Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc lathe projects
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing CNC lathe projects can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. As organizations seek to enhance their production capabilities, the complexity of selecting the right lathe projects—ranging from intricate components to high-volume production runs—requires a well-informed approach. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of CNC lathe projects, detailing various types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
Understanding the diverse functionalities of CNC lathes, from precision machining to complex part fabrication, is essential for optimizing operational efficiency. Our resource equips buyers with the necessary insights into cost structures, project feasibility, and the technological advancements that can influence purchasing decisions. Special attention is given to the unique needs of buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Germany and Vietnam, which are rapidly expanding their manufacturing sectors.
By delving into the critical factors that affect sourcing, including quality assurance and logistical considerations, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed choices. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the CNC landscape, the actionable insights provided here will help streamline your procurement process and enhance your competitive edge in the global market.
Understanding cnc lathe projects Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Machining Projects | Focus on fundamental skills; often simple shapes. | Prototyping, small batch production. | Pros: Easy to execute, great for skill development. Cons: Limited complexity may not meet all needs. |
| Complex Component Fabrication | Involves intricate designs and multi-step processes. | Aerospace, automotive, medical devices. | Pros: High precision and functionality. Cons: Longer lead times and higher costs. |
| Custom Tooling and Fixtures | Designed specifically for unique applications. | Manufacturing, assembly lines. | Pros: Tailored solutions enhance efficiency. Cons: Requires detailed specifications and longer design phases. |
| Artistic and Decorative Items | Emphasizes aesthetics; often unique or one-off pieces. | Luxury goods, art installations. | Pros: High market value and differentiation. Cons: Time-consuming and may require specialized skills. |
| Prototyping and R&D | Focuses on developing new products or improving existing ones. | Product development across industries. | Pros: Rapid iteration and testing of concepts. Cons: May not be cost-effective for small runs. |
What Are Basic Machining Projects and Their B2B Relevance?
Basic machining projects are typically straightforward and focus on fundamental lathe skills such as turning and facing. They often include simple shapes like rings or hammers, making them ideal for novice machinists. For B2B buyers, these projects serve as an excellent entry point for businesses looking to train new employees or build foundational skills in metalworking. The low complexity allows for quick production and prototyping, which can be beneficial in fast-paced environments.
How Do Complex Component Fabrication Projects Enhance Precision?
Complex component fabrication involves intricate designs that require advanced CNC programming and multiple machining steps. This type of project is essential in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precision and reliability are paramount. B2B buyers in these sectors should consider the capabilities of their CNC lathes, as well as the expertise of their machinists, to ensure they can meet demanding specifications. While these projects offer high functionality, they can also lead to longer production times and increased costs.
Why Are Custom Tooling and Fixtures Important for Manufacturing?
Custom tooling and fixtures are designed to meet specific operational needs, enhancing efficiency in manufacturing processes. These projects are vital for assembly lines and production environments where standard tools may not suffice. B2B buyers should prioritize investing in CNC lathes capable of producing tailored solutions that improve workflow. However, the design phase may require more time and detailed specifications, which can be a challenge for some organizations.
What Role Do Artistic and Decorative Items Play in B2B Markets?
Artistic and decorative items produced on CNC lathes focus on aesthetics and uniqueness, catering to markets such as luxury goods and art installations. For B2B buyers, these projects can create differentiation in product offerings, allowing businesses to command higher prices. However, the time investment and specialized skills required can pose challenges, making it crucial for buyers to assess their workforce capabilities and production timelines.
How Can Prototyping and R&D Projects Drive Innovation?
Prototyping and R&D projects utilize CNC lathes to develop new products or refine existing ones, making them essential in various industries. These projects allow businesses to rapidly iterate and test concepts, which can accelerate time-to-market for new innovations. B2B buyers must weigh the benefits of quick prototyping against potential costs, especially if the production volume is low. This approach is particularly valuable for companies focused on staying competitive through continuous improvement and innovation.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc lathe projects
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cnc lathe projects | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision components manufacturing | Enhanced precision and reliability in critical components | Supplier certifications, quality control processes |
| Automotive | Production of engine components | Improved performance and reduced lead times | Material quality, delivery reliability, cost-effectiveness |
| Oil & Gas | Custom tooling and parts for drilling equipment | Increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Technical expertise, compliance with industry standards |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments | High precision and compliance with health regulations | Regulatory certifications, material traceability |
| Electronics | Production of heat sinks and enclosures | Optimized performance and thermal management | Design capabilities, prototyping services |
How Are CNC Lathe Projects Applied in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, CNC lathe projects are crucial for manufacturing precision components such as turbine blades, landing gear parts, and structural elements. The stringent safety and performance standards in this industry necessitate high accuracy in machining, which CNC lathes provide. International buyers, particularly from Europe and the Middle East, must prioritize suppliers with robust quality assurance processes and relevant certifications to ensure compliance with aerospace regulations.
What Role Do CNC Lathe Projects Play in the Automotive Sector?
