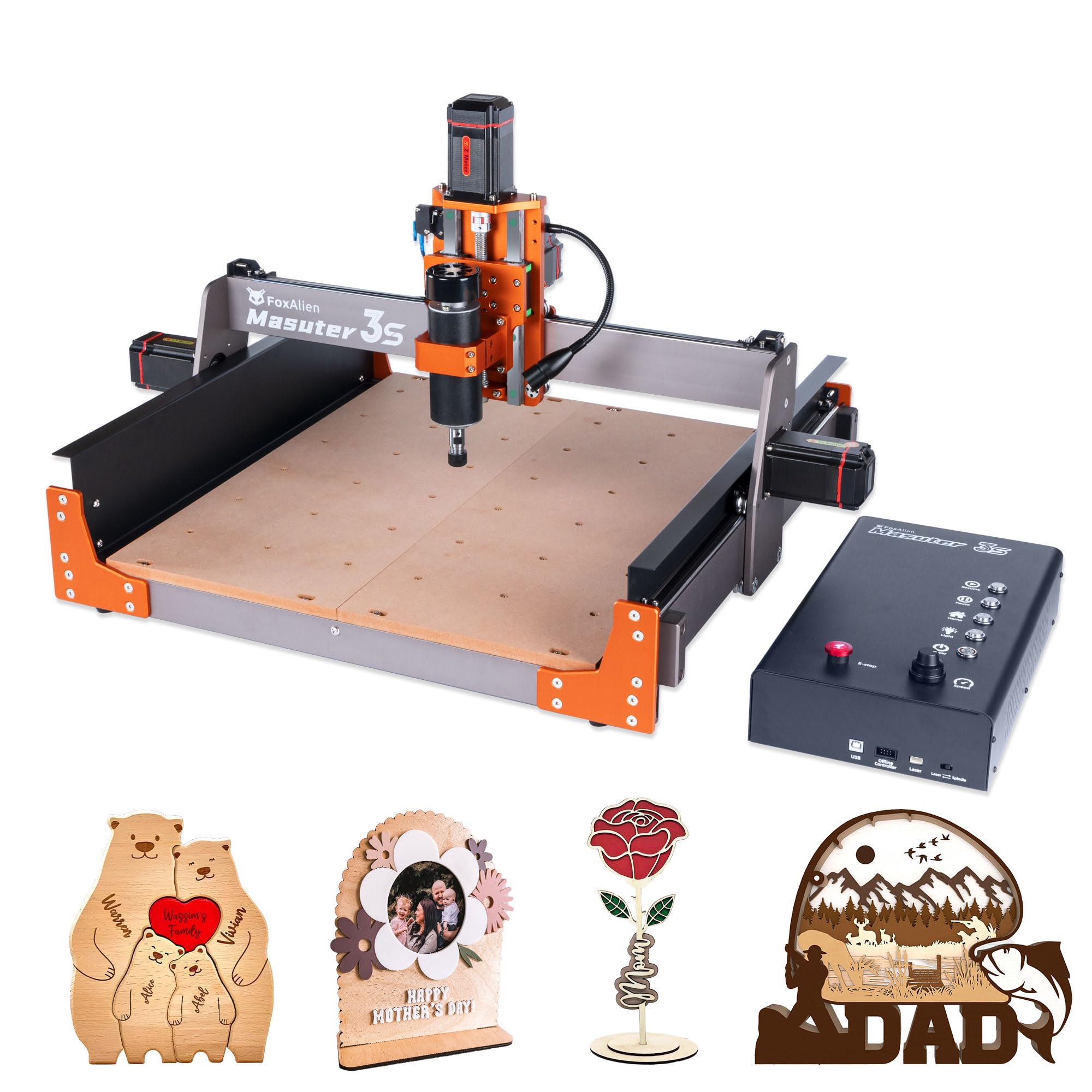
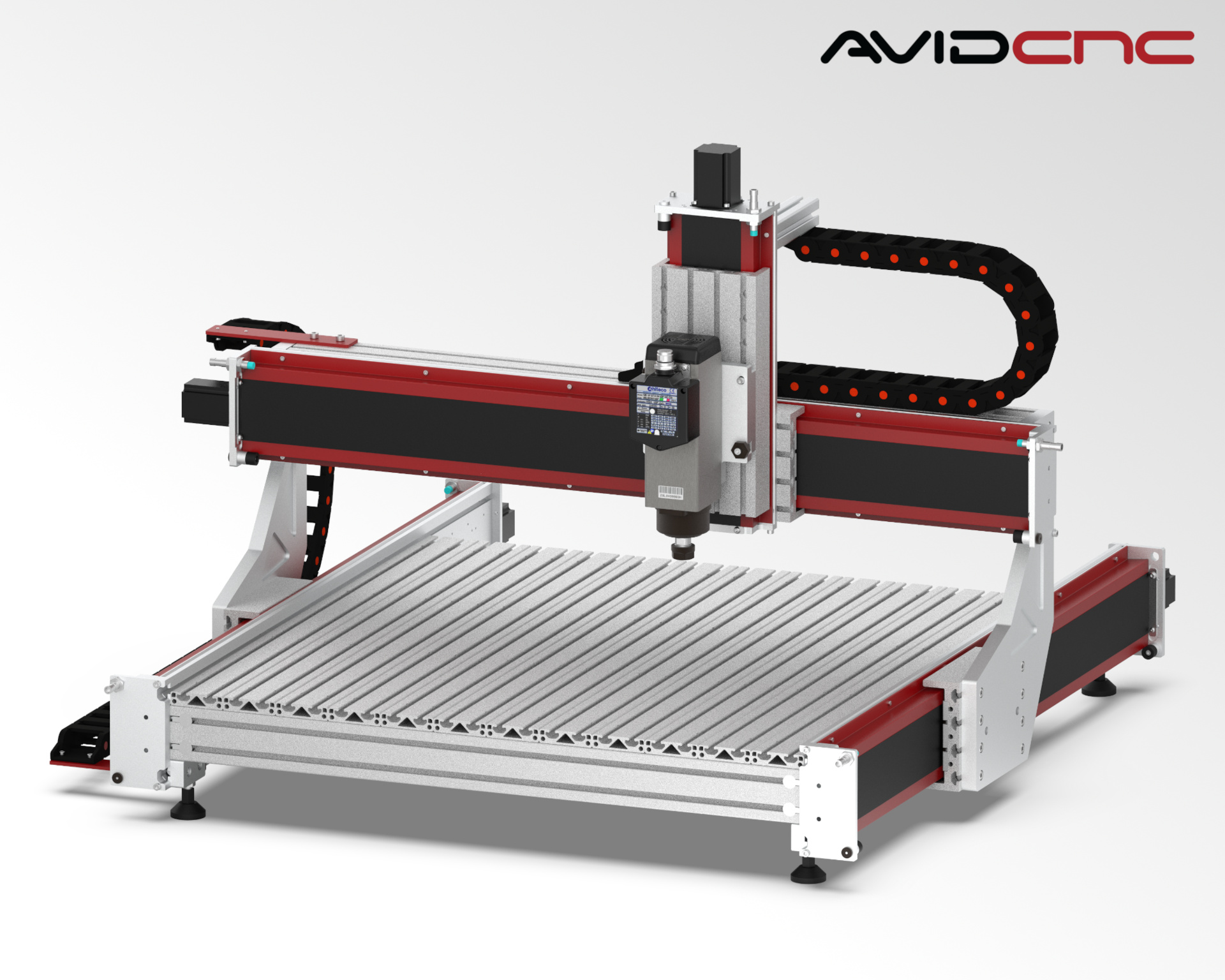
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc machine 3
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, sourcing a reliable CNC machine 3 can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With the growing demand for precision and efficiency in production processes, businesses must navigate a myriad of options, each with unique specifications, capabilities, and price points. This comprehensive guide aims to simplify the sourcing process by providing an in-depth exploration of various CNC machine types, their applications across different industries, and essential factors to consider when evaluating suppliers.
Understanding the intricacies of CNC machining is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, especially for buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria. The guide covers critical topics such as machine specifications, operational capabilities, and the importance of supplier vetting to ensure quality and reliability. Additionally, we delve into cost considerations, helping buyers align their budgets with their operational needs.
By equipping decision-makers with actionable insights and practical knowledge, this guide empowers businesses to invest wisely in CNC technology, ultimately enhancing their manufacturing capabilities and competitive edge in the global market. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to CNC machining, the information contained herein will facilitate strategic decision-making tailored to your unique requirements.
Understanding cnc machine 3 Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Axis CNC Mill | Moves along X, Y, and Z axes; simpler parts; cost-effective | Prototyping, simple part production | Pros: Affordable, easy to use; Cons: Limited complexity, longer setups for intricate designs |
| 5-Axis CNC Mill | Moves along X, Y, Z, and rotational A & B axes; high precision | Aerospace, automotive, complex molds | Pros: High accuracy, efficient for complex parts; Cons: Higher cost, requires specialized training |
