Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Cnc Machine Code
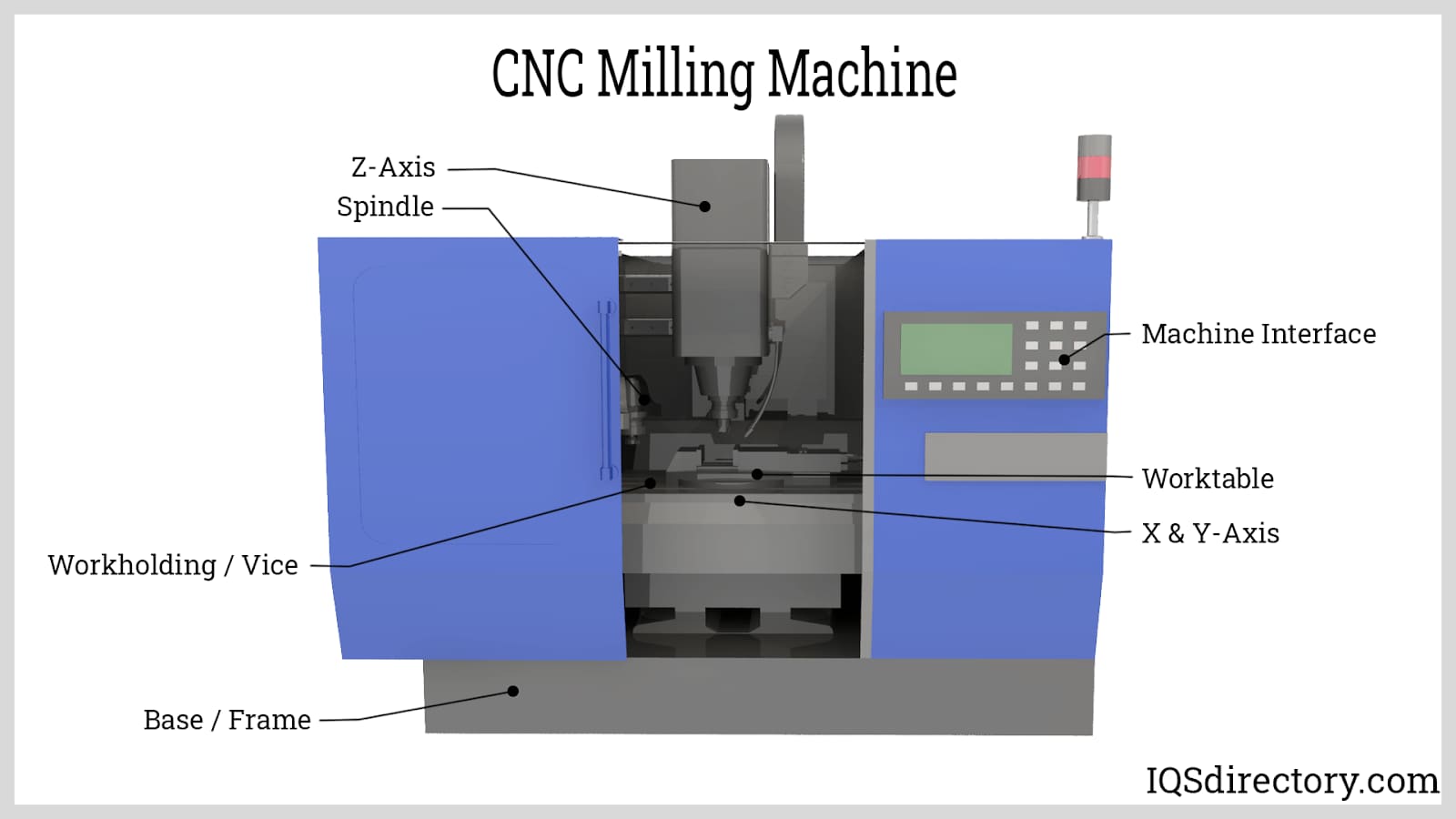
Precision CNC Machining: Transforming Digital Designs into High-Fidelity Physical Components
At Honyo Prototype, our CNC machining services represent the convergence of advanced manufacturing technology and engineering expertise to deliver exceptional precision for prototyping and low-volume production. We specialize in executing complex CNC machine code—optimized for 3-, 4-, and 5-axis milling centers and precision turning platforms—to transform CAD models into functional parts with tolerances as tight as ±0.0002 inches. Our process leverages high-speed machining, rigorous material science protocols, and real-time in-process inspection to ensure every component meets stringent industry standards for aerospace, medical, and industrial automation applications.
