Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc laser marking
Navigating the global market for CNC laser marking can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses seek to invest in efficient marking solutions that enhance traceability and brand integrity, the challenge of sourcing the right equipment becomes paramount. This guide aims to demystify CNC laser marking by providing a comprehensive overview of the various types of machines available, their applications across different industries, and critical insights on supplier vetting and cost considerations.
Understanding the nuances of CNC laser marking technology is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. From fiber and UV lasers to pulsed and continuous wave options, each type offers unique benefits depending on your specific needs. Furthermore, this guide delves into the practical applications of laser marking, including engraving, etching, and marking for compliance, which are vital for industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare.
By equipping international buyers with actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of the CNC laser marking market confidently. Whether you’re in Brazil or Nigeria, the knowledge contained within these pages will help you identify reliable suppliers, assess pricing structures, and ultimately choose the right CNC laser marking solutions to elevate your business operations.
Understanding cnc laser marking Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Laser | High speed, precision, and versatility; ideal for metals | Electronics, automotive, aerospace, and medical | Pros: Fast processing, minimal maintenance. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| CO2 Laser | Excellent for organic materials and non-metals; versatile | Wood, acrylic, glass, and textiles | Pros: Cost-effective for non-metals. Cons: Slower than fiber lasers. |
| UV Laser | Short wavelength ideal for delicate materials; minimal heat-affected zone | Medical devices, packaging, and electronics | Pros: High precision, less thermal impact. Cons: Limited to specific materials. |
| Green Laser | Effective for marking on metals and plastics; high absorption rates | Jewelry, electronics, and medical components | Pros: Clean, precise markings. Cons: More expensive than CO2 lasers. |
| Pulsed Laser | Produces high-energy bursts; suitable for deep engraving | Industrial parts, automotive, and tooling | Pros: Deep engraving capabilities. Cons: Slower marking speed. |
What are the characteristics of Fiber Laser Marking?
Fiber lasers are known for their efficiency and speed, making them a preferred choice for marking metals and some plastics. They utilize a solid-state laser source, which results in minimal maintenance and operational costs. The ability to deliver high precision and consistency makes fiber lasers ideal for industries such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, and medical. When considering a fiber laser marking machine, buyers should evaluate the initial investment against long-term operational savings and the specific materials they intend to work with.
How does CO2 Laser Marking differ from other types?
CO2 lasers are particularly effective for marking organic materials and non-metals, such as wood, acrylic, and glass. They operate at a longer wavelength, which allows them to engrave and cut with high efficiency. This type of laser is often more cost-effective for applications involving non-metal materials. However, buyers should note that CO2 lasers typically have a slower marking speed compared to fiber lasers. It’s essential for B2B buyers to assess their material needs and production speed requirements when selecting a CO2 laser marking system.
Why choose UV Laser Marking for specific applications?
UV lasers are distinguished by their short wavelength, which provides high precision and is ideal for marking delicate materials without causing thermal damage. This makes them suitable for applications in medical device manufacturing, packaging, and electronics, where fine details and minimal heat-affected zones are critical. Buyers should consider the specific requirements of their projects, as UV lasers tend to be more expensive and are limited to certain materials. Understanding the balance between precision and cost is vital for informed purchasing decisions.
What advantages do Green Lasers offer in marking?
Green lasers are designed for high absorption rates in metals and certain plastics, making them effective for applications in jewelry, electronics, and medical components. They produce clean and precise markings, which can enhance product branding and traceability. However, the cost of green laser systems can be higher than that of CO2 lasers. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of high-quality markings against their budget constraints and the specific materials they plan to work with.
In what scenarios are Pulsed Lasers most effective?
Pulsed lasers generate high-energy bursts that are particularly effective for deep engraving, making them suitable for industrial parts, automotive components, and tooling applications. They allow for detailed engravings and are ideal for materials requiring significant penetration. Buyers should consider the slower marking speeds of pulsed lasers and whether their production needs align with the capabilities of this technology. Understanding the trade-offs between speed and engraving depth is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their production processes.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc laser marking
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Laser Marking | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Marking of VINs and part numbers on components | Enhances traceability and compliance with regulations | Consider machine compatibility with various materials |
| Electronics | Marking of serial numbers and QR codes on devices | Improves inventory management and customer support | Look for machines with high-speed capabilities |
| Medical Devices | Marking of inspection and lot numbers on devices | Ensures regulatory compliance and product safety | Verify the machine’s precision and material compatibility |
| Aerospace | Marking of components with aerospace standards | Increases accountability and traceability in manufacturing | Assess the durability of markings under extreme conditions |
| Jewelry and Fashion | Custom engraving of designs and logos on products | Enhances brand visibility and customer personalization | Evaluate the machine’s versatility for different materials |
How is CNC Laser Marking Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, CNC laser marking is employed to engrave Vehicle Identification Numbers (VINs) and part numbers directly onto components. This application not only enhances traceability but also ensures compliance with stringent regulations governing vehicle manufacturing. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should consider sourcing machines that can handle various materials like metals and plastics commonly used in automotive parts.
