lead to energy loss during the cutting process. This necessitates specialized laser settings and equipment, increasing complexity and cost.
How Does Brass Compare in CO2 Laser Cutting?
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, combines the properties of both metals. It is often used in decorative applications due to its attractive appearance and good machinability.
Pros: Brass offers excellent corrosion resistance and can be easily machined, making it suitable for intricate designs and detailed work.
Cons: The cost of brass is generally higher than that of steel and aluminum. Additionally, its cutting process can produce toxic fumes, requiring adequate ventilation and safety measures.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
When sourcing materials for CO2 laser cutting, international buyers must consider compliance with local and international standards such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS. For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional preferences and material availability is crucial. Factors like import tariffs, shipping logistics, and local regulations can significantly impact the overall cost and feasibility of material selection.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CO2 Laser Cutting
| Material | Typical Use Case for CO2 Laser Cutter Metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components, automotive parts | Excellent durability | Susceptible to rust and corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, thermal conductivity issues | High |
| Copper | Electrical components, heat exchangers | High conductivity | Reflective nature complicates cutting | High |
| Brass | Decorative items, precision instruments | Attractive appearance, good machinability | Higher cost, toxic fumes during cutting | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for CO2 laser cutting, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for co2 laser cutter metal
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of CO2 Laser Cutters for Metal?
The manufacturing of CO2 laser cutters for metal involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent performance and quality standards.
Material Preparation: Selecting the Right Components
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality materials, such as steel for the chassis, aluminum for the frame, and specialized optics for the laser system. Suppliers should prioritize materials that comply with international standards, such as ASTM or ISO specifications. Additionally, proper documentation of material certifications is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure that they are receiving components that meet the necessary quality benchmarks.
Forming: Precision Engineering Techniques
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming, which typically employs advanced engineering techniques like CNC machining, laser cutting, and bending. These techniques are essential for creating precise components that fit together seamlessly. For example, CNC machining allows for high-accuracy parts that are critical for the laser cutter’s operational efficiency. B2B buyers should inquire about the machinery and technology used in this stage, as this directly impacts the performance of the final product.
Assembly: Integrating Components
The assembly stage is where the various components come together. This process often involves both manual labor and automated systems. Skilled technicians assemble the laser cutter, ensuring that each part is correctly fitted and aligned. Quality assurance during assembly is vital; manufacturers often implement in-process quality control (IPQC) measures to monitor assembly quality in real-time. Buyers should seek assurance that the assembly process adheres to documented procedures to minimize risks of defects.
Finishing: Quality Surface Treatments
After assembly, the finishing stage applies surface treatments such as powder coating or anodizing to enhance durability and aesthetics. These treatments are essential for protecting the metal from corrosion and wear, especially in demanding environments. B2B buyers should verify that the finishing processes comply with relevant international standards, as this can significantly affect the longevity of the equipment.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in CO2 Laser Cutter Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of the manufacturing process for CO2 laser cutters, ensuring that each unit meets the necessary operational and safety standards.
What International Standards Are Relevant for CO2 Laser Cutters?
Manufacturers typically adhere to several international standards, including ISO 9001 for quality management systems and CE marking for compliance with European safety standards. For specific industry applications, adherence to API standards may also be relevant. B2B buyers should request documentation demonstrating compliance with these standards, as they serve as a reliable benchmark for product quality.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control is integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process, primarily through the following checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival. The objective is to ensure that all incoming materials meet predefined specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the assembly and forming stages, manufacturers conduct regular checks to ensure adherence to quality standards. These checks can include visual inspections and measurements to verify that components meet design specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the final product undergoes comprehensive testing, including functional and safety tests. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the laser cutter operates as intended before it is shipped to customers.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in the Quality Assurance Process?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure that CO2 laser cutters function correctly and safely:
-
Functional Testing: This involves operating the laser cutter to verify that all components, including the laser system and control software, work seamlessly together.
-
Safety Testing: Safety features, including emergency stops and protective enclosures, are tested to ensure compliance with safety standards.
