Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc quality control
In today’s competitive landscape, navigating the global market for CNC quality control presents a pressing challenge for international B2B buyers. The demand for precision and reliability in CNC machining has never been higher, and sourcing the right quality control solutions is crucial to maintaining operational efficiency and client satisfaction. This comprehensive guide addresses the intricacies of CNC quality control, covering essential aspects such as types of quality control methods, applications across various industries, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
As businesses expand across borders—from Africa to South America, and throughout the Middle East and Europe (including key markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia)—the need for robust quality assurance systems becomes paramount. This guide equips decision-makers with actionable insights and best practices to enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they select quality control solutions that meet their specific needs. By understanding the critical parameters of CNC quality control, including dimensional accuracy and on-machine inspections, buyers can mitigate risks associated with defects and inefficiencies.
With an emphasis on empowering informed purchasing decisions, this guide serves as a vital resource for international buyers seeking to improve their manufacturing processes. By leveraging the knowledge contained within, companies can forge stronger partnerships with suppliers and achieve higher standards of excellence in their CNC machining operations.
Understanding cnc quality control Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inspection | Focuses on measuring physical dimensions and tolerances. | Aerospace, Automotive, Medical Devices | Pros: Ensures precision; Cons: Time-consuming. |
| Material Verification | Confirms the quality and type of raw materials used. | Construction, Electronics | Pros: Reduces defects; Cons: May increase costs. |
| On-Machine Inspection | Real-time quality checks integrated into the CNC process. | High-volume production | Pros: Enhances efficiency; Cons: Initial setup cost. |
| Final Quality Audits | Comprehensive review of finished products before delivery. | All manufacturing sectors | Pros: Ensures compliance; Cons: Potential delays. |
| Process Control | Monitors and adjusts CNC machining parameters continuously. | Industrial Manufacturing | Pros: Maintains consistency; Cons: Requires training. |
What Are the Characteristics of Dimensional Inspection in CNC Quality Control?
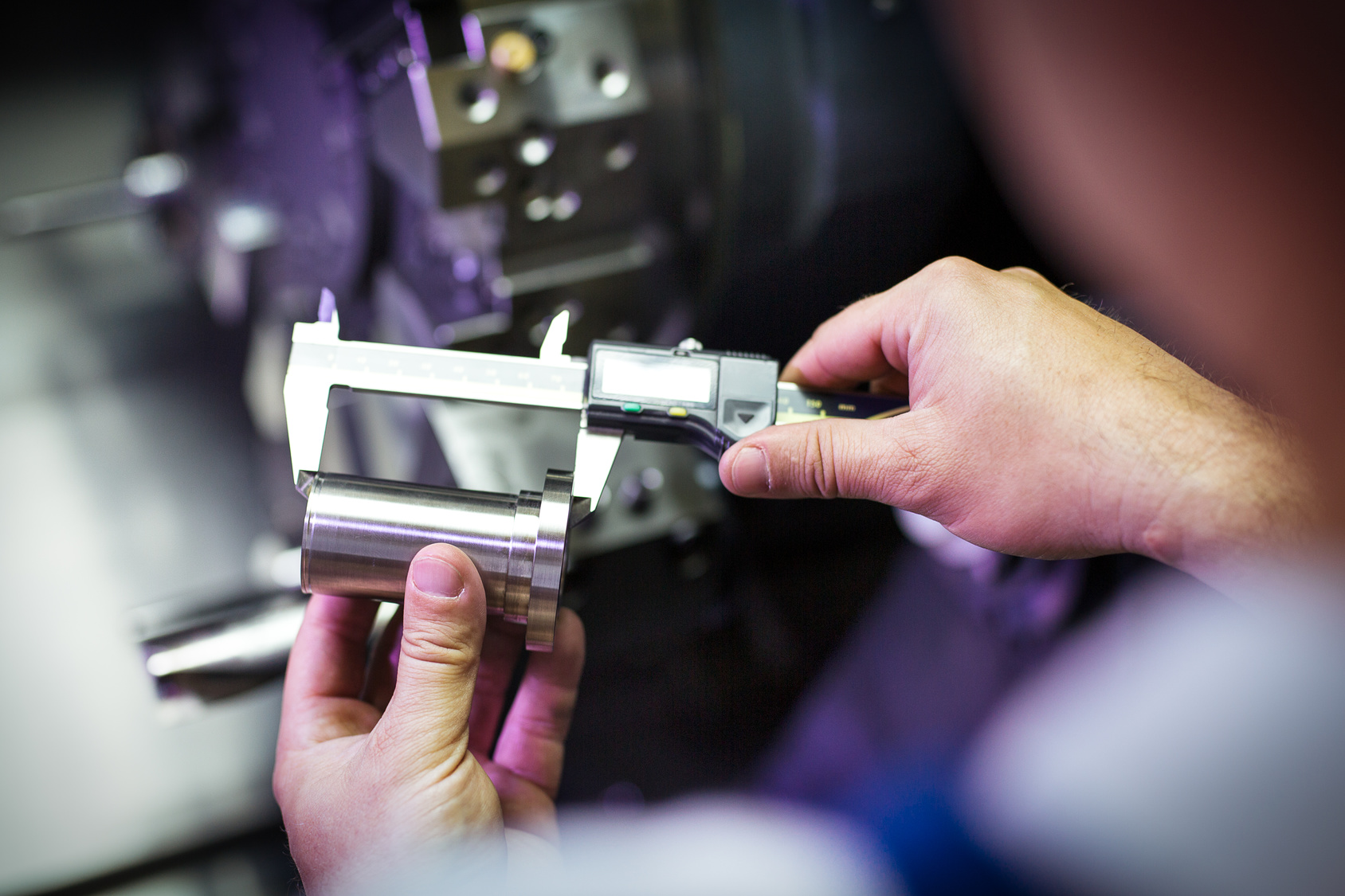
Dimensional inspection is a critical quality control type in CNC machining, focusing on verifying that machined components meet specified dimensional tolerances. This process typically employs tools such as calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to ensure precision. It is particularly suitable for industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where the accuracy of components is paramount. Buyers should consider the time and resources required for thorough inspections, as this method, while effective, can be labor-intensive and may slow down production.
