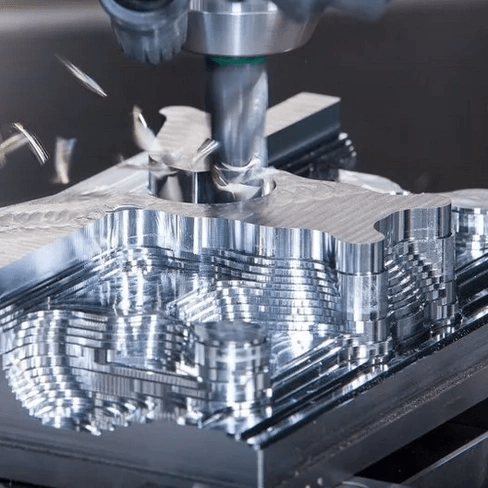
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc mill for steel
Navigating the global market for CNC mills for steel presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers often grapple with sourcing equipment that not only meets their production needs but also aligns with their budget constraints and technological capabilities. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of acquiring CNC mills designed for steel machining, providing a comprehensive overview of various machine types, their applications, and essential supplier vetting processes.
Throughout this guide, readers will discover valuable insights into the latest CNC technologies, including desktop models and industrial-grade machines capable of handling tough materials like titanium and hardened steel. We will explore the cost considerations associated with these machines, including initial investment, operational efficiency, and potential returns on investment. Furthermore, we will highlight best practices for evaluating suppliers, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their manufacturing capabilities.
By empowering B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate this intricate landscape, this guide serves as a crucial resource for those looking to optimize their procurement strategies. Whether you’re a manufacturer in Brazil seeking to expand your production line or a workshop owner in Nigeria looking for reliable machinery, the insights provided here will help you make strategic purchasing decisions tailored to your specific market needs.
Understanding cnc mill for steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop CNC Mills | Compact size, portability, and ability to handle various materials, including steel and titanium. | Prototyping, small-scale production, educational purposes. | Pros: Affordable, easy to use, versatile. Cons: Limited production capacity compared to larger mills. |
| Vertical CNC Mills | Vertical spindle orientation, suitable for complex geometries, and high precision. | Aerospace, automotive, and mold-making industries. | Pros: High precision, versatile tooling options. Cons: Requires more floor space, can be costlier. |
| Gantry CNC Mills | Large cutting area, robust construction for heavy-duty machining, and multi-axis capabilities. | Heavy manufacturing, large part fabrication, and construction. | Pros: Excellent for large workpieces, high rigidity. Cons: Higher initial investment, complex setup. |
| Bed Mills | Sturdy design with a stationary bed, ideal for heavier workpieces and high-volume production. | Metal fabrication, tool and die manufacturing. | Pros: Stronger structure, excellent for heavy cuts. Cons: Less flexible than vertical mills, can be slower. |
| Multi-Tasking CNC | Combines milling and turning capabilities, often with integrated automation features. | Aerospace, automotive, and complex part production. | Pros: Versatile, can reduce production time. Cons: Higher cost, requires skilled operators. |
What are Desktop CNC Mills and Their B2B Relevance?
Desktop CNC mills are compact machines designed for versatility and ease of use, capable of machining materials like steel and titanium. They are particularly suited for prototyping and small-scale production, making them ideal for startups or educational institutions. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the machine’s power, precision, and software compatibility, as these factors can significantly impact production efficiency and output quality.
How Do Vertical CNC Mills Serve Different Industries?
Vertical CNC mills are characterized by their vertical spindle orientation, allowing for intricate cutting and high precision. These mills are commonly used in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where detailed components are essential. Buyers should consider the machine’s footprint, tooling options, and software capabilities when selecting a vertical CNC mill, as these elements influence both operational efficiency and production scalability.
What Advantages Do Gantry CNC Mills Offer?
Gantry CNC mills feature a robust design that allows for significant cutting areas and the ability to handle heavy-duty machining tasks. They are well-suited for applications in heavy manufacturing and large part fabrication. B2B buyers should assess the machine’s rigidity, power, and multi-axis capabilities, as these aspects determine the mill’s performance with large workpieces and complex geometries.
Why Choose Bed Mills for Heavy Workpieces?
Bed mills provide a sturdy design with a stationary bed, making them ideal for high-volume production and heavy workpieces. They are widely utilized in metal fabrication and tool and die manufacturing. When purchasing a bed mill, buyers should focus on the machine’s weight capacity and cutting speed, as these factors directly affect productivity and the ability to handle tough materials.
What are the Benefits of Multi-Tasking CNC Machines?
