Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc machine quality control
In today’s competitive landscape, ensuring the highest standards of CNC machine quality control poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As manufacturers increasingly rely on computer numerical control technology to produce precision components, the stakes have never been higher. The quest for reliable quality control processes is essential for businesses looking to maintain operational efficiency and uphold customer satisfaction. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricate world of CNC machine quality control by exploring various types of quality testing, inspection methodologies, and the impact of advanced technologies on the quality assurance process.
Throughout this guide, readers will gain insights into the essential parameters of CNC machining quality, including dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and material integrity. We will also delve into the critical aspects of supplier vetting, cost considerations, and best practices for sourcing high-quality CNC machines tailored to specific manufacturing needs. By equipping B2B buyers from diverse regions—such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—with actionable strategies and expert knowledge, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions. Ultimately, a solid understanding of CNC machine quality control will enable businesses to enhance their production capabilities, reduce waste, and foster long-term customer relationships.
Understanding cnc machine quality control Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inspection | Focuses on measuring physical dimensions against specifications. | Aerospace, Automotive, Medical Device Manufacturing | Pros: Ensures precision; Cons: Time-consuming and may require specialized equipment. |
| Surface Finish Evaluation | Assesses the smoothness and texture of machined parts. | Consumer Electronics, Automotive, Aerospace | Pros: Enhances product aesthetics; Cons: Additional processes may increase costs. |
| Material Testing | Examines material properties like hardness and tensile strength. | Construction, Aerospace, Heavy Machinery | Pros: Ensures durability; Cons: Can delay production timelines. |
| Geometric Tolerancing | Involves ensuring parts meet specific geometric specifications. | Aerospace, Automotive, Precision Engineering | Pros: Critical for complex assemblies; Cons: Requires advanced measurement tools and expertise. |