How Does Material Verification Enhance CNC Quality Control?
Material verification plays a vital role in CNC quality control by ensuring that the raw materials used in production meet the required specifications. This involves testing samples for material composition, mechanical properties, and structural integrity. Industries such as construction and electronics benefit significantly from this process, as it helps prevent defects that could arise from subpar materials. When purchasing, buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced defects against potential increases in procurement costs, ensuring they source materials from reputable suppliers.
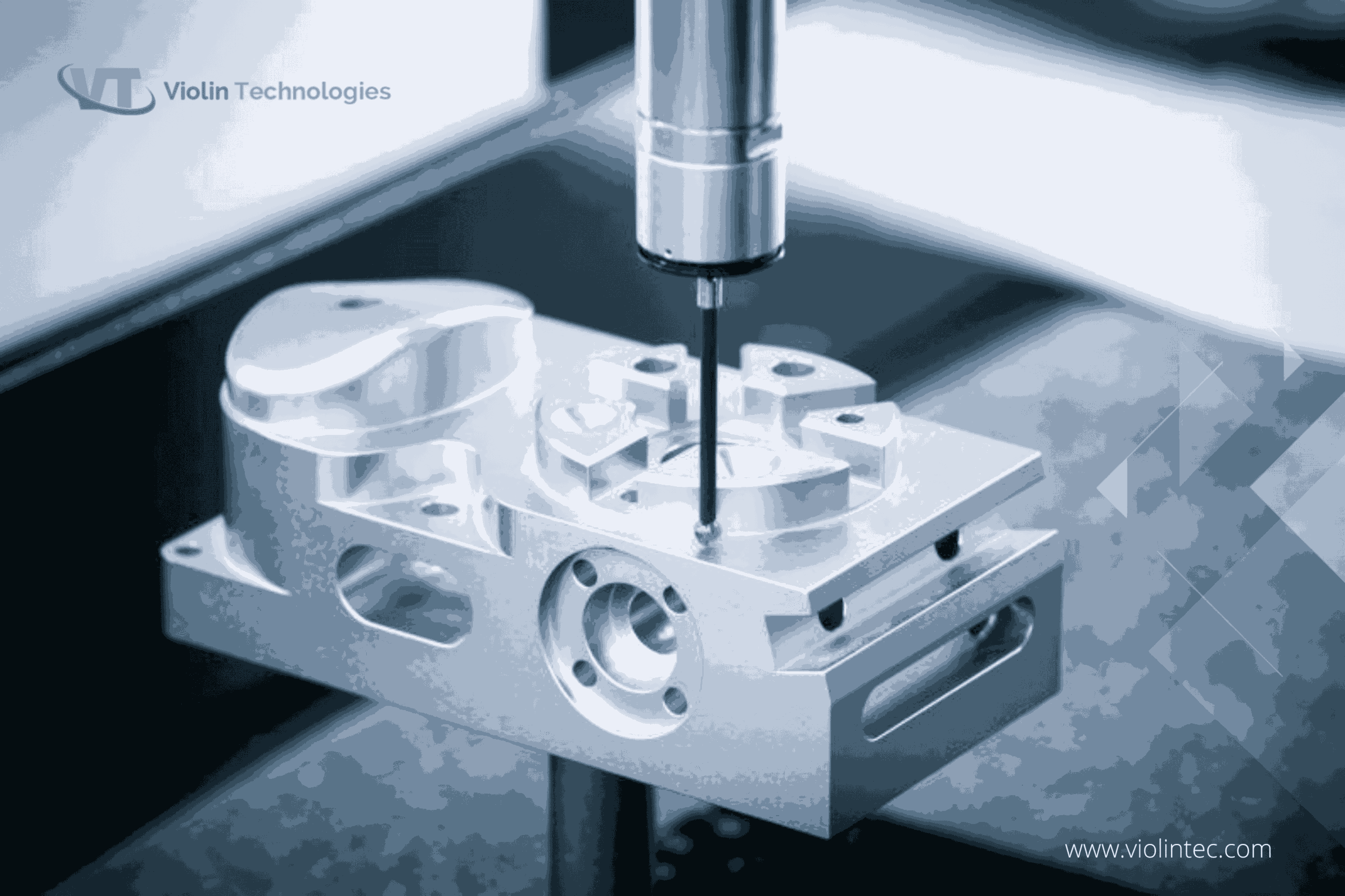
Why Is On-Machine Inspection Essential for Efficiency?