Multi-tasking CNC machines combine milling and turning capabilities, often with automation features to streamline production processes. They are particularly beneficial in industries that require complex part production, such as aerospace and automotive. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment, as well as the skill level required for operation, to ensure that the machine aligns with their production needs and workforce capabilities.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc mill for steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Mill for Steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision components for aircraft | High precision and reliability in critical applications | Certification for aerospace standards and material traceability |
| Automotive | Custom tooling and parts manufacturing | Enhanced production efficiency and reduced lead times | Compatibility with existing systems and scalability options |
| Oil & Gas | Machining of valves, fittings, and pipeline parts | Durability and resistance to harsh environments | Supplier reliability and compliance with industry safety standards |
| Construction | Structural steel components and frameworks | Cost-effective production of large-scale projects | Bulk material sourcing and delivery timelines |
| Renewable Energy | Fabrication of components for wind turbines | Support for sustainable energy initiatives | Material specifications and environmental certifications |
How is CNC Milling for Steel Used in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, CNC mills are used to manufacture precision components such as brackets, housings, and structural elements that require stringent tolerances. These components must withstand extreme conditions while maintaining structural integrity. Buyers in this industry must ensure that their CNC mills are capable of high precision and are compliant with international aerospace standards, including certifications like AS9100. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who provide material traceability is critical to ensure safety and reliability in aircraft manufacturing.
What Role Does CNC Milling Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
CNC mills are essential in the automotive industry for creating custom tooling, engine parts, and various components that require intricate designs and high durability. The ability to produce parts with reduced lead times enhances overall production efficiency, allowing manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands. Automotive buyers should consider mills that can integrate with existing manufacturing systems and offer scalability for future production needs, ensuring that they can meet fluctuating market demands without significant delays.
How Does CNC Milling Benefit the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, CNC milling is utilized to machine critical components such as valves, fittings, and pipeline parts that must endure high pressures and corrosive environments. The durability and precision of these parts are vital for operational safety and efficiency. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that adhere to stringent industry safety standards, as well as those who can guarantee the quality and reliability of their products in extreme conditions.
Why is CNC Milling Important for Construction Projects?
CNC milling serves a crucial role in the construction industry by enabling the production of structural steel components and frameworks that are essential for large-scale projects. The ability to produce these components cost-effectively and with high precision can significantly impact project timelines and budgets. For international buyers, considerations should include the supplier’s capability for bulk material sourcing and their ability to meet delivery timelines, which are critical for the smooth execution of construction projects.
How is CNC Milling Used in Renewable Energy Applications?
CNC milling is increasingly being used in the renewable energy sector for fabricating components for wind turbines and other energy systems. These components must meet strict performance criteria while supporting sustainable energy initiatives. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing materials that meet specific environmental certifications and standards. Additionally, understanding the capabilities of CNC mills to produce complex geometries efficiently will be vital in supporting the industry’s growth and innovation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc mill for steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming Limited Material Compatibility in CNC Milling
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing CNC mills that can effectively handle a variety of materials, especially when dealing with steel and other tough metals. Buyers often find that some machines are only designed for softer materials, leading to frustration when attempting to expand their production capabilities. This limitation can hinder business growth, especially for companies looking to diversify their product offerings or serve different industries.
The Solution: When sourcing a CNC mill for steel, it’s essential to prioritize machines specifically engineered for hard materials. Look for machines that advertise compatibility with a broad spectrum of materials, including stainless steel, titanium, and other high-strength alloys. For instance, mills like the Tormach 1100M or Coast Runner CNC offer robust specifications that enable them to cut through tough materials with precision. Ensure the CNC mill features high spindle speeds and sufficient power to handle the thermal and mechanical stresses of steel machining. Additionally, consider investing in tooling and accessories that are designed for these materials to enhance performance and prolong tool life. Regular training for operators on best practices for milling steel can also minimize errors and improve production efficiency.
Scenario 2: Addressing High Operational Costs of CNC Milling
The Problem: Operational costs associated with CNC milling, including machine maintenance, tooling, and energy consumption, can be a significant burden for B2B buyers, especially in regions with limited budgets. For small to medium-sized enterprises, these costs can quickly accumulate, leading to reduced profitability and competitiveness in the market.
The Solution: To mitigate high operational costs, consider investing in CNC mills that offer energy-efficient designs and low-maintenance features. For instance, machines with a reputation for durability and reliability, like the MR-1 CNC Gantry Mill, can help reduce long-term expenses. Furthermore, look for CNC mills that come with software solutions offering efficient toolpath generation and scheduling, which can optimize machining time and reduce waste. Regularly evaluate your production processes to identify inefficiencies and explore options for upgrading to more advanced machines that offer better energy consumption rates and less downtime. Establishing a routine maintenance schedule can also prevent costly repairs and extend the lifespan of the machinery.