| Statistical Process Control (SPC) | Utilizes statistical methods to monitor and control processes. | Mass Production, Electronics, Automotive | Pros: Reduces variability; Cons: Initial setup can be complex and resource-intensive. |
What Are the Characteristics of Dimensional Inspection in CNC Quality Control?
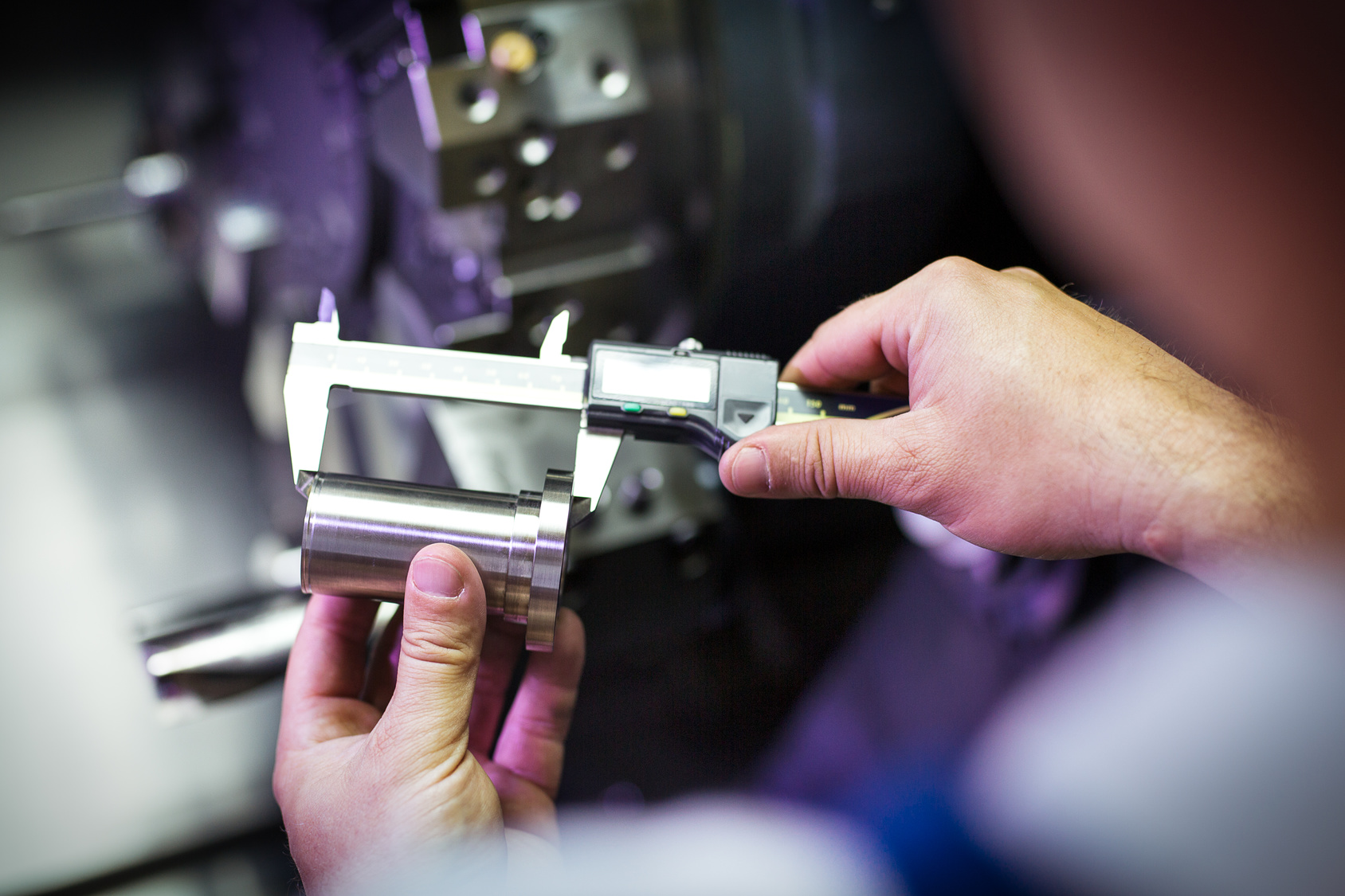
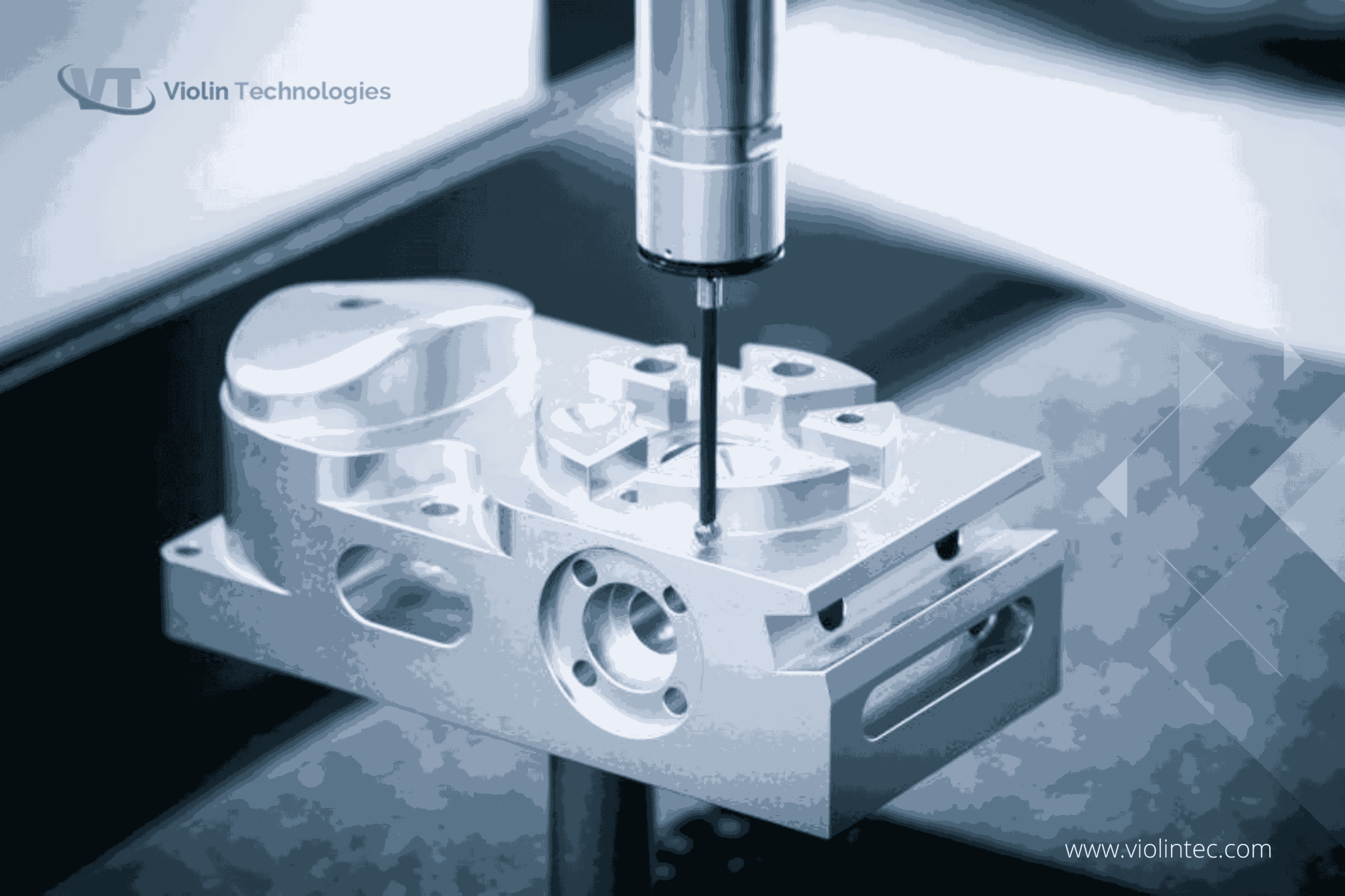
Dimensional inspection is a fundamental aspect of CNC quality control, focusing on the precise measurement of a part’s physical dimensions. This process ensures that components meet specified tolerances and fit within the designed assembly. It is highly suitable for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precision is critical. Buyers should consider the necessary measuring equipment, such as Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs), and the expertise required to interpret results accurately.
How Does Surface Finish Evaluation Impact Product Quality?
Surface finish evaluation is essential for assessing the quality of machined parts, particularly in applications where aesthetics and performance are crucial, such as in consumer electronics and automotive components. This evaluation measures the smoothness and texture of surfaces, which can affect both functionality and visual appeal. Buyers must weigh the benefits of improved aesthetics against the potential for increased production costs and time, as additional finishing processes may be necessary.
Why Is Material Testing Crucial for CNC Machined Parts?
Material testing examines the physical properties of materials used in CNC machining, such as hardness and tensile strength. This quality control type is vital in industries like construction and aerospace, where material integrity is paramount. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who conduct thorough material testing to ensure that components can withstand operational demands. However, it’s important to recognize that this testing can extend lead times, impacting overall project timelines.
What Is the Importance of Geometric Tolerancing in CNC Machining?
Geometric tolerancing ensures that parts conform to specific geometric specifications, which is crucial for complex assemblies in sectors like aerospace and precision engineering. This quality control method assesses features such as flatness and roundness, ensuring that components fit and function correctly. Buyers should consider the need for advanced measurement tools and skilled personnel, as these can be significant investments in maintaining high-quality standards.