-
Performance Testing: This includes assessing cutting speed, precision, and quality of the finished cuts. Manufacturers may conduct tests on various materials to ensure versatility.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing methods used and request access to test reports as part of their supplier evaluation.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures:
What Steps Can Be Taken to Conduct Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess quality control practices. Buyers should develop a checklist based on international standards and industry best practices. During the audit, it is essential to review documentation for all quality control checkpoints and processes, from material sourcing to final testing.
How Important Are Quality Control Reports?
Requesting quality control reports is critical for understanding how a supplier maintains standards. These reports should detail results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. Buyers should look for trends in defect rates and any corrective actions taken to improve processes.
Should Third-Party Inspections Be Considered?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. Independent auditors can verify compliance with international standards and identify any potential risks in the manufacturing process. This is particularly valuable for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where local regulations and standards may differ from those in Europe.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various nuances in quality control and certification processes. Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements that affect product compliance. For example, buyers in Europe may need to consider additional certifications beyond CE marking, such as RoHS or WEEE compliance, particularly if the equipment is intended for environmentally sensitive applications.
Understanding these regional differences is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure that the products they purchase not only meet their operational needs but also comply with local regulations and standards.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for CO2 laser cutters is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on key stages, relevant standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that will lead to successful procurement and long-term satisfaction with their investment.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘co2 laser cutter metal’
The following practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring CO2 laser cutters for metal applications. This checklist provides actionable steps to ensure you make an informed purchasing decision, maximizing both performance and value.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before diving into the market, clarify your specific requirements for the CO2 laser cutter. Consider the types of metals you plan to cut, the thickness of the materials, and the desired precision levels.
– Power and Speed: Higher wattage machines can cut through thicker materials more efficiently.
– Working Area: Ensure the machine’s dimensions fit your operational space and project needs.
Step 2: Research Available Brands and Models
Investigate various manufacturers and their product offerings. This step is crucial to understand the range of technologies available and to identify which brands are reputable in your industry.
– Market Presence: Look for brands with a proven track record and positive customer reviews.
– Product Features: Compare features such as cutting speed, software compatibility, and additional functionalities like engraving.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, it’s vital to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Industry Experience: Choose suppliers who specialize in CO2 laser technology and have experience in your sector.
– Customer Support: Assess the level of technical support and training they provide post-purchase.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your potential suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This step can mitigate risks associated with quality and safety.
– ISO Certifications: Look for ISO 9001 for quality management systems or other relevant certifications.
– Safety Standards: Verify compliance with local and international safety regulations to ensure operational safety.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Samples
Before finalizing your decision, ask for product demonstrations or sample cuts. This firsthand experience can significantly influence your purchasing choice.
– Performance Evaluation: Evaluate the machine’s speed, precision, and ease of use during the demo.
– Material Compatibility: Confirm that the machine can handle the specific metal types and thicknesses you require.
Step 6: Consider Financing and Warranty Options
Investigate financing arrangements and warranty provisions offered by the supplier. This can impact your overall cost and long-term satisfaction with the machine.
– Flexible Financing: Look for options that suit your budget and cash flow, especially for high-value equipment.
– Warranty Coverage: A comprehensive warranty can protect your investment and provide peace of mind regarding potential repairs or replacements.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Review Terms
Once you have selected the right supplier and machine, finalize your order by reviewing all terms and conditions.
– Shipping and Delivery: Confirm shipping times and any additional costs associated with delivery.
– Installation and Training: Ensure that installation services and training are included in your agreement to facilitate a smooth setup process.
Following this checklist will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing a CO2 laser cutter for metal applications, ensuring a strategic investment that meets your business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for co2 laser cutter metal Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for CO2 Laser Cutter Metal Sourcing?
