Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc calculator
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, one of the most pressing challenges faced by international B2B buyers is efficiently sourcing a reliable CNC calculator that meets their specific operational needs. As businesses strive for precision and efficiency in machining processes, understanding the nuances of CNC calculators becomes crucial. This guide delves into the diverse types of CNC calculators available, their applications in various machining operations, and best practices for supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will explore the key features and functionalities of CNC calculators, including speed and feed calculations, material compatibility, and customization options. Additionally, we will discuss cost considerations and potential return on investment, providing valuable insights tailored for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Nigeria and Vietnam.
By equipping international B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the global market for CNC calculators, this guide empowers them to optimize their sourcing strategies. Understanding these tools will not only enhance machining efficiency but also drive greater profitability in their operations. Whether you’re a seasoned machinist or new to CNC technology, this guide serves as your go-to resource for making strategic purchasing decisions that align with your business goals.
Understanding cnc calculator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed and Feed Calculator | Calculates optimal cutting speeds and feed rates for various tools | CNC machining, metal fabrication | Pros: Increases efficiency, reduces tool wear. Cons: Requires accurate input data. |
| Tool Path Optimization Software | Enhances tool path efficiency to minimize machining time | Aerospace, automotive, high-precision industries | Pros: Maximizes productivity, reduces waste. Cons: Can be complex to integrate. |
| Machining Power Calculator | Estimates power requirements for machining operations | Manufacturing, production planning | Pros: Helps in selecting appropriate machinery. Cons: May not account for all variables. |
| Material Database Calculator | Provides material-specific cutting parameters and recommendations | Material selection, machining strategy | Pros: Tailors processes to material properties. Cons: Limited to available materials in the database. |
| Geometry Calculation Tool | Assists in calculating dimensions and tolerances for machining parts | Design engineering, quality assurance | Pros: Ensures precision, aids in compliance. Cons: May require manual data entry. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Speed and Feed Calculators?
Speed and Feed Calculators are essential tools for CNC machinists, allowing them to determine the optimal cutting speeds and feed rates for a wide range of materials and tooling options. These calculators take into account factors such as material type, tool geometry, and desired finish quality. B2B buyers in industries like metal fabrication and machining benefit from these tools as they enhance operational efficiency and reduce tool wear, ultimately leading to lower production costs. However, accurate input data is critical; incorrect parameters can lead to suboptimal results.
How Does Tool Path Optimization Software Enhance CNC Operations?
Tool Path Optimization Software is designed to refine the movement of CNC tools, maximizing machining efficiency while minimizing cycle times. This software analyzes the part geometry and suggests the most efficient paths for the cutting tools. It is particularly valuable in sectors such as aerospace and automotive, where precision and efficiency are paramount. While the benefits include significant productivity gains and reduced material waste, the software’s complexity can pose integration challenges for some organizations.
Why Is a Machining Power Calculator Important for Manufacturers?
Machining Power Calculators estimate the power requirements necessary for various machining operations, helping manufacturers select the right equipment for their production needs. By factoring in variables such as cutting speed, feed rate, and material properties, these calculators provide insights that are crucial for production planning. They are particularly useful in manufacturing environments where power consumption impacts operational costs. However, buyers should note that these calculators may not account for every variable affecting power requirements, necessitating further evaluation.
What Are the Advantages of Material Database Calculators?
Material Database Calculators offer machinists access to a wealth of information regarding cutting parameters tailored to specific materials. This feature is crucial for B2B buyers involved in material selection and machining strategy, as it allows them to optimize processes based on the unique characteristics of the materials they work with. While these calculators provide valuable insights, their effectiveness is limited to the range of materials included in the database, which may not cover all potential options.
How Do Geometry Calculation Tools Support Precision in CNC Machining?
Geometry Calculation Tools assist engineers and machinists in calculating dimensions, tolerances, and other critical parameters for machining parts. These tools are vital in design engineering and quality assurance processes, ensuring that components meet exact specifications. By facilitating precision, these calculators help organizations maintain compliance with industry standards. However, they may require manual data entry, which can introduce the potential for human error if not handled carefully.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc calculator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Calculator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision Machining of Aircraft Parts | Enhanced accuracy and reduced production time | Supplier reliability, material certification, and tooling compatibility |
| Automotive | Custom Tooling for Engine Components | Improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness in production | Proven experience with automotive standards and regulations |
| Electronics | PCB Manufacturing and Assembly | Streamlined processes and reduced waste | Access to advanced materials and technology support |
| Metal Fabrication | Sheet Metal Cutting and Forming | Increased productivity and reduced lead times | Availability of diverse materials and cutting tools |
| Oil and Gas | Machining of Heavy Equipment Components | High durability and performance in extreme conditions | Compliance with industry standards and safety regulations |
How is the CNC Calculator Used in Aerospace Precision Machining?
