Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc skills
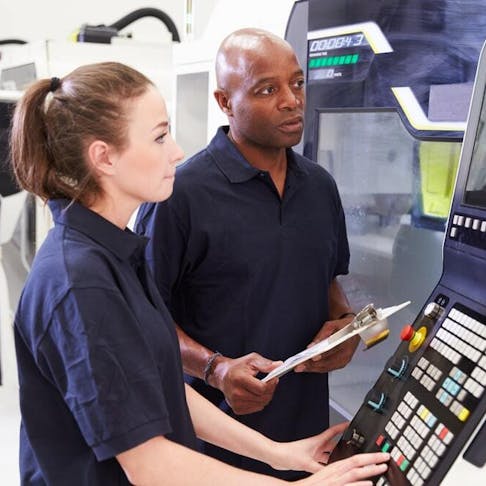
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing skilled CNC operators presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The rapid advancement of technology has transformed CNC machining into a highly specialized field, making it essential for businesses to not only understand the critical CNC skills required but also to identify qualified suppliers who can meet their unique needs. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the various types of CNC skills, their applications across diverse industries, and strategic approaches for vetting suppliers effectively.
Through a detailed analysis of essential skills—such as attention to detail, practical engineering knowledge, and problem-solving capabilities—this resource equips buyers with the insights necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, it delves into cost considerations, providing a framework for assessing the value of CNC expertise against budgetary constraints. By leveraging the information contained within this guide, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing CNC talent, ensuring they align with reputable suppliers who can deliver precision and quality in their machining projects. Empower your business with the knowledge to secure the right CNC skills, enhancing productivity and competitiveness in a global marketplace.
Understanding cnc skills Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Programming Skills | Proficiency in G-code and CAM software; ability to optimize machining processes. | Aerospace, automotive, and precision engineering | Pros: Enhances efficiency and reduces errors. Cons: Requires ongoing training and updates. |
| Technical Drawing Interpretation | Ability to read and visualize 2D and 3D designs; critical for setup. | Manufacturing and prototype development | Pros: Ensures accuracy in production. Cons: Misinterpretation can lead to costly errors. |
| Quality Control Skills | Focus on inspection and compliance with industry standards; familiarity with measurement tools. | Aerospace, medical devices, and automotive | Pros: Guarantees product reliability and safety. Cons: Can slow down production if not streamlined. |
| Mechanical Aptitude | Understanding of machine mechanics; hands-on experience with CNC equipment. | General manufacturing and custom fabrication | Pros: Facilitates maintenance and troubleshooting. Cons: May require specialized training for advanced machines. |
| Problem-Solving Skills | Ability to quickly identify issues and implement solutions; adaptive thinking. | All sectors utilizing CNC machinery | Pros: Reduces downtime and enhances productivity. Cons: Dependence on individual skills can be a risk. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of CNC Programming Skills?
CNC programming skills are essential for creating efficient and precise machining processes. Operators proficient in G-code and CAM software can optimize tool paths, minimize cycle times, and enhance overall productivity. These skills are particularly crucial in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is paramount. When considering suppliers or partners, businesses should evaluate the programming capabilities of their CNC machinists, as this directly impacts production efficiency and product quality.
How Important Is Technical Drawing Interpretation in CNC Machining?
The ability to interpret technical drawings is a foundational skill for CNC machinists. This includes understanding both 2D and 3D designs, which are vital for accurate setup and machining. Misinterpretation can lead to significant production errors, making this skill critical in manufacturing and prototype development. Buyers should prioritize CNC service providers who demonstrate strong capabilities in reading and executing technical drawings to ensure high-quality output.
Why Is Quality Control Skills Essential for CNC Operations?
Quality control skills are vital for ensuring that finished products meet stringent industry standards. CNC operators must inspect parts throughout the manufacturing process and utilize various measurement tools to guarantee compliance. This is particularly important in sectors such as aerospace and medical devices, where product failure can have severe consequences. Buyers should look for CNC partners with robust quality control protocols to mitigate risks associated with product defects.
What Role Does Mechanical Aptitude Play in CNC Machining?
Mechanical aptitude encompasses a machinist’s understanding of how CNC machines operate, including the ability to perform maintenance and troubleshoot issues. This skill is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring efficient operations in general manufacturing and custom fabrication. Buyers should assess the mechanical competencies of CNC operators, as those with strong hands-on experience can better handle unexpected challenges and maintain productivity.
How Do Problem-Solving Skills Impact CNC Machining Efficiency?