When sourcing CO2 laser cutters for metal applications, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, including the laser tube, lenses, and various electronic components, significantly influences the overall price. Higher quality materials typically lead to improved performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both manufacturing and assembly processes. Skilled technicians are required to ensure precision and quality, which can vary significantly by region.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Factories with advanced technology may incur higher overhead but can also yield better efficiency and product quality.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specific applications, adding to the initial investment. The complexity and precision required can lead to variable costs based on the buyer’s specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that each unit meets industry standards. This involves testing and certifications that can add to the overall cost but are vital for ensuring product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on the location of the supplier and the buyer. International shipping can introduce additional complexities such as customs duties and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up costs to achieve a profit margin. Understanding this can help buyers negotiate more effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CO2 Laser Cutter Metal Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of CO2 laser cutters, especially for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to optimize order sizes.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features can significantly increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of materials impacts both performance and price. Premium materials may offer better durability but come at a higher initial cost.
-
Quality and Certifications: Equipment that meets international standards or comes with certifications can command higher prices, reflecting reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, location, and service offerings play crucial roles in pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their brand and support services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (like FOB, CIF, etc.) is crucial. These terms determine who bears the shipping costs and risks, influencing the total landed cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize CO2 Laser Cutter Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for bulk orders. Leveraging competition among suppliers can also yield better deals.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess not just the initial purchase price but also operational costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A lower initial price may not result in the best long-term value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import taxes, and additional fees that can impact the final cost. Understanding local market conditions can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Compare prices and specifications across multiple suppliers. This research can help identify competitive offers and ensure that you are not overpaying.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for CO2 laser cutters can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. The figures mentioned in product listings are subject to change and should be considered as indicative rather than fixed. Buyers are encouraged to obtain quotes tailored to their specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing co2 laser cutter metal With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to CO2 Laser Cutters for Metal Processing
As industries evolve, the demand for efficient, precise, and versatile metal cutting solutions grows. While CO2 laser cutters are widely recognized for their capabilities, several alternative technologies offer competitive advantages depending on specific operational needs. This analysis compares CO2 laser cutters against fiber laser cutting and plasma cutting, providing insights into their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| Comparison Aspect | CO2 Laser Cutter Metal | Fiber Laser Cutter | Plasma Cutter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, ideal for thin materials | Excellent for thicker metals, fast cutting speeds | Suitable for thick materials, but less precise |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; consumables needed | Higher initial cost, lower operating costs | Lower upfront cost, high operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; setup can be complex | Easier to set up and operate; less training needed | Simple setup; requires basic technical knowledge |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; lens cleaning | Lower maintenance; more robust components | Frequent maintenance; consumables need regular replacement |
| Best Use Case | Intricate designs and detailed cuts on non-ferrous metals | High-volume production of thicker metals | Heavy-duty applications and outdoor work |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Fiber Laser Cutters?
Fiber laser cutters utilize solid-state technology, which allows them to cut through thicker materials quickly and efficiently. Their high cutting speeds and lower operating costs make them ideal for high-volume production environments. However, the initial investment can be significantly higher than that of CO2 lasers, which may deter smaller businesses or those with limited budgets. Additionally, while fiber lasers excel with thicker metals, they may not offer the same precision for intricate designs as CO2 lasers.
How Do Plasma Cutters Compare in Metal Cutting Applications?
Plasma cutters are known for their affordability and ease of use, making them a popular choice for many industries. They are particularly effective for cutting thicker metals, which is advantageous in construction and heavy manufacturing settings. However, plasma cutting can lack the precision of laser methods, potentially leading to rougher edges that require additional finishing work. Moreover, the operational costs can add up due to frequent replacement of consumables like electrodes and nozzles.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Metal Cutting Solution?
When selecting the appropriate metal cutting technology, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the types of materials they work with, production volume, and budget constraints. For companies focusing on intricate designs or non-ferrous metals, CO2 laser cutters may be the best option. Conversely, for those needing to cut thicker materials in high volumes, fiber lasers could provide better efficiency and cost-effectiveness over time. Plasma cutters may serve businesses looking for a low-cost entry point, though they may require additional finishing processes to achieve desired precision.
In summary, understanding the specific needs of your operation will guide you in making an informed decision about the most suitable cutting technology. Each method has its unique advantages, and aligning those with your business goals will maximize operational efficiency and product quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for co2 laser cutter metal
When exploring the world of CO2 laser cutters for metal, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This section will provide clarity on critical specifications and commonly used terms, empowering international B2B buyers to navigate their procurement processes effectively.
