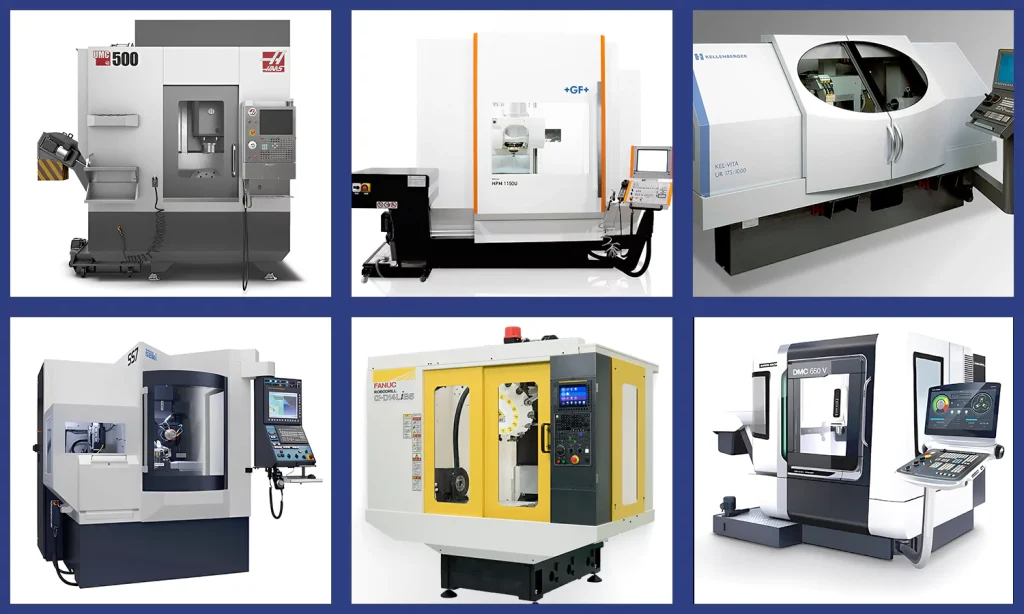
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc lathe brands
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing CNC lathe brands can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With a myriad of manufacturers and models available, understanding which CNC lathe will meet your specific production needs is crucial for optimizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This comprehensive guide addresses these challenges by exploring the diverse types of CNC lathes, their applications across various industries, and the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
From high-precision machines suited for the aerospace sector to robust models designed for heavy-duty manufacturing, the selection of the right CNC lathe can significantly impact your operational success. Our guide delves into the intricacies of each brand, detailing their unique features, performance metrics, and pricing structures. Furthermore, we provide insights into the procurement process, helping you navigate potential pitfalls and ensuring that you make informed purchasing decisions.
This resource is particularly valuable for B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia. By equipping you with the knowledge to assess various CNC lathe brands effectively, this guide empowers you to enhance your supply chain, optimize production capabilities, and ultimately drive business growth in a global market.
Understanding cnc lathe brands Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Turning Centers | Multi-tasking capabilities, integrated milling, and turning. | Aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. | Pros: Versatile, reduces setup time. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Swiss CNC Lathes | High precision, small parts machining, and automatic tool changers. | Watchmaking, electronics, and medical devices. | Pros: Exceptional accuracy, efficient for small parts. Cons: Limited to small workpieces. |
| Vertical CNC Lathes | Vertical spindle orientation, compact design. | Space-constrained workshops, small batch production. | Pros: Space-saving, ideal for certain geometries. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Horizontal CNC Lathes | Horizontal spindle layout, better chip management. | Heavy machining, large components in oil & gas. | Pros: Efficient for larger workpieces, better cooling. Cons: Requires more floor space. |
| CNC Lathes with Live Tooling | Equipped with live tooling for drilling and milling. | Complex parts in automotive and aerospace. | Pros: Increased functionality, reduces need for multiple machines. Cons: More complex maintenance. |
What Are CNC Turning Centers and Their B2B Suitability?
CNC turning centers are advanced machines that combine both turning and milling operations in a single setup. Their multi-tasking capabilities allow manufacturers to produce complex geometries efficiently, making them ideal for industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision and speed are crucial. When considering a CNC turning center, B2B buyers should evaluate their production volume needs and the complexity of parts to ensure they select a machine that meets their operational demands.
How Do Swiss CNC Lathes Meet Precision Needs?
Swiss CNC lathes are designed for high precision machining of small parts, often featuring automatic tool changers to enhance productivity. They excel in industries such as watchmaking and electronics, where tolerances are tight and production runs are often large. Buyers should consider the size of the parts they intend to produce, as Swiss lathes are best suited for small, intricate components. The investment in a Swiss CNC lathe can lead to significant long-term savings through efficiency and reduced waste.
