Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Cnc Machine G Code M Code List
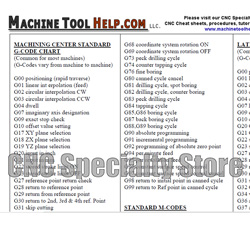
Mastering CNC Fundamentals: Precision Through Code Execution
Understanding G codes and M codes is essential for achieving optimal results in CNC machining, as these指令 form the foundational language that directs machine tool movement, spindle control, coolant management, and auxiliary functions. At Honyo Prototype, our engineering team leverages deep expertise in these critical programming elements to ensure every component meets stringent precision and repeatability standards. Our comprehensive CNC machining services—from complex 3-axis milling to high-speed 5-axis operations—are built on rigorous validation of G and M code sequences, minimizing errors and maximizing efficiency across diverse materials including aerospace alloys, medical-grade plastics, and hardened steels.
This G code M code reference list underscores our commitment to transparency and technical excellence, providing valuable insight into the precise machine control methodologies we employ. By mastering these codes, we consistently deliver prototypes and low-volume production parts with tolerances as tight as ±0.0002 inches, surface finishes down to Ra 0.8 μm, and accelerated turnaround times. For engineering teams seeking rapid validation of manufacturability and cost, Honyo Prototype offers an Online Instant Quote platform. Upload your CAD file to receive a detailed technical assessment and competitive pricing within hours—no manual submissions or delays. Accelerate your product development cycle with machining precision engineered from the ground up.
Technical Capabilities
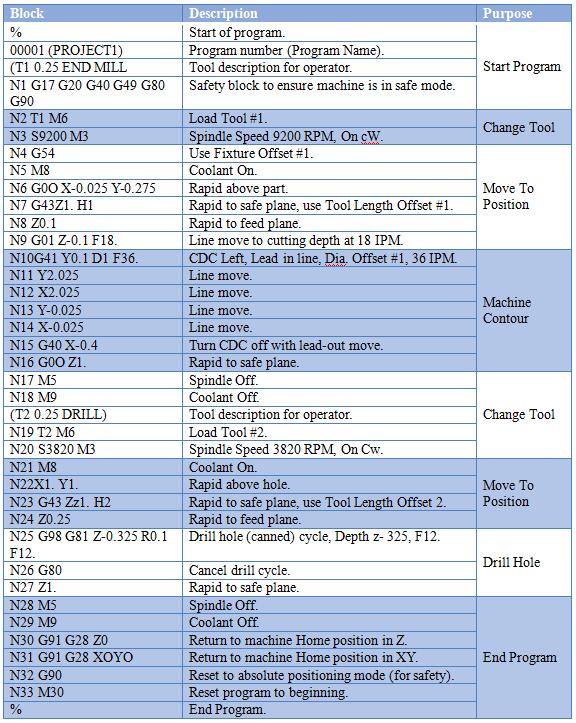
CNC Machine G-Code and M-Code Reference for 3/4/5-Axis Milling, Turning, and Tight Tolerance Applications
Below is a technical summary of commonly used G-codes and M-codes across multi-axis CNC milling and turning platforms, particularly relevant for high-precision machining of materials such as aluminum, steel, ABS, and nylon. These codes are standard across Fanuc-compatible controls and widely adopted by Haas, DMG MORI, Makino, and Okuma systems. Applications include tight tolerance components (±0.0005″ / ±0.0127 mm) in aerospace, medical, and industrial tooling.
