Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc fixture
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing the right CNC fixtures can be a pivotal challenge for international B2B buyers. These essential workholding tools are crucial for ensuring precision and efficiency in CNC machining processes, yet navigating the diverse options available can feel overwhelming. This guide aims to demystify the global market for CNC fixtures by providing a comprehensive overview of various types, applications, and design considerations. Whether you are in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—countries like Brazil and Saudi Arabia included—understanding these components is vital for optimizing production workflows and enhancing operational performance.
Throughout this guide, you will discover the different types of CNC fixtures tailored for specific machining processes, such as milling, turning, and drilling. Additionally, we will delve into practical insights on supplier vetting, cost considerations, and best practices for implementing these fixtures in your operations. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you will be empowered to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your unique manufacturing needs. This guide not only highlights the importance of CNC fixtures but also serves as a valuable resource for fostering efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness in your business.
Understanding cnc fixture Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Vise Fixtures | Precision clamping with inclined planes | General machining, automotive, aerospace | Pros: High precision, versatile; Cons: Can be costly for specialized designs. |
| Milling Fixtures | Rotary table fixtures, vise fixtures, fixture plates | CNC milling operations | Pros: Adaptable to various setups; Cons: Setup complexity may require skilled operators. |
| Turning Fixtures | Includes faceplates, collets, and chucks | CNC turning operations, especially for cylindrical parts | Pros: Excellent for round objects; Cons: Limited to specific shapes and sizes. |
| Grinding Fixtures | Centerless, magnetic chucks, and sine bars | Precision grinding applications | Pros: Ensures stability during grinding; Cons: May require additional setup time. |
| Vacuum Fixtures | Utilizes vacuum pressure to hold workpieces | Woodworking, plastic machining, and composite materials | Pros: Even distribution of pressure; Cons: Limited to flat or non-porous surfaces. |
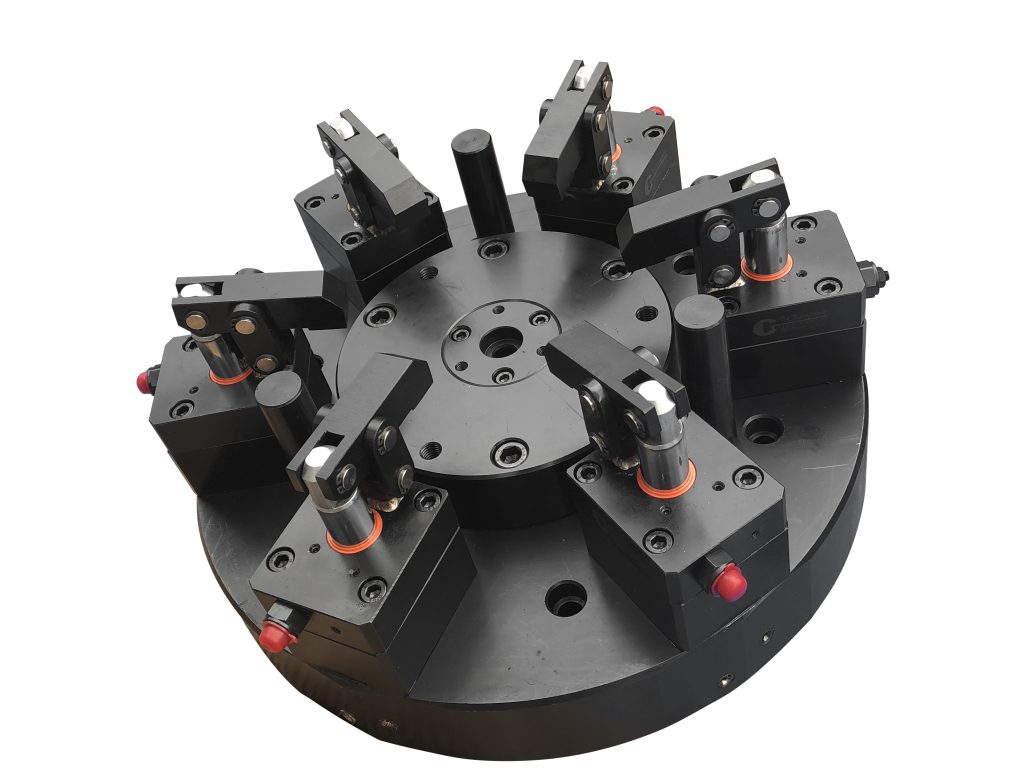
What are CNC Vise Fixtures and Their Applications in B2B?
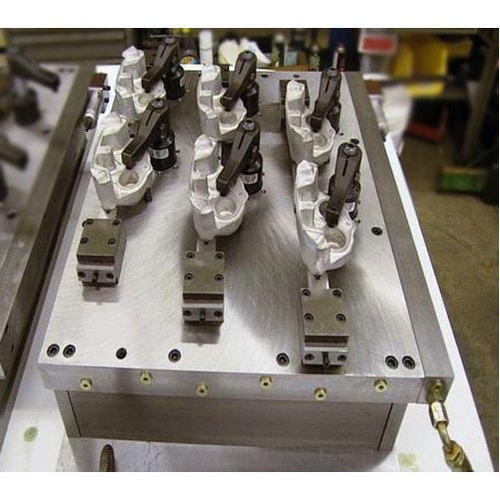
CNC vise fixtures are a cornerstone in machining setups, offering precise clamping through the use of inclined planes that enhance grip. Commonly employed in general machining, automotive, and aerospace industries, these fixtures excel in ensuring stability and accuracy. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the fixture’s clamping force, material compatibility, and the potential need for customization, as specialized designs can drive up costs. The versatility and high precision of CNC vises make them a preferred choice, despite their investment requirements.