What Advantages Do Vertical CNC Lathes Offer?
Vertical CNC lathes are characterized by their vertical spindle orientation, making them an excellent choice for operations where floor space is limited. These machines are suitable for small batch production and specific geometries, allowing for efficient machining of parts in tight spaces. B2B buyers should assess their shop layout and the types of parts they produce to determine if a vertical CNC lathe aligns with their production strategy.
Why Choose Horizontal CNC Lathes for Heavy Machining?
Horizontal CNC lathes are favored in heavy machining applications due to their robust design and efficient chip management system. They are particularly effective for large components in industries such as oil and gas. Buyers should consider the available floor space and the scale of their operations, as horizontal lathes typically require a larger footprint but offer enhanced performance for substantial workpieces.
What Are the Benefits of CNC Lathes with Live Tooling?
CNC lathes equipped with live tooling allow for simultaneous drilling and milling, significantly increasing the functionality of the machine. This feature is particularly beneficial for producing complex parts in the automotive and aerospace sectors. When purchasing, buyers should weigh the advantages of increased capabilities against the potential complexities in maintenance and operation, ensuring they have the necessary expertise to manage such advanced machinery.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc lathe brands
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Lathe Brands | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | Enhanced accuracy and reduced waste | Certifications for aerospace standards, reliable support |
| Automotive | Engine and transmission parts production | High-volume output with consistent quality | Availability of spare parts, after-sales service |
| Oil & Gas | Valve and pump housing fabrication | Durable and reliable components for harsh conditions | Material compatibility, adherence to safety regulations |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instrument production | High precision and compliance with health standards | Certifications (ISO, FDA), customization capabilities |
| Electronics | Housing for electronic components | Improved design flexibility and faster prototyping | Lead times, integration with CAD/CAM systems |
How Are CNC Lathe Brands Utilized in Aerospace Manufacturing?
CNC lathe brands are crucial in the aerospace industry for manufacturing precision components such as turbine blades, landing gear parts, and engine casings. The high accuracy of CNC lathes reduces material waste and enhances the quality of components, which is vital in an industry where safety and performance are paramount. International buyers should ensure that manufacturers hold relevant certifications, such as AS9100, which guarantees compliance with aerospace standards.
What Role Do CNC Lathes Play in Automotive Parts Production?
In the automotive sector, CNC lathes are utilized for producing intricate engine and transmission parts that require high precision and consistency. This technology enables manufacturers to achieve high-volume output while maintaining quality, which is critical in a competitive market. Buyers should consider the availability of spare parts and robust after-sales service to minimize downtime and ensure operational efficiency.
Why Are CNC Lathe Brands Important in Oil & Gas Applications?
The oil and gas industry relies on CNC lathes for fabricating durable valve and pump housings designed to withstand extreme conditions. The precision offered by CNC lathes ensures that these critical components operate reliably over extended periods. When sourcing CNC lathes for this sector, international buyers must prioritize material compatibility and adherence to safety regulations to mitigate risks associated with equipment failure.
How Are CNC Lathes Used in the Production of Medical Devices?
CNC lathes are essential in the medical device industry for producing surgical instruments and implants that require high precision and adherence to stringent health standards. The ability to customize components quickly allows manufacturers to respond to market demands effectively. Buyers in this sector should ensure that their suppliers have the necessary certifications, such as ISO 13485, which indicates compliance with medical device regulations.
What Benefits Do CNC Lathes Offer in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics industry, CNC lathes are employed to create housings for various electronic components, allowing for improved design flexibility and faster prototyping. This capability is crucial for companies looking to innovate and bring products to market quickly. Buyers should assess lead times and the ability of suppliers to integrate with existing CAD/CAM systems, which can significantly enhance workflow efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc lathe brands’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Precision and Quality Control in CNC Lathe Operations
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges when it comes to achieving the necessary precision and quality control in their CNC lathe operations. This issue can stem from various factors, including subpar machinery, inadequate training of operators, or lack of real-time monitoring systems. For example, a manufacturing company in Saudi Arabia may invest in a high-end CNC lathe but still struggle to meet the strict tolerances required for aerospace components. This leads to increased production costs, wasted materials, and ultimately, dissatisfied customers.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, buyers should prioritize sourcing CNC lathes from reputable brands known for their precision engineering, such as Yamazaki Mazak or DMG MORI. Investing in CNC lathes equipped with advanced features such as real-time monitoring and integrated quality control systems can significantly enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, it is crucial to implement comprehensive training programs for operators, focusing on best practices for machine setup and maintenance. This not only empowers the workforce but also minimizes the risk of human error. Establishing a feedback loop where operators can report issues will further enhance the machine’s precision over time.