On-machine inspection integrates quality control directly into the CNC machining process, utilizing probing systems to conduct real-time checks while machining occurs. This approach allows for immediate detection and correction of errors, significantly enhancing operational efficiency. It is particularly advantageous in high-volume production settings, where maintaining throughput is critical. Buyers should consider the initial investment in probing technology against the long-term savings in reduced scrap and rework costs, as well as the potential for improved product quality.
What Are the Benefits of Conducting Final Quality Audits?
Final quality audits involve a comprehensive review of finished products to ensure they meet all specified requirements before delivery. This process is applicable across various manufacturing sectors and is crucial for maintaining compliance with industry standards. While this method guarantees high-quality output, it can introduce delays in the production timeline. Buyers should assess the trade-offs between the assurance of quality and the potential for slower delivery times, ensuring that their operational schedules can accommodate these audits.
How Does Process Control Contribute to Consistent Quality?
Process control in CNC machining involves the continuous monitoring and adjustment of machining parameters to maintain consistent quality throughout production. This proactive approach helps identify deviations from desired outcomes, allowing for immediate corrective actions. It is particularly relevant for industrial manufacturing, where consistency is vital for meeting production targets. Buyers should consider the necessity for training and investment in monitoring technology, as these factors are essential for effectively implementing process control strategies.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc quality control
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Quality Control | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision Component Manufacturing | Ensures safety and compliance with stringent regulations | Suppliers must meet international aerospace standards (e.g., AS9100). |
| Automotive | Engine and Transmission Parts Production | Enhances reliability and performance of vehicles | Focus on suppliers with advanced CNC capabilities and certifications. |
| Medical Devices | Surgical Instrument Fabrication | Guarantees high precision and safety for patient care | Look for ISO 13485 certified manufacturers to ensure compliance with medical standards. |
| Electronics | Circuit Board and Component Production | Improves product reliability and reduces defects | Source from vendors with expertise in electronic component tolerances. |
| Energy | Turbine and Generator Component Production | Increases efficiency and longevity of equipment | Consider vendors with experience in high-stress applications and robust quality control processes. |
How is CNC Quality Control Applied in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace sector, CNC quality control is critical for the fabrication of precision components such as turbine blades and structural parts. These components must meet strict safety and performance standards, necessitating rigorous quality checks throughout the manufacturing process. Issues like dimensional inaccuracies can lead to catastrophic failures, making it essential for international buyers to partner with suppliers who hold certifications like AS9100. Ensuring that raw materials and finished products undergo comprehensive inspections helps mitigate risks associated with subpar components.
What Role Does CNC Quality Control Play in Automotive Parts Production?
CNC quality control in the automotive industry focuses on the production of engine and transmission parts that require high precision to ensure vehicle reliability. By implementing stringent quality control measures, manufacturers can prevent defects that may lead to costly recalls or safety issues. Buyers from regions like Europe and South America should prioritize suppliers with advanced machining capabilities and adherence to quality certifications. This commitment to quality not only enhances vehicle performance but also builds consumer trust in automotive brands.
Why is CNC Quality Control Crucial for Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device industry, CNC quality control is paramount for producing surgical instruments and implants that demand exceptional precision and reliability. Any deviation from specifications can jeopardize patient safety, making it essential for manufacturers to implement robust quality management systems. International buyers should seek vendors certified under ISO 13485 to ensure compliance with medical standards. Early inspection of materials and ongoing quality checks during production can significantly reduce the risk of defects in critical medical applications.
How Does CNC Quality Control Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
CNC quality control is vital in the electronics sector, where the production of circuit boards and components requires exacting tolerances. Quality control processes help identify and rectify defects early in the production cycle, thus enhancing the reliability of electronic devices. Buyers, particularly from the Middle East and Africa, should focus on sourcing from vendors with a proven track record in electronic component fabrication and robust quality assurance practices. This diligence ensures that the final products meet the necessary performance and reliability standards.
In What Ways is CNC Quality Control Applied in Energy Sector Production?
In the energy sector, CNC quality control is essential for manufacturing components for turbines and generators, which must withstand extreme conditions. The implementation of quality control measures helps enhance the efficiency and lifespan of these critical components. International buyers should prioritize suppliers experienced in high-stress applications and capable of providing detailed quality documentation. Ensuring adherence to stringent quality standards can prevent costly downtime and improve overall operational efficiency in energy production.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc quality control’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality Leading to Client Complaints
The Problem: A manufacturing firm in Europe faces significant issues with inconsistent quality in their CNC machined components. Frequent client complaints about defects have strained relationships and threatened contracts. This inconsistency often stems from a lack of rigorous quality control measures, leading to variations in product specifications that can be costly both in terms of reputation and financial loss.
The Solution: To address this issue, the firm should implement a comprehensive Quality Management System (QMS) that emphasizes early detection of defects. This system should include detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) for quality checks at various stages of production. Regular training sessions for staff on these procedures will ensure everyone understands their roles in maintaining quality. Additionally, adopting machine tool probing systems for real-time inspections can significantly enhance quality control. These systems allow for immediate adjustments, reducing the likelihood of defects reaching the customer and thus improving client satisfaction.
