Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Cnc M-Code
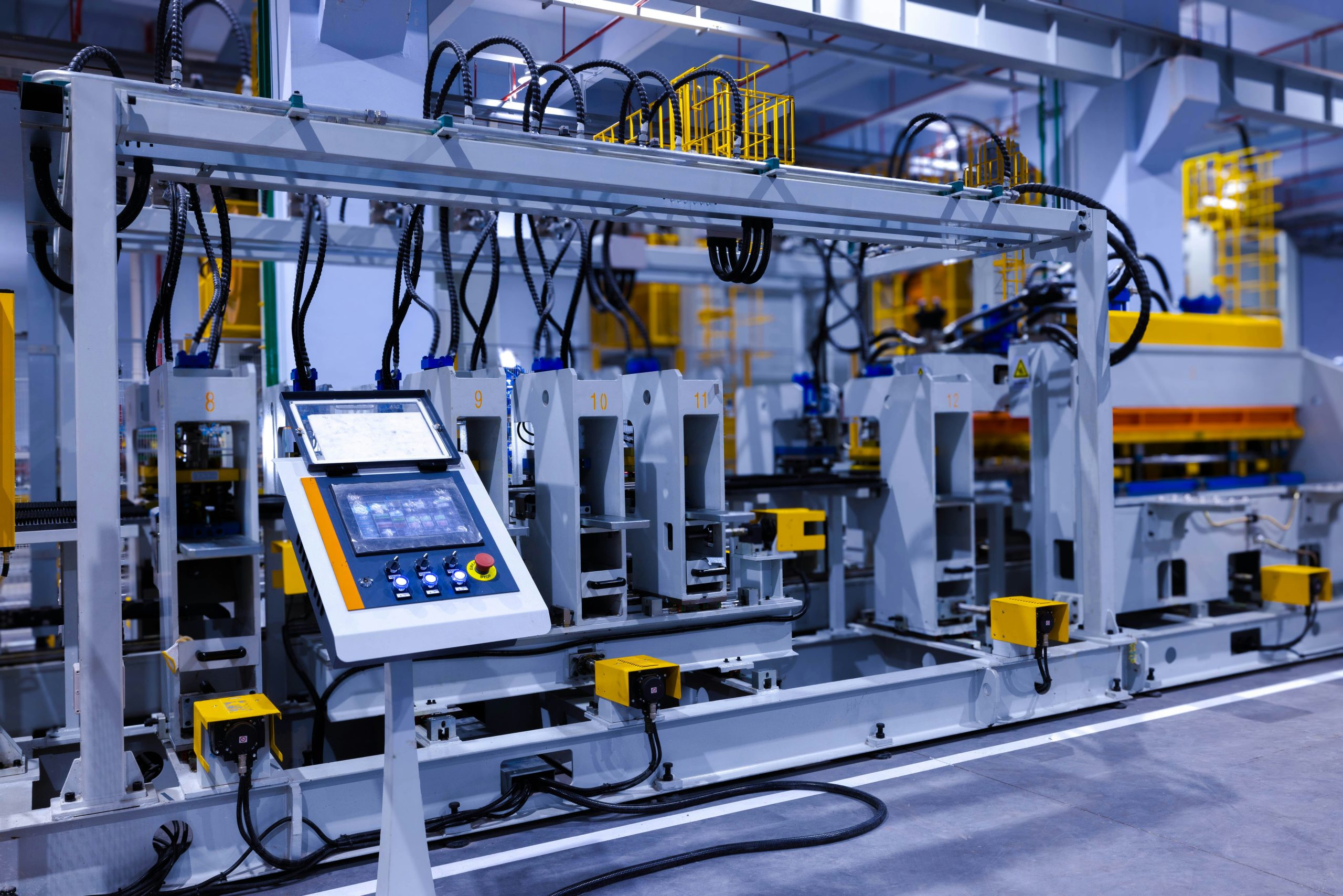

Understanding CNC M-Code: Precision Control for Advanced Manufacturing
CNC M-code represents the critical auxiliary commands within machine tool programming, governing essential functions beyond axis movement such as spindle control, coolant activation, tool changes, and program termination. Mastery of M-code execution is fundamental to achieving repeatability, minimizing cycle times, and ensuring flawless part production—particularly for complex, tight-tolerance components demanded in aerospace, medical, and industrial applications. At Honyo Prototype, our engineering team leverages deep expertise in CNC programming protocols, including precise M-code implementation, to optimize machine performance across our full spectrum of milling, turning, and multi-axis machining services.