How Does Statistical Process Control (SPC) Enhance CNC Quality Management?
Statistical Process Control (SPC) employs statistical methods to monitor and control CNC machining processes, helping to minimize variability and enhance product quality. This approach is especially beneficial in mass production environments, such as electronics and automotive manufacturing. Buyers should evaluate the initial resource investment required for SPC implementation, as setting up an effective system can be complex. However, the long-term benefits of reduced defects and increased efficiency often outweigh these initial challenges.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc machine quality control
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Machine Quality Control | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | Ensures safety and reliability of critical flight components | Certification of suppliers, adherence to international standards |
| Automotive | Engine and transmission part production | Reduces defects and enhances performance of automotive parts | Material traceability, compliance with industry regulations |
| Medical Devices | Custom surgical instruments and implants | Guarantees high precision and safety for patient care | Certification for biocompatibility, strict quality assurance |
| Electronics | PCB and component fabrication | Enhances product lifespan and functionality | Supplier reliability, capability for high-volume production |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling and extraction equipment manufacturing | Improves durability and efficiency in harsh environments | Material quality, adherence to safety standards |
How is CNC Machine Quality Control Applied in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, CNC machine quality control is critical for manufacturing precision components such as turbine blades and structural parts. The high stakes of safety require that every part meets stringent specifications to ensure reliability during flight. By implementing rigorous quality control processes, manufacturers can detect and rectify defects early, thus minimizing the risk of catastrophic failures. International buyers should prioritize suppliers with certifications like AS9100 and a proven track record in meeting aerospace standards.
What Role Does CNC Quality Control Play in Automotive Production?
The automotive sector relies heavily on CNC machining for producing engine and transmission components. Quality control in this context focuses on dimensional accuracy and material integrity, as even minor defects can lead to significant performance issues or safety concerns. By utilizing advanced inspection techniques, manufacturers can reduce defects and enhance the overall performance of vehicles. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider sourcing from suppliers who demonstrate compliance with ISO/TS 16949 to ensure high-quality automotive parts.
Why is Quality Control Essential for Medical Device Manufacturing?
CNC machine quality control is paramount in the production of medical devices, where precision is crucial for patient safety. This includes the manufacturing of custom surgical instruments and implants, where even slight deviations can lead to severe consequences. Rigorous quality control measures ensure that all products meet biocompatibility and safety standards. International buyers must seek out suppliers with FDA approvals and ISO certifications to guarantee the highest quality standards are upheld throughout the manufacturing process.
How Does CNC Quality Control Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, CNC machine quality control is vital for producing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other components. The focus here is on achieving high precision and minimizing defects, which can affect the lifespan and functionality of electronic devices. Implementing effective quality control processes allows manufacturers to maintain consistency and reliability in high-volume production. Buyers, particularly from Europe and the Middle East, should assess the supplier’s capability for rapid prototyping and their adherence to IPC standards to ensure quality.
What Benefits Does CNC Quality Control Provide in Oil & Gas Equipment Manufacturing?
In the oil and gas industry, CNC machine quality control is essential for fabricating drilling and extraction equipment that must withstand extreme conditions. The focus is on ensuring the durability and efficiency of components, which can significantly impact operational costs and safety. Quality control processes help identify material weaknesses and dimensional inaccuracies before products are deployed. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate expertise in high-performance materials and compliance with industry-specific safety standards to mitigate risks associated with equipment failures.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc machine quality control’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality Leading to Production Delays
The Problem: A manufacturing company in Nigeria specializes in producing precision components for the automotive industry. Recently, they have encountered significant inconsistencies in the dimensions of parts produced by their CNC machines. These discrepancies not only lead to rejected batches but also result in costly production delays, as rework and replacements strain their schedules and budgets. The buyer feels trapped in a cycle of poor quality that jeopardizes client contracts and damages their reputation in a competitive market.
The Solution: To tackle the issue of inconsistent quality, the buyer should implement a robust Quality Management System (QMS) that incorporates real-time monitoring of CNC machining processes. This involves investing in advanced CNC machines equipped with in-process measurement capabilities, such as laser scanning or vision systems. These technologies can help detect dimensional deviations as parts are being machined, allowing for immediate adjustments before the production runs are completed. Additionally, establishing a routine maintenance schedule for CNC machines can prevent wear and tear that contributes to inaccuracies. Regular training sessions for operators on quality control techniques will also empower them to identify potential issues early, fostering a culture of quality throughout the production process.
Scenario 2: Insufficient Raw Material Inspection Compromising End Product Quality
The Problem: A Brazilian manufacturer of aerospace components has faced recurrent quality issues stemming from the use of subpar raw materials. Despite following established machining protocols, the final products often fail to meet stringent industry standards due to defects in the materials themselves. This oversight has resulted in costly recalls and loss of business, leaving the buyer frustrated and searching for a solution to ensure the integrity of their products from the outset.
The Solution: Implementing a comprehensive incoming inspection process for raw materials is essential. The buyer should establish partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide certifications of material quality and undergo regular audits to ensure compliance with industry standards. Additionally, investing in quality control testing equipment, such as hardness testers and material analyzers, will allow the manufacturer to verify the properties of materials before they are machined. By adopting a proactive approach to quality control at the raw material stage, the manufacturer can significantly reduce the risk of defects in the final products, ensuring compliance with aerospace standards and preserving their reputation.
Scenario 3: Complex Geometric Tolerances Leading to Misalignment Issues
The Problem: A Middle Eastern company specializing in custom machinery has been grappling with misalignment issues in components that require complex geometric tolerances. These problems arise from inadequate understanding and application of geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) principles among the design and machining teams. As a result, the company experiences increased scrap rates and rework, impacting their bottom line and project timelines.