What is the Role of CNC Laser Marking in Electronics?
CNC laser marking in the electronics industry is crucial for marking serial numbers, barcodes, and QR codes on devices. This application aids in improving inventory management and facilitates customer support through easy identification of products. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should prioritize machines that offer high-speed marking capabilities to keep pace with the fast-moving electronics market.
Why is CNC Laser Marking Important for Medical Devices?
In the medical device industry, CNC laser marking is utilized for engraving inspection and lot numbers on products. This practice is vital for ensuring regulatory compliance and enhancing product safety. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the laser marking machines they choose offer high precision and compatibility with a range of materials, including those that are sensitive to heat.
How Does CNC Laser Marking Benefit the Aerospace Sector?
CNC laser marking is employed in the aerospace industry for marking components with specific aerospace standards and certifications. This application increases accountability and traceability throughout the manufacturing process, which is critical in an industry where safety is paramount. Buyers should assess the durability of the markings produced, especially under extreme conditions, to ensure they meet industry requirements.
What Advantages Does CNC Laser Marking Offer in Jewelry and Fashion?
In the jewelry and fashion industries, CNC laser marking is used for custom engraving designs and logos on various products. This enhances brand visibility and allows for customer personalization, which can significantly improve customer loyalty. For international buyers, evaluating the versatility of the marking machine for different materials, such as precious metals and plastics, is essential for effective branding strategies.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc laser marking’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Consistent Quality in Marking
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those in industries like manufacturing and aerospace, often struggle with inconsistent quality in laser marking. Variations can occur due to several factors such as material inconsistencies, machine calibration, or environmental conditions. This inconsistency can lead to costly rework, potential loss of customer trust, and issues with compliance regulations, especially in sectors that require precise identification and traceability of parts.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality in CNC laser marking, it is essential to implement a thorough quality control process. Start by investing in a reliable laser marking machine that is well-reviewed for performance, such as those from reputable brands like FORSUN or Haas. Regularly calibrate your machines based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and conduct routine maintenance checks to avoid discrepancies in output.
Additionally, consider using materials with standardized properties to reduce variability. Training your operators on the specific requirements of different materials can also enhance consistency. Implementing a feedback loop where operators can report anomalies will help in adjusting processes promptly, ensuring high-quality output that meets industry standards.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs and Downtime
The Problem: Operational costs can become a significant burden for companies utilizing CNC laser marking technology, particularly for those in developing markets like Nigeria or Brazil, where budgets may be tighter. Frequent machine downtimes due to maintenance issues or inefficient operations can hamper productivity and inflate costs, leading to decreased competitiveness.
The Solution: To mitigate high operational costs and minimize downtime, B2B buyers should prioritize investment in high-quality CNC laser marking machines that are known for durability and low maintenance requirements. When sourcing equipment, look for models that offer advanced features such as automated calibration and self-diagnostic capabilities, which can proactively identify issues before they lead to downtime.
Furthermore, adopting a preventive maintenance schedule can significantly reduce unexpected breakdowns. This includes regular inspections and timely replacement of parts that are prone to wear. Training staff on basic troubleshooting techniques will empower them to address minor issues on-site, further reducing downtime. Lastly, consider implementing a tracking system for maintenance activities to identify patterns and optimize machine usage.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Compliance and Traceability
The Problem: Compliance with industry regulations is a critical concern for B2B buyers in sectors like pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and automotive. Many organizations face challenges in ensuring that their laser marking processes produce the necessary traceability marks, such as barcodes or unique identifiers, required for regulatory compliance. Failure to meet these standards can result in penalties, product recalls, or damage to reputation.
The Solution: To address compliance and traceability challenges, it is crucial to select a CNC laser marking machine that supports various marking formats, including 2D barcodes, data matrix codes, and text. Ensure that the machine is capable of creating high-resolution markings that are easily readable and durable under various conditions.
Invest in software that integrates with your laser marking machines, allowing for the automation of data input and ensuring that all marks are generated consistently and accurately. Regular audits of your marking processes should be conducted to ensure compliance with industry standards. Establishing a partnership with a knowledgeable supplier who can provide insights into regulatory requirements can also be beneficial. This proactive approach not only helps in maintaining compliance but also builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc laser marking
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for CNC Laser Marking?
