Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Cnc Medical Devices
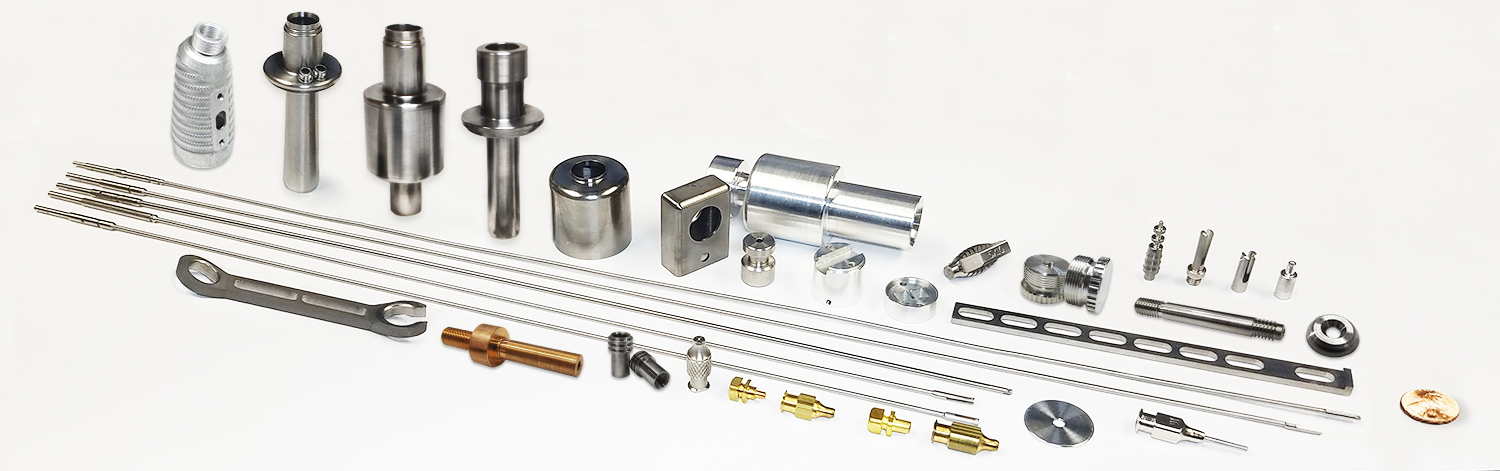

Precision CNC Machining for Critical Medical Device Applications
Honyo Prototype delivers advanced CNC machining services engineered specifically for the stringent demands of medical device manufacturing. Our ISO 13485-certified facility combines multi-axis milling and turning capabilities with deep expertise in biocompatible materials—including titanium alloys, PEEK, and medical-grade stainless steels—to produce components meeting exacting regulatory and functional requirements. Every process adheres to rigorous traceability protocols, ensuring full compliance with FDA and global standards for implantable and surgical instrumentation.
We specialize in transforming complex geometries into high-integrity parts with micron-level tolerances, surface finishes, and repeatable accuracy essential for life-critical applications. From rapid prototyping to low-volume production, Honyo’s engineering team collaborates closely with medical OEMs to optimize designs for manufacturability while maintaining uncompromised quality. Accelerate your development timeline with our Online Instant Quote system, providing detailed cost and lead time analysis within hours—enabling faster project initiation without sacrificing precision or regulatory diligence.
