Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc machine basics
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, understanding CNC machine basics is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their operations. With the increasing demand for precision and efficiency, sourcing the right CNC technology can be daunting, especially for businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Nigeria and Brazil. This comprehensive guide addresses the key challenges faced by these buyers by providing an in-depth exploration of CNC machines, including various types such as lathes, milling machines, and laser cutters, along with their applications in diverse industries.
Throughout this guide, we will also cover essential aspects of the CNC procurement process, from supplier vetting to cost considerations, ensuring that you are equipped to make informed purchasing decisions. By delving into the intricacies of CNC technology, including programming basics and machine setup, you will gain the insights necessary to navigate the complexities of the global market effectively. Whether you are a seasoned manufacturer or a newcomer to CNC machining, this resource empowers you to enhance your production capabilities, improve product quality, and ultimately drive your business success in an increasingly competitive environment.
Understanding cnc machine basics Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Milling Machine | Utilizes rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece. | Aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing. | Pros: High precision, versatile for complex shapes. Cons: Higher initial investment and maintenance costs. |
| CNC Lathe | Rotates the workpiece against stationary cutting tools. | Production of cylindrical parts like shafts and fittings. | Pros: Excellent for repetitive tasks, high accuracy. Cons: Limited to symmetrical parts. |
| CNC Plasma Cutter | Uses a high-energy plasma arc to cut through conductive materials. | Heavy metal fabrication and automotive industries. | Pros: Fast cutting speeds, effective for thick materials. Cons: Limited precision compared to milling machines. |
| CNC Laser Cutter | Employs a focused laser beam to cut or engrave materials. | Sign-making, aerospace, and custom fabrication. | Pros: High precision, minimal material wastage. Cons: Higher operational costs for thick materials. |
| CNC Waterjet Cutter | Uses a high-pressure water jet mixed with abrasives to cut materials. | Aerospace, automotive, and glass industries. | Pros: Can cut virtually any material, no heat-affected zone. Cons: Slower cutting speeds compared to plasma and laser. |
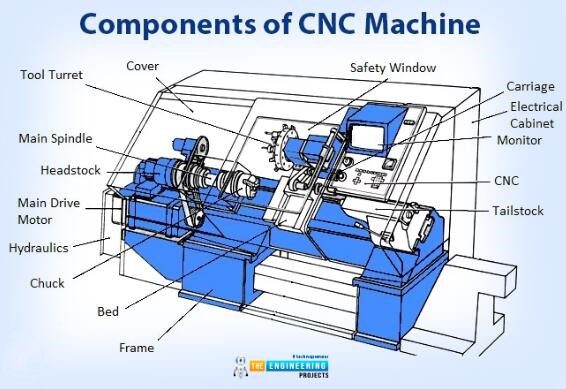
What Are the Key Characteristics of CNC Milling Machines?
CNC milling machines are designed to remove material from a workpiece using rotary cutters, allowing for the creation of intricate shapes and features. They are highly versatile, capable of performing operations such as drilling, tapping, and contouring. Ideal for industries requiring high precision, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing, buyers should consider factors like machine size, spindle speed, and tooling options to ensure they meet production demands.
How Do CNC Lathes Differ from Other CNC Machines?
CNC lathes are specialized for producing cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece against stationary cutting tools. This method is particularly effective for manufacturing components like shafts and fittings. When purchasing a CNC lathe, businesses should focus on the machine’s capability to handle different materials, the maximum diameter and length of the workpiece, and the automation features available to enhance productivity.
What Are the Advantages of CNC Plasma Cutters in Heavy Metal Fabrication?
CNC plasma cutters utilize a high-energy plasma arc to efficiently cut through conductive materials, making them a favorite in heavy metal fabrication. These machines excel in speed and are particularly useful for thick materials. However, potential buyers should assess the precision required for their projects, as plasma cutting may not achieve the same level of detail as milling or laser cutting. Understanding the specific thickness and type of materials to be processed is crucial for selecting the right plasma cutter.
Why Choose CNC Laser Cutters for Precision Work?
CNC laser cutters are known for their ability to deliver high precision and minimal material wastage. They are widely used in industries such as sign-making and aerospace for intricate cutting and engraving tasks. When considering a CNC laser cutter, buyers should evaluate the machine’s wattage, which affects cutting speed and material thickness capability, as well as the software compatibility for efficient design processing.
What Makes CNC Waterjet Cutters Unique in Material Cutting?