Problem-solving skills are essential in the fast-paced environment of CNC machining. Operators must quickly identify and address issues that arise during production, which can significantly affect timelines and costs. Industries that rely on CNC machining benefit from operators who can think on their feet and implement effective solutions. When selecting CNC service providers, businesses should consider the problem-solving capabilities of the workforce, as this directly influences operational efficiency and reliability.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc skills
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Skills | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | High-quality, lightweight parts that meet stringent safety regulations | Compliance with industry standards, advanced materials, and tooling capabilities |
| Automotive | Custom tooling and prototype development | Reduced lead times and enhanced product innovation | Supplier reliability, experience with complex geometries, and rapid prototyping capabilities |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments and implants | Precision and biocompatibility, ensuring patient safety | Regulatory compliance, material certifications, and quality assurance processes |
| Electronics | Production of enclosures and circuit boards | Cost-effective mass production with high precision | Scalability, integration with assembly processes, and technology updates |
| Energy | Manufacturing components for renewable energy systems | Efficiency improvements and reduced operational costs | Technical expertise in diverse materials and adaptability to evolving technologies |
How Are CNC Skills Applied in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, CNC skills are crucial for manufacturing precision components such as turbine blades, brackets, and housings. The application of CNC machining ensures that parts are produced to exact specifications, which is vital for safety and performance. International buyers, especially in regions like Africa and Europe, must consider suppliers that comply with stringent aerospace standards, possess advanced tooling capabilities, and demonstrate a track record of producing lightweight materials that meet rigorous performance criteria.
What Role Do CNC Skills Play in Automotive Custom Tooling?
CNC machining is integral to the automotive sector, particularly for custom tooling and prototype development. By leveraging CNC skills, manufacturers can significantly reduce lead times while maintaining high-quality standards. Buyers in South America and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing from suppliers with experience in complex geometries and rapid prototyping capabilities. This ensures that they can innovate efficiently and keep pace with market demands, ultimately enhancing their competitive edge.
Why Are CNC Skills Essential in Medical Device Fabrication?
In the medical device industry, CNC skills are indispensable for fabricating surgical instruments and implants that require exceptional precision and reliability. The ability to create components that are not only accurate but also biocompatible is critical for patient safety. B2B buyers from Europe and Africa must focus on sourcing suppliers who adhere to strict regulatory compliance and possess robust quality assurance processes, as these factors directly impact the efficacy and safety of medical products.
How Do CNC Skills Enhance Electronics Production?
CNC machining is widely used in the electronics industry for producing enclosures and circuit boards with high precision. This technology allows for cost-effective mass production while ensuring that components meet tight tolerances. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should seek suppliers who offer scalability and can integrate CNC processes with assembly lines. Keeping abreast of technological updates is also essential for maintaining a competitive advantage in this fast-paced sector.
What Benefits Do CNC Skills Provide in Energy Sector Manufacturing?
In the energy sector, particularly within renewable energy, CNC skills are applied to manufacture components that enhance system efficiency, such as turbine parts and structural components. The precise fabrication of these parts contributes to reduced operational costs and improved energy output. International buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and South America, should evaluate suppliers based on their technical expertise with diverse materials and their adaptability to evolving technologies, ensuring alignment with sustainability goals and performance standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc skills’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Finding Skilled CNC Machinists
The Problem: In many regions, especially in developing markets across Africa and South America, there is a significant shortage of skilled CNC machinists. B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing high-quality machining services and products, which can result in delays, increased costs, and compromised quality. This shortage often stems from a lack of training programs and educational resources in CNC skills, leaving companies struggling to fill essential roles.
The Solution: To combat this issue, companies should invest in partnerships with local vocational schools and technical colleges to create tailored training programs. These collaborations can help bridge the skill gap by providing hands-on training in CNC operations, programming, and maintenance. Additionally, companies can offer apprenticeships or internships to attract talent. By developing a robust in-house training program, organizations can cultivate a skilled workforce that meets their specific needs, ensuring a steady pipeline of qualified CNC machinists who can enhance productivity and quality in operations.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Keeping Up with Technology Advancements
The Problem: CNC machining technology is evolving rapidly, with new software and hardware innovations emerging frequently. B2B buyers often struggle to keep their teams updated on the latest CNC technologies, leading to inefficiencies and potential losses in competitiveness. This gap in knowledge can result in mismanaged projects, errors in production, and a lack of optimized processes, which can be particularly detrimental in industries that demand precision, such as aerospace and automotive.
The Solution: Companies should implement continuous learning programs to ensure that their CNC machinists stay abreast of technological advancements. This can include regular training sessions, online courses, and workshops focusing on the latest CNC software, tools, and techniques. Furthermore, investing in subscription-based platforms that offer up-to-date resources and training materials can facilitate ongoing education. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, organizations can ensure their workforce remains competitive and capable of leveraging new technologies effectively.
Scenario 3: Quality Control Issues Due to Lack of Attention to Detail
The Problem: A common issue faced by B2B buyers is the inconsistency in product quality, often stemming from a lack of attention to detail among CNC machinists. When operators fail to adhere to precise specifications, it can lead to defects in parts, rework, and increased material waste. This not only affects customer satisfaction but also escalates production costs and can damage a company’s reputation in the market.
