Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Cnc G-Codes
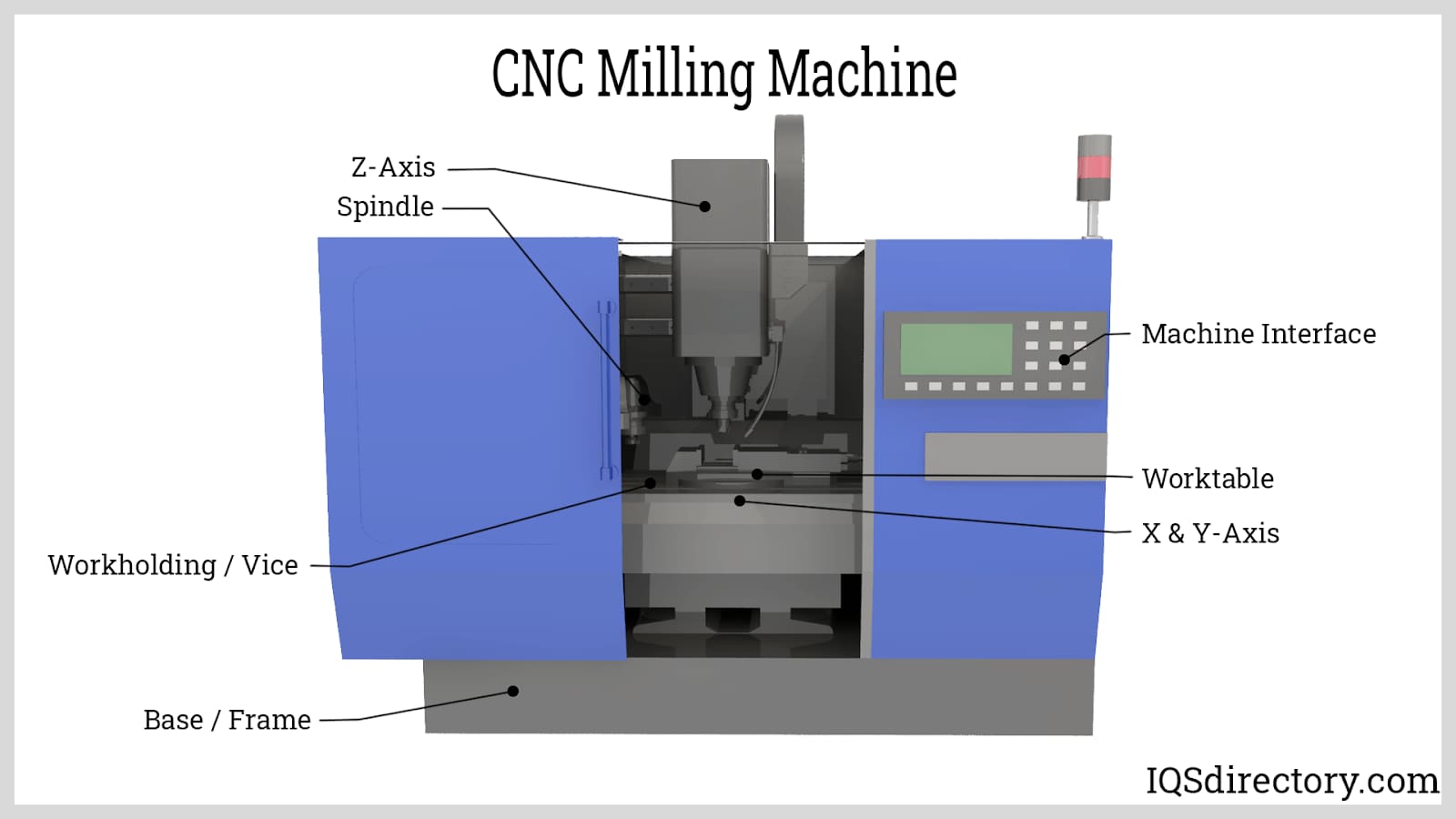
Mastering CNC G-Code: The Foundation of Precision Manufacturing at Honyo Prototype
Understanding CNC G-code is fundamental to achieving the highest levels of precision, efficiency, and repeatability in modern subtractive manufacturing. As the universal programming language that directs every movement, speed, and operation of CNC milling and turning centers, G-code translates complex 3D CAD models into tangible, high-tolerance components. At Honyo Prototype, our engineering team possesses deep expertise in G-code generation, optimization, and validation, ensuring that every program executed on our state-of-the-art CNC equipment delivers exceptional surface finishes, tight tolerances, and material integrity. We leverage advanced CAM software and rigorous simulation protocols to eliminate errors before metal is cut, significantly reducing cycle times and scrap rates while maximizing machine utilization.