How Do Milling Fixtures Enhance CNC Operations?
Milling fixtures encompass a range of tools, including rotary tables and fixture plates, designed specifically for CNC milling operations. They are adaptable and can accommodate various setups, making them ideal for industries that require flexibility in machining processes. However, the complexity of setting up these fixtures may necessitate skilled operators, which can be a consideration for businesses looking to streamline production. Buyers should assess the fixture’s adaptability to their existing machinery and the learning curve associated with its operation.
What Makes Turning Fixtures Essential for CNC Machining?
Turning fixtures, such as faceplates and collets, are crucial for CNC turning operations, particularly for cylindrical parts. Their design allows for secure holding of round materials, ensuring precision during machining. While they provide excellent stability for specific shapes, buyers must consider their limitations regarding non-cylindrical parts. When purchasing turning fixtures, businesses should focus on the range of sizes supported and compatibility with their CNC lathes to ensure seamless integration into their production processes.
Why Choose Grinding Fixtures for Precision Applications?
Grinding fixtures, including centerless and magnetic chucks, are designed to maintain stability during precision grinding applications. They are essential in industries that demand high accuracy, such as aerospace and automotive sectors. However, the setup time for these fixtures can be longer, which may affect production schedules. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced stability against the time required for setup, ensuring that the investment aligns with their operational efficiency goals.
What are the Advantages and Limitations of Vacuum Fixtures?
Vacuum fixtures leverage vacuum pressure to secure workpieces, making them particularly effective in woodworking and plastic machining. Their ability to distribute pressure evenly allows for consistent results across flat or non-porous materials. However, the use of vacuum fixtures is limited to specific applications, and they may not be suitable for all types of materials. Buyers should consider the types of materials they typically work with and the need for specialized setups when evaluating vacuum fixture options.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc fixture
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Fixture | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Precision machining of engine components | Enhanced accuracy and reduced production time | Compatibility with specific machinery and materials |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of airframe structures | Lightweight yet robust fixtures for complex shapes | Certification standards and material quality |
| Electronics | Assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs) | Improved assembly speed and reliability | Customization options for unique PCB designs |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments | High precision to meet regulatory requirements | Compliance with industry standards and safety |
| Energy | Machining turbine components | Increased efficiency and reduced downtime | Sourcing durable materials for high-stress parts |
How is CNC Fixture Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, CNC fixtures are pivotal in the precision machining of engine components, such as cylinder heads and crankshafts. These fixtures ensure that workpieces are securely held in place, allowing for accurate cutting and shaping. By reducing human error and streamlining the production process, businesses can achieve higher output rates and lower manufacturing costs. Buyers should consider the compatibility of CNC fixtures with their existing machinery and the specific materials used in their components to ensure optimal performance.
What Role Does CNC Fixture Play in Aerospace Manufacturing?
Aerospace manufacturing involves the creation of complex airframe structures that require both lightweight materials and high precision. CNC fixtures facilitate the machining of intricate designs while maintaining the structural integrity of components. This efficiency not only shortens production timelines but also enhances the overall quality of the products. International buyers must prioritize suppliers who can provide fixtures that meet stringent certification standards and utilize high-quality materials to withstand the rigors of aerospace applications.
How are CNC Fixtures Essential for Electronics Assembly?
In the electronics industry, CNC fixtures are crucial for the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs). These fixtures enable precise positioning and clamping of components during assembly, which significantly improves the speed and reliability of the process. As the demand for smaller, more complex electronic devices grows, businesses require customized fixtures that can accommodate unique designs. Buyers should seek suppliers who offer tailored solutions and can guarantee the durability of fixtures against the rigors of high-volume production.
Why are CNC Fixtures Important in Medical Device Fabrication?
The medical device industry demands the highest levels of precision, especially in the fabrication of surgical instruments. CNC fixtures are used to ensure that these instruments are manufactured to exact specifications, which is critical for compliance with regulatory requirements. The use of CNC fixtures minimizes the risk of human error, leading to safer and more reliable medical devices. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing fixtures that comply with industry standards and are made from materials that meet safety regulations.
How Do CNC Fixtures Enhance Efficiency in the Energy Sector?
