Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Cnc G-Code M Code
Precision CNC Manufacturing: Mastering G-Code and M-Code Execution
At Honyo Prototype, our CNC machining services are engineered around the foundational language of precision manufacturing: G-code for geometric motion control and M-code for machine auxiliary functions. We translate complex part geometries into optimized, error-free programs that drive multi-axis CNC mills, lathes, and Swiss-type machines with micron-level accuracy. Our engineering team leverages deep expertise in custom G-code generation and M-code sequencing to eliminate manual intervention points, reduce cycle times, and ensure consistent repeatability—critical for aerospace, medical, and automotive prototypes and low-volume production.
Unlike standard job shops, we treat G-code and M-code not as mere instructions but as strategic assets. Our proprietary validation protocols simulate toolpaths in virtual environments before metal cutting begins, preempting collisions, optimizing feed rates, and minimizing material waste. This meticulous approach directly translates to higher first-pass yield rates and accelerated time-to-part for your precision-critical components. Every operation, from 3-axis milling to 5-axis complex contouring, undergoes rigorous program verification to uphold Honyo’s zero-defect commitment.
To streamline your prototyping workflow, we integrate this technical mastery with immediate accessibility through our Online Instant Quote platform. Upload your CAD file, specify materials and tolerances, and receive a detailed manufacturing assessment—including G-code optimization impact on lead time and cost—within minutes. No sales calls or email delays. This transparency empowers engineering teams to make informed decisions faster while leveraging Honyo’s full-service capabilities: from design-for-manufacturability feedback to post-processing and metrology.
Experience the difference where code precision meets operational excellence. Submit your design today and validate how Honyo’s CNC expertise transforms digital models into certified, high-integrity components.
Technical Capabilities
CNC G-Code and M-Code Technical Specifications for 3/4/5-Axis Milling, Turning, and Tight Tolerance Applications
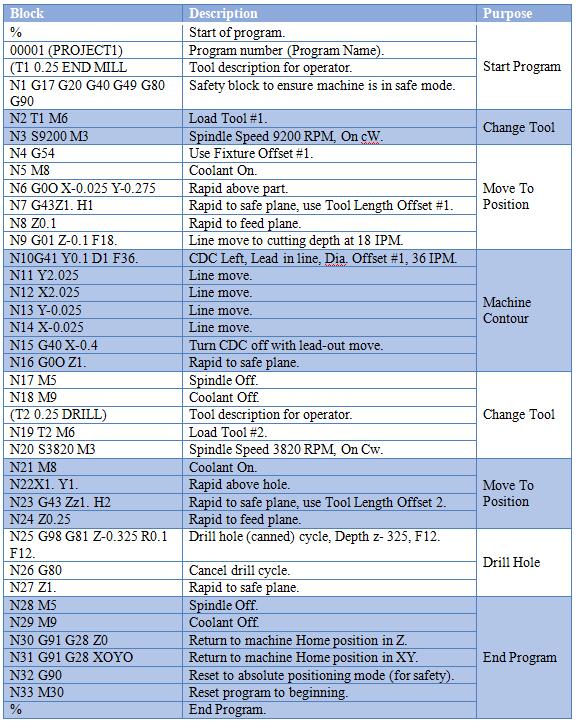
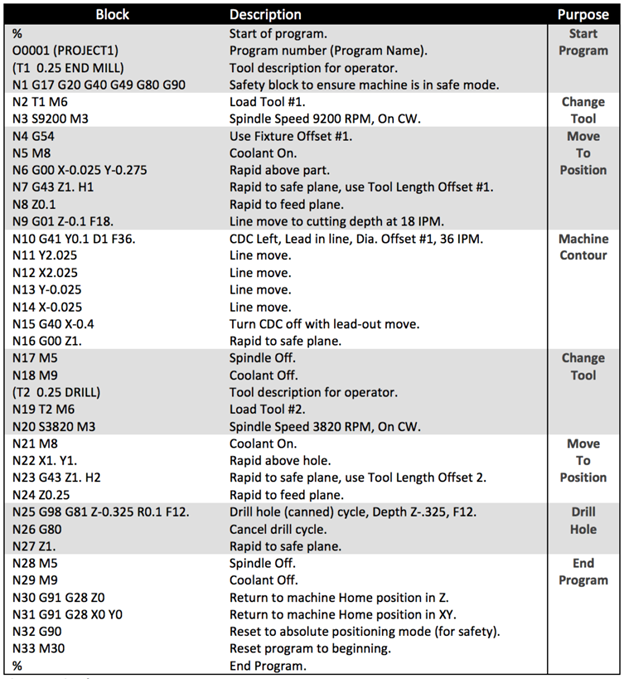
CNC machining relies on standardized G-code (geometric code) and M-code (miscellaneous function code) to control machine tool movements, spindle behavior, coolant flow, and auxiliary functions. In high-precision environments such as 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling, as well as CNC turning, these codes are optimized for tight tolerance work (±0.0002″ to ±0.001″) across a range of engineering materials including aluminum, steel, ABS, and nylon.