In the aerospace sector, CNC calculators are pivotal for precision machining of aircraft parts, ensuring that components meet stringent safety and performance standards. These calculators help engineers determine optimal cutting speeds and feed rates for various materials, such as titanium and aluminum alloys, which are commonly used in aircraft manufacturing. By accurately calculating these parameters, businesses can reduce machining time and improve the quality of the final product, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency. For international buyers, sourcing tools that comply with aerospace quality certifications is crucial to maintain safety and reliability.
What Role Does the CNC Calculator Play in Automotive Custom Tooling?
In automotive manufacturing, CNC calculators facilitate the creation of custom tooling for engine components, ensuring that parts fit together seamlessly and function optimally. By utilizing these calculators, manufacturers can optimize machining processes, leading to reduced production costs and improved turnaround times. This is particularly important for businesses in regions like Africa and South America, where cost efficiency can significantly impact competitiveness. Buyers should consider suppliers with a proven track record in automotive applications and familiarity with local regulations.
How Does the CNC Calculator Streamline PCB Manufacturing in Electronics?
In the electronics industry, CNC calculators are essential for the precision machining required in PCB manufacturing and assembly. They enable manufacturers to calculate the appropriate speeds and feeds for drilling and milling operations, which are critical for creating intricate circuit designs. By optimizing these processes, businesses can minimize material waste and enhance production efficiency. For international buyers, sourcing advanced materials that meet electrical specifications, along with reliable tooling, is vital to ensure product quality and compliance with industry standards.
Why is the CNC Calculator Important for Sheet Metal Cutting in Metal Fabrication?
CNC calculators play a significant role in the metal fabrication industry, particularly for sheet metal cutting and forming. They assist in calculating the ideal cutting speeds and feed rates for various metals, which can lead to increased productivity and reduced lead times. This is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to fulfill large orders efficiently. Buyers in this sector should focus on suppliers that offer a wide range of materials and cutting tools to meet diverse project requirements and ensure compatibility with existing machinery.
How Does the CNC Calculator Assist in Machining Heavy Equipment Components in Oil and Gas?
In the oil and gas industry, CNC calculators are crucial for machining heavy equipment components that must withstand extreme conditions. These calculators help determine the best machining parameters for materials like high-strength steel and alloys used in drilling and extraction equipment. By ensuring that the machining processes are optimized, businesses can enhance the durability and performance of their products. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to industry standards and have a strong understanding of safety regulations, ensuring that components are reliable and compliant with operational demands.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc calculator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Cutting Performance Leading to Material Waste
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the manufacturing sector often struggles with inconsistent cutting performance when using CNC machines. This inconsistency typically arises from improper speeds and feeds calculations, which can lead to excessive tool wear, suboptimal cutting conditions, and ultimately, wasted material. For instance, a company producing precision parts might find that their tools are not lasting as long as expected, resulting in increased downtime and costs associated with replacing worn tools. This scenario not only impacts production efficiency but also affects the bottom line due to higher material consumption and labor costs.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should leverage advanced CNC calculators that take into account multiple variables, including material type, tool geometry, and machine capabilities. When selecting a CNC calculator, it is crucial to choose one that offers a comprehensive database of materials and tooling options. For example, FSWizard provides a built-in material and tool database that allows users to input specific cutting parameters tailored to the job at hand. By accurately calculating cutting speeds and feed rates, users can optimize their machining processes, reduce tool wear, and minimize material waste. Additionally, implementing a regular review of these calculations can help in adjusting the parameters as necessary, ensuring ongoing efficiency.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Tools for Complex Projects
The Problem: In many manufacturing environments, selecting the appropriate cutting tools for specific applications can be a daunting task. B2B buyers often face challenges in finding the right tools that match their machining requirements, particularly when working with complex geometries or exotic materials. This difficulty can result in subpar machining results, increased production times, and higher operational costs. A company specializing in aerospace components, for instance, may struggle to determine the best tooling options for machining titanium alloys, leading to trial-and-error approaches that are both time-consuming and costly.