Scenario 2: Material Quality Complications Impacting Production
The Problem: A South American company specializing in CNC machining discovers that the raw materials supplied by local vendors frequently fail quality checks, leading to production delays and increased costs. The reliance on subpar materials not only hampers production efficiency but also results in a higher rate of waste and rework, ultimately impacting the bottom line.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, the company should establish a robust supplier evaluation and selection process. This includes setting clear quality standards for raw materials and requiring vendors to provide certifications of compliance. Conducting audits of suppliers can ensure that they adhere to these standards. Additionally, implementing an incoming inspection protocol will allow the company to assess the quality of materials before they enter the production line. This proactive approach will not only enhance product quality but also foster stronger relationships with reliable suppliers, leading to better overall material management.
Scenario 3: Inefficiencies Caused by Outdated Inspection Processes
The Problem: A manufacturer in the Middle East finds that their quality inspection processes are outdated and inefficient, often leading to bottlenecks in production. Manual inspections take too long and result in inconsistent quality checks, which can allow defects to slip through and necessitate costly rework later in the process.
The Solution: To streamline quality inspections, the manufacturer should invest in advanced inspection technologies such as automated optical inspection systems and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs). These technologies can provide precise measurements and faster evaluations, significantly reducing inspection time while enhancing accuracy. Additionally, integrating these systems with CNC machines can facilitate real-time monitoring of production quality, allowing for immediate feedback and corrections. By modernizing their inspection processes, the manufacturer can eliminate bottlenecks, reduce cycle times, and ensure a consistently high standard of quality in their outputs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc quality control
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in CNC Quality Control?
When selecting materials for CNC machining, understanding their properties is crucial for ensuring quality control. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, stainless steel, polycarbonate, and titanium, focusing on their performance, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Champion
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easy to machine and transport, reducing overall production costs. However, its lower tensile strength compared to steel can limit its use in high-stress applications, and it may require surface treatments to enhance durability.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a range of media, including water and air, but may not perform well in harsh chemical environments without proper coating.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN for aluminum alloys, as these can vary significantly across markets.
Stainless Steel: The Durable Workhorse
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its high corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its robustness, which extends the lifespan of components. However, it is more challenging to machine than aluminum, which can increase production costs and complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for a variety of media, including corrosive substances, making it a preferred choice in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers: When sourcing stainless steel, buyers should be aware of certifications and standards, such as JIS in Japan and ASTM in the U.S., to ensure material quality and compliance.
Polycarbonate: The Versatile Plastic
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a high-impact thermoplastic known for its transparency, lightweight nature, and good thermal resistance. It can endure moderate temperatures and is resistant to UV light.
Pros & Cons: The ease of machining polycarbonate allows for intricate designs and lower production costs. However, it has lower mechanical strength compared to metals, which may limit its application in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is compatible with various media, including water and oils, making it suitable for electrical enclosures and protective shields.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local regulations regarding plastic materials, particularly in regions with stringent environmental laws, such as Europe.
Titanium: The Premium Choice
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its exceptional strength, low density, and high corrosion resistance. It can withstand extreme temperatures and is highly biocompatible, making it suitable for medical applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium is its strength-to-weight ratio, which is superior to that of aluminum and stainless steel. However, it is the most expensive option and requires specialized machining techniques, increasing overall costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium is ideal for high-performance applications, including aerospace and medical devices, where durability and reliability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Due to its cost and machining complexity, buyers should ensure that suppliers are certified and adhere to international standards such as ASTM and ISO for titanium products.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Quality Control
| Material | Typical Use Case for CNC Quality Control | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment | High corrosion resistance | More difficult to machine | High |
| Polycarbonate | Electrical enclosures | Easy to machine and lightweight | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical applications | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex machining | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that enhance quality control in CNC machining processes.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc quality control
What Are the Main Stages of CNC Manufacturing Processes?
The CNC manufacturing process is a multifaceted approach that includes several key stages, each critical for producing high-quality components. Understanding these stages will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: How to Ensure Quality Starts with the Right Raw Materials
Material preparation is the foundation of the CNC manufacturing process. This stage involves selecting and inspecting raw materials to ensure they meet specific quality criteria. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who source materials from reputable vendors and conduct thorough inspections. Common inspection methods include visual checks for defects, hardness tests, and dimensional assessments. Ensuring that materials are free from cracks or inconsistencies can significantly reduce errors during machining, ultimately leading to higher-quality end products.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Components?
The forming stage encompasses various techniques, including CNC milling, turning, and routing. Each method has its advantages and is selected based on the complexity and requirements of the component. For instance, CNC milling is ideal for creating intricate shapes, while CNC turning is suited for cylindrical parts. During this stage, precision is paramount. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific CNC machines used by their suppliers, as the type of machinery directly impacts the accuracy of the final product. Sophisticated multi-axis machines can undertake more complex tasks, thereby minimizing the likelihood of errors.
Assembly: How Is Quality Maintained During Assembly Processes?
Once individual components are machined, the next step is assembly. This stage may involve welding, fastening, or joining various parts to create a complete assembly. Quality control during assembly is crucial, as misalignment or improper fitting can lead to functional issues. B2B buyers should look for suppliers who utilize advanced assembly techniques and equipment, such as automated assembly lines or robotic systems, which enhance accuracy and efficiency. Additionally, it is beneficial to confirm that suppliers have established protocols for verifying the integrity of assembled components.
Finishing: What Are the Common Finishing Techniques to Enhance Quality?
