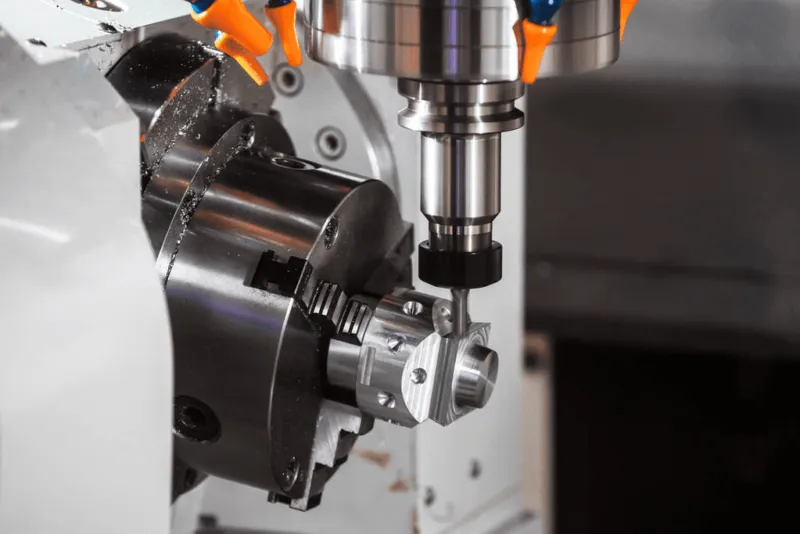
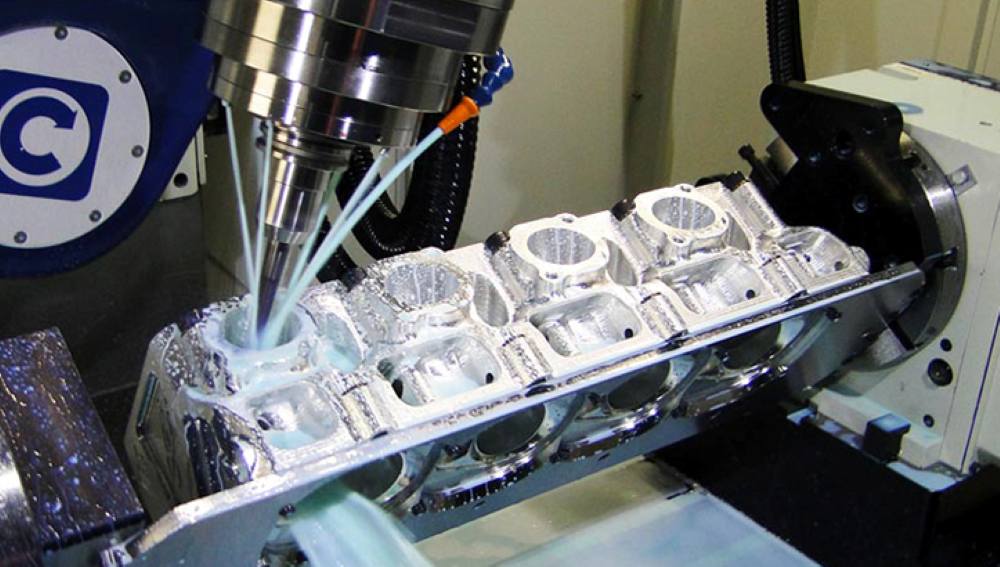
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc machine cost per hour
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, accurately determining the CNC machine cost per hour poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With fluctuating labor rates, varying material costs, and the complexities of different machining applications, sourcing the right CNC services can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify the factors influencing CNC machining costs, offering insights into the types of machines, their applications, and how to effectively vet suppliers.
Understanding these elements not only aids in cost calculation but also enhances strategic decision-making. For businesses operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia—this guide is tailored to empower you with the knowledge needed to navigate the global market effectively.
By delving into the various components that contribute to CNC machining costs—from the intricacies of job costing to the importance of optimizing labor and material use—this resource equips you to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you’re looking to streamline production, enhance profitability, or establish long-term supplier relationships, our comprehensive analysis will help you achieve your business objectives in a rapidly evolving market.
Understanding cnc machine cost per hour Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard CNC Machining Rate | Fixed hourly rate based on average operational costs | General manufacturing, prototyping | Pros: Predictable costs; easy budgeting. Cons: May not reflect actual job complexity. |
| Variable CNC Machining Rate | Pricing adjusts based on job complexity and material used | Custom part production, low-volume jobs | Pros: More accurate cost reflection; adaptable. Cons: Can lead to unpredictable budgeting. |
| High-Precision Machining Rate | Higher costs for specialized machinery and skilled labor | Aerospace, medical devices, high-tolerance parts | Pros: Ensures quality and precision; suitable for critical applications. Cons: Higher costs may limit project scope. |
| Setup and Changeover Costs | Additional fees for initial setup and tool changes | Batch production, complex parts manufacturing | Pros: Covers time and resources for setups; encourages efficiency. Cons: Can inflate costs for small runs. |
| Material-Specific Rates | Different rates based on the type of material being machined | Industries requiring diverse materials (e.g., automotive, aerospace) | Pros: Reflects true material costs; promotes informed decisions. Cons: Requires detailed material knowledge for accurate quoting. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard CNC Machining Rates?