In the energy sector, particularly in the machining of turbine components, CNC fixtures play a vital role in enhancing operational efficiency. These fixtures allow for the precise machining of high-stress components, which are essential for the performance of turbines. By optimizing the production process, businesses can reduce downtime and improve overall productivity. Buyers should consider sourcing durable materials that can withstand the demanding conditions typical in energy applications, ensuring longevity and performance of the fixtures.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc fixture’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Machining Results Due to Poor Fixture Design
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges with inconsistent machining results, primarily caused by poorly designed CNC fixtures. When fixtures fail to provide adequate support or positioning, it can lead to variations in the final product’s dimensions and tolerances. This inconsistency not only affects the quality of the output but also results in increased material waste and the need for rework, ultimately impacting production timelines and costs. Buyers may feel frustrated as they struggle to achieve the precision required for their applications, especially in industries such as automotive or aerospace, where tolerances are critical.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality CNC fixtures specifically tailored to their machining processes. Collaborating with manufacturers that specialize in custom fixture design can lead to solutions that meet unique production requirements. Buyers should clearly specify their needs, including the types of materials being machined, the expected tolerances, and any specific operational constraints. Additionally, investing in advanced design software can assist in simulating fixture performance before actual production, allowing for adjustments and optimizations that enhance stability and precision. Regularly reviewing and updating fixture designs based on performance feedback can also foster continuous improvement, ensuring that machining operations remain efficient and accurate.
Scenario 2: High Setup Times Leading to Production Delays
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the lengthy setup times associated with CNC fixtures. In industries where time is money, prolonged setup can significantly disrupt workflow and delay production schedules. Buyers may find themselves losing valuable hours as machinists struggle to align and secure workpieces, especially when dealing with complex parts that require multiple operations. This challenge can be exacerbated in regions with limited access to skilled labor, making it even more crucial to streamline the setup process.
The Solution: To mitigate setup times, buyers should consider investing in modular and quick-change CNC fixtures. These fixtures allow for rapid reconfiguration and adjustment, enabling machinists to switch between different workpieces with minimal downtime. Additionally, implementing standardized procedures for fixture setup can enhance efficiency. Creating detailed setup guides and training programs for operators can help ensure that everyone involved understands the process and can execute it swiftly. Furthermore, leveraging technologies such as digital tooling and automated setup systems can significantly reduce human error and improve overall productivity.
Scenario 3: Cost Overruns Due to Inefficient Fixture Utilization
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face financial challenges stemming from inefficient utilization of CNC fixtures, which can lead to unexpected costs. Fixtures that are not optimally designed or utilized may require more complex setups, leading to increased labor costs and longer cycle times. Additionally, the inability to effectively manage multiple workpieces or varying sizes can result in excess inventory or unproductive machine time. This inefficiency not only affects the bottom line but can also strain relationships with clients expecting timely deliveries.
The Solution: To combat cost overruns, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their current CNC fixture usage and identify areas for improvement. Implementing a fixture management system that tracks the performance and utilization rates of each fixture can provide valuable insights. Buyers should also prioritize investing in versatile fixtures that can accommodate a range of workpiece sizes and types. By focusing on standardization and modularity, companies can reduce the need for multiple specialized fixtures, leading to lower inventory costs and simplified storage solutions. Regular audits of fixture performance and adjustments based on production data can further enhance efficiency, leading to more predictable costs and improved customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc fixture
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for CNC Fixtures?
When selecting materials for CNC fixtures, it is crucial to consider their properties, performance under various conditions, and the specific needs of the application. Here, we analyze four common materials used in CNC fixture manufacturing: aluminum, steel, cast iron, and composite materials.
How Does Aluminum Perform as a Material for CNC Fixtures?
Aluminum is a lightweight and versatile material often used in CNC fixtures. It boasts excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for environments where moisture or chemicals are present. Its thermal conductivity allows for effective heat dissipation during machining processes, which is particularly beneficial in high-speed operations.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively easy to machine, which reduces manufacturing complexity and costs. It is also lightweight, making it easier to handle and adjust during setup.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it may not withstand high-pressure applications as effectively as steel or cast iron. Additionally, it can be more expensive than some alternatives, depending on the alloy used.
Impact on Application: Aluminum fixtures are suitable for applications involving non-ferrous materials and lighter components. However, they may not be ideal for heavy-duty machining tasks.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM) regarding aluminum grades. Understanding the specific alloy’s properties is essential for performance expectations.
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Using Steel for CNC Fixtures?
Steel, particularly carbon steel, is a popular choice for CNC fixtures due to its strength and durability. Steel fixtures can handle high-pressure applications and maintain stability during machining.
Pros: Steel is robust and offers excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for high-volume production environments. It is also cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: Steel fixtures are heavier, which can complicate handling and setup. They are also prone to corrosion if not properly treated, necessitating additional protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Steel is ideal for heavy-duty machining tasks, especially in industries such as automotive and aerospace where precision and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers: Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should be aware of compliance with standards such as DIN and JIS, particularly regarding steel grades and treatments.
Why Is Cast Iron a Preferred Material for CNC Fixtures?
Cast iron is known for its excellent vibration-damping properties, making it a preferred choice for CNC fixtures in precision machining applications. It offers high rigidity and stability, which helps maintain accuracy during the machining process.
Pros: Cast iron is highly durable and can withstand significant wear, making it suitable for long-term use. Its ability to absorb vibrations helps improve the quality of the machined parts.
Cons: Cast iron is heavy and can be brittle, which may lead to breakage under extreme stress. It is also more complex to machine compared to aluminum or steel.