Below is a summary of relevant G-codes and M-codes, their applications, and how they relate to material-specific machining strategies:
| Code Type | Code | Function Description | Application in Milling (3/4/5-Axis) | Application in Turning | Material Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-Code | G00 | Rapid positioning | Used for non-cutting tool movements between positions; critical for 5-axis toolpath efficiency | Rapid traverse to position | Minimizes non-productive time across all materials |
| G-Code | G01 | Linear interpolation (controlled feed move) | Primary command for precision contouring; essential for tight tolerance features | Linear cutting feed motion | Critical for aluminum and steel to maintain ±0.0005″ tolerances |
| G-Code | G02 | Clockwise circular interpolation | Used in pocketing, filleting, and complex 3D surfacing | Threading, radius turning | Useful in nylon and ABS for smooth internal radii without tool deflection |
| G-Code | G03 | Counterclockwise circular interpolation | Same as G02; used in sculpted surfaces on 5-axis mills | Profile turning | Required for high-precision steel molds with curved features |
| G-Code | G17 | XY plane selection | Default for 3-axis milling; base plane for most operations | Not typically used | Standard for flat milling of aluminum plates |
| G-Code | G18 | XZ plane selection | Used in 4-axis setups involving indexing or rotational alignment | Default plane for turning | Essential for turning steel shafts with axial features |
| G-Code | G19 | YZ plane selection | Applied in complex 5-axis contouring and side-milling operations | Rare in turning | Used in 5-axis aluminum aerospace components with angled features |
| G-Code | G40 | Cutter compensation cancel | Disables tool radius compensation after use | Same in turning | Prevents overcutting in thin-wall nylon parts |
| G-Code | G41 | Cutter radius compensation left | Adjusts toolpath to left of programmed path; critical for tight tolerance finishing passes | Used in finish turning | Improves dimensional accuracy in ABS when using small end mills |
| G-Code | G42 | Cutter radius compensation right | Adjusts toolpath to right; used depending on tool engagement side | Same as G41 | Helps maintain wall thickness in steel enclosures |
| G-Code | G43 | Tool length compensation ON | Critical in 4/5-axis machining to account for tool length variations | Used with turret tools | Ensures Z-depth accuracy in stacked aluminum machining |
| G-Code | G54–G59 | Work coordinate system selection (WCS) | Allows multiple setups and angled workplanes in 5-axis; essential for fixturing | Part zero setting | Enables multi-part steel fixtures to be machined in one setup |
| G-Code | G90 | Absolute programming | Standard for high-accuracy programming; used in all tight tolerance work | Absolute dimensioning | Required for precision-machined nylon insulators |
| G-Code | G91 | Incremental programming | Used for subroutines or relative moves | Incremental tool adjustments | Occasionally used in ABS prototyping for iterative features |
| G-Code | G94 | Feed per minute | Standard feed mode in milling; ensures consistent surface finish | Feed rate control | Optimized for chip load in steel and aluminum |
| G-Code | G95 | Feed per revolution | Less common in milling; primarily in turning | Required for threading and facing | Used when precise chip formation is needed in nylon |
| M-Code | M03 | Spindle ON clockwise | Standard for most milling operations | Start spindle (cutting) | High RPM for aluminum, lower for steel, moderate for ABS/nylon |
| M-Code | M04 | Spindle ON counterclockwise | Used for left-hand tools or specific tapping scenarios | Reverse threading | Rare; used in specialty nylon thread repair |
| M-Code | M05 | Spindle stop | Safety command between operations or tool changes | End of turning cycle | Prevents vibration in thin aluminum parts |
| M-Code | M06 | Tool change | Automated tool change in milling; critical for multi-tool 5-axis programs | Turret indexing | Required for switching between roughing/finishing tools in steel machining |
| M-Code | M08 | Coolant ON (flood) | Used in high-heat operations (e.g., steel, aluminum) | Coolant during cutting | Prevents melting in ABS; reduces burring in aluminum |
| M-Code | M09 | Coolant OFF | Used when coolant interferes (e.g., with plastics or during probing) | End of cut or dry machining | Recommended for nylon to avoid static or moisture absorption |
| M-Code | M30 | Program end and reset | Final command; resets program counter and may unload tape or file | End of turning program | Standard for all materials to ensure safe machine state |
Material-Specific Notes:
Aluminum: High-speed machining with G00/G01/G02/G03; M08 coolant recommended to prevent built-up edge. G43 and G54 critical for multi-cavity molds.