The automotive industry leverages CNC lathe projects for producing engine components, transmission parts, and custom tooling. These projects enhance the performance of vehicles while reducing lead times, which is essential in a highly competitive market. Buyers from regions like South America and Africa should consider sourcing from manufacturers with a proven track record in automotive applications and a strong commitment to quality and timely delivery.
How Are CNC Lathe Projects Utilized in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, CNC lathe projects are employed to create custom tooling and parts for drilling and extraction equipment. The unique demands of this industry require high durability and precision to minimize downtime and maximize efficiency. Buyers must seek suppliers who demonstrate technical expertise and adherence to industry standards, especially when operating in remote or challenging environments.
What Are the Applications of CNC Lathe Projects in Medical Devices?
CNC lathe projects are vital in the medical device industry for fabricating surgical instruments and implants. The need for high precision and compliance with health regulations makes CNC lathes an ideal solution. International buyers, particularly those from Africa and Europe, should focus on sourcing from manufacturers that ensure regulatory compliance and can provide material traceability to meet stringent health and safety standards.
How Are CNC Lathe Projects Applied in the Electronics Sector?
In the electronics industry, CNC lathe projects are used to manufacture components such as heat sinks and enclosures. These projects contribute to optimized performance and effective thermal management of electronic devices. Buyers from South America and the Middle East should consider the design capabilities and prototyping services offered by suppliers to ensure that their specific requirements are met efficiently and effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc lathe projects’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Scaling Production for Complex Parts
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter challenges when attempting to scale production of complex components using CNC lathes. As demand increases, the need for precision and efficiency becomes critical. This can lead to situations where existing workflows are insufficient to meet output goals, resulting in delays and higher operational costs. Additionally, managing the intricacies of programming CNC lathes for intricate designs can overwhelm teams lacking advanced expertise, leading to costly errors and wasted materials.
The Solution:
To effectively scale production, buyers should invest in robust CAD/CAM software that integrates seamlessly with CNC lathes. This software not only streamlines the design-to-production process but also enables the simulation of machining operations before actual production begins. For complex parts, utilizing a modular approach to tooling can significantly enhance flexibility and adaptability on the shop floor. Buyers should also consider ongoing training programs for their operators, focusing on advanced CNC programming and machining techniques. This will empower their teams to efficiently handle complex projects while minimizing the risk of errors, thus optimizing both time and resources.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Quality Control Measures Leading to Rework
The Problem:
Quality control is paramount in CNC lathe projects, but many buyers struggle to implement effective measures, particularly when dealing with high-volume production. Inconsistent quality can lead to a significant amount of rework, which not only consumes additional labor and materials but can also jeopardize client relationships and project timelines. Often, this issue stems from insufficient inspection protocols or a lack of real-time monitoring during the machining process.
The Solution:
To enhance quality control, buyers should incorporate advanced measurement and inspection technologies, such as automated vision systems and in-process measurement tools. By integrating these technologies into their production line, companies can monitor dimensions and tolerances in real time, ensuring that each component meets specifications before moving to the next stage. Furthermore, establishing a culture of quality within the organization can be transformative; this includes training employees on quality standards and involving them in continuous improvement initiatives. Regular audits of quality control processes and feedback loops will also aid in identifying areas for improvement, ultimately reducing the rate of rework and enhancing overall product reliability.
Scenario 3: Limited Access to Skilled Operators and Technicians
The Problem:
A common pain point for B2B buyers in the CNC lathe sector is the scarcity of skilled operators and technicians. As the demand for CNC machined parts grows, the competition for qualified labor intensifies. Many companies find themselves unable to fully utilize their CNC lathe capabilities due to a lack of expertise in programming, setup, and maintenance. This skill gap can hinder production efficiency and compromise the quality of the finished products.
The Solution:
To address the shortage of skilled labor, companies should consider partnering with local technical schools and vocational training programs to create apprenticeship opportunities. This not only helps cultivate a pipeline of skilled workers but also fosters loyalty and reduces turnover. Additionally, implementing a mentorship program within the organization can enhance the skill sets of less experienced employees, allowing them to learn from seasoned operators. Investing in user-friendly CNC systems that feature intuitive interfaces and simplified programming can also help bridge the skill gap, making it easier for less experienced staff to operate complex machinery efficiently. By taking these proactive steps, businesses can build a competent workforce capable of maximizing the potential of their CNC lathe projects.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc lathe projects
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for CNC Lathe Projects?
When selecting materials for CNC lathe projects, understanding the properties of each option is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four commonly used materials: Aluminum, Steel, Brass, and Plastic. Each material has unique characteristics that can influence the outcome of machining projects.
How Does Aluminum Perform in CNC Lathe Applications?
Aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal known for its excellent machinability. It has a good strength-to-weight ratio and can withstand moderate temperatures, making it ideal for a variety of applications, including automotive and aerospace components. However, while it is relatively durable, aluminum can be less resistant to wear compared to harder metals.