The Solution: To mitigate quality control issues, companies should emphasize the importance of attention to detail in their training programs. Implementing standardized operating procedures (SOPs) that clearly outline the machining process can help ensure consistency. Additionally, employing advanced quality control tools, such as statistical process control (SPC) and real-time monitoring systems, can assist machinists in identifying and correcting deviations promptly. Regular feedback sessions and quality audits will reinforce a culture of precision and accountability. By prioritizing quality at every stage of the machining process, organizations can enhance their product reliability and reduce the risk of costly errors.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc skills
What Are the Key Properties of Common CNC Machining Materials?
When selecting materials for CNC machining, understanding their properties is essential for ensuring optimal product performance. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, stainless steel, plastic, and titanium, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Perform in CNC Machining?
Aluminum is widely used in CNC machining due to its excellent machinability, lightweight nature, and corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of around 150°C and is resistant to oxidation, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros: Aluminum is durable yet lightweight, which reduces shipping costs. Its low density makes it easy to machine, and it can be anodized for additional surface protection.
Cons: While aluminum is cost-effective, it may not withstand high-stress applications compared to metals like steel. Additionally, its softness can lead to wear on cutting tools.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. However, it may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should also consider local availability and pricing fluctuations.
What Are the Advantages of Using Stainless Steel in CNC Machining?
Stainless steel is known for its high strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures, with ratings often exceeding 300°C. It is commonly used in industries requiring durability, such as medical and food processing.
Pros: Stainless steel provides excellent durability and longevity, making it suitable for high-stress environments. Its resistance to corrosion ensures that products maintain their integrity over time.
Cons: The machining process for stainless steel can be more complex and costly due to its hardness, requiring specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications in the medical, aerospace, and food industries, where hygiene and strength are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN EN 10088. In Europe, for instance, adherence to these standards is often mandatory.
How Do Plastics Compare as a CNC Machining Material?
Plastics, including polycarbonate and nylon, offer versatility and are lightweight, with temperature ratings typically around 80-120°C. They are often used for prototyping and low-stress applications.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective, easy to machine, and can be produced in various colors and finishes. They also exhibit good chemical resistance.
Cons: Plastics are generally less durable than metals and may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stress, limiting their application range.
Impact on Application: Suitable for consumer products, packaging, and electronic housings, plastics can be a great choice for low-cost, high-volume production.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 is essential. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of plastic use, particularly in Europe, where regulations are tightening.
What Makes Titanium a Preferred Material for CNC Machining?
Titanium is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, with temperature ratings often exceeding 400°C. It is commonly used in aerospace and medical applications.
Pros: Titanium’s strength and lightweight nature make it ideal for high-performance applications. Its biocompatibility also makes it suitable for medical implants.
Cons: The high cost of titanium and the complexity of machining it can be significant drawbacks. Specialized tools and techniques are often required, increasing production costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium is perfect for aerospace components, medical devices, and high-performance automotive parts, where durability and weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM B348 is important. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should also consider the availability of titanium and its associated costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Skills
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc skills | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive parts | Lightweight, excellent machinability | Less durable under high stress | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing | High strength, corrosion resistant | More complex machining process | High |
| Plastic | Consumer products, prototypes | Cost-effective, versatile | Less durable, limited high-temperature use | Low |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | High strength-to-weight ratio | High cost, complex machining requirements | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for CNC machining, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc skills
What Are the Main Stages of CNC Manufacturing Processes?
CNC machining is a sophisticated process that transforms raw materials into precise components through various stages. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess suppliers’ capabilities and ensure that their products meet quality and performance standards.
How Is Material Prepared in CNC Machining?
The first stage in CNC manufacturing is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate material, which can range from metals to plastics and composites, based on the final product requirements. The chosen material is then cut into manageable sizes, often referred to as billets or blanks. Key techniques in this phase include:
- Squaring and Facing: This is essential for ensuring that the material is flat and square, providing a stable foundation for further machining.
- Surface Finishing: A smooth surface is critical for accurate machining and can be achieved through processes such as grinding or sanding before CNC operations begin.
Proper material preparation is crucial, as it lays the groundwork for the subsequent machining steps.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of CNC Machining?
The forming stage is where the actual machining occurs. CNC machines use various tools and techniques to shape the material into the desired form. Common techniques include:
- Milling: This involves using rotating cutting tools to remove material from the workpiece. It is versatile and can create complex shapes.
- Turning: This technique is used on a lathe, where the workpiece is rotated against a stationary cutting tool to produce cylindrical parts.
- Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): This method is ideal for creating intricate shapes and is often used for hard materials.
Each of these techniques requires precise programming and setup, highlighting the importance of skilled CNC machinists who can optimize the machining process for efficiency and quality.
How Is Assembly Managed in CNC Manufacturing?
In cases where multiple components are produced, assembly becomes a critical stage. Effective assembly ensures that all parts fit together correctly and function as intended. Key considerations include:
- Jigs and Fixtures: These are used to hold parts in place during assembly, ensuring accuracy and reducing the risk of errors.
- Calibration: Ensuring that all components are calibrated properly is essential for maintaining tolerances and overall product quality.