| Desktop CNC Machine | Compact design, suitable for small workshops; versatile | Hobbyists, small businesses, education | Pros: Space-efficient, affordable; Cons: Limited cutting area, may lack industrial-grade features |
| Benchtop CNC Router | Larger cutting area than desktop models; robust build | Furniture manufacturing, signage | Pros: Greater versatility, good for medium production runs; Cons: More expensive than desktop models |
| CNC Plasma Cutter | Uses plasma to cut metal; efficient for thick materials | Metal fabrication, HVAC, automotive | Pros: Fast cutting speed, effective for thick metals; Cons: Limited to metal materials, requires ventilation |
What are the characteristics and suitability of a 3-Axis CNC Mill for B2B buyers?
The 3-Axis CNC Mill is a staple in many manufacturing environments due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. It operates along three linear axes (X, Y, and Z), allowing for straightforward machining of flat parts. This machine is ideal for startups and small to medium-sized businesses that require precision for 2D and 2.5D parts. Buyers should consider the limitations of this machine in terms of complexity and setup time, as intricate designs may necessitate multiple setups, which can slow down production.
How does a 5-Axis CNC Mill enhance capabilities for complex machining needs?
The 5-Axis CNC Mill expands on the capabilities of the 3-Axis version by adding rotational movements, allowing for the machining of complex geometries and intricate details with high precision. This makes it a preferred choice for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precision and efficiency are paramount. While the initial investment is higher, the ability to perform continuous milling without repositioning parts can significantly reduce cycle times and improve throughput. Buyers should ensure they have the necessary expertise or training to operate these advanced machines.
Why should businesses consider a Desktop CNC Machine?