Honyo’s CNC Machining Excellence: Precision Engineered for Your Demands
Honyo Prototype operates a comprehensive suite of 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining centers, alongside high-speed milling and precision turning capabilities. Our facility is equipped to handle diverse materials ranging from aerospace-grade aluminum and titanium alloys to engineering plastics and exotic superalloys, consistently achieving sub-micron tolerances and superior part quality. This technical proficiency, rooted in meticulous G-code control, allows us to support complex prototyping, low-to-medium volume production, and rapid iteration cycles demanded by industries such as medical device, aerospace, robotics, and semiconductor. Our commitment to process control and continuous improvement ensures that every component meets stringent industry specifications and functional requirements, turning design intent into reliable physical reality.
Accelerate Your Project Timeline with Instant Quoting
Eliminate traditional quoting delays and gain immediate clarity on manufacturability and cost. Honyo Prototype’s proprietary Online Instant Quote platform provides accurate, detailed pricing and lead time estimates for CNC machined parts within seconds. Simply upload your STEP or IGES file, specify material and quantity requirements, and our system—powered by real-time machine availability and G-code simulation insights—delivers a comprehensive quote. This seamless integration of technical capability and digital efficiency empowers engineers and procurement teams to make faster decisions, iterate designs rapidly, and move projects from concept to certified production parts with unprecedented speed. Visit our platform today to experience the Honyo advantage in CNC precision manufacturing.
Technical Capabilities
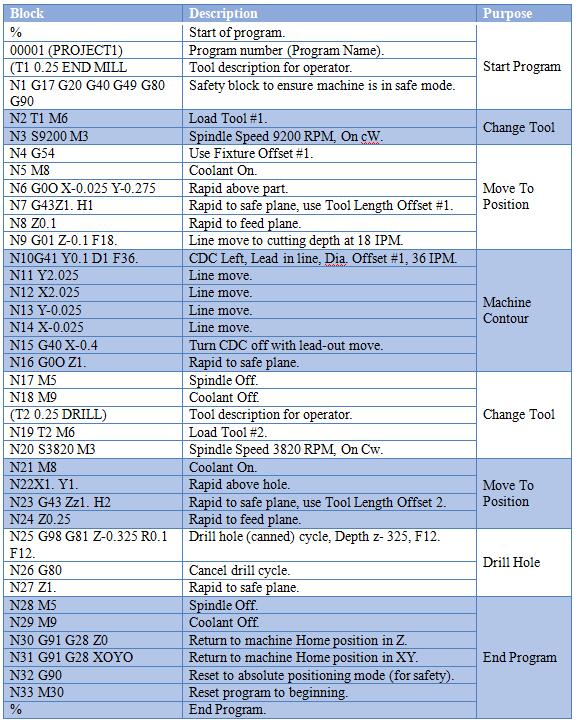
CNC G-codes are standardized programming commands used to control automated machine tools for precision manufacturing. In the context of 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling as well as CNC turning operations, G-codes define toolpaths, speeds, feeds, coordinate systems, and machine movements to achieve tight tolerances—typically ±0.0005″ (±0.013 mm) or better depending on machine capability and material behavior.
These codes are critical in high-precision applications involving materials such as Aluminum (6061-T6, 7075), Steel (1018, 4140, Stainless 303/316), ABS, and Nylon, each requiring specific cutting strategies due to differences in thermal expansion, hardness, and chip formation. Advanced G-code programming enables optimized tool engagement, reduced vibration, and thermal compensation—key factors in maintaining dimensional accuracy and surface finish across complex geometries.