CNC laser marking is a versatile technology that can be applied to various materials, each with distinct properties that influence their suitability for different applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in CNC laser marking: metals, plastics, ceramics, and wood.
How Do Metals Perform in CNC Laser Marking Applications?
Metals such as steel, aluminum, and titanium are widely used in CNC laser marking due to their durability and strength. Key properties include high-temperature resistance, excellent corrosion resistance, and the ability to withstand mechanical stress. The pros of using metals include their long lifespan and ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions. However, the cons involve higher costs and manufacturing complexity, particularly when dealing with thicker materials.
In terms of application impact, metals can be marked with high precision, allowing for the inclusion of serial numbers, barcodes, and logos. For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential to ensure product quality and safety, especially in industries like automotive and aerospace.
What Advantages and Disadvantages Do Plastics Offer for CNC Laser Marking?
Plastics, including ABS, PVC, and polycarbonate, are popular for CNC laser marking due to their lightweight nature and versatility. Key properties include lower melting points, which can be advantageous for specific applications, and a wide range of colors and finishes. The primary advantages of plastics are their lower cost and ease of manufacturing, making them suitable for high-volume production runs.
However, plastics can be less durable than metals and may not withstand extreme temperatures or harsh environments. In applications such as consumer electronics and packaging, compliance with international standards like RoHS is critical, particularly for buyers in regions like Europe and South America where environmental regulations are stringent.
How Do Ceramics Contribute to CNC Laser Marking Solutions?
Ceramics are increasingly used in CNC laser marking due to their hardness and resistance to wear and corrosion. Key properties include high-temperature resistance and electrical insulation capabilities. The advantages of ceramics include their aesthetic appeal and suitability for high-end applications, such as medical devices and luxury goods. However, they can be brittle and more challenging to machine, leading to higher costs.
For international buyers, understanding the specific standards related to ceramics, such as ISO and ASTM, is crucial. This ensures that the marked products meet quality expectations and regulatory requirements in diverse markets, including Africa and the Middle East.
What Role Does Wood Play in CNC Laser Marking?
Wood is a popular choice for CNC laser marking, especially in the crafting and furniture industries. Key properties include natural aesthetics, ease of engraving, and a variety of finishes. The advantages of using wood include its availability and relatively low cost, making it an attractive option for custom designs and artisanal products.
However, wood can be sensitive to moisture and temperature changes, which may affect the longevity of the markings. International buyers should consider compliance with sustainability standards, such as FSC certification, particularly in regions like South America and Europe, where eco-friendly practices are increasingly prioritized.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Laser Marking
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc laser marking | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metals | Automotive parts, aerospace components | High durability and strength | Higher cost and complexity | High |
| Plastics | Consumer electronics, packaging | Lower cost and easy to manufacture | Less durable, sensitive to temperature | Low |
| Ceramics | Medical devices, luxury goods | High wear resistance and aesthetics | Brittle, higher machining costs | Medium |
| Wood | Custom furniture, crafts | Natural aesthetics and low cost | Sensitive to moisture, less durable | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials suitable for CNC laser marking. Understanding the properties, advantages, and compliance requirements can help businesses make informed decisions that align with their production needs and market standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc laser marking
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of CNC Laser Marking?
The manufacturing process of CNC laser marking encompasses several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality machines suited for various applications.
Material Preparation: How is the Right Material Chosen?
The first stage involves selecting appropriate materials, which can vary based on the intended application. Common materials include metals like steel and aluminum, plastics, ceramics, and even wood. Each material type requires specific handling and processing techniques to ensure optimal marking quality. For instance, metals may need pre-treatment to remove any surface contaminants, while plastics may require a different approach to avoid damage during marking.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Components?
Once the materials are prepared, forming techniques come into play. This may involve cutting, bending, or shaping components to fit the design specifications of the CNC laser marking machine. Advanced CNC machining centers are often employed in this stage to ensure precision and repeatability. This is vital for maintaining the machine’s integrity and performance, especially since laser marking requires high accuracy.
Assembly: How Are Components Integrated into a Final Product?
The assembly stage involves integrating the various components, including the laser source, optics, control systems, and mechanical parts. This stage is critical as it determines the operational efficiency of the machine. Skilled technicians typically perform assembly under strict protocols to ensure that all parts fit seamlessly and function as intended.
Finishing: What Final Touches Ensure Quality?
After assembly, the machines undergo a finishing process that may include surface treatments, painting, or coating. These treatments not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also improve durability and resistance to environmental factors. Quality control checks are often integrated into the finishing process to ensure that every unit meets the required specifications before leaving the factory.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in CNC Laser Marking Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in CNC laser marking to ensure that machines perform reliably and meet international standards.
