Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc for dummies
Navigating the intricacies of sourcing CNC machinery can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly when considering the diverse options available in the global market. This guide on CNC for dummies is designed to demystify the complexities associated with Computer Numerical Control technology, providing you with the insights necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. From understanding the various types of CNC machines—including routers, lathes, and mills—to exploring their applications across industries such as manufacturing, woodworking, and metalworking, this comprehensive resource covers all essential aspects.
Additionally, we will delve into critical topics such as supplier vetting processes, cost analysis, and maintenance considerations. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you will be better positioned to evaluate suppliers, negotiate terms, and ultimately enhance your operational efficiency.
Whether you are based in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or anywhere across South America and Europe, this guide empowers you to confidently navigate the global CNC market. With actionable insights tailored to your unique business needs, you can streamline your procurement process and ensure that you invest wisely in CNC technology that meets your operational demands. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your manufacturing capabilities and drive innovation within your organization.
Understanding cnc for dummies Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Router | Utilizes rotary cutting tools for shaping materials. | Woodworking, Sign Making, Prototyping | Pros: Versatile; ideal for intricate designs. Cons: Limited to softer materials like wood and plastics. |
| CNC Mill | Employs rotary cutters and can work on various materials. | Metalworking, Aerospace, Automotive | Pros: High precision; suitable for complex parts. Cons: Higher cost and maintenance compared to routers. |
| CNC Lathe | Rotates the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool. | Shaft Production, Medical Devices | Pros: Excellent for cylindrical parts; efficient. Cons: Limited to rotationally symmetrical objects. |
| CNC Plasma Cutter | Uses plasma to cut through conductive materials. | Metal Fabrication, Automotive Repair | Pros: Fast cutting speed; effective for thick materials. Cons: Less precision for intricate designs. |
| CNC Laser Cutter | Employs laser technology for precise cutting and engraving. | Signage, Electronics, Jewelry Making | Pros: Exceptional detail; clean edges. Cons: Limited to thinner materials; potentially higher operational costs. |
What are the characteristics of a CNC Router and its B2B relevance?
CNC routers are designed to cut and shape materials using rotary tools, making them ideal for woodworking and sign-making industries. They excel in creating intricate designs and can handle various materials, including wood, plastics, and composites. For B2B buyers, the versatility and cost-effectiveness of CNC routers make them an attractive option for businesses looking to enhance their production capabilities without a significant investment.
How does a CNC Mill differ from other CNC types in terms of applications?
CNC mills are characterized by their ability to utilize rotary cutters to remove material from a stationary workpiece. They are primarily used in metalworking, aerospace, and automotive sectors for producing complex parts with high precision. B2B buyers must consider the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs, but the ability to create intricate metal components justifies the expense for many businesses, especially those requiring rigorous quality standards.
In what scenarios is a CNC Lathe the best choice for businesses?
CNC lathes are specialized for turning operations, where the workpiece rotates against a fixed cutting tool. They are particularly suited for producing cylindrical parts, such as shafts and medical device components. For B2B buyers, investing in a CNC lathe can lead to increased efficiency and reduced waste, especially when mass-producing symmetrical objects. However, their application is limited to rotationally symmetrical designs, which should be considered when evaluating production needs.
What advantages do CNC Plasma Cutters offer for B2B applications?
CNC plasma cutters utilize high-velocity plasma to cut through conductive materials, making them ideal for industries such as metal fabrication and automotive repair. Their speed and ability to cut through thick materials are significant advantages for businesses needing quick turnaround times. However, while plasma cutters excel in speed, they may not achieve the precision required for intricate designs, which is a consideration for buyers looking for versatility in their cutting processes.
Why should businesses consider CNC Laser Cutters for their production needs?
CNC laser cutters employ laser technology to achieve precise cutting and engraving, making them suitable for applications in signage, electronics, and jewelry making. They are known for their exceptional detail and clean edges, which can enhance the quality of finished products. However, B2B buyers should be aware that laser cutters are typically more effective on thinner materials and may incur higher operational costs, making them a strategic investment for businesses focused on high-quality output.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc for dummies
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC for Dummies | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | Enhanced accuracy and reduced waste in production | Supplier certifications, material quality, delivery times |
| Automotive | Custom part fabrication for vehicles | Improved design flexibility and faster prototyping | Machine capabilities, software compatibility, support services |
| Furniture | Woodworking and intricate design production | High-quality finishes and repeatability | Material sourcing, CNC machine size, tooling options |
| Electronics | PCB prototyping and assembly | Faster time-to-market and cost efficiency | Precision requirements, lead times, supplier reliability |
| Medical Devices | Manufacturing of surgical instruments and implants | Strict compliance with health standards and precision | Regulatory certifications, material specifications, traceability |
How is CNC Used in the Aerospace Industry and What Problems Does it Solve?