Scenario 3: Navigating the Learning Curve of CNC Mill Operation
The Problem: Many businesses struggle with the steep learning curve associated with operating CNC mills, particularly when transitioning from manual to automated systems. This challenge can lead to underutilization of equipment, production delays, and increased labor costs as employees require extensive training to become proficient in operating these machines.
The Solution: To ease the transition to CNC milling for steel, choose machines equipped with user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive training resources. For example, the Tormach 1100M features the PathPilot controller, which offers an intuitive touchscreen interface and built-in conversational programming that simplifies the learning process. Additionally, consider investing in training programs or workshops that provide hands-on experience with the equipment. Online resources, including video tutorials and community forums, can also be invaluable for ongoing support. Building a culture of continuous learning within the organization will empower employees to become more proficient, ultimately enhancing productivity and reducing operational errors. Encourage collaboration among staff to share knowledge and best practices, further streamlining the adoption of CNC technologies in your operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc mill for steel
What Are the Key Materials for CNC Milling Steel?
When selecting materials for CNC milling steel, it is essential to consider the specific properties and applications of various materials. This guide analyzes four common materials—carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium—focusing on their performance, advantages, and limitations from a B2B perspective.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in CNC Milling?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and hardness, making it suitable for various machining applications. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°C and exhibits good wear resistance. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its durability and cost-effectiveness. It is relatively inexpensive compared to other materials, making it a popular choice for high-volume production. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can be a significant drawback, particularly in humid or corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is ideal for applications requiring high strength and toughness, such as structural components. However, its corrosion vulnerability necessitates protective coatings or treatments, especially for products used in outdoor or marine environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers can meet local regulations regarding material quality and environmental impact.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for CNC Milling?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance, high-temperature stability, and aesthetic appeal. It can withstand temperatures exceeding 800°C and is often used in food processing and medical applications due to its hygienic properties.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and low maintenance requirements, making it suitable for high-end applications. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to machine due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications requiring cleanliness and resistance to corrosion, such as in the food industry or medical devices. Its durability ensures that products maintain their integrity over time, even in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM A304 or A316 and ensure compliance with local regulations. In regions like the Middle East, where corrosion resistance is critical, stainless steel is often preferred.
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum in CNC Milling?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent corrosion resistance, and offers good thermal conductivity. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 200°C and is non-magnetic, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which reduces shipping costs and makes it easier to handle. However, it is softer than steel, leading to potential wear and deformation under heavy loads.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. However, its lower strength compared to steel limits its use in high-stress applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B221 is essential. Buyers in Europe and South America should consider the availability of aluminum alloys that meet local specifications for strength and corrosion resistance.
How Does Titanium Compare in CNC Milling Applications?
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, high corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures (up to 600°C). It is also biocompatible, making it ideal for medical applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of titanium is its strength and lightness, making it suitable for demanding applications like aerospace and medical implants. However, it is significantly more expensive than other materials and can be challenging to machine due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Titanium is ideal for applications requiring high strength and low weight, such as in aerospace components. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for marine environments, but its cost can be a limiting factor for many businesses.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM F136 for medical applications is vital. Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should assess the availability and cost of titanium, as it may not be as readily accessible as other materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Milling Steel
| Material | Typical Use Case for CNC Mill for Steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural components | Cost-effective and durable | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical devices | Corrosion resistant and hygienic | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | High strength-to-weight ratio | Very expensive and hard to machine | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc mill for steel
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of CNC Mills for Steel?
The manufacturing process of CNC mills specifically designed for machining steel encompasses several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they select a machine that meets their operational needs and quality standards.
Material Preparation: What Is Involved?
The first step in manufacturing a CNC mill involves selecting high-grade materials, typically steel alloys, that can withstand the stresses of machining. This phase includes cutting raw materials to size, stress-relieving them through heat treatment, and ensuring they are free from defects. Manufacturers often employ advanced techniques like laser cutting or waterjet cutting for precision, ensuring that the dimensions meet design specifications.
Forming: How Is the CNC Mill Shaped?
The forming stage is where the raw materials are machined into the components of the CNC mill. Techniques such as casting, forging, or machining are commonly used. For CNC mills designed for steel, machining operations like milling, turning, and grinding are prevalent. Precision is crucial, as even minor deviations can affect the machine’s performance. Manufacturers often use CNC machining centers during this stage to ensure high accuracy and repeatability.
Assembly: What Are the Key Considerations?
Once individual components are formed, they are assembled to create the final product. This stage requires meticulous attention to detail, as misalignment can lead to operational inefficiencies. Many manufacturers follow a standardized assembly process, which may include the integration of electronic systems, drive mechanisms, and control software.