Technical Capabilities
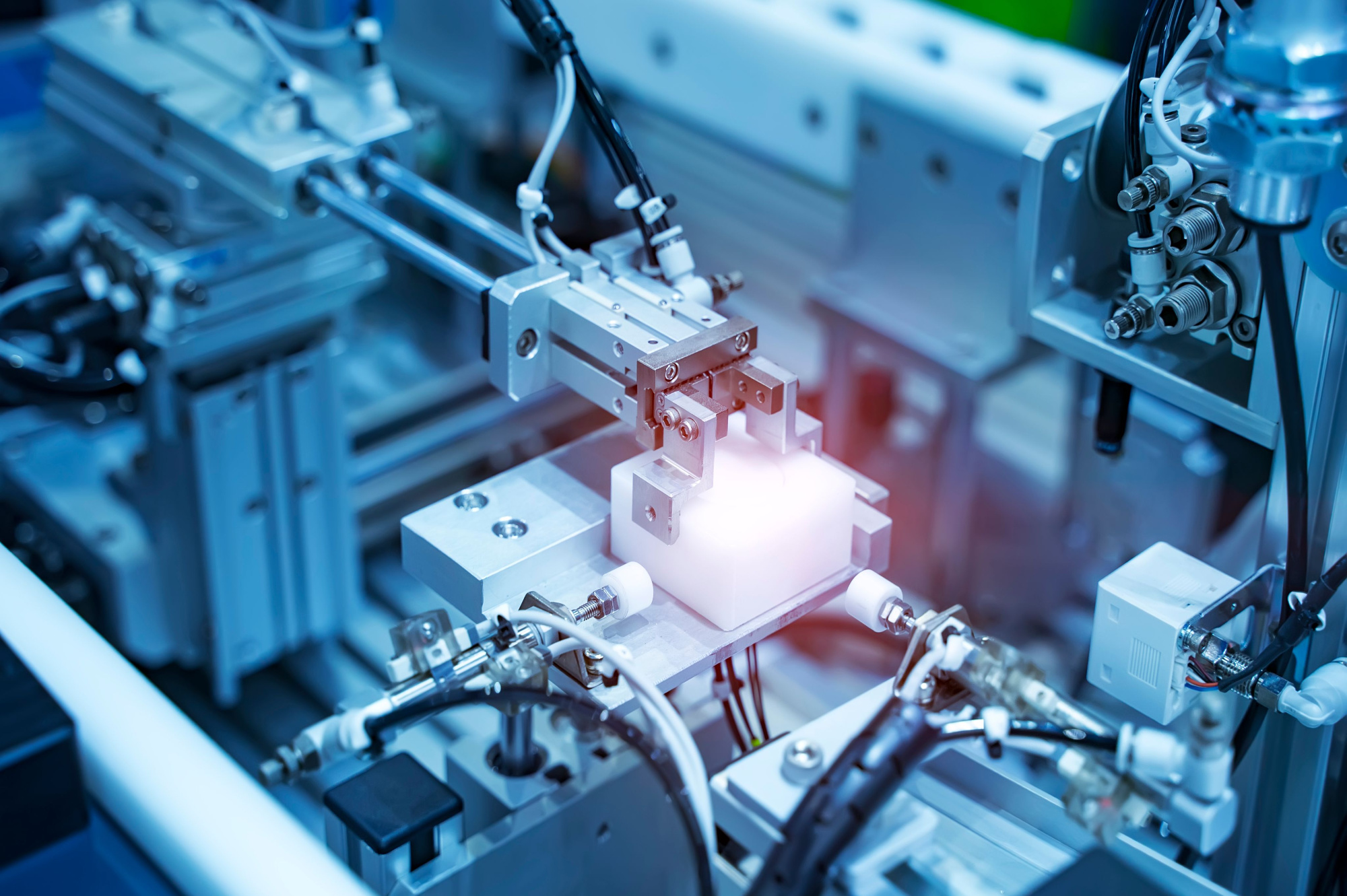
Technical specifications for CNC-machined medical devices require high precision, strict adherence to regulatory standards, and compatibility with biocompatible materials. These components often include surgical instruments, implantable devices, diagnostic equipment parts, and fluid handling systems. Manufacturing processes such as 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling, as well as precision turning, are essential to meet complex geometries and tight tolerance requirements.
Multi-axis milling allows for intricate contours and undercuts without multiple setups, improving accuracy and surface finish. Turning is used for cylindrical components such as instrument shafts or connectors. Tolerances typically range from ±0.0002″ (5 µm) to ±0.001″ (25 µm), depending on part function and regulatory classification.
Common materials used include aluminum and stainless steel for structural and surgical components, while engineering thermoplastics like ABS and nylon are selected for housings, enclosures, and non-implantable disposable parts due to their sterilizability and chemical resistance.
| Parameter | Specification Details |
|---|---|
| Machining Process | 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC milling; CNC turning (including Swiss-type for small parts) |
| Typical Tolerances | ±0.0002″ to ±0.001″ (5–25 µm); critical features held to tightest end of range |
| Surface Finish (Ra) | 16–32 µin (0.4–0.8 µm) standard; down to 8 µin (0.2 µm) for critical sealing surfaces |
| Common Materials | Aluminum (6061, 7075), Stainless Steel (316L, 17-4 PH), ABS, Nylon (6, 66, 12) |
| Material Properties | Biocompatible grades available; corrosion-resistant steels for implantables; sterilizable plastics |
| Part Complexity | High; multi-faceted geometries, thin walls, micro-features, internal channels |
| Regulatory Compliance | ISO 13485 certified processes; full traceability; cleanroom options for Class I/II/III |
| Secondary Operations | Passivation (stainless steel), anodizing (aluminum), precision cleaning, metrology (CMM) |
These technical capabilities ensure that CNC-machined medical components meet functional, safety, and regulatory demands across diagnostic, surgical, and therapeutic applications.