Pros: Aluminum is cost-effective, easy to machine, and provides a smooth finish, making it suitable for intricate designs.
Cons: It may not be ideal for high-stress applications due to lower tensile strength compared to steel.
For international buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for extruded aluminum is essential. Additionally, the availability of specific aluminum alloys can vary by region, impacting project timelines.
What Advantages Does Steel Offer for CNC Machining?
Steel, particularly carbon steel, is widely used in CNC lathe projects due to its exceptional strength and durability. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications such as machinery parts and structural components. Steel’s hardness allows it to resist wear and deformation effectively.
Pros: Steel is highly versatile, available in various grades, and can be heat-treated to enhance its properties.
Cons: It is generally more expensive than aluminum and can be more challenging to machine, requiring specialized tools and techniques.
For B2B buyers in Africa and South America, understanding the local availability of specific steel grades and compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 is critical. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of steel production, which may influence sourcing decisions.
How Does Brass Compare in Terms of Machinability and Application?
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It is often used in applications requiring good electrical conductivity, such as in connectors and fittings. Brass can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for plumbing and decorative items.
Pros: Brass offers a good balance of strength, machinability, and aesthetic appeal, often used in high-end products.
Cons: It is generally more expensive than aluminum and may not perform well under extreme conditions.
International buyers should be aware of the specific brass grades they require, such as C36000 for machining applications. Compliance with standards like ASTM B16 is also essential, especially for products intended for plumbing or electrical applications.
What Role Does Plastic Play in CNC Lathe Projects?
Plastic materials, such as acrylic and polycarbonate, are increasingly popular in CNC lathe projects due to their lightweight and versatile properties. They can be machined to create intricate designs and are often used in applications like prototypes, signage, and consumer products. Plastics can withstand a range of temperatures, but their mechanical strength is generally lower than metals.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective, easy to work with, and available in various colors and finishes.
Cons: They can be less durable than metals and may degrade under UV exposure or extreme temperatures.
For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and Europe, understanding the specific plastic grades and their compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 can enhance product quality and marketability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Lathe Projects
| Material | Typical Use Case for CNC Lathe Projects | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty machinery parts | Exceptional strength and durability | More expensive and challenging to machine | High |
| Brass | Electrical connectors and fittings | Excellent machinability and aesthetic appeal | Higher cost and limited performance in extreme conditions | Medium |
| Plastic | Prototypes and consumer products | Cost-effective and versatile | Less durable than metals | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for CNC lathe projects, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc lathe projects
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing CNC Lathe Projects?
Manufacturing CNC lathe projects involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality, precise components. Understanding these stages can aid B2B buyers in making informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Is Material Sourced and Prepared?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Suppliers often source raw materials such as metals (steel, aluminum, brass), plastics, or composites from reputable vendors. Material specifications must align with project requirements, including mechanical properties and tolerances.
Once materials are sourced, they undergo inspection to verify their quality and compliance with industry standards. Common practices include checking for surface defects, hardness, and chemical composition. This initial quality control (QC) step is crucial, as it sets the foundation for the entire manufacturing process.
How Are Components Formed Using CNC Lathes?
The forming stage is where CNC lathes come into play. These machines use computer numerical control to automate the cutting process, allowing for greater precision and repeatability. The primary techniques employed in this stage include:
- Turning: The workpiece rotates while cutting tools shape the material, creating cylindrical parts.
- Facing: The tool moves across the end of the workpiece to create a flat surface.
- Threading: A specialized tool creates threads on the exterior or interior of a component, essential for fasteners and fittings.
CNC lathes are capable of producing complex geometries that would be challenging to achieve with manual lathes. The integration of CAD/CAM software enhances design capabilities, allowing for rapid prototyping and adjustments as needed.
What Is the Assembly Process for CNC Lathe Projects?
After individual components are formed, the next stage is assembly. This can involve:
- Joining: Components may be welded, bolted, or glued together, depending on the project requirements.
- Integration: In some cases, parts manufactured on CNC lathes are combined with elements created through other machining processes, such as milling or grinding.
Effective assembly requires skilled labor and adherence to precise tolerances. Quality checks during this phase ensure that assembled products meet specifications and function as intended.
How Is Finishing Achieved in CNC Lathe Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetics and functional properties of the final product. Techniques include:
- Polishing: This process removes surface imperfections and enhances the shine of the material.
- Coating: Applying protective coatings can improve corrosion resistance and wear properties.
- Heat Treatment: This can alter the material’s hardness and strength, ensuring that the final product performs well under stress.
Finishing is critical, particularly for components used in demanding environments, such as aerospace and automotive applications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for CNC Lathe Projects?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the CNC lathe manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are fundamental for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes. ISO 9001 focuses on the quality management system (QMS) that organizations must implement to enhance customer satisfaction through effective process management.
Industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for the oil and gas sector, are equally important. These certifications demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements, enhancing trust among international buyers.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in CNC Lathe Manufacturing?