Scenario 2: Navigating Complex Supply Chains for CNC Lathe Components
The Problem: International B2B buyers often encounter difficulties in managing complex supply chains for CNC lathe components. For instance, a company in South America may rely on multiple suppliers for tooling and replacement parts, leading to delays and inconsistencies in production schedules. This situation can be exacerbated by geopolitical factors or trade regulations, which can disrupt supply lines and impact manufacturing timelines.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should consider consolidating their supply chains by partnering with CNC lathe manufacturers that offer comprehensive packages, including tooling, maintenance, and support services. Establishing long-term relationships with a single supplier can enhance reliability and ensure that all components are compatible with the CNC lathe. Additionally, leveraging technology such as supply chain management software can provide greater visibility into inventory levels and lead times, allowing companies to forecast needs more accurately and avoid stockouts. Regular communication with suppliers about potential disruptions and contingencies can also help in maintaining seamless operations.
Scenario 3: Adapting to Rapid Technological Changes in CNC Machining
The Problem: The rapid pace of technological advancements in CNC machining poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers looking to stay competitive. Companies in Europe, for instance, may find themselves struggling to keep up with the latest software updates or machine capabilities, leading to inefficiencies and an inability to meet market demands. This can result in increased operational costs and lost opportunities in a fast-evolving industry.
The Solution: To effectively adapt to technological changes, buyers should prioritize investing in CNC lathe brands that emphasize continuous innovation and customer support. Brands like Haas and Okuma often provide regular software updates and access to training resources that can help operators stay informed about the latest advancements. Additionally, attending industry trade shows and participating in workshops can provide valuable insights into emerging technologies and best practices. Creating a culture of continuous learning within the organization encourages staff to embrace new technologies, ensuring that the company remains agile and competitive. Regular assessments of machinery and technology alignment with industry standards can also identify areas for improvement and investment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc lathe brands
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in CNC Lathes?
When selecting materials for CNC lathe applications, understanding the properties and performance characteristics is crucial. Below, we analyze four common materials: Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel, and Brass. Each material has its unique advantages and considerations that can significantly impact production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and end-product quality.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Versatile
Aluminum is known for its lightweight nature and excellent machinability, making it a popular choice in various industries. Key properties include a temperature rating of around 600°F and good corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, offers excellent thermal conductivity, and is relatively inexpensive compared to other metals. Its low density makes it suitable for applications requiring weight savings, such as aerospace components.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it is not as durable as steel, especially under high-stress conditions. Additionally, it can be more expensive than some lower-grade metals.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a wide range of media, including air and water, but may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
International Considerations: Buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for extruded aluminum and ensure that suppliers can provide certifications for quality assurance.
Steel: Strength and Durability
Steel is one of the most commonly used materials in CNC machining due to its high strength and durability. With a temperature rating exceeding 1,500°F, steel can withstand extreme conditions.
Pros: Steel is robust, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. It also offers excellent wear resistance and can be heat-treated for added strength.
Cons: The primary drawback is its weight, which can increase shipping costs and complicate handling. Additionally, steel may be more expensive to machine due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for high-stress applications, including automotive and industrial machinery, but may not be ideal for environments prone to corrosion unless treated.
International Considerations: Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel and ensure that their suppliers meet international quality certifications.
Stainless Steel: Corrosion Resistance and Strength
Stainless steel combines the strength of steel with enhanced corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments. It typically has a temperature rating of around 1,200°F.
Pros: Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for medical, food processing, and marine applications. Additionally, stainless steel can maintain its strength at high temperatures.
Cons: The cost of stainless steel can be significantly higher than that of regular steel or aluminum. It also requires specialized tooling for machining due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a variety of media, including corrosive substances, making it ideal for chemical processing applications.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 is essential, especially for industries with strict hygiene and safety requirements.
Brass: A Blend of Machinability and Aesthetics
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, known for its excellent machinability and attractive appearance. It typically has a temperature rating of around 400°F.
Pros: Brass is easy to machine, making it a favorite for intricate designs. It also has good corrosion resistance and is often used in decorative applications.
Cons: While durable, brass is softer than steel and may not withstand high-stress applications. Additionally, it can be more expensive than aluminum.
Impact on Application: Brass is often used in plumbing fittings and electrical connectors due to its conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B16 for brass fittings and verify the alloy composition for specific applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Lathe Brands
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc lathe brands | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components | Lightweight and excellent machinability | Less durable under high stress | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty machinery | High strength and wear resistance | Heavy and costly to machine | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Medical and food processing equipment | Corrosion resistance and strength | Higher cost and requires special tooling | High |
| Brass | Plumbing fittings and electrical parts | Excellent machinability and aesthetics | Softer than steel, limited stress resistance | Medium |
This analysis provides a foundational understanding for international B2B buyers in selecting the right materials for their CNC lathe applications, ensuring compliance with relevant standards while optimizing performance and cost.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc lathe brands
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of CNC Lathes?