CNC waterjet cutters employ a high-pressure water stream mixed with abrasives to cut various materials without creating a heat-affected zone. This characteristic allows them to cut delicate materials like glass and composites without damaging them. Businesses should consider the operational speed and the types of abrasives that can be used when investing in a waterjet cutter, as these factors will influence production efficiency and costs.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc machine basics
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cnc machine basics | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | High accuracy in parts leading to enhanced safety and performance | Certification of machines and materials, lead times, and after-sales support |
| Automotive | Prototyping and production of automotive parts | Reduction in time-to-market and improved product quality | Compatibility with CAD/CAM systems, cost-effectiveness, and scalability |
| Medical Devices | Custom surgical instruments and implants | Tailored solutions that meet stringent regulatory standards | Compliance with medical regulations, quality assurance, and material sourcing |
| Electronics | Circuit board production and enclosures | Increased efficiency in mass production and reduced waste | Precision specifications, supplier reliability, and technology integration |
| Construction | Fabrication of structural components | Enhanced durability and precision in building materials | Material quality, delivery timelines, and machine capabilities |
How Are CNC Machines Used in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, CNC machines are vital for manufacturing precision components, such as turbine blades and structural parts. These components require extreme accuracy to ensure safety and performance during flight. CNC machining solves the problem of achieving consistent tolerances that manual machining cannot guarantee. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing machines with certifications like ISO 9001 and AS9100, which signify adherence to aerospace standards, as well as consider the availability of technical support and spare parts.
What Role Do CNC Machines Play in Automotive Prototyping?
CNC machines are instrumental in the automotive sector for both prototyping and mass production of parts such as engine components and body panels. They enable rapid prototyping, which significantly reduces time-to-market and improves product quality through precise manufacturing. International buyers should focus on the compatibility of CNC machines with popular CAD/CAM software and assess the cost-effectiveness of the machinery, ensuring it can scale with production demands.
How Are CNC Machines Transforming Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical devices industry, CNC machining is used to create custom surgical instruments and implants tailored to specific patient needs. This application addresses the challenge of adhering to stringent regulatory standards while delivering high-quality products. Buyers should ensure that their CNC suppliers comply with medical regulations, particularly in terms of materials and quality assurance processes, to mitigate risks associated with product recalls or failures.
In What Ways Are CNC Machines Used in Electronics Production?
CNC technology is crucial in the electronics sector for producing circuit boards and enclosures. The precision offered by CNC machining leads to increased efficiency in mass production while minimizing waste. For B2B buyers in this field, it is essential to consider the precision specifications of the CNC machines, the reliability of suppliers, and how well the machinery integrates with existing production technologies to optimize workflow.
How Are CNC Machines Beneficial in Construction?
CNC machines are employed in the construction industry for fabricating structural components, which enhances durability and precision in building materials. This application solves the issue of inconsistent quality that can arise from traditional fabrication methods. Buyers in construction should evaluate the quality of materials used in CNC machines, delivery timelines for components, and the capabilities of the machinery to handle various types of construction materials.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc machine basics’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Lack of Understanding of CNC Programming
The Problem: Many B2B buyers venturing into CNC machining basics often struggle with the complexities of programming CNC machines. This can be particularly challenging for companies looking to transition from manual machining to automated processes. Without a clear understanding of G-code and M-code, buyers may face difficulties in translating their designs from CAD software into actionable commands for CNC machines. This confusion can lead to costly errors, wasted materials, and delayed production timelines, impacting overall profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate programming challenges, companies should invest in comprehensive training programs for their staff. Online platforms such as Coursera and LinkedIn Learning offer courses specifically on CNC programming, which can help demystify the process. Additionally, utilizing user-friendly CAM software like Fusion 360 can simplify the conversion of CAD designs into CNC code, reducing the reliance on manual programming. It’s also beneficial to create a knowledge-sharing environment within the organization where experienced machinists can mentor newcomers. Establishing a library of resources, including manuals and video tutorials, will further empower employees to troubleshoot programming issues effectively.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Machine Setup and Calibration
The Problem: Proper setup and calibration of CNC machines are critical for achieving precision and quality in production. Many businesses, especially startups, may overlook the importance of this step due to time constraints or lack of experience. Inadequate setup can result in misaligned tools, incorrect cutting speeds, and ultimately, flawed products. This not only leads to wasted materials but also affects customer satisfaction and trust in the brand.
