Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc drawing
In the competitive landscape of modern manufacturing, sourcing CNC drawing services can present a labyrinth of challenges for B2B buyers. Many international businesses, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—like Brazil and Nigeria—struggle to communicate their precise requirements and find reliable suppliers able to translate technical concepts into high-quality, machined parts. This guide provides a thorough examination of CNC drawing, encompassing various types, applications, and best practices, alongside essential tips for supplier vetting and cost analysis.
By demystifying the nuances of CNC drawings, this resource empowers buyers to make informed and strategic purchasing decisions. We will explore critical elements like the importance of technical drawings, the role of CAD files, and the intricacies of manufacturing processes. Furthermore, our guide emphasizes the value of clear communication and documentation to ensure that your specifications are met, reducing costly errors and enhancing production efficiency.
Ultimately, navigating the global market for CNC drawing becomes less daunting with the right knowledge and insights. This guide aims to streamline your sourcing journey, providing actionable advice and industry expertise needed to foster successful partnerships that meet your business’s unique needs in a dynamic international marketplace.
Understanding cnc drawing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2D Technical Drawing | Flat representations with dimensions, tolerances, and annotations | Machining, laser cutting, injection molding | Pros: Clear communication; industry standard. Cons: May lack depth perception for complex parts. |
| 3D CAD Models | Three-dimensional visualizations capturing detailed geometry | Rapid prototyping, high-precision manufacturing | Pros: Comprehensive detail; direct CNC machine interfacing. Cons: Requires software compatibility. |
| Isometric Drawings | Pictorial view offering a visual representation with depth | Marketing, assembly instructions, and design reviews | Pros: Easy to comprehend; aids visualization. Cons: Less precise for engineering specs. |
| Section Views | Cross-sectional illustrations to show internal structure | Product design, analysis, and quality control | Pros: Internal feature clarity; identifies material distribution. Cons: May complicate layout in dense designs. |
| Assembly Drawings | Composite illustrations indicating the assembly of multiple parts | Assembly line manufacturing, maintenance documentation | Pros: Simplifies complex assembly; guides non-engineers. Cons: Limited technical detail can mislead. |
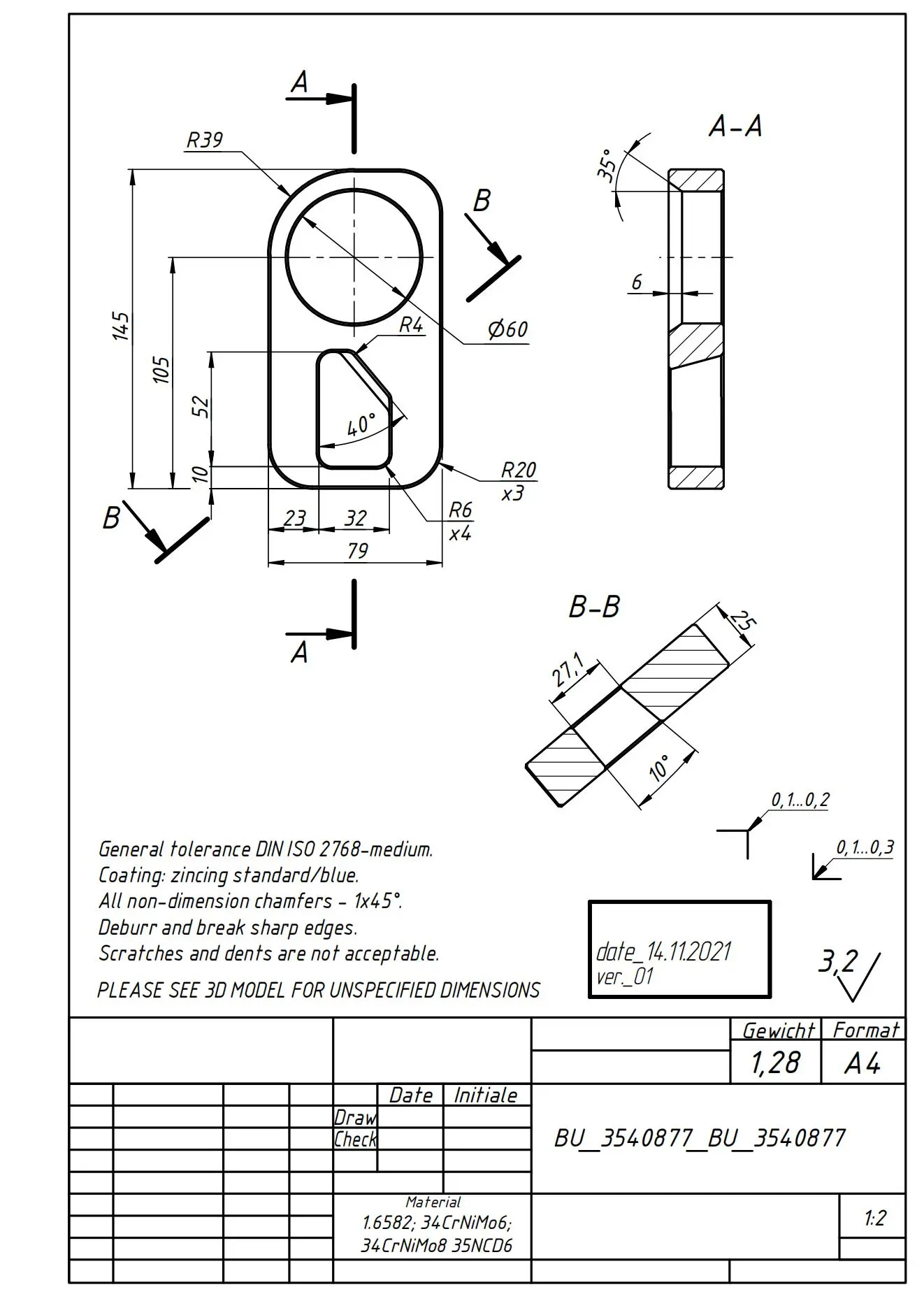
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of 2D Technical Drawings?