Our technical team collaborates directly with design engineers to refine toolpaths, minimize cycle times, and address manufacturability challenges before cutting metal. This proactive approach guarantees that intricate geometries, thin walls, and critical surface finishes are achieved without compromising structural integrity. Supported by a certified ISO 9001-2015 quality management system, we maintain full traceability across material sourcing, machining parameters, and final inspection documentation. For rapid project initiation, our Online Instant Quote platform provides detailed cost and lead-time estimates within minutes—eliminating traditional quoting delays while factoring in material selection, complexity, and required certifications. Accelerate your development cycle with Honyo’s turnkey CNC machining solutions, where engineering rigor meets operational agility.
Technical Capabilities

CNC Machine Code Technical Specifications for 3/4/5-Axis Milling and Turning – Focus on Tight Tolerance Applications
CNC machine code, commonly referred to as G-code (and M-code for auxiliary functions), drives precision machining across 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling systems, as well as multi-axis turning centers. For tight tolerance applications (±0.0005″ or ±0.0127 mm), code generation must account for kinematic complexity, toolpath accuracy, material behavior, and machine dynamics. Below is a summary of technical specifications relevant to high-precision CNC operations on common engineering materials.
| Parameter | 3-Axis Milling | 4-Axis Milling | 5-Axis Milling | CNC Turning (2/3-Axis) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coordinate System | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z, A (rotary around X) | X, Y, Z, A, B (or C) | X, Z (radial and axial) | 5-axis supports simultaneous motion in 5 axes for complex contours |
| Typical Tolerance | ±0.001″ (±0.025 mm) | ±0.0008″ (±0.020 mm) | ±0.0005″ (±0.0127 mm) | ±0.0005″ to ±0.001″ | Tight tolerance requires thermal stability, high-end tooling, and calibrated machines |
| Surface Finish (Ra) | 32–125 μin | 32–63 μin | 16–32 μin (with finishing passes) | 16–63 μin | Achievable via optimized feed rates and tool nose radius |
| Common G-Codes | G00, G01, G02/G03, G40–G43, G80–G89 | Same as 3-axis + G10, G68.2 | G00–G01, G43.4, G68.2, G108–G109 | G00–G03, G70–G76, G90–G92 | G68.2 enables coordinate rotation in 4/5-axis; G43.4 for tool vector control |
| M-Codes | M03, M05, M06, M08, M09 | Same as 3-axis + M19, M101–M103 | M03, M05, M19 (orient spindle) | M03, M08, M10, M11 (tailstock, etc.) | M19 used for spindle orientation in multi-axis setups |
| Materials – Aluminum (6061-T6) | High feed rates; coolant required; tool wear low | Smooth contouring; high RPM (8k–15k) | Complex geometries; use of ball end mills | High-speed turning; low cutting forces | Avoid built-up edge; use sharp carbide tools |
| Materials – Steel (4140, 1018) | Moderate speeds; rigid setup; HSS/carbide tools | Slower feed rates; high torque needed | High-precision toolpaths; peck drilling | Hard turning possible; use CBN inserts | Thermal management critical; minimize deflection |
| Materials – ABS | Low melting point; sharp tools, low RPM | Vacuum fixturing; avoid excessive heat | Shallow depth cuts; climb milling | Not typically turned; milling only | Use air blast cooling; avoid chip recutting |
| Materials – Nylon (PA6, PA66) | Low clamping pressure; sharp tools | Sensitive to heat; frequent tool changes | Use polished tools; maintain clearance | Possible with support; low feed rates | Hygroscopic; pre-dry material if critical |
| Toolpath Strategy | Layered roughing + finish passes | Indexed rotary features + contouring | Simultaneous 5-axis toolpath (e.g., RTCP) | OD/ID turning, threading, grooving | RTCP (Rotational Tool Center Point) essential for 5-axis accuracy |
| Verification Tools | CAM simulation (e.g., Mastercam, Fusion 360) | Machine-specific post-processors | G-code verification via Vericut or NCSimul | In-process probing, tool setters | Post-processing must match machine kinematics |
| Machine Requirements | High repeatability, linear scales | Rotary axis backlash < 5 arc-sec | Dual rotary tables or tilting spindle | Live tooling for mill-turn (Y-axis) | Encoder feedback and thermal compensation recommended |
Notes on Tight Tolerance Machining
Achieving tight tolerances requires not only precise G-code but also machine calibration, in-process inspection (e.g., touch probes), and environmental control. Materials like aluminum and steel respond well to high-precision CNC processes when thermal expansion and tool deflection are minimized. Plastics such as ABS and nylon require specialized toolpaths due to their low stiffness and thermal sensitivity. 5-axis milling enables single-setup machining of complex parts, reducing cumulative error and improving geometric accuracy.