The manufacturing of CNC lathes is a complex process that typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is critical to ensure that the final product meets the high precision and quality standards required in various industries.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, which are often high-grade metals such as steel or aluminum. The materials are then cut to size, cleaned, and inspected for defects. This step is crucial as the quality of the raw materials directly impacts the performance and durability of the CNC lathe.
-
Forming: In this phase, the prepared materials undergo various machining processes, including turning, milling, and drilling, using CNC technology. Advanced techniques such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) are utilized to ensure precision. The use of automated tools allows for consistent replication and reduction of human error, which is essential for achieving tight tolerances.
-
Assembly: After forming, the components are assembled. This stage may include the integration of electronic systems, motors, and control units. Manufacturers often employ advanced assembly techniques, including modular assembly, to streamline the process and enhance efficiency. Workers typically use real-time monitoring systems to track progress and quality during assembly.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves surface treatment and finishing processes such as polishing, coating, or anodizing. These treatments not only improve the aesthetic appearance of the CNC lathe but also enhance its corrosion resistance and overall durability. Quality checks are performed to ensure that the final product meets specifications before it is packaged and shipped.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in CNC Lathe Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of CNC lathe manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. The following are essential components of the QA process:
-
Adherence to International Standards: Most reputable CNC lathe manufacturers comply with international quality standards such as ISO 9001. This standard outlines a framework for consistent quality management systems, focusing on customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Industry-specific certifications, like CE marking for compliance in Europe or API standards for the oil and gas sector, further enhance credibility.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Throughout the manufacturing process, several quality control checkpoints are established:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet the specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted at various stages to detect any deviations from quality standards.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the finished product undergoes a comprehensive inspection to verify that it meets all specifications and performance criteria. -
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods are employed to assess the functionality and performance of CNC lathes. These may include:
– Dimensional Checks: Using precision measuring instruments to ensure components meet specified dimensions.
– Functional Testing: Running the CNC lathe under operational conditions to verify performance and reliability.
– Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection are used to detect internal defects without damaging the components.
What Are the Best Practices for B2B Buyers to Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are some best practices:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Buyers should assess not only the manufacturing facilities but also the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and certifications.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality assurance reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. Reviewing these documents helps buyers understand the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These organizations can conduct inspections at various stages of production and provide certification of compliance with relevant standards.
-
Understand QC Certification Nuances: Different regions may have specific quality certifications that are critical for doing business. For example, CE marking is essential for products sold in Europe, while compliance with API standards is crucial for suppliers in the oil and gas industry. Buyers should ensure that suppliers possess the necessary certifications for their target markets.
How Can International B2B Buyers Ensure Consistent Quality in CNC Lathes?
To maintain a consistent quality of CNC lathes from suppliers, international buyers should adopt a proactive approach:
-
Establish Clear Specifications: Providing detailed specifications and quality expectations upfront can help suppliers understand the requirements and reduce the risk of defects.
-
Foster Long-Term Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better communication and collaboration on quality assurance efforts. Long-term partnerships often result in suppliers being more invested in meeting quality expectations.
-
Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Regularly providing feedback on the quality of delivered products can help suppliers identify areas for improvement. Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement can enhance the overall quality of CNC lathes.
By understanding the intricacies of manufacturing processes and quality assurance in CNC lathe production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select suppliers who meet their high standards for quality and reliability. This knowledge not only enhances procurement strategies but also contributes to successful partnerships in the global manufacturing landscape.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc lathe brands’
To successfully procure CNC lathe brands, B2B buyers must follow a systematic approach. This guide outlines essential steps to ensure informed decisions, leading to optimal investment and operational efficiency.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you start sourcing, it’s critical to have a clear understanding of your technical requirements. Determine the materials you’ll be working with, the size of the components, and the desired precision levels. This clarity will help narrow down your options and ensure that you select a CNC lathe that aligns with your production goals.
2. Research Leading CNC Lathe Brands
Familiarize yourself with the top CNC lathe manufacturers in the market. Brands like Yamazaki Mazak, DMG MORI, and Haas have established reputations for quality and innovation. Look for reviews, case studies, and industry reports to understand their strengths and weaknesses in relation to your specific needs.
3. Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify the certifications and standards that potential suppliers adhere to. Look for ISO certifications or specific industry-related qualifications that indicate a commitment to quality and safety. This step is essential in ensuring that you engage with reputable manufacturers who meet international standards.