In the aerospace sector, CNC technology is pivotal for manufacturing precision components like turbine blades and fuselage parts. The need for exacting tolerances and lightweight materials makes CNC machining an ideal solution. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and Europe, it’s essential to source suppliers with appropriate certifications (e.g., AS9100) to ensure compliance with stringent aerospace standards. This technology minimizes waste and enhances production efficiency, making it a valuable investment for manufacturers.
What Role Does CNC Play in Automotive Custom Part Fabrication?
CNC machines are widely used in the automotive industry for fabricating custom parts, allowing manufacturers to create complex geometries that traditional machining methods cannot achieve. This flexibility reduces lead times and enables rapid prototyping, essential for staying competitive in a fast-paced market. Buyers from South America and the Middle East should focus on suppliers that offer advanced CNC capabilities, as well as robust support services to address any operational challenges that may arise.
How Does CNC Enhance Furniture Production?
In furniture manufacturing, CNC routers are employed for woodworking and intricate design production. They enable the creation of detailed patterns and high-quality finishes with remarkable consistency. This technology addresses common challenges such as labor shortages and the need for customization. Buyers in regions like Nigeria should consider the machine size and tooling options available, ensuring they can handle the specific materials and designs required for their projects.
Why is CNC Important for Electronics PCB Prototyping?
CNC machining is critical in the electronics industry for prototyping printed circuit boards (PCBs) and assembling components. The precision offered by CNC technology helps reduce errors and accelerates the development process, which is vital for meeting market demands. International buyers should prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in precision machining and reliable lead times to ensure that they can bring their products to market swiftly and efficiently.
What Advantages Does CNC Offer in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical devices sector, CNC machining is utilized for producing surgical instruments and implants with high precision and adherence to health regulations. The ability to maintain strict tolerances is crucial for ensuring patient safety and device efficacy. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East must ensure that their suppliers have the necessary regulatory certifications and can provide traceability for the materials used, thereby guaranteeing compliance with healthcare standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc for dummies’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding CNC Basics
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers, particularly those new to CNC technology, struggle to grasp the fundamental concepts of CNC operations. This lack of understanding can lead to poor decision-making when selecting machines or software, resulting in costly investments that do not meet their manufacturing needs. For instance, a buyer might purchase a CNC router without comprehending the specific capabilities and limitations of the machine, which can lead to frustration and underutilization.
The Solution:
To overcome this knowledge gap, it is essential for buyers to invest time in educational resources that explain the CNC process in a structured manner. Online courses, tutorials, and comprehensive guides tailored for beginners can provide the foundational knowledge needed to navigate CNC technology effectively. Additionally, engaging with community forums or local CNC workshops can facilitate peer learning and mentorship. Buyers should prioritize understanding the differences between CNC types, such as routers versus mills, and familiarize themselves with essential software tools like CAD and CAM. By building a solid understanding of these basics, buyers can make informed choices about the machinery that best fits their production requirements.
Scenario 2: Ineffective Design-to-Manufacturing Workflow
The Problem:
A common challenge faced by businesses is the inefficient transition from design concepts to actual manufacturing. Many beginners lack experience in creating designs that are optimized for CNC machining, leading to designs that are difficult or impossible to manufacture. For example, a company might invest in advanced CNC machinery only to find that their initial designs require significant modifications to be feasible, resulting in wasted time and resources.
The Solution:
To address this issue, companies should implement a systematic approach to design optimization. This includes utilizing software that allows for simulation and validation of designs before they reach the CNC machine. Buyers should consider training their design teams in Design for Manufacturability (DFM) principles, ensuring that they understand how to create parts that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also practical for production. Additionally, investing in CAD/CAM software that includes features for assessing manufacturability can significantly streamline the workflow. By fostering collaboration between design and manufacturing teams, businesses can ensure that their designs are well-suited for CNC machining from the outset, ultimately reducing lead times and production costs.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Machine Setup and Calibration
The Problem:
Another pain point for B2B buyers is the complexity involved in the setup and calibration of CNC machines. Beginners often face difficulties in configuring machines correctly, which can lead to inaccuracies in production and increased downtime. For instance, a business might experience inconsistent cutting results due to improper tool settings or incorrect machine alignment, ultimately affecting product quality and customer satisfaction.
