Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Cnc Router Vs Laser Engraver
Selecting the optimal fabrication method between CNC routing and laser engraving is critical for achieving precise, production-ready results in prototyping and low-volume manufacturing. While laser systems excel at surface marking and cutting thin, non-reflective materials through thermal ablation, they face significant limitations with depth control, 3D contouring, material versatility, and thermal effects on structural integrity. CNC routing, conversely, utilizes subtractive mechanical cutting with multi-axis precision to machine complex 3D geometries, deep cavities, and functional features across an extensive material spectrum—including metals, engineering plastics, composites, and hardwoods—without inducing heat-affected zones that compromise part performance.
Honyo Prototype CNC Machining Capabilities
Our advanced 3-, 4-, and 5-axis CNC machining centers deliver micron-level accuracy for end-use parts and functional prototypes requiring tight tolerances, superior surface finishes, and structural reliability. We directly address the shortcomings of laser-based processes by providing true 3D milling, thread forming, undercuts, and seamless integration of multiple materials within a single workflow. This capability is essential for applications in aerospace, medical devices, robotics, and industrial equipment where dimensional stability and mechanical properties are non-negotiable.
Material and Process Advantages
| Factor | CNC Routing (Honyo) | Laser Engraving |
|———————–|—————————|————————–|
| Material Range | Metals, Plastics, Composites, Wood | Limited to organics/thin metals |
| Depth Control | Precise 3D profiling to 0.001″ | Shallow engraving/cutting only |
| Thermal Impact | None (mechanical process) | Heat-affected zone (HAR) risk |
| Part Functionality | Production-ready strength | Often decorative/weak |
For engineering teams prioritizing manufacturability and performance, Honyo Prototype’s CNC machining services transform digital designs into rigorously validated components. Validate your next project’s feasibility immediately—access our Online Instant Quote platform to receive a detailed manufacturability analysis and competitive pricing within hours, accelerating your path from concept to certified prototype.
Technical Capabilities

Technical Comparison: CNC Router vs Laser Engraver – Focus on Multi-Axis Milling, Turning, and Tight Tolerances
The following table outlines the technical capabilities of CNC routers and laser engravers with emphasis on multi-axis machining (3/4/5-axis), turning operations, achievable tolerances, and compatibility with common engineering materials including aluminum, steel, ABS, and nylon.
| Feature / Capability | CNC Router (High-End 3/4/5-Axis) | Laser Engraver (Fiber/CO₂) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Material removal via rotating cutting tools (milling) | Non-contact surface marking or cutting via focused laser beam |
| Multi-Axis Capability | Full 3-axis standard; 4-axis (rotary indexing) and 5-axis (simultaneous complex contouring) available | Typically 2-axis (X-Y galvo); limited Z-control; no true 4/5-axis functionality |
| Turning Capability | Not applicable unless hybrid mill-turn or lathe attachment is used | Not capable of turning operations |
| Tight Tolerance Machining | Capable of ±0.001″ (25 µm) or better with precision spindles, thermal compensation, and high-rigidity frames | Limited to ±0.005″ (125 µm) for cut accuracy; engraving registration can be tighter but not for dimensional control |
| Material Compatibility – Metals | Excellent for aluminum and mild steel; capable of machining hardened steels with appropriate tooling and speeds | Fiber lasers can mark or cut thin aluminum and steel; not suitable for bulk material removal or deep milling |
| Material Compatibility – Plastics | Suitable for ABS, nylon, and other engineering thermoplastics; risk of melting if feeds/speeds not optimized | Effective for engraving and cutting ABS and nylon; CO₂ lasers may cause melting or charring on nylon |
| Surface Finish Quality | High; finish depends on toolpath strategy, tool selection, and spindle quality | Good for surface marking; cut edges may show heat-affected zones or burring |
| Production Use Case | Ideal for functional prototypes, end-use parts, molds, and high-precision components requiring tight tolerances | Best suited for labeling, aesthetic engraving, thin-sheet cutting, and low-force surface modification |
| Tooling Requirements | Requires end mills, drills, collets, tool holders; tool wear monitoring critical | No physical tooling; laser lens and assist gas (e.g., O₂, N₂) required |
| Setup Complexity | High; requires workholding, tool calibration, and alignment | Low; minimal fixturing, digital file upload, focus adjustment |
| Lead Time for High-Precision Parts | Moderate to long, depending on complexity and tolerances | Fast for marking; limited for structural part fabrication |
Summary:
For applications requiring 3/4/5-axis milling, turning integration, or tight-tolerance part production in aluminum, steel, ABS, or nylon, a high-precision CNC router (or CNC machining center) is the appropriate solution. Laser engravers excel in non-contact marking and thin-material processing but lack the rigidity, tooling versatility, and dimensional accuracy required for precision milling and turning operations.