Quality checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, operators perform regular checks to monitor dimensions and tolerances, ensuring that any deviations are corrected promptly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection involves a comprehensive evaluation of the finished product, including functionality tests and dimensional checks.
Implementing these checkpoints helps minimize defects and ensures a high level of product integrity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are effective strategies:
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Requesting and reviewing supplier quality audit reports can provide insight into their QC processes. Audits should cover compliance with international standards and internal protocols. A supplier with a robust audit history is likely to maintain high-quality standards.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing processes. These inspections can be conducted at various stages, from material sourcing to finished product evaluations, ensuring transparency and reliability.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of the nuances in QC and certification requirements. Compliance with local regulations may vary, and understanding these differences is crucial for successful procurement.
For instance, European buyers must ensure that products comply with CE marking requirements, while those in the Middle East may need to adhere to specific local standards. Buyers should also consider the reputation and reliability of suppliers in their region to ensure that they can meet these diverse requirements.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions in CNC Lathe Procurement
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with CNC lathe projects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations. Prioritizing suppliers with robust QC practices and adherence to international standards will ultimately contribute to the success of their projects.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc lathe projects’
In the realm of CNC lathe projects, effective sourcing is crucial for ensuring quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. This checklist serves as a practical guide for B2B buyers seeking to procure CNC lathe projects, helping you navigate the complexities of supplier selection and project specifications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of a successful CNC lathe project. Identify the materials, dimensions, tolerances, and production volumes required for your project. A well-defined specification allows suppliers to provide accurate quotes and ensures that the final product meets your operational needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers with expertise in CNC lathe projects. Look for companies that specialize in your specific industry or project type. Utilize online resources, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of candidates that have a proven track record.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing, assess the capabilities of potential suppliers. Inquire about their equipment, technology, and workforce expertise. Ensure they have the necessary CNC lathes and tools to handle your project specifications effectively.
- Key considerations:
- Ask for details on their CNC machine models and configurations.
- Evaluate their production capacity and lead times to meet your deadlines.
Step 4: Request and Analyze Quotes
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotes. Analyze these quotes not just for pricing, but also for the scope of services included, such as design assistance, prototyping, and post-production support. A comprehensive quote will provide insight into the supplier’s understanding of your project requirements.
- Look for:
- Breakdown of costs for materials, labor, and overhead.
- Any additional services that may enhance the project.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your selected suppliers adhere to industry standards and regulations. Check for relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management, which can indicate a commitment to quality and consistency. This step is crucial for mitigating risks associated with production quality and compliance.
Step 6: Review Past Projects and Client Testimonials
Gain insight into a supplier’s reliability and quality by reviewing their past projects and client testimonials. Request case studies or examples of similar CNC lathe projects they have completed. This will help you assess their capability to deliver on your specific requirements.
- Inquire about:
- Challenges faced in past projects and how they were resolved.
- Feedback from previous clients regarding quality and service.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is vital throughout the sourcing process and project execution. Establish clear points of contact and preferred communication methods with your chosen supplier. Regular updates and feedback loops will help keep the project on track and address any issues promptly.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source CNC lathe projects that meet their operational needs while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc lathe projects Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Lathe Projects?
When evaluating the costs associated with CNC lathe projects, it’s essential to break down the cost structure into several key components:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts overall costs. Common materials used in CNC lathe projects include aluminum, steel, and various alloys. Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, availability, and quality. For instance, high-grade aerospace aluminum will command a premium over standard aluminum.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial for operating CNC lathes, especially for complex projects that require precision. Labor costs vary by region, with countries like Germany typically having higher wage standards compared to regions in Africa or South America. It’s important to account for both direct labor costs and any training expenses for operators.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. For international buyers, understanding the overhead costs in the supplier’s country can provide insights into overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling may be required for specific projects, which can add to initial costs. The lifespan of tools and their maintenance also affect long-term expenses. Investing in high-quality tools can reduce replacement frequency and improve production efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that products meet specifications and standards. This often requires additional resources, including testing equipment and personnel, contributing to overall project costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties should be considered. Incoterms play a vital role in defining responsibilities for shipping costs and risks.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their risks and ensure profitability. Understanding industry standards for margins can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Lathe Project Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC lathe projects, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower unit costs due to economies of scale. Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can also impact pricing, as suppliers may require a certain volume to justify production runs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom projects that deviate from standard offerings may incur additional costs. Detailed specifications can lead to variations in pricing based on the complexity of the design and the additional resources required.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Projects requiring high-quality materials or specific certifications (e.g., ISO standards) will generally have higher costs. Buyers should clarify these requirements early in negotiations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurance, while newer suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms can significantly impact total project costs. Different Incoterms can dictate who bears the cost of shipping, insurance, and customs duties, thus affecting the final price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in CNC Lathe Projects?
International B2B buyers can enhance cost efficiency through several strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing. Highlighting long-term partnership potential or bulk purchasing can lead to better terms.