The Solution:
To mitigate these setup challenges, businesses should develop a standard operating procedure (SOP) for CNC machine setup and calibration. This SOP should include step-by-step instructions and checklists to ensure that all operators follow the same protocol, minimizing the risk of errors. Furthermore, investing in training programs for machine operators can enhance their understanding of setup techniques, tool selection, and calibration processes. It is also beneficial to leverage CNC simulation software that allows operators to visualize the machining process and identify potential issues before actual production begins. By establishing a robust setup protocol and providing thorough training, companies can enhance the reliability and precision of their CNC operations, leading to improved output quality and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc for dummies
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in CNC Machining?
When selecting materials for CNC machining, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, steel, plastic, and wood, focusing on their relevance to B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Perform in CNC Applications?
Aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal that is widely used in CNC machining. Its key properties include excellent thermal and electrical conductivity and a relatively low melting point, making it easy to machine. Aluminum alloys, such as 6061 and 7075, are particularly popular due to their strength-to-weight ratio and versatility.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, lightweight, and offers good machinability. It is also cost-effective for mass production, making it suitable for various applications, including automotive and aerospace components.
Cons: While aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it can be less durable than steel under high-stress conditions. Additionally, its lower melting point can limit its use in high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including air and water, but may not be suitable for harsh chemical environments without proper coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM and DIN is crucial, especially for buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should also consider local sourcing to reduce costs and lead times.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Steel in CNC Machining?
Steel, particularly stainless steel and carbon steel, is renowned for its strength and durability. Key properties include high tensile strength, good wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Pros: Steel is extremely durable and can be used in demanding applications, such as machinery parts and structural components. Its high strength makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Cons: Steel can be more challenging to machine due to its hardness, leading to increased tool wear and manufacturing complexity. It is also generally heavier and more expensive than aluminum.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including oils and fuels, making it suitable for automotive and industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding steel grades and certifications, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where compliance may vary.
How Do Plastics Compare in CNC Machining?
Plastics, such as acrylic, polycarbonate, and nylon, are increasingly popular in CNC applications due to their versatility and ease of machining. They are lightweight and can be manufactured in various colors and finishes.
Pros: Plastics are generally less expensive than metals and offer good corrosion resistance. They are also lightweight and can be easily shaped, making them ideal for prototypes and low-volume production.
Cons: Plastics may not have the same strength or durability as metals, limiting their use in high-stress applications. They can also be sensitive to temperature changes and may deform under heat.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for non-structural applications, such as enclosures, signage, and consumer products, but may not be compatible with high-temperature or high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with relevant safety and environmental regulations, especially in regions with strict compliance standards.
What Role Does Wood Play in CNC Machining?
Wood is a traditional material used in CNC machining, especially for furniture and decorative items. Key properties include natural aesthetics, ease of machining, and a variety of finishes.
Pros: Wood is readily available and cost-effective, with excellent machinability. It offers unique aesthetic qualities and can be finished in various ways.
Cons: Wood can be susceptible to warping, moisture absorption, and insect damage. Its mechanical properties can vary significantly based on the type of wood used.
Impact on Application: Wood is suitable for applications that require aesthetic appeal, such as furniture and cabinetry, but may not be appropriate for structural components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local wood sourcing and compliance with sustainability certifications, especially in regions like Europe, where environmental standards are stringent.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Machining
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc for dummies | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable than steel under stress | Medium |
| Steel | Machinery parts and structural components | Extremely durable and strong | Challenging to machine, heavier | High |
| Plastic | Prototypes and consumer products | Cost-effective and versatile | Less strength, sensitive to heat | Low |
| Wood | Furniture and decorative items | Aesthetic appeal and easy to machine | Susceptible to warping and damage | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc for dummies
What Are the Main Stages of CNC Manufacturing Processes?
CNC manufacturing involves several critical stages that ensure the transformation of raw materials into finished products. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding each stage can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting CNC suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for CNC Machining?
The first step in CNC manufacturing is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate raw material based on the specific requirements of the project. Common materials used in CNC machining include metals (like aluminum and steel), plastics, and composites. The material must be cut to size and cleaned to remove any contaminants that could affect the machining process. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s sourcing practices and the quality of the materials used, as this can significantly impact the end product’s quality.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in CNC Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This is where the actual CNC machining occurs. Various techniques are employed depending on the desired outcome, including milling, turning, and laser cutting. Each technique utilizes specific CNC machines designed for precision and efficiency. For instance, milling machines are ideal for creating complex shapes, while lathes are used for cylindrical objects. B2B buyers should assess suppliers’ capabilities in these techniques to ensure they can meet their manufacturing needs.
How Is Assembly Managed in CNC Manufacturing?