The Solution: To address setup and calibration issues, organizations should develop a standardized checklist for machine setup, which includes steps like cleaning the machine, selecting the right tools, and executing warm-up procedures. Moreover, investing in training sessions focused on machine setup can significantly reduce errors. Utilizing advanced calibration tools, such as laser alignment systems, can also enhance precision. Regular maintenance schedules should be implemented to ensure machines are always operating optimally. By fostering a culture of meticulous attention to detail in setup processes, companies can enhance productivity and product quality.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Material Selection for CNC Machining
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in selecting the right materials for CNC machining, particularly when transitioning from manual methods. The variety of materials available—ranging from metals to plastics—can be overwhelming, and the specific properties required for different machining processes may not be well understood. Incorrect material selection can lead to machining difficulties, increased wear on tools, and subpar finished products, ultimately affecting production efficiency and costs.
The Solution: To overcome material selection difficulties, companies should conduct thorough research into the properties of various materials relative to their intended applications. Collaborating with material suppliers who can provide samples and technical data sheets will enhance understanding of material performance. Additionally, developing a database of successful material-machine combinations from past projects can serve as a valuable reference for future jobs. Training sessions on material properties and their impact on machining processes can also empower staff to make informed decisions. Establishing partnerships with experienced machinists who can provide insights into material selection can further streamline this process and optimize production outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc machine basics
When selecting materials for CNC machining, it is essential to consider various factors that influence product performance, manufacturing complexity, and cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in CNC machining, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Which Metals Are Commonly Used in CNC Machining?
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It typically withstands temperatures up to 150 °C without significant degradation.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum is favored for its durability and ease of machining, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive parts to aerospace components. However, it can be more expensive than other metals and may require specialized tooling to achieve the best results.
Impact on Application: Due to its lightweight nature, aluminum is ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in transportation and aerospace. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local availability and pricing fluctuations. Compliance with standards such as ASTM and ISO is crucial, especially for aerospace applications.
Steel
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, with temperature ratings that can exceed 300 °C depending on the alloy. Its corrosion resistance varies based on the specific type of steel.
Pros & Cons: Steel is versatile and can be used for a wide array of applications, from construction to precision machinery. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can be more challenging to machine, which may increase production costs and time.
Impact on Application: Steel’s strength makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications, including structural components and machinery parts. However, its weight may limit its use in applications where weight is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: In Europe and the Middle East, compliance with DIN and JIS standards is critical. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific steel grades and any import tariffs that may affect cost.
Plastics (e.g., Acrylic, Polycarbonate)
Key Properties: Plastics are lightweight, have good chemical resistance, and can withstand temperatures up to 100 °C. They are also available in various grades, each with unique properties.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are generally more cost-effective than metals and can be machined quickly. However, they may not provide the same level of strength or durability as metals, making them unsuitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, such as in consumer products and medical devices. Their chemical resistance makes them suitable for environments where exposure to harsh substances is common.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of plastics that comply with local regulations, especially in the medical and food industries. Standards such as FDA compliance may be necessary.
Composites
Key Properties: Composites combine materials to achieve superior strength-to-weight ratios and can withstand temperatures up to 200 °C. They are often resistant to corrosion and fatigue.
Pros & Cons: Composites offer excellent performance in demanding applications, such as aerospace and automotive. However, they can be more expensive and complex to machine, often requiring specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly beneficial in applications where weight savings and high strength are critical, such as in high-performance vehicles and aircraft.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Africa and South America, the availability of composite materials may be limited. Compliance with international standards is essential, especially in industries like aerospace where safety is paramount.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Machining
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc machine basics | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and specialized tooling needed | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components, machinery parts | High strength and durability | Heavier and more challenging to machine | Medium to High |
| Plastics | Consumer products, medical devices | Cost-effective and quick to machine | Lower strength and durability than metals | Low |
| Composites | Aerospace, automotive high-performance | Superior strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive and complex to machine | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for CNC machining, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc machine basics
What Are the Main Stages of CNC Machine Manufacturing Processes?
CNC machining is a critical process in modern manufacturing, characterized by precision and efficiency. The typical manufacturing process can be divided into four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specific techniques that ensure the final product meets the desired specifications.
How Is Material Prepared for CNC Machining?
Material preparation involves selecting and preparing the raw materials for machining. This may include metals such as aluminum, steel, or titanium, as well as plastics and composites. Key techniques in this stage include:
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate material based on the product requirements, such as strength, weight, and resistance to corrosion.
- Cutting to Size: Raw materials are often cut to manageable sizes using saws or shears before being loaded into the CNC machine.