The finishing stage includes processes such as sanding, polishing, coating, and anodizing, which enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of the components. This stage is essential for achieving the desired surface finish and ensuring that the components meet industry-specific standards. B2B buyers should inquire about the finishing techniques employed by their suppliers and the quality checks in place to verify the effectiveness of these processes.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware of for Quality Control?
Quality control in CNC machining is governed by various international standards that ensure consistency and reliability. The most recognized standard is ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a supplier has implemented processes to consistently meet customer requirements and enhance satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may also apply. For example, the CE mark is crucial for manufacturers supplying products to the European market, while API certification is essential for suppliers in the oil and gas sector. B2B buyers should confirm that their suppliers hold the relevant certifications to ensure adherence to quality and safety standards.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in CNC Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to ensuring that each phase of the manufacturing process meets established standards. The three primary checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production process. IQC helps identify defects early, preventing them from affecting the overall production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, IPQC involves real-time monitoring and inspections. Techniques such as machine tool probing systems can be employed to detect issues immediately, allowing for corrective actions to be taken without disrupting production.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This stage encompasses comprehensive inspections of the finished product. This may include dimensional checks, functional testing, and visual inspections to ensure that the final output meets quality standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in CNC Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality of CNC machined components. These include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Measuring the dimensions of components using tools such as calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to ensure they fall within specified tolerances.
-
Material Testing: Conducting hardness tests, tensile tests, and chemical composition analyses to verify that materials meet the required specifications.
-
Functional Testing: Assessing the performance of components in real-world conditions to ensure they operate as intended.
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers employ a combination of these testing methods to comprehensively assess quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in international markets. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess a supplier’s quality management systems and manufacturing processes firsthand. This engagement helps build trust and transparency.
-
Quality Control Reports: Requesting regular quality control reports can provide insights into a supplier’s performance and adherence to quality standards. These reports should detail inspections, testing results, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. This approach is particularly valuable for buyers sourcing from international suppliers, as it mitigates risks associated with distance and communication barriers.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances when it comes to quality control and certification. Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that suppliers must adhere to. For example, the European Union has stringent safety and quality regulations that may not apply in other markets.
Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific quality requirements relevant to their industry and region. Establishing clear communication with suppliers regarding these requirements is essential to avoid misunderstandings and ensure compliance.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the CNC manufacturing process and quality assurance practices is vital for B2B buyers. By prioritizing quality at every stage, from material preparation to final inspection, and by verifying supplier capabilities, buyers can ensure they receive high-quality components that meet their specifications and industry standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc quality control’
In the competitive landscape of CNC machining, ensuring quality control is essential for maintaining product integrity and customer satisfaction. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers to effectively source CNC quality control solutions, enabling them to enhance their manufacturing processes.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes tolerances, materials, and the complexity of the components you need. A precise specification helps suppliers understand your needs and ensures that the quality control measures are aligned with your production standards.
- Consider the types of materials you will be machining, as different materials may require distinct quality control processes.
- Identify the specific tolerances required for your parts, as this will influence the choice of inspection methods.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in CNC machining quality control. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of potential partners.
- Look for suppliers with experience in your industry, as they will be more familiar with the specific quality control challenges you may face.
- Check online reviews and testimonials to gauge the reputation of potential suppliers.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your shortlisted suppliers hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 or AS9100. These certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to established quality management standards.
- Request copies of their certificates and check their validity with the issuing bodies.
- Assess their quality management systems to understand how they maintain compliance with these standards.
Step 4: Evaluate Quality Control Methods
Investigate the quality control techniques employed by each supplier. Understanding their methodologies helps you determine if they can meet your specific quality requirements.
- Inquire about their inspection processes, including dimensional checks and material analysis.
- Evaluate the technologies they use, such as on-machine inspections and probing systems, which can enhance real-time quality assessments.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Audits
Before finalizing a supplier, request samples of their work and, if possible, conduct on-site audits. This provides insight into their manufacturing capabilities and quality control practices.
- Analyze the samples against your specifications to ensure they meet your standards.
- Observe their quality control processes firsthand during an audit, which can reveal their commitment to quality.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is vital for a successful partnership. Establish clear channels for ongoing dialogue about quality expectations and issues that may arise during production.
- Set up regular meetings to discuss quality metrics and address any concerns.
- Utilize project management tools to facilitate transparency and track progress on quality control measures.
Step 7: Monitor Performance and Provide Feedback
Once you begin working with a supplier, continuously monitor their performance and provide constructive feedback. This helps maintain high standards and fosters a collaborative relationship.
- Implement a performance review system that evaluates quality control effectiveness and identifies areas for improvement.
- Encourage open dialogue about any quality issues, ensuring that both parties are committed to resolving them promptly.
By following this comprehensive sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their CNC quality control processes, leading to improved product quality and customer satisfaction.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc quality control Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Quality Control Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of CNC quality control is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts costs. High-quality materials that meet stringent specifications often come at a premium. For CNC machining, materials like metals and plastics are common, with prices varying based on availability and market demand.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in CNC quality control, where precision is paramount. Labor costs can vary by region; for instance, labor in Europe may be more expensive than in South America or Africa. Furthermore, the level of expertise required for specific tasks can also influence labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to the production process, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. These overheads are typically allocated per unit of production and can vary depending on the manufacturing environment.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs encompass the expenses associated with the tools and equipment used in the CNC process. Custom tooling can be a significant upfront investment but can lead to long-term savings if optimized for production efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing effective QC measures involves both personnel and technology costs. Investments in on-machine inspection systems or automated quality checks can enhance precision but may require higher initial capital.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing expenses also play a critical role in the overall cost structure. These costs can be influenced by the geographic location of suppliers and buyers, as well as chosen Incoterms, which dictate responsibilities for shipping and handling.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on market competition, the supplier’s position, and the perceived value of their services.