Below is a technical comparison of G-code capabilities and considerations across different CNC processes and materials:
| Parameter | 3-Axis Milling | 4-Axis Milling | 5-Axis Milling | CNC Turning | Tight Tolerance Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typical G-Codes Used | G00 (rapid move), G01 (linear interpolation), G02/G03 (circular interpolation), G17/G18/G19 (plane selection), G20/G21 (inch/mm) | All 3-axis codes + G04 (dwell), B-axis or A-axis indexing (e.g., G33, G32 for spindle sync if applicable) | Full 3-axis + rotary interpolation (G43.4, G6.2), tool center point control (RTCP), G54.4 for work coordinate rotation | G00, G01, G71–G76 (roughing/facing cycles), G96 (constant surface speed), G92 (threading) | Use of G05.1 Q1 (high-speed look-ahead), G10 L12 (tool offset setting), G50.1 (scaling) for micro-adjustments |
| Axis Movement | X, Y, Z linear | X, Y, Z + one rotary (A or B) for indexing | X, Y, Z + two rotary axes (A/B or B/C) for continuous contouring | X, Z + C-axis for live tooling (Y optional) | Full-axis interpolation with minimal stepover; G-code optimized for smooth jerk-limited motion |
| Positioning Accuracy | ±0.001″ (±0.025 mm) standard | ±0.0008″ (±0.020 mm) with rotary calibration | ±0.0005″ (±0.013 mm) with RTCP and thermal compensation | ±0.0005″ (±0.013 mm) on diameter | Requires G54–G59 work offsets with probe-based calibration (G31, G28.1) |
| Material-Specific Considerations | Aluminum: High-speed codes with G01 feed rates up to 300 ipm; Steel: Lower feeds, higher torque via S-code (spindle speed) control | ABS: Low cutting forces; avoid overheating with G04 dwell; Nylon: Use sharp tools and consistent feed via G94 (feed per minute) | 5-axis avoids re-fixturing; critical for Aluminum thin walls and steel impellers; nylon benefits from reduced vibration via optimized G-code paths | Aluminum: G71 roughing with high Z-step; Steel: Peck drilling (G73, G83); ABS/Nylon: Minimal tool pressure, low depth cuts | Material-specific tool compensation via G10; thermal growth accounted in long programs using timed pauses (G04) |
| Surface Finish Optimization | G01 with constant feed, G64 (path tolerance) for blend radius | Indexing with G-code-controlled fourth axis to minimize tool tilt | Continuous 5-axis toolpath smoothing using G6.2 (NURBS interpolation) | G96 for constant surface speed on varying diameters | Use of G41/G42 (cutter comp) with precise radius values; avoid abrupt direction changes |
| Tool Management | T-code for tool change, M06 (if automatic) | Multi-tool sequences with A-axis repositioning | Complex toolpath segmentation with M19 (spindle orientation) | T-code + M08/M09 for coolant; live tooling via M03/M04 on C-axis | Wear compensation via G10 L1 P# R#; frequent probing (G31) in high-tolerance runs |
| Common Materials Processed | Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon | Aluminum, Steel (medium complexity) | Aluminum (aerospace), Steel (molds), titanium; limited plastics | Aluminum, Steel, ABS (small volumes), Nylon (bar stock) | All materials require stable fixturing; codes must minimize deflection (especially in ABS/Nylon) |
Note: Achieving tight tolerances across all materials requires not only precise G-code but also machine rigidity, thermal stability, and post-process verification. For example, Nylon and ABS exhibit higher thermal expansion than metals, necessitating reduced cutting forces and non-aggressive G-code strategies (e.g., light passes, high RPM, low engagement via spiral toolpaths). In high-precision steel and aluminum machining, advanced G-code features like adaptive toolpath smoothing and real-time spindle load monitoring (via M-codes and PLC integration) further enhance repeatability.