- Surface Treatment: Sometimes, materials undergo surface treatments, such as deburring or cleaning, to ensure optimal machining conditions.
By ensuring high-quality materials and proper preparation, manufacturers can significantly enhance the efficiency and quality of subsequent machining processes.
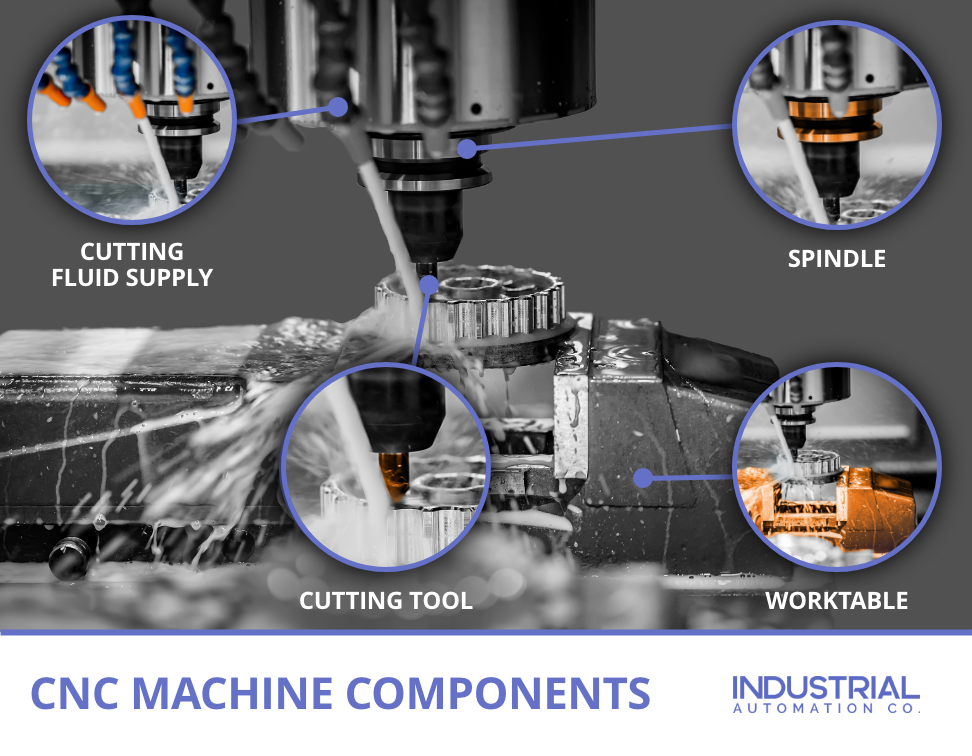
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of CNC Machining?
The forming stage is where the actual machining occurs. CNC machines, such as lathes and milling machines, use various techniques to shape the material according to the CAD design. Key techniques include:
- CNC Milling: Rotary cutters remove material from the workpiece to create intricate shapes and features. This is essential for producing complex parts with high precision.
- CNC Turning: Involves rotating the workpiece against a cutting tool to produce cylindrical parts. This method is particularly useful for producing shafts and spindles.
- Other Processes: Depending on the requirements, manufacturers may also use laser cutting, plasma cutting, or waterjet cutting to achieve specific shapes or finishes.
The choice of technique directly impacts the precision and quality of the final product, making it vital for B2B buyers to understand these processes when evaluating suppliers.
How Does Assembly Fit Into the CNC Manufacturing Process?
In many cases, CNC machined components are part of a larger assembly. The assembly stage involves integrating various parts to create a finished product. Key considerations include:
- Alignment and Fitting: Ensuring that all components fit together correctly, which may require additional machining or adjustments.
- Use of Fasteners: Depending on the design, various fasteners such as screws, bolts, or adhesives may be employed to secure components.
- Quality Checks: Regular quality checks should be conducted during assembly to confirm that specifications are met.
A well-executed assembly process can prevent costly rework and delays, which is critical for B2B buyers focused on timely delivery.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in CNC Machining?
Finishing techniques are crucial for enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of machined parts. Common finishing methods include:
- Deburring: Removing sharp edges and burrs that may have formed during machining to ensure safety and improve appearance.
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing, powder coating, or plating can enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Polishing: This technique is often used for components that require a high level of shine or smoothness.
Understanding these finishing techniques is essential for B2B buyers, as they can significantly affect the quality and performance of the final product.