Additionally, manufacturers often conduct a preliminary quality check during assembly, ensuring that parts fit correctly and function as intended. This is a vital step to minimize issues during the final testing phase.
Finishing: What Processes Are Used?
The finishing stage includes surface treatments such as anodizing, powder coating, or painting to enhance durability and corrosion resistance. These treatments not only improve the aesthetic appeal but also protect the machine in various operating environments.
Manufacturers may also implement precision grinding and polishing to achieve the desired surface finish and tolerances. This stage is crucial for ensuring the machine operates smoothly and efficiently over its lifespan.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in CNC Mill Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that each CNC mill meets international standards and customer expectations.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for CNC Mill Quality?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a pivotal role in quality assurance for CNC mill manufacturers. ISO 9001 outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS), emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for compliance with European health and safety standards) and API certification (for oil and gas equipment) are crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those from regulated markets in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial phase involves inspecting raw materials to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, ongoing inspections are conducted to identify any deviations from quality standards. This may involve measuring dimensions, checking tolerances, and assessing machining accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the finished CNC mill undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance specifications. This stage may include functional tests, accuracy checks, and safety assessments.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to ensure quality:
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing and magnetic particle inspection are used to detect internal and surface defects without damaging the components.
-
Functional Testing: This involves running the CNC mill through its paces to ensure it operates correctly under real-world conditions.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Using precision instruments like calipers and CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines), manufacturers verify that the dimensions of the components meet design specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is critical to ensuring that the CNC mills they purchase meet their operational needs.
What Steps Should Buyers Take?
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. This can include on-site visits to evaluate their facilities and practices.
-
Request Quality Assurance Documentation: Buyers should request certificates of compliance, inspection reports, and details of the supplier’s quality management system to understand their commitment to quality.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly beneficial for buyers operating in regions with stringent compliance requirements.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must navigate various regulatory environments and cultural expectations regarding quality. Familiarity with local standards and practices is essential. For instance, buyers in Europe may prioritize CE certification, while those in Africa may focus on cost-effectiveness and local support.
Additionally, language barriers and differing business practices can complicate communication. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication with suppliers can help mitigate these challenges.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for CNC mills designed for steel is vital for B2B buyers. By comprehending the stages of manufacturing, relevant international standards, and effective quality control measures, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and compliance obligations. This comprehensive approach not only ensures the acquisition of high-quality machinery but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc mill for steel’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring a CNC mill for steel, this practical sourcing guide offers a structured checklist. Each step is designed to ensure you make an informed decision that aligns with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital to ensure the CNC mill meets your operational requirements. Consider factors such as the types of steel you will be milling, desired precision levels, and the volume of production. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and select a machine that fits your specific applications.
Step 2: Assess Your Budget Constraints
Before diving into the procurement process, determine your budget for the CNC mill. This includes not just the purchase price, but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs. A thorough budget assessment will help you avoid overspending and ensure you select a machine that offers the best value for your investment.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers that have a proven track record with CNC mills for steel, as this experience can significantly impact the quality and reliability of the machinery.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure the suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO or CE, which indicate compliance with international quality standards.
- Assess Customer Support: Investigate the level of technical support and service offered, as strong after-sales support is essential for long-term operational success.
Step 4: Compare Technical Features
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, compare the technical features of the CNC mills they offer. Focus on aspects like spindle speed, power, and axis movement capabilities. A machine that can handle a variety of materials and offers high precision will provide more versatility and longevity for your operations.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Before making a final decision, request demonstrations or trials of the CNC mills you are considering. This hands-on experience allows you to evaluate the machine’s performance, ease of use, and compatibility with your existing processes. Observing the machine in action can also help you better understand its capabilities and limitations.