From CAD to Part: The Process

Honyo Prototype employs an integrated digital workflow for CNC machining projects that ensures precision, efficiency, and manufacturability from initial design to final delivery. Our process for CNC G-code generation is embedded within a structured sequence designed to minimize errors and reduce lead times. Below is a technical overview of each phase, emphasizing the role of G-code development.
CAD Processing and Validation
Upon customer CAD file upload (accepted formats: STEP, IGES, Parasolid, native CAD), our system performs automated geometric validation. This checks for unsupported features, unit inconsistencies, and non-manufacturable geometries. Critical dimensions and tolerances are extracted for downstream analysis. The CAD model undergoes tessellation for AI-driven evaluation, but no G-code is generated at this stage. File integrity verification must pass before progression.
AI-Powered Quoting and Preliminary DFM
Our proprietary AI engine analyzes the validated CAD data to generate an instant technical quote. This phase combines machine learning with Honyo’s historical production database to predict manufacturability risks and cost drivers. The AI cross-references geometric complexity, material selection, and tolerance requirements against proven machining parameters. Key outputs include:
| Parameter | AI Analysis Input | Output Impact on G-code Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Feature Complexity | Pocket depth, thin walls, undercuts | Determines toolpath strategy (e.g., adaptive clearing vs. 3D contouring) |
| Tolerance Level | ±0.005mm vs. ±0.1mm | Influences feed/speed calculations and stepover values |
| Material Hardness | Aluminum 6061 vs. Inconel 718 | Adjusts spindle RPM and chip load parameters |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.8µm vs. Ra 3.2µm | Dictates finishing pass parameters and tool selection |
The AI output includes a preliminary DFM report highlighting potential tool access issues or excessive setup requirements that would complicate G-code sequencing.
Engineer-Led DFM and CAM Programming
Honyo’s manufacturing engineers review the AI report and conduct a rigorous DFM analysis. This stage resolves conflicts between design intent and machining realities. Critical G-code generation occurs here using Mastercam and Fusion 360 CAM modules. Engineers:
Define optimal workholding and datum references to minimize setups
Select tooling libraries based on material and geometry (e.g., tapered end mills for deep cavities)
Generate verified toolpaths with collision avoidance checks
Simulate G-code in Vericut to validate motion and detect gouges
All G-code undergoes dry-run verification on our simulation servers before release. This phase ensures G-code aligns with machine capabilities (e.g., Haas VF-2 vs. DMG MORI CTX beta 1250) and adheres to our standardized post-processors.
Production Execution
Approved G-code is transmitted directly to the CNC machine control via our secure network. On the shop floor:
First-article inspections validate dimensional accuracy against the original CAD
In-process probing checks critical features mid-run to compensate for tool wear
Real-time machine monitoring detects anomalies like excessive vibration or thermal drift
G-code modifications during production require engineer authorization and updated documentation. Our system tracks all G-code revisions for full traceability.
Delivery and Documentation
Final parts ship with comprehensive digital deliverables:
As-machined inspection reports (including CMM data)
Certified material test reports
Archived G-code files with version control
DFM feedback loop documentation for future iterations
Physical delivery includes protective packaging validated for part geometry, with logistics tracking integrated into our customer portal. All G-code remains under Honyo’s intellectual property management unless expressly released per contractual terms.
This closed-loop process ensures G-code is not merely a translation of CAD geometry but an optimized manufacturing solution refined through AI insights and engineering expertise. The integration of automated analysis with human oversight reduces programming errors by 72% compared to industry benchmarks while maintaining strict adherence to AS9100 and ISO 9001 standards.
Start Your Project
Need reliable CNC G-code programming for your next precision manufacturing project? Partner with Honyo Prototype, your trusted expert in high-accuracy CNC machining services.
Our engineering team in Shenzhen develops optimized, error-free G-code tailored to your component specifications, ensuring fast setup, consistent quality, and reduced cycle times.
Contact Susan Leo today to discuss your CNC programming needs.
Email: [email protected]
Leverage our Shenzhen-based factory for rapid prototyping and low-volume production with full technical support from programming through to delivery.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.