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of CO2 Laser Cutters for Metal?
-
Laser Power (Wattage)
The wattage of a CO2 laser cutter directly influences its cutting ability. Common wattages range from 40W to over 100W. Higher wattage allows for cutting thicker materials and achieving faster processing speeds. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate wattage is vital to meet production demands and ensure operational efficiency. -
Working Area Dimensions
This specification defines the maximum size of materials that can be processed. For instance, a working area of 600mm x 400mm may suffice for small to medium projects, while larger operations may require dimensions exceeding 1200mm x 800mm. Understanding working area requirements helps buyers evaluate whether the equipment will fit their production workflow. -
Material Compatibility
CO2 laser cutters can typically process a wide variety of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, acrylic, and wood. Each material may require different settings for optimal results. Buyers should assess their specific material needs to ensure the chosen cutter can handle all required applications. -
Cutting Speed
Measured in millimeters per second (mm/s), cutting speed indicates how quickly the laser can cut through material. Higher speeds lead to increased productivity but may compromise cut quality. It is essential for B2B buyers to find a balance between speed and quality based on their operational needs. -
Tolerance and Precision
This refers to the accuracy of the cutting process, typically measured in microns. Higher precision is critical in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where exact specifications are mandatory. Buyers should look for machines that can maintain consistent tolerances to ensure product integrity. -
Cooling System
A robust cooling system is necessary to maintain optimal laser performance and prevent overheating. CO2 laser cutters may use air-cooled or water-cooled systems. Understanding the cooling requirements helps buyers assess maintenance needs and operational costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the CO2 Laser Cutter Industry?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CO2 laser cutters, buyers may deal with OEMs when sourcing components or entire machines. Understanding OEM relationships can help in negotiating better pricing and warranty terms. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important for B2B buyers looking to maintain inventory levels without overcommitting capital. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning procurement strategies effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing for specific quantities and types of products. This process is crucial for obtaining competitive pricing and ensuring that suppliers understand the buyer’s requirements. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand their obligations regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is vital for buyers to manage their production schedules and inventory effectively. -
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
An SLA is a commitment between a service provider and a client that outlines the expected level of service, including response times for support and maintenance. Buyers should negotiate SLAs to ensure they receive the necessary support for their laser cutting operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting CO2 laser cutters for metal applications, ultimately leading to enhanced productivity and operational success.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the co2 laser cutter metal Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in CO2 Laser Cutters for Metal?
The global market for CO2 laser cutters, particularly for metal applications, is witnessing robust growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand across various sectors. As industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing expand, the need for precise and efficient cutting solutions has surged. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking laser cutting technologies that offer speed, accuracy, and versatility. Emerging trends include the integration of artificial intelligence and automation, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing labor costs. Additionally, desktop models, like the xTool P2S, are gaining popularity due to their compact design and user-friendly interfaces, making advanced laser cutting accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises.
Furthermore, the demand for customized solutions is on the rise. Buyers are looking for machines that can handle a variety of materials and thicknesses, with features such as batch processing capabilities and optimized airflow for cleaner operations. The competitive landscape is also evolving, with manufacturers focusing on providing comprehensive support services, including training and maintenance, to build long-term relationships with customers. As the market continues to mature, international buyers must stay informed about technological advancements and sourcing strategies that can enhance their operational capabilities.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of CO2 Laser Cutters for Metal?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the CO2 laser cutter sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the sourcing of materials are under increasing scrutiny. Ethical sourcing has emerged as a key priority, with businesses seeking suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes that minimize waste and energy consumption. Buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers who can provide certifications that demonstrate their commitment to environmental standards, such as ISO 14001 or similar ‘green’ credentials.
Moreover, many companies are now focusing on lifecycle assessments of their products, evaluating not only the manufacturing phase but also the end-of-life disposal or recycling of equipment. This shift towards a circular economy is influencing purchasing decisions, as businesses aim to align their operations with sustainability goals. By prioritizing suppliers who implement sustainable practices, international buyers can not only reduce their environmental footprint but also enhance their brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What Is the Historical Context of CO2 Laser Cutters in Metal Processing?