What Influences Pricing in CNC Quality Control Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC quality control services:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes or Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for bulk pricing to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts or complex specifications can increase costs. Suppliers may charge more for specialized services or non-standard components.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications (such as ISO) can significantly impact pricing. Certified materials often come with higher costs due to additional testing and validation processes.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge a premium for their services due to perceived lower risks.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international buyers as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk management.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in CNC Quality Control?
To maximize cost-efficiency, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Highlighting long-term partnerships can often yield better pricing terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, logistics, and potential defects. This holistic view can guide better decision-making.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and local regulations that may influence pricing. Building relationships with local suppliers can also help mitigate some of these costs.
Disclaimer
Prices for CNC quality control services can vary widely based on numerous factors including market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific project requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc quality control With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CNC Quality Control
In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing, businesses are constantly seeking effective solutions for quality control. While CNC quality control offers precision and efficiency, several alternative methods can also achieve similar goals. This analysis compares CNC quality control with two prominent alternatives: Manual Inspection and Automated Optical Inspection (AOI). Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each approach can help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Quality Control | Manual Inspection | Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy with minimal human error | Variable accuracy, dependent on inspector’s skill | High speed and consistency in detection |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; ongoing operational costs | Lower initial costs; potential for higher labor costs | Moderate investment with reduced labor costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training and integration into existing systems | Simple to implement, no special tools needed | Requires specialized equipment and setup |
| Maintenance | Regular calibration needed; ongoing training required | Minimal maintenance; reliant on personnel training | Regular software updates and hardware maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Complex parts requiring tight tolerances | Small-scale operations or low-complexity tasks | High-volume production with consistent quality checks |
Understanding the Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
Manual Inspection
Manual inspection involves trained personnel examining products for defects. This method is straightforward and incurs lower upfront costs since it does not require sophisticated machinery. However, it is highly dependent on the skill and experience of the inspectors, leading to variability in performance. In high-stakes environments where precision is crucial, relying solely on manual inspection may lead to missed defects and increased rework costs. Manual inspection is best suited for small-scale operations or when dealing with low-complexity tasks, where the costs of advanced technologies may not be justified.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
Automated Optical Inspection employs cameras and software to detect defects in products. This method offers high-speed and consistent results, making it ideal for high-volume production lines. AOI systems can quickly analyze components and identify defects that might be missed by the human eye. However, the initial investment can be moderate to high, and the technology requires ongoing maintenance and updates. AOI is particularly effective for processes that require rapid inspections and consistent quality checks, especially in electronics and other industries with high production demands.
Making an Informed Decision for Quality Control Solutions
When considering the right quality control solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, production scale, and budget constraints. CNC quality control is unmatched in terms of precision for complex machining tasks, but it requires a significant investment and expertise. Conversely, manual inspection offers simplicity and lower costs, though it may lack the accuracy needed for high-stakes applications. AOI stands out for high-volume environments, delivering speed and consistency, but comes with higher initial costs and maintenance requirements.
Ultimately, the choice between these alternatives should align with the buyer’s production goals, complexity of parts, and long-term quality assurance strategies. By evaluating these factors, businesses can optimize their quality control processes to enhance efficiency and maintain high standards in their manufacturing operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc quality control
What Are the Key Technical Properties in CNC Quality Control?
Understanding the critical specifications in CNC quality control is essential for maintaining high standards in manufacturing. Here are several key properties that play a vital role in ensuring the precision and reliability of machined components:
1. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of a part. It defines how much a dimension can deviate from the specified measurement without affecting the part’s functionality. In B2B contexts, precise tolerances are crucial as they directly impact the interchangeability of parts and the overall quality of the final product. An understanding of tolerance levels can help businesses avoid costly rework or product failures.
2. Material Grade
The material grade indicates the specific classification of the raw material used in manufacturing. Different grades possess distinct mechanical properties, including strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for ensuring that the final product meets performance requirements. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing materials from reputable suppliers to guarantee quality and reliability.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture and smoothness of a machined surface, which can significantly influence the performance and aesthetics of a part. Different applications may require varying surface finishes, ranging from rough to polished. Understanding the required surface finish is essential for manufacturers to meet client specifications and enhance product durability.
4. Dimensional Accuracy
Dimensional accuracy refers to how closely a manufactured part’s dimensions align with the intended design specifications. High dimensional accuracy is crucial for ensuring that components fit together correctly and function as intended. In a B2B context, maintaining strict dimensional accuracy reduces the risk of defects and enhances customer satisfaction.
5. Hardness
Hardness measures a material’s resistance to deformation and wear. It is particularly important in CNC machining for parts that will be subjected to high-stress conditions. A thorough understanding of hardness requirements helps manufacturers select appropriate materials and machining processes, ultimately impacting product longevity and performance.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Quality Control?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiations in the CNC machining sector. Here are several common terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In CNC machining, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can deliver high-quality components tailored to specific needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers, as understanding MOQs can influence purchasing decisions and inventory management. Suppliers often set MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness in production, so buyers should align their order sizes accordingly.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ can help streamline the procurement process and ensure competitive pricing. It allows buyers to compare offers and select suppliers based on cost, quality, and delivery timelines.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. These terms clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transport. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in global sourcing to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions.
5. CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
CAD refers to the use of computer software to create precise drawings and technical illustrations of parts. In CNC machining, CAD files are often used to program CNC machines. B2B buyers should understand CAD’s role in the manufacturing process to ensure that their specifications are accurately translated into production.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making process, ultimately leading to improved sourcing and quality control in CNC machining.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc quality control Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in CNC Quality Control?
The CNC quality control sector is currently experiencing significant growth driven by technological advancements and an increasing emphasis on precision manufacturing. Global demand for high-quality machined components across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics is propelling the need for robust quality control systems. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers that can guarantee consistency and reliability in product quality.
Emerging technologies, such as AI and machine learning, are reshaping quality control practices. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. Additionally, automation in inspection processes, such as on-machine probing systems, is becoming a standard practice, enabling manufacturers to detect and rectify issues during production rather than post-process.
Another critical trend is the focus on comprehensive quality management systems that integrate various quality control methods—ranging from dimensional accuracy checks to automated inspections. This holistic approach ensures that all potential errors are addressed at multiple stages of production, thus reinforcing the integrity of the final product. For international buyers, aligning with suppliers who leverage these technologies can lead to improved product quality and reduced operational costs.
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing in CNC Quality Control?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone in sourcing practices within the CNC quality control sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt greener practices. This includes sourcing materials that are not only high-quality but also environmentally friendly. Suppliers are increasingly expected to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or implementing energy-efficient processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. B2B buyers are prioritizing vendors who maintain transparent supply chains and adhere to fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other green certifications are becoming prerequisites for suppliers aiming to enter international markets. These certifications not only validate a supplier’s commitment to sustainability but also enhance their competitive edge in a market that increasingly values corporate responsibility.
By choosing suppliers who prioritize sustainability and ethical practices, international buyers can reduce their own environmental footprint while ensuring compliance with global standards. This alignment not only meets consumer demand for responsible products but also fosters long-term partnerships built on shared values.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Quality Control?
The evolution of CNC quality control can be traced back to the advent of CNC machining in the mid-20th century. Initially, quality control processes were rudimentary, relying heavily on manual inspections and basic measurement tools. However, as CNC technology advanced, so did the methods of ensuring quality. The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) allowed for greater precision and consistency in production, necessitating more sophisticated quality control measures.
By the 1990s, the incorporation of statistical process control (SPC) and total quality management (TQM) principles began to shape the landscape of CNC quality control. Manufacturers recognized the importance of integrating quality assurance into every stage of the production process rather than relegating it to the final inspection phase. Today, the focus is on implementing advanced technologies such as AI and IoT to facilitate real-time quality monitoring, ensuring that CNC machined components meet rigorous standards of excellence.
This historical context not only highlights the progression of quality control methodologies but also underscores the importance of continuous improvement and innovation in meeting the demands of an increasingly competitive global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc quality control
-
How do I ensure quality control in CNC machining?
To ensure quality control in CNC machining, implement a comprehensive Quality Management System (QMS) that includes regular inspections at multiple stages. Start with raw material inspection to prevent defects, followed by on-machine inspections using probing systems that monitor quality in real time. Finally, conduct human-driven inspections post-machining to catch any errors. Utilizing a combination of these methods will help maintain high standards and reduce the risk of defects in the final products. -
What is the best CNC quality control method for international suppliers?
The best CNC quality control method for international suppliers involves a multi-faceted approach that includes both automated and manual inspections. Automated systems can provide real-time feedback during production, while manual inspections serve as a final checkpoint. Additionally, sourcing from certified vendors ensures compliance with international quality standards. This combination allows for consistent quality across different manufacturing locations, essential for meeting diverse international regulations and customer expectations. -
What are the key parameters to consider when evaluating CNC quality control?
Key parameters to consider when evaluating CNC quality control include dimensional accuracy, tolerances, surface finish, and material integrity. Dimensional accuracy ensures parts fit correctly, while tolerances determine acceptable variations in measurements. Surface finish affects the aesthetic and functional qualities of the parts, and material integrity ensures that the components will withstand operational demands. A thorough understanding of these parameters will help buyers assess potential suppliers effectively. -
How can I vet suppliers for CNC machining quality control?
Vetting suppliers for CNC machining quality control involves several steps. Start by checking for relevant certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request references and case studies to evaluate their past performance. Additionally, consider conducting site visits to assess their facilities and quality control processes. Engaging in direct communication regarding their quality assurance practices will also provide insights into their commitment to maintaining high standards. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect from CNC suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) from CNC suppliers can vary significantly based on the complexity of the parts, the materials used, and the supplier’s production capabilities. Generally, MOQs can range from a few dozen to several hundred units. It’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront with potential suppliers to ensure they align with your project needs. Some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs for long-term contracts or consistent order volumes. -
What payment terms are typical in international CNC machining contracts?
Typical payment terms in international CNC machining contracts often include a combination of upfront deposits and milestone payments. A common structure is a 30% deposit upon order confirmation, followed by further payments at various stages of production, with the remaining balance due upon delivery. Terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s creditworthiness, so it’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide both security and flexibility. -
How do logistics impact CNC quality control in international shipments?