The Solution: To resolve the misalignment issues caused by complex geometric tolerances, the buyer should invest in specialized training for their engineering and machining teams on GD&T principles. This training should include practical workshops that emphasize the importance of precise tolerancing in relation to the machining process. Furthermore, utilizing advanced software tools that facilitate GD&T during the design phase can ensure that tolerances are accurately communicated to CNC operators. Implementing a thorough inspection process using Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) will allow the company to verify that parts meet geometric specifications before they proceed to final assembly. By enhancing their understanding of GD&T and employing precise inspection methods, the company can improve alignment and overall product quality, thus minimizing waste and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc machine quality control
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in CNC Machining?
When selecting materials for CNC machining, it is crucial to understand their properties and how they influence product performance. Below are analyses of four common materials used in CNC machining, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Do Aluminum Alloys Perform in CNC Machining?
Aluminum alloys are among the most popular materials for CNC machining due to their lightweight and excellent machinability. Key properties include a good strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. These alloys can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for various applications, including automotive and aerospace components.
Pros: Aluminum alloys are durable, cost-effective, and easy to machine, allowing for high precision and intricate designs. They also have a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for applications where weight savings are critical.
Cons: While aluminum alloys are versatile, they can be less durable than some steel options and may not perform well under extreme temperatures or heavy loads. Additionally, they can be more expensive than some plastics.
Impact on Application: Aluminum alloys are compatible with a wide range of media, including water and oils, but may not be suitable for highly corrosive environments without proper coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing may be affected by local availability and import regulations.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in CNC Machining?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, making it a preferred choice for many industrial applications. Key properties include high tensile strength, resistance to oxidation, and the ability to withstand high temperatures.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable and maintains its integrity in harsh environments. It is suitable for applications in the food and medical industries due to its hygienic properties.
Cons: The main drawback is the higher cost and complexity in machining compared to aluminum. Stainless steel requires specialized tooling and techniques, which can increase production time and costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a variety of media, including acidic and alkaline solutions, making it ideal for chemical processing and food handling applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of stainless steel that meet local regulations, especially in the food and medical sectors. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 is essential.
How Does Plastic Material Affect CNC Machining Quality?
Plastics, particularly engineering plastics like polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in CNC machining due to their versatility and lightweight nature. Key properties include good chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and varying degrees of thermal stability.
Pros: Plastics are generally less expensive than metals and are easier to machine, allowing for faster production times. They are also lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes.
Cons: The primary limitation is their lower strength and temperature resistance compared to metals. They may not be suitable for high-stress applications or environments with extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastics are compatible with many media, but their performance can degrade in high-heat or high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with local regulations, particularly in industries like food and pharmaceuticals. Standards such as FDA compliance may be required.
What Role Does Titanium Play in CNC Machining?
Titanium is a high-performance material known for its strength, lightweight, and corrosion resistance. Key properties include high tensile strength, low density, and excellent fatigue resistance.
Pros: Titanium is ideal for demanding applications, particularly in aerospace and medical devices, where high strength and low weight are crucial. Its corrosion resistance extends its lifespan in harsh environments.
Cons: Titanium is one of the more expensive materials and can be challenging to machine due to its toughness, requiring specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application: Titanium is compatible with various media, including seawater, making it suitable for marine applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of the specific titanium grades required for their applications and ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B348.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Machining Quality Control
| Material | Typical Use Case for CNC Machine Quality Control | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight and easy to machine | Less durable under extreme conditions | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food and medical applications | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher machining complexity | High |
| Plastics | Consumer products and housings | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower strength and heat resistance | Low |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical devices | High strength and lightweight | Expensive and difficult to machine | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, ensuring informed decisions that align with quality control standards and application requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc machine quality control
What Are the Main Stages of CNC Manufacturing Processes?
The CNC machining process consists of several key stages that ensure the production of high-quality components. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers to assess the capabilities and quality assurance measures of potential suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for CNC Machining?
Material preparation is the foundational stage of CNC machining. It involves selecting and preparing raw materials, which can range from metals like aluminum and steel to plastics and composites. The choice of material directly impacts the machining process and the final product’s performance.
In this stage, suppliers often conduct initial inspections of raw materials to verify their quality, dimensions, and material properties. This can include checks for hardness, surface defects, and chemical composition. For B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers have stringent material inspection protocols in place is essential for minimizing defects in the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in CNC Machining?
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This is where CNC machines, guided by computer programs, precisely cut, mill, or shape the material into the desired form. Common techniques include:
- CNC Milling: Utilizes rotating cutters to remove material from a workpiece, allowing for intricate designs and complex shapes.
- CNC Turning: Involves rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool to create cylindrical parts.
- Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): Uses electrical discharges to shape conductive materials, ideal for intricate designs that traditional cutting methods might not achieve.
These techniques require careful programming and tool selection to ensure accuracy and minimize waste. B2B buyers should evaluate suppliers’ equipment capabilities, including machine types and the technology used, to ensure they can meet specific project requirements.
How Does the Assembly Process Work in CNC Machining?
The assembly stage involves putting together various machined components to create a finished product. This may include fastening, welding, or integrating parts that were produced separately.
Quality assurance during assembly is critical to ensure that all components fit correctly and function as intended. Manufacturers may use jigs and fixtures to maintain consistency during assembly, and B2B buyers should inquire about the methods used to ensure precise assembly in their potential suppliers’ operations.
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed in CNC Machining?
Finishing processes are the final steps in CNC machining, enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of the components. Techniques such as polishing, anodizing, and coating can be employed to achieve the desired surface finish.