Standard CNC machining rates are fixed hourly fees that manufacturers set based on their average operational costs, including labor, machine maintenance, and overhead. This pricing model is suitable for general manufacturing and prototyping where job complexity is relatively uniform. Buyers benefit from predictable costs, making budgeting straightforward; however, this model may not account for variations in job complexity, potentially leading to overcharges for simpler tasks.
How Do Variable CNC Machining Rates Benefit Custom Projects?
Variable CNC machining rates adjust based on the complexity of the job and the materials used. This pricing structure is particularly beneficial for custom part production and low-volume jobs, where each project can significantly differ in requirements. The adaptability of this model allows for a more accurate reflection of costs. However, it can complicate budgeting, as prices may fluctuate based on unforeseen complexities.
What Defines High-Precision Machining Rates?
High-precision machining rates are significantly higher due to the specialized machinery and skilled labor required for intricate tasks, often found in industries like aerospace and medical devices. These rates ensure quality and precision, making them ideal for applications where tolerances are critical. While they guarantee superior outcomes, the elevated costs can limit the scope of projects for some buyers, necessitating careful consideration of budget constraints.
Why Are Setup and Changeover Costs Important in CNC Machining?
Setup and changeover costs are additional fees incurred for the initial setup of machines and tools for specific jobs. This pricing is especially relevant in batch production and when manufacturing complex parts that require extensive setup time. By charging for these costs, manufacturers encourage efficient operations. However, for small production runs, these additional fees can inflate the overall cost, potentially deterring clients.
How Do Material-Specific Rates Impact B2B Buyers?
Material-specific rates vary according to the type of material being machined, reflecting the true costs associated with different materials. This pricing model is essential for industries like automotive and aerospace, where diverse materials are frequently used. It promotes informed decision-making and enables buyers to understand the impact of material selection on overall costs. However, it requires buyers to have detailed knowledge of material costs to ensure accurate quoting and budgeting.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc machine cost per hour
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cnc machine cost per hour | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing for aircraft | High accuracy and compliance with safety standards | Certification of machinery and materials; skilled labor availability |
| Automotive | Production of custom parts and prototypes | Reduced lead times and enhanced design flexibility | Material sourcing; tooling compatibility; scalability of operations |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments | High precision and regulatory compliance | Quality assurance processes; material biocompatibility; traceability of parts |
| Electronics | PCB and housing production | Cost-effective mass production and rapid prototyping | Equipment capabilities; supply chain reliability; technological integration |
| Energy | Manufacturing components for renewable energy systems | Optimized performance and sustainability | Compliance with industry standards; material durability; supplier certifications |
How Is CNC Machine Cost Per Hour Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, CNC machining is crucial for producing high-precision components such as turbine blades and structural parts. The cost per hour is closely monitored to ensure that manufacturing processes remain efficient while meeting stringent safety regulations. Buyers in this industry must consider the certification of machinery and the availability of skilled labor, as well as the need for advanced materials that can withstand extreme conditions. By optimizing CNC machine costs, aerospace manufacturers can enhance their competitiveness while ensuring compliance with international standards.
What Are the Benefits of CNC Machining in Automotive Production?
The automotive industry relies heavily on CNC machining for the production of custom parts and prototypes. The cost per hour plays a significant role in determining the feasibility of producing complex components, as it directly affects overall project budgets. Buyers must focus on material sourcing and tooling compatibility to ensure that production runs smoothly and efficiently. Additionally, the ability to scale operations is vital for meeting fluctuating market demands, allowing automotive manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in consumer preferences while keeping costs in check.
How Is CNC Machine Cost Per Hour Relevant in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical devices sector, CNC machining is essential for fabricating surgical instruments and implants with high precision. The cost per hour is an important metric that helps manufacturers maintain profitability while adhering to strict regulatory requirements. Buyers should prioritize quality assurance processes and ensure that materials used are biocompatible and traceable. By effectively managing CNC costs, medical device manufacturers can produce reliable products that meet the high standards expected in healthcare, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Why Is CNC Machining Important for Electronics Production?
The electronics industry utilizes CNC machining for producing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and enclosures. The cost per hour is a critical factor in achieving cost-effective mass production and rapid prototyping. Buyers need to evaluate equipment capabilities and the reliability of the supply chain to ensure that production schedules are met without compromising quality. By optimizing CNC machine costs, electronics manufacturers can enhance their product offerings and maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
How Does CNC Machine Cost Per Hour Impact Energy Sector Manufacturing?