Step 6: Review Warranty and Service Agreements
A comprehensive warranty and service agreement is essential when purchasing a CNC mill. Review the terms thoroughly to understand what is covered, the duration of the warranty, and the availability of extended service options. A robust service agreement can save your business significant costs in the long run by minimizing downtime and maintenance expenses.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Plan for Installation
After selecting a CNC mill, finalize your purchase and plan for its installation. Coordinate with the supplier regarding delivery schedules and any necessary site preparations. Proper planning for installation ensures a smooth transition and operational readiness, allowing your business to maximize the benefits of the new machinery right away.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of procuring a CNC mill for steel with confidence and clarity, ensuring they make a well-informed investment that meets their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc mill for steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing CNC Mills for Steel?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing CNC mills for steel, several critical components must be considered. The primary cost elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the pricing of CNC mills. High-quality steel and other robust materials often lead to higher upfront costs but ensure durability and performance. The price of raw materials fluctuates based on market demand, which can affect overall costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in both the production and assembly of CNC mills. Depending on the region, labor costs can vary widely, influencing the final pricing. Manufacturers in regions with higher labor costs may pass these expenses on to buyers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs, which directly impacts the final price of the CNC mill.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and fixtures required for machining steel can contribute significantly to costs. Custom tooling designed for specific operations can increase initial expenses but can also enhance productivity and precision.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent quality control measures is vital in ensuring the reliability and performance of CNC mills. However, these measures add to the overall cost structure. Buyers should seek suppliers who balance quality with cost-effectiveness.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs, especially for international buyers, can vary significantly based on distance, weight, and shipping method. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) play a crucial role in determining which party bears these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up their prices to cover costs and secure a profit margin. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position, reputation, and the level of service provided.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Mill Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of CNC mills for steel, including volume, specifications, materials, quality certifications, supplier characteristics, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to discounts. Suppliers are generally willing to negotiate prices for bulk orders, which can significantly reduce the cost per unit.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features and specifications can raise costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses. Standardized models typically have lower pricing due to economies of scale.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: The choice of materials and the level of quality assurance certifications (like ISO) can influence price. Higher quality and certified machines often come at a premium but provide better reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices, but their products often come with better support and reliability. Conversely, newer suppliers may offer lower prices but could lack in quality or service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) affect cost responsibility and should be negotiated clearly to avoid unexpected costs.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating CNC Mill Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can lead to substantial savings.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research to understand standard pricing and features across different suppliers. This knowledge empowers you during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with the CNC mill, including maintenance, parts, and operational efficiency. This approach helps justify higher initial prices for machines that offer lower TCO.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better deals. Regular communication and establishing trust can often yield favorable pricing terms.
-
Be Prepared to Walk Away: If the terms are not favorable, be willing to explore other suppliers. This stance can often prompt suppliers to reconsider their offers.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Local suppliers may offer lower shipping costs and shorter lead times, which can be beneficial for overall pricing.
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and the various factors influencing pricing is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions in the CNC mill market. By leveraging this knowledge, buyers can negotiate better deals and ultimately enhance their operational efficiency.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc mill for steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CNC Milling for Steel
In the world of metal fabrication, CNC milling for steel is a popular choice due to its precision and versatility. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit the specific needs of businesses, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section evaluates CNC mills against other viable solutions, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Mill for Steel | Laser Cutting | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, up to 0.001 in. | Excellent for intricate designs | Very high tolerances, minimal heat-affected zone |
| Cost | Moderate to high (e.g., $14,119) | Moderate (equipment costs vary) | High initial investment (e.g., $50,000+) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators | Easier to operate, less training needed | Complex setup, requires skilled technicians |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Low maintenance, easy to clean | High maintenance due to abrasive materials |
| Best Use Case | Complex shapes, tight tolerances | Thin materials, intricate designs | Thick materials, large-scale cuts |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is an effective alternative for businesses focusing on precision and speed. This method utilizes focused laser beams to cut through materials, making it ideal for intricate designs and thin sheets of metal. The primary advantages include a shorter learning curve and faster operation, which can enhance productivity. However, it may struggle with thicker materials and is less effective for applications requiring deep cuts or high tolerances compared to CNC milling.
Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet cutting employs high-pressure water mixed with abrasives to slice through materials, including steel. This method excels in cutting thick materials and is known for producing minimal thermal distortion, preserving the integrity of the metal. The high upfront cost and complex setup can be drawbacks, making it less accessible for smaller businesses. However, for industries that require precision in thicker metals or wish to avoid heat-affected zones, waterjet cutting can be an excellent investment.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating which solution to adopt for steel machining, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including the type of materials they work with, the complexity of designs, budget constraints, and the skill level of their workforce. CNC mills offer unparalleled precision for complex tasks but come with higher operational and maintenance demands. In contrast, laser cutting provides speed and ease of use for thinner materials, while waterjet cutting is best suited for heavier applications. By aligning these factors with business objectives and operational capabilities, buyers can select the most appropriate machining solution for their specific needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc mill for steel
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of a CNC Mill for Steel?
When selecting a CNC mill for steel, understanding the technical specifications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical properties to consider:
1. Material Compatibility
CNC mills must be capable of machining various grades of steel, such as stainless steel, tool steel, and titanium. Different materials have unique hardness and cutting requirements, which can significantly impact the choice of milling equipment. For B2B buyers, ensuring that the CNC mill can handle the specific materials they plan to work with is crucial for operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In CNC machining, common tolerances can range from ±0.001 inches to ±0.0005 inches, depending on the complexity of the part being produced. High tolerance levels are critical for industries like aerospace or automotive, where precision is paramount. Buyers must evaluate whether the machine can meet their specific tolerance requirements to avoid costly rework or rejects.