A well-executed finishing process not only improves the appearance of the product but also contributes to its durability and resistance to corrosion and wear. B2B buyers should assess the finishing capabilities of suppliers to ensure they can deliver products that meet both functional and aesthetic standards.
How Is Quality Control Implemented in CNC Machining?
Quality control (QC) is integral to CNC machining, ensuring that each component produced meets international standards and customer specifications.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for CNC Quality Control?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems in manufacturing. This standard emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction, making it a critical benchmark for B2B buyers when evaluating suppliers.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for products sold within the European Economic Area) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards are essential for suppliers in sectors like oil and gas. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with these certifications to ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Machining?
Quality control checkpoints are essential throughout the CNC machining process. These checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials before they enter production to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring production processes to detect and rectify issues in real time, thus preventing defects from proceeding to the next stage.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting thorough inspections of finished products to ensure they meet all quality standards before delivery.
Implementing these checkpoints helps maintain high quality and reduces the likelihood of defects that could impact customer satisfaction.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in CNC Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality of CNC machined parts. Common techniques include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers to measure critical dimensions and ensure they meet specified tolerances.
- Surface Roughness Measurement: Assessing the texture of a machined part to ensure it meets required surface finish specifications.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection can identify internal defects without damaging the part.
B2B buyers should inquire about the testing methods employed by potential suppliers to ensure that they can consistently deliver high-quality products.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing internationally.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Audit Supplier Quality Control?
Buyers can conduct audits to evaluate a supplier’s quality control processes. This includes reviewing their quality management systems, inspecting production facilities, and assessing compliance with international standards.
Additionally, requesting quality control reports and documentation can provide insight into a supplier’s performance history and adherence to standards.
How Do Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance quality assurance. Independent inspectors can conduct assessments at various stages of production, providing an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly beneficial for B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where establishing trust in supplier capabilities may be more challenging.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances, including differences in regulations, cultural practices, and operational standards.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Control in CNC Machining?
Buyers should be aware of the specific standards and certifications relevant to their region. For instance, while ISO standards are widely recognized, certain markets may require additional certifications or compliance with local regulations.
Understanding these regional nuances helps buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers and ensures that their products meet the necessary quality and regulatory requirements.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in CNC machining, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain efficiency and product quality.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc machine quality control’
To ensure the procurement of CNC machine quality control solutions aligns with your operational needs, this guide provides a step-by-step checklist. It is designed for B2B buyers aiming to enhance their manufacturing processes through effective quality management. By following these steps, you can make informed decisions that lead to improved product quality and operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Quality Control Requirements
Before sourcing CNC machine quality control systems, clearly outline your specific quality requirements. Consider the types of materials you will be machining, the complexity of your parts, and the tolerances needed. This clarity will help you identify the necessary features and capabilities in quality control tools.
- Examples of requirements: dimensional accuracy, surface finish specifications, and material hardness testing.
Step 2: Research Available Technologies
Explore the various technologies available for CNC machine quality control. This includes both hardware and software solutions, such as Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs), laser scanners, and statistical process control (SPC) software. Understanding these options will enable you to select tools that best fit your manufacturing processes.
- Key considerations: compatibility with existing machinery, ease of integration, and the ability to provide real-time data.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from businesses in similar industries or regions. A reliable supplier should demonstrate proven experience and expertise in CNC quality control.
- What to assess: supplier certifications, their history of successful implementations, and the support they offer post-purchase.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your potential suppliers hold relevant certifications that reflect their commitment to quality. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a robust quality management system, or industry-specific standards that pertain to CNC machining.
- Importance: Certifications provide assurance that the supplier adheres to recognized quality standards, which can significantly reduce your risk.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Before finalizing a purchase, ask for product demonstrations or trial periods. This allows you to assess the functionality and effectiveness of the quality control tools in real-world scenarios. Observing how the tools perform with your specific materials and processes is critical.
- What to observe: ease of use, accuracy of measurements, and the responsiveness of the software.
Step 6: Review Support and Training Options
Inquire about the training and support that the supplier offers. Effective implementation of quality control systems often requires training for your staff. A supplier that provides comprehensive training and ongoing support can facilitate a smoother transition and maximize your investment.
- Key aspects: availability of online resources, on-site training, and customer service responsiveness.
Step 7: Establish a Continuous Improvement Plan
After implementing CNC machine quality control solutions, develop a continuous improvement plan. Regularly review performance metrics, gather feedback from operators, and stay updated on technological advancements. This proactive approach will help maintain high quality and adapt to evolving manufacturing needs.
- Focus areas: periodic assessments of quality control processes, feedback loops for operational improvements, and integration of new technologies as they emerge.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for CNC machine quality control, ensuring they invest in solutions that enhance their manufacturing capabilities and meet their quality standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc machine quality control Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Machine Quality Control Sourcing?
When sourcing CNC machine quality control, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality materials often come with a premium price but ensure better performance and durability. For instance, the use of specialized alloys or high-grade plastics can elevate costs but reduce long-term failures.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial for quality control processes, which include inspection and testing of CNC machined parts. Labor costs vary by region; in countries like Nigeria or Saudi Arabia, labor may be less expensive than in Europe, yet the availability of skilled technicians can influence pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with maintaining equipment, utilities, and facility expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, but initial investments in technology and training are necessary.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling, including specialized fixtures and cutting tools, is a critical factor. Tooling costs can vary widely based on the complexity of the parts being manufactured and the frequency of tool replacement.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes involves costs related to inspection tools, testing equipment, and personnel. Regular calibration and maintenance of QC instruments are also necessary to ensure accuracy.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary depending on the supplier’s location and the destination market. Understanding the implications of Incoterms is crucial, as they dictate who bears the cost of logistics at different stages of the supply chain.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a margin to cover risks and profit. Understanding the market landscape helps buyers gauge what constitutes a reasonable margin for quality control services.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Machine Quality Control Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in CNC machine quality control sourcing:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate volume discounts when possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts or specialized tolerances usually incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected pricing changes.