What International Standards Apply to CNC Laser Marking Machines?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a crucial role in guiding quality management systems. Compliance with these standards ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer requirements and enhance customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE for European markets and API for the oil and gas sector, can be vital for B2B buyers who need assurance of quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control in CNC laser marking typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Suppliers should provide documentation and certifications that confirm material quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing checks are performed to ensure that each stage adheres to predefined standards. This can include visual inspections and measurements to verify alignment and fit.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, the entire machine undergoes thorough testing. This includes functional testing of laser operations, precision checks, and verification of compliance with safety standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in CNC Laser Marking Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to assess the performance and reliability of CNC laser marking machines.
-
Functional Testing: This involves operating the machine under typical conditions to ensure it performs as expected.
-
Laser Performance Testing: Specific tests measure beam quality, pulse duration, and wavelength to confirm that the laser meets specified operational parameters.
-
Durability Testing: Machines may be subjected to stress tests to evaluate their resilience and longevity under different operational conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should actively seek ways to validate the quality control practices of potential suppliers to mitigate risks.
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Supplier Verification?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess their quality management systems. Buyers can request audit reports that detail the supplier’s compliance with relevant standards and their internal quality processes. This provides insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality assurance.
Are Third-Party Inspections Useful for Ensuring Quality?
Utilizing third-party inspection services can further enhance confidence in a supplier’s quality control measures. Independent inspectors can conduct thorough evaluations of manufacturing practices and product quality, providing an unbiased assessment that helps buyers make informed decisions.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding quality control and certification nuances is crucial.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that affect product acceptance. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE certification for compliance with EU directives, while buyers in other regions might focus on ISO certifications. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these standards to ensure that suppliers meet local requirements.
What Challenges Might Buyers Face in Verifying Quality?
Buyers may encounter challenges such as language barriers, differing regulatory landscapes, and varying levels of supplier transparency. To navigate these issues, establishing clear communication channels and leveraging local expertise can be invaluable. Additionally, buyers should consider forming partnerships with local representatives who understand the market dynamics and can assist in the verification process.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for CNC laser marking machines are intricate and essential for ensuring high-quality output. By understanding these processes and actively engaging in supplier verification, B2B buyers can secure reliable, efficient, and compliant machinery that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc laser marking’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring CNC laser marking machines. It aims to streamline the procurement process, ensuring that buyers select the right equipment tailored to their specific needs while also considering supplier reliability and compliance.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining the technical requirements for your CNC laser marking machine. Consider factors such as laser type (fiber, UV, CO2), power output (measured in watts), and the materials you intend to mark. Establishing these specifications is crucial as it directly influences the machine’s performance and suitability for your applications.
- Laser Type: Different lasers are optimal for various materials. For instance, fiber lasers are excellent for metals, while UV lasers are better for plastics.
- Power Output: Higher wattage typically equates to faster processing speeds and the ability to mark thicker materials.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers of CNC laser marking machines. Look for manufacturers that have a strong presence in your region and specialize in the specific type of machine you need. This step is essential to ensure that you are dealing with credible suppliers who can meet your requirements.
- Supplier Reputation: Check online reviews, industry forums, and testimonials from other businesses.
- Local vs. International: Consider the advantages of local suppliers for service support versus international ones for potentially better pricing.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a decision, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This evaluation helps ensure that the supplier has a proven track record of reliability and quality.
- Ask for Documentation: Request certifications (e.g., ISO) that demonstrate compliance with international quality standards.
- Check References: Speak with past clients to gauge their satisfaction with both the machine and the supplier’s service.
Step 4: Verify Warranty and After-Sales Support
Review the warranty terms and after-sales support offered by the supplier. A robust warranty and reliable support system are vital for minimizing downtime and ensuring long-term operational efficiency.
- Warranty Duration: Look for warranties that cover parts and labor for at least two years.
- Support Availability: Confirm that the supplier offers timely support through various channels, including phone, email, and onsite service.
Step 5: Assess Total Cost of Ownership
Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for the CNC laser marking machine. This includes the initial purchase price, installation costs, maintenance fees, and operational expenses such as energy consumption. Understanding TCO is critical for budget planning and maximizing return on investment.
- Operational Costs: Investigate the energy efficiency of the machine and any recurring costs for consumables.
- Maintenance Needs: Consider the availability of spare parts and the expected maintenance frequency.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations and Samples
Where possible, request a demonstration of the machine’s capabilities and ask for sample markings on materials similar to what you will use. This step allows you to evaluate the machine’s performance firsthand and assess if it meets your quality standards.
- Sample Materials: Bring your own materials for testing to ensure compatibility and quality.