2D technical drawings remain a staple in CNC machining and manufacturing for their clarity and precision. Differentiated by their flat representations, these drawings include essential dimensions, tolerances, and annotations comprehensive enough to guide machinists. They are particularly suitable for traditional manufacturing techniques like laser cutting and machining. Buyers should consider that while these drawings effectively communicate technical requirements, their lack of three-dimensional depth can make complex geometries harder to visualize.
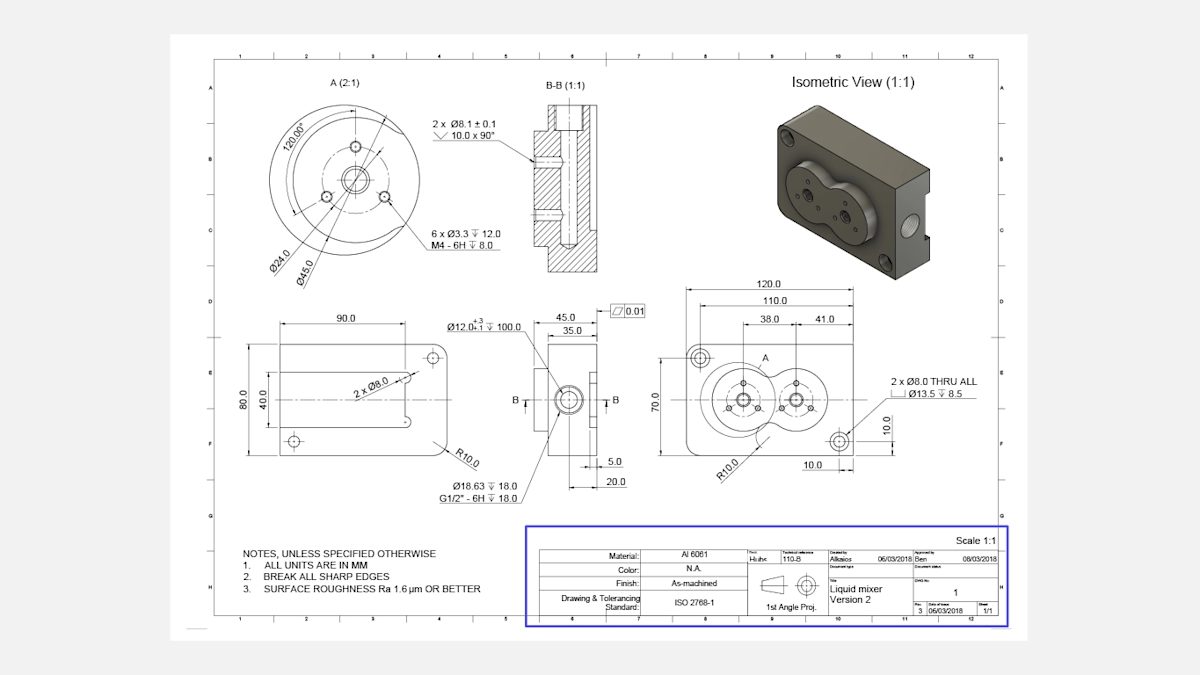
How Do 3D CAD Models Enhance CNC Machining Processes?
3D CAD models provide a sophisticated digital representation of parts, capturing intricate details that are crucial for high-precision manufacturing. The primary advantages of 3D CAD are its direct integration with CNC machines and the comprehensive nature of the data provided, facilitating processes like rapid prototyping. However, companies must ensure that their software infrastructure aligns with CAD file requirements, as compatibility can sometimes pose a barrier in B2B transactions. Overall, 3D models are ideal for industries seeking to minimize errors due to misinterpretation in technical drawings.
Why Are Isometric Drawings Beneficial in Marketing and Design Reviews?
Isometric drawings are renowned for their ability to visually represent three-dimensional objects in a two-dimensional format, providing a clear perspective with depth. This type of drawing is particularly useful in marketing and design reviews, enabling stakeholders to grasp the product’s form without technical jargon. Although they enhance understanding, these drawings lack the precision necessary for manufacturing specifications, which could lead to ambiguities if relied upon exclusively for production-oriented decisions.
What Advantages Do Section Views Offer in Product Design and Quality Control?
Section views serve as an invaluable tool in product design and quality control, revealing critical internal features that are not visible in standard drawings. By showcasing the interior structure of parts, these illustrations assist engineers in identifying material distributions and potential weaknesses. While section views enhance clarity for complex designs, their detailed nature can sometimes result in cluttered layouts, complicating the overall understanding of a product when not managed effectively in the design phase.
How Do Assembly Drawings Facilitate Effective Manufacturing Processes?
Assembly drawings play a crucial role in guiding the assembly process of complex parts by illustrating how various components fit together. They are particularly beneficial for production lines and maintenance documentation, streamlining communication across teams, including those without engineering backgrounds. However, these drawings may sacrifice some technical details, leading to potential misinterpretations if the assembly instructions are not rigorously followed or if they lack precise measurements. Ultimately, assembly drawings combine simplicity with functionality, enhancing workflow efficiency in manufacturing settings.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc drawing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Drawing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Production of aircraft components | Ensures precision and reliability in critical parts | Certification standards and material specifications |
| Automotive | Creating tooling for part manufacturing | Reduces lead time and manufacturing costs | Compatibility with the latest technologies and materials |
| Electronics Manufacturing | PCB design and assembly | Enhances product reliability and reduces defects | Compliance with international safety and quality standards |
| Medical Devices | Customizing surgical instruments | Delivers high precision and meeting stringent regulations | Expertise in biocompatible materials and cleanroom standards |
| Consumer Goods | Production of packaging and branding elements | Increases marketability through customizable designs | Sustainability and waste management considerations |
How is CNC Drawing Used in Aerospace and What Problems Does it Solve?