-
Materials: The material selected for machining plays a significant role in determining the price. Premium materials or those requiring special processing can escalate costs.
-
Quality Certifications: Parts requiring specific industry certifications (e.g., ISO, AS9100) may have increased costs due to additional testing and documentation requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record in quality and delivery.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipment is vital. Different Incoterms can shift cost burdens and risks between buyer and seller, affecting overall pricing.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating CNC Machine Quality Control Costs?
Effective negotiation can yield significant savings in CNC machine quality control sourcing. Here are essential tips:
-
Conduct Thorough Research: Understand the market landscape and price benchmarks. This knowledge empowers you during negotiations and helps in justifying your pricing expectations.
-
Emphasize Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than focusing solely on initial costs, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. Suppliers may be more flexible on pricing if they see the long-term value of your business.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can ease cash flow. Propose staggered payments based on milestones or delivery schedules.
-
Be Open to Alternatives: If a supplier cannot meet your price, explore alternatives such as modifying specifications or changing materials to align with budget constraints.
-
Leverage Volume: If you anticipate ongoing business, use potential future orders as leverage in negotiations. Suppliers may offer better pricing for long-term commitments.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider in CNC Quality Control Pricing?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of unique pricing nuances:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be mindful of exchange rates as they can significantly affect costs. Locking in prices or negotiating in stable currencies can mitigate risks.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have various compliance standards. Ensure that the supplier can meet local regulations, as non-compliance can lead to additional costs.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural nuances in negotiation styles can enhance communication and lead to more favorable outcomes.
-
Supply Chain Challenges: Global supply chain issues can affect lead times and costs. Anticipate potential delays and factor them into your planning.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for CNC machine quality control services can vary widely based on numerous factors, including the specifics of the project, location, and market conditions. Therefore, the figures provided in this analysis are indicative and should be validated through direct supplier engagement and market research.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc machine quality control With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CNC Machine Quality Control
When evaluating CNC machine quality control, it is essential to consider various alternative solutions that can also enhance manufacturing precision and reliability. Each method comes with its own set of advantages and drawbacks, impacting performance, cost, and ease of implementation. In this analysis, we will compare CNC machine quality control with two viable alternatives: Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and Traditional Manual Inspection.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Machine Quality Control | Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) | Traditional Manual Inspection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and consistency | Very high accuracy for visual defects | Variable accuracy based on inspector skill |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing costs for maintenance | Higher initial investment; lower ongoing costs | Low initial investment; labor-intensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized training and setup | Requires integration with existing systems; relatively straightforward | Simple implementation but requires skilled labor |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required for machinery | Minimal maintenance; software updates needed | Regular training and quality checks for inspectors |
| Best Use Case | Complex, high-volume production environments | High-speed production lines needing visual quality checks | Low-volume, custom manufacturing or prototyping |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
Automated Optical Inspection utilizes advanced imaging technology to detect defects in manufactured components. This method excels in environments where speed and precision are paramount. AOI systems can rapidly scan products for visual anomalies, offering very high accuracy in identifying surface defects, color variations, and misalignments.
Pros: AOI systems can operate continuously without fatigue, reducing the risk of human error. They also provide data analytics, allowing manufacturers to track defect rates and improve processes over time.
Cons: The initial investment for AOI technology can be substantial, and integration with existing manufacturing systems may require additional resources. While maintenance is relatively low, it is essential to keep software updated to ensure optimal performance.
Traditional Manual Inspection
Traditional manual inspection involves human inspectors evaluating components for quality assurance. This method is often employed in low-volume or custom manufacturing settings where each part’s uniqueness necessitates a hands-on approach.
Pros: The initial setup costs are low, as it does not require sophisticated technology. Manual inspection allows for flexible evaluations based on the inspector’s expertise and intuition, which can be beneficial for intricate or custom parts.
Cons: The accuracy of manual inspection can be inconsistent and highly dependent on the inspector’s skill and experience. Additionally, this method can be labor-intensive, leading to increased costs in terms of workforce management and potential delays in production.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Quality Control Solution
For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate quality control method hinges on specific operational needs, production volume, and budget constraints. CNC machine quality control stands out for its precision and consistency, making it ideal for high-volume production. However, for manufacturers focused on rapid visual inspections, AOI may offer a technologically advanced solution with lower long-term costs. Conversely, businesses in custom manufacturing might find traditional manual inspection more suitable due to its flexibility and lower initial investment. Assessing these factors will help ensure that buyers choose a quality control solution that aligns with their strategic objectives and operational requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc machine quality control
What Are the Key Technical Properties for CNC Machine Quality Control?
Understanding the essential technical properties in CNC machine quality control is critical for B2B buyers to ensure high-quality outputs. Here are some key specifications:
1. Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerance
Dimensional accuracy refers to how closely a manufactured part matches its specified dimensions, while tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from these dimensions. In CNC machining, tight tolerances are crucial for parts that must fit together precisely, such as in automotive or aerospace applications. Ensuring dimensional accuracy minimizes rework and scrap, ultimately saving costs and time.
2. Material Grade
The grade of material used significantly impacts the performance and durability of the final product. Different applications may require specific material properties, such as hardness, corrosion resistance, or tensile strength. By selecting the appropriate material grade, manufacturers can enhance the reliability of their components and cater to diverse market needs, making this a vital consideration for B2B buyers.