What International Standards Apply to CNC Machining Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance is paramount in CNC machining, and international standards help ensure that products meet specific quality benchmarks. One of the most recognized standards is ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers consistently produce products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may be relevant, such as:
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
- API Standards: Particularly important in the oil and gas sector, ensuring products meet stringent operational requirements.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with relevant certifications, as this reflects their commitment to quality and compliance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Machining?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of CNC machining, with several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before being used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during machining help identify any deviations from specifications in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of finished products to ensure they meet all quality standards before shipment.
By implementing these checkpoints, manufacturers can minimize defects and enhance overall product quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
When sourcing CNC machined components, B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify supplier quality control processes. Key methods include:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality systems, and compliance with standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation demonstrating compliance with international standards and internal quality metrics.
- Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services: Independent inspections can verify that products meet specified standards before shipment.
For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where supply chain complexities may arise, these verification methods are essential for ensuring product quality and reliability.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Assurance?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances related to quality assurance, particularly when sourcing from different regions. Key considerations include:
- Understanding Regional Standards: Different countries may have varying regulations and standards, so it is critical to understand these before entering into agreements.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Quality perception may vary across cultures. Buyers should communicate their expectations clearly to avoid misunderstandings.
- Logistical Challenges: Transporting products across borders can introduce risks to quality. Proper packaging and handling protocols should be established to mitigate these risks.
By being aware of these nuances, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions and establish stronger partnerships with suppliers.
Through a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in CNC machining, B2B buyers can ensure they select the right suppliers, ultimately enhancing their own operational efficiency and product quality.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc machine basics’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to equip B2B buyers with a systematic checklist for procuring CNC machines. Understanding the nuances of CNC technology and selecting the right equipment is vital for optimizing manufacturing processes, enhancing precision, and ensuring cost-effectiveness. This checklist will guide you through essential steps to ensure you make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. Identify the types of materials you will be working with, the required precision levels, and the specific machining processes (e.g., milling, turning, or laser cutting). This clarity will help you narrow down options and communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Available CNC Machines
Explore various CNC machine types and their capabilities to find a suitable fit for your needs. Popular options include CNC lathes, milling machines, and laser cutters. Consider the machine’s size, speed, and versatility to ensure it aligns with your production requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, certifications, and case studies to assess their credibility and experience. Look for suppliers who have successfully delivered similar solutions in your industry or region, as this can indicate their reliability and understanding of your specific needs.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Obtain detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to understand the market pricing for the CNC machines you’re considering. Ensure that quotes include all costs, such as shipping, installation, and training. Comparing these details will help you make an informed decision and identify any hidden costs.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or CE marking can indicate a commitment to quality and safety. This step is crucial to mitigate risks associated with equipment failure or non-compliance.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Training
Inquire about after-sales support, including warranty terms, maintenance services, and training programs for your staff. A supplier that offers comprehensive support can significantly reduce downtime and enhance your team’s proficiency in operating the CNC machines.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Negotiate Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize the purchase by negotiating terms that benefit both parties. Clarify payment schedules, delivery timelines, and installation processes to avoid misunderstandings. A well-structured agreement lays the groundwork for a successful long-term partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing CNC machines effectively, ensuring they invest in equipment that meets their operational needs while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc machine basics Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Machine Basics Sourcing?
When considering CNC machine sourcing, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials used in CNC machining, such as aluminum, steel, and plastics, vary in price based on market conditions. Buyers should consider the long-term availability and sustainability of materials, as these factors can influence costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for operating CNC machines and programming them effectively. Labor costs can vary by region, with countries in Africa or South America often having lower labor rates compared to Europe. However, the skill level and experience of the workforce can affect productivity and quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the facility, utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Overhead costs can differ widely between suppliers, depending on their operational efficiencies and technology investments.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs include the purchase of cutting tools, fixtures, and other equipment necessary for CNC operations. High-precision tools can be expensive, and their longevity can affect overall production costs. Buyers should assess the tooling requirements for their specific projects to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing quality control processes ensures that the final products meet specifications. QC costs can include inspection tools, staff, and testing procedures. Investing in robust QC measures can prevent costly rework and maintain customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can significantly influence the final pricing, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and tariffs should be considered. Incoterms play a vital role in determining who bears the shipping costs and risks during transportation.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their costs and generate profit. The margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the supplier’s reputation. Understanding the average margins in the CNC industry can aid buyers in evaluating supplier quotes.