-
Assessing Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase prices, consider long-term operational costs, including maintenance, tool replacements, and logistics. A lower upfront cost may not always equate to lower overall expenses.
-
Understanding Pricing Nuances for Different Regions: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should familiarize themselves with local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and trade regulations, as these can all affect pricing.
-
Supplier Diversification: Exploring multiple suppliers can help in understanding market prices and may lead to better deals. It also reduces dependency on a single source, which can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Conclusion
While the costs associated with CNC lathe projects can vary widely based on numerous factors, understanding the components and price influencers can help B2B buyers make informed decisions. Keeping a strategic approach to sourcing and procurement will not only optimize costs but also enhance project outcomes. Always consider seeking out multiple quotes and conducting thorough due diligence on suppliers to ensure the best value for your investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc lathe projects With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to CNC Lathe Projects
In the realm of machining and manufacturing, CNC lathe projects represent a versatile and efficient solution for precision part production. However, several alternative technologies and methods can achieve similar outcomes, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages. This analysis will compare CNC lathe projects with two viable alternatives: manual machining and 3D printing.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Cnc Lathe Projects | Manual Machining | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, repeatable production | Variable precision, dependent on operator skill | Moderate precision, suitable for complex geometries |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment; cost-effective for large runs | Lower initial costs but higher labor costs | Lower initial investment; material costs can vary widely |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires programming skills; setup time can be significant | Requires skilled labor; longer setup time | User-friendly software; quick setup but learning curve for new users |
| Maintenance | Requires regular calibration and tooling changes | Low maintenance if properly handled | Low maintenance; however, printer parts may need replacement |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of complex parts | Custom, one-off parts and repairs | Rapid prototyping and low-volume production of intricate designs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Manual Machining: Pros and Cons
Manual machining involves the use of traditional machine tools operated by skilled craftsmen. This method excels in producing custom, one-off parts where high precision is less critical. While the initial investment in equipment may be lower than CNC lathes, the costs can escalate due to labor expenses, as manual machining typically requires more time and skill. Moreover, the variability in performance can lead to inconsistencies in product quality, making it less suitable for high-volume production.
3D Printing: Pros and Cons
3D printing technology has revolutionized prototyping and production processes, enabling the creation of complex geometries that would be challenging with traditional methods. This approach is cost-effective for small production runs and allows for rapid design iterations. However, the precision of 3D printing may not match that of CNC lathe projects, especially for functional components requiring tight tolerances. Additionally, the range of materials compatible with 3D printing is still limited compared to machining methods, which may restrict its application in certain industries.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right production method hinges on the specific requirements of your project. CNC lathe projects are ideal for high-precision, high-volume production, making them a preferred choice for manufacturers focused on efficiency and consistency. In contrast, manual machining is more suited for custom jobs where flexibility is key, while 3D printing shines in rapid prototyping scenarios. B2B buyers should assess their production volume, precision requirements, and budget constraints to determine the most suitable solution that aligns with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc lathe projects
What Are the Key Technical Properties for CNC Lathe Projects?
Understanding the technical specifications of CNC lathe projects is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure product quality and compatibility. Here are some essential properties:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the specific classification of the metal being used, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or brass. Each material has unique properties regarding strength, machinability, and corrosion resistance. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade impacts the durability and performance of the final product, ensuring it meets industry standards and customer expectations.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In CNC machining, tight tolerances are often required to ensure parts fit together correctly. For international buyers, understanding tolerance levels is vital, as it affects the interchangeability of components, particularly in industries like automotive and aerospace, where precision is paramount.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture of a machined part, which can range from rough to smooth. The finish affects not only the aesthetic appeal but also the functionality, such as reducing friction and improving corrosion resistance. Buyers need to specify the required surface finish to ensure the parts meet their operational needs and customer satisfaction.
4. Cutting Speed and Feed Rate
Cutting speed is the speed at which the cutting tool moves through the material, while the feed rate is how quickly the tool advances into the workpiece. Both parameters influence the efficiency and quality of the machining process. Understanding these metrics allows buyers to optimize production rates and maintain consistent quality, ultimately affecting cost and lead times.
5. Tooling and Fixture Requirements
This specification includes the types of tools and fixtures needed for the machining process. Different projects may require specialized tools to achieve the desired results. For B2B buyers, knowing the tooling requirements is crucial for budgeting and ensuring that the necessary equipment is available for timely project execution.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in CNC Lathe Projects?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is important for B2B buyers to identify reliable suppliers and ensure product quality aligns with their brand standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for buyers, as it impacts inventory management and cost efficiency. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchasing strategy effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ is an essential step in the procurement process, allowing them to compare options and negotiate better deals.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping and freight. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B transactions, as they clarify who bears the risk and costs associated with the delivery of goods.
5. CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
CAD refers to the use of software to create precise drawings and technical illustrations. In CNC lathe projects, CAD files are essential for programming the lathe and ensuring accuracy. Buyers should consider suppliers’ capabilities in CAD to streamline the design and manufacturing process.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, foster effective communication, and optimize their CNC lathe projects for success.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc lathe projects Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing CNC Lathe Projects?