Desktop CNC Machines are designed for small workshops and educational settings, offering a compact solution without sacrificing versatility. These machines can handle a variety of materials, including wood, plastics, and some metals, making them suitable for prototyping and small-scale production. Their affordability and ease of use make them attractive to hobbyists and small businesses. However, potential buyers should be aware of the limited cutting area, which may restrict the scale of projects.
What advantages do Benchtop CNC Routers provide for medium-scale production?
Benchtop CNC Routers are larger than desktop models and provide a robust platform for cutting and shaping materials. They are particularly effective for applications in furniture manufacturing and signage, where larger workpieces are common. These machines offer a good balance between size, capability, and cost, making them suitable for businesses looking to scale up production without the overhead of industrial-grade equipment. Buyers should evaluate their production needs and budget to determine if the investment aligns with their growth strategies.
How can CNC Plasma Cutters benefit metal fabrication businesses?
CNC Plasma Cutters are specialized machines designed for cutting metal using a high-temperature plasma arc. They excel in speed and efficiency, particularly for thicker materials, making them ideal for industries like metal fabrication and automotive manufacturing. While they offer fast cutting capabilities, buyers need to consider the limitations in terms of material compatibility and safety requirements, such as adequate ventilation. Investing in a CNC Plasma Cutter can enhance productivity but requires careful planning to integrate into existing workflows.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc machine 3
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cnc machine 3 | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | High accuracy and repeatability in parts | Certifications, material specifications, and lead times |
| Automotive | Prototyping and custom parts production | Rapid development and cost-effective solutions | Tooling compatibility and software integration |
| Electronics | PCB prototyping and small-scale production | Increased efficiency and reduced waste | Compatibility with different CAD/CAM software |
| Furniture Manufacturing | Custom furniture design and production | Unique designs and faster production cycles | Material types and machine size for specific projects |
| Medical Devices | Manufacturing specialized medical components | Compliance with stringent safety standards | Regulatory compliance and material sourcing |
How Is CNC Machine 3 Used in Aerospace Component Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, the CNC machine 3 is utilized for manufacturing precision components such as brackets, housings, and fixtures. These components require high accuracy and repeatability due to the critical safety standards in aviation. By automating the machining process, manufacturers can achieve tighter tolerances, reduce human error, and ensure that parts are produced consistently. International buyers should consider sourcing machines that meet specific certifications, such as AS9100, which is essential for compliance in the aerospace sector.
What Role Does CNC Machine 3 Play in Automotive Prototyping?
The automotive industry leverages CNC machine 3 for prototyping and producing custom parts, enabling rapid development cycles. This application allows manufacturers to create intricate designs and test fit and function before mass production. The ability to quickly iterate designs helps reduce costs and shorten time-to-market. For international buyers, it is crucial to evaluate tooling compatibility with existing systems and the integration of CAD/CAM software to optimize the design process.
How Is CNC Machine 3 Beneficial for PCB Prototyping in Electronics?
In the electronics sector, CNC machine 3 is particularly effective for PCB prototyping and small-scale production. This machine can efficiently cut and mill circuit boards, allowing for rapid iterations and modifications in design. The increased efficiency reduces waste and accelerates the development process, making it a valuable asset for electronics manufacturers. Buyers should ensure that the machine is compatible with various CAD/CAM software platforms to streamline their design workflows.
How Does CNC Machine 3 Enhance Custom Furniture Manufacturing?
Custom furniture manufacturers employ CNC machine 3 for creating unique designs and efficiently producing various furniture pieces. This capability allows for intricate detailing and precise cuts, which are essential for high-quality finishes. The machine’s ability to handle different materials, such as wood and composites, further expands design possibilities. Buyers should consider the machine’s footprint and capabilities to ensure it meets the specific requirements of their production needs.
What Is the Importance of CNC Machine 3 in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical devices sector, CNC machine 3 is critical for manufacturing specialized components, such as surgical instruments and implants. These components must adhere to stringent safety and quality standards, making precision machining vital. The automation of production minimizes human error and ensures consistent quality, which is paramount in medical applications. Buyers should prioritize sourcing machines that comply with industry regulations and consider the sourcing of materials that meet safety standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc machine 3’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming Limited Material Compatibility Challenges
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries such as manufacturing and prototyping often encounter limitations with CNC machines when it comes to material compatibility. For instance, while the CNC machine 3 can work with a variety of materials, including plastics and metals, buyers may find that their specific materials—like certain alloys or engineered plastics—are not easily machinable. This can lead to production delays, increased costs due to material wastage, and frustration when the desired results are not achieved.
The Solution: To overcome material compatibility issues, buyers should conduct thorough research on the specific capabilities of CNC machine 3 before making a purchase. It’s essential to understand the machine’s specifications regarding spindle speed, torque, and tool compatibility. For example, if working with aluminum alloys, investing in specialized cutting tools designed for non-ferrous materials can significantly improve outcomes. Additionally, collaborating with suppliers who can provide tailored recommendations and possibly even test runs can help ensure that the chosen CNC machine will meet the demands of your specific materials. Engaging in pre-purchase consultations with manufacturers or experienced users can provide valuable insights and minimize the risk of investing in a machine that does not meet your needs.
Scenario 2: Navigating Software Integration Issues
The Problem: In today’s digital manufacturing landscape, software integration is crucial for the efficiency of CNC machines. A common pain point for buyers is the challenge of integrating CNC machine 3 with existing CAD/CAM software platforms. Many manufacturers rely on various software for design, simulation, and machine control, and incompatibility can lead to workflow disruptions, erroneous outputs, and a steep learning curve for staff.