The assembly stage involves putting together the machined components to create the final product. This may include welding, fastening, or bonding parts, depending on the design specifications. Effective assembly processes are crucial for maintaining the integrity and functionality of the final product. Buyers should look for suppliers that have well-defined assembly protocols and skilled labor to minimize errors during this critical phase.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential in CNC Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of the machined parts. Techniques such as sanding, painting, anodizing, and plating are commonly used. The choice of finishing technique can influence both the appearance and durability of the product. B2B buyers should discuss finishing options with suppliers to ensure that the final product aligns with their quality standards and brand expectations.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in CNC Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital component of CNC manufacturing, ensuring that the products meet international standards and customer specifications. Key international standards, such as ISO 9001, provide a framework for implementing effective quality management systems. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and consistency.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in CNC Manufacturing?
QC checkpoints play a crucial role in maintaining quality throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify any deviations from the desired specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection ensures that the finished product meets all quality standards before it is shipped to the customer.
B2B buyers should inquire about their suppliers’ QC protocols and ask for documentation to verify compliance.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in CNC Manufacturing?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure product quality and performance. Common techniques include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers to measure the physical dimensions of parts against specifications.
- Functional Testing: Assessing the product’s performance in real-world conditions to ensure it operates as intended.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the product.
B2B buyers should understand the testing methods used by suppliers and request test reports to confirm the quality of the manufactured parts.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider the following verification methods:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s performance over time.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the specific certifications that may be required in their markets. For instance, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European Union, while API certification is crucial for oil and gas equipment. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers possess the necessary certifications to facilitate smooth trade and compliance with local regulations.
How Do Regional Differences Affect CNC Manufacturing Quality Standards?
Understanding regional differences in quality standards is essential for B2B buyers. Different countries may have varying requirements for materials, manufacturing processes, and safety standards. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure that all aspects of quality assurance align with the regulations of their respective markets.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of CNC manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is critical for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and rigorous quality control practices, buyers can ensure they select suppliers that deliver high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc for dummies’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of procuring CNC equipment and resources tailored for beginners. Understanding the CNC process is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, especially for businesses in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This checklist provides actionable steps to ensure you secure the right equipment and support for your CNC endeavors.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin sourcing CNC equipment, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes understanding the type of CNC machine you need—be it a router, mill, or lathe—and the materials you will be working with.
– Consider the scale of your operations: Are you a hobbyist or a manufacturer?
– Identify your project needs: What dimensions and tolerances do you require?
Step 2: Research Supplier Credentials
It is crucial to vet potential suppliers for their credentials and experience in the CNC industry. Look for suppliers who have a proven track record and can demonstrate their expertise through certifications and customer testimonials.
– Verify industry certifications: Look for ISO certifications or other relevant accreditations.
– Request case studies: These can provide insights into the supplier’s capability and reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website.
– Assess their customer support: Ensure they offer technical support and training for beginners.
– Check for local presence: A supplier with local representatives can facilitate better communication and service.
Step 4: Assess Equipment Features and Compatibility
Examine the features of the CNC machines you are considering. Look for user-friendly interfaces and compatibility with popular CAD/CAM software, which is essential for beginners.
– Investigate software options: Ensure that the machine can work with software you are familiar with or are willing to learn.
– Consider future scalability: Will the machine accommodate your growth as you take on more complex projects?
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Samples
Whenever possible, request live demonstrations of the CNC equipment. This will allow you to assess the machine’s capabilities firsthand and determine if it meets your needs.
– Ask for sample parts: Evaluate the quality of the output to ensure it aligns with your expectations.
– Test user-friendliness: Ensure that the machine is easy to operate, especially for beginners.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier and equipment, carefully negotiate the terms of purchase. This includes pricing, warranties, and support services.
– Clarify payment terms: Understand the payment structure, including any upfront costs and financing options.
– Discuss after-sales support: Ensure that you have access to maintenance services and technical support.
Step 7: Plan for Training and Integration
Finally, consider how you will integrate the CNC machine into your existing operations. Plan for necessary training sessions for your team to maximize the machine’s potential.
– Evaluate training programs: Check if the supplier offers training sessions or resources.
– Prepare your workspace: Ensure that you have adequate space and resources for the new equipment.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for CNC equipment tailored for beginners, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc for dummies Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Sourcing for Beginners?
When sourcing CNC machinery and services, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the total cost. Common materials like wood, plastics, and metals vary in price and availability. For example, sourcing aluminum may be more expensive in certain regions due to import tariffs or local supply chain limitations.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial for CNC operations. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region and the expertise required. For instance, hiring skilled CNC operators in countries with lower labor costs, such as Nigeria or certain parts of South America, can lead to substantial savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, maintenance, and facility operations. Overhead can be higher in regions with less efficient energy sources or where real estate costs are significant.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling, such as cutting tools and fixtures, can be substantial. Custom tooling for specific projects may increase these costs further.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that products meet specifications, which can increase costs but reduce the risk of defects and rework.