3. Surface Finish and Roughness
Surface finish refers to the texture of the part’s exterior, which can influence its aesthetic appeal and functional performance. A smoother finish often leads to better performance in parts that experience friction or require a seal. Understanding surface finish specifications is essential for manufacturers aiming to meet customer expectations and industry standards, particularly in sectors like medical devices and electronics.
4. Geometric Tolerancing
Geometric tolerancing involves applying specific tolerances to the geometric features of a component, such as flatness, straightness, and roundness. This specification is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assemblies. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who utilize geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) to guarantee the precision and functionality of complex components.
5. Tool Wear and Life
Monitoring tool wear is essential for maintaining quality control in CNC machining. Worn tools can lead to inaccuracies and poor surface finishes, affecting the integrity of the final product. Implementing a systematic approach to track tool life ensures consistent quality and minimizes production delays, which is critical for maintaining competitive advantage in the market.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Machine Quality Control?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the CNC machining sector. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In CNC machining, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure that they receive quality components that meet specific standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs can help B2B buyers manage inventory costs and ensure that they are not overcommitting to stock that may not be needed. This is particularly important in regions with fluctuating demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer submits to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. Knowing how to prepare a clear and detailed RFQ can streamline the procurement process and facilitate better negotiations, ensuring that all parties understand the requirements.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers clarify shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs, minimizing misunderstandings in cross-border transactions.
5. SPC (Statistical Process Control)
SPC is a method of quality control that uses statistical methods to monitor and control a process. By applying SPC, manufacturers can identify variations in the machining process and make timely adjustments, ensuring consistent quality and reducing waste.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain efficiency and product quality in CNC machining.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc machine quality control Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the CNC Machine Quality Control Market?
The CNC machine quality control sector is experiencing dynamic shifts influenced by various global drivers. Key among these is the increasing demand for precision manufacturing across diverse industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek reliable suppliers, the emphasis on stringent quality control measures has intensified. This trend is further fueled by advancements in technology, such as the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, which enhance the accuracy and efficiency of quality inspections.
Emerging technologies like real-time monitoring systems and automated quality assurance tools are also shaping the landscape. These innovations enable manufacturers to identify defects early in the production process, reducing waste and improving overall operational efficiency. Moreover, the shift towards Industry 4.0 is prompting companies to adopt smart manufacturing practices, which include the use of IoT devices for continuous quality assessment.
International buyers are also increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with global quality standards and certifications. In regions such as Saudi Arabia and Nigeria, where industrial growth is accelerating, the need for robust quality control systems is paramount. As these markets mature, the importance of comprehensive quality management systems that encompass all stages of production—from raw material inspection to final product testing—cannot be overstated.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting CNC Machine Quality Control?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the CNC machine quality control sector. Companies are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions, and many are seeking suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. The use of eco-friendly materials and processes not only reduces environmental footprints but also meets the growing consumer demand for ethical products.
Ethical sourcing extends beyond the materials used; it encompasses the entire supply chain. Buyers are now favoring suppliers who can ensure transparency and fair labor practices throughout their operations. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like Africa and South America, where ethical concerns can directly influence market access and brand reputation.
Additionally, certifications for sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, are becoming vital for suppliers aiming to attract international buyers. Implementing ‘green’ initiatives, such as waste reduction programs and energy-efficient machining processes, not only enhances a company’s marketability but also contributes to long-term cost savings. For buyers, partnering with ethically responsible suppliers can enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives, which is increasingly important in today’s global market.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Machine Quality Control?
The evolution of CNC machine quality control can be traced back to the early days of numerical control in the 1940s and 1950s, where manual input was replaced by automated systems. Initially, quality assurance was a reactive process, focusing on inspecting finished products for defects. However, as technology advanced, so did the methodologies surrounding quality control.
The introduction of CAD/CAM systems in the 1980s marked a significant turning point, allowing for more precise designs and improved quality management practices. Over the years, the integration of digital technologies has transformed quality control from a mere inspection phase to a comprehensive quality management system that encompasses every stage of the manufacturing process.
Today, CNC machining quality control is characterized by a proactive approach, emphasizing early detection of defects and continuous improvement. The rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as AI and IoT, has further revolutionized the sector, enabling real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making. This historical context underscores the ongoing transformation within the CNC machine quality control landscape, highlighting the importance of innovation in meeting the demands of international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc machine quality control
-
How do I solve quality control issues in CNC machining?
To address quality control issues in CNC machining, first implement a robust Quality Management System (QMS) that includes regular inspections throughout the production process. Utilize Statistical Process Control (SPC) to monitor trends and identify deviations early. Additionally, ensure that you select the appropriate CNC machine for your specific tasks, as using the wrong equipment can lead to errors. Training your staff on quality standards and best practices is also crucial in maintaining high-quality output. -
What is the best quality control process for CNC machining?
The best quality control process for CNC machining involves a multi-step approach: start with raw material inspection to ensure compliance with specifications, followed by in-process monitoring using tools like Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) for dimensional accuracy. Implement a final inspection phase to verify that the finished product meets all quality standards. Utilizing a combination of automated inspections and manual checks can enhance the reliability of your quality control process. -
How can I verify the quality of CNC machines from suppliers?
To verify the quality of CNC machines from suppliers, request detailed documentation including machine specifications, maintenance records, and quality control certifications. Conduct a factory visit if possible, to observe the manufacturing process and quality assurance practices in place. Additionally, ask for samples of previous work and customer references to assess their reputation in quality management. Lastly, consider third-party inspections to provide an unbiased evaluation of the machine’s quality. -
What customization options are available for CNC machining?