The Solution: To effectively navigate software integration issues, B2B buyers should prioritize machines that offer comprehensive compatibility with popular CAD/CAM software, such as Fusion 360 or Vectric. Before purchasing, it’s beneficial to request a demonstration of how well the CNC machine integrates with your existing software systems. Moreover, opting for machines that come with robust support packages—including training sessions and customer service—can ease the transition. Buyers should also consider investing in training for their team to ensure they are well-versed in using both the CNC machine and associated software effectively. This dual approach will not only enhance productivity but also reduce the time needed to achieve a seamless integration.
Scenario 3: Addressing Maintenance and Downtime Concerns
The Problem: B2B buyers often face anxiety regarding maintenance and potential downtime associated with CNC machines. CNC machine 3, like any precision equipment, requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Buyers may fear that unexpected breakdowns could lead to costly downtime, negatively impacting production schedules and client commitments.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance and downtime concerns, buyers should implement a proactive maintenance strategy from the outset. This includes scheduling regular maintenance checks and utilizing monitoring systems that can predict wear and tear on machine components. When selecting CNC machine 3, inquire about the availability of maintenance support, warranty coverage, and the ease of sourcing replacement parts. Additionally, creating a maintenance log that tracks performance issues and servicing can help identify patterns and prevent future breakdowns. Investing in training for operators to recognize early signs of mechanical issues can further enhance machine longevity and reliability, ultimately leading to smoother operations and higher customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc machine 3
When selecting materials for CNC machining, particularly for the Nomad 3, it is essential to consider the properties and suitability of various materials in relation to specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials that are frequently used with CNC machines, highlighting their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Wood in CNC Machining?
Wood is a versatile material with excellent machinability, making it a popular choice for CNC applications. Key properties include its lightweight nature, ease of cutting, and ability to be finished smoothly. However, wood is sensitive to moisture and temperature changes, which can affect its dimensional stability and durability.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of wood is its cost-effectiveness and aesthetic appeal, particularly for furniture and decorative items. However, it is less durable than metals and can warp or crack under extreme conditions, which may limit its use in demanding environments.
Impact on Application: Wood is suitable for applications requiring intricate designs and fine details, such as cabinetry and signage. Its compatibility with various finishes also enhances its appeal in consumer-facing products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local wood species and their availability. Compliance with environmental regulations, such as those governing sustainable forestry practices, is also crucial.
How Does Plastic Perform in CNC Machining Applications?
Plastics, such as ABS and acrylic, are widely used in CNC machining due to their lightweight and versatile nature. They exhibit good chemical resistance and can be easily molded into complex shapes. Key properties include a broad temperature range and low thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are generally more affordable than metals and can be machined quickly, making them ideal for prototypes and low-volume production. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stress as well as metals, which can limit their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for applications in the automotive and consumer goods industries, where lightweight and corrosion resistance are critical. Their ability to be colored and finished adds to their versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of plastic available in their regions and any associated regulations on plastic use and recycling. Compliance with international standards, such as ASTM for material properties, is also essential.
What Are the Advantages of Using Metals in CNC Machining?
Metals such as aluminum, brass, and copper are favored in CNC machining for their strength and durability. Key properties include high tensile strength, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, and good corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of metals is their robustness, making them suitable for high-stress applications like aerospace and automotive components. However, they are generally more expensive than wood and plastics and may require more complex machining processes.
Impact on Application: Metals are ideal for applications requiring high precision and durability, such as mechanical parts and structural components. Their compatibility with various finishing processes adds to their utility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe should consider local regulations regarding metal sourcing and machining. Compliance with standards such as DIN and JIS is crucial for ensuring product quality and safety.
How Do Composites Enhance CNC Machining Capabilities?
Composite materials, often made from a combination of plastics and fibers, offer unique properties such as enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and improved resistance to environmental factors. Key properties include low thermal expansion and high impact resistance.
Pros & Cons: Composites provide excellent durability and can be tailored for specific applications, making them suitable for high-performance environments. However, they can be more expensive and complex to machine compared to traditional materials.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods applications where performance and weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the availability of composite materials and their compliance with international standards. Understanding the local market’s acceptance of composites is also vital for successful integration into product lines.
Summary of Material Selection for CNC Machine 3
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc machine 3 | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Furniture, cabinetry, signage | Cost-effective and aesthetically pleasing | Susceptible to warping and cracking | Low |
| Plastic | Prototypes, consumer goods | Lightweight and versatile | Limited high-temperature resistance | Medium |
| Metal | Mechanical parts, structural components | High strength and durability | More expensive and complex to machine | High |
| Composite | Aerospace, automotive, sporting goods | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
This guide serves as a strategic resource for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc machine 3
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for CNC Machine 3?
The manufacturing process of CNC Machine 3 involves several critical stages that ensure precision, efficiency, and quality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers appreciate the complexities of production and the importance of quality assurance.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Processed?
The initial stage involves selecting suitable materials, which can include various metals (like aluminum, brass, and copper), plastics (such as ABS and PVC), and different types of wood. Material preparation typically includes cutting the raw materials into manageable sizes, ensuring they meet the specifications required for machining. This step is crucial as the quality of the raw material directly impacts the final product’s quality.