In the energy sector, CNC machining is used to manufacture components for renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and solar panels. The cost per hour is vital for optimizing performance and ensuring sustainability in production processes. Buyers must consider compliance with industry standards and the durability of materials used in manufacturing. By effectively managing CNC costs, energy sector manufacturers can improve their operational efficiency and contribute to a more sustainable future.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc machine cost per hour’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Fluctuating CNC Machine Hourly Rates
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the variability in CNC machine costs per hour, particularly when negotiating contracts or budgeting for projects. Factors such as machine type, job complexity, and material requirements can lead to significant differences in hourly rates. This unpredictability can make it challenging for businesses to estimate project costs accurately, leading to budget overruns and strained relationships with clients.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should develop a comprehensive understanding of their specific machining needs and the associated costs. Start by conducting a detailed analysis of past projects to identify patterns in hourly rates based on machine type and job complexity. Create a standardized pricing matrix that reflects the various factors influencing cost—such as setup time, labor, and material wastage. Additionally, engage in open discussions with suppliers to establish transparent pricing structures. By having a well-defined cost framework, businesses can provide more accurate quotes and maintain competitive pricing without compromising on quality.
Scenario 2: Managing Labor Costs in CNC Machining
The Problem: Labor costs represent a significant portion of CNC machining expenses, and as wage rates continue to rise globally, B2B buyers face the challenge of maintaining profitability without passing excessive costs onto customers. Many companies find themselves in a bind, unable to fully utilize their workforce due to labor shortages or inefficiencies, which further exacerbates the issue.
The Solution: To effectively manage labor costs, companies should invest in workforce training and process automation. Upskilling existing employees can enhance productivity and reduce the need for additional hiring, while automation technologies can streamline repetitive tasks, allowing skilled workers to focus on higher-value activities. Additionally, implementing a robust job costing system can help track labor time more accurately, enabling businesses to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. By optimizing labor allocation and enhancing employee capabilities, companies can reduce costs per hour and improve overall operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Accounting for Material Costs in CNC Machining
The Problem: B2B buyers often overlook the impact of material costs on CNC machining hourly rates, leading to inaccurate job costing. Variations in material prices can significantly affect overall project expenses, especially when dealing with specialty metals or fluctuating market conditions. This oversight can result in underquoting jobs, ultimately harming profitability and client relationships.
The Solution: To address this pain point, businesses should implement a dynamic material cost tracking system that reflects real-time market prices. Regularly updating material costs in your job costing calculations will provide a more accurate picture of project expenses. Additionally, consider negotiating long-term contracts with suppliers to secure better rates and reduce the risk of price fluctuations. By incorporating material cost considerations into the overall CNC hourly rate calculations, companies can ensure more accurate quotes and safeguard their margins against market volatility.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc machine cost per hour
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in CNC Machining?
Aluminum is one of the most commonly used materials in CNC machining due to its favorable properties. It is lightweight, has excellent corrosion resistance, and can withstand moderate temperature and pressure conditions. Aluminum alloys, such as 6061 and 7075, are particularly popular due to their enhanced strength and machinability. The lower density of aluminum allows for easier handling and reduced shipping costs, making it an attractive option for international buyers.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum in CNC Machining
The primary advantage of aluminum is its combination of strength and weight, which makes it suitable for various applications, including automotive and aerospace components. Its excellent machinability allows for faster production rates, reducing the overall cost per hour of CNC machining. However, aluminum can be more expensive than some alternative materials, and its lower strength compared to steel may limit its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, the wear of tooling can be higher when machining aluminum, necessitating more frequent tool changes.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for CNC Machining?
Steel, particularly carbon steel and stainless steel, is another staple in CNC machining. It boasts high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and deformation under stress. Stainless steel, in particular, offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in harsh environments.
Pros and Cons of Using Steel in CNC Machining
Steel’s key advantage lies in its high tensile strength and toughness, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as construction and machinery components. However, the complexity of machining steel can lead to higher costs due to longer processing times and increased tool wear. Moreover, the weight of steel can increase shipping and handling costs, particularly for international buyers. The need for specialized tooling and longer machining times can also elevate the CNC machine cost per hour.
What Are the Benefits of Using Titanium in CNC Machining?
Titanium is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice in aerospace and medical applications. It can withstand extreme temperatures and is biocompatible, which is essential for medical implants.
Pros and Cons of Using Titanium in CNC Machining
The main advantage of titanium is its ability to perform well in demanding environments, offering durability and longevity. However, titanium is significantly more expensive than aluminum or steel, leading to higher CNC machining costs. The material’s hardness also presents challenges during machining, requiring specialized tools and techniques, which can further increase the cost per hour.
Why is Plastic an Important Material in CNC Machining?
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly being used in CNC machining due to their versatility, lightweight nature, and resistance to corrosion and chemicals. They are often used in consumer goods, automotive parts, and medical devices.
Pros and Cons of Using Plastic in CNC Machining
Plastics offer a significant cost advantage, as they are generally less expensive than metals and can be machined quickly. They also provide excellent design flexibility and can be molded into complex shapes. However, plastics may not be suitable for high-stress applications due to their lower strength compared to metals. Additionally, certain plastics can be sensitive to temperature changes, which may affect their performance in specific applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Machining Costs
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc machine cost per hour | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight with good corrosion resistance | Higher tooling wear rates | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty machinery and construction parts | High strength and durability | Longer machining times increase costs | Medium to High |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Very high material and machining costs | High |
| Plastic | Consumer goods and automotive parts | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower strength limits high-stress applications | Low |
This analysis of materials highlights the importance of strategic material selection in optimizing CNC machining costs. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their production needs and budget constraints.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc machine cost per hour
What Are the Main Stages of CNC Manufacturing Processes?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a sophisticated method that integrates various manufacturing processes to create precision parts. The cost per hour for CNC machining is significantly influenced by the efficiency and effectiveness of these processes. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages involved in CNC manufacturing:
How Does Material Preparation Impact CNC Costs?