Customization options for CNC machining can vary widely depending on the supplier and the type of CNC machine used. Common customizations include specific dimensions, material selection, surface finishes, and tolerances tailored to your needs. Discuss your project requirements with the supplier to explore available options, as many manufacturers are willing to adapt their processes to meet unique specifications. Always ensure that the customization aligns with your quality control standards. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC machining services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC machining services can differ significantly among suppliers. Some may offer flexible MOQs for prototyping or small runs, while others may have stricter requirements for mass production. It’s essential to communicate your project needs upfront to negotiate suitable terms. Understanding the supplier’s capabilities and production scale can also help in determining a feasible MOQ that meets both parties’ requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing CNC machining services?
Payment terms for CNC machining services can vary based on the supplier and the scope of your project. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50% of the total cost), with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established relationships. Always clarify payment schedules and acceptable methods (e.g., wire transfer, credit card) before finalizing contracts to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do logistics impact CNC machining quality control?
Logistics play a crucial role in CNC machining quality control, as they affect the timely delivery of materials and finished products. Delays in raw material shipments can lead to production halts, risking quality if rushed processes are used. It’s vital to establish a reliable logistics partner who understands your quality standards and can ensure consistent supply chain performance. Effective communication about shipping schedules and handling practices is essential to maintaining quality throughout the logistics process. -
What are the key quality assurance (QA) practices for CNC machining?
Key quality assurance practices for CNC machining include implementing comprehensive inspection protocols at various production stages, conducting regular equipment maintenance, and training operators on quality standards. Additionally, adopting ISO 9001 or similar quality management certifications can enhance your credibility and operational efficiency. Continuous improvement processes, such as Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma, can also be beneficial in identifying and mitigating quality issues, ensuring that your production consistently meets high standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Cnc Machine Quality Control Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. amfg.ai – CNC Machining Quality Control Strategies
Domain: amfg.ai
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining Quality Control strategies include: 1. Choosing the Right CNC Machine Type – selecting appropriate machines (three-axis for simpler designs, four or five-axis for complex components) to reduce errors. 2. Inspecting Raw Materials – evaluating quality before machining to prevent wastage and ensure optimal performance of CNC machines. 3. Implementing On-Machine Inspection – using machin…
2. American Micro Industries – CNC Machining Services
Domain: americanmicroinc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: American Micro Industries offers a range of CNC machining services, including CNC machine milling, CNC turning, and specialized machining for various materials such as foam, plastics, rubber, and metals. They emphasize the importance of quality control in CNC machining to ensure precision, cost-efficiency, compliance, consistency, and customer satisfaction. Their services include die cutting, lase…
3. Frog3D – CNC Machining Quality Control
Domain: frog3d.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: CNC machining quality control and inspection involves precise instruments and techniques to ensure that final outputs meet industry standards. Key parameters include dimensional accuracy and tolerance, surface finish and roughness, and regular inspections to maintain quality. Instruments used include micrometers, calipers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM). The process minimizes errors, addr…
4. GN Corporations – Precision CNC Machining Services
Domain: gncorporations.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: CNC machining services for various industries including aerospace, automotive, defense, and oil & gas. Key services include precision CNC machining, quality assurance services, deep hole & gun drilling, protective coating, painting, induction-hardening, pressure-testing, sand blasting, and waterjet cutting. Quality control processes involve dimensional accuracy and tolerance checks, surface finish…
5. Makerverse – Quality Control Solutions for CNC Machining
Domain: makerverse.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Quality Control Options for CNC Machined Parts include: 1. Visual Inspection: Every part undergoes a visual inspection by engineering experts. 2. Material Certificate 3.1: Verification of material quality and composition with an official test report. 3. Dimensional Measurement Report: Records measurements and dimensions for sample parts to ensure adherence to specified tolerances. 4. Certificate o…
6. Machining Concept Serie – Key Product Details
Domain: machiningconceptserie.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Key product details include: 1. Quality Assurance Department: Essential for ensuring high-quality parts that meet strict specifications. 2. Dimensional Inspection: Utilizes precision tools like CMMs, calipers, micrometers, and gauges. 3. In-process Inspection: Conducts inspections during production to catch errors early. 4. First Article Inspection (FAI): Detailed inspection of the first part prod…
7. Aerostar MFG – Precision CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: aerostarmfg.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: CNC Production Machining, Precision CNC Machining, Machined Castings, Prototype and Low Volume CNC Machining, Machined Forgings, Sheet Metal Fabrication, Stamping, Aluminum Extrusions, Gear Manufacturing, Machined Assemblies, Inspection Services.
8. Wayken – Quality Control & Inspection for CNC Machining
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Quality Control and Inspection for CNC Machining involves various technologies and methods to ensure high-quality output that meets industry standards. Key parameters include Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerance, Surface Finish and Roughness, and Assembly and Fit. Industry standards referenced include ISO 9001, ISO 16949, and AS9100. The quality control process includes steps such as Raw Materials &…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc machine quality control
In the rapidly evolving landscape of CNC machining, the importance of robust quality control measures cannot be overstated. As global supply chains expand and diversify, particularly across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital component for maintaining high standards in manufacturing. By investing in the right machinery, implementing comprehensive inspection protocols, and utilizing advanced quality management systems, companies can significantly reduce defects and enhance product reliability.
Key takeaways for international B2B buyers include the need for selecting appropriate CNC machine types tailored to specific manufacturing tasks, prioritizing early-stage material inspections, and leveraging statistical process control to monitor production quality continuously. These strategies not only mitigate risks but also foster customer trust and satisfaction.
Looking ahead, the commitment to quality control will be paramount as industries strive for operational excellence and competitive advantage. We encourage B2B buyers to embrace these insights and invest in quality-centric practices that ensure their products meet the highest standards. By doing so, they position themselves not only for immediate success but also for sustainable growth in the global market.