The assembly stage often requires collaboration between CNC machinists and assembly technicians to ensure seamless integration of various parts.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Applied in CNC Machining?
Finishing is the final stage of CNC machining, where components are refined to meet aesthetic and functional requirements. Common finishing techniques include:
- Anodizing: This is often used for aluminum parts to enhance corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
- Painting or Coating: This adds a protective layer and can improve the visual appeal of the product.
- Polishing: This technique is used to achieve a smooth, shiny surface, particularly for aesthetic components.
Finishing not only improves the appearance of the parts but also enhances durability and performance, making it a vital step in the manufacturing process.
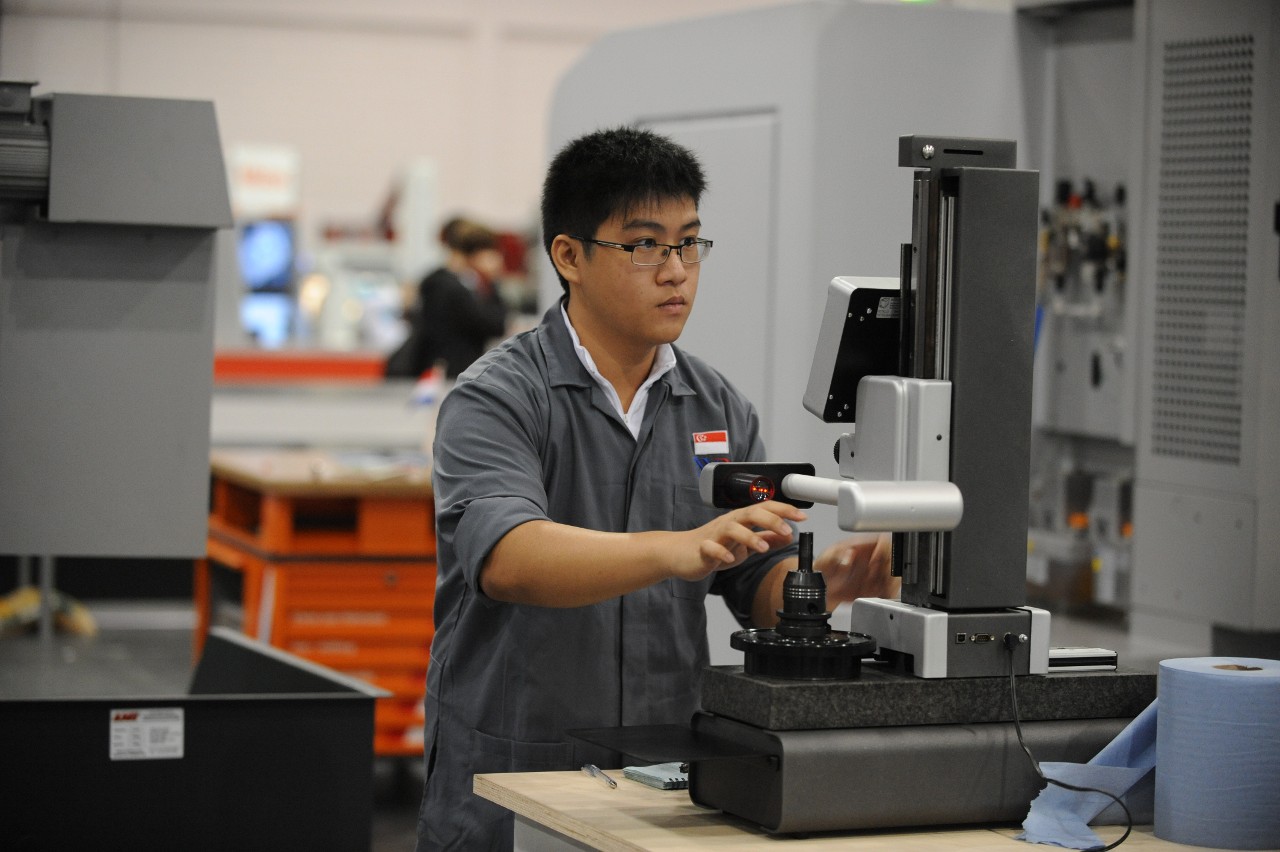
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards Relevant to CNC Machining?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of CNC machining, ensuring that products meet specific standards and customer expectations. For international B2B buyers, understanding these standards is essential for supplier evaluation.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
One of the most recognized international standards is ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a supplier has established processes for consistent quality and continuous improvement. Other industry-specific certifications may include:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for suppliers in the oil and gas industry, ensuring that products meet stringent quality and safety criteria.
Buyers should verify that their suppliers hold the relevant certifications to ensure compliance with international standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated into the CNC manufacturing process to monitor quality at various stages. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the machining process, operators conduct inspections to verify that dimensions and tolerances are maintained.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After machining is complete, finished products are thoroughly inspected against specifications to ensure they meet quality standards.