Impact on Application: Cast iron fixtures are particularly effective in applications where precision is critical, such as in the production of intricate components.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers: Buyers should ensure that cast iron fixtures meet relevant standards (e.g., ASTM A48) and are suitable for their specific machining requirements.
How Do Composite Materials Compare for CNC Fixtures?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics, are increasingly used in CNC fixtures due to their lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio. They offer excellent corrosion resistance and dimensional stability.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and can be tailored to specific applications, providing flexibility in design. They also resist environmental degradation, making them suitable for various conditions.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost of composites compared to metals. Additionally, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for applications requiring lightweight fixtures, such as in aerospace or automotive industries where reducing weight is critical.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the certifications and standards applicable to composite materials, particularly in regions with stringent safety regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Fixtures
| Material | Typical Use Case for CNC Fixture | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight fixtures for non-ferrous machining | Excellent corrosion resistance | Less suitable for high-pressure applications | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty machining in automotive/aerospace | High strength and wear resistance | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Cast Iron | Precision machining for intricate components | Excellent vibration damping | Heavy and brittle under stress | Medium |
| Composite | Lightweight fixtures in aerospace/automotive | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and not suitable for high temperatures | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in CNC fixtures, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc fixture
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of CNC Fixtures?
The manufacturing process of CNC fixtures involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision and quality. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing CNC fixtures is the careful selection and preparation of materials. Common materials used include aluminum, steel, and composite materials, chosen for their strength, durability, and machinability. Suppliers often conduct an initial inspection of raw materials to ensure they meet specified standards. This may include checking for material properties like tensile strength and hardness, as well as dimensional accuracy, which are crucial for the fixture’s performance. -
Forming Techniques
The forming stage utilizes various machining techniques, such as CNC milling, turning, and grinding, to create the necessary shapes and dimensions for the fixture components. Advanced CNC machines are programmed with precise specifications derived from CAD designs, enabling high accuracy and repeatability. Techniques like laser cutting and water jet cutting may also be employed for intricate designs, ensuring that complex geometries are achieved without compromising the material’s integrity. -
Assembly Processes
After forming, the components are assembled. This stage may involve welding, bolting, or using adhesives, depending on the fixture design and application. Rigorous alignment is critical here, as any misalignment can lead to inaccuracies in the machining process. Automation in assembly can enhance consistency, but manual checks are often employed to ensure each part fits correctly and functions as intended. -
Finishing Techniques
The final stage involves surface finishing, which enhances the durability and aesthetic of the fixture. Techniques such as anodizing, powder coating, or grinding can be utilized to achieve the desired surface characteristics. This stage is crucial for protecting the fixture from wear and corrosion, particularly in demanding environments. Moreover, the finishing process often includes a final inspection to ensure that the surface quality meets the required standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for CNC Fixture Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of CNC fixture manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Key elements of QA include adherence to relevant standards, implementing systematic checkpoints, and employing various testing methods.
-
International Standards for Quality Assurance
Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for manufacturers targeting global markets. ISO 9001 outlines requirements for a quality management system, focusing on consistent quality and continuous improvement. Other industry-specific standards, such as CE marking in Europe or API specifications in the oil and gas sector, may also apply depending on the fixture’s intended use. These standards help build trust with international buyers by ensuring that products meet stringent quality criteria. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified criteria before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, periodic checks are conducted to monitor the quality of the processes and components. This can include dimensional checks and functional tests to confirm that the fixtures are being produced to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, a comprehensive inspection is performed. This includes verifying that the fixture meets all design specifications, surface finish requirements, and functional tests.
- Common Testing Methods for Quality Assurance
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality of CNC fixtures. These can include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools like calipers and CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) to verify the dimensions and tolerances of the finished product.
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that the fixture operates as intended under real-world conditions, which may involve simulating operational stresses.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or dye penetrant inspection can be used to identify internal flaws without damaging the fixture.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is crucial for ensuring product reliability.
-
Supplier Audits
Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality management systems. These audits can assess compliance with international standards, evaluate the effectiveness of their QA processes, and ensure that they have robust systems in place for material handling, production, and testing. -
Requesting Quality Assurance Documentation
Buyers should request documentation that demonstrates the supplier’s commitment to quality. This includes certificates of compliance with ISO standards, test reports, and records of previous quality inspections. A reputable supplier should be able to provide detailed reports that outline their quality assurance processes and results. -
Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services
Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control practices. These services can conduct independent inspections and provide reports on compliance with specified standards, which can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing from international suppliers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When engaging with suppliers across different continents, B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Standards
Different regions may have varying interpretations of quality standards. For instance, what is considered acceptable in one country may not meet the expectations of buyers in another. It is essential for buyers to communicate their quality requirements clearly and ensure that suppliers understand the significance of adhering to those standards. -
Regulatory Compliance
Understanding the regulatory landscape in the supplier’s country is vital. Some regions may have less stringent regulations, which can affect the quality of products. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international regulations, particularly if the fixtures are intended for critical applications. -
Logistical Considerations
The logistics involved in sourcing and transporting CNC fixtures can impact quality. Buyers must consider how fixtures are packaged and transported to prevent damage during transit. Additionally, understanding the lead times and potential delays in delivery can help in planning for contingencies.