From CAD to Part: The Process
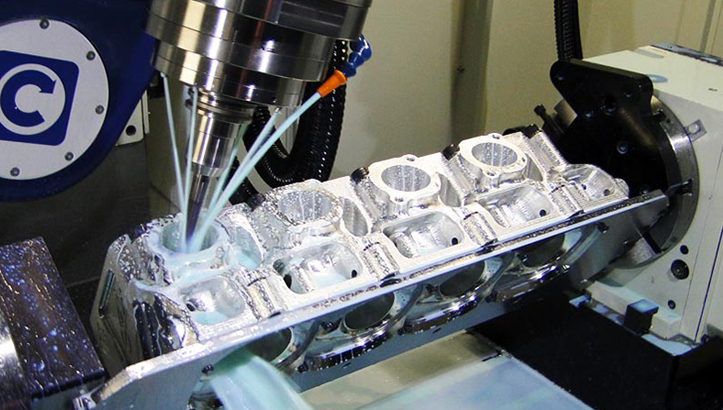
CAD Upload and Validation
Clients initiate the process by uploading native CAD files or industry-standard neutral formats such as STEP or IGES through Honyo’s secure customer portal. Our system automatically validates geometric integrity, unit consistency, and file completeness against ISO 10303 standards. For medical devices, we specifically check for critical feature annotations including surface finish callouts per ASTM F86, radii for stress concentration, and tolerance stacks compliant with ASME Y14.5. Any discrepancies trigger an immediate automated notification to the client with precise error localization.
AI-Powered Quoting Engine
Validated CAD data feeds into our proprietary AI quoting system, which analyzes over 200 parametric variables including material grade (e.g., ASTM F138 stainless steel or ISO 5832-3 titanium), geometric complexity, and secondary operation requirements. The engine cross-references real-time machine utilization data, material costs from certified medical-grade suppliers, and historical cycle time databases to generate quotes within 90 minutes. Crucially, it flags potential regulatory red flags such as inadequate draft angles for molding or unachievable tolerances per ISO 2768-mK, providing actionable alternatives before formal commitment.
Medical-Specific DFM Analysis
Following quote acceptance, our engineering team conducts a rigorous Design for Manufacturability review focused on medical device requirements. This phase includes:
| DFM Check Category | Medical Device Specific Criteria | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | USP Class VI / ISO 10993 biocompatibility documentation | Supplier certificate audit |
| Feature Manufacturability | Minimum wall thickness for sterilization integrity (e.g., 0.5mm for gamma) | CNC simulation with thermal deformation modeling |
| Regulatory Alignment | Traceability of critical dimensions to FDA 21 CFR 820.250 | GD&T compliance mapping against design history file |
| Post-Processing Feasibility | Passivation validation per AMS 2700 for implantables | Chemical process flow validation |
Engineers collaborate with clients via secure video review sessions to resolve conflicts, ensuring designs meet both functional requirements and ISO 13485 documentation standards.
Precision Production Execution
Approved designs move to our ISO 13485-certified cleanroom facility where medical-grade CNC machining occurs under controlled environmental conditions (Class 8 ISO 14644-1). Key production protocols include:
Machines undergo daily laser calibration per ISO 230-2 with compensation for thermal drift. All titanium and cobalt-chrome alloys originate from mill-certified lots with full material traceability. Critical dimensions are verified in-process using calibrated CMMs (NIST-traceable to 1.5μm) with real-time SPC monitoring. Every component receives a unique serialized identifier linked to digital work instructions, ensuring full traceability from raw material to finished part. Secondary operations such as electropolishing or laser marking occur in dedicated stations with documented process validation.
Regulatory-Compliant Delivery
Final inspection packages include comprehensive documentation meeting FDA QSR and MDR Annex II requirements: material certificates, first-article inspection reports (FAIR) with ballooned drawings, process validation summaries, and sterilization compatibility data. Parts ship in validated packaging systems with environmental monitoring logs (temperature/humidity) where required. All shipments include electronic device history records (eDHR) accessible via client portal with full chain-of-custody tracking. Delivery timelines are guaranteed through our integrated logistics network with medical device-specific carriers compliant with IMDRF GHTF/SG1/N99-10:2008 guidelines.
Start Your Project

Looking for precision CNC machining for medical devices? Honyo Prototype delivers high-accuracy, ISO-compliant manufacturing solutions tailored to the stringent demands of the medical industry. Our Shenzhen-based factory is equipped with advanced CNC technology and a quality-driven process to ensure every component meets exact specifications.
For project inquiries or technical discussions, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. Let’s collaborate to bring your medical device prototypes or production runs to life with reliability and speed.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.