4. Assess After-Sales Support and Service
Inquire about the after-sales services provided by the manufacturer. Strong support can include installation, training, maintenance, and timely spare parts availability. Reliable after-sales support is vital for minimizing downtime and ensuring that your CNC lathe operates smoothly post-purchase.
5. Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Solicit detailed quotes from multiple suppliers, ensuring that they include all costs associated with the purchase, such as shipping and installation. Comparing pricing alongside features and support will provide a clearer picture of the value each supplier offers. Remember, the cheapest option may not always be the best in terms of quality and service.
6. Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Tours
If possible, arrange site visits to the manufacturers’ facilities or request virtual tours. Observing the production process can provide insights into their operational capabilities and quality control measures. This step enhances your confidence in the supplier’s ability to meet your specifications.
7. Check References and Client Feedback
Before making a final decision, ask for references from previous clients who have purchased similar CNC lathes. Speak directly to these clients about their experiences regarding the machine’s performance and the supplier’s responsiveness. This firsthand feedback can be invaluable in assessing the reliability of both the machine and the supplier.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing CNC lathe brands with confidence, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc lathe brands Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Lathe Manufacturing?
When sourcing CNC lathes, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-grade steel or specialized alloys used in CNC lathe production may lead to higher upfront costs but can enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, influenced by local wage standards and the skill level required for assembly and quality control. Countries with a highly skilled workforce may demand higher wages, affecting the overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, factory maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, directly affecting the final price.
-
Tooling: The cost of tools required for CNC lathe production can be substantial. Custom tooling designed for specific applications can add to the initial investment but may improve operational efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures that the machines meet industry standards. While this adds to the cost, it can prevent costly failures and downtime in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary significantly based on the destination, size, and weight of the CNC lathe. International buyers should account for these costs in their total sourcing budget.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin, which can vary based on brand reputation and market demand. Recognizing the balance between cost and quality is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Lathe Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of CNC lathes, which international buyers should consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger orders, so negotiating MOQ can be beneficial.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price hikes during the manufacturing process.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) often come at a premium. Buyers must weigh the benefits of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and geographic location can impact pricing. Established brands may charge more due to their proven track record and service support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for cost management. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, influencing total landed costs.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to substantial savings:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Before negotiations, research pricing trends and benchmarks for similar CNC lathes. This knowledge empowers buyers during discussions.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO, which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operating costs, and potential downtime. This holistic view can justify a higher upfront investment if it leads to lower long-term costs.
-
Flexibility in Payment Terms: Offering flexible payment terms can make a deal more attractive for suppliers. This might include partial payments upon delivery or extended payment periods.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Regular communication and trust can facilitate smoother negotiations.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers should be mindful of specific pricing nuances when sourcing CNC lathes:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can significantly affect pricing. Buyers should consider locking in rates or negotiating in a stable currency to mitigate risks.
-
Regulatory and Tariff Implications: Import tariffs and regulations can add to the cost. Understanding local laws and potential duties is crucial to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varied negotiation styles and business practices. Being culturally aware can enhance communication and foster better deals.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of cost components, price influencers, negotiation tactics, and international pricing nuances will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing CNC lathes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc lathe brands With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to CNC Lathe Brands
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, B2B buyers are increasingly exploring alternatives to traditional CNC lathe brands. These alternatives can offer different benefits in terms of performance, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility. This section will compare CNC lathe brands against two viable alternatives: manual lathes and 3D printing technology. Each option presents unique advantages and challenges, making it crucial for international buyers to assess which solution best aligns with their operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Lathe Brands | Manual Lathes | 3D Printing Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and automation | Moderate precision, skill-dependent | Variable precision, material-dependent |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront costs | Variable costs based on materials |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators and setup | Simple setup, but requires training | User-friendly, minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Lower maintenance, but more manual work | Minimal maintenance, but technology-dependent |
| Best Use Case | High-volume, complex parts production | Small-scale, custom jobs | Rapid prototyping, complex geometries |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Manual Lathes?
Manual lathes represent a traditional method of machining that relies on the operator’s skill to perform various tasks. The primary advantage of manual lathes is their lower initial cost compared to CNC lathes, making them accessible for small businesses or startups. They are particularly effective for low-volume, custom jobs where flexibility is essential. However, the downside is that the precision and consistency of output can vary significantly depending on the operator’s skill. Additionally, they require more labor-intensive processes, which can affect productivity.
How Does 3D Printing Technology Compare to CNC Lathes?
3D printing technology is revolutionizing manufacturing by allowing for complex geometries and rapid prototyping. One of the significant advantages of 3D printing is its ability to produce intricate designs that may be challenging or impossible to achieve with CNC lathes. Additionally, 3D printing can be more cost-effective for small production runs due to reduced waste and material costs. However, the technology does come with limitations, such as slower production speeds for larger items and dependency on specific materials, which may not meet the same durability standards as machined components.
