Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Cnc Machining Surface Finish
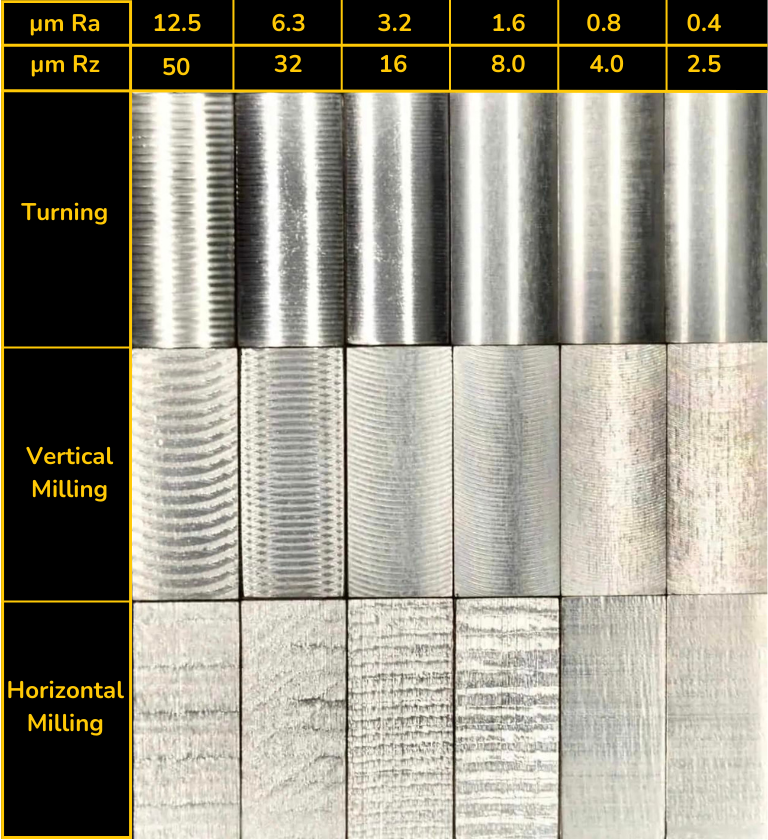
Surface Finish: More Than Just Aesthetic in Precision CNC Machining
Achieving the precise surface finish required for functional performance, fatigue resistance, and component longevity is a critical outcome of advanced CNC machining, extending far beyond mere visual appeal. At Honyo Prototype, our comprehensive CNC machining services—encompassing 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling alongside precision turning—are engineered to deliver exacting surface finishes across aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, plastics, and exotic alloys. We meticulously control parameters like feed rate, spindle speed, tool geometry, and coolant application to consistently meet stringent Ra, Rz, or customer-specified finish requirements, whether producing coarse textures for grip or mirror-polished surfaces for optical applications. Our integrated quality assurance process, featuring calibrated profilometers and rigorous in-process inspection, ensures every machined part adheres to dimensional tolerances and surface integrity standards. Streamline your path from concept to certified prototype or low-volume production by leveraging Honyo Prototype’s Online Instant Quote system, which provides transparent pricing and lead times for your CNC machining project within minutes, backed by our engineering team’s expertise in optimizing manufacturability and surface finish outcomes.
Technical Capabilities
CNC machining surface finish refers to the texture or roughness of a machined part’s surface, typically measured in microinches (µin) or micrometers (µm) of Ra (arithmetic average roughness). In high-precision applications involving 3-, 4-, and 5-axis milling and turning, surface finish is critical for part functionality, fit, sealing, and appearance—especially in tight tolerance environments (±0.0005″ or tighter). The achievable surface finish depends on machine rigidity, tooling, cutting parameters, material properties, and post-processing.
Below is a summary of typical surface finish specifications for common materials under precision CNC machining conditions:
| Process | Material | Typical Surface Finish (Ra) | Tight Tolerance Capability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3/4/5-Axis Milling | Aluminum (6061, 7075) | 32–64 µin (0.8–1.6 µm) | ±0.0005″ to ±0.001″ | Easily achieves fine finishes; minimal built-up edge. Use sharp carbide tools for best results. |
| 3/4/5-Axis Milling | Steel (1018, 4140, Stainless 303/304) | 64–125 µin (1.6–3.2 µm) | ±0.0005″ to ±0.001″ | Harder materials require rigid setups; finishing passes with coated carbide improve surface quality. |
| 3/4/5-Axis Milling | ABS (Thermoplastic) | 64–250 µin (1.6–6.3 µm) | ±0.002″ to ±0.005″ | Lower thermal resistance; prone to melting if feeds/speeds not optimized. Use high-speed cutting with sharp tools. |
| 3/4/5-Axis Milling | Nylon (PA6, PA66) | 125–250 µin (3.2–6.3 µm) | ±0.002″ to ±0.005″ | Flexible and soft; can exhibit dimensional creep. Requires sharp tooling and light cuts to avoid deformation. |
| CNC Turning | Aluminum (6061, 2024) | 16–32 µin (0.4–0.8 µm) | ±0.0002″ to ±0.0005″ | Excellent surface finish achievable with single-point turning; ideal for shafts and bushings. |
| CNC Turning | Steel (4140, 17-4 PH) | 32–64 µin (0.8–1.6 µm) | ±0.0002″ to ±0.0005″ | Tight tolerances maintained with steady rest and minimal tool deflection. Coolant improves finish. |
| CNC Turning | ABS | 125–250 µin (3.2–6.3 µm) | ±0.003″ to ±0.006″ | Limited by thermal deformation; turning not ideal for thin-walled ABS parts. |
| CNC Turning | Nylon | 125–500 µin (3.2–12.5 µm) | ±0.003″ to ±0.006″ | Material compliance leads to chatter; support structures and low feed rates recommended. |
Notes on High-Precision Machining:
5-axis milling allows complex geometries with consistent tool engagement, improving surface finish on contoured surfaces.
