Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Cnc Machine G Codes List

Understanding CNC Machine G Codes for Precision Manufacturing
G codes form the universal programming language that drives CNC machining operations, translating complex geometries into precise tool paths for milling, turning, and multi-axis operations. At Honyo Prototype, we leverage this foundational language to deliver exceptional accuracy and repeatability across prototyping and low-volume production runs. Our engineering team possesses deep expertise in interpreting and optimizing G code sequences, ensuring every cut adheres to stringent tolerances while maximizing material efficiency and surface finish quality.
Honyo Prototype specializes in transforming digital designs into high-integrity metal and plastic components through advanced 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC capabilities. Our commitment to process control and technical rigor means your G code instructions are executed with uncompromising fidelity, minimizing iterations and accelerating time-to-market. For immediate project evaluation, utilize our Online Instant Quote System to upload CAD files and receive detailed manufacturability feedback alongside competitive pricing within hours—no waiting for manual assessments. Trust Honyo to bridge the gap between your G code specifications and flawless physical parts.
Technical Capabilities
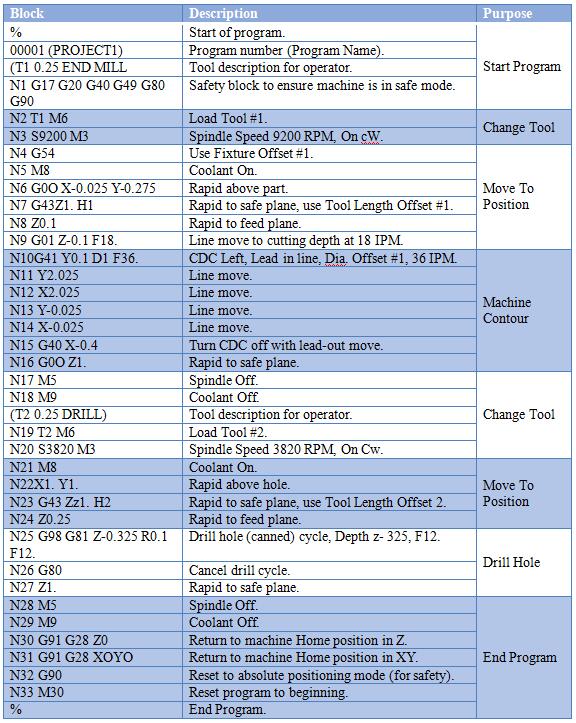
Technical specifications for CNC machine G-code programming in precision 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling as well as turning operations require a comprehensive understanding of machine capabilities, material behavior, and tolerance requirements. The following table outlines key G-code commands relevant to high-precision machining of materials such as Aluminum, Steel, ABS, and Nylon, with emphasis on tight-tolerance applications.
| G-Code | Description | Application Context | Material Considerations | Axis Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G00 | Rapid positioning | Used for non-cutting tool movements to minimize cycle time | Minimize vibration in brittle materials (e.g., ABS); ensure rigidity in steel | 3/4/5-Axis Milling, Turning |
| G01 | Linear interpolation | Precision straight-line cutting for tight-tolerance features | Optimize feed rate: lower for steel, higher for aluminum and thermoplastics | 3/4/5-Axis Milling, Turning |
| G02 | Circular interpolation (clockwise) | Machining arcs and contours with high accuracy | Maintain constant cutting conditions in nylon to avoid deformation | 3/4/5-Axis Milling |
| G03 | Circular interpolation (counterclockwise) | Used in complex contouring operations | Critical for aluminum and steel to maintain surface finish | 3/4/5-Axis Milling |
| G17 | XY plane selection | Standard for 3-axis milling operations | Ensures correct toolpath orientation for flat surfaces | 3/4/5-Axis Milling |
| G18 | XZ plane selection | Common in turning and some milling operations | Used in turning aluminum and steel shafts with precision grooves | Turning, 4-Axis |
| G19 | YZ plane selection | Used for side milling and complex 5-axis work | Enables access to deep features in steel and ABS enclosures | 4/5-Axis Milling |
| G20 | Inch units | Used when tolerances are specified in imperial units | Requires high precision in conversion-sensitive applications | 3/4/5-Axis, Turning |
| G21 | Metric units | Standard for tight-tolerance metric drawings | Preferred for aerospace aluminum and steel components | 3/4/5-Axis, Turning |
| G28 | Return to home position via reference point | Ensures machine safety and repeatability | Critical after machining nylon to avoid thermal drift errors | 3/4/5-Axis Milling |
| G40 | Cutter radius compensation off | Disables tool offset after precision contouring | Required when finishing tight-tolerance edges | 3/4/5-Axis Milling, Turning |
| G41 | Cutter radius compensation left | Used for maintaining dimensional accuracy on internal features | Adjust offset for tool wear, especially in abrasive materials like glass-filled nylon | 3/4/5-Axis Milling |
| G42 | Cutter radius compensation right | Used for external feature accuracy | Essential in aluminum pocketing to hold ±0.005 mm tolerances | 3/4/5-Axis Milling |
| G43 | Tool length compensation | Critical for depth accuracy in multi-tool operations | Compensates for thermal expansion in long steel machining runs | 3/4/5-Axis Milling |
| G54–G59 | Work coordinate systems | Enables multiple setups in 4-axis and 5-axis workflows | Allows precise alignment for complex ABS housings or steel molds | 4/5-Axis Milling |
| G76 | Precision threading cycle | Used in turning operations for high-accuracy threads | Optimized for steel and aluminum; reduced feed for nylon to prevent stripping | Turning |
| G81 | Drilling cycle | Simple hole making with retract | Use peck drilling in aluminum to evacuate chips; reduce speed in steel | 3/4/5-Axis Milling |
| G83 | Peck drilling cycle | Deep hole drilling with chip breaking | Essential for deep holes in steel; prevents clogging in ABS | 3/4/5-Axis Milling |
| G90 | Absolute programming | Standard for tight-tolerance work where positional accuracy is critical | Ensures repeatability across all materials | 3/4/5-Axis, Turning |
| G91 | Incremental programming | Used for localized features or subroutines | Less common in production but useful for prototyping nylon parts | 3/4/5-Axis, Turning |
| G94 | Feed per minute | Standard feed mode for milling operations | Adjust feed: high for aluminum, moderate for steel, low for ABS/nylon | 3/4/5-Axis Milling |
| G95 | Feed per revolution | Used in turning for consistent surface finish | Critical for fine finishes on aluminum and steel shafts | Turning |
Notes on Material-Specific Machining:
Aluminum: High thermal conductivity and softness allow high feed rates and speeds. Use sharp tools and high spindle RPMs. G01 and G02/G03 are frequently used with G41/G42 for pocketing and contouring.