Conclusion: Which Solution Should a B2B Buyer Choose?
Choosing the right machining solution requires a thorough understanding of operational needs, production volume, and budget constraints. For high-volume production with complex parts, CNC lathes are often the preferred choice due to their precision and automation capabilities. Manual lathes may be suitable for smaller operations focusing on custom work, while 3D printing stands out for rapid prototyping and unique designs. B2B buyers should consider their specific manufacturing requirements, including desired output quality, cost implications, and available technical expertise, to select the most appropriate solution for their business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc lathe brands
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Lathe Brands?
CNC lathes are essential tools in modern manufacturing, and understanding their technical specifications is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are several critical specifications that influence purchasing decisions:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a CNC lathe determines its durability, resistance to wear, and overall performance. Common materials include cast iron, steel, and aluminum alloys. For businesses, choosing the right material grade can significantly affect the lifespan of the machine, maintenance costs, and the quality of the final product. A durable material helps minimize downtime and repair expenses, ensuring a more efficient production process.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension. In CNC lathes, tighter tolerances lead to higher precision and better product quality. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels is vital, especially in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is critical. Selecting a CNC lathe that meets specific tolerance requirements can enhance product reliability and customer satisfaction.
3. Spindle Speed
Spindle speed is a measure of how fast the spindle can rotate, typically expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM). Higher spindle speeds allow for faster machining, which can lead to increased productivity. However, this must be balanced against the type of material being machined and the required finish quality. B2B buyers should consider the spindle speed capabilities of a CNC lathe to ensure it aligns with their production goals and material specifications.
4. Control System
The control system of a CNC lathe dictates how the machine interprets instructions from CAD/CAM software. Common systems include Fanuc, Siemens, and Haas. A sophisticated control system enhances usability, precision, and integration with other machinery. For international buyers, understanding the control system’s compatibility with existing equipment is crucial for seamless operations and maximizing ROI.
5. Maximum Turning Diameter and Length
These specifications define the largest diameter and length of material that can be processed on the lathe. Understanding these limits is essential for manufacturers who work with larger components. Selecting a CNC lathe with adequate turning capacity ensures that businesses can handle a variety of projects without needing additional machinery, optimizing space and costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Lathe Purchasing?
Navigating the world of CNC lathe brands requires familiarity with industry-specific terminology. Here are several essential terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the CNC lathe industry, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of machines. Purchasing from reputable OEMs often ensures better support and parts availability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. For CNC lathes, this can affect purchasing decisions, particularly for smaller manufacturers. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their budgets and inventory accordingly, ensuring they do not overcommit financially.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer submits to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. For CNC lathe procurement, issuing an RFQ helps buyers gather competitive offers, enabling informed decision-making. It is a vital step in the sourcing process, particularly for larger purchases.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa or South America, understanding Incoterms is crucial to avoid unexpected costs and ensure smooth logistics during the purchase of CNC lathes.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. In the CNC lathe market, shorter lead times can enhance a company’s responsiveness to market demands. Buyers should consider lead times in their procurement strategy to maintain production schedules and avoid delays.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc lathe brands Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in CNC Lathe Brands?
The CNC lathe market is experiencing transformative growth driven by several global factors. Rapid industrialization in emerging economies, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, is propelling demand for advanced manufacturing technologies. Countries such as Vietnam and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in modern manufacturing capabilities, which increases the need for efficient and precise machinery like CNC lathes. Moreover, the ongoing digital transformation across industries is pushing manufacturers toward integrating smart technologies, including IoT and AI, into their CNC systems. This shift enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and improves precision, making advanced CNC lathe brands more appealing to international buyers.
Another significant trend is the customization of CNC lathes to meet specific industry requirements. Manufacturers are increasingly offering tailored solutions, which can include software integration, automation features, and specialized tooling. This trend is particularly relevant for sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices, where precision and adaptability are crucial. Furthermore, B2B buyers are increasingly focused on supplier reliability and service support, leading to a preference for brands that offer comprehensive after-sales services and technical assistance.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the CNC Lathe Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the CNC lathe sector. Environmental impact assessments are now integral to sourcing decisions, with companies seeking to partner with manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices. This includes reducing waste in production processes, utilizing energy-efficient technologies, and minimizing carbon footprints. Many CNC lathe brands are responding by adopting eco-friendly manufacturing techniques and investing in renewable energy sources for their operations.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, as businesses increasingly recognize the importance of transparent supply chains. Buyers are looking for suppliers who provide documentation of ethical practices, including fair labor conditions and responsible material sourcing. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential credentials for CNC lathe brands aiming to establish credibility and trust in the marketplace. Additionally, the trend toward using recycled materials and sustainable components in machine manufacturing is on the rise, allowing companies to appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
What Is the Historical Context Behind CNC Lathe Development?