Steel: Requires lower feed rates (G94), rigid setups, and frequent tool changes (M06). G41/G42 used for precision finishing to ±0.0002″.
ABS: Lower spindle speeds (M03), minimal or no coolant (M09), and incremental moves (G91) for fine adjustments to avoid deformation.
Nylon: Low thermal conductivity; use air blast instead of flood coolant. G95 (feed per revolution) in turning ensures consistent chip control.
These codes are implemented in CAM software and post-processed for specific machine controllers (e.g., Fanuc, Siemens, Heidenhain) to ensure compatibility and precision in high-tolerance manufacturing environments.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype executes CNC machining through an integrated digital workflow where G-code and M-code generation is a critical automated phase within production. Our process ensures precision, efficiency, and traceability from design to delivery. Below is a technical breakdown of each stage with emphasis on CNC programming integration.
Upload CAD
Clients submit native or neutral CAD formats (STEP, IGES, Parasolid) through our secure portal. Our system performs initial geometry validation, checking for non-manifold edges, gaps, or unsupported features. This stage establishes the foundation for automated downstream processing, ensuring the model is suitable for CNC toolpath generation without manual cleanup.
AI-Powered Quoting
Our proprietary AI engine analyzes the validated CAD geometry, material specifications, and tolerance requirements. It automatically identifies machinable features (pockets, contours, holes), estimates machine time based on feature complexity, and factors in tool selection logic. Crucially, the AI pre-optimizes for G-code efficiency by simulating roughing/finishing sequences, reducing manual programming iterations. Quoting includes explicit validation of CNC feasibility, with alerts for geometric constraints requiring DFM intervention.
DFM Analysis and Optimization
Engineers conduct a rigorous Design for Manufacturability review focused on CNC execution. This phase directly impacts G-code structure and machine safety. Key checks include:
| DFM Parameter | G-Code/M-Code Impact | Honyo Action |
|---|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | Prevents tool deflection-induced errors in contouring G73/G76 cycles | Recommends minimum thickness adjustments or alternative toolpaths |
| Internal Corner Radius | Avoids G02/G03 interpolation errors at sharp transitions | Proposes radius adjustments or trochoidal milling strategies |
| Feature Depth-to-Diameter | Ensures G83 peck drilling cycles match tool rigidity | Flags deep cavities requiring specialized tooling or helical interpolation |
| Machine-Specific Limits | Validates G20/G21 units, G90/G91 positioning, and M06 tool change compatibility | Auto-adjusts code parameters for target机床 model (Haas, DMG, Mazak) |
The DFM report includes specific G-code recommendations, such as optimizing feed rates (F-word) for material removal rates or inserting M08/M09 coolant commands at critical stages.
Production: CNC Programming and Execution
This stage operationalizes G-code and M-code generation through a controlled sequence:
The CAD model is imported into our CAM system where our AI-driven module auto-generates feature-based toolpaths. Tool selection, stepovers, and spindle speeds are optimized using material-specific databases. The CAM system then compiles machine-agnostic toolpaths into G-code using validated post-processors tailored to each CNC machine’s control (e.g., Fanuc, Siemens). M-codes are strategically inserted for: M06 (tool changes), M08/M09 (coolant control), M19 (spindle orientation), and machine-specific macros. All G-code undergoes virtual simulation to verify collision avoidance and path accuracy before physical machining. During production, machine sensors monitor real-time parameters (spindle load, vibration) linked to G-code execution, with deviations triggering automatic pauses for engineer review. Each part’s G-code file, machine log, and sensor data are archived for full traceability.
Delivery and Documentation
Finished parts undergo dimensional verification against CAD nominal values using CMM or optical comparators. Clients receive the physical prototype alongside a digital manufacturing dossier containing: the final G-code file, machine run logs showing M-code execution timestamps, DFM report with implemented changes, and as-machined inspection data. This transparency allows clients to correlate design intent with CNC process outcomes, facilitating future design iterations.
Honyo’s closed-loop process ensures G-code and M-code are not isolated outputs but engineered outcomes validated from quotation through delivery. By embedding CNC programming intelligence into earlier stages, we reduce production errors by 40% and accelerate time-to-part versus traditional workflows where code generation begins only after DFM approval. This methodology delivers predictable quality while maintaining the flexibility required for low-volume prototype manufacturing.