- Performance Metrics: Observe the speed, precision, and clarity of the markings produced.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract and Payment Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, carefully review the contract and payment terms before finalizing the purchase. Ensure that all agreed-upon specifications, warranty details, and support services are documented.
- Payment Flexibility: Look for suppliers that offer flexible payment options, such as installment plans or financing.
- Contractual Clauses: Pay attention to clauses related to delivery timelines, installation, and training to avoid potential disputes later.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc laser marking Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in CNC Laser Marking?
In the realm of CNC laser marking, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost. Common materials used for laser marking include metals like steel and aluminum, plastics, ceramics, and glass. Each material has a different cost associated with it, which can affect the overall pricing.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for operating CNC laser marking machines and ensuring quality output. Labor costs can vary based on the region, expertise required, and the scale of operations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, facility rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and parts used in the marking process also contribute to the cost. Investment in high-quality tooling can enhance productivity and reduce waste.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that products meet specific standards incurs additional costs. Investing in robust QC processes can prevent costly defects and enhance customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, especially for international buyers, can significantly impact the total cost. Factors such as shipping distance, customs duties, and Incoterms should be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary widely based on competition and the perceived value of the product.
What Influences CNC Laser Marking Prices?
Several factors play a crucial role in determining CNC laser marking prices, particularly for international buyers.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it more cost-effective for businesses with larger demands.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized machines or specific configurations can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the level of quality certification (such as ISO) can impact pricing. High-quality materials and certified processes typically command higher prices.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence costs. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and quality assurance practices.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can affect the overall cost. Understanding Incoterms is essential for buyers to manage shipping risks and responsibilities effectively.
What are the Best Practices for Negotiating CNC Laser Marking Prices?
Effective negotiation strategies can significantly enhance cost-efficiency for international B2B buyers.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research to understand standard pricing and supplier offerings. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: Rather than just the initial purchase price, consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If planning to order in bulk, negotiate for volume discounts. Suppliers are often willing to lower prices for larger commitments.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term relationships can lead to better pricing and terms. Trust and reliability can often translate into cost savings.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be mindful of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and regional economic factors that may affect pricing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics of CNC laser marking is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on key cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their procurement processes. Always consider the total cost of ownership and maintain open communication with suppliers to foster successful partnerships.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc laser marking With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to CNC Laser Marking
When evaluating CNC laser marking solutions, it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider alternative marking technologies that may meet their operational needs. Each method offers unique advantages and drawbacks, influencing factors such as performance, cost, and implementation ease. Below, we compare CNC laser marking with two prominent alternatives: inkjet printing and dot peen marking.
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Laser Marking | Inkjet Printing | Dot Peen Marking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with permanent marks on various materials. | Moderate precision, suitable for non-permanent applications. | Good precision, ideal for hard surfaces. |
| Cost | $1,000 – $5,000 per set; low operational costs over time. | Lower initial investment; ink and maintenance costs can add up. | Moderate initial cost; requires regular maintenance. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators for setup and programming. | User-friendly and easy to integrate into existing processes. | Moderate complexity; training required for effective use. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; generally reliable with minimal downtime. | Moderate maintenance; ink clogging can be an issue. | Regular maintenance needed to ensure consistent performance. |
| Best Use Case | Permanent marking on metals, plastics, and ceramics; ideal for serial numbers and logos. | Temporary markings on packaging and products; suitable for high-speed production. | Marking on hard surfaces like metals; effective for industrial applications. |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternative Solutions
Inkjet Printing
Inkjet printing is a popular alternative for product marking, particularly in industries where non-permanent labeling is sufficient. The technology utilizes liquid ink sprayed through nozzles to create images or text on surfaces. Its primary advantages include lower initial costs and ease of integration into existing production lines. However, the permanence of the markings is a significant drawback, especially in industries requiring traceability and durability, as ink can fade or wash away over time.
Dot Peen Marking
Dot peen marking uses a stylus to create a series of dots that form characters or images on the surface of materials. This method is particularly effective for marking hard surfaces like metals, making it a go-to choice in heavy industries. The technology provides good precision and durability, offering permanent marks that resist wear and corrosion. However, the initial setup can be more complex compared to inkjet printing, and it may require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Marking Solution
Selecting the appropriate marking solution hinges on your specific operational needs, production environment, and budget constraints. If you require permanent, high-precision markings on a variety of materials, CNC laser marking is likely your best choice. However, if your focus is on cost-effectiveness and ease of use for temporary applications, inkjet printing may be more suitable. For industries dealing with hard surfaces where durability is crucial, dot peen marking offers a reliable alternative. Careful consideration of these factors will help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc laser marking
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Laser Marking Machines?