The CNC lathe projects sector is witnessing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands. Global drivers such as the increasing automation of manufacturing processes, the rise of Industry 4.0, and a growing emphasis on precision engineering are reshaping the landscape. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic sourcing decisions.
Emerging trends in the B2B tech landscape, such as the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) with CNC machinery, are enhancing operational efficiencies. Smart lathes equipped with sensors can provide real-time data on machine performance and product quality, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. This shift towards smarter manufacturing not only optimizes production but also helps in minimizing waste and improving overall product quality.
Another trend is the increasing demand for customized solutions. Buyers are seeking CNC lathe projects that can be tailored to specific requirements, driven by market differentiation and unique consumer needs. This has led to a rise in collaborative manufacturing platforms where B2B buyers can directly engage with suppliers and manufacturers to co-create projects.
Furthermore, international trade dynamics and geopolitical factors are influencing sourcing strategies. As supply chains become more complex, buyers must consider the reliability and stability of suppliers, especially in regions prone to economic fluctuations. Establishing strong partnerships with suppliers in various regions can mitigate risks and enhance supply chain resilience.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shape the Future of CNC Lathe Projects?
Sustainability is becoming an integral aspect of the CNC lathe projects sector. As environmental regulations tighten globally, B2B buyers are increasingly focusing on sourcing practices that minimize environmental impact. This includes selecting materials and processes that reduce carbon footprints and waste.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now more aware of the social implications of their sourcing decisions, seeking suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and transparent operations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming vital for suppliers aiming to attract environmentally-conscious buyers.
In terms of materials, there is a growing interest in ‘green’ alternatives. This includes the use of recyclable metals and eco-friendly coatings that not only meet aesthetic requirements but also contribute to sustainability goals. Suppliers who adopt such materials often find a competitive edge in the market as buyers increasingly prioritize eco-friendly options in their sourcing decisions.
Adopting sustainable practices not only enhances brand reputation but can also lead to cost savings in the long run. Efficient resource management and waste reduction can significantly lower operational costs, making sustainability a win-win for both buyers and suppliers in the CNC lathe projects sector.
How Has the CNC Lathe Projects Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the CNC lathe projects sector has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in manufacturing paradigms. Initially, traditional metal lathes were manual and labor-intensive, requiring skilled craftsmen to operate them. Over the decades, the introduction of CNC technology revolutionized the industry, enabling automation and precision that was previously unattainable.
The transition from manual to CNC lathes allowed for complex designs and higher production rates, catering to the growing demand for customized parts across various industries. This evolution has been further accelerated by the integration of digital technologies, including CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), allowing for seamless design-to-production workflows.
Today, CNC lathe projects are not just about metalworking; they encompass a wide range of applications from artistic creations to critical components in aerospace and automotive industries. As the sector continues to advance, the focus on efficiency, sustainability, and ethical sourcing will likely shape its future trajectory, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed and adaptable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc lathe projects
-
How do I select a reliable supplier for CNC lathe projects?
To choose a dependable supplier for CNC lathe projects, assess their industry reputation, experience, and client testimonials. Request references from previous customers, and verify their ability to meet your project specifications, including material quality and precision requirements. It’s also crucial to evaluate their production capabilities, lead times, and after-sales support. Engaging in direct communication can provide insights into their responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your needs. -
What customization options are available for CNC lathe projects?
Customization options for CNC lathe projects can vary significantly based on the supplier’s capabilities. Common customizations include specific dimensions, material choices, and surface finishes. Some suppliers may offer additional features, such as engraving or unique designs. When discussing your project, clearly outline your requirements and inquire about the supplier’s flexibility and past custom projects to ensure they can deliver exactly what you need. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC lathe projects?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC lathe projects can differ widely among suppliers, often ranging from a few units to several hundred, depending on the complexity and cost of production. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and inquire if they can accommodate smaller orders, especially for prototyping or initial runs. Understanding MOQs can help you manage inventory and budget effectively. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing CNC lathe projects?
Payment terms for CNC lathe projects typically include options like upfront deposits, milestone payments, or payment upon delivery. Standard practices may require a 30% deposit before production begins, with the remaining balance due upon completion or delivery. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk tolerance, and ensure that these terms are clearly documented in the purchase agreement to avoid any misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in CNC lathe projects?
To ensure quality assurance in CNC lathe projects, request detailed documentation on the supplier’s QA processes, including inspections and testing protocols. It’s beneficial to establish clear specifications and tolerances for your products. Consider arranging for third-party inspections or audits during production, and maintain open communication with the supplier throughout the process to address any concerns promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing CNC lathe projects?
When sourcing CNC lathe projects, logistics considerations include shipping methods, delivery times, and customs regulations. Discuss with your supplier their shipping options and whether they can handle logistics for international deliveries. Understanding import duties and taxes in your country is also crucial to avoid unexpected costs. Establishing a reliable logistics plan can help ensure timely delivery and minimize disruptions. -
What are the key benefits of using CNC lathes over traditional lathes?