What Influences Pricing in CNC Machine Basics Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC machines, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Negotiating favorable terms for bulk purchases can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions typically come at a premium. Clear communication of requirements can help suppliers provide accurate quotes and avoid unexpected costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO standards) can increase costs but may provide better performance and reliability. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and stability of a supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better service and reliability, justifying higher costs.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs and Pricing in CNC Machine Basics?
To maximize cost efficiency, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better pricing. Engage in open discussions about costs and explore options for discounts based on order size or long-term contracts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime when making decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand local market dynamics, currency fluctuations, and import/export regulations that can impact pricing. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should also consider local supplier options to reduce logistics costs.
Final Thoughts on CNC Machine Basics Sourcing
While this analysis provides a foundational understanding of CNC machine sourcing costs and pricing, it is crucial to approach each procurement decision with a clear strategy. Prices can vary widely based on numerous factors, so conducting thorough market research and supplier evaluations is essential. Always consider this information as indicative; actual costs may vary based on specific project requirements and market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc machine basics With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CNC Machine Basics: What Other Solutions Exist?
When evaluating manufacturing processes, businesses often seek alternatives to CNC machining that can fulfill similar needs. Each method comes with its unique strengths and weaknesses, which can significantly impact production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and product quality. In this analysis, we will compare CNC machine basics with two viable alternatives: manual machining and additive manufacturing (3D printing).
| Comparison Aspect | Cnc Machine Basics | Manual Machining | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and repeatability | Varies significantly based on skill | Excellent for complex geometries |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial costs | Moderate initial setup costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires CAD/CAM knowledge | Minimal training required | Requires design software familiarity |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Generally lower maintenance | Minimal maintenance for printers |
| Best Use Case | Mass production of complex parts | Custom, low-volume production | Prototyping and intricate designs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Manual Machining
Manual machining involves the use of traditional tools operated by skilled labor. This method allows for a high degree of flexibility and customization, as skilled machinists can easily adapt to changes in designs or specifications. However, performance can vary greatly depending on the operator’s experience, leading to inconsistent quality. While manual machining requires lower initial investment and has simpler implementation, it is generally slower than CNC machining and may not be suitable for high-volume production. Additionally, as production scales, labor costs can escalate, making it less economical for larger runs.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, builds objects layer by layer from a digital model. This technology excels in producing complex geometries that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional machining methods. It has a moderate initial setup cost, particularly for high-quality industrial printers. While 3D printing is ideal for rapid prototyping and small batch production, the material options and finish quality may not always match those of CNC machined parts. Moreover, the speed of production is usually slower compared to CNC, especially for larger items, which may limit its application in mass manufacturing scenarios.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Choosing the right manufacturing solution involves a careful assessment of your specific needs, including production volume, material requirements, and budget constraints. CNC machining stands out for its precision and efficiency, particularly in mass production of complex components. However, for custom projects or lower volumes, manual machining might be more cost-effective. Conversely, if your focus is on rapid prototyping or intricate designs, additive manufacturing could be the best fit. By analyzing these alternatives, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc machine basics
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Machines?
Understanding the technical properties of CNC machines is essential for B2B buyers, as these specifications directly impact production efficiency and product quality. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
– The type of material that a CNC machine can process is crucial. Common materials include aluminum, steel, plastic, and composite materials. Buyers need to consider the material grades that align with their production needs. For instance, aerospace components often require high-grade aluminum (like 7075), which offers superior strength-to-weight ratios. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In CNC machining, this is critical because it determines how precise the machined parts will be. Standard tolerances can range from ±0.1 mm to ±0.005 mm, depending on the application. Tight tolerances are essential for high-tech industries like medical devices and aerospace, where even minor deviations can lead to failures. -
Feed Rate
– The feed rate is the speed at which the cutting tool moves through the material. It is typically measured in millimeters per minute (mm/min) or inches per minute (IPM). Optimizing the feed rate can significantly affect production speed and surface finish. Buyers should ensure that the CNC machines they are considering can handle the feed rates required for their specific operations. -
Spindle Speed
– Spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), indicates how fast the cutting tool rotates. Higher spindle speeds generally allow for faster machining but may also lead to increased wear on the tool. Buyers must balance spindle speed with the material being cut and the desired finish quality. -
Axis Configuration
– CNC machines can have various axis configurations, typically ranging from 3-axis to 5-axis systems. A 3-axis machine can move in three dimensions (X, Y, and Z), while a 5-axis machine can rotate around two additional axes. The complexity of the workpiece often dictates the need for more axes, especially for intricate designs. Understanding axis configuration helps buyers choose machines suitable for their production demands.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in CNC Machining?