Material preparation is the initial stage in the CNC machining process. This stage involves selecting the appropriate raw material based on the part specifications. Common materials include aluminum, steel, titanium, and plastics, each impacting the overall cost due to price variations and machining complexities.
Once the material is selected, it is cut to size, often requiring additional processes like shearing or sawing. The choice of material and its preparation directly affects machine run time and tooling requirements, which are significant contributors to the hourly cost of CNC machining.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in CNC Machining?
The forming stage involves the actual machining operations where the CNC machine executes programmed instructions to shape the material. Key techniques include milling, turning, drilling, and grinding. Each technique has its own operational costs based on factors like tool wear, machine type, and complexity of the part.
For instance, milling operations are generally more complex and may require more advanced tooling compared to turning operations. The programming time and machine setup also vary, further influencing the cost per hour. Efficient programming and tool path optimization can help reduce machining time, thereby lowering costs.
Why Is Assembly Important in CNC Manufacturing?
In CNC machining, assembly may not be a primary function but can be crucial for complex parts requiring multiple components. This stage involves fitting and fastening the machined parts together to create the final product. Depending on the assembly complexity, additional labor costs and time may be incurred, affecting the overall hourly rate.
Moreover, the assembly process may require specialized skills and tools, further impacting costs. For B2B buyers, understanding the assembly requirements is essential for accurate cost estimation and ensuring that the supplier can meet the necessary quality standards.
How Does Finishing Affect CNC Machining Costs?
Finishing processes such as deburring, polishing, and coating are critical for achieving the desired surface quality and aesthetics of the final product. These processes can significantly add to the machining time and cost per hour, especially if high-quality finishes are required for functional or aesthetic purposes.
For instance, a simple deburring task may take a few minutes, while intricate polishing could extend the machining time significantly. B2B buyers should factor in these finishing processes when evaluating quotes, as they can vary widely between suppliers.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for CNC Machining?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in maintaining high standards in CNC machining, ensuring that parts meet specifications and customer expectations. The following are essential aspects of QA in CNC manufacturing:
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
International standards like ISO 9001 provide frameworks for quality management systems that organizations can implement to ensure consistent quality in their processes. Compliance with such standards is crucial for B2B buyers as it reflects the supplier’s commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe or API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications for oil and gas components can also be significant. These certifications ensure that the products meet specific safety and performance standards.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the CNC machining process and typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials before machining.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors processes during machining to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts thorough inspections of finished parts against specifications.
Implementing these checkpoints helps in identifying potential issues early, reducing waste, and ensuring that the final products meet quality standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in CNC Quality Assurance?
Testing methods in CNC machining can include dimensional inspections using calipers and micrometers, surface finish measurements, and functional testing of assembled parts. Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic or X-ray inspection, may also be employed for critical components, especially in industries like aerospace and automotive.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing methods a supplier employs and the frequency of these tests to ensure that their products meet the required specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for mitigating risks in international transactions. Here are several strategies B2B buyers can use:
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Supplier Verification?
Conducting audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality control processes and adherence to standards. Buyers should request documentation of quality procedures, inspection reports, and any certifications the supplier holds. This information can help assess the supplier’s capability to deliver consistent quality.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Employing third-party inspection services can provide an objective evaluation of the supplier’s processes and products. These inspections can be especially valuable for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct on-site audits. Third-party inspectors can verify that quality standards are being met and provide detailed reports on compliance.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control in different markets is vital. Factors such as local regulations, material availability, and cultural attitudes toward quality can significantly influence supplier relationships.
Establishing clear communication regarding quality expectations and requirements upfront can help mitigate misunderstandings. Additionally, familiarity with local certifications and standards can enhance trust and facilitate smoother transactions.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with CNC machining is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement strategies. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make more informed decisions that align with their quality and cost objectives.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc machine cost per hour’
Introduction
When sourcing CNC machining services, understanding the cost per hour is crucial for budget management and profitability. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of determining CNC machine costs. By following these steps, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and financial goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your CNC machining project. This includes the type of materials, dimensions, tolerances, and complexity of the parts you need. Precise specifications help suppliers provide accurate quotes and ensure that the capabilities of their machinery align with your project demands.
- Material Types: Identify whether you need aluminum, steel, titanium, or other materials, as this impacts both cost and machine requirements.
- Part Complexity: More intricate designs may require specialized tooling and higher skill levels, affecting overall costs.
Step 2: Research Market Rates for CNC Machining
Conduct thorough research to understand the prevailing hourly rates for CNC machining in your target regions. Rates can vary significantly based on the type of work, machine capabilities, and market demand.
- Comparative Analysis: Look for industry benchmarks or forums where professionals discuss their rates, giving you insight into what to expect.
- Local Variations: Consider regional economic factors that might influence pricing, particularly if sourcing from countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, perform a comprehensive evaluation. This includes checking their capabilities, past performance, and customer feedback.