-
Logistics: Transporting materials to the manufacturing site and finished products to customers can incur significant costs, especially for international shipments. Understanding local logistics networks is vital for effective cost management.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to their costs, which can vary based on the competitive landscape and relationship with buyers.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect CNC Costs for International Buyers?
Several factors influence pricing for CNC services and machinery, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes can often lead to bulk discounts. Establishing minimum order quantities (MOQ) can help negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs can lead to increased costs, particularly if they require specialized materials or tooling. Buyers should clearly communicate their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications (like ISO) can affect pricing. Suppliers may charge more for certified materials, but this often leads to better quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can also influence pricing. Engaging with established suppliers who have a track record of reliability can yield better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact total costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices in CNC Sourcing?
Effective negotiation strategies can enhance cost-efficiency for international B2B buyers:
-
Conduct Thorough Research: Understanding the market rates for CNC services and machinery in different regions can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price but also long-term costs associated with maintenance, operations, and potential downtime.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing flexibility. Regular communication and feedback can foster trust and collaboration.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Engaging multiple suppliers can create competitive pressure, potentially leading to better pricing and terms.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing structures based on local economic conditions, import duties, and labor costs. Understanding these nuances can help buyers make informed decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for CNC machinery and services can fluctuate based on numerous factors, including market demand, material availability, and economic conditions. It is advisable for buyers to obtain multiple quotes and conduct due diligence before finalizing any agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc for dummies With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives in CNC Solutions
When exploring CNC (Computer Numerical Control) solutions, especially for beginners, it’s crucial to consider various alternatives. Each method or product serves different needs, budget levels, and operational complexities. By comparing ‘CNC for Dummies’ with other viable solutions, businesses can make informed decisions tailored to their specific requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | CNC For Dummies | Alternative 1: Traditional CNC Training | Alternative 2: CNC Workshops |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Basic understanding of CNC operations, ideal for novices | Comprehensive knowledge, suitable for professionals | Hands-on experience, practical skills development |
| Cost | Low-cost or free resources | Higher upfront costs for courses and materials | Moderate costs for short-term programs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple concepts, easy to grasp | Requires commitment and time investment | Requires initial registration and scheduling |
| Maintenance | Minimal ongoing support | Continuous learning required | Networking opportunities and support from instructors |
| Best Use Case | Beginners needing foundational knowledge | Professionals seeking advanced skills | Individuals wanting hands-on experience |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Alternative 1: Traditional CNC Training
Traditional CNC training programs provide comprehensive courses designed for individuals aiming to deepen their understanding of CNC technologies. These programs often cover advanced topics such as G-code programming, machine setup, and troubleshooting. However, the investment is significantly higher, both in terms of time and money. While these courses are beneficial for those pursuing a career in CNC machining, they may overwhelm beginners who are just starting.
Alternative 2: CNC Workshops
CNC workshops are short-term, hands-on training sessions that focus on practical skills. Participants get the chance to work directly with CNC machines, enhancing their learning through real-world applications. These workshops are typically more affordable than full-fledged training programs and are ideal for hobbyists or small business owners looking to gain immediate skills. However, they may lack the depth of knowledge found in traditional training, leaving participants with a limited understanding of CNC theory.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right CNC Solution for Your Business Needs
Selecting the right CNC solution hinges on understanding your specific goals and resources. For absolute beginners, ‘CNC for Dummies’ offers a solid foundation, equipping you with essential knowledge without substantial investment. If your aim is to develop advanced skills for professional purposes, traditional CNC training might be the best fit despite its higher costs. On the other hand, CNC workshops provide a balanced approach, offering practical experience at a moderate cost. By evaluating these alternatives based on performance, cost, and specific use cases, B2B buyers can confidently choose the solution that aligns best with their operational needs and learning objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc for dummies
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Machines?
Understanding the technical properties of CNC machines is crucial for B2B buyers, as these specifications directly impact the performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of manufacturing processes. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of material used for CNC machining, such as aluminum, steel, or plastics. Different grades have varying properties, including strength, durability, and machinability. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade ensures that the final products meet industry standards and performance requirements, which is essential for maintaining competitive advantage.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in a manufactured part. It is expressed in units of measurement (e.g., millimeters or inches) and can significantly affect the functionality of the final product. High precision tolerances are crucial in industries like aerospace and automotive, where even minor discrepancies can lead to failure. For buyers, understanding tolerance requirements helps in selecting the right machining process and avoiding costly rework.