CNC lathes offer significant advantages over traditional lathes, including higher precision, repeatability, and efficiency. They allow for complex shapes and designs to be machined with minimal human intervention, reducing the risk of errors. Furthermore, CNC lathes can operate continuously, optimizing production times and lowering labor costs. For businesses looking to scale operations or enhance product quality, investing in CNC lathe technology can yield substantial returns. -
How do I handle communication barriers when sourcing from international suppliers?
To effectively manage communication barriers with international suppliers, ensure clarity in your specifications and expectations by using clear, concise language. Consider using visual aids, such as drawings or prototypes, to convey your ideas more effectively. Utilizing professional translation services can also help bridge language gaps. Establishing regular communication channels, such as video calls or messaging apps, can foster better relationships and facilitate smoother project management.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Cnc Lathe Projects Manufacturers & Suppliers List
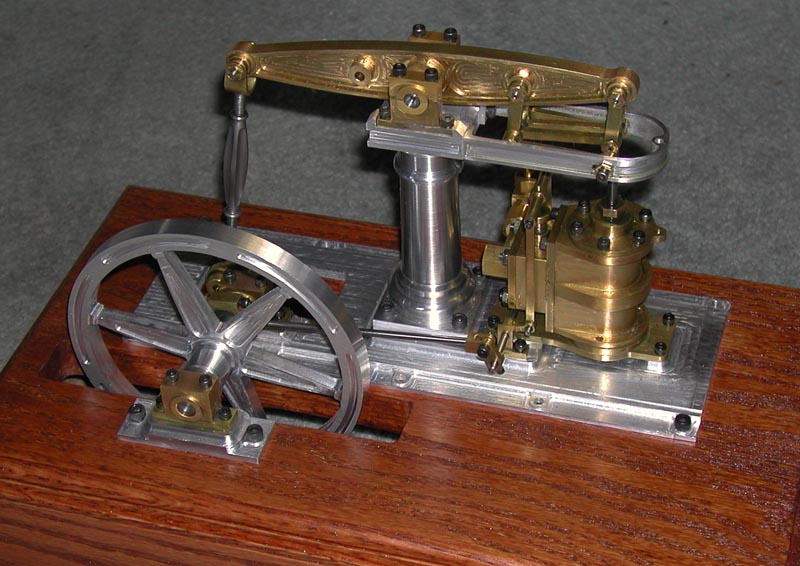
1. Summit MT – Metal Lathe Project Guide
Domain: summitmt.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: From Novice to Master – Metal Lathe Projects: An expansive list of projects for metal lathe users, categorized by skill level. Beginner projects include making rings, hammers, candlesticks, replica bullets, tap guides, cylindrical squares, and cups/goblets/bowls. Intermediate projects include slide hammers, toolmaker’s vises, bolts with captive rings, machinist’s scribes, and pens. The text explai…
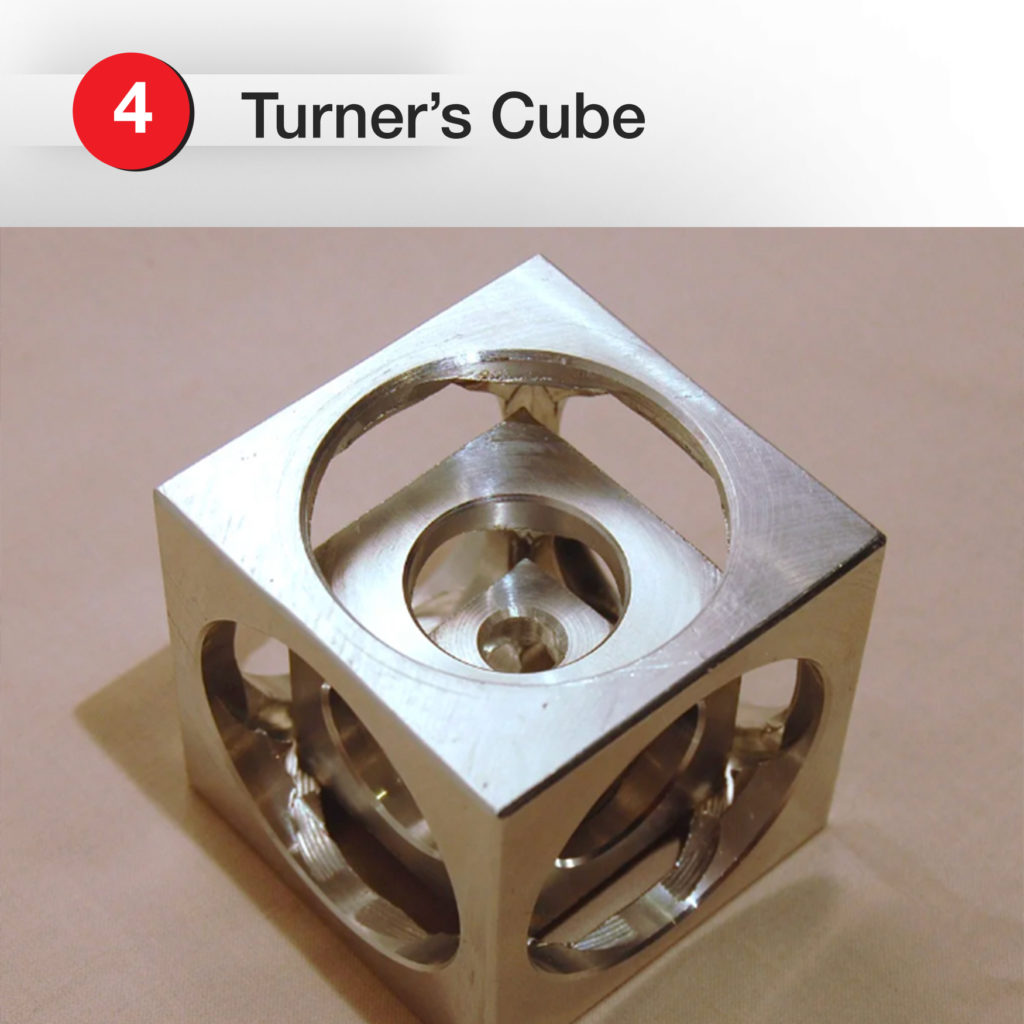
2. GoShoot.com – Precision Machined Metal Dice
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Precision Machined Metal Dice – Floating d6 and Fudge Dice; CNC machined ‘machinist cube’; All aluminium; Made on Tormach PCNC 1100; Socket Head cap screw press fit & aluminium handle; GoShoot.com Cube – Advanced Scotch Tape Dispenser; Homemade Mini Fly Cutter; Brass Shop Hammer; 9×20 Lathe Ball Turners & Knurlers.
3. Reddit – CNC Lathe Projects for High School Kids
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC Lathe Projects for high school kids, specifically using a Tormach 8L lathe. Suggested project ideas include making pens, metal snowmen, and chess pieces. Emphasis on teaching skills such as deep hole drilling, internal and external threading, turning a taper, knurling, and parting.
4. Tormach – CNC Project Library
Domain: tormach.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: CNC Project Library offers free CNC machining files and project ideas for hobbyists, educators, and professional machinists. Projects include: 1. CNC Fidget Spinner – a brass spinner designed by Tormach Brand Ambassador Caleb Kraft. 2. DIY Jack Stand – a tool for leveling machines. 3. Automotive MAF Sensor Relocation Part – allows relocation of the MAF sensor in Mitsubishi Evolution. 4. TTS Tighte…