By understanding these aspects of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for CNC fixtures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc fixture’
Introduction
This sourcing guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure CNC fixtures. CNC fixtures are essential for ensuring precision and efficiency in machining operations, making the right choice critical for your manufacturing processes. Following this step-by-step checklist will help you make informed decisions when selecting the best CNC fixtures for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before beginning your search, clearly define the technical requirements for your CNC fixtures. Consider factors such as the type of machining operation (milling, turning, drilling), the material being processed, and the dimensions of the workpieces. This clarity will help you communicate your needs effectively to potential suppliers.
- Identify specific fixture types: Know whether you need milling fixtures, turning fixtures, or specialized types like angle fixtures.
- Consider material compatibility: Ensure the fixture material can withstand the machining process and environment.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in CNC fixtures. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry and experience relevant to your specific needs.
- Utilize online platforms: Leverage B2B marketplaces and industry directories to find suppliers.
- Seek recommendations: Consult industry contacts or forums for referrals to reputable suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before committing to a supplier, verify their certifications and quality management systems. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate that the supplier adheres to international quality standards.
- Request documentation: Ask for copies of their certifications and quality assurance processes.
- Assess their manufacturing capabilities: Ensure they have the equipment and technology to produce high-quality fixtures.
Step 4: Request Samples or Prototypes
To assess the quality and suitability of the CNC fixtures, request samples or prototypes from shortlisted suppliers. This step is essential to evaluate the fixture’s design, materials, and overall performance.
- Test for precision and durability: Use the samples in your machining processes to gauge their effectiveness.
- Ensure compatibility: Confirm that the fixture fits well with your existing CNC machinery.
Step 5: Analyze Pricing and Terms of Service
Once you have identified potential suppliers and evaluated their offerings, compare pricing structures and terms of service. This analysis will help you identify the best value without compromising quality.
- Look beyond the price: Consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement parts.
- Negotiate terms: Discuss payment terms, lead times, and warranty options to ensure you’re protected.
Step 6: Check Customer Reviews and References
Before finalizing your decision, check customer reviews and request references from previous clients. Understanding others’ experiences can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s reliability and service quality.
- Assess feedback: Look for patterns in customer satisfaction, particularly regarding quality and support.
- Contact references: Ask about their experiences with the supplier and how effectively they resolved any issues.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all agreed-upon terms, including delivery schedules and quality expectations, are documented.
- Clarify responsibilities: Outline warranty terms, maintenance support, and return policies.
- Stay in communication: Maintain open lines of communication with the supplier to address any concerns that may arise post-purchase.
Following this comprehensive checklist will ensure that you make informed decisions when sourcing CNC fixtures, ultimately enhancing your machining operations’ efficiency and precision.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc fixture Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Fixture Sourcing?
When sourcing CNC fixtures, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. High-quality metals such as aluminum or steel often command higher prices but offer better durability and performance. The specific material used will depend on the fixture’s intended application and the machining processes it will support.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the overall price. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to assess the skill level and experience of the workforce, as this can affect the quality of the final product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, equipment, and utilities. Higher overhead costs can lead to increased pricing, particularly in regions with stringent regulations or higher operational costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant expense, especially for specialized fixtures. The investment in tooling is often amortized over the production run, making it crucial to consider volume when evaluating costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that fixtures meet specific standards often requires additional QC processes. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s QC measures and certifications, as this can influence both cost and product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can be substantial, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and import duties should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically apply a markup to cover their costs and generate profit. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Impact CNC Fixture Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC fixtures, which international buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant savings. Suppliers often offer discounts for higher minimum order quantities (MOQs), so it’s advantageous to consolidate orders when possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom fixtures tailored to specific applications may incur higher costs due to the need for specialized design and manufacturing processes. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (like ISO or AS9100) can increase costs. However, they may also enhance the fixture’s reliability and lifespan, impacting the total cost of ownership positively.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can affect pricing. It’s advisable to evaluate multiple suppliers and understand their pricing models and service offerings.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) will determine who bears the risk and costs during shipping. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating CNC Fixture Prices?
Negotiating effectively can lead to cost efficiencies in sourcing CNC fixtures. Here are several tips for international buyers:
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the market rates for CNC fixtures can empower buyers during negotiations. Compare quotes from multiple suppliers to establish a baseline.
-
Explore Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and potential downtime. A higher upfront investment might result in lower TCO.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Regular communication and feedback can foster collaboration and trust.
-
Be Clear About Requirements: Clearly define specifications and expectations to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to additional costs. Transparency can streamline the process and reduce revisions.
-
Consider Payment Terms: Negotiating favorable payment terms can improve cash flow and reduce financial strain. Options such as extended payment periods or installment payments can be beneficial.