These checkpoints help identify and rectify issues early in the manufacturing process, reducing the risk of defects in the final product.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for mitigating risks associated with product quality. Here are effective strategies:
What Methods Can Be Used for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to evaluate a supplier’s quality control practices. These audits can be performed internally or through third-party organizations. Key elements to review during an audit include:
- Documented Processes: Ensure that the supplier has documented procedures for quality control and that they adhere to them consistently.
- Equipment Calibration Records: Verify that machinery and tools are regularly calibrated and maintained to ensure accuracy in machining.
- Employee Training Records: Assess whether operators are properly trained in quality assurance processes and have the necessary skills for their roles.
What Role Do Quality Control Reports Play?
Quality control reports provide insights into a supplier’s performance over time. Buyers should request these reports to evaluate:
- Defect Rates: A high defect rate may indicate issues in the manufacturing process or inadequate quality control measures.
- Corrective Actions: Understanding how suppliers address defects can provide insights into their commitment to quality improvement.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections in Supplier Evaluation?
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These services can verify compliance with international standards and provide detailed reports on product quality. This is particularly important for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct on-site inspections.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider in Quality Control?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context can influence communication and expectations around quality. Buyers should establish clear guidelines and expectations from the outset.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations to avoid legal issues.
- Logistical Challenges: Shipping and transportation can impact product quality. Buyers should discuss how suppliers manage logistics to maintain product integrity during transit.
By addressing these nuances, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships with their CNC machining suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc skills’
To effectively procure CNC skills for your business, it is essential to follow a structured approach. This guide outlines the key steps to ensure you source the right capabilities that align with your operational needs, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specific CNC skills required for your projects. This includes understanding the types of materials to be machined, the complexity of designs, and the level of precision needed.
– Key Considerations:
– Identify whether you need expertise in CAD/CAM software or specific CNC machinery.
– Determine if additional skills like quality control or programming are essential for your operations.
Step 2: Identify Qualified Suppliers
Search for suppliers or training organizations that specialize in CNC skills relevant to your industry. This step is crucial to ensure you partner with entities that possess the necessary technical know-how.
– Key Actions:
– Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your sector.
– Check for partnerships with recognized certification bodies or industry associations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, conduct a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers. This involves requesting company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients, particularly those in similar industries or regions.
– What to Look For:
– Testimonials highlighting successful projects that demonstrate the supplier’s capability.
– Evidence of adherence to international standards and quality control processes.
Step 4: Assess Skill Development Programs
Investigate the training programs offered by your suppliers. Continuous learning and skill enhancement are vital in the rapidly evolving field of CNC machining.
– Important Factors:
– Ensure the training covers the latest technologies and software updates.
– Check if the program includes practical hands-on experience with CNC machinery.
Step 5: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications and comply with local and international standards. This step mitigates risks associated with subpar skills and non-compliance.
– Certification Types:
– Look for ISO certifications or other industry-specific qualifications.
– Verify if the suppliers adhere to safety and environmental regulations.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, negotiate terms that align with your business needs. This includes delivery timelines, costs, and any support services offered post-procurement.
– Key Points to Discuss:
– Clarify expectations regarding skill transfer and ongoing support.
– Discuss potential for long-term partnerships and flexibility in service offerings.
Step 7: Monitor Performance and Feedback
After procurement, establish a system to monitor the performance of the CNC skills provided. Gathering feedback from your team can help assess the effectiveness of the skills in practice and identify areas for improvement.
– Monitoring Strategies:
– Implement regular performance reviews and skill assessments.
– Encourage open communication between your team and the supplier to address any concerns promptly.
By following these steps, you can ensure that you effectively source CNC skills that meet your business requirements while fostering a productive relationship with your suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc skills Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for CNC Skills Sourcing?
When sourcing CNC skills, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials required for CNC machining can significantly impact costs. Common materials like metals, plastics, and composites each have different price points. Additionally, sourcing high-quality materials that meet industry standards may incur higher costs, but they can lead to better product quality and lower failure rates.
-
Labor: Skilled CNC machinists command varying wage rates depending on their expertise and regional labor market conditions. In regions like Africa and South America, labor costs may be lower compared to Europe or the Middle East. However, investing in highly skilled machinists can yield greater efficiency and quality in production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facility operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Overhead can be a significant factor, especially for companies with large manufacturing setups. Optimizing operations to reduce waste can enhance overall cost efficiency.
-
Tooling: The cost of tools and equipment necessary for CNC machining can be substantial. High-quality tooling often leads to improved precision and reduced wear, but it requires a larger initial investment. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of tools are also crucial for sustaining production capabilities.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing effective QC measures ensures that products meet specified standards and reduces the risk of defects. This can involve additional costs for inspection tools, testing, and certification processes. However, the long-term savings from minimizing defects can justify these investments.
-
Logistics: Shipping and transportation costs can vary significantly based on the distance and mode of transport. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is vital to clarify who bears these costs during the transaction.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the skills and services offered.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Skills Sourcing?