2. Forming: How Is the Material Shaped?
Forming is a fundamental aspect of CNC machining. It involves using CNC mills and routers to shape the prepared materials according to design specifications. CNC machines utilize computer numerical control to guide the cutting tools along the X, Y, and Z axes, allowing for high precision. Techniques such as milling, drilling, and routing are employed to achieve the desired shapes and tolerances. The advanced capabilities of CNC Machine 3 enable it to execute complex designs that may be challenging with manual machining.
3. Assembly: What Are the Assembly Techniques Used?
Once components are shaped, assembly takes place. This can involve the integration of various parts, such as motors, spindles, and electronic controls. Depending on the machine’s design, assembly techniques can vary; however, precision is paramount. Automated assembly systems may be used to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Each part must fit together perfectly to ensure the machine operates smoothly.
4. Finishing: What Finishing Techniques Are Implemented?
The final stage of the manufacturing process is finishing, which enhances the machine’s appearance and performance. Techniques such as sanding, painting, and anodizing are commonly used to improve surface quality and protect against corrosion. Finishing processes are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of CNC machines, particularly in demanding environments.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in CNC Machine Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process for CNC Machine 3, ensuring that the final product meets both industry standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Are Relevant to Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are crucial for establishing a quality management system that emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Compliance with ISO standards ensures that the manufacturing processes are efficient and that products meet specified requirements.
In addition to ISO, industry-specific certifications such as CE (for European markets) and API (for the oil and gas industry) may also apply, depending on the machine’s intended use. These certifications demonstrate adherence to safety and performance standards, which can be particularly important for B2B buyers looking to operate in regulated markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in CNC manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the first line of defense, where raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards. This step is crucial to prevent defects from entering the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, periodic inspections are conducted to monitor quality. This may include checking dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes at various stages of production.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, the complete machine undergoes a final inspection. This step ensures that all components function correctly and meet the required specifications before shipping.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Verify Quality?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality of CNC Machine 3. These may include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers, gauges, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify that dimensions conform to specifications.
-
Functional Testing: Ensuring that all machine functions operate as intended, including the spindle speed and movement along axes.
-
Material Testing: Conducting tests to evaluate the strength, durability, and other material properties to ensure they meet industry standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to mitigate risks. Here are several strategies to ensure supplier reliability:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help assess a supplier’s compliance with quality standards and practices. These audits may focus on manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to relevant certifications.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed QA reports that outline testing procedures, results, and compliance with international standards. This documentation can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and final products. This approach is particularly beneficial for buyers in regions with limited oversight capabilities.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate specific nuances in quality control and certification. Different regions may have varying regulations, standards, and expectations regarding machine quality.
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific quality and safety regulations in their region. For example, the CE mark is mandatory for products sold in the European Economic Area, while other regions may have different compliance requirements.
-
Language Barriers: When dealing with international suppliers, language differences can lead to misunderstandings regarding quality specifications. Clear communication and possibly translating key documents can mitigate this risk.
-
Cultural Differences: Variations in business practices and quality expectations across cultures can affect negotiations and partnerships. Establishing clear quality benchmarks and expectations upfront can help bridge these gaps.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for CNC Machine 3 are intricate and multifaceted. By understanding these elements, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable suppliers capable of delivering high-quality machines that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc machine 3’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring a CNC machine, specifically the ‘CNC Machine 3’. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs, budget constraints, and quality requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your search for a CNC machine, it’s essential to outline your specific technical requirements. Consider factors such as the size of the cutting area, the types of materials you will be machining (e.g., wood, plastics, metals), and the complexity of parts you intend to produce. This clarity will guide your selection process and help you identify machines that meet your operational needs.
Step 2: Research Available Models and Features
Once you have defined your specifications, research the various models available in the market. Focus on features that enhance performance, such as spindle power, RPM range, and axis movement capabilities. Comparing different machines will provide insights into which models offer the best value for your requirements.
- Key Features to Consider:
- Spindle motor power and speed
- Cutting area dimensions
- Compatibility with CAM software
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your needs. Request company profiles, product certifications, and case studies to assess their credibility. Additionally, seek references from other businesses within your industry or region to gather insights about their reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Check for Warranty and Support Options
Investigate the warranty terms and customer support services offered by the supplier. A solid warranty can protect your investment, while responsive support can help resolve issues swiftly. Look for suppliers that provide training sessions or extensive resources to assist you in getting the most out of your CNC machine.
- Support Features to Look For:
- Duration and coverage of warranty
- Availability of training sessions
- Access to technical support (e.g., phone, email, chat)
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Financing Options
Pricing can vary significantly among suppliers. It’s crucial to compare prices not only for the machine but also for additional costs such as shipping, installation, and maintenance. Explore financing options that may be available, as these can make the purchase more manageable.
Step 6: Review Compliance and Certification Standards
Ensure that the CNC machine complies with relevant industry standards and regulations. This is particularly important for international purchases, as compliance can affect the machine’s operation and maintenance in your region. Verify certifications such as ISO or CE that indicate adherence to quality and safety standards.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Plan Installation
Once you have selected the ideal CNC machine and supplier, finalize your purchase. Coordinate with the supplier for delivery and installation, ensuring that all logistics align with your operational schedule. Prepare your facility for the new equipment by planning for space, power supply, and any necessary modifications to support the machine.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing a CNC machine effectively, ensuring that they invest wisely and enhance their production capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc machine 3 Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for CNC Machine 3 Sourcing?