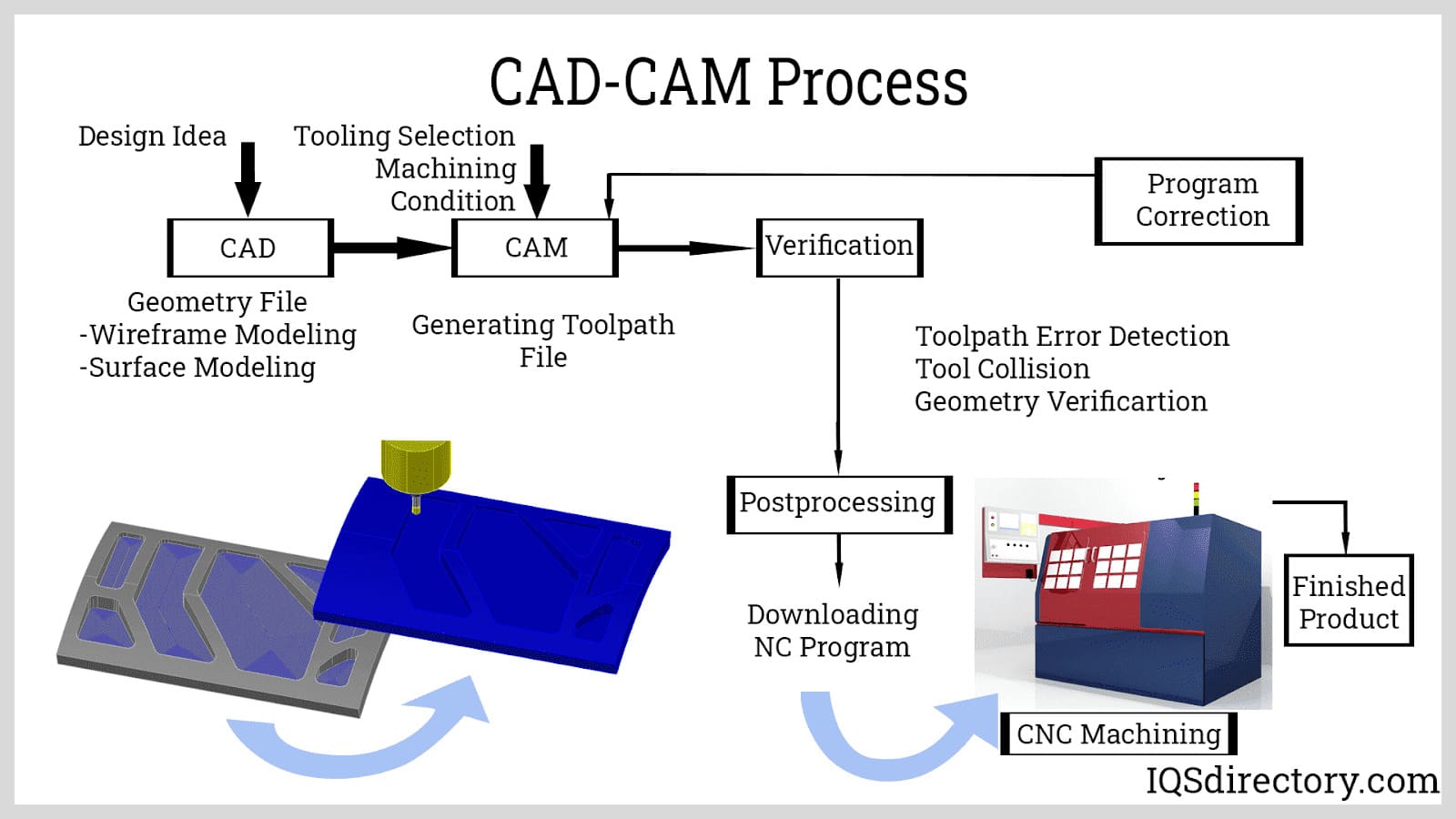
From CAD to Part: The Process

Honyo Prototype’s CNC machine code workflow integrates advanced digital tools with engineering expertise to ensure precision, efficiency, and manufacturability from initial design to final delivery. The process begins when a client uploads native CAD files (STEP, IGES, Parasolid) or industry-standard 2D drawings to our secure portal. Our system immediately validates file integrity, identifies critical tolerances, and extracts geometric data for downstream processing. This foundational step ensures no time is lost to incompatible formats or incomplete geometry.