- Supplier Profiles: Request detailed company profiles and inquire about their experience with similar projects.
- References and Reviews: Seek testimonials from clients in your industry or region to gauge reliability and quality of service.
Step 4: Assess Labor and Overhead Costs
Understand how labor and overhead contribute to the overall CNC machining cost. This includes not only the hourly wage of the machinists but also indirect costs like setup time and machine maintenance.
- Labor Breakdown: Ask suppliers for a detailed breakdown of labor costs associated with your project.
- Overhead Considerations: Inquire about any additional overhead that may be factored into the hourly rate, as this can significantly impact your total costs.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have identified potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that break down costs per hour. This transparency allows you to compare offers effectively.
- Cost Components: Ensure that the quotes include all aspects of the job, from setup and running time to material costs and finishing processes.
- Negotiation Space: Look for areas where you might negotiate better rates or terms, especially if you plan to provide repeat business.
Step 6: Verify Quality Control Measures
Quality assurance is vital in CNC machining to avoid costly errors and rework. Ask potential suppliers about their quality control processes.
- Certifications and Standards: Check if the supplier adheres to international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications).
- Inspection Procedures: Understand how they monitor quality throughout the machining process to ensure that your parts meet the required specifications.
Step 7: Plan for Future Needs
Consider your long-term machining requirements and how the supplier can accommodate them. Establishing a relationship with a reliable supplier can lead to better pricing and service in the future.
- Scalability: Discuss potential for scaling up production as your business grows.
- Partnership Opportunities: Explore if the supplier offers additional services or technologies that may benefit your future projects.
By following these steps, you can make informed decisions when sourcing CNC machining services and effectively manage your costs per hour.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc machine cost per hour Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components Influencing CNC Machine Hourly Rates?
When assessing CNC machine costs per hour, it’s crucial to dissect the various components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of material being machined significantly affects the hourly cost. For instance, machining titanium or high-performance alloys incurs higher material costs compared to aluminum. Additionally, fluctuations in material prices due to market conditions can impact overall expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass not only direct wages but also overhead expenses such as benefits and training. As labor markets evolve, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, companies must adjust their pricing strategies to account for rising wage demands and labor shortages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient management of overhead can lead to more competitive pricing. Companies should regularly review their overhead costs to identify areas for savings.
-
Tooling and Setup: Custom tooling and machine setup can add significant costs, particularly for complex parts. Understanding the specific tooling needs for different jobs can help buyers negotiate better terms and reduce overall production costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet specific standards necessitates investment in QC processes. The costs associated with inspections, testing, and certifications can vary widely based on industry standards and customer requirements.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can impact the final pricing of CNC machined parts, particularly for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms and their implications on shipping responsibilities can help mitigate unforeseen logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover risks and ensure profitability. Buyers should be aware of industry standards for margins to ensure they are receiving fair pricing.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect CNC Pricing?
Pricing can fluctuate based on the volume of parts ordered and the level of customization required. Generally, larger orders benefit from economies of scale, leading to lower per-unit costs. Conversely, small batch runs often carry higher costs due to the increased setup time relative to production volume.
Customization also plays a significant role; highly specialized parts require unique tooling and programming, which can raise costs. International buyers should clearly communicate their specifications to suppliers to avoid unexpected charges and ensure that their unique needs are met.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize CNC Machining Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can optimize CNC machining costs:
-
Negotiation: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating prices based on volume commitments. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes not just the initial price but also long-term costs such as maintenance, downtime, and logistics. This holistic view can lead to better decision-making.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Be aware of currency fluctuations and how they affect pricing when dealing with suppliers from different regions. Establishing fixed pricing contracts can help mitigate this risk.
-
Supplier Factors: Assess suppliers based on their capabilities, certifications, and past performance. A reliable supplier may justify a higher price due to their quality assurance processes, potentially reducing overall costs associated with defects and rework.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Conduct thorough research on industry benchmarks for CNC machining costs. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions when comparing quotes and evaluating supplier proposals.
Are There Indicative Prices for CNC Machining Services?
While CNC machining costs can vary widely, indicative hourly rates typically range from $50 to over $500, depending on complexity, material, and service quality. It’s essential to understand that these prices are subject to change based on market dynamics and specific project requirements. Always request detailed quotes that itemize costs to ensure transparency and facilitate better budgeting.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc machine cost per hour With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to CNC Machine Cost Per Hour
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, understanding various solutions for production efficiency and cost-effectiveness is crucial for B2B buyers. While CNC machining is a powerful method for precision manufacturing, exploring alternatives can provide insights into potential savings and performance benefits. This analysis compares the cost per hour of CNC machining with other viable production methods, including traditional machining and additive manufacturing (3D printing).
| Comparison Aspect | Cnc Machine Cost Per Hour | Traditional Machining | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, consistent output | Moderate precision, variable output | High precision for complex geometries |
| Cost | $50 – $500+ per hour, depending on complexity | $30 – $100 per hour, but depends on setup | $20 – $150 per part, varies by material |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and setup | Requires skilled labor and tooling | Easier setup for simple designs, less skilled labor |
| Maintenance | High maintenance due to complexity | Moderate maintenance, simpler machines | Low maintenance but requires quality control |
| Best Use Case | High-volume, complex parts requiring precision | Low to medium-volume, simpler parts | Prototyping, complex geometries, low-volume production |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Traditional Machining Compared to CNC Machining?