3. Axis Configuration
CNC machines operate on multiple axes, commonly in three dimensions (X, Y, Z). However, more advanced machines may have additional axes (e.g., 4-axis or 5-axis) to allow for more complex geometries and improved efficiency. Buyers must assess the axis configuration based on their project requirements to ensure that the CNC machine can handle the intended designs without compromising quality.
4. Spindle Speed
Spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), indicates how fast the CNC machine can rotate its cutting tool. Higher spindle speeds can lead to faster machining times and smoother finishes. However, they also require careful consideration of material compatibility and tool wear. For B2B buyers, understanding spindle speed helps in optimizing production schedules and reducing operational costs.
5. Feed Rate
Feed rate refers to the speed at which the CNC machine moves the material during the cutting process, usually measured in millimeters per minute. A well-calibrated feed rate ensures efficient material removal while maintaining the quality of the finished product. Buyers should consider the feed rate to improve productivity and achieve the desired surface finish.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the CNC Industry?
Navigating the CNC landscape requires familiarity with industry jargon. Here are some common trade terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that are then marketed by another company under its brand name. Understanding the role of OEMs is essential for buyers looking to source components or collaborate on product development.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to produce or sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cost calculations. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their orders effectively and avoid overstocking or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing them to compare offers and make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. These terms clarify aspects such as shipping, insurance, and duties. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in global trade, as it helps mitigate risks and ensure smooth logistics.
5. CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
CAM refers to the software used to control machine tools in the manufacturing process. It converts CAD designs into machine-readable code (G-code). Understanding CAM is essential for buyers involved in product design and production, as it directly impacts efficiency and accuracy in manufacturing.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their supply chains, and enhance their competitiveness in the CNC manufacturing landscape.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc for dummies Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the CNC Sector for International Buyers?
The CNC market is experiencing a transformative phase, driven by technological advancements and a growing demand for precision manufacturing across various industries. International B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly recognizing the importance of CNC technology in enhancing operational efficiency and product quality. Key trends include the rise of automation and Industry 4.0, where interconnected machines and data analytics are revolutionizing traditional manufacturing processes. Buyers are not only interested in CNC machines but also in software solutions that facilitate better design and production planning, thus enhancing their competitive edge.
Emerging technologies such as 3D printing and additive manufacturing are also influencing CNC sourcing strategies. These innovations allow for rapid prototyping and customized production, which can significantly reduce lead times and costs. Moreover, the increasing adoption of cloud-based CNC solutions enables businesses to manage their operations remotely, offering flexibility that is crucial in today’s fast-paced market. As buyers from diverse regions engage with suppliers, understanding local market dynamics and regulatory requirements is essential to navigate sourcing challenges effectively.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Relationships in the CNC Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of B2B procurement strategies, particularly in the CNC sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has led buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. This includes sourcing raw materials that are sustainably harvested and employing production techniques that minimize waste and energy consumption. For international buyers, particularly those from regions facing environmental challenges, aligning with suppliers committed to sustainability can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to a growing base of environmentally conscious consumers.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are crucial in building trust and long-term relationships with suppliers. Buyers should consider suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and provide transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. By prioritizing these factors, international buyers can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and enhance their overall procurement strategy.
What Is the Evolution of CNC Technology and Its Relevance to Today’s B2B Landscape?
CNC technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1940s, transitioning from mechanical systems to sophisticated digital controls. Initially, CNC machines were limited to a few applications, but advancements in computer technology and software have expanded their capabilities across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and woodworking. This evolution has made CNC machines more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises, enabling them to compete on a global scale.
Today, CNC technology is characterized by precision, speed, and versatility, making it an essential tool for manufacturers looking to optimize production processes. The integration of AI and machine learning into CNC operations is also on the rise, allowing for predictive maintenance and enhanced performance monitoring. For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial in making informed purchasing decisions and leveraging CNC technology for their manufacturing needs. As the market continues to advance, staying abreast of these developments will be key to maintaining a competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc for dummies
-
How do I choose the right CNC machine for my business needs?
Choosing the right CNC machine involves assessing your specific requirements such as the type of materials you will work with, desired production volume, and the complexity of parts you intend to manufacture. Evaluate machines based on their capabilities, including cutting speed, precision, and the range of operations they can perform (like milling, routing, or plasma cutting). Additionally, consider factors like available space, power requirements, and your budget. Engaging with suppliers for demonstrations and comparisons can also provide valuable insights. -
What is the best CNC machine for small-scale production?