The Solution: To streamline the tool selection process, buyers should utilize CNC calculators equipped with tool recommendation features. Tools like Kennametal’s Speed and Feed Calculator not only calculate optimal speeds and feeds but also provide tailored tool suggestions based on the inputted parameters. By registering for an account, users can gain access to additional application data that can help in selecting the best tools for their specific jobs. Furthermore, maintaining a close relationship with tool suppliers can provide valuable insights into the latest advancements in tooling technology, ensuring that companies are always equipped with the best solutions for their machining needs.
Scenario 3: Complexity in Understanding and Implementing G-Code
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter significant challenges when it comes to understanding and implementing G-code for CNC programming. This complexity can lead to errors in programming, resulting in incorrect machining operations and potential damage to both tools and workpieces. For instance, a small business might experience frequent production halts due to G-code errors, which not only delays project timelines but also increases labor costs as operators troubleshoot these issues.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, it is essential to adopt CNC calculators that simplify the G-code generation process. Many modern CNC calculators offer integrated features that generate G-code based on the input parameters, significantly reducing the risk of human error. Moreover, investing in training programs for operators can enhance their understanding of CNC programming and G-code, enabling them to use these calculators effectively. Providing access to online resources and forums where operators can share tips and solutions can also foster a collaborative environment that promotes learning and reduces programming errors. By equipping teams with the right tools and knowledge, businesses can enhance their machining accuracy and efficiency, ultimately leading to improved production outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc calculator
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum for CNC Machining?
Aluminum is a widely used material in CNC machining due to its favorable properties. It exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight characteristics, and good thermal and electrical conductivity. Its melting point ranges from 660°C to 680°C, making it suitable for various machining processes. Aluminum’s machinability is high, allowing for intricate designs and precise tolerances.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum in CNC Machining
The advantages of aluminum include its low density, which reduces manufacturing costs and weight in end products, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. However, its lower strength compared to steel can limit its use in high-stress environments. Additionally, while aluminum is relatively affordable, the cost can escalate with specialized alloys.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and oils, making it versatile for different applications. International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN for aluminum grades. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing quality aluminum can be challenging, necessitating reliable suppliers.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in CNC Machining?
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and construction. It typically has a melting point of around 1400°C to 1450°C, which allows it to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Pros and Cons of Using Stainless Steel in CNC Machining
The key advantages of stainless steel include its durability and resistance to rust and staining, making it suitable for harsh environments. However, it is more challenging to machine than aluminum, often requiring specialized tooling and techniques, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Stainless steel’s compatibility with various media, including acids and alkalis, makes it suitable for diverse applications. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM A240 for stainless steel. Additionally, understanding the specific grade required for their application is crucial, as different grades offer varying levels of corrosion resistance and strength.
What Are the Benefits of Using Plastics in CNC Machining?
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly popular in CNC machining due to their lightweight and versatile nature. They generally have lower melting points, ranging from 200°C to 300°C, allowing for easier machining processes.
Pros and Cons of Using Plastics in CNC Machining
The primary advantages of plastics include their low cost, ease of machining, and resistance to chemicals. However, they may not provide the same level of strength and durability as metals, which can limit their use in high-stress applications. Additionally, the environmental impact of plastic waste is a growing concern for manufacturers.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Plastics are compatible with a variety of media, making them suitable for applications in electronics and consumer goods. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local regulations regarding plastic use and disposal. Ensuring compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 can also enhance product quality and marketability.
How Does Tool Steel Compare in CNC Machining Applications?
Tool steel is specifically designed for manufacturing cutting tools and dies, offering exceptional hardness and wear resistance. Its high melting point, typically around 800°C to 1200°C, allows it to maintain performance under extreme conditions.
Pros and Cons of Using Tool Steel in CNC Machining
The main advantage of tool steel is its ability to withstand high temperatures and wear, making it ideal for high-performance applications. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized machining techniques, increasing overall production costs.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Tool steel is particularly suited for applications involving high-stress conditions, such as automotive and aerospace components. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should ensure adherence to standards such as DIN 1.2379 for tool steel grades, as this can impact product reliability and performance.
Summary Table of Strategic Material Selection for CNC Calculators
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc calculator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment | High durability and corrosion resistance | Difficult to machine | High |
| Plastics | Consumer goods | Low cost and easy to machine | Lower strength and durability | Low |
| Tool Steel | Cutting tools and dies | Exceptional hardness and wear resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc calculator
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for CNC Calculators?