In the aerospace sector, CNC drawing plays a vital role in producing aircraft components such as wing structures and fuselage sections. These components require extremely high precision to ensure safety and compliance with regulatory standards. CNC drawings help in clearly defining tolerances and specifications that meet rigorous safety regulations. For buyers in this sector, sourcing parts from certified manufacturers that specialize in aerospace components is critical, as is ensuring adherence to International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards.
What Is the Role of CNC Drawing in Automotive Tooling Production?
CNC drawing is extensively used in the automotive industry for creating tooling necessary for manufacturing vehicle parts. By utilizing CNC drawings, manufacturers can produce precise tools and dies that enhance productivity while reducing manufacturing time. This results in lower costs and faster time to market for new vehicle models. B2B buyers should pay attention to suppliers with advanced CNC capabilities and experience in producing complex geometries to maximize cost-effectiveness and efficiency.
How Do Electronics Manufacturers Benefit from CNC Drawing?
In electronics manufacturing, CNC drawing is essential for designing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and ensuring proper layout for component placement. The precision in CNC drawings helps to minimize defects and improve the overall reliability of electronic devices. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from suppliers who comply with international quality standards and offer robust technical support is crucial in maintaining operational efficiency and product quality.
Why Is CNC Drawing Significant in the Medical Device Industry?
CNC drawing is significant in the medical device sector, where custom surgical instruments must be manufactured to precise specifications. Effective CNC drawings help to achieve the high level of accuracy required for medical applications, thus complying with strict industry regulations. For buyers from the Middle East and Europe, it’s essential to partner with manufacturers experienced in handling biocompatible materials while ensuring that cleanroom standards are met during production to guarantee the safety and efficacy of medical products.
How Can CNC Drawing Improve Customization in Consumer Goods?
In the consumer goods sector, CNC drawing facilitates the production of custom packaging and branding elements that capture market attention. This flexibility in design allows brands to differentiate themselves in competitive environments. For businesses in developing regions, like Nigeria and Brazil, collaborating with suppliers who understand local market aesthetics while ensuring sustainability in their productions can significantly enhance product appeal and brand loyalty.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc drawing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Specifications for CNC Drawings
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter difficulties when dealing with complex specifications in CNC drawings. Specific features, such as tolerances or surface finishes, can be lost in translation between CAD files and technical drawings. Buyers may assume that a 3D CAD file alone suffices, but critical information can be omitted, leading to manufacturing errors, increased costs, and delays. This is particularly challenging for companies unfamiliar with the nuances of CNC machining and technical drawing requirements.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the intricacies of CNC drawings, B2B buyers should adopt a comprehensive approach. This includes integrating detailed documentation alongside CAD files. Specifically, prepare clear technical drawings that include key elements such as tolerances, surface finish requirements, and dimensions. Collaborate with your technical teams to annotate critical features directly on the drawings, ensuring they are highlighted for manufacturers. Using standardized drawing practices tailored to the service provider’s preferences (e.g., ISO or ASME standards) can further facilitate communication and ensure that your needs are accurately interpreted. Regularly engage with your CNC service provider to refine your documentation approach, as this can lead to enhanced accuracy in the parts produced and ultimately reduce rework and costs.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Language Barriers in International CNC Sourcing
The Problem: International sourcing of CNC machined parts frequently exposes B2B buyers to language barriers that complicate the ordering process. Misinterpretations of technical specifications or terms can lead to discrepancies in product output. This is particularly prevalent when sourcing from countries with differing manufacturing standards, which can affect everything from capturing dimensions to specifying materials, ultimately leading to frustration and potential losses.
The Solution: To counteract language barriers, B2B buyers should prioritize clear and effective communication. Start by translating technical drawings and specifications into the native language of the supplier, ensuring they comprehend critical aspects like material types and machining processes. Utilizing visualization tools, such as annotated images or videos, can bridge gaps in understanding. Engaging a local technical expert or translation service can help frame your requirements accurately, avoiding costly misunderstandings. Establishing regular communication channels, such as weekly check-ins or using collaborative platforms, encourages transparency, allowing for real-time clarifications and adjustments to the project as necessary. This proactive strategy not only mitigates risks but also fosters deeper partnerships with suppliers.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards in CNC Machining
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to ensure that their CNC machining projects comply with the specific industry standards required in their regions. Failure to meet these standards on CNC drawings can lead to regulatory issues, costly reworks, or even legal complications. With the global market being diverse in its requirements—ranging from safety standards in North America to environmental regulations in Europe—navigating this landscape can be overwhelming.
The Solution: To ensure compliance with industry standards, B2B buyers should invest in thorough research and collaboration with industry-specific experts. Start by identifying the relevant standards for your sector, such as ISO, ASTM, or ASTM standards. Incorporate these requirements into your technical drawings from the outset, highlighting compliance considerations such as material certifications and manufacturing tolerances. Establish partnerships with suppliers who are already compliant with these standards and encourage them to provide documentation that demonstrates their adherence. Additionally, consider regular audits and reviews of supplier capabilities, which can provide insights into maintaining compliance. By embedding these practices in your sourcing process, you can secure quality and compliance, reducing risks and enhancing your brand’s reputation in the market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc drawing
When selecting materials for CNC drawing, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for specific applications. This analysis examines four common materials used in CNC machining: Aluminum, Steel, Plastics (especially Acrylic), and Brass. Each material has distinct characteristics and operational benefits that can significantly impact the performance and cost-effectiveness of end products.
How Does Aluminum Perform in CNC Drawing Applications?
Aluminum is a widely popular choice due to its lightweight nature, high corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability. With a melting point around 660°C, it can withstand moderate heat without warping, making it suitable for a range of applications. However, its softness can lead to a lack of durability in high-stress situations.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum in CNC Machining
– Pros: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, easy to machine, and cost-effective for large volumes.