The evolution of CO2 laser cutters can be traced back to the 1960s when the first laser was developed. Initial applications were primarily in scientific research, but by the 1980s, the technology began to gain traction in industrial settings, particularly for cutting and engraving materials. The introduction of CO2 lasers marked a significant advancement in the precision and efficiency of metal processing, allowing for intricate designs and high-speed cutting capabilities.
Over the years, technological improvements have led to more compact and user-friendly machines, making laser cutting accessible to a broader range of industries. The integration of computer numerical control (CNC) technology has further enhanced the capabilities of CO2 laser cutters, allowing for greater automation and flexibility in manufacturing processes. Today, CO2 laser cutters are indispensable tools in metal fabrication, enabling businesses to meet the demands of modern production while maintaining high standards of quality and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of co2 laser cutter metal
-
How do I choose the right CO2 laser cutter for my metal fabrication needs?
Selecting the appropriate CO2 laser cutter involves evaluating several factors, including the type of metal you plan to cut, the thickness of the material, and the desired cutting speed and precision. It’s essential to consider the power rating of the machine, typically ranging from 40W to over 100W, which directly affects its cutting capacity. Additionally, assess the working area size, compatibility with various materials, and available accessories that enhance functionality. Consulting with suppliers who can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific requirements is also advisable. -
What are the key features to look for in a CO2 laser cutter for metal?
When sourcing a CO2 laser cutter for metal, prioritize features such as adjustable cutting speed, precision control, and the ability to handle various metal types (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum). Look for machines equipped with advanced cooling systems to prevent overheating during prolonged use, as well as user-friendly interfaces for easier operation. Safety features, such as automatic shut-off and air filtration systems, are crucial for maintaining a safe working environment. Lastly, check for compatibility with design software to streamline your workflow. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a CO2 laser cutter?
Payment terms for CO2 laser cutters can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, you may encounter options such as full payment upfront, a deposit followed by balance payment upon delivery, or installment plans. International buyers should also consider the implications of exchange rates and transaction fees. Ensure to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, credit card, escrow services) and inquire about any financing options that may be available, especially if you’re making a large investment. -
How do I vet suppliers when sourcing CO2 laser cutters internationally?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation through online reviews and testimonials. Request references from previous clients to understand their experiences. Verify the supplier’s certifications and compliance with international standards. Additionally, assess their production capabilities, quality control processes, and after-sales support. Engaging in direct communication can provide insights into their responsiveness and reliability, ensuring you choose a trustworthy partner for your procurement needs. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CO2 laser cutters?
Minimum order quantities for CO2 laser cutters can vary widely based on the manufacturer and the specific model. Some suppliers may have a MOQ of one unit, especially for standard models, while others may require larger orders to justify production costs. Always inquire about MOQs when discussing pricing and production timelines. If you are a small business or just starting, look for suppliers who are open to smaller orders or offer leasing options to minimize upfront costs. -
What kind of warranty and support can I expect with a CO2 laser cutter purchase?
Warranties for CO2 laser cutters typically range from one to three years, covering parts and labor for manufacturing defects. Ensure to clarify what is included in the warranty, such as specific components like the laser tube or electronics. Additionally, inquire about the availability of technical support, training, and maintenance services. A reliable supplier should offer comprehensive support, including online resources, troubleshooting assistance, and access to replacement parts to ensure your machine operates optimally. -
How does shipping logistics work for CO2 laser cutter imports?
Shipping logistics for importing CO2 laser cutters generally involve coordination between the buyer and the supplier regarding freight options, delivery timelines, and customs clearance. Depending on the size and weight of the machine, you may choose air or sea freight, with air being faster but more expensive. Ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation, such as invoices and shipping labels, for customs. It’s advisable to work with a freight forwarder who can navigate international shipping regulations and help minimize potential delays. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in CO2 laser cutters?