Conclusion
Sourcing CNC fixtures involves a complex interplay of cost components and pricing influencers. By understanding these elements and employing strategic negotiation techniques, international B2B buyers can optimize their purchasing decisions. Always approach sourcing with a clear understanding of the total cost of ownership and be prepared to adapt to the nuances of different markets. Prices can vary widely based on numerous factors, so it’s advisable to conduct thorough research and maintain flexibility in negotiations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc fixture With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CNC Fixtures: A Comparative Analysis
In the landscape of CNC machining, the choice of workholding solutions is critical for optimizing production efficiency and precision. While CNC fixtures are a popular option, several alternative methods can also achieve similar outcomes. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Fixture | Vacuum Workholding | Manual Clamping Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and stability; minimizes human error. | Excellent for flat and non-porous materials; allows for multiple parts. | Varies widely; depends on operator skill and tool quality. |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment; durable and reusable. | Generally high setup costs but can reduce labor costs. | Low initial cost; requires ongoing labor and potential for errors. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires design and customization; potentially complex setup. | Easy to use with pre-designed setups; limited to specific applications. | Simple to implement; labor-intensive and time-consuming. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional recalibration required. | Requires regular checks for vacuum integrity; can be complex. | Minimal maintenance; frequent adjustments needed. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for complex and precise machining tasks in various industries. | Best for high-volume production of flat parts, like sheet metal. | Suitable for small-scale operations or one-off projects. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Vacuum Workholding?
Vacuum workholding is an innovative solution that employs suction to hold parts securely in place during machining. This method excels in scenarios where flat or non-porous materials are involved. The advantages include the ability to hold multiple parts simultaneously and reduced setup times. However, its effectiveness diminishes with complex geometries or porous materials, which can complicate the setup and limit versatility. Furthermore, while initial costs can be high, the labor savings in high-volume applications often justify the investment.
How Do Manual Clamping Systems Compare?
Manual clamping systems, such as traditional vises and clamps, offer a cost-effective alternative with low initial investment. These systems are simple to use and can be adapted for various tasks. However, they rely heavily on operator skill, which can introduce variability in performance and precision. Additionally, while they are suitable for smaller operations or one-off projects, they may not meet the efficiency requirements of larger-scale manufacturing. Frequent adjustments and manual oversight can lead to increased labor costs over time.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs?
When selecting a workholding solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific machining needs, production volume, and budget constraints. CNC fixtures are well-suited for projects requiring high precision and repeatability, making them ideal for complex operations across various industries. Conversely, vacuum workholding may be advantageous for high-volume, flat part production, while manual clamping systems can serve smaller operations effectively. By assessing the unique requirements of their projects, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and enhance their overall production efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc fixture
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Fixtures That B2B Buyers Should Know?
When selecting CNC fixtures, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and compatibility with machining processes. Here are several essential specifications:
Material Grade
The material grade of a CNC fixture significantly influences its durability and performance. Common materials include aluminum, steel, and high-grade plastics. Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for applications requiring mobility. Steel, particularly tool steel, offers superior strength and wear resistance, suitable for heavy-duty machining. Understanding material grade helps buyers choose fixtures that will withstand the specific conditions of their production environment.
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the machining process. Tight tolerances are critical in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precision is paramount. Fixtures designed with high tolerance levels ensure that workpieces are held securely, minimizing the risk of errors during machining. For B2B buyers, specifying the required tolerance can directly impact product quality and production efficiency.
Clamping Force
Clamping force is the strength with which a fixture holds a workpiece in place. This is vital for maintaining accuracy and preventing movement during machining. Different applications may require varying clamping forces; for example, softer materials may need less force to avoid deformation. Buyers should consider the clamping force specifications to ensure the fixture can handle the demands of their specific machining tasks.
Repeatability
Repeatability measures a fixture’s ability to position a workpiece consistently across multiple setups. High repeatability is essential for batch production, where the same part must be produced repeatedly with minimal variation. This property is particularly important for industries focused on high-volume manufacturing, as it directly affects production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Size and Configuration
The size and configuration of a CNC fixture must align with the dimensions and shape of the workpieces being machined. Custom fixtures may be required for unique part geometries. Buyers should assess their workpiece specifications to determine the necessary fixture size and design, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance during machining operations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to CNC Fixtures That Buyers Should Understand?
In the world of CNC machining, certain jargon and trade terms are commonly used. Familiarity with these terms can aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CNC fixtures, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for high-quality fixtures that meet their specific machining needs.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it can influence inventory management and initial capital investment. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their procurement strategies effectively.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. It is an essential tool for buyers when seeking competitive pricing for CNC fixtures. Providing detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate and favorable quotes.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers navigate logistics, including shipping costs and risk management, when sourcing CNC fixtures from global suppliers.
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. For CNC fixtures, shorter lead times can significantly impact production schedules. Buyers should inquire about lead times when sourcing fixtures to ensure alignment with their project timelines.
Customization
Customization refers to the ability to tailor a fixture to specific requirements, including size, material, and design features. Understanding the extent of customization options available can help buyers select fixtures that best suit their unique machining needs and enhance operational efficiency.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their machining capabilities and overall production efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc fixture Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing the CNC Fixture Sector?
The global CNC fixture market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for precision engineering across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. As manufacturers strive to improve efficiency and reduce production costs, the adoption of CNC machining technologies has surged. Key trends impacting this market include the rise of automation and Industry 4.0, which facilitate higher productivity levels and lower operational costs. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can offer advanced CNC fixtures that enhance machining accuracy and reduce setup times.