– Cons: Less durable under high-stress conditions compared to metals like steel, and can be prone to scratching.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, understanding local aluminum standards (such as ASTM or JIS) is essential for compliance. This ensures products meet local regulatory requirements and manufacturing practices.
What Makes Steel a Preferred Choice for CNC Drawing?
Steel offers exceptional strength, durability, and a high temperature rating, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Its ability to withstand pressure and wear makes it an ideal choice for parts requiring high tensile strength. It is often alloyed to improve corrosion resistance, essential for applications in harsh environments.
Pros and Cons of Steel in CNC Machining
– Pros: Strong, durable, and versatile for various applications; excellent shock resistance.
– Cons: Heavier and typically more expensive than aluminum; can be prone to rust if not properly treated.
Steel’s varying grades (e.g., stainless vs. carbon) may affect international sourcing options. Buyers should consider the specific alloy suited for their application’s environmental conditions, which may involve complying with DIN or ASTM standards.
Why Should Buyers Consider Plastics like Acrylic for CNC Drawing?
Acrylic is an excellent alternative to glass, offering good aesthetic properties and easy machinability. It is lightweight and has a high impact resistance, making it suitable for applications such as displays and panels. However, its thermal resistance is limited, making it unsuitable for high-temperature environments.
Pros and Cons of Acrylic in CNC Machining
– Pros: Lightweight, high clarity, and impact resistance; suitable for visual applications.
– Cons: Cannot endure high temperatures; limited durability under rigorous mechanical stress.
Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding plastic materials, especially concerning recyclability and sustainability. This can also influence the choice of plastics based on environmental regulations in the region.
How Does Brass Compare for CNC Machining Applications?
Brass is favored for components that require excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. With a melting point of around 900°C, it performs well in both electrical and aesthetic applications, such as fittings and decorative elements. Brass has a high tensile strength and good thermal stability, making it an ideal material for situations that require conductivity, like in electrical connectors.
Pros and Cons of Brass in CNC Machining
– Pros: Excellent machinability, corrosion-resistant, and a beautiful finish; well-suited for decorative applications.
– Cons: More expensive than aluminum and plastics; can be brittle under certain conditions.
For businesses operating in developing regions, sourcing brass may come with higher costs. Understanding local market dynamics and import/export regulations is critical for efficient procurement.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Drawing
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc drawing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight parts, automotive components | Corrosion-resistant and easy to machine | Less durable in high-stress applications | Medium |
| Steel | High-stress applications, structural components | Superior strength and durability | Heavier and potentially rusting without treatment | High |
| Acrylic | Displays and panels, artistic applications | Lightweight and high clarity | Limited thermal resistance and mechanical durability | Low |
| Brass | Electrical connectors, decorative components | Excellent machinability and aesthetic finish | Higher cost and possible brittleness | High |
This guide serves as a strategic framework for international B2B buyers aiming to select appropriate materials for their CNC drawing needs, ensuring compliance and efficiency in their manufacturing processes.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc drawing
To effectively navigate the intricate world of CNC drawing for manufacturing, it’s essential to understand the various stages of the manufacturing process, the quality assurance protocols followed, and how to engage effectively with suppliers. Here is an in-depth overview tailored for B2B buyers from diverse global regions including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for CNC Drawing?
The manufacturing process for CNC drawing involves several critical stages, each contributing to the final quality of the product. Here’s a breakdown of these main stages:
How Is Material Prepared During CNC Processes?
Material preparation is the cornerstone of ensuring a successful CNC drawing project. This includes:
-
Selection of Material: The type of material impacts both the design and machining processes. Common materials include metals like aluminum, steel, and plastic. Depending on the end-use and specific characteristics required (such as weight, durability, and resistance), the appropriate material must be selected beforehand.
-
Cutting to Size: Once materials have been chosen, they must be cut to manageable sizes. This can involve shearing, sawing, or laser cutting. Precision at this stage is paramount to avoid wastage and ensure that the raw material will yield the required final dimensions.
-
Surface Treatment: Prior to shaping, surfaces may require preparation such as sanding or grinding to alleviate any roughness and prepare substrates for optimal adherence during subsequent processes.
What Steps Are Involved in Forming and Machining?
The forming stage is where CNC machining truly comes to life. This involves:
-
CNC Programming: Utilizing software to create a digital representation of the part based on CAD models. The generated G-code directs the CNC machine on how to move, cut, and finish the part.
-
Machining Operations: This stage can involve various techniques, such as:
– Milling: Removing material from a solid block using rotating tools.
– Turning: Using a lathe to shape cylindrical parts.
– Drilling: Creating precise holes.
– Routing: Cutting shapes into materials or decorative designs on the surface. -
Assembly (if required): For components that are designed to be part of a larger assembly, a precise assembly process is crucial. This may involve manual assembly or further CNC processes to create fixtures and parts that fit together seamlessly.
How Is Finishing Achieved in CNC Parts?
Finishing processes are vital for enhancing the appearance and longevity of CNC machined products. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Deburring and Finishing: Removing sharp edges and burrs created during machining operations, which can affect the product’s functionality and safety.
-
Surface Treatments: Coating or anodizing to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, ensuring components can withstand environmental factors for their intended application.
-
Final Inspection: Conducting a thorough inspection of dimensions, surface finish, and functional attributes before packaging and shipping.
What Quality Assurance Protocols Are Standard in CNC Drawing?
Quality assurance is critical to maintaining standards and fulfills the reliability expectations of B2B buyers. The following aspects highlight the processes involved:
Which International Standards Apply to CNC Manufacturing?
Adhering to recognized international standards can enhance credibility and quality assurance in CNC machining. The prominent standards include:
- ISO 9001: This covers the requirements for quality management systems, promoting consistent products and services that meet customer expectations.