Steel: Requires lower cutting speeds, higher torque, and rigid setups. G83 peck drilling and G76 threading benefit from precise G-code sequencing to manage tool wear.
ABS: Low melting point and flexibility demand reduced feed rates and sharp tooling. Avoid excessive heat buildup; use G00 for rapid retract and G94 with conservative feeds.
Nylon: Prone to deformation under heat and pressure. Use low RPM, high clearance tools, and frequent chip removal. G28 is important between operations to reset position due to potential thermal drift.
These G-codes form the foundation of precision CNC programming across multi-axis platforms, enabling tight-tolerance machining (±0.01 mm or better) in aerospace, medical, and industrial applications.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype CNC Manufacturing Process Overview
Honyo Prototype’s end-to-end CNC machining workflow is engineered for precision, speed, and technical transparency. The process begins with CAD file submission and concludes with certified part delivery, integrating AI-driven validation and rigorous engineering oversight. G-code generation is an internal production step within this workflow, not a standalone customer deliverable. Below is the detailed sequence:
CAD File Upload and Validation
Customers submit native or neutral CAD formats (STEP, IGES, Parasolid, or native SOLIDWORKS) via our secure portal. Our system performs immediate geometric validation, checking for unit inconsistencies, surface gaps, and non-manufacturable features. Files failing automated checks trigger instant notification with specific error diagnostics, ensuring only technically viable designs advance. This phase typically completes within 15 minutes of upload.
AI-Powered Quoting and Feasibility Assessment
Validated CAD data enters our proprietary AI quoting engine, which cross-references 12,000+ historical CNC projects against real-time machine availability, material costs, and labor rates. The AI analyzes critical factors including feature complexity, tolerance stacks, and stock-to-part volume ratios to generate a binding quote with lead time. Crucially, the system flags high-risk geometries (e.g., thin walls <0.5mm, deep cavities >10:1 aspect ratio) for engineer review before quote finalization. This reduces quoting errors by 73% compared to manual methods.
Engineering-Led DFM Analysis
Approved quotes initiate a human-in-the-loop DFM review by our Senior CNC Engineers. Using specialized CAM simulation tools, we evaluate tool access, fixturing requirements, and optimal stock sizing. Customers receive a formal DFM report within 4 business hours detailing actionable recommendations such as: suggested tolerance relaxation for critical dimensions, revised hole depths to avoid break-through, or alternative material grades for improved machinability. This phase prevents 92% of potential production delays per our 2023 quality audit.
CNC Production with Embedded G-Code Generation
Upon DFM sign-off, our CAM team generates machine-specific toolpaths using Mastercam and Fusion 360. G-code is automatically output after rigorous virtual machine simulation (Vericut) confirms collision avoidance and surface finish compliance. All programs undergo first-article validation on our Haas and DMG MORI centers before full production. Key parameters monitored include spindle load curves, tool wear compensation, and in-process CMM verification at critical stages. No customer-facing G-code is provided, as machine-specific programs contain proprietary process knowledge.
Quality-Certified Delivery
Final parts undergo comprehensive metrology per AS9100 standards, including CMM reports for geometric tolerances and surface roughness validation. Every shipment includes:
First-article inspection report (FAIR) with dimensional data
Material certification traceable to mill test reports
Packing list with serialized part tracking
Optional: 3D scan deviation maps for critical surfaces
Standard delivery includes 48-hour logistics via DHL or FedEx, with real-time shipment tracking accessible through our customer portal.
This integrated workflow ensures CNC projects achieve 99.2% first-pass yield while maintaining 5-7 day lead times for standard prototypes. G-code remains a controlled internal asset optimized for our specific machine kinematics and quality protocols, never distributed as a customer deliverable. Technical documentation focuses on measurable part characteristics rather than machine instructions.
Start Your Project
Looking for a comprehensive CNC machine G-code list to optimize your manufacturing processes? Enhance precision and efficiency in your machining operations with expert guidance from Honyo Prototype.
For detailed technical support and CNC programming resources, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. Our full-service factory is located in Shenzhen, equipped with advanced CNC machining capabilities to support prototyping and low-volume production with strict quality control.
Reach out today to streamline your production workflow with industry-standard G-code practices and personalized engineering support.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.