Familiarity with industry terminology can greatly enhance communication and negotiation processes. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking for quality components that meet specific standards and specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the minimum number of units that a supplier is willing to produce or sell. This is a critical term for B2B buyers as it directly affects inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their production schedules and budget effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting price quotes for specified products or services. It is a key step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices, terms, and conditions. A well-prepared RFQ can lead to better pricing and service agreements. -
Incoterms
– International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Knowledge of Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border transactions, as they clarify obligations and reduce potential disputes. -
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
– CAM software is used to control machine tools and automate manufacturing processes. It converts CAD drawings into machine-readable code. Understanding CAM is essential for buyers involved in CNC machining, as it affects the efficiency and accuracy of the production process.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select CNC machines that meet their operational needs and industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc machine basics Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the CNC Machine Basics Sector?
The CNC machining sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in automation and the increasing demand for precision manufacturing across various industries. Key global drivers include the push for enhanced productivity, the rise of smart manufacturing practices, and the need for customization in production processes. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices are particularly influential, as they require high-quality, intricate parts that CNC machining can deliver efficiently.
Emerging trends include the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, which enable real-time monitoring and optimization of machine performance. This data-driven approach allows manufacturers to enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve product quality. Furthermore, the adoption of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques, such as additive manufacturing, is reshaping sourcing strategies. For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to stay informed about these technological advancements to remain competitive.
Additionally, the CNC market is witnessing a shift towards localized sourcing as businesses aim to mitigate risks associated with global supply chains. This trend is particularly relevant for companies in emerging markets, where establishing strong relationships with local suppliers can lead to cost savings and increased agility in production.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affecting the CNC Machine Basics Sector?
As environmental awareness rises, sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount considerations for B2B buyers in the CNC machining sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes—including energy consumption, waste generation, and emissions—has led companies to seek more sustainable practices. This includes the use of energy-efficient machines, recycling waste materials, and reducing the carbon footprint associated with operations.
Incorporating “green” certifications and materials into sourcing strategies is crucial for companies aiming to enhance their brand reputation and meet regulatory requirements. Buyers should consider suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems) and materials that are recyclable or sourced from sustainable practices.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are gaining importance as consumers and businesses alike demand transparency. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards not only mitigates risks but also fosters trust with end customers. For B2B buyers, partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainability can enhance their market positioning and appeal to a broader audience.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Machining and Its Relevance to Today’s B2B Landscape?
CNC machining has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1940s, when early machines were controlled by analog computers. The transition to digital control systems marked a turning point, enabling greater precision and efficiency. Over the decades, advancements in computer technology and software have made CNC machining more accessible and versatile, expanding its applications across various sectors.
Today, CNC machines are integral to modern manufacturing, providing the capability to produce complex parts with minimal human intervention. Understanding this evolution is crucial for B2B buyers, as it highlights the ongoing technological advancements and the importance of investing in up-to-date machinery and software. The ability to adapt to these changes will be a key factor in maintaining competitiveness in the rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc machine basics
-
How do I solve common issues when setting up a CNC machine?
Setting up a CNC machine can be challenging, but common issues can often be resolved through systematic troubleshooting. Start by ensuring that all components are clean and properly aligned. Check that tools are securely loaded and calibrated according to manufacturer specifications. If you encounter software-related issues, confirm that the correct post-processor is selected in your CAM software. Lastly, always refer to the user manual for specific troubleshooting guidelines. Regular maintenance and pre-operation checks can prevent many setup problems. -
What is the best CNC machine type for small-scale production?
For small-scale production, CNC milling machines or CNC routers are often the best choices. CNC milling machines excel in precision and versatility, allowing for intricate designs in various materials. CNC routers are ideal for larger sheet materials and can handle different substrates, including wood and plastics. When selecting a machine, consider your specific production needs, the materials you will work with, and the complexity of the designs you plan to create. Always evaluate the machine’s specifications to ensure it meets your operational requirements. -
How do I vet suppliers when sourcing CNC machines internationally?
Vetting suppliers for CNC machines involves several steps. Begin by checking their industry reputation through online reviews and testimonials. Request references from previous clients, particularly those within your region. Verify the supplier’s certifications, such as ISO, to ensure quality standards. Conduct a factory visit if possible, or utilize third-party inspection services to evaluate their manufacturing processes. Finally, assess their communication responsiveness and willingness to provide after-sales support, as these factors are crucial for ongoing business relationships. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machines?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machines can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of machine. Typically, larger manufacturers may require higher MOQs due to production costs, while smaller or specialized suppliers might accept lower quantities. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify the MOQ and consider your current needs and budget. If your requirements are below the MOQ, inquire about customization options or the possibility of grouping orders with other buyers to meet the supplier’s minimum. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing CNC machines?