When considering CNC laser marking machines, several technical specifications are critical for B2B buyers to understand. These specifications not only influence the machine’s performance but also affect production efficiency and overall costs.
-
Laser Power (Wattage)
The wattage of a laser marking machine typically ranges from 20W to over 150W. Higher wattage allows for faster marking speeds and the ability to mark on a wider variety of materials, including harder substrates like metals. B2B buyers should assess their production requirements to select an appropriate power level, ensuring that it aligns with their material processing needs. -
Engraving Speed
Measured in millimeters per second (mm/s), engraving speed indicates how quickly the machine can complete a marking job. Speeds can vary from 0 to 1200 mm/s, depending on the machine’s configuration. A higher engraving speed can lead to increased productivity, essential for businesses aiming to maximize output and minimize turnaround times. -
Positioning Accuracy
This specification, often quantified as ±0.05mm, reflects the machine’s ability to place marks precisely. High accuracy is crucial in industries such as aerospace and medical devices, where precise markings are essential for traceability and compliance with regulatory standards. For B2B buyers, ensuring that a machine meets their accuracy requirements can reduce waste and errors in production. -
Cooling Method
CNC laser marking machines typically use air or water cooling systems. Water-cooled systems tend to offer better thermal management, allowing for longer continuous operation without overheating. Buyers should consider their operational environment and production volume when selecting a cooling method, as it can impact machine longevity and performance. -
Material Compatibility
Different laser marking machines can process various materials, including metals, plastics, glass, and wood. Understanding the range of materials that can be marked is vital for buyers to ensure that their chosen machine aligns with their product offerings. This compatibility will directly affect the machine’s versatility and utility in production. -
Operating Environment
The specified temperature and humidity range (e.g., 0-45°C, 5%-95% humidity) indicates the conditions under which the machine can function optimally. Buyers in regions with extreme climates must ensure that their facilities can accommodate these requirements, as environmental factors can affect machine performance and reliability.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in CNC Laser Marking?
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the CNC laser marking sector.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces components or products that may be marketed by another company under its brand name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reputable suppliers and assess the quality of equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers, as it can influence purchasing decisions and inventory management, particularly for smaller businesses or startups. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. This process is vital for comparing costs and terms among different suppliers, enabling informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, covering aspects such as shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and rights, reducing the risk of misunderstandings in cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and managing customer expectations. -
Technical Support
This term encompasses the assistance provided by manufacturers or vendors regarding the installation, operation, and maintenance of laser marking machines. Access to reliable technical support can greatly influence a buyer’s choice, ensuring they receive the necessary help to optimize machine performance.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed purchasing decisions, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and market competitiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc laser marking Sector
What Are the Key Trends and Dynamics Shaping the CNC Laser Marking Market?
The CNC laser marking sector is witnessing robust growth driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for precision marking, and the need for traceability across various industries. Global drivers include the rise of e-commerce, stringent regulations regarding product identification, and the growing trend towards automation in manufacturing processes. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly looking for solutions that enhance operational efficiency while reducing waste. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is also gaining traction, allowing for smarter production systems that optimize laser marking processes.
Emerging trends in sourcing include a shift towards modular and customizable laser marking solutions that can adapt to diverse materials and applications. Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who offer comprehensive after-sales support and training, ensuring that their teams are equipped to utilize the technology effectively. Additionally, the availability of financing options is becoming crucial for businesses in emerging markets, enabling them to invest in high-quality CNC laser marking machines without straining their budgets.
With the expansion of global supply chains, buyers must navigate challenges such as fluctuating tariffs and regulatory compliance, particularly concerning safety and environmental standards. Understanding these dynamics is essential for making informed sourcing decisions that align with both operational goals and market demands.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in CNC Laser Marking?
As environmental concerns take center stage, sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the CNC laser marking sector. The production and operation of laser marking machines can have significant environmental impacts, including energy consumption and waste generation. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who implement energy-efficient practices and utilize materials with lower carbon footprints.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance, with businesses seeking suppliers that adhere to responsible manufacturing processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or the use of ‘green’ materials in machine construction and operation are becoming key differentiators in the purchasing decision. By aligning with suppliers committed to sustainability, businesses can not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the growing demand from consumers for environmentally friendly products.
Furthermore, integrating sustainable practices can lead to cost savings in the long run. For instance, using laser marking technology that minimizes material waste and energy consumption can significantly reduce operational costs, making it an attractive option for companies looking to enhance their bottom line while meeting regulatory requirements.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Laser Marking in B2B Applications?