When sourcing CNC Machine 3, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects pricing. Common materials like aluminum and various plastics may cost less than specialized alloys or composites. For instance, the Nomad 3 CNC machine can handle materials ranging from wood to metals, each with different cost implications.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary by region. In countries with lower labor costs, like some in Africa or South America, you may find more competitive pricing. However, skilled labor for CNC programming and operation is essential, which can increase overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility costs, and equipment maintenance. High-quality manufacturers typically have more substantial overheads, reflecting in the final price of the machine.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling, such as collets and end mills, must be considered. For instance, the Nomad 3 includes essential tools, which can reduce initial costs for buyers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality assurance is vital. Machines with higher QC standards may have a premium price but can save costs in the long run through reduced failure rates.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can be significant, especially for international buyers. The choice of Incoterms will influence who bears these costs and risks.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary. Established brands may have higher margins due to their reputation and support services, while new entrants might offer lower prices to penetrate the market.
How Do Price Influencers Impact CNC Machine 3 Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC machines:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk can lead to discounts. Buyers in regions like the Middle East or Europe may negotiate better terms due to their purchasing power.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications will generally increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price hikes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines made from high-grade materials with certifications (ISO, CE) tend to command higher prices. This is especially pertinent for industries requiring compliance with stringent quality standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may offer better warranties and support, which can justify a higher price.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms affect overall costs. Understanding whether shipping costs, duties, and insurance are included can prevent unexpected expenses.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in CNC Machine 3 Sourcing?
To maximize value while minimizing costs, international B2B buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Smartly: Leverage your purchasing volume to negotiate better pricing or additional services such as training or extended warranties. Building a relationship with suppliers can also lead to favorable terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A machine with a higher initial cost might offer lower TCO due to its durability and efficiency.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware that currency fluctuations can impact pricing. Additionally, import duties and taxes vary by country, affecting the total landed cost of the machine.
-
Research and Compare: Analyze multiple suppliers and models to ensure you are getting the best value for your investment. Resources like comparison charts can help identify the best options based on your specific needs.
In conclusion, sourcing CNC Machine 3 involves navigating a complex landscape of costs and pricing influencers. By understanding these dynamics, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc machine 3 With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in CNC Solutions
When evaluating CNC machines, it’s crucial for B2B buyers to consider various alternatives to ensure they select the most effective solution for their specific manufacturing needs. Different CNC technologies offer unique advantages and disadvantages that can impact performance, cost, and usability. Here, we compare ‘CNC Machine 3’ against two viable alternatives: the Nomad 3 Desktop CNC Mill and the Benchtop PRO 3636 CNC Machine.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Machine 3 | Nomad 3 Desktop CNC Mill | Benchtop PRO 3636 CNC Machine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, versatile for 2D and 3D machining | Excellent for small-scale projects, effective for wood, plastics, and soft metals | High performance, suitable for larger projects and complex parts |
| Cost | $2,800 | $2,800 | $4,000+ |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires moderate training and software knowledge | User-friendly, includes training sessions | More complex setup, requires technical expertise |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance needs | Low, easy to replace parts | Moderate, more components to manage |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for small to medium businesses needing diverse applications | Best for hobbyists and small workshops focused on prototyping | Excellent for medium to large businesses needing robust, high-volume production |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Nomad 3 Desktop CNC Mill
The Nomad 3 is a compact, entry-level CNC mill designed for a variety of materials including wood, plastics, and soft metals. Its strengths lie in its user-friendly interface and built-in software, which simplifies the design-to-production process. However, while it’s excellent for prototyping and small-scale manufacturing, its cutting area is limited (8″x8″x3″), making it less suitable for larger parts or complex assemblies. The price point aligns with CNC Machine 3, making it a feasible option for similar budget-conscious buyers.