- ISO 2768: General tolerances for linear dimensions and angular dimensions, which guide manufacturers in maintaining accuracy and reducing risk of defect.
- CE Marking: Ensures that products meet European Union safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Checkpoints in the Quality Control Process?
Quality control in CNC manufacturing typically consists of several checkpoints to ensure part integrity:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon delivery to ensure they meet predetermined specifications before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous inspections conducted throughout the manufacturing process. This is done through measuring tools and visual checks at various phases, helping to catch errors early and avoid costs related to reworking.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Final inspections to verify that finished products meet design specifications, tolerances, and customer requirements before shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to quality standards, B2B buyers can take multiple steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help verify that manufacturers are compliant with quality management systems and industry standards. These can be performed in-house or by third-party agencies.
-
Reviewing Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting reports that outline past inspections can provide insight into the supplier’s quality history, identifying consistency and areas of concern.
-
Third-Party Inspection Services: Engaging third-party inspectors who specialize in quality verification can add an extra layer of assurance, especially for international buyers who may be unfamiliar with local manufacturing practices.
What QC/CERT Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International B2B buyers should be mindful of specific quality control nuances:
-
Cultural Differences: Be aware that production controls may vary by country, and buyers should familiarize themselves with regional standards and practices. For example, countries in Europe may have stricter adherence to standards like ISO and CE than some regions in Africa or South America.
-
Communication: Clear communication is essential when it comes to specifying quality requirements and expectations. Engaging in initial discussions and continuous dialogue fosters a relatable partnership.
-
Documentation and Compliance: Understanding necessary documentation is crucial. Buyers should confirm that suppliers can provide relevant certifications and compliance documents that align with international standards.
By following these detailed guidelines on manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can strategically enhance their sourcing initiatives for CNC drawings, ensuring not only cost-effectiveness but also superior quality and reliability in their supply chains.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc drawing’
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of modern manufacturing, sourcing high-quality CNC drawings is critical for ensuring efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness in production. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers actively engaged in procuring CNC drawings. By following the outlined steps in this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process, establish effective communication with suppliers, and ultimately, achieve the best results for your projects.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of a successful CNC drawing procurement process. This includes determining the dimensions, tolerances, materials, and surface finishes required for your project. Consider specifying features that may not be evident in a CAD file, such as internal threading or specific finishing requirements.
Step 2: Gather Necessary Documentation
While CAD files play a crucial role in CNC machining, supplementary documents like technical drawings provide essential details that CAD files may overlook. Create comprehensive technical drawings to facilitate better communication of your requirements to suppliers. Include the title block with material specifications, finishing requirements, and any additional notes that may assist the manufacturer.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a procurement decision, vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, references, and case studies from previous clients, especially those in your industry or region. Assess their ability to interpret technical drawings and CAD files efficiently; this ensures that your plans are understood clearly, thus reducing the risk of errors.
Step 4: Assess Manufacturing Capabilities
Not all CNC service providers have the same capabilities. Investigate whether the suppliers can handle the complexity of your designs. Consider factors such as the types of CNC machines they operate, their experience with similar projects, and the range of materials they can process. This is particularly important to ensure that they can meet your specific standards and requirements without compromising quality.
Step 5: Request and Review Quotes
Once you have chosen potential suppliers, request detailed quotations based on your specifications and provided technical documents. Ensure that quotes include breakdowns of costs, lead times, and any additional fees. Review the quotations carefully to compare value rather than just price; sometimes, a higher initial cost may lead to better long-term benefits in terms of quality and service.
Step 6: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Confirm that your chosen supplier complies with necessary industry standards and regulations. This may include obtaining certifications for quality management systems, such as ISO 9001. Compliance with these standards not only assures you of the quality but also shows that the supplier values safety and reliability in the manufacturing process.
Step 7: Establish Communication Protocols
Set up clear communication channels with your suppliers before and during the procurement process. Specify how updates, revisions, and any issues will be communicated. Establishing a relationship based on clear communication can help alleviate potential misunderstandings and ensure that your projects progress smoothly.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for CNC drawings more effectively, ensuring they select the right suppliers and obtain the best possible results for their manufacturing projects.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc drawing Sourcing
In order to effectively analyze the cost structure and pricing associated with sourcing CNC drawings, it is important to break down the various cost components and price influencers at play. Understanding these aspects will empower international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Drawing Sourcing?
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the cost of CNC drawings. Common materials include metals, plastics, and composites, each with its own price point. Materials that require specific certifications or specialized processing, such as aerospace-grade aluminum, will generally incur higher costs.
-
Labor Costs: Skilled labor is essential in creating detailed CNC drawings. With tasks ranging from designing to programming machines, labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location and the expertise of the workforce. For instance, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs may be attractive but could risk quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses fixed and variable expenses related to the production environment. It includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Understanding overhead is crucial as it is typically factored into the pricing structure provided by suppliers.
-
Tooling Costs: Tooling refers to the equipment and machinery involved in the CNC process. The depreciation of these assets, along with the costs for new tools necessary for unique specifications, significantly affects overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality control measures ensures the finished product meets specified tolerances and standards. While this may increase upfront costs, it ultimately leads to better reliability and lower scrap rates, contributing to overall efficiency.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling are critical components for international buyers. Costs can vary greatly based on distance, shipment method, and Incoterms. Tariffs and taxes also need to be considered, especially when importing materials or finished products.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a margin to cover operational costs and generate profit. This margin can vary significantly based on supplier reputation, service quality, and market competition.
What Factors Influence CNC Drawing Prices?
Several factors can influence prices beyond basic cost components:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to reduced unit costs. Buyers should negotiate for lower prices by increasing minimum order quantities (MOQ).
-
Specifications & Customization: Customized CNC parts with specific tolerances or features can significantly affect pricing. It is advisable for buyers to balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Quality & Certifications: Suppliers offering certified parts may charge a premium. Current market trends indicate that high-quality materials with necessary certifications attract buyers willing to invest more for assurance.