Traditional machining often utilizes lathes and milling machines that operate with manual input. One of the key advantages is the lower hourly cost, which can be appealing for simpler jobs or low-volume runs. However, the precision and consistency of output may not match CNC machining, especially for intricate designs. Additionally, traditional methods can require more time for setup, which can diminish efficiency in jobs with frequent changes.
How Does Additive Manufacturing Stack Up Against CNC Machining?
Additive manufacturing, particularly 3D printing, has emerged as a compelling alternative to CNC machining. It allows for the creation of complex geometries that are often difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. The cost per part can be lower, especially for prototypes or small production runs. However, the material costs can vary significantly, and the technology may not yet match the durability of parts produced through CNC machining. While the implementation of 3D printing can be more straightforward for simple designs, it may require specialized knowledge for more complex projects.
Making the Right Choice: How Can B2B Buyers Decide on the Best Solution?
When evaluating which manufacturing method to adopt, B2B buyers should consider several factors specific to their operational needs. If high precision and volume are critical, CNC machining may be the best choice despite its higher hourly rate. For businesses focused on cost and lower complexity, traditional machining may suffice. Conversely, companies looking to innovate with complex designs should explore additive manufacturing. Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s production goals, budget constraints, and the nature of the products being manufactured. By carefully analyzing these alternatives, buyers can make informed choices that enhance their operational efficiency and profitability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc machine cost per hour
When determining the cost per hour for CNC machining, understanding essential technical properties and industry terminology is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also ensures clarity in communications with suppliers and manufacturers.
What Are the Key Technical Properties Impacting CNC Machine Cost per Hour?
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of materials used in CNC machining, such as aluminum, steel, or titanium. Different grades have varying mechanical properties, affecting machining difficulty, tooling requirements, and ultimately, cost. For instance, titanium, known for its strength and light weight, demands higher machining costs due to its hardness and the specialized tools required for processing it. Understanding material grades helps buyers evaluate quotes and anticipate potential costs related to material procurement and processing. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the finished part. Tight tolerances typically require more precise machining processes, which can significantly increase the cost due to longer machining times and potential tool wear. For example, parts requiring tolerances of ±0.001 inches will incur higher costs compared to those with tolerances of ±0.01 inches. Buyers should assess tolerance requirements carefully, as they directly impact the pricing structure of CNC services. -
Setup Time
Setup time is the duration required to prepare the CNC machine for a specific job, including programming, tool changes, and calibration. Longer setup times can lead to increased hourly costs, especially for low-volume runs. Understanding the implications of setup time is essential for buyers, as it can affect the overall production timeline and cost efficiency of a project. -
Run Time
Run time refers to the actual time a CNC machine spends processing a part. This time is critical when calculating the cost per hour since it directly correlates with labor and operational costs. Buyers should consider the expected run times for their orders, as higher run times can lead to better cost efficiencies, especially for bulk orders. -
Batch Size
The batch size is the quantity of parts produced in a single setup. Larger batch sizes typically reduce the per-unit cost due to economies of scale, whereas smaller batches may incur higher costs per part. Buyers need to balance their production needs with batch sizes to optimize costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Machining Cost Calculations?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking for quality assurance and compatibility in parts, as OEM products often meet higher standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help in planning orders and negotiations with suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for price quotes on specific products or services. This process is essential for buyers to compare costs effectively and ensure they are getting competitive pricing for their CNC machining needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is important for B2B buyers, as they dictate shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery responsibilities, impacting the overall cost per hour of CNC machining services. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the total time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. Understanding lead times is essential for buyers to manage production schedules and ensure timely delivery of parts, affecting overall operational efficiency.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, negotiate better contracts, and ultimately optimize their CNC machining costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc machine cost per hour Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing CNC Machine Cost per Hour?
The CNC machining sector is witnessing a transformative phase driven by several global dynamics that significantly impact the cost per hour for CNC machines. Key trends include the rising labor costs, which have seen an increase of 4.1% year-on-year, particularly in regions such as Europe and North America. This trend necessitates that manufacturers adopt more efficient labor allocation and consider automation to maintain profitability. Additionally, the complexity of parts being produced is increasing, leading to higher costs associated with specialized setups and tooling. This complexity is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where the demand for precision engineering is growing rapidly.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced job costing software and AI-driven production analytics, are becoming essential tools for manufacturers. These technologies enhance visibility into operational costs, enabling businesses to make informed decisions regarding pricing and resource allocation. Moreover, the trend towards lean manufacturing practices is gaining traction, as companies seek to minimize waste and optimize processes. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, understanding these technological advancements can lead to more competitive pricing structures and improved service delivery.
International market dynamics, influenced by economic fluctuations and geopolitical events, also play a crucial role. For instance, fluctuations in material costs due to supply chain disruptions can directly affect the overall CNC machining costs. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam must stay abreast of these changes to ensure they negotiate favorable terms and maintain their competitive edge.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the CNC Machine Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become increasingly vital in the CNC machining industry, influencing the cost per hour significantly. Manufacturers are now held accountable not only for the quality of their products but also for their environmental impact. This shift is particularly important for B2B buyers who prioritize suppliers with sustainable practices, as they seek to align with global environmental standards.