Tight tolerance work demands thermal stability, high-precision spindles (≤1 µm runout), and in-process probing.
Post-machining treatments (e.g., vibratory finishing, bead blasting, or polishing) can further reduce Ra values.
Aluminum and steel are most suitable for tight tolerance and fine finish requirements; plastics like ABS and Nylon require careful process control due to lower stiffness and thermal sensitivity.
From CAD to Part: The Process

Honyo Prototype maintains rigorous control over CNC machining surface finish through an integrated workflow designed to ensure specifications are met consistently from initial design to final delivery. Our process begins when the customer uploads a native CAD file or industry-standard neutral format such as STEP or IGES to our secure portal. This file undergoes automated validation for geometric integrity and critical metadata. Crucially, our system parses surface finish requirements directly from the CAD model’s annotations, including Ra values, machining marks direction, and any localized finish specifications on specific faces or features. Incomplete or ambiguous finish callouts trigger immediate alerts to the quoting team for clarification before proceeding.
The AI Quote engine then processes the validated CAD data, leveraging Honyo’s extensive historical machining database to generate an initial technical and commercial assessment. For surface finish, the AI cross-references the specified requirements against achievable standards for the requested material, feature geometry, and machine tool capabilities. It identifies potential conflicts, such as requesting a Ra 0.4 µm finish on deep, narrow cavities where tool access limits are physically constraining, and flags these for engineering review. The preliminary quote includes a baseline surface finish recommendation aligned with standard machining practices if explicit requirements are absent, alongside any cost or lead time implications of non-standard finishes.
This triggers the mandatory Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review conducted by our senior manufacturing engineering team. Engineers perform a granular analysis of all surface finish specifications against the part’s functional requirements and manufacturability. We assess whether the specified finish is necessary for the part’s application or if a more economical standard finish (e.g., Ra 3.2 µm vs. Ra 0.8 µm) would suffice without compromising performance. Critical areas undergo evaluation for toolpath feasibility, including verification that required surface roughness can be achieved within geometric constraints using appropriate tooling and machining strategies. We provide actionable feedback, such as suggesting alternative finishes for non-critical surfaces or proposing design modifications to facilitate machining, always with justification based on metrology data and process capability studies.
Upon DFM approval and customer sign-off, the part enters Production. Our CNC programming team generates optimized toolpaths specifically tailored to achieve the validated surface finish requirements. This involves precise selection of cutting tools (e.g., fine-pitch end mills for finishing passes), strict control of machining parameters (spindle speed, feed rate, stepover, depth of cut), and implementation of specialized strategies like high-speed machining (HSM) or slow-tool servo techniques for ultra-fine finishes. Coolant application and machine rigidity are monitored to prevent chatter marks. Throughout machining, in-process inspections verify dimensional accuracy and surface quality against checkpoints, with real-time adjustments made if deviations are detected. Critical finish requirements undergo 100% inspection using calibrated profilometers or non-contact optical systems.
Final verification occurs during Quality Control prior to Delivery. All surfaces are inspected against the approved specifications using methods appropriate to the required Ra range. Results are documented in the inspection report, including actual measured Ra values and comparison to print requirements. We adhere strictly to industry-standard measurement practices per ISO 4287 or ASME B46.1. Parts failing to meet surface finish criteria are reworked or scrapped; we do not compromise on finish quality. The final shipment includes comprehensive documentation: the inspection report with surface finish data, material certification, and a detailed process summary confirming adherence to the agreed specifications. This closed-loop process ensures surface finish is treated as a critical quality characteristic, not an afterthought.
Achievable surface finishes are directly tied to machining methodology and material. Honyo’s standard capabilities and their typical applications are summarized below:
| Machining Process | Typical Ra Range (µm) | Typical Ra Range (µin) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Milling (Standard) | 1.6 – 6.3 | 63 – 250 | Non-critical structural components, internal features |
| CNC Milling (Fine Finish) | 0.8 – 1.6 | 32 – 63 | Exposed surfaces, mating surfaces requiring moderate sealing |
| CNC Milling (High Precision) | 0.4 – 0.8 | 16 – 32 | Hydraulic components, precision fittings, cosmetic surfaces |
| Grinding | 0.1 – 0.4 | 4 – 16 | Bearing surfaces, sealing diameters, high-wear applications |
| Polishing (Post-Process) | < 0.1 | < 4 | Medical implants, optical components, decorative surfaces |
This structured approach, integrating AI-driven initial assessment with deep engineering expertise in DFM and process control, guarantees that surface finish requirements are not only understood early but are manufacturable, verifiable, and consistently delivered to our customers’ exact specifications.
Start Your Project
Achieve precision surface finishes with our CNC machining services at Honyo Prototype. Our advanced manufacturing processes ensure consistent quality and tight tolerances for your critical components.
For expert support and custom solutions, contact Susan Leo at [email protected].
Our factory is located in Shenzhen, providing efficient production and fast turnaround for global clients.
| Service Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Location | Shenzhen, China |
| Contact | Susan Leo |
| [email protected] | |
| Process | CNC Machining |
| Key Capability | Precision Surface Finishing (Ra values down to 0.4 μm and below) |
Reach out today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our CNC machining expertise can meet your surface finish specifications.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.