| Code | Type | Function | Relevance to 3/4/5-Axis Milling | Relevance to Turning | Material-Specific Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G00 | G-Code | Rapid positioning | Used for non-cutting travel between positions in complex 3D toolpaths; essential for minimizing cycle time in 5-axis contours | Rapid traverse to safe positions during tool changes or parting | Minimizes thermal effects in thermoplastics (ABS, Nylon) by reducing non-productive time |
| G01 | G-Code | Linear interpolation | Critical for precision linear moves in tight tolerance milling; used with high feed smoothing in 5-axis联动 (synchronized motion) | Straight turning, facing, and taper cutting | High rigidity required for steel; optimized feed rates for nylon to prevent deformation |
| G02 | G-Code | Circular interpolation (CW) | Used for helical milling, circular tool entry, and complex contours in aluminum and steel molds | Threading, radius turning | Avoid excessive stepovers in ABS to prevent edge lifting |
| G03 | G-Code | Circular interpolation (CCW) | As above, for counter-clockwise arcs in cavity machining | As above | Critical for smooth finishes in reflective aluminum components |
| G17 | G-Code | XY plane selection | Default for 3-axis milling; base plane for most 2.5D operations | Used in face grooving | Less relevant in 5-axis where dynamic plane selection is used |
| G18 | G-Code | XZ plane selection | Used in mill-turn setups | Standard for turning operations on Z-axis symmetry | Key for cylindrical features in steel and aluminum shafts |
| G19 | G-Code | YZ plane selection | Enables side milling and complex 4-axis operations | Used in off-center drilling/milling on multitask lathes | Useful for nylon manifolds requiring perpendicular ports |
| G20 | G-Code | Inch units | Required for U.S. aerospace and automotive prints | Common in imperial-based turning shops | Essential when matching legacy tooling for steel components |
| G21 | G-Code | Metric units | Standard in European and medical device manufacturing | Widely used globally | Preferred for precision nylon gears with metric pitch |
| G28 | G-Code | Return to home via reference point | Used for safe tool retraction in 5-axis to avoid collisions | Tool change positioning | Critical when switching tools for multi-material prototypes |
| G40 | G-Code | Cutter radius compensation off | Disables compensation before complex 5-axis moves | Ends compensation after finishing cuts | Prevents overcuts in thin-wall aluminum parts |
| G41 | G-Code | Cutter radius compensation left | Used with 3-axis contouring; caution required in 5-axis | Rough/finish turning with offset | Improves edge accuracy in ABS enclosures |
| G42 | G-Code | Cutter radius compensation right | As above | As above | As above |
| G43 | G-Code | Tool length compensation | Mandatory for multi-tool 4/5-axis programs; uses H-code | Applies to turret tools in mill-turn centers | Ensures depth accuracy in deep pockets (steel) and shallow cuts (nylon) |
| G49 | G-Code | Cancel tool length compensation | Used before setup changes | Rarely used; typically overridden | Safety measure during material transitions |
| G54–G59 | G-Code | Work coordinate systems | Essential for multiple fixtures in 3+ axis workholding | Multiple part setups on chuck/faces | Allows quick switch between aluminum and steel workpieces |
| G68 | G-Code | Coordinate rotation | Enables angular feature machining without re-fixturing in 4-axis | Rotational indexing on C-axis | Reduces setups for nylon manifolds with angled ports |
| G68.2 | G-Code | 3D coordinate rotation | Core for 5-axis simultaneous milling; aligns toolpath to angled surfaces | Advanced mill-turn with B/C-axis | Vital for aerospace titanium/steel impellers (also applicable) |
| G81 | G-Code | Drilling cycle | Simple hole-making in 3-axis; limited in 5-axis | Peck drilling on face or OD | Use reduced feed in ABS to avoid chip clogging |
| G83 | G-Code | Deep hole peck drilling | Critical for long-reach tools in aluminum and steel | Deep boring cycles | Prevents heat buildup in nylon; use sharp tools and air blast |
| G90 | G-Code | Absolute programming | Standard for all tight tolerance work | Standard in turning cycles | Required for precision step-downs in steel molds |
| G91 | G-Code | Incremental programming | Used in subroutines or local moves | Occasionally in repetitive cycles | Limited use in high-accuracy workflows |
| G94 | G-Code | Feed per minute | Standard for milling feeds | Used in facing and turning | Optimize for thermal control in nylon (lower SFM) |
| G95 | G-Code | Feed per revolution | Not used in milling | Essential for threading and finish turning | Critical for consistent chip load in aluminum and steel |
| M03 | M-Code | Spindle clockwise | Standard for most milling cutters | Standard for right-hand turning | Match with climb milling in aluminum |
| M04 | M-Code | Spindle counterclockwise | Used for left-hand tools or specific deburring | For left-hand threading | Rare; used in specialty nylon cutting tools |
| M05 | M-Code | Spindle stop | Required before tool change or probing | After cut completion | Prevents vibration marks on mirror-finish aluminum |
| M06 | M-Code | Tool change | Automated in 4/5-axis with tool magazines | On turret lathes with tool change command | Critical when switching between roughing (steel) and finishing (ABS) tools |
| M08 | M-Code | Coolant on (flood) | Flood or through-spindle coolant for steel/aluminum | Coolant during cutting | Avoid in nylon (causes swelling); use air blast |
| M09 | M-Code | Coolant off | Turn off before tool change or dry runs | After cycle end | Mandatory before machining hygroscopic materials like nylon |
| M19 | M-Code | Spindle orientation | Aligns tool for boring bar entry or probing | Key for tool tip positioning in turning | Ensures repeatability in precision boring of steel |
| M30 | M-Code | Program end and reset | Final code; resets program counter | End of part program | Standard for batch runs in high-mix environments |
Material-Specific Machining Notes:
Aluminum (6061, 7075): High-speed machining with sharp carbide tools; use peck drilling (G83) for deep holes; climb milling (G01, M03) preferred.