Benchtop PRO 3636 CNC Machine
The Benchtop PRO 3636 offers a larger cutting area and more robust capabilities, making it ideal for medium to large-scale operations. It supports a wider range of materials and is suitable for more complex machining tasks. However, the higher initial cost and the need for more technical expertise can be significant drawbacks for smaller businesses or those new to CNC machining. Maintenance requirements are also higher, as more components can lead to increased upkeep. This machine is best suited for established businesses looking for scalability and efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right CNC Solution for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate CNC solution requires a thorough understanding of your business’s specific needs, including the types of materials you work with, the complexity of your projects, and your budget constraints. CNC Machine 3 stands out for its versatility and ease of use, making it a strong candidate for small to medium enterprises. Meanwhile, the Nomad 3 is perfect for hobbyists or startups focusing on prototypes, while the Benchtop PRO 3636 caters to businesses with greater production demands. By weighing these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and financial resources.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc machine 3
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Machine 3?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of CNC Machine 3 is critical for B2B buyers looking to optimize their manufacturing processes. Here are some key properties:
-
Spindle Motor Power (Wattage)
The spindle motor power, typically around 130W for CNC Machine 3, directly impacts the machine’s cutting efficiency and the types of materials it can process. A higher wattage allows for faster cutting speeds and the ability to work with tougher materials, which is vital for production quality and turnaround times. -
Spindle RPM (Revolutions Per Minute)
The spindle speed, which can range from 9,000 to 24,000 RPM, determines how finely the machine can cut different materials. Higher RPMs are essential for achieving finer finishes and working with harder materials, making this a crucial factor for manufacturers aiming for precision and quality. -
Cutting Area Dimensions
The dimensions of the cutting area (e.g., 8″ x 8″ x 3″ for CNC Machine 3) define the maximum size of the workpiece that can be machined. Understanding these dimensions helps businesses evaluate whether the machine fits their production requirements and whether it can accommodate the specific parts they intend to manufacture. -
Material Compatibility
CNC Machine 3 is designed to work with a range of materials including wood, plastics, and metals like aluminum and brass. Knowing the material compatibility is essential for businesses to ensure they can produce the desired components without needing additional machines or tools, thus optimizing their operations. -
Precision and Tolerance Levels
CNC machines typically offer different precision levels, often measured in microns. The tolerance levels define the allowable deviation from a specified measurement. High precision is crucial for industries such as aerospace and medical devices, where even minor inaccuracies can lead to significant issues. -
Software Compatibility
The integration of software such as MeshCAM and CAD/CAM solutions is vital for streamlining the machining process. Understanding software compatibility ensures that businesses can efficiently generate G-code and manage their workflows without additional software investments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in CNC Machining?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the CNC industry, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and evaluate the quality of components used in machines. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for businesses to understand their purchasing power and the implications for inventory management, especially when sourcing CNC machines or parts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific goods or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ can streamline procurement processes and ensure competitive pricing for CNC machines and related components. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for managing shipping logistics and ensuring compliance with international trade laws. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving it. For CNC machines, understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and maintaining operational efficiency. -
Tolerances
Tolerances define the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension. In CNC machining, tighter tolerances often lead to higher costs but are essential for precision applications. Understanding tolerances helps buyers ensure the parts meet their specifications without incurring excessive costs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, streamline their procurement processes, and enhance their operational efficiencies in CNC machining.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc machine 3 Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting CNC Machine 3 Sourcing?
The CNC machine sector is witnessing transformative changes driven by advancements in technology and evolving market demands. Internationally, there is a rising emphasis on automation and precision manufacturing, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. For B2B buyers, this translates into a growing need for machines that offer enhanced capabilities, such as 3-axis and 5-axis machining, which can produce complex parts with greater efficiency. Countries like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria are increasingly investing in local manufacturing capabilities to reduce dependency on imports, creating opportunities for suppliers of CNC machines.
Emerging technologies such as IoT integration and smart manufacturing systems are also shaping sourcing trends. These innovations enable real-time monitoring and data analytics, allowing businesses to optimize production processes and reduce downtime. Furthermore, the demand for smaller, more compact machines, like the Nomad 3 desktop CNC mill, reflects a trend toward more flexible and adaptable manufacturing solutions, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) looking to enter the CNC market.
Another significant driver is the push for digital transformation, where B2B buyers are seeking CNC machines compatible with advanced CAD/CAM software, facilitating seamless design-to-production workflows. This trend is particularly relevant for industries focused on rapid prototyping and low-volume production runs, where speed and accuracy are critical.
How Does Sustainability Influence B2B Sourcing in the CNC Machine Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in the sourcing decisions of B2B buyers in the CNC machine industry. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, leading companies to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing materials from ethical suppliers and adopting energy-efficient technologies in the production of CNC machines.
Buyers are increasingly interested in ‘green’ certifications and materials, such as recyclable plastics and sustainably sourced metals, to ensure their operations align with global sustainability goals. Manufacturers that offer machines designed for lower energy consumption and reduced waste generation are likely to gain a competitive edge. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions where regulatory frameworks are evolving to support environmental responsibility, such as the European Union.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are becoming a prerequisite for many organizations. Buyers are seeking transparency in sourcing practices to ensure that materials are obtained responsibly, without adverse impacts on communities or ecosystems. This focus on ethical sourcing not only enhances a company’s brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Machines and Their Evolution?
The evolution of CNC machines dates back to the 1950s when the first numerical control machines were developed. Initially, these machines were limited in capability and primarily used in large manufacturing facilities. Over the decades, advancements in computer technology and software have revolutionized CNC machining, making it accessible to a broader range of businesses, including SMEs.
The introduction of 3-axis CNC machines paved the way for greater precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes. As industries began to recognize the potential of CNC technology, manufacturers started developing more advanced models, including 5-axis machines capable of producing intricate designs. Today, CNC machines are integral to various sectors, from automotive to aerospace, providing manufacturers with the tools needed to meet the complexities of modern production demands.
The shift towards desktop CNC mills, like the Nomad 3, signifies a democratization of CNC technology, allowing hobbyists and small businesses to leverage advanced machining capabilities. This historical context underscores the adaptability of CNC technology in meeting the evolving needs of global markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc machine 3
-
How do I select the right CNC machine for my business needs?
Choosing the right CNC machine involves evaluating your specific production requirements, including the types of materials you plan to work with, the complexity of the parts you need to produce, and your budget. Consider the machine’s capabilities, such as axis count (3-axis vs. 5-axis), cutting area, and speed. Additionally, assess the available software compatibility and support services offered by suppliers. It’s also wise to consult with industry experts or existing users to gather insights on performance and reliability. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for CNC machines?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their reputation and experience in the CNC industry. Look for reviews and testimonials from previous clients, and check if they offer post-purchase support, warranties, and training. Verify their compliance with international standards and certifications, especially if you’re importing machinery. Additionally, consider their logistical capabilities, including shipping times and customs handling, particularly for international orders from regions like Africa and South America. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC machines?