Logistics play a crucial role in CNC quality control, as delays or mishandling during transport can compromise the integrity of machined components. It’s essential to work with reliable logistics partners who understand the specific needs of CNC parts, including temperature control and protection from physical damage. Additionally, incorporating quality checks at the point of delivery ensures that any issues can be addressed promptly, maintaining the overall quality of the supply chain. -
What role does customization play in CNC machining quality control?
Customization significantly impacts CNC machining quality control by necessitating tailored quality assurance processes for unique specifications. When parts require specific dimensions, materials, or finishes, quality control measures must be adapted accordingly. This may involve developing specialized inspection protocols and utilizing advanced machining technologies. Clear communication with suppliers about customization requirements ensures that quality standards are met, reducing the risk of defects in specialized orders.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Cnc Quality Control Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AMFG – CNC Machining Quality Control Strategies
Domain: amfg.ai
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining Quality Control strategies include: 1. Choosing the right CNC machine type (three-axis for simpler designs, four- or five-axis for complex components). 2. Inspecting raw materials before machining to ensure quality and prevent defects. 3. Implementing on-machine inspection using probing systems for real-time quality checks during operation. 4. Employing multiple quality control metho…
2. IIoT World – Essential Manufacturing Insights
Domain: iiot-world.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: 1. CNC Machines: Importance of selecting suitable machines for specific operations; recommendation for 4-or 5-axis machines for complex tasks. 2. Raw Material Quality: Emphasis on inspecting raw materials before production to avoid faults; importance of procuring from reliable vendors. 3. Quality Control Procedures: Need for multiple quality control techniques; suggestion for pre-machining, in-pro…
3. Violintec – Quality Control in CNC Machining
Domain: violintec.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Quality Control in CNC Machining involves using specific instruments and techniques to ensure output meets industry standards. Key parameters include: 1. Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerance: Measures how closely actual dimensions match specifications, with tolerances typically around ±0.1mm. 2. Material Hardness and Strength: Critical for ensuring materials can withstand intended conditions. 3. Rou…
4. Quality Control – Starting Salary Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Quality Control – Starting Salary Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Fadal – CNC Machining Centers and Workholding Solutions
Domain: fadal.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Fadal is a premier CNC machine builder in North America, offering various CNC machining centers including VMC’s such as VMC 2015HS, VMC 2520, VMC 3320, VMC 4020, VMC 4022, VMC 6032, VMC 8032, VMC 6032/50T, and VMC 8032/50T 5-Axis Machine. They also provide workholding solutions like MULTIRISERS, RISERS, ADJUSTABLE RISERS, FAST MILL ZERO, SPECIAL, STANDARD AND MODULAR PLATES, and MINI RANGE THIRD C…
6. GN Corporations – CNC Machining Services
Domain: gncorporations.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: CNC machining services for various industries including aerospace, automotive, defense, and oil & gas. Key processes include quality control and inspection, focusing on dimensional accuracy, surface finish, material hardness, and strength. Techniques and tools used for quality control include coordinate measuring machines (CMM), optical comparators, surface profilometers, and hardness testers. Ins…
7. MakerVerse – Quality Control Solutions for CNC Machined Parts
Domain: makerverse.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Quality Control Options for CNC Machined Parts include: 1. Visual Inspection: Every part undergoes a visual inspection by engineering experts. 2. Material Certificate 3.1: Verification of material quality and composition with an official test report. 3. Dimensional Measurement Report: Records measurements and dimensions for sample parts to ensure adherence to specified tolerances. 4. Certificate o…
8. Frog3D – CNC Machining Quality Control
Domain: frog3d.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: CNC machining quality control and inspection involves precise instruments and techniques to ensure final outputs meet industry standards. Key parameters include dimensional accuracy and tolerance, surface finish and roughness, and the use of instruments like micrometers, calipers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) for measurement checks. Regular inspections are crucial for maintaining qualit…
9. Aerostar Manufacturing – CNC Production Machining
Domain: aerostarmfg.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: CNC Production Machining, Precision CNC Machining, Machined Castings, Prototype and Low Volume CNC Machining, Machined Forgings, Sheet Metal Fabrication, Stamping, Aluminum Extrusions, Gear Manufacturing, Machined Assemblies, Inspection Services, Global Manufacturing, U.S. Operations, India Operations, Global Supply Chain Locations.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc quality control
In the realm of CNC quality control, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in ensuring the consistency and excellence of manufactured components. By prioritizing the selection of high-quality raw materials, utilizing the appropriate CNC machinery, and implementing a multi-faceted quality control approach, businesses can significantly reduce errors and enhance production efficiency. Engaging with certified vendors not only streamlines the quality assurance process but also fosters long-term partnerships that are essential for growth in competitive markets.
As international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of CNC machining, it is crucial to embrace a proactive stance on quality control. Investing in advanced inspection technologies, such as on-machine probing systems, and maintaining rigorous quality checks throughout the production cycle can lead to substantial cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Looking ahead, the landscape of CNC quality control will continue to evolve with advancements in technology and materials. To remain competitive, buyers must stay informed and adapt their sourcing strategies accordingly. Now is the time to leverage these insights and strengthen your quality control processes to ensure your products meet the highest standards of excellence.