Emerging technologies, such as additive manufacturing and digital twin simulations, are reshaping how CNC fixtures are designed and utilized. These innovations allow for the creation of custom fixtures that are tailored to specific machining processes, enabling manufacturers to optimize their workflows. Furthermore, the shift towards lean manufacturing practices is leading to a greater focus on the integration of fixtures with other production tools, such as robotics and smart sensors, enhancing overall system efficiency.
For international B2B buyers, understanding these market dynamics is crucial. There is a growing emphasis on sourcing from suppliers who can provide not only high-quality products but also comprehensive support services, including design assistance and after-sales support. As global supply chains evolve, establishing partnerships with reliable manufacturers who prioritize innovation and quality will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of CNC Fixtures?
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has become a critical concern for B2B buyers in the CNC fixture sector. As sustainability continues to gain traction globally, businesses are increasingly pressured to adopt ethical sourcing practices. This shift is particularly evident among international buyers in emerging markets, where regulatory frameworks are evolving to promote sustainability.
Companies are now seeking CNC fixture suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly materials and sustainable production methods. Utilizing recyclable materials, such as aluminum or biodegradable composites, can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of CNC fixtures. Furthermore, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can provide assurance to buyers regarding a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Ethical supply chains are also becoming a focal point for businesses, as consumers and stakeholders demand greater transparency. Suppliers who can demonstrate ethical sourcing practices, such as fair labor conditions and responsible resource management, are more likely to gain the trust of international buyers. By aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals, businesses can not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute positively to the global environmental landscape.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Fixtures in Manufacturing?
The evolution of CNC fixtures is closely tied to advancements in manufacturing technology. Initially, traditional workholding solutions were primarily mechanical, relying on manual adjustments and limited precision. As CNC machining emerged in the late 20th century, the need for more sophisticated fixtures became apparent.
The introduction of computer-controlled systems allowed for greater accuracy and repeatability in machining processes. Consequently, CNC fixtures were developed to accommodate these advancements, incorporating features that enhance stability, positioning, and clamping. Over the years, the design and materials used in CNC fixtures have evolved significantly, with an increasing focus on customization and efficiency. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of selecting fixtures that are not only compatible with modern CNC machines but also tailored to specific production needs.
In summary, understanding the market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical evolution of CNC fixtures equips international B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc fixture
-
How do I choose the right CNC fixture for my machining needs?
Choosing the right CNC fixture depends on several factors, including the type of machining operation (milling, turning, drilling, etc.), the material being processed, and the specific geometry of the workpiece. Consider the required precision, clamping force, and accessibility for tool changes. Collaborate with your supplier to assess your production volume and part complexity, as they can recommend fixtures that balance efficiency and cost-effectiveness. It’s often beneficial to prototype different fixtures to determine which design best meets your operational requirements. -
What types of CNC fixtures are available for various machining processes?
CNC fixtures can be categorized based on the machining process they support. Common types include milling fixtures, turning fixtures, drilling fixtures, grinding fixtures, and boring fixtures. Each type has unique designs tailored for specific operations, such as rotary table fixtures for milling or collet fixtures for turning. Understanding these categories will help you select a fixture that aligns with your machining objectives and enhances production efficiency. -
What should I consider when customizing CNC fixtures for my operations?
When customizing CNC fixtures, evaluate factors such as part geometry, material compatibility, and production volume. Discuss your specific requirements with your supplier to ensure the fixture design accommodates your machining processes effectively. Consider modular designs that allow for flexibility in production, as well as ease of setup and changeover. Finally, ensure that your custom fixture design adheres to quality standards and undergoes thorough testing before full-scale implementation. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC fixtures?
Minimum order quantities for CNC fixtures can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the fixture design. Typically, suppliers may set MOQs ranging from 5 to 50 units for standard fixtures, while custom designs could have higher MOQs due to setup costs. It’s advisable to negotiate with suppliers, especially if you’re a smaller company or if you’re looking to establish a long-term relationship. Some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs for first-time orders or prototypes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for CNC fixtures sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance for CNC fixtures, start by conducting thorough research on potential suppliers, focusing on their certifications and quality control processes. Request samples or prototypes to assess the workmanship and precision of the fixtures. Establish clear quality standards and inspection criteria before placing an order. Regular communication with your supplier during production can help address any potential issues early, ensuring that the final products meet your specifications. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing CNC fixtures from international suppliers?
Payment terms for CNC fixtures can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include upfront payments, partial payments with balance upon delivery, or payment after inspection. It’s essential to negotiate terms that protect your interests while also accommodating the supplier’s requirements. Consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services for larger orders to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How can I effectively vet suppliers for CNC fixtures in international markets?
Vetting suppliers for CNC fixtures involves several steps. Start by checking their industry reputation through reviews and testimonials from other clients. Request references and case studies that demonstrate their capability in producing fixtures similar to your needs. Verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible or arranging virtual audits to assess their manufacturing processes and capabilities firsthand. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC fixtures?