3. Spindle Power and Speed
The spindle power (measured in horsepower or kilowatts) and maximum spindle speed (RPM) are vital for determining the milling machine’s cutting capabilities. A higher spindle power allows for effective machining of tougher materials, while higher RPM can improve surface finish and reduce machining time. For B2B buyers, understanding these metrics helps gauge the machine’s performance in their production environment.
4. Travel and Work Envelope
The travel specifications (X, Y, and Z axes) define the maximum size of the workpiece that can be machined. A larger work envelope allows for more flexibility in production, enabling the machining of larger components without the need for multiple setups. Buyers should assess their production needs against the machine’s travel specifications to ensure compatibility.
5. Control System
Modern CNC mills utilize advanced control systems that offer user-friendly interfaces and capabilities for complex machining tasks. Systems like Tormach’s PathPilot provide intuitive programming options and built-in calculators for speeds and feeds. A robust control system can enhance productivity and reduce the learning curve for operators, which is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to minimize downtime.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with CNC Mills for Steel?
Understanding industry terminology can greatly enhance communication with suppliers and help streamline procurement processes. Here are some essential trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CNC mills, buyers may source machines or components from OEMs to ensure high-quality and reliable equipment tailored to their specific needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management, especially when considering bulk purchases of CNC machinery or replacement parts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. It helps buyers compare offers from different manufacturers, ensuring they receive competitive pricing and favorable terms for CNC mills and related equipment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the shipping and delivery of goods. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in international transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for costs and risks during transportation.
5. CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
CAM software is used to automate the manufacturing process by converting design data into machine-readable code. It is essential for CNC mills, as it enables efficient and precise machining of components. Buyers should consider machines that integrate seamlessly with CAM systems to enhance their production workflows.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when investing in CNC mills for steel, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc mill for steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting CNC Mills for Steel?
The CNC milling market for steel is experiencing a robust transformation driven by several global factors. Increased demand for precision-engineered components across various sectors—such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing—fuels the market’s growth. International B2B buyers, especially from emerging economies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking affordable yet high-performance CNC milling solutions. The proliferation of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and AI-driven automation, is reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling companies to optimize production processes and reduce operational costs.
Furthermore, the trend towards modular and adaptable machinery allows businesses to invest in equipment that can evolve alongside their production needs. This adaptability is particularly valuable for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) that require flexibility without compromising quality. Companies like Tormach and Coast Runner exemplify this trend by offering CNC mills that provide advanced capabilities while remaining accessible to businesses with varying budgets.
Additionally, the rise of online communities and knowledge-sharing platforms facilitates collaboration among manufacturers, engineers, and designers, thereby enhancing innovation and reducing the time to market for new products. As global supply chains become more interconnected, understanding the nuances of sourcing CNC mills for steel is crucial for international buyers aiming to stay competitive.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the CNC Mill for Steel Industry?
Sustainability has become a central theme in the sourcing of CNC mills for steel, with environmental impact and ethical supply chains gaining prominence among B2B buyers. The production of CNC machinery often involves significant energy consumption and material waste, prompting manufacturers to adopt greener practices. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who prioritize sustainability by utilizing recyclable materials, reducing emissions, and implementing energy-efficient technologies.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies aim to ensure that their supply chains do not exploit labor or harm communities. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of green materials can enhance a company’s reputation and marketability. For instance, sourcing CNC mills from manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also appeals to a growing consumer base that values ethical considerations.
As international regulations regarding environmental standards tighten, companies that proactively adopt sustainable practices will likely find themselves at a competitive advantage. This trend is especially relevant for buyers in regions like Europe and North America, where regulatory scrutiny is increasingly stringent.
What Is the Brief Evolution of CNC Mills for Steel?
The evolution of CNC mills for steel has been marked by significant technological advancements and increased accessibility for a broader range of users. Initially, CNC technology was confined to large industrial players due to high costs and complexity. However, the introduction of more compact and affordable models, such as desktop CNC mills, has democratized access to precision machining.
Over the years, the integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software has streamlined the milling process, allowing for greater precision and efficiency. The emergence of advanced materials and coatings has enhanced the performance of CNC mills, enabling them to cut harder materials like titanium and stainless steel with ease.
Today, international B2B buyers benefit from a diverse range of CNC milling options tailored to various applications, from prototyping to small-scale production. As the market continues to evolve, the focus on user-friendly interfaces and automation will likely shape the future of CNC milling technology, making it an indispensable tool for manufacturers worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc mill for steel
-
How do I choose the right CNC mill for steel machining?