5. South Bend – 13 x 6 Lathe
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: South Bend Lathes, 13 x 6 model, sold in 1945 to the War Battery Co. Kansas City, Missouri. Material preferences include CR steel, plastic, with no preference for aluminum and brass not being an option. Mention of a book titled ‘Machine Shop Projects’ containing 70 projects with drawings and step-by-step instructions.
6. Make It From Metal – Slide Hammer & Machinist’s Hammer
Domain: makeitfrommetal.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: 1. Slide Hammer: A tool for pulling 1/2 dowels from tight holes. BOM: Ø 2.0″ x 4-5/8″ long stainless (1 pc), Ø 0.50″ x 12-1/8″ long stainless (1 pc), Ø 1.0″ x 5/8″ long stainless (1 pc), 1/2″ E-clip (1 pc), 1/2-13 x 1″ long socket head set screw (1 pc).
2. Machinist’s Hammer: A modified hammer design with flats on the handle for better grip. BOM: Ø 1.25″ x 10.125″ long steel (1 pc), Ø 1.25″ x 2….
7. Hobby Machinist – DIY CNC Metal Lathe Project
Domain: hobby-machinist.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: DIY CNC metal lathe project, almost completed, requires fine tuning for concentricness. Uses NEMA 23 stepper motors with 3Nm (425oz.in) holding torque. Issues encountered include runout from the backplate and vibration during face cuts. Design considerations include reducing toolpost extension for improved rigidity.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc lathe projects
As the landscape of CNC lathe projects continues to evolve, the importance of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated. By carefully selecting suppliers and partners, businesses can ensure access to high-quality materials, advanced technology, and skilled expertise. This strategic approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters innovation and supports long-term growth in competitive markets.
For international B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the opportunity to leverage CNC lathe capabilities is significant. Engaging with reliable suppliers who understand local market dynamics can provide a competitive edge, enabling the production of intricate components and customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs.
Looking ahead, the integration of emerging technologies such as automation and AI in CNC lathe operations presents exciting possibilities. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about these advancements and consider partnerships that can enhance their production capabilities. By investing in strategic sourcing now, businesses can position themselves as leaders in their respective markets, ready to tackle the challenges of tomorrow and capitalize on new opportunities.