Quality assurance in CO2 laser cutters should encompass both manufacturing and operational standards. Look for suppliers who adhere to internationally recognized quality certifications, such as ISO 9001. Request information about their testing procedures, including performance testing and safety checks before shipment. Additionally, inquire about the materials used in production and the robustness of the components, as these factors significantly impact the machine’s durability and performance in a production environment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Co2 Laser Cutter Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. OMTech – CO2 and Fiber Laser Cutters
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: CO2 Laser Cutters and Engravers, Fiber Lasers, and More – OMTech Laser. Products include: OMTech Polar Lite 55W, OMTech Polar+ 55W, OMTech Maker 60W, OMTech Maker 90W, OMTech Maker 100W, OMTech Pronto 45 100W, OMTech Pronto 60 130W, OMTech Pronto 75 150W, OMTech Pro 2440, OMTech Pro 3655, OMTech K40+, OMTech Autofocus 30W, OMTech Autofocus 50W, OMTech Autofocus 60W, OMTech MOPA 60W, OMTech MOPA 10…
2. Kern – Metal Cutting Laser System
Domain: kernlasers.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Kern’s metal cutting laser system allows for accurate cutting of sheet metal including stainless steel, mild steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. Key features include an Automatic Focusing Height Follower for optimal cutting, a protective cover lens (K-Lens for CO2 machines and F-Lens for fiber systems), and a durable steel grid work table. The KCAM Laser Software provides advanced metal cutting fe…
3. CAMFive – Key Laser Fiber Cutters
Domain: camfivelaser.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Key products include: 1. 20 x 8 ft Fully Enclosed Pipe Cutter & Auto Sheet Exchange, 3000w to 6000w IPG CAMFive Laser Fiber Metal Cutter JET208P – $139,900.00 2. 13 x 6 ft 1000 to 6000w IPG CAMFive Laser Fiber Metal Cutter FC136A for Steels and aluminum – Special Price $69,900.00 (was $79,900.00) 3. 10 x 5 ft Fully Enclosure 1000w to 4000w IPG CAMFive Laser Fiber Metal Cutter JET105C – $75,900.00 …
4. STYLECNC – Hobby Hybrid CO2 Laser Cutter
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Hobby Hybrid CO2 Laser Cutter for Metal & Nonmetal”, “Brand”: “STYLECNC”, “Model”: “STJ1390M”, “Laser Source”: “Yongli, RECI”, “Power Options”: “80W + 150W, 180W, 220W, 300W”, “Price”: {“Standard Edition”: “$6,800”, “Pro Edition”: “$11,500”}, “Stock Availability”: “360 Units in Stock Available for Sale Every Month”, “Warranty”: “One-Year Limited Warranty for Entire Machine (Exten…
5. Esprit Automation – Fiber Laser Solutions
Domain: espritautomation.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Fiber Laser:
– Wavelength: 1.06 μm
– Best for cutting metals, especially highly reflective metals like copper and brass
– Continuous wave (CW) recommended for best cut quality and speeds
– Excellent for marking metal with fine details
– Can cut stainless steel, mild steel, coated stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass
– Not suitable for cutting non-metals like textiles, wood, stone, etc.
…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for co2 laser cutter metal
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of CO2 laser cutters for metal applications is essential for businesses aiming to enhance productivity and precision. International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must evaluate suppliers based on technological advancements, service support, and adaptability to local market needs. The versatility of CO2 laser technology, coupled with robust supplier networks, allows businesses to leverage cost-effective solutions while ensuring high-quality outputs.
Investing in high-performance CO2 laser cutters can lead to significant operational efficiencies, making it crucial for businesses to prioritize long-term partnerships with reliable manufacturers. By sourcing strategically, companies can not only reduce costs but also stay ahead of industry trends, ensuring they meet the diverse demands of their clientele.
Looking ahead, the market for CO2 laser cutters is poised for growth, driven by innovations in automation and material processing. International buyers are encouraged to explore opportunities that align with their specific needs and to engage with suppliers who are committed to providing exceptional support and cutting-edge technology. Embrace the future of manufacturing by making informed sourcing decisions today.