When importing CNC fixtures, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable logistics partner with experience in handling industrial equipment to navigate potential challenges. Be aware of import duties and taxes that may apply, as these can affect overall costs. It’s also wise to plan for contingencies, such as delays in shipping or customs clearance, by maintaining open communication with your supplier and logistics provider throughout the process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Cnc Fixture Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AT Machining – CNC Fixtures
Domain: at-machining.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: CNC fixtures are essential tools in CNC machining that provide stability and positioning for workpieces. They ensure coherence and interchangeability in machining processes, reducing human effort. CNC fixtures are classified based on machining operations and uses. Types include: 1. Milling Fixtures: Used in CNC milling with rotary table fixtures, vise fixtures, fixture plates, T-slot, and indexing…
2. Saunders Machine Works – Fixture Plates
Domain: saundersmachineworks.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: SMW Fixture Plates from Saunders Machine Works include a variety of options for different CNC machines such as Brother, Doosan, Fadal, FANUC, Haas, Hurco, Okuma, SYIL, SMART, Tormach, TRAK/Bridgeport/Jet, and more. The collection features custom plates, RFQ options, and various accessories including fixture plate plugs, accessory kits, hardware kits, and locating pins. Additional products include …
3. Reddit – Aluminum Plate Clamping Solutions
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Thin aluminum plates (10mm or 3/8″ thick, 20cm by 20cm size); recommended clamping methods include vacuum chuck, double stick tape, sacrificial block with bolts, and toe clamps; considerations for clamping depth (4mm); potential vacuum chuck setup available for under $2000.
4. AME – Custom Workholding Fixtures
Domain: ame.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Custom Workholding Fixtures designed to solve specific machining needs. Services include: 1. Collaborative Engineering – Partnering with fixture experts from concept to completion. 2. Flexible Design Input – Custom solutions based on customer drawings or designs. 3. Proven Expertise – Deep knowledge in workholding to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. 4. Quality & Precision – Fixtures built to e…
5. WDS Components – CNC Fixtures
Domain: wdscomponents.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: CNC Fixtures include various products such as CNC Cubes, CNC Double Siders, Tombstones, CNC Fixture Plates, and Baseplates. Key products listed are: 1. SKU WDS 7060 – Stock cast iron double siders (light duty) – Starting at $2,205.18 2. SKU WDS 7002 – Wharton rectangular base cast iron plate – Starting at $568.48 3. SKU WDS 7081 – Steel fixture plates – Starting at $539.67 4. SKU WDS 7070 – Cast i…
6. CNC Cookbook – Workholding Solutions
Domain: cnccookbook.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: The text discusses various workholding solutions for CNC milling, including jigs and fixtures. Key components include: 1. **Workholding Devices**: Tools like milling vises that secure workpieces during machining. 2. **Jigs vs. Fixtures**: Jigs guide the cutter, while fixtures hold the workpiece. 3. **T-Slots**: Common method for positioning workholding solutions, but can lead to inefficiencies. 4….
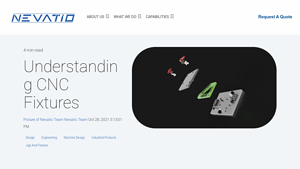
7. Nevatio – CNC Fixtures
Domain: nevatio.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: CNC fixtures are devices designed to hold CNC machined workpieces during cutting operations on CNC machines such as mills, lathes, laser cutters, and router machines. They ensure dimensional accuracy by holding parts rigidly in place and are typically made from materials like aluminum castings to prevent distortion. CNC fixtures can accommodate various materials including metal, plastic, and wood….
8. Practical Machinist – Custom Machining Fixture for Whistle Parts
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Custom machining fixture for whistle parts used in herding dogs. Accommodates two designs with rough dimensions of 1.75 X 1.25 X 0.25 inches. Designed for a 3-axis vertical mill requiring 3 operations. Annual usage is low, but the fixture needs to be durable and simple to set up. Tolerances are not critical but must appear visually accurate. Initial run used standard vise with Talon grip jaws and …
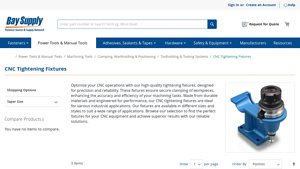
9. Bay Supply – CNC Tightening Fixtures & Tooling Systems
Domain: baysupply.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: CNC Tightening Fixtures, Toolholding & Tooling Systems from Bay Supply.
10. Wayken – CNC Fixture Solutions
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: CNC Fixture Types: 1. CNC Vise Fixture: Versatile and easy to use, offers high clamping power through hydraulic/pneumatic mechanisms, features inclined surfaces for rigidity, and precision ground edges for accurate positioning. 2. Angle Fixture: Holds workpieces at specific angles, useful for chamfering, beveling, and drilling; often includes a hole grid for part placement and adjustable angles wi…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc fixture
In the realm of CNC machining, strategic sourcing of fixtures is paramount for enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and operational excellence. As we have explored, the selection of appropriate CNC fixtures—be it vises, milling fixtures, or custom solutions—directly influences production timelines and product quality. By investing in high-quality fixtures tailored to specific machining processes, businesses can achieve greater consistency and reduce waste, ultimately driving down costs.
For international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of CNC fixtures is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. The ability to source fixtures that align with unique operational requirements not only streamlines workflows but also fosters innovation in product development.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced CNC fixtures is expected to rise, driven by technological advancements and the increasing need for precision in manufacturing. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and partner with suppliers who can provide customized solutions that meet your specific needs. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your machining capabilities and position your business for future growth.