CNC laser marking technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 20th century. Initially, laser marking was limited to high-end applications in industries like aerospace and defense. Over the years, advancements in laser technology have made it more accessible and affordable, allowing broader adoption across various sectors, including automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
The introduction of fiber laser technology in the early 2000s marked a turning point, offering faster marking speeds, improved precision, and the ability to work with a wider range of materials. This evolution has facilitated the proliferation of laser marking applications, such as barcoding and serialization, which are now integral to supply chain management and product traceability.
As the technology continues to advance, CNC laser marking is expected to play an increasingly vital role in manufacturing processes, helping businesses meet the demands of modern consumers while adhering to stringent regulatory standards. Understanding this historical context allows B2B buyers to appreciate the value and potential of CNC laser marking in enhancing their operational capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc laser marking
-
How do I select the right CNC laser marking machine for my business?
Choosing the right CNC laser marking machine involves assessing your specific marking needs, including material types, desired marking depth, and production speed. Consider the range of laser types available—fiber, UV, or CO2—and their compatibility with your materials. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s power options and features such as automation capabilities, ease of use, and maintenance requirements. Consulting with suppliers about your application can provide insights into the best model for your operations. -
What are the typical applications of CNC laser marking in various industries?
CNC laser marking is versatile and widely used across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and healthcare. Common applications include engraving part numbers, barcodes, and logos on components, ensuring traceability and compliance with industry standards. The technology is suitable for a variety of materials including metals, plastics, and ceramics, making it ideal for manufacturing, branding, and product identification. -
What should I consider regarding payment terms when sourcing CNC laser marking machines internationally?
When sourcing CNC laser marking machines internationally, it’s essential to clarify payment terms upfront. Common options include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), credit cards, or letters of credit. Understand the supplier’s payment schedule—whether full payment is required upfront or if a deposit is acceptable. Additionally, consider currency exchange rates and transaction fees, which can affect overall costs. Ensure that payment terms align with your cash flow and financing capabilities. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC laser marking machines?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC laser marking machines can vary significantly by supplier and machine type. While some manufacturers may offer individual units, others might require bulk orders to ensure cost-effectiveness. Inquire about the MOQ during your supplier discussions, as negotiating lower quantities may be possible, especially for new buyers. This can help you manage initial investment risks while assessing the machine’s performance in your operations. -
How do I verify the credibility of CNC laser marking machine suppliers?
To verify the credibility of CNC laser marking machine suppliers, conduct thorough research. Check their business licenses, certifications, and customer reviews. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources for supplier ratings and feedback. Request references from past clients and inquire about their after-sales support and warranty policies. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facility or attending trade shows to gauge their operations and reliability. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from CNC laser marking machine manufacturers?
Reputable CNC laser marking machine manufacturers should implement strict quality assurance (QA) measures. Expect to see ISO certifications or similar quality management standards. Inquire about their testing protocols, such as performance tests and safety compliance checks before shipment. Additionally, ask about the warranty terms and what support is available for troubleshooting or repairs post-purchase. A strong QA process ensures that you receive a machine that meets your specifications and operates reliably. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC laser marking machines?
When importing CNC laser marking machines, logistics play a crucial role in the overall success of your purchase. Consider shipping options, including air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost savings. Understand the import duties and taxes in your country, as these can significantly impact the total cost. Collaborate with a freight forwarder who can assist with customs clearance, ensuring all necessary documentation is prepared to avoid delays. -
Can CNC laser marking machines be customized to meet specific business needs?