Steel (4140, 1018): Lower RPMs, rigid setups, consistent coolant (M08); G76 for precision threading in turning.
ABS: Low melting point; use high rake-angle tools, air blast cooling (avoid M08), and light cuts to prevent edge melting.
Nylon (6, 66): Highly flexible; use sharp tools, high clearance angles, and low feed rates; avoid coolant; secure fixturing to prevent deformation.
This G/M-code set supports ISO and ASME-compliant manufacturing with emphasis on geometric accuracy, surface finish, and process repeatability across hybrid machining platforms.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype executes CNC machining projects through a rigorously defined workflow designed for precision, efficiency, and client transparency. The process you referenced—Upload CAD → AI Quote → DFM → Production → Delivery—accurately outlines our core stages, though it is important to clarify that G-code and M-code generation is not a standalone client-facing step but an integral technical component occurring within the Production phase. Below is a precise explanation of how these machine codes interface with our workflow.
Upon receiving a client’s CAD file upload through our secure portal, our SmartQuote™ AI system performs initial geometry analysis and material compatibility checks. This generates a preliminary cost and lead time estimate, but crucial technical validation occurs next. The file enters our collaborative Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review, where senior manufacturing engineers assess feature feasibility, tooling requirements, and potential geometric conflicts. This stage often involves direct client consultation to resolve ambiguities or suggest optimizations—reducing downstream rework.
Only after DFM sign-off does the project advance to Production. Here, our CAM programming team converts the approved CAD model into machine-executable instructions. This is where G-code (geometric motion commands) and M-code (miscellaneous machine functions like coolant activation or tool changes) are systematically generated. We utilize industry-standard CAM software (Mastercam, Fusion 360) configured to match our specific CNC machine kinematics, tool libraries, and workholding setups. Critical to our quality assurance, every G/M-code program undergoes:
- Rigorous simulation within CAM software to verify collision avoidance and toolpath accuracy
- Dry-run validation on the target machine using laser-probed workpiece alignment
- First-article inspection against GD&T callouts per AS9102 standards
It is essential to note that raw G/M-code files are proprietary operational data and not standard client deliverables. Clients receive certified inspection reports, dimensional validation data, and finished parts—not machine code—to protect intellectual property and ensure process integrity. Sharing unverified G-code could risk misapplication on dissimilar equipment.
The final Delivery phase includes comprehensive documentation: material certifications, first-article reports, and shipping manifests. For complex multi-axis projects, we provide process validation summaries detailing critical parameters, though machine code remains internal. This structured approach ensures that G/M-code execution—while technically foundational—never compromises client confidentiality or part quality.
| Process Stage | Key Actions | G/M-Code Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Upload CAD | Secure file ingestion, format validation | Input for CAM programming |
| AI Quote | Automated cost/time estimation, material analysis | Preliminary tooling assumptions |
| DFM | Engineering review, manufacturability optimization | Finalizes tooling strategy for code generation |
| Production | CAM programming, G/M-code generation, machine validation | Core execution phase where codes are created and verified |
| Delivery | Final inspection, documentation, shipment | Code not delivered; inspection data provided instead |
Start Your Project

If you’re looking for a comprehensive CNC machine G-code and M-code list, or need expert support for your precision manufacturing projects, contact Susan Leo at [email protected].
Honyo Prototype operates a fully equipped manufacturing facility in Shenzhen, providing high-accuracy CNC machining services with full programming and technical documentation, including standardized G-code and M-code references tailored to your machining needs.
Reach out today to streamline your production workflow with reliable, factory-direct support from our engineering team.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.