We specialize in transforming intricate designs into high-integrity prototypes and production runs using advanced CNC equipment capable of handling aluminum, titanium, stainless steel, and engineered plastics with micron-level accuracy. Our end-to-end process integrates rigorous quality control, from material sourcing to final inspection, ensuring every component meets stringent industry specifications. Accelerate your development timeline with Honyo’s Online Instant Quote system, which provides transparent, real-time pricing and manufacturability feedback within minutes—eliminating procurement delays while maintaining engineering excellence.
| Service Capability | Technical Scope | Turnaround Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Milling & Turning | 3-5 axis, ±0.0001″ tolerances, complex geometries | Prototype: 3-5 days |
| Material Expertise | Metals, plastics, composites, exotic alloys | Production scalability |
| Digital Integration | CAD/CAM optimization, M-code validation | Instant Quote: <2 minutes |
Partner with Honyo Prototype to harness precision-driven CNC manufacturing where technical mastery meets operational efficiency. Initiate your project today through our seamless Online Instant Quote platform.
Technical Capabilities

CNC M-codes are auxiliary commands used in CNC programming to control machine functions such as spindle start/stop, coolant flow, tool changes, and program termination. While G-codes define motion and geometry, M-codes manage the operational state of the machine. The following table outlines key M-codes relevant to 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling, CNC turning, and tight-tolerance manufacturing across common engineering materials including Aluminum, Steel, ABS, and Nylon.
| M-Code | Function | Application Context | Material Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| M03 | Spindle start (clockwise) | Used in milling and turning to initiate cutting. Critical for maintaining consistent surface finish in tight-tolerance parts. | Applicable to all materials; spindle speed must be optimized per material (e.g., high RPM for Aluminum, lower for Steel). |
| M04 | Spindle start (counterclockwise) | Rarely used; occasionally in thread milling or specific turning operations. | Used with Aluminum and Steel when reverse threading is required. Less relevant for thermoplastics like ABS and Nylon. |
| M05 | Spindle stop | Ensures spindle halts before tool change or part inspection. Essential in multi-axis setups to avoid collisions. | Required across all materials; especially important in precision work to prevent thermal drift in Steel and Nylon. |
| M06 | Tool change | Automates tool swapping in multi-operation setups. Critical in 4/5-axis milling where multiple tools access complex geometries. | Required for Aluminum (face/end mills), Steel (carbide inserts), and plastics (sharp, polished tools for ABS/Nylon to prevent melting). |
| M08 | Coolant on (flood) | Maintains temperature during extended cuts. Vital in Steel and Aluminum machining to preserve tool life and dimensional accuracy. | Strongly used in Steel and Aluminum; generally avoided in ABS and Nylon to prevent softening or warping. |
| M09 | Coolant off | Deactivates coolant post-operation or when not required. Important when machining hygroscopic or thermally sensitive materials. | Standard practice with ABS and Nylon; used after Steel/Aluminum operations to prevent contamination. |
| M19 | Spindle orientation | Positions spindle at a fixed angle. Required for tool changes in turning centers and probing operations in 5-axis systems. | Supports tight-tolerance alignment in all materials, especially during probing and precision boring. |
| M30 | Program end and reset | Signals end of program and resets the control. Used after final inspection routines in high-precision workflows. | Universal across all materials; ensures safe machine state post-processing. |
| M41 / M42 | Gear range selection (low/high) | Found in CNC lathes; selects mechanical gear ratios for optimal torque/speed. | Critical for turning hardened Steel; less impactful for Aluminum and thermoplastics due to lower cutting forces. |
| M98 / M99 | Subprogram call / return | Enables modular programming for repetitive features (e.g., pockets, threads). Enhances repeatability in tight-tolerance production. | Applied across materials for consistent feature replication, especially in Aluminum housings or Nylon gears. |
Note: Tight-tolerance machining (±0.0005″ or better) demands precise M-code sequencing to control thermal conditions, tool engagement, and machine state transitions. Material-specific strategies include using minimal or air cooling for ABS and Nylon to avoid deformation, while flood coolant is maintained for Steel and Aluminum to manage heat and improve surface integrity. In multi-axis environments, M-codes are synchronized with A, B, or C-axis movements (4th/5th axes) to ensure safe and accurate tool positioning.