For small-scale production, CNC routers or desktop CNC mills are often recommended due to their versatility and relatively lower cost. These machines can handle various materials like wood, plastics, and soft metals. Look for models that offer user-friendly software, reliable customer support, and a strong community for shared resources. Brands like Shapeoko or X-Carve are popular among small businesses for their affordability and ease of use. -
How can I ensure the quality of CNC machines when sourcing internationally?
To ensure quality when sourcing CNC machines internationally, start by vetting suppliers through third-party certifications and reviews. Request detailed specifications, including material quality, machine tolerances, and manufacturing processes. It’s beneficial to ask for samples or visit the supplier’s facility if possible. Establishing clear quality assurance protocols and agreements on warranties can further safeguard your investment. -
What are the common payment terms when purchasing CNC machines?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on the supplier and the region. Common terms include a deposit upon order (typically 30-50%), with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers might offer financing options or payment plans. Ensure to clarify terms regarding currency, payment methods (like wire transfers or letters of credit), and any penalties for late payments to avoid misunderstandings. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC machines?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC machines can vary by supplier and machine type. Some manufacturers may have an MOQ of one unit, especially for small or custom machines, while others might require bulk orders to justify production costs. When sourcing, always inquire about MOQs and negotiate based on your needs, especially if you are looking for a single unit for a pilot project. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for CNC machines?
Handling logistics for CNC machines involves coordinating with your supplier to determine the best shipping method, whether by sea, air, or land. Assess the costs, transit times, and customs regulations for your destination. Working with a freight forwarder can streamline this process, ensuring compliance with import regulations and handling necessary documentation. Always factor in insurance for high-value machinery during transit. -
What customization options should I consider when ordering CNC machines?
Customization options for CNC machines can include modifications to size, cutting capabilities, software integration, and additional tooling. Discuss your specific production needs with the supplier to determine what modifications are possible. Custom features may enhance productivity and efficiency, but it’s essential to balance these with budget constraints. Request detailed quotes for any customizations to avoid unexpected costs. -
How can I ensure ongoing support and maintenance for my CNC machine?
To ensure ongoing support and maintenance, choose a supplier known for excellent customer service and technical support. Investigate warranty options and what they cover regarding repairs or replacement parts. Additionally, consider training programs for your staff to maximize machine usage and efficiency. Establishing a maintenance schedule and keeping a stock of essential spare parts can also help prevent downtime in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Cnc For Dummies Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Practical Machinist – CNC Programming Essentials
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1. Book: CNC Programming Handbook, 2nd Edition by Peter Smid – Price: $53.95 from Enco. Recommended for beginners as a standard text for CNC programming.
2. Book: Principles of Numerical Control by James J. Childs – Published in 1965, recommended for its historical value and basics of CNC.
3. Website: Beta Technical – Offers a beginner-friendly book for $48, includes a simulator for practice.
4. R…
2. Autodesk – Fusion 360
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Fusion 360 (Mac / Windows) – Autodesk product, free for Hobbyists/Enthusiasts/Startups making less than $100K/year, powerful 3D modeling software, easy to learn, cross-platform, sophisticated CAM environment, not a web app, ideal for digital fabrication including CNC milling.
3. Tamiyaclub – CNC Setup for Hobbyists
Domain: tamiyaclub.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: CNC setup for 1600 euros, excluding software. Designed for hobby use, potentially based on a Dremel Multi-tool. Discussion on its suitability for beginners with some knowledge of metal and computers. Concerns about precision and cost of Dremel bits. Interest in 3D polymer printers for prototyping, with a starting price of 14K euros. Mention of the ability to produce parts for vacuforming and other…
4. American Micro Inc – CNC Programming Solutions
Domain: americanmicroinc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: CNC Programming for Beginners, CNC Machining Services, Types of CNC Programming (Manual, CAM, Conversational), Software for CNC Programming (CAD, CAE, CAM), Key Codes Used in CNC Programming (G-codes, M-codes, S-codes, T-codes, D-codes, F-codes), Tips for Beginners, Request a Free Quote.