-
Supplier Factors: The choice of supplier plays a critical role in price negotiations. Assess suppliers based on their reputation, experience, and past performance rather than solely on cost.
-
Incoterms: The terms of delivery affect overall cost. Understanding the nuances of various Incoterms can help buyers control risks and expenses by deciding who bears shipping responsibilities and costs.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency?
-
Negotiate Thoughtfully: Establish clear objectives and leverage volume to negotiate favorable pricing structures. Building relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms over time.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on upfront costs, considering TCO that includes maintenance, operational expenses, and warranty costs will provide deeper insights into pricing effectiveness.
-
Be Aware of Nuances for International Purchases: When sourcing from different regions, such as Africa, South America, or the Middle East, variations in tariffs, import duties, and regulations may affect pricing. Understanding these nuances can improve overall cost management.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Always ask for itemized quotes from suppliers to ensure transparency in pricing and to facilitate better comparisons between potential vendors.
In conclusion, thorough comprehension of the cost structure and pricing influences surrounding CNC drawing sourcing can facilitate smarter purchasing decisions in an international market. Buyers should leverage relationships, remain vigilant about quality, and understand the dynamics of pricing to achieve effective cost control.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc drawing With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CNC Drawing: Practical Comparisons for B2B Buyers
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, companies often seek various solutions to achieve precision and efficiency in their production processes. While CNC drawing offers a reliable method for generating technical drawings that guide machining operations, alternative approaches may also fit certain business requirements. Below, we compare CNC drawing against two viable alternatives: Manual Drawing and 3D CAD Modeling.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Cnc Drawing | Manual Drawing | 3D CAD Modeling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision & accuracy | Variable, depends on skill level | Very high, allows for complex geometry |
| Cost | Moderate operational costs | Low initial cost, but longer turnaround | Higher upfront software costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires technical knowledge | Simple tools, but can be time-consuming | Requires training, software setup |
| Maintenance | Low, primarily software updates | Regular skills refresh needed | Software updates and hardware maintenance needed |
| Best Use Case | Mass production of precise parts | Prototyping & small-scale work | Complex designs and rapid iterations |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Manual Drawing: Is It Still Relevant?
Manual drawing, although an outdated method, remains appealing for certain applications, especially among small businesses or startups that operate with limited resources. Pros include very low setup costs and minimal equipment requirements. However, manual drawings can vary greatly in precision based on the drafter’s skills, which may lead to inconsistencies. While useful for initial product concepting or artisanal projects, manual drawing is less effective for precision-dependent industrial applications.
3D CAD Modeling: The Modern Approach
3D CAD modeling has revolutionized how designs are created and interpreted in manufacturing. This method enables an extensive range of designs, including complex shapes that would be difficult to describe with traditional 2D drawings. CAD models can easily integrate with CNC machines, translating designs into precise machining instructions. However, the upfront costs for software and training can be significant, alongside the need for ongoing technical expertise. This option is most suitable for companies looking to innovate with complex products and who have the resources to invest in advanced software.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between CNC drawing and its alternatives, businesses should assess their specific manufacturing needs, costs, and the complexity of their projects. CNC drawing stands out for precision and efficiency in large-scale production, while manual drawing may suffice for smaller projects where cost is a primary concern. Meanwhile, 3D CAD modeling provides flexibility for intricate designs but requires a higher investment and expertise. Ultimately, the right solution will align with your operational goals, budgetary constraints, and the complexity of the products you aim to produce.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc drawing
What are the Critical Technical Properties for CNC Drawing?
When engaging in CNC drawing for manufacturing, understanding key technical specifications is vital for businesses to ensure quality, precision, and compatibility. Here are several critical properties that should be noted:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of material chosen for the CNC machined part (e.g., aluminum, steel, plastic). Each material has unique properties—including strength, thermal resistance, and weight—that can significantly affect the performance of the final product. B2B buyers must specify the appropriate material grade to ensure that the components meet their operational requirements.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible variation in dimensions and physical properties of the manufactured parts. In CNC drawing, tighter tolerances offer higher precision, which is crucial for components that are part of complex assemblies where fit and finish directly impact functionality. Buyers should specify tolerances clearly to avoid reworks or product failures, ensuring that machinery operates seamlessly.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture of the part’s exterior, which can be specified in terms of roughness grade (Ra). Different applications may necessitate varying levels of surface finish, such as a smooth surface for aesthetic purposes or a textured one for better grip. Communicating the required surface finish helps manufacturers align their processes with the buyer’s expectations, affecting both visual quality and functionality.
4. Dimensions and Geometrical Features
The precise dimensions and geometric features, such as holes, slots, or complex contours, are vital elements in CNC drawings. The ability to convey these specifications accurately is essential for ensuring that the final part fits within the intended assembly and functions correctly. Detailed dimensioning on drawings aids in reducing production errors, increasing efficiency, and ensuring component interoperability.
5. Fabrication Processes
Understanding the various fabrication processes applicable to CNC machining—such as milling, turning, and drilling—is critical. These processes dictate the method used to produce the parts and directly influence factors like cost, material waste, and lead time. Buyers should provide context around the intended application to ensure the selected process aligns with their production standards and budget.
Which Common Trade Terms are Important in CNC Drawing?
Navigating the complexities of CNC drawing requires familiarity with industry-specific terminology. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another firm. When sourcing for CNC machined parts, understanding whether the supplier is an OEM can clarify the origins of the components and the potential for customization or proprietary designs in the final product.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to produce or sell in a single order. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budget planning and production schedules, allowing businesses to align their purchasing needs with their operational capacity and financial resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers based on specific parameters outlined in the CNC drawing. Understanding how to formulate a clear and comprehensive RFQ can significantly streamline sourcing processes and ensure better pricing and service conditions from manufacturers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that describe the responsibilities of buyers and sellers during the shipment of goods. Knowledge of these terms helps clarify shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs, which is vital in minimizing misunderstandings and ensuring smooth logistics.
5. CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
CAD is technology used for creating detailed drawings and models of parts in 3D. A solid grasp of CAD principles can benefit B2B buyers by enabling them to better communicate specifications with suppliers and appreciate the capabilities and limitations of CNC machining.
Familiarity with these technical properties and trade terms will enhance decision-making and increase the efficiency of sourcing CNC machined components, ultimately supporting successful project outcomes in the global manufacturing landscape.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc drawing Sector
What Are the Global Drivers for Growth in the CNC Drawing Sector?
The CNC drawing sector is experiencing a significant transformation driven by several global dynamics. First, increasing demand for precision-engineered products across industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods is pushing manufacturers to adopt advanced CNC drawing and machining technologies. This trend is particularly pronounced in emerging markets in Africa and South America, where local demands for quality and innovation are surging. Additionally, the growing integration of Industry 4.0—characterized by IoT, AI, and automation—plays a vital role in enhancing operational efficiencies, leading to better productivity and reduced costs for international B2B buyers.
B2B sourcing trends are increasingly favoring platforms that offer real-time data analytics and instant quoting systems, such as CAD file submissions for CNC machining. This empowers buyers to streamline procurement processes and make informed decisions quickly, catering to the fast-paced market demands. Furthermore, the accessibility of low-cost CNC technologies, including 3D printing and DIY CNC machines, is democratizing the sector, enabling small enterprises and startups to participate actively in the market.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting CNC Drawing Practices?
As sustainability becomes a key concern in global manufacturing, the CNC drawing sector is not lagging. The environmental impact of machining practices—through waste generation, energy consumption, and resource utilization—has prompted organizations to prioritize ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. This includes using recycled materials, optimizing manufacturing processes to reduce waste, and implementing energy-efficient technologies.
Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers with ‘green’ certifications such as ISO 14001, indicating adherence to environmental management standards. The emphasis on ethical supply chains is also gaining traction, especially among B2B organizations that operate in markets such as the Middle East and Africa, where regulatory scrutiny is on the rise. By aligning with sustainable suppliers, businesses not only mitigate their environmental impact but also enhance their brand reputation among increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
In this context, sourcing from suppliers who utilize eco-friendly materials and processes is becoming crucial. This not only satisfies regulatory requirements but can also lead to cost savings over time as processes become more efficient and waste reductions are realized.
How Has CNC Drawing Evolved to Better Serve International B2B Buyers?
The evolution of CNC drawing technologies can be traced back to the early days of computer-aided design (CAD) systems. Initially, technical drawings were labor-intensive, requiring skilled workers to interpret manual blueprints. With advancements in CAD technology, particularly the emergence of 3D modeling, the CNC machining landscape has evolved to allow for much greater precision and efficiency.
The introduction of CNC machines in the late 20th century represented a significant leap forward, automating the manufacturing process and reducing reliance on manual labor. Over time, these advancements have further integrated software capabilities that allow for direct interpretation of CAD files, streamlining the entire workflow from design to production.
For B2B buyers today, this translates to faster turnaround times on orders, lower production costs, and enhanced accuracy in the final products. Furthermore, the integration of AI and real-time data analysis promises to continue enhancing the precision of CNC drawing and machining processes, making it an exciting time for international B2B stakeholders to engage with the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc drawing
-
1. How do I ensure the quality of CNC drawings from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of CNC drawings from suppliers, it’s crucial to establish clear communication and expectations upfront. Request samples of their previous work and certifications to assess their capabilities. Implement a standardized Quality Assurance (QA) process, including a thorough review of the drawings against your specifications. Using tools like digital checklists can help maintain consistency. Lastly, consider conducting audits or site visits to verify the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. -
2. What is the best format for submitting CNC drawings to suppliers?
The best format for submitting CNC drawings to suppliers typically includes both a 3D CAD file and accompanying 2D technical drawings. While CAD files provide comprehensive geometric information, 2D drawings clearly communicate critical dimensions, tolerances, and internal details. Formats such as STEP (.step), IGES (.iges), or STL (.stl) for 3D models, alongside PDFs or DXF files for 2D drawings, are widely accepted. Providing both formats enhances clarity and ensures the supplier can accurately interpret your requirements. -
3. What are typical payment terms for CNC drawing projects?
Typical payment terms for CNC drawing projects can vary significantly among suppliers. A common structure includes a deposit of 30-50% upon order confirmation, with the remainder due upon delivery or before shipment. For larger contracts or ongoing partnerships, net terms (e.g., Net 30 or Net 60) might be negotiable. Ensure that the payment terms are clearly defined in the contract, and consider using secure payment methods, especially for international transactions, to protect against fraud or disputes. -
4. How can I assess the reliability of a CNC drawing supplier?
To assess the reliability of a CNC drawing supplier, start by checking their industry reputation through online reviews, testimonials, and case studies. Request references from previous clients, especially those in your industry, to gauge their experience. Evaluate their adherence to timelines and quality standards in prior projects, and review their certifications and adherence to international standards. Engaging in a trial project can also provide insights into their reliability before committing to larger orders. -
5. What should I consider regarding customization in CNC drawings?
When considering customization in CNC drawings, clearly define your specific requirements, such as dimensions, materials, finishings, and any unique design features. Ensure that your chosen supplier has the capacity and experience to meet your customization needs. Request a sample or prototype to evaluate their ability to deliver on your specifications. Additionally, be aware of potential lead times and how customization might impact cost, as highly tailored projects may require more significant resources. -