The adoption of environmentally friendly materials and processes can lead to a reduction in waste and energy consumption, ultimately lowering the costs associated with CNC machining. For instance, using recyclable materials or implementing energy-efficient machinery can enhance a company’s sustainability profile while reducing operational costs. Buyers from Africa and South America, where environmental regulations are evolving, should consider partnering with manufacturers who have certifications for sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 or similar “green” certifications.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are becoming a key factor in supplier selection. Companies that demonstrate transparency and social responsibility in their sourcing practices not only enhance their brand reputation but also attract more business. For international buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental stewardship can mitigate risks associated with compliance and reputational damage, ultimately influencing the overall cost per hour for CNC machining services.
What Is the Evolution of CNC Machining and Its Relevance to Today’s Market?
The evolution of CNC machining dates back to the 1940s when the first numerical control machines were developed. Initially, these machines were limited in functionality and primarily used for simple tasks. Over the decades, advancements in technology have transformed CNC machining into a highly sophisticated process capable of producing intricate components with precision.
Today, CNC machines are integral to various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. The modern landscape is characterized by the integration of automation, robotics, and advanced materials, which have enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of machining processes. As a result, the cost per hour for CNC machining has become a reflection not only of labor and material costs but also of the technological investments made by manufacturers.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial in navigating the current market dynamics. Buyers should evaluate potential suppliers based on their technological capabilities and their ability to adapt to emerging trends, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment. This historical context emphasizes the importance of innovation in achieving competitive pricing and high-quality outputs in the CNC machining sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc machine cost per hour
-
1. How can I determine the hourly cost of CNC machining for my project?
To accurately determine the hourly cost of CNC machining, consider factors like labor rates, machine operational costs, and overhead expenses. Calculate the cost per hour by combining direct costs (like wages and materials) with indirect costs (such as utilities and maintenance). Additionally, analyze the complexity and volume of your project, as intricate designs or smaller batches can significantly impact pricing. Collaborating with multiple suppliers for quotes can also provide a clearer picture of market rates. -
2. What factors influence CNC machining costs per hour?
CNC machining costs are influenced by several factors including material type, part complexity, machine setup time, and labor costs. Materials vary in price; for example, titanium is more expensive than aluminum. The complexity of the parts affects the skill level required and the time taken for production. Additionally, longer setup times for low-volume jobs can increase costs. Understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions when sourcing suppliers. -
3. What is the typical range for CNC machining costs per hour?
The typical range for CNC machining costs per hour can vary widely, generally falling between $50 to $500 or more. Simpler parts produced in high volumes typically incur lower rates, while complex, high-tolerance components command higher prices. To ensure competitive pricing, it’s advisable to gather multiple quotes from suppliers and assess their capabilities against your specific project requirements. -
4. How do I vet CNC machining suppliers for international trade?
To vet CNC machining suppliers, start by reviewing their credentials, certifications, and industry experience. Assess their production capabilities, quality assurance processes, and past client testimonials. Request samples of their work to evaluate quality firsthand. It’s also beneficial to conduct factory audits, if possible, and understand their compliance with international trade regulations. Building a relationship with suppliers through clear communication can also enhance trust. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machining services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machining services can vary based on the supplier and the specifics of your project. Some suppliers may have low or no MOQs for prototype runs, while others may require larger quantities to justify setup costs. Always clarify MOQs upfront to avoid surprises and ensure that the supplier can accommodate your production needs without compromising on quality. -
6. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing CNC machining services?
Payment terms for CNC machining services can differ significantly among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront deposits (typically 30-50%), payment upon completion, or net payment terms (like net 30 or net 60). Discussing payment terms early in the negotiation process is crucial to establish a mutually beneficial agreement. Consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection, especially for international transactions. -
7. How do logistics affect the cost of CNC machined parts?
Logistics play a crucial role in the overall cost of CNC machined parts. Transportation costs, shipping times, and customs duties can significantly impact your budget, especially for international orders. It’s important to consider the proximity of the supplier to your location, shipping methods, and any potential tariffs. Collaborating with suppliers who have efficient logistics strategies can help minimize costs and ensure timely delivery of your components. -
8. What quality assurance measures should I expect from CNC machining suppliers?
Quality assurance measures are essential to ensure that CNC machined parts meet your specifications. Expect suppliers to implement rigorous inspection processes, including material certifications, dimensional checks, and surface finish evaluations. Suppliers should also have established protocols for handling defects, such as rework or replacement policies. Inquire about their quality management systems, such as ISO certifications, to gauge their commitment to maintaining high standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Cnc Machine Cost Per Hour Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. XEBEC – Deburring Solutions
Domain: deburringtechnologies.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: XEBEC Brush™ Surface, XEBEC Brush™ Surface Extra-Large, XEBEC Brush™ End Type, XEBEC Brush™ Wheel Type, XEBEC Brush™ Crosshole, XEBEC Back Burr Cutter & Deburring Path™, XEBEC Stone™ Flexible Shaft, XEBEC Stone™ Mounted Point, XEBEC Floating Holder™, XEBEC Self-Adjusting Sleeve™, XEBEC Brush Length Adjustment Tool™, XEBEC Ceramic Stone™, XEBEC Mobile Micromotor, XEBEC Burrless Chamfering Cutter.