The AI Quote engine then analyzes the validated CAD model using Honyo’s proprietary algorithm, trained on 12 million+ production parts. It cross-references real-time material costs, machine availability, and historical cycle times to generate an instant technical and commercial quotation. Unlike basic quoting tools, our AI evaluates geometric complexity, identifies potential high-precision zones requiring 5-axis machining, and flags surface finish requirements against achievable standards. The output includes material utilization metrics, estimated lead time, and a preliminary process plan—reducing quoting time from days to minutes while maintaining 95% accuracy against final production costs.
Engineering rigor intensifies during the mandatory Design for Manufacturability (DFM) phase. Honyo’s senior CNC engineers conduct a dual-path review: automated analysis checks wall thicknesses, hole depths, and tool access against ISO 2768 tolerances, while human experts assess dynamic factors like chatter risk in thin-wall features or optimal stock orientation. Crucially, our DFM process generates actionable optimization suggestions rather than simple pass/fail reports. For instance, we might propose modifying internal radii to match standard end mill sizes or splitting a complex part into two operations to maintain ±0.005mm tolerances. This collaborative stage typically reduces machining iterations by 40–60% compared to industry baselines.
Upon DFM approval, our CAM team generates machine-specific G-code using hyperMILL and Mastercam, with critical distinctions from standard workflows. Toolpath strategies are optimized for Honyo’s certified Haas, DMG MORI, and Makino equipment—leveraging machine-specific kinematic models to avoid collisions in 5-axis operations. We implement adaptive clearing for high-efficiency roughing and trochoidal milling for hardened materials, with all code rigorously verified in NCSIMUL simulation software. Each program includes in-process probing routines for on-machine verification, ensuring dimensional accuracy before part completion.
Production occurs in our climate-controlled facility with real-time monitoring. Every CNC machine feeds spindle load, temperature, and positional accuracy data to our MES platform. For critical features, automated in-cycle measurements via Renishaw probes trigger corrective actions without operator intervention. All parts undergo first-article inspection using Zeiss CMMs, with full GD&T reports provided. Final delivery includes not just the physical components but also digital artifacts: machine logs, inspection certificates, and the exact G-code version used—enabling full traceability for aerospace or medical clients. This closed-loop system ensures 99.2% on-time delivery while maintaining sub-micron repeatability across production runs.
The following table contrasts standard DFM practices with Honyo’s value-added approach:
| DFM Aspect | Industry Standard Practice | Honyo Prototype Value-Add |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerance Analysis | Basic pass/fail against drawing specs | Proposes achievable alternatives with cost/lead time impact |
| Tool Access Verification | Static 3D clearance check | Dynamic simulation of multi-axis tool approaches |
| Material Utilization | Standard stock size calculation | Nesting optimization across shared material batches |
| Process Planning | Generic operation sequencing | Machine-specific cycle time prediction within ±7% |
| Output Format | PDF report with redlines | Interactive 3D markup with clickable tolerance suggestions |
Start Your Project
For expert CNC machine code development and precision manufacturing solutions, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. With our advanced CNC capabilities and quality-driven processes, Honyo Prototype delivers accurate, efficient, and scalable results for your prototyping and production needs. Our factory is located in Shenzhen, a global hub for high-speed manufacturing and innovation, ensuring fast turnaround times and seamless collaboration. Reach out today to optimize your manufacturing workflow with professional-grade CNC programming and support.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.