Selecting the right CNC mill for steel involves evaluating several key factors: the machine’s rigidity, power, and capabilities for cutting various steel grades. Consider the size of the parts you intend to produce and the machine’s footprint to ensure it fits your workspace. Additionally, assess the software compatibility, ease of operation, and customer support from the manufacturer. Researching user reviews and case studies can provide insights into the machine’s performance in real-world applications, helping you make an informed decision. -
What is the best CNC milling machine for small to medium-sized businesses?
For small to medium-sized businesses, machines like the Tormach 1100M and Coast Runner CR-1 are excellent choices. They offer a balance of affordability, power, and precision, making them suitable for machining steel and other materials. Look for features such as easy-to-use control software, support for various tooling options, and the ability to upgrade as your production needs grow. These machines are designed to thrive in confined spaces while providing the capability to handle tough materials effectively. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing CNC mills internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers, but common practices include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the balance due prior to shipping. Some suppliers may offer financing options or payment plans, especially for larger purchases. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfer, credit card) and any associated fees. Ensure that the terms are documented in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings later. -
How can I ensure quality and reliability when sourcing CNC mills from overseas suppliers?
To ensure quality and reliability, start by thoroughly vetting potential suppliers. Check for certifications, such as ISO 9001, and request references from previous customers. It’s advisable to visit the manufacturing facility if possible or utilize third-party inspection services to assess the machinery before shipment. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer warranties and post-purchase support, which can be indicative of their commitment to quality. -
What is the average lead time for CNC mill deliveries?
The average lead time for CNC mill deliveries can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on factors such as the manufacturer’s location, production schedule, and customization requirements. Standard models may have shorter lead times, while custom configurations can take longer. It’s advisable to communicate your timeline needs upfront and ask for a detailed production and shipping schedule to ensure timely delivery. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC mills?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC mills can vary widely by supplier. Some manufacturers may allow single-unit purchases, while others may require bulk orders to justify production costs. When negotiating with suppliers, discuss your needs and explore options for smaller orders or pilot programs that allow you to test the machine’s capabilities before committing to larger quantities. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for CNC mills?
Handling logistics and shipping for CNC mills requires careful planning. Coordinate with your supplier to understand the shipping options available, including freight costs, insurance, and estimated delivery times. Consider using a freight forwarder experienced in handling heavy machinery to manage customs clearance and ensure compliance with local regulations. Always inspect the machine upon arrival for any damage during transit and verify that it matches the specifications agreed upon. -
What factors should I consider for CNC mill maintenance and support?
When evaluating CNC mills, consider the availability of maintenance support and spare parts. Look for suppliers that offer comprehensive service packages, including routine maintenance, technical support, and training. Understanding the warranty terms is also crucial; longer warranties often indicate confidence in the machine’s durability. Additionally, assess the community and online resources available for troubleshooting and learning, as these can enhance your operational efficiency over time.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Cnc Mill For Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Coast Runner – CR-1 Desktop CNC
Domain: coastrunner.net
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Coast Runner CNC – Desktop CNC for Steel and Titanium
– Model: CR-1
– Weight: 42 lbs
– Dimensions: 15″ x 17″
– Capable of cutting: steel, titanium, wood, Delrin, aluminum, brass, stainless and tool steels
– Precision: holds true cuts to 1/1000 of an inch
– Movement: simultaneous three-axis movement