From CAD to Part: The Process
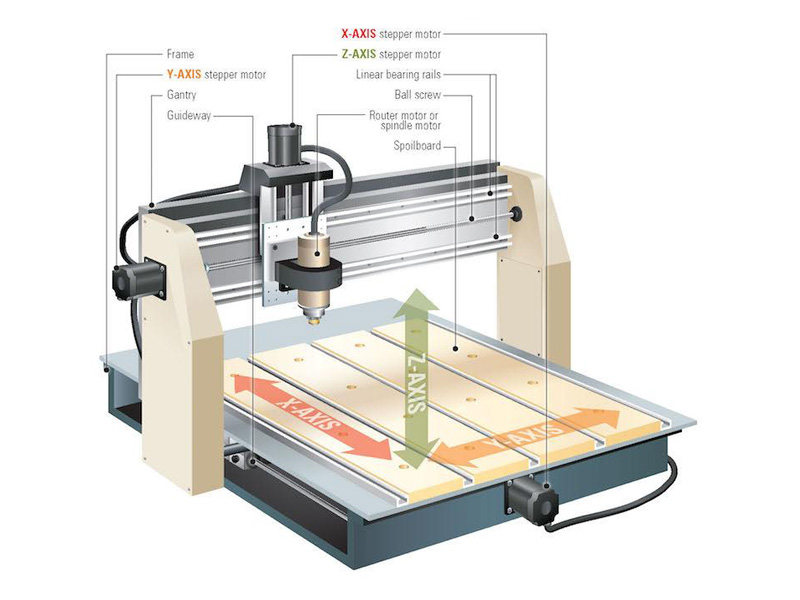
Honyo Prototype CNC Router vs. Laser Engraver Process Integration
Honyo Prototype’s workflow intelligently routes projects between CNC routers and laser engravers during the AI Quote stage based on technical analysis of the uploaded CAD file. This ensures optimal technology selection for precision, cost, and lead time. Below is the end-to-end process with critical decision logic for technology assignment.
CAD Upload
Clients submit industry-standard CAD files (STEP, IGES, DXF, or native formats). The system validates geometry integrity and extracts key parameters: material type, part thickness, feature complexity, depth requirements, tolerance specifications, and surface finish needs. This data feeds directly into the AI Quote engine.
AI Quote
Our proprietary AI engine evaluates the CAD data against predefined technology rules to auto-select between CNC routing and laser engraving:
Laser engraving is prioritized for 2D/2.5D features on materials ≤20mm thick (e.g., acrylic, wood, anodized aluminum) where depth tolerance >±0.1mm is acceptable. Ideal for etching, shallow engraving, or through-cutting thin sheets.
CNC routing is assigned for 3D geometries, materials >20mm thick (e.g., solid metals, dense composites), tight tolerances (±0.05mm), or when feature depth exceeds laser capabilities. Required for undercut features or non-planar surfaces.
The quote includes technology justification, cost breakdown, and lead time. Clients may override the recommendation with engineering approval.
| Parameter | Laser Engraver Assignment Criteria | CNC Router Assignment Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Max Thickness | ≤20mm | >20mm (up to 150mm) |
| Depth Tolerance | >±0.1mm | ≤±0.05mm |
| Geometry Complexity | 2D/2.5D only | Full 3D, undercuts, complex contours |
| Material Suitability | Plastics, wood, coated metals | Metals, dense composites, thick stock |
| Typical Use Case | Panel labels, signage, decorative cuts | Structural brackets, precision molds |
DFM (Design for Manufacturability)
Honyo engineers validate the AI’s technology choice during DFM review. For laser projects, they check kerf width compensation, heat-affected zones, and material flammability. For CNC projects, they verify toolpath feasibility, fixture requirements, and surface finish achievability. Any conflicts (e.g., laser-selected for 25mm steel) trigger automatic reassignment to CNC routing with client notification.
Production
Laser engraving uses CO₂ or fiber lasers (60–150W) with vector/raster processing. In-process checks monitor focus alignment and exhaust filtration to prevent material charring.
CNC routing employs 3–5 axis routers (spindle speed 24,000 RPM) with tool libraries optimized for material hardness. First-article inspection confirms dimensional accuracy before full production.
Both processes follow ISO 9001 traceability protocols, with real-time status updates via client portal.
Delivery
Finished parts undergo final QA: laser-engraved items are inspected for edge consistency and depth uniformity; CNC parts are CMM-verified against critical dimensions. All deliverables include process documentation specifying the technology used, material batch traceability, and QA reports. Standard lead time is 3–5 business days, with laser projects typically shipping 1–2 days faster for simple 2D designs.
This integrated workflow eliminates client guesswork in technology selection, ensuring every project leverages the most capable and cost-effective process while maintaining Honyo’s 99.5% first-pass yield rate. Clients receive transparent technical rationale for all equipment assignments, reducing resubmissions and accelerating time-to-prototype.
Start Your Project

Considering whether a CNC router or laser engraver is right for your manufacturing needs? The choice depends on material type, precision requirements, and production volume. CNC routers excel in heavy-duty cutting and shaping of materials like wood, aluminum, and plastics, while laser engravers offer high-precision marking and cutting for thinner materials.
For expert guidance tailored to your application, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. With our advanced manufacturing facility based in Shenzhen, Honyo Prototype delivers reliable, high-quality solutions in CNC machining and laser processing to meet your project demands.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.