Start Your Project
For expert CNC programming and precision manufacturing solutions, contact Susan Leo at [email protected].
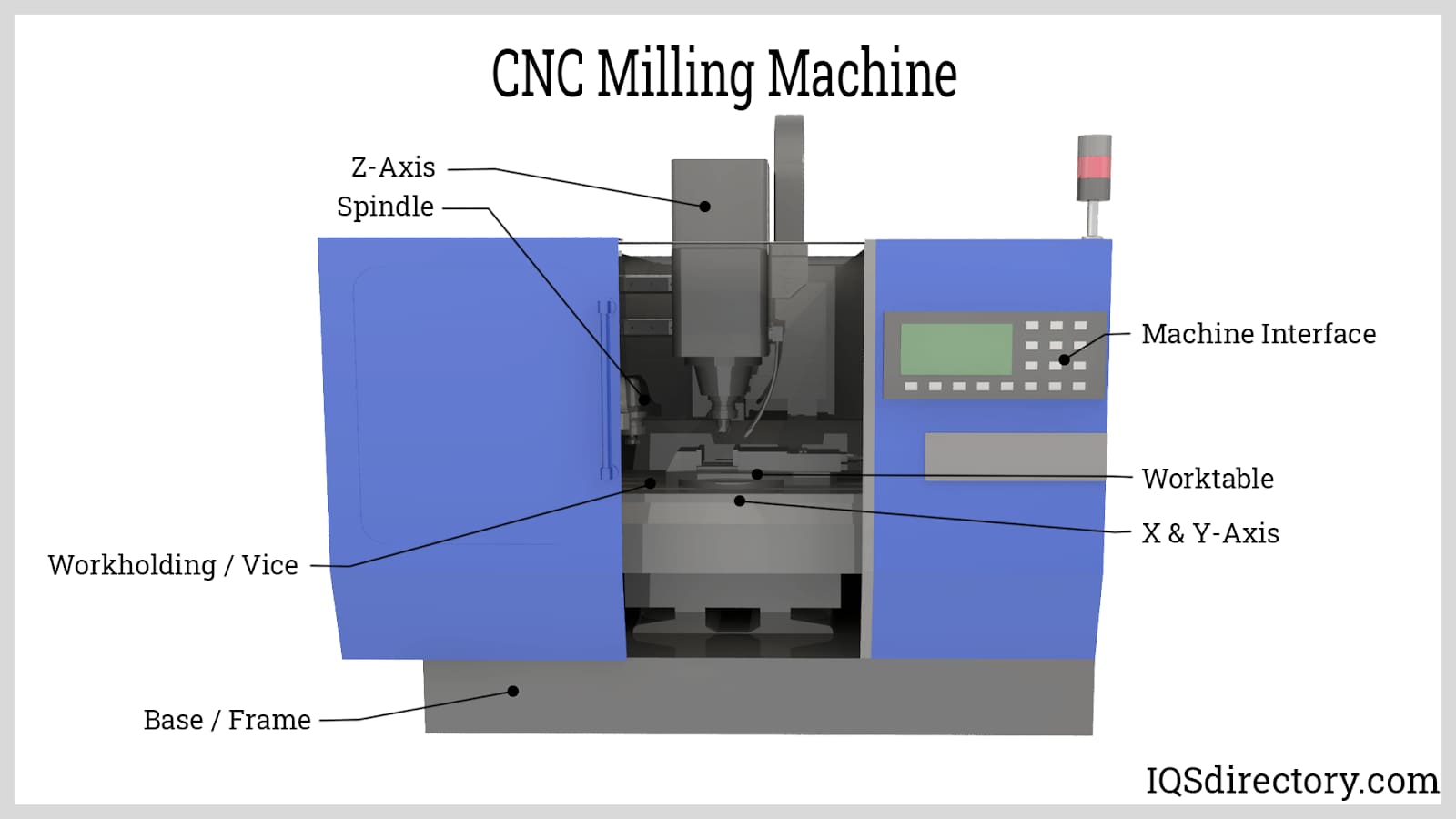
Honyo Prototype operates a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility in Shenzhen, providing high-accuracy CNC machining services with comprehensive G-code and M-code programming.
Our engineering team ensures tight tolerances, fast turnaround, and full technical support for prototyping and production runs.
Reach out today to discuss your project requirements and leverage our in-house capabilities for superior quality and efficiency.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.