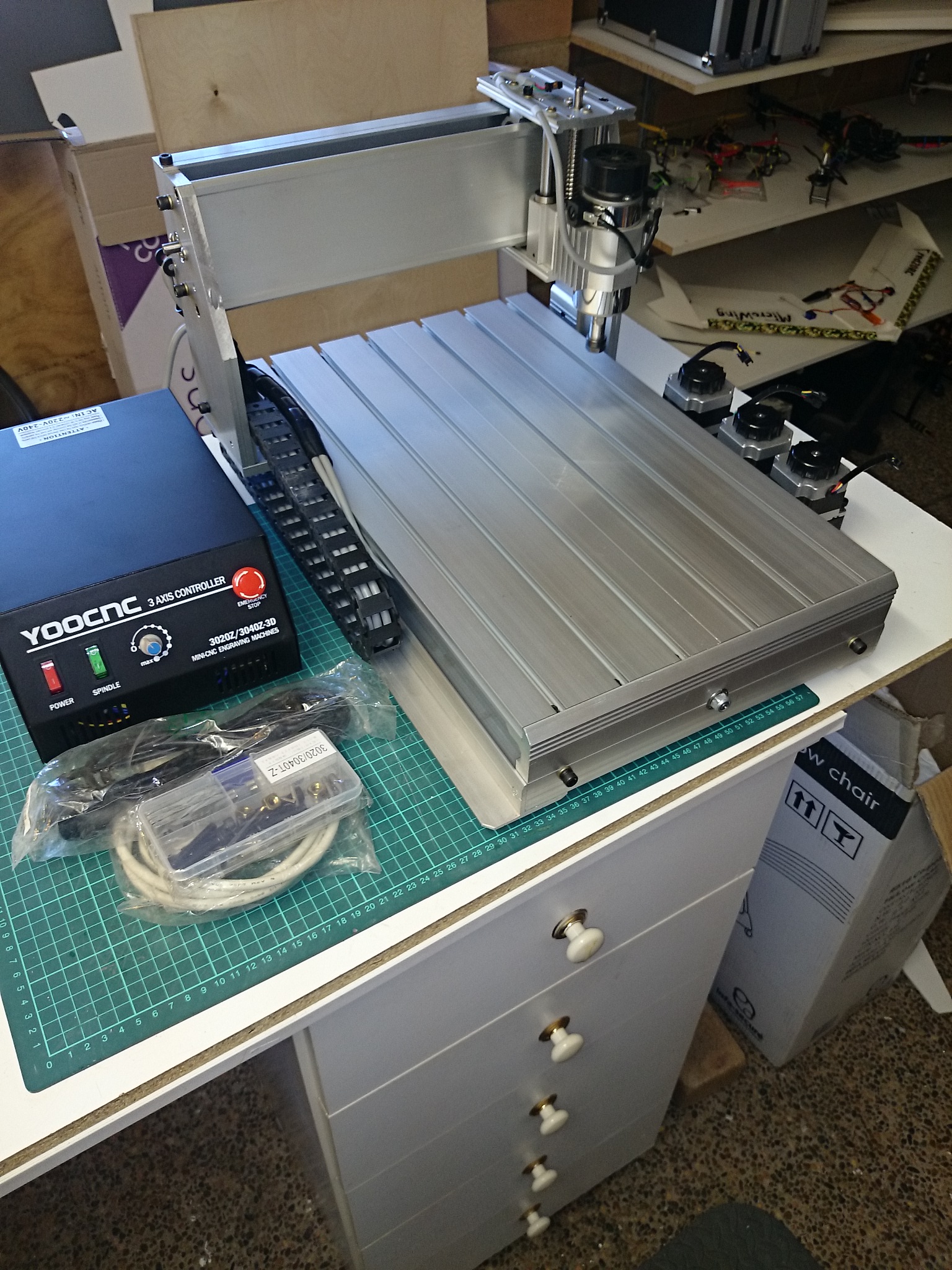
5. Flite Test – CNC3040Z CNC Machine
Domain: flitetest.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: CNC3040Z CNC machine; USB driven; requires software for toolpaths and GCode; compatible with 32-bit Windows; needs a proper serial port; not suitable for laptops; requires router bits, specifically end mills; sacrifice board needed for cutting; recommended software includes Sketchup for design, Adobe Illustrator for vector conversion, Vectric Cut2D for toolpaths, and Mach3 Mill for motion control.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc for dummies
In the evolving landscape of CNC technology, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers looking to enhance their manufacturing capabilities. By understanding the nuances of CNC systems—from routers to mills—businesses can make informed decisions that align with their production needs and budget constraints. Emphasizing the importance of initial design considerations and the role of software in the CNC process can lead to significant cost savings and efficiency gains.
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the opportunity to leverage advanced CNC solutions is substantial. Investing in quality machines and software not only enhances production precision but also boosts competitiveness in global markets.
As we look ahead, the integration of automation and smart technologies into CNC operations is set to redefine the manufacturing landscape. Now is the time for B2B buyers to explore partnerships with reputable suppliers and invest in training for their teams to fully utilize CNC capabilities. Embrace this journey to transform your manufacturing process and stay ahead in the dynamic marketplace.