MOQs for CNC machines can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the type of machine. While some suppliers may offer single-unit purchases, others might require bulk orders to ensure cost-effectiveness. It’s essential to clarify the MOQ during initial discussions and to negotiate terms that align with your production needs. For smaller businesses, consider exploring options for leasing or financing to manage costs effectively. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing CNC machines internationally?
Payment terms can vary, but common practices include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and the balance upon delivery. Some suppliers may also offer financing options or installment plans, which can ease cash flow concerns. It’s crucial to discuss and agree upon payment methods (e.g., wire transfer, credit terms) and ensure that these terms are documented in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for CNC machines purchased from international suppliers?
To ensure quality assurance, request certifications and documentation related to the machine’s manufacturing processes and quality standards. Consider asking for samples or visiting the manufacturing site if feasible. Establish a clear agreement regarding quality checks and performance metrics before shipment. Additionally, consider engaging third-party inspection services to assess the machine’s condition before final acceptance, especially for high-value purchases. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing CNC machines?
Logistics for importing CNC machines involves several factors, including shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Ensure you understand the incoterms (International Commercial Terms) that define the responsibilities of the buyer and seller. Work with a logistics provider experienced in heavy machinery to navigate customs clearance and potential tariffs. Additionally, factor in the costs of insurance and handling during transportation to avoid unexpected expenses. -
Can CNC machines be customized to meet specific production requirements?
Yes, many CNC manufacturers offer customization options tailored to specific production needs. This can include modifications to the machine’s size, spindle type, or additional features like automatic tool changers. When discussing customization, clearly outline your requirements and expectations with the supplier. Keep in mind that customization can affect lead times and costs, so it’s essential to factor these into your purchasing decision. -
What support and training should I expect after purchasing a CNC machine?
Most reputable CNC suppliers provide post-purchase support that includes installation assistance, technical support, and training on machine operation. Look for suppliers that offer comprehensive training programs, either on-site or via webinars, to help your team efficiently operate the machine. Additionally, inquire about ongoing support options, such as maintenance services or troubleshooting assistance, to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your CNC machine.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Cnc Machine 3 Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tormach – 3-Axis CNC Milling Machines
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the best 3-axis CNC milling machines for a small startup business. Key mentions include Tormach and Haas as notable brands, with opinions suggesting they are good starter machines despite being lower in quality compared to higher-end options. The context is provided by a college student interested in machining, considering future purchases for a small job-shop style …
2. AMFG – 3-Axis CNC Machine
Domain: amfg.ai
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: 3-Axis CNC Machine: Operates along three directions (X, Y, Z); suitable for simpler, flat, and less intricate cuts; ideal for creating straightforward molds or basic components like rectangular plates; commonly used in prototyping and general machining. Key Features: X-Axis (horizontal movement), Y-Axis (vertical movement), Z-Axis (depth movement). Industries: Prototyping, general machining. 5-Axi…
3. Instructables – 3 Axis CNC Milling Machine
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 3 Axis CNC Milling Machine with a working space of 900 x 400 x 120 mm, designed for milling aluminum parts. Features include a relatively silent spindle with high power at low rotation rates, high stiffness, precision, USB interface, and a budget under 2000€. Constructed using 30-B type nut 8 aluminum frames, 16mm ball-circulation spindles, 15mm ball-circulation rail bearings, and 3Amp NEMA23 step…
4. Hurco – VM Series CNC Machines
Domain: hurco.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: VM Series – 3 Axis CNC Machines
– Designed for job shops needing high performance in limited space.
– Features the WinMax control system for both conversational and G-code users.
– Compact footprint with a large work cube for handling larger parts.
– Built for reliability and precision to optimize productivity and reduce overhead.
– One-piece machine base and solid cast iron frame for durability.
…
5. Automation Technologies Inc – 3 Axis CNC 3040T Router Engraver
Domain: automationtechnologiesinc.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Product Name: 3 Axis CNC 3040T Router Engraver/Engraving Drilling and Milling Machine UC100 USB Connection
Price: $699.95
Stock Status: In stock
Specifications:
– Driving Unit: X/Y/Z axis: 1204 trapezoidal screws, Chrome plate shaft
– Maximum Speed: 0-200 inch/min
– Carving Speed: 120 inch/min
– Structure: 6061/6063 Aluminum alloy
– Carving Depth: 2.16 inch
– Repeat Accuracy: 0.002
– Stepping Moto…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc machine 3
As the CNC machining landscape continues to evolve, strategic sourcing remains essential for international B2B buyers seeking competitive advantages. The Nomad 3 and other advanced CNC machines offer a range of capabilities that cater to diverse manufacturing needs, particularly in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. With their ability to process various materials and deliver precision, these machines enhance operational efficiency and product quality, making them invaluable assets for businesses.
Investing in CNC technology not only streamlines production processes but also positions companies to respond swiftly to market demands. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of different CNC models—such as the advantages of 3-axis versus 5-axis machining—can guide informed purchasing decisions.
Looking ahead, the demand for sophisticated CNC solutions is likely to grow, driven by globalization and technological advancements. To capitalize on these trends, B2B buyers should engage with reliable suppliers, explore collaborative opportunities, and embrace innovative solutions that can propel their businesses forward. Now is the time to invest in cutting-edge CNC technology to ensure a competitive edge in an increasingly dynamic market.