2. CNC Woodworking – Birch Plywood Circles
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC woodworking job details: 900 small circles, lightly sanded; material: b/bb birch plywood, 2.5 inches diameter, 0.5 inches thickness; machine: ShopBot Buddy with extensions, surface area approximately 32 x 60 inches; material costs: $200 (2 sheets of 5ft x 5ft); labor estimate: 8 hours; suggested charge: $17/hour, considered low by community; industry standards discussed: $100+ per hour for CNC…
3. Haas – CNC Machining Equipment
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining Equipment: 7x Haas SL-20, 2x Haas SL-30, 2x Kia Skt-21, 3x Kia SKT-21LMS, 2x Kia SKT-25, 13x Haas VF-4, 1x Haas VF-2, 1x Doosan Puma 700, 1x Doosan Puma 700LM, 1x Toyoda 630mm Horizontal, 1x Doosan 630mm Horizontal, 3x Doosan 2600 SY, 1x Doosan 1800TTSY, 1x Citizen L20, 1x Citizen A20, 1x Citizen A32, 1x Fanuc Robodril with pallet changer.
4. JCAD USA – CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: jcadusa.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: CNC machining costs range from $50 to $150 per hour, depending on equipment and precision. Setup fees start at $50 and can exceed $1,000 based on complexity. Prototyping costs range from $500 to $2,000+, influenced by part complexity and production volume. Material costs vary: aluminum costs $10 to $50 per kg, steel around $800 per metric ton, and titanium $100 to $200 per kg. Setup costs for simp…
5. Carbide 3D – Machining Services for Small Businesses
Domain: community.carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Services offered include machining time for wooden signs and prototypes, targeting small businesses and entrepreneurs. Suggested pricing for machining time is around $1 per minute plus setup time, with a minimum charge of about $50/hr for larger machines and up to $180/hr for high-end routers. Emphasis on flat rate billing rather than hourly rates to provide clients with predictable costs. Importa…
6. Elimold – CNC Machine Hourly Rates
Domain: elimold.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Hourly rates for CNC machines in the U.S. market: Entry-level CNC milling machine: $25 – $50 per hour; Mid-range CNC milling machine: $50 – $100 per hour; High-end CNC milling machine: $100 – $200 per hour; Entry-level CNC lathe: $30 – $60 per hour; Mid-range CNC lathe: $60 – $120 per hour; High-end CNC lathe: $120 – $240 per hour. Factors affecting pricing include machine type and size, project c…
7. Onefinity – Woodworker CNC Machine
Domain: forum.onefinitycnc.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Onefinity Woodworker; expected life: 4000 hours; salvage value: $500; brush changes every 100 hours; router replacement at 500 hours; average tooling life in hardwoods: 20 hours; Fein Turbo I dust collection: 1000 hours; salvage value: $0; maintenance and parts replacement cost: $1.00 per hour; electricity cost per kilowatt/hour; replacement spoilboards; machine time rates: $1.25 per minute for th…
8. TFG USA – CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: CNC machining is an automated subtractive process using high-speed cutting tools to shape plastic or metal workpieces. Key CNC machines include CNC lathes, CNC mills (three to five axes), CNC routers, CNC waterjet cutters, and CNC laser cutters. Costs are calculated per hour or per part, with hourly rates ranging from $20 to $50 depending on machine type and complexity. Per-part costs range from $…
9. CNC Cookbook – Hourly Rate Calculator
Domain: cnccookbook.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: CNC Machine Hourly Rate Calculator from CNC Cookbook includes features to help estimate job costs and quotations based on machine Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). Key inputs for the calculator include: Purchase Price, Finance options, Deposit, Loan Term, Annual Interest, Total Loan Interest Paid, Useful Life, Trade-in Value, Annual Consumables Cost, Operator Rate per Hour, Working Hours per Day, Wor…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc machine cost per hour
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance CNC Machine Cost Management?
In the competitive landscape of CNC machining, understanding the cost per hour is paramount for international B2B buyers. Key factors such as labor, material costs, and machine complexity directly influence pricing strategies. By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can optimize these elements, ensuring they remain competitive while maximizing profitability.
Effective job costing not only aids in accurate quoting but also identifies areas for cost reduction. For instance, automating repetitive tasks can alleviate labor costs, enabling businesses to allocate resources more efficiently. Moreover, recognizing the fluctuation of material prices can inform purchasing decisions and reduce waste, further enhancing profit margins.
As you navigate the complexities of CNC machining, consider the potential of strategic sourcing as a tool for long-term success. By embracing advanced job costing methodologies and investing in innovative technologies, your organization can achieve a sustainable competitive edge.
We encourage international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to take proactive steps in refining their sourcing strategies. The future of CNC machining is bright, and with informed decision-making, you can position your business for growth and resilience in an ever-evolving market.