The CNC lathe has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Originally, lathes were purely mechanical devices operated by skilled machinists. The advent of computer numerical control technology revolutionized this sector, enabling automation and precision that were previously unattainable. Early CNC lathes used simple programmable logic, but advancements in software and hardware have led to highly sophisticated systems capable of complex operations.
Today, major players in the CNC lathe market, such as Yamazaki Mazak and DMG MORI, are at the forefront of innovation, incorporating smart technologies and data analytics into their machines. This evolution reflects a broader trend in manufacturing toward greater efficiency, adaptability, and sustainability, setting the stage for a future where CNC lathes will play an even more critical role in global production capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc lathe brands
-
How do I choose the right CNC lathe brand for my business needs?
Selecting the right CNC lathe brand involves evaluating several key factors, including your specific machining requirements, production volume, and budget. Start by assessing the technical capabilities of various brands, such as precision, speed, and automation features. Consider the manufacturer’s reputation and customer support services, as well as the availability of spare parts and service in your region. Reading customer reviews and seeking recommendations from industry peers can also provide valuable insights into the reliability and performance of different brands. -
What is the best CNC lathe brand for small to medium enterprises?
For small to medium enterprises, brands like Haas and Hardinge are often recommended due to their affordability and user-friendly interfaces. These brands offer a range of CNC lathes that balance performance and cost, making them suitable for businesses with limited budgets. Additionally, they provide strong customer support and a wide network for service and parts, essential for minimizing downtime. Always assess your specific production needs and consult with suppliers to ensure the chosen brand aligns with your operational goals. -
What factors should I consider when vetting CNC lathe suppliers?
When vetting CNC lathe suppliers, focus on their manufacturing capabilities, quality certifications, and customer references. Check their experience in your industry and whether they can customize machines to meet your specific needs. It’s also crucial to evaluate their after-sales support, including warranty terms, maintenance services, and response times. A reliable supplier should have a transparent communication process and be willing to provide a detailed service agreement to ensure you receive the support you need throughout the machine’s lifecycle. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC lathes?
Minimum order quantities for CNC lathes can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the specific machine model. Some manufacturers may offer single-unit purchases, while others may require orders of five or more machines to secure bulk pricing. It’s essential to discuss MOQs with potential suppliers and explore whether they offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially for new businesses or those testing the market. Understanding the MOQ can help you plan your budget and inventory management effectively. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by CNC lathe suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely among CNC lathe suppliers, but they typically include options such as upfront payment, installment plans, or financing solutions. Many suppliers may require a deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due upon delivery or installation. It’s advisable to negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow and financial capabilities. Additionally, inquire about any available financing options or discounts for early payments to optimize your purchasing strategy. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when purchasing CNC lathes?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing CNC lathes, request documentation of quality certifications such as ISO 9001 from the manufacturer. Ask for detailed specifications and test reports for the machines you are considering. It is also beneficial to visit the manufacturing facility if possible or request a virtual tour to observe their production processes. Establishing clear communication with the supplier about your QA expectations and conducting thorough inspections upon delivery will further help maintain the quality standards you require. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC lathes?
When importing CNC lathes, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial machinery to ensure smooth transport. Be aware of potential tariffs and import regulations in your country that could affect costs. It’s also important to plan for the machine’s installation and setup upon arrival, including any necessary training for your staff on its operation and maintenance. -
How do I assess the long-term support offered by CNC lathe brands?
Assessing long-term support from CNC lathe brands involves researching their customer service track record and the availability of spare parts. Look for brands that have a global support network, ensuring prompt assistance regardless of your location. Evaluate warranty conditions and the manufacturer’s commitment to ongoing maintenance services. Engaging with existing customers through forums or industry events can provide firsthand insights into the brand’s reliability and responsiveness in after-sales support.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Cnc Lathe Brands Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Makino – Impressive Graphics
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Most trusted CNC machine brands mentioned: Makino, Okuma, Haas, DMG Mori, Mazak. Key points: Makino is noted for impressive graphics; Okuma lathes are described as invincible and reliable; Haas is considered a good starting machine but may not last long under heavy use; DMG Mori is recognized for quality; Japanese brands are generally viewed positively.