– Software: CoastCAD (design community), CRWrite (G-code generation), CAM Assist plugin for producti…
2. Langmuir Systems – MR-1 CNC Gantry Mill
Domain: langmuirsystems.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: MR-1 CNC Gantry Mill is a 3-Axis vertical CNC milling machine designed for hobbyist, light industrial, and educational uses. It is capable of machining aluminum, steel, titanium, and stainless steel with high accuracy and precision. The machine starts at $4495, with a limited-time offer of $500 off MSRP. Key specifications include:
– Machine Table Size: 20″ x 20.25″ x 0.700″
– Maximum Weight on Ta…
3. Tormach – 1100M CNC Milling Machine
Domain: tormach.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Tormach’s 1100M CNC Milling Machine is an affordable and easy-to-use mill designed for small businesses, starting at $14,119 with payments as low as $298/month. It can cut tough materials like titanium, stainless steel, and hardened steel, as well as softer materials like plastic and wood. The machine runs on single-phase power and is designed to thrive in confined spaces. Key specifications inclu…
4. Tormach – CNC Mill for Precision Metal Machining
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: CNC mill under 10k that can cut steel; budget slightly less than 10k; required x-axis reach: 10″-20″; required z-axis reach: 7″-15″; focus on machines capable of creating smaller engine and car parts made of aluminum or steel; examples of considered machines: Tormach 440/770, CNC Express from Microkinetics, CNC Baron Mill, PRO4824, older models like Fadal Model 904-1, Haas 1997 VF1, Mazak VQC15; i…
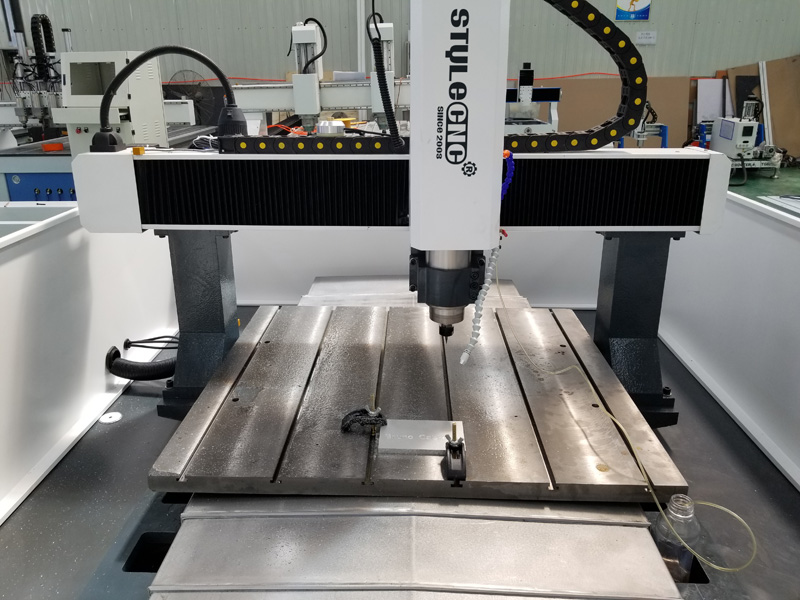
5. STYLECNC – Automatic CNC Metal Milling Machine
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Automatic CNC Metal Milling Machine for Sale – STYLECNC
– Brand: STYLECNC
– Model: ST4040H
– Price: $6,000 (Standard Edition) / $10,000 (Pro Edition)
– Stock: 360 Units available for sale every month
– Standards: Meeting CE Standards in terms of quality & safety
– Warranty: One-Year Limited Warranty for entire machine (extended warranties available for major parts)
– Money Back Guarantee: 30-Day …
6. Onefinity – Steel Cutting Spindles
Domain: forum.onefinitycnc.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Spindles for cutting steel: HFPD-8015-12-ER20 (4 magnetic poles, 1,500 – 12,000 rpm), HFPM-8022-24-ER20 (4 magnetic poles, 3,000 – 24,000 rpm), ATC-12575-12 (4 magnetic poles, 1,500 – 12,000 rpm). Typical spindle choices for Onefinity CNC are not suitable for steel cutting due to high RPM and low torque. Recommended spindle characteristics include low speed (1,500 – 3,000 rpm) and high torque. The…
7. Shariff DMC – DMC2 Mini CNC Machine
Domain: shariffdmc.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Metal Desktop CNC Machines
– Model: DMC2 Mini
– Axis Configuration: 3 and 4 Axis
– X Axis Travel: 12″
– Y Axis Travel: 7″
– Z Axis Travel: 5.5″
– Cutting Accuracy: < 0.01mm
– Spindle Power: 2.2kW (3HP)
– Spindle Speed: 24,000 RPM
– Motor Type: High Speed Closed Loop XYZ Motors
– Rail Size: 15mm rails
– Ballscrew Size: 12mm Ballscrews on all axes
– Coolant System: Enclosed and Recirculating Flood C…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc mill for steel
What Are the Key Takeaways for Strategic Sourcing of CNC Mills for Steel?
In the evolving landscape of CNC milling, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in maximizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness for international buyers. Key considerations include evaluating machine capabilities, such as the ability to handle diverse materials like steel and titanium, while also ensuring ease of use and adaptability to your specific production needs. Machines like the Tormach 1100M and Coast Runner CR-1 exemplify the balance of affordability and advanced features, making them ideal choices for businesses looking to scale.
How Can International Buyers Benefit from Strategic Sourcing?
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging strategic sourcing can open doors to competitive pricing and access to cutting-edge technology. As global supply chains become more interconnected, the ability to source high-quality CNC mills that meet local manufacturing demands is crucial. By focusing on suppliers that offer comprehensive support and customization options, businesses can enhance their production capabilities while minimizing downtime.
What’s Next for CNC Milling in Your Business?
As you consider your next investment in CNC milling technology, now is the time to act. Embrace the opportunities presented by innovative suppliers and advanced machinery to stay ahead of the competition. Engage with vendors, assess their offerings, and explore how a strategic sourcing approach can elevate your operational efficiency. The future of your manufacturing capabilities starts with informed decisions today.