Yes, many CNC laser marking machines can be customized to suit specific business requirements. Customization options may include adjusting the laser power, adding rotary attachments for cylindrical marking, or integrating software solutions for enhanced functionality. Discuss your unique needs with potential suppliers, as they may offer tailored solutions that enhance productivity and fit seamlessly into your existing manufacturing processes. Customization can lead to improved operational efficiency and greater return on investment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Cnc Laser Marking Manufacturers & Suppliers List
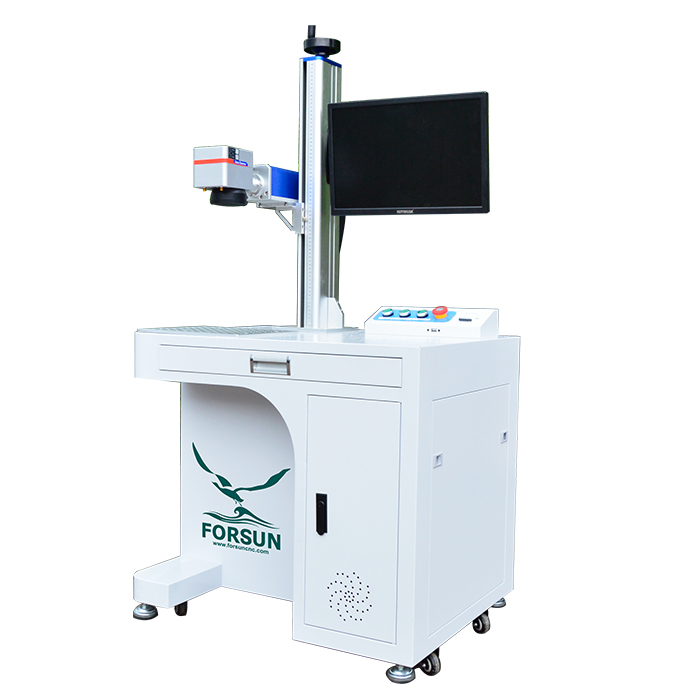
1. FORSUN CNC – CNC Laser Marking Machine
Domain: forsuncnc.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: CNC Laser Marking Machine
– Brand: FORSUN CNC
– Model: CNC Laser Marking Machine
– Price: $1000.00 / Set
– Price Range: $1000.00 to $5000.00 / Set based on configuration
– Payment Terms: T/T, Visa, Mastercard, American Express, Discover cards
– Warranty: 2 Years
– Supply Ability: 30 Sets / Month
– Key Features: Permanent marking process using concentrated light; high-speed automation; applicable t…
2. Boss Laser – Laser Machines
Domain: shop.bosslaser.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Laser Machines – Boss Laser offers a variety of laser cutting, engraving, and marking machines including CO2 lasers, UV lasers, and fiber laser markers. Key product series include LS-Series (4 products), HP-Series (3 products), FC-Series (8 products), FM-Series (3 products), and UV-Series (1 product). The machines are capable of cutting and engraving various materials such as acrylic, aluminum, br…
3. Style CNC – Laser Marking Machines
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Laser Marking Machines are automatic fine engraving tools using CNC or DSP controllers to direct fiber, CO2, or UV laser beams for permanent marking on various materials including metals (aluminum, stainless steel, etc.), wood, fabric, leather, plastic, glass, and more. They offer high speed, quality, precision, pollution-free operation, safety, easy handling, and low maintenance costs. Types incl…
4. OMTech – MOPA 100W Fiber Laser Engraving Machine
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: OMTech MOPA 100W Split Fiber Laser Engraving Machine with 6.9″ x 6.9″ Working Area
Price: $8,299.99
Regular Price: $11,999.99
Sale Price: Save $3,700
Options: Machine or Machine with LightBurn
5. TYKMA Electrox – Industrial Laser Engraving Systems
Domain: permanentmarking.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: TYKMA Electrox is a leading manufacturer of industrial laser engraving systems designed for precision and repeatability. Their product range includes: 1. **Laser Marking Systems**: Standard and high-throughput options for various applications. 2. **Custom Laser Systems**: Tailored solutions for specific business needs. 3. **Laser Accessories**: Tools for marking around cylinders and complex shapes…
6. Amada Weld Tech – Laser Marking Solutions
Domain: amadaweldtech.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Laser Marking, also known as ‘laser engraving’ or ‘laser etching,’ is a marking method utilizing laser light to mark materials with a fine spot diameter. Laser markers engrave using short pulses (10’s-100’s of nanoseconds), providing precise control and negligible heat input to the part. This fast and clean technology is rapidly replacing older marking methods like dot peen and chemical etching. I…
7. FOBA Laser – Industrial Laser Marking Solutions
Domain: fobalaser.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: FOBA Laser offers a range of industrial laser marking and engraving solutions, including: 1. Laser Marking Systems: – Ultrashort Pulse Laser Markers – CO2 Laser Markers – Fiber Laser Markers – UV Laser Markers – Green Laser Markers 2. Laser Marking Machines: – M-Series Fiber Laser – M-Series UV-Laser 3. New Products: – Next Gen Y-Series: 20- and 60-watt fiber laser markers for dynamic multi-level …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc laser marking
As the CNC laser marking industry continues to evolve, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse applications of CNC laser marking—ranging from engraving to etching—enables businesses to identify machines that meet their specific needs. Moreover, the ability to mark various materials, including metals and plastics, underscores the versatility of these machines, making them indispensable across multiple sectors.
Investing in quality CNC laser marking machines not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with quality control and counterfeiting. By prioritizing suppliers that offer robust warranties and reliable support, businesses can ensure a sustainable and productive investment.
Looking ahead, international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should capitalize on the growing demand for laser marking technology. Engaging with reputable manufacturers and distributors will be essential for securing competitive pricing and innovative solutions. Make your move now to leverage the full potential of CNC laser marking, positioning your business at the forefront of technological advancement and operational excellence.