2. CNC Machine Brands – Key Products
Domain: matterhackers.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: CNC Machine Brands available at MatterHackers include: APSX, Carbide 3D, Inventables, LDO Milo, WAZER, Laguna Tools, Shaper Tools, Snapmaker, and TwoTrees. Key products include: APSX-NANO Desktop CNC Swiss Lathe ($13,250), Carbide 3D Nomad 3 CNC Machine (Bamboo, White, Gray) at $2,800 each, Carbide 3D Shapeoko 4 CNC Router (various models) ranging from $2,150 to $2,480, and Snapmaker 2.0 A350T Mod…
3. CNC Machine Compatibility – Complete Manufacturer List
Domain: bobcad.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Complete List of Compatible CNC Machine Manufacturers: ABCTech, Brother, EMC, HoneyBee, Mitsubishi, Romero, Testra, Ability Systems, Bridgeport, Emco, Hurco, Mori-Seki, Sabre, Thermwood, Acramatic, Burny, EZ, Hust, NC Studio, Seib-Meyer, Torchmate, ACS, Camsoft, Fadal, Hycut, Nee, Selexx, Tormach, Acu-Rite, Centroid, Fanuc, Hypertherm, Nice, Sharanoa, Toshiba, Adtech, Centurion, FlashCut, Hyundai,…
4. TSINFA – CNC Lathes & Milling Machines
Domain: tsinfa.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Top 27 CNC Lathe Manufacturers in the World: 1. TSINFA – Founded in 2005, leading CNC lathe manufacturer in China, offers CNC milling machines, CNC turning machines, CNC pipe threading lathes, universal milling machines, turret milling machines, hydraulic presses, and manual lathes. 2. Okuma – Established in 1898, leading CNC machine factory in Japan, diverse clientele in aviation, machinery, elec…
5. Uptive MFG – Advanced Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: uptivemfg.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining, Rapid Prototyping, Additive Manufacturing, Sheet Metal Fabrication, Injection Molding, Tooling, Post Processing & Finishing. Materials: Metals, Polymers, Composites. Capabilities: CNC milling (3, 4, or 5-axis), CNC turning (2-to-8 axis, Swiss Turning), CNC prototyping (various materials including Teflon, Titanium), Additive manufacturing (no tooling, design freedom), Sheet metal fab…
6. CNC Machines – Used Milling & Lathes
Domain: cncmachines.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Used CNC Machine Brands In Stock – CNCMachines.com offers a variety of used CNC machines including milling machines, CNC lathes, and machining centers. Key brands include Haas, Mazak, DMG Mori Seiki, Doosan, Hurco, Fadal, FANUC, Mori Seiki, Tsugami, Stratasys, Makino, MultiCam, AMADA, Brother, Tormach, Daewoo, Flow Waterjet, Matsuura, Laguna Tools, Milltronics, Ganesh Machinery, STAR, Toyoda, Hwac…
7. Star CNC – Swiss-type Automatic Lathes
Domain: starcnc.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Star CNC – Swiss-type Automatic Lathes, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. CNC Lathe – Prototyping and Production Recommendations
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: CNC Lathe Recommendations:
– Intended Use: Prototyping, potential for production
– Key Features Desired:
– Horsepower: 7.5-15 hp
– Voltage: 230v, 3-phase
– Between Centers: 20+ inches
– Bar Capacity: 2+ inches
– Turret: Nice to have, not required
– Control: Decent control with conversational and G-code programming
– Size: Fits through an 8′ x 8′ garage door
– Footprint: Smaller tha…
9. ProtoTool – CNC Machines
Domain: prototool.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: CNC machines are automatic power tools used in industrial manufacturing for operations such as turning, milling, engraving, cutting, drilling, grinding, welding, spinning, and winding. They are controlled by a computer using CAD/CAM software and G code, allowing for precision manufacturing of components and parts. Key types of CNC machines include: 1. Milling machines 2. CNC Lathes 3. CNC Routers …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc lathe brands
In the evolving landscape of CNC lathe manufacturing, strategic sourcing has become paramount for international B2B buyers. By prioritizing brands such as Yamazaki Mazak, DMG MORI, and Haas, companies can leverage cutting-edge technology, ensuring high precision and efficiency in their operations. It’s crucial to assess not just the machinery’s capabilities but also the support infrastructure and technological advancements that each brand offers.
Investing in reliable CNC lathe brands can lead to significant long-term benefits, including reduced downtime, enhanced production capabilities, and improved product quality. Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must evaluate their unique manufacturing needs and market conditions when selecting suppliers. This tailored approach will optimize procurement strategies and ultimately drive business growth.
Looking ahead, the CNC lathe market is poised for innovation, with trends in automation and data integration shaping the future. As you consider your next investment, engage with reputable manufacturers and explore collaborative opportunities that align with your strategic goals. Equip your business with the best tools available, and unlock the full potential of your manufacturing capabilities.