Payment terms for CNC machine purchases can vary widely by supplier and region. Common arrangements include full payment upfront, a deposit followed by balance on delivery, or financing options. Always clarify the payment schedule and accepted methods (e.g., wire transfer, credit terms) before finalizing the purchase. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and project timelines. Additionally, consider using letters of credit or escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risk. -
What quality assurance (QA) measures should I look for in CNC machines?
Quality assurance in CNC machines is critical to ensure performance and durability. Look for suppliers that adhere to industry standards, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Request information on the supplier’s QA processes, including material inspections, machine calibration protocols, and testing procedures. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and post-sale support, as these reflect the manufacturer’s confidence in their product quality and commitment to customer satisfaction. -
How can logistics impact the sourcing of CNC machines internationally?
Logistics play a significant role in international sourcing of CNC machines, affecting cost, lead times, and overall efficiency. Factors to consider include shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs clearance processes, and potential tariffs or duties. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to ensure smooth transport. Additionally, plan for adequate insurance coverage to protect your investment during transit. Understanding local regulations and working with reliable logistics partners can help mitigate delays and unexpected costs. -
What are the customization options available for CNC machines?
Customization options for CNC machines can enhance functionality and meet specific production needs. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions, including modifications to machine size, additional tooling, and specialized software configurations. When discussing customization, clearly communicate your requirements and the intended applications. Be prepared to discuss lead times and costs associated with custom features. Engaging in early dialogue with your supplier can lead to a more effective and efficient machine tailored to your unique operational demands.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Cnc Machine Basics Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Protolis – CNC Machining & Prototyping Solutions
Domain: protolis.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining Guide – Protolis specializes in rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing of high-quality plastic and metal parts. Key production methods include CNC Machining, Injection Molding, 3D Printing, Vacuum Casting, Extrusion, Sheet Metal Fabrication, and Compression Molding. Materials offered include all metals (Aluminum, Brass, Stainless Steel, Steel, Copper, Zamak) and all plastics….
2. Reddit – CNC Course Offer
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC course available for ₹6000 ($81); recommended to learn CAD/CAM basics; suggested software: Fusion 360 (free student edition); practice CAD design and consider using a small CNC router like a 3018 for hands-on learning.
3. Hubs – CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing technology that creates parts by removing material from a solid block using various cutting tools. It is a digital manufacturing technology that produces high-accuracy parts directly from a CAD file. CNC machining is price-competitive for both one-off custom parts and medium-volume productions. Common materials for CNC machining include metals (aluminum…
4. Instructables – CNC Machine Essentials
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC Machine, CAD/CAM Software (Fusion360), Machinable materials (wood stock, aluminum block), Considerations for material choice (load requirements, durability, tolerance), Best practices for dimensions (1mm external trim, clamping height), Limitations of internal geometries, Importance of minimizing part rotations, Guidelines for internal pockets (width to depth ratio of 1:4 or 1:5), Focus on iso…
5. Kesmt – CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: kesmt.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: CNC machines function by interpreting G-code to cut materials into desired shapes with minimal human intervention. Types of CNC machines include milling machines, which create complex parts, and turning machines, which shape cylindrical parts. CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process using rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. Key components include the controller…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc machine basics
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your CNC Machining Operations?
In today’s competitive landscape, understanding the fundamentals of CNC machining is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their operations. Key takeaways include the importance of leveraging advanced technologies, such as CNC turning and milling, to achieve unparalleled precision and efficiency in production. Buyers should prioritize strategic sourcing to identify reliable suppliers that can provide high-quality machines and components tailored to their specific needs.
Moreover, the integration of CAD and CAM software into CNC processes not only streamlines design and production but also enhances the capability to innovate. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, adopting CNC technology can position businesses ahead of the curve, allowing them to respond swiftly to changing demands.
Looking ahead, it is essential for B2B buyers to invest in training and development for their teams to fully harness the potential of CNC machinery. By embracing strategic sourcing and staying informed about the latest advancements in CNC technology, businesses can ensure they remain competitive and resilient. Take the next step today—explore your sourcing options and elevate your CNC machining capabilities to drive growth in your industry.