Several factors influence pricing in the CNC skills market:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders may qualify for volume discounts, making it more cost-effective for buyers. However, small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs without incurring excess costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Highly customized products often come with increased costs due to the additional time and resources required for design and production. Standardized components, on the other hand, may offer cost advantages.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with recognized quality certifications may charge a premium for their services. However, these certifications often translate into higher reliability and reduced risk, which can be beneficial in the long term.
-
Supplier Factors: The choice of supplier can significantly impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices due to their reputation and reliability, while newer entrants might provide competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipment and delivery can affect the total cost. For instance, opting for DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) means the supplier takes on most of the logistics costs, potentially simplifying the buying process.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize CNC Skills Sourcing Costs?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing CNC skills, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, potential discounts for bulk orders, and payment terms. Establishing a long-term partnership can also lead to better pricing arrangements.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing costs like maintenance, operational efficiency, and quality assurance. A lower upfront cost may not always be the most economical choice in the long run.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and trade regulations that can influence costs. Researching regional suppliers may also uncover more competitive pricing.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize software solutions for better project management and resource allocation, which can lead to optimized production processes and reduced waste.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of industry trends, emerging technologies, and shifts in the market that could impact pricing and availability of CNC skills.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing influences in CNC skills sourcing is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on key cost components, leveraging negotiation strategies, and considering the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and achieve better value in their investments. Remember that indicative prices may vary based on specific project requirements and market conditions, so always conduct thorough research before finalizing contracts.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc skills With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to CNC Skills in Manufacturing
In the manufacturing landscape, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) skills are essential for precision machining and automation. However, there are alternative methods and technologies that can achieve similar goals, catering to different operational needs and business contexts. This section explores viable alternatives to CNC skills, comparing their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Cnc Skills | Additive Manufacturing | Manual Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and repeatability; ideal for complex geometries | Excellent for rapid prototyping; good for complex shapes | Varies based on operator skill; generally lower precision |
| Cost | High initial investment in machinery and training | Lower initial cost but can escalate with materials | Generally lower equipment costs; labor-intensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators and training programs | Easier to start with fewer skill requirements | Relies heavily on skilled labor; longer learning curve |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required for machines | Minimal maintenance; mainly software updates | High maintenance due to wear and tear on tools |
| Best Use Case | Mass production of precise parts | Prototyping and low-volume production | Custom, one-off parts and repairs |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing, often known as 3D printing, allows for the creation of objects layer by layer. The primary advantage of this method is its ability to produce highly complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional machining methods. Additionally, it significantly reduces material waste and allows for rapid prototyping, making it an excellent choice for small production runs or custom projects. However, the technology can be limited by the types of materials it can use and may not provide the same level of precision and finish as CNC machining for larger-scale manufacturing.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Manual Machining?
Manual machining involves the use of hand-operated tools and machines to shape materials. This traditional method is often more cost-effective in terms of initial investment, as it does not require the high-tech equipment associated with CNC or additive manufacturing. Manual machining is particularly suited for one-off custom parts or repairs where precision is less critical. However, the disadvantages include a higher dependency on the skill and experience of the machinist, which can lead to variability in quality and longer production times compared to automated methods.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the appropriate manufacturing method, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the required level of precision. CNC skills are invaluable for high-volume, precision-driven production environments, while additive manufacturing may be best suited for innovation and rapid prototyping. Manual machining might serve companies looking for flexibility and lower costs in custom part production. Ultimately, the choice should align with the business’s long-term goals, production capacity, and workforce capabilities. By carefully assessing these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc skills
What Are the Essential Technical Properties in CNC Skills?
Understanding the key technical properties related to CNC skills is critical for B2B buyers involved in manufacturing and engineering. Here are some essential specifications that should be on your radar:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of materials based on their mechanical and chemical properties. In CNC machining, selecting the right material grade—be it metals, plastics, or composites—can significantly impact the performance and durability of the final product. For buyers, understanding material grades is essential for ensuring that the manufactured parts meet industry standards and customer expectations.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable variation in a part’s dimensions. In CNC machining, tight tolerances are often required to ensure that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. For B2B buyers, specifying the required tolerances helps in maintaining quality control and minimizing waste, which can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of a machined surface. Different applications require different surface finishes, which can affect both aesthetic quality and functionality. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to ensure that the end products meet their operational needs and enhance their marketability.
4. Feed Rate
Feed rate is the speed at which the cutting tool moves through the material. This specification can affect machining efficiency and the quality of the finished product. Understanding feed rates is crucial for buyers to optimize production processes, reduce cycle times, and ultimately lower manufacturing costs.
5. Tooling Specifications
Tooling specifications include the type and dimensions of the tools used in the CNC machining process. Selecting appropriate tooling is vital for achieving the desired outcomes in both precision and efficiency. B2B buyers should communicate specific tooling requirements to ensure compatibility with their machinery and to enhance productivity.
6. Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time required to complete one machining process, from setup to part removal. Understanding cycle times helps buyers assess production efficiency and plan their manufacturing schedules accordingly. Reducing cycle time can lead to increased output and improved profitability.