From CAD to Part: The Process
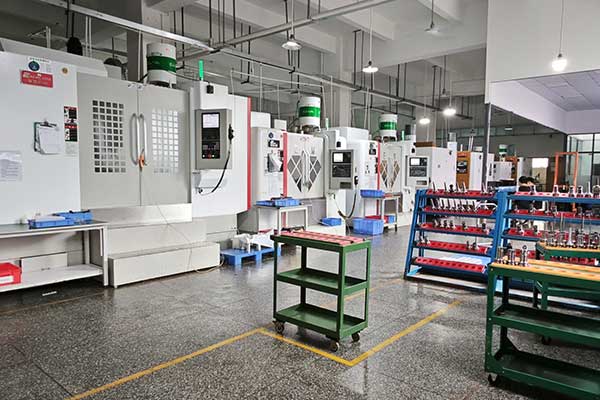

Honyo Prototype employs a rigorously defined workflow for CNC machining projects, ensuring precision, efficiency, and transparency from initial concept to final delivery. The term “CNC M-code” refers to auxiliary machine control commands within CNC programs (e.g., coolant on/off, tool changes), not our core process. Our standardized client-facing workflow follows these key stages:
CAD File Upload and Initial Processing
Clients initiate the process by uploading native or neutral format CAD files (STEP, IGES, Parasolid, native SOLIDWORKS) via our secure portal. Our system performs immediate validation checks for file integrity, unit consistency, and geometric completeness. This step ensures manufacturability begins with a technically sound digital foundation, eliminating ambiguities before formal quoting.
AI-Powered Instant Quoting Engine
Uploaded geometry is processed by our proprietary AI quoting engine, which analyzes part complexity, material requirements, dimensional envelope, and geometric features. The engine cross-references real-time data on machine availability, material costs, and labor rates to generate a detailed preliminary quote within minutes. This quote includes estimated lead time, material options with cost differentials, and a preliminary manufacturability risk score, providing immediate budgetary clarity without manual intervention.
Engineering-Led DFM Analysis and Optimization
All quotes trigger a mandatory Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review by our senior CNC engineering team. This is not an automated step but a value-added engineering service where our experts identify potential issues and optimize the design for cost-effective, high-yield production. Critical DFM checks include:
| Check Type | Parameter | Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometric Feasibility | Internal radii, wall thickness | Recommend minimum tool diameter adjustments | Prevents tool breakage, ensures accuracy |
| Tolerance Analysis | Critical GD&T callouts | Validate achievable tolerances vs. print | Eliminates over-engineering costs |
| Setup Efficiency | Feature orientation | Propose optimal fixturing strategy | Reduces machine time, improves repeatability |
| Material Utilization | Raw stock dimensions | Optimize billet size and nesting | Minimizes material waste, lowers cost |
The DFM report details actionable recommendations, cost-impact analysis for each suggestion, and a final go/no-go determination for production readiness. Client approval of the DFM report is required before proceeding.
Precision CNC Production Execution
Approved designs enter production on our monitored CNC fleet (3-axis, 5-axis, mill-turn). Each job receives a unique production ID linked to our MES (Manufacturing Execution System). Key production protocols include:
First-article inspection per AS9102 standards for critical features
In-process CMM verification at defined milestones
Real-time machine telemetry monitoring for tool wear and process stability
Strict material traceability from certified mills with full CoC documentation
Our facility maintains ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949 certifications, with all CNC operators certified to NIMS Level 2 standards.
Quality-Controlled Delivery and Documentation
Final inspection generates a comprehensive dimensional report against the original CAD model, including surface finish verification and material certification. Parts ship in ESD-safe packaging with serialized tracking. Every delivery includes:
As-built dimensional inspection report (PDF and XML)
Material test certificates (MTRs)
Process non-conformance log (if applicable)
Digital DFM report archive
Standard lead time is 5-7 business days for 1-10 parts after DFM approval, with expedited options available. All deliveries include real-time shipment tracking and post-delivery technical support for assembly or integration queries. This closed-loop process ensures zero surprises and maximum value realization for our industrial clients.
Start Your Project
Interested in learning more about CNC M-code programming and its role in precision manufacturing? Contact Susan Leo at [email protected] for expert insights and technical support. Honyo Prototype, with our manufacturing facility based in Shenzhen, delivers high-accuracy CNC machining services tailored to your prototyping and production needs. Reach out today to streamline your manufacturing process.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.