6. What are the implications of Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) in CNC drawing sourcing?
Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) in CNC drawing sourcing can impact your procurement strategy significantly. Suppliers often set MOQs to ensure production efficiency and profitability. It’s crucial to evaluate whether the MOQ aligns with your project needs and budget. If your requirements do not meet the MOQ, consider negotiating terms, collaborating with other companies for shared orders, or seeking suppliers with more flexible policies. Understanding MOQ implications helps in maintaining cost-effectiveness while ensuring product availability. -
7. How do I handle logistics and shipping for CNC drawing projects?
Handling logistics and shipping for CNC drawing projects involves planning and coordination from order placement to delivery. Discuss shipping options with your supplier to determine the most economical and timely method based on your location and urgency. Factor in customs regulations and import duties that may apply to international shipping, particularly in regions like Africa and South America. Using reliable courier services can ensure timely and safe delivery of your CNC parts, while tracking options provide real-time updates. -
8. What role do international trade regulations play in sourcing CNC drawings?
International trade regulations play a crucial role in sourcing CNC drawings, as they dictate the legal and compliance frameworks for cross-border transactions. Factors such as tariffs, import/export restrictions, and local regulations can significantly affect cost and feasibility. Before engaging a supplier, familiarize yourself with the regulations governing your industry in both your country and your supplier’s. Leveraging trade agreements between regions, such as those within Europe or between Africa and South America, can facilitate smoother transactions and favorable terms.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Cnc Drawing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – 3D Printed Pen Holder for CNC Projects
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 3D printed pen holder for CNC, poster-sized drawing, SVG format compatibility with Fusion360, importing and cleanup in Adobe Illustrator, usage of Inkscape with axidraw plugin for fills, examples of projects include large signs and educational posters.
2. Protolabs – Custom CNC Machining Services
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: The Protolabs Network offers a custom manufacturing service focused on CNC machining, which includes CNC milling and CNC turning. It supports various materials, including metals (e.g., Alloy steel, Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless steel, Titanium) and plastics (e.g., ABS, Nylon, Polycarbonate, POM). The service provides on-demand prototypes and production parts, which can be sourced quickly by u…
3. Instructables – Easy 3D Printed Arduino CNC Drawing Machine
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Easy 3D Printed Arduino CNC Drawing Machine; Cost of components: approximately £75; Designed for drawing on various surfaces; Uses open source software; Steps include assembly, configuration of GRBL on Arduino Uno, creating GCODE from Inkscape, and controlling through Google Chrome; Capable of creating detailed drawings for t-shirts, cake decorations, scale drawings, wedding invitations, etc.; Key…
4. DIY Machines – Arduino CNC Drawing Machine
Domain: diymachines.co.uk
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Arduino CNC Drawing Machine designed for creating detailed drawings on various surfaces. Key components include: 2 x 8x15x45mm Linear Bearings, 1 x 8x15x25mm Linear Bearing, 2 x 12v Nema 17 Stepper Motors, GT2 Timing Belt and Pulleys, 1 x Micro Servo, 1 x Elegoo Arduino Uno, 2 x TMC2208 Stepper Drivers, 2 x Contact Switches, 1 x Arduino CNC Shield, 1 x 30mm 5V Fan, 2 x 35cm 8mm Chromed Steel Rods …
5. Pinterest – CNC Turning Ideas
Domain: in.pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Pinterest – CNC Turning Ideas, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Carbide 3D – Free CNC Software Options
Domain: carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Free CNC Software Options: 1. FreeCAD: Free 3D CAD parametric program. Outputs STL, STEP, SVG, DXF. Runs on Mac, Windows, Linux. 2. Solvespace: Free 3D CAD program with a focus on mechanical parts. Exports STL, STEP. Runs on Mac, Windows, Linux. 3. Inkscape: Free 2D design software for CNC, exports SVG, DXF. Runs on Mac, Windows, Linux. 4. Carbide Create: 2D CAM software for Carbide 3D machines, i…
7. Onefinity CNC – Artists’ Cutting Edge
Domain: forum.onefinitycnc.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Onefinity CNC; Target user: Artists expanding formats; Hardware: CNC carving and laser printing capabilities; Software compatibility: No Windows, only Mac; Recommended software: Inkscape, VCarve, MeshCAM, Adobe Illustrator; Vector file conversion options: picsvg.com, Afinity Designer; Use case examples: Converting pen and ink drawings to SVG files for carving or laser printing; Current user: John …
8. Vectric – Cut2D and VCarve
Domain: vectric.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Vectric offers powerful and easy to use design software for CNC machining. Their key products include: 1. Cut2D: A vector drawing and editing software package focused on 2D machining strategies for CNC routing, milling, or engraving. 2. VCarve: Builds on the Cut2D interface, adding 2.5D toolpath functionalities such as v-carving, chamfering, fluting, prism, and moulding, along with the capability …
9. Pinterest – CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: CNC turning drawing; programming parts for a two-axis lathe; G-code programming; contour turning; CNC machining for cylindrical parts such as shafts and hollow tubes; precise tolerances; Fanuc G73 pattern repeating cycle; technical drawings of mechanical parts; includes turning and milling; example programs for turning operations.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc drawing
The significance of effective strategic sourcing in the CNC drawing domain cannot be overstated. International B2B buyers must leverage technical drawings alongside CAD files to eliminate ambiguities and ensure that manufacturers fully understand their needs. Well-crafted technical drawings facilitate better communication, reduce manufacturing costs, and enhance the precision of the final products, especially when operating in varied regulatory environments and expectations across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As you move forward, consider local sourcing strategies that can further optimize logistics, enabling quicker turnaround times and potentially lower shipping costs. Engage suppliers who are responsive and equipped to interpret technical requirements accurately, ensuring quality and efficiency in production.
The global CNC drawing market presents vast opportunities for ambitious buyers willing to invest in refining their specifications and nurturing strong supplier relationships. By adopting meticulous sourcing practices today, you can position your business for success in the future, ensuring that your CNC machined parts meet both your standards and the expectations of your customers. Start exploring the right partnerships and enhance your sourcing strategies, setting the stage for sustained growth and innovation.