Which Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in CNC Skills?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate better communication and negotiations in the CNC machining sector. Here are some common trade terms that every B2B buyer should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and the origin of components, which is crucial for maintaining quality and compliance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to align their purchasing strategies with their production needs and budget constraints. It can also affect inventory management and cash flow.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price quotations from suppliers for specific products or services. By issuing an RFQ, buyers can compare pricing, quality, and delivery terms from different suppliers, enabling informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, insurance, and risks associated with the delivery of goods, thus facilitating smoother transactions.
5. CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automated control of machining tools via computer programming. Understanding CNC is fundamental for buyers as it underpins the technology used in modern manufacturing, influencing both the capabilities and costs of production.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, optimize their procurement processes, and build stronger partnerships within the CNC machining industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc skills Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Impacting CNC Skills?
The global CNC skills market is experiencing significant evolution, driven by advancements in technology and shifts in manufacturing practices. With the rise of Industry 4.0, international B2B buyers are witnessing an increasing integration of automation, artificial intelligence, and IoT into CNC machining processes. This transformation is not just enhancing productivity but also facilitating remote monitoring and predictive maintenance, which can lead to reduced operational costs and improved quality control.
In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there’s a growing emphasis on skill development to meet the demands of modern manufacturing. Countries like Nigeria are ramping up technical training programs to equip the workforce with necessary CNC skills, ensuring alignment with global standards. Conversely, in Europe, particularly Germany, the focus is on upskilling existing employees to adapt to new technologies, thereby enhancing workforce agility.
Moreover, sustainability is emerging as a critical factor in sourcing decisions. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that not only offer high-quality CNC skills but also adhere to sustainable practices. This trend is amplified by regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. As a result, the market is witnessing a shift towards suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through green certifications and eco-friendly materials.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping CNC Skills in B2B?
The environmental impact of CNC machining is a growing concern for B2B buyers, particularly as industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint. The sourcing of materials and the efficiency of machining processes play a pivotal role in mitigating environmental effects. CNC machining, often characterized by waste generation, can benefit significantly from practices that prioritize sustainability, such as optimizing cutting paths and recycling scrap materials.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly becoming a priority, as buyers demand transparency in sourcing practices. Companies that can demonstrate ethical sourcing not only enhance their brand reputation but also attract discerning customers who prioritize social responsibility. This shift is prompting CNC suppliers to adopt sustainable practices, including the use of certified green materials and the implementation of energy-efficient technologies.
Furthermore, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to compete in the global market. Buyers are more likely to collaborate with CNC skill providers who can prove their commitment to environmental stewardship and ethical labor practices, thus ensuring that their sourcing decisions align with their corporate values.
What Is the Evolution of CNC Skills and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of CNC skills can be traced back to the early 20th century when numerical control was first introduced. Initially, CNC machines were limited in functionality and required skilled operators to manage basic tasks. However, advancements in computer technology and software have drastically transformed the landscape, enabling the automation of complex machining processes.
As CNC technology matured, the skill set required for operators expanded significantly. Modern CNC machinists are not only responsible for programming and operating machines but also for quality control, troubleshooting, and maintenance. This evolution has led to a demand for more sophisticated training programs that encompass both technical and soft skills, such as problem-solving and attention to detail.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial. It highlights the importance of investing in suppliers that prioritize skill development and technological adaptability. As the CNC landscape continues to evolve, partnering with skilled providers will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge in manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc skills
-
How do I solve quality control issues in CNC machining?
Quality control in CNC machining can be addressed by implementing a systematic approach. Start by establishing clear specifications and tolerances for each project. Utilize statistical process control (SPC) techniques to monitor machining processes and detect variations early. Regularly calibrate and maintain machinery to ensure precision. Additionally, investing in quality assurance training for operators can enhance their ability to identify defects. Collaborating with suppliers who have robust quality management systems can also mitigate risks associated with product quality. -
What is the best approach for selecting a CNC machining supplier?
Selecting the right CNC machining supplier involves several steps. First, assess their technical capabilities, including equipment, technology, and expertise in your required materials. Check their certifications and quality assurance practices to ensure compliance with industry standards. Request references and conduct site visits to evaluate their operations firsthand. It’s also crucial to discuss lead times, customization options, and flexibility in meeting your production needs. A supplier that demonstrates reliability and transparency in communication can significantly enhance your project’s success. -
What should I consider regarding minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machining?
When dealing with MOQs in CNC machining, consider your production needs and budget constraints. Suppliers often set MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness in their operations, so it’s essential to communicate your project scale clearly. If your order volume is below the MOQ, inquire about the possibility of combining orders with other clients or negotiating lower quantities. Additionally, evaluate the potential for future projects that may increase your order volume, as a long-term relationship with a supplier can lead to more favorable terms over time. -
How can I ensure effective communication with my CNC machining supplier?
Effective communication with your CNC machining supplier is vital for project success. Start by establishing clear expectations regarding timelines, specifications, and quality standards at the outset. Utilize project management tools and regular check-ins to keep both parties aligned. Encourage open dialogue for addressing challenges, and ensure that both sides understand technical terms and requirements. Document all agreements and changes to prevent misunderstandings. Building a collaborative relationship fosters trust and ensures that any issues are resolved promptly. -
What payment terms are common in CNC machining contracts?
Payment terms in CNC machining contracts can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and the project’s scale. Common terms include upfront deposits (often ranging from 30% to 50% of the total cost) with the balance due upon completion or delivery. For larger projects, suppliers may offer milestone payments tied to specific deliverables. Ensure that payment terms are clearly defined in the contract, including any penalties for late payments or incentives for early settlement. Establishing mutually agreeable terms can enhance the working relationship and project success. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing CNC machined parts internationally?
When sourcing CNC machined parts internationally, logistics considerations are paramount. Evaluate shipping options, including air freight for speed or sea freight for cost savings, depending on your urgency and budget. Understand customs regulations and duties in both the exporting and importing countries to avoid unexpected delays and costs. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can assist with documentation. Additionally, consider the impact of lead times on your overall production schedule and plan accordingly. -
How do I handle customization requests for CNC machined products?
Handling customization requests for CNC machined products requires a clear understanding of your client’s needs and the capabilities of your supplier. Start by discussing the specific requirements, such as dimensions, materials, and finishes. Ensure that your supplier has the technology and expertise to accommodate these customizations. Document all specifications to avoid discrepancies during production. It may also be beneficial to provide prototypes or samples for approval before full-scale production begins, ensuring that the final product meets the client’s expectations. -
What are the key certifications to look for in CNC machining suppliers?
When evaluating CNC machining suppliers, key certifications to look for include ISO 9001 for quality management systems, ISO 13485 for medical devices (if applicable), and AS9100 for aerospace manufacturing. These certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to recognized standards for quality and operational excellence. Additionally, check for any industry-specific certifications that may be relevant to your products. Certifications not only assure quality but also demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction, making them crucial factors in your supplier selection process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Cnc Skills Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CNC Machinists – Skill Level Breakdown
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The text discusses the levels of CNC Machinists, breaking them down into four categories: Level I (basic machinist skills), Level II (moderate machinist skills), Level III (advanced machinist skills), and Level IIII (highly advanced and skilled, handling top-tier, high dollar, tight tolerance, and risky jobs). It emphasizes that the level of a machinist can depend on various factors including the …
2. Indeed – CNC Machinist Skills
Domain: ca.indeed.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Indeed – CNC Machinist Skills, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Practical Machinist – Essential Skills for CNC Operators
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Basic skills for CNC operators/machinists include: 1. Inspection skills: Scale, Dial calipers, Micrometers, Vernier calipers, Hole gauges/mics, Height gauge. 2. Milling skills: Care of machinery and tools, Tramming head, Indicating vises, Edge finder, Tram to a hole/shaft, Align to two holes, Tool selection, Feeds and speeds, Drilling/reaming, Climb/conventional milling, Boring head, Indexing devi…
4. ZipRecruiter – Essential Skills for Employers
Domain: ziprecruiter.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: This company, ZipRecruiter – Essential Skills for Employers, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Total Aviation Staffing – Essential CNC Operator Skills
Domain: totalaviationstaffing.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: 8 essential skills for CNC operators in aviation: 1. Technical Skills: Knowledge of programming languages (G-code, M-code), CAD/CAM software, reading technical drawings, familiarity with cutting tools, metrology, machine maintenance, and safety procedures. 2. Math Skills: Basic arithmetic, working with decimals and fractions, knowledge of trigonometry and geometry, familiarity with algebraic formu…
6. Illinois WorkNet – Numerical Control Tool Operator Skills
Domain: apps.illinoisworknet.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Numerical control tool operators need to: Communicate effectively, understand spoken and written information, listen actively, and speak clearly. Reason and problem solve by noticing potential issues, analyzing ideas, following guidelines, and using logic to find solutions. Use math and science skills for quick calculations. Manage oneself and others, including time management. Work with machinery…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc skills
In the rapidly evolving landscape of CNC machining, strategic sourcing of skilled professionals is essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive. The key skills identified—attention to detail, IT and math abilities, practical skills, problem-solving, and a commitment to continuous learning—are pivotal in ensuring precision and efficiency in production processes. Companies that prioritize these competencies not only enhance their operational capabilities but also position themselves to innovate and adapt to market demands.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in a workforce that embodies these CNC skills will yield significant returns. By fostering a culture of skill development and leveraging advanced technologies, organizations can streamline operations and improve product quality, ultimately driving profitability.
As you navigate the strategic sourcing of CNC skills, consider building partnerships with educational institutions and training centers that can provide a steady pipeline of qualified talent. The future of CNC machining is bright for those who invest wisely in their human resources. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your competitive edge and lead your industry forward.