The manufacturing of CNC calculators involves a series of systematic processes designed to ensure precision, reliability, and functionality. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage incorporates specific techniques that contribute to the overall quality of the final product.
How Is Material Prepared for CNC Calculators?
Material preparation is crucial for the performance of CNC calculators. Typically, high-quality metals such as aluminum, steel, or plastics are selected based on the intended application. The preparation process involves cutting raw materials into manageable sizes, followed by machining operations to achieve the necessary dimensions. During this phase, manufacturers may utilize CNC milling machines to ensure precise cutting, which is vital for the accuracy of the calculator’s components.
Additionally, materials undergo surface treatments to enhance durability and resistance to wear. This may include anodizing for aluminum parts or protective coatings for steel components. Proper material preparation ensures that the subsequent forming processes are efficient and yield components that meet stringent specifications.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in CNC Calculator Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into functional components of the CNC calculator. Common techniques include:
-
CNC Machining: This is the cornerstone of CNC calculator manufacturing, where computer-controlled machines cut and shape materials with high precision. CNC turning and milling are frequently employed to create complex geometries and tight tolerances.
-
Injection Molding: For plastic components, injection molding is often utilized. This process allows for high-volume production of intricately designed parts, such as buttons and housing casings.
-
Stamping: Metal stamping may be used for creating flat components or enclosures. This technique is efficient for mass production and can achieve high levels of consistency across parts.
These forming techniques are selected based on the material properties and the specific design requirements of the CNC calculator.
How Is Assembly Conducted for CNC Calculators?
The assembly phase is critical in ensuring that all components of the CNC calculator fit and function together seamlessly. This stage typically involves:
-
Component Integration: All machined parts, including the electronic circuits, display units, and housing, are assembled. Precision is key, as even minor misalignments can affect the calculator’s functionality.
-
Soldering and Wiring: For calculators with electronic components, soldering techniques are employed to connect circuit boards and ensure reliable electrical connections. This process may also include the installation of sensors and input devices.
-
Quality Control Checks: Throughout the assembly process, manufacturers conduct initial quality control checks (IQC) to catch defects early. This includes visual inspections and functional tests of individual components before final assembly.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in CNC Calculator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of CNC calculators, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. The following outlines key QA measures:
Which International Standards Apply to CNC Calculators?
To maintain high-quality standards, manufacturers often adhere to internationally recognized certifications such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates a commitment to consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may be relevant. For example, products sold in the European Union may require CE marking, indicating conformity with safety, health, and environmental protection standards. Similarly, products intended for oil and gas applications might need to comply with API standards.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Essential During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that any deviations from quality standards are identified and addressed promptly. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before processing begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, ongoing checks are conducted to monitor the quality of components as they are being produced. This may involve measuring dimensions, checking surface finishes, and conducting performance tests.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the completed CNC calculators undergo thorough testing to verify functionality and performance against established benchmarks. This step is critical for identifying any issues before products are shipped to customers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are effective strategies for verification:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Assess Supplier Quality?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide valuable insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Buyers should look for evidence of compliance with international standards and observe practices firsthand.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to share their quality assurance documentation, including inspection reports, testing results, and certifications. This transparency can help buyers assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and quality control practices. These inspections can be tailored to specific requirements and provide detailed reports.
-
Reference Checks: Buyers should seek references from other clients who have worked with the supplier. Feedback from existing customers can reveal important information about product quality and supplier reliability.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers face unique challenges when navigating quality control practices across different regions. Understanding local regulations and standards is crucial, as they may vary significantly. For instance, certifications required in Europe may differ from those in Africa or South America.
Additionally, cultural factors can influence business practices. Building strong relationships with suppliers and understanding their operational context can enhance communication and lead to better quality outcomes. B2B buyers should also consider language barriers and time zone differences when coordinating quality assurance efforts.
By being proactive in assessing manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, international B2B buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers who deliver high-quality CNC calculators tailored to their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc calculator’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of a CNC calculator can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a structured checklist to help you make informed decisions, ensuring you select a solution that meets your operational needs while optimizing machining processes.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before seeking suppliers, it’s essential to outline your specific requirements. Consider factors such as the types of materials you will be machining, the range of tools you’ll need to calculate speeds and feeds for, and whether you require additional features like power calculations or chip load adjustments. This clarity will guide your search and help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Available CNC Calculators
Begin by exploring the various CNC calculators available in the market. Look for software that not only meets your technical specifications but also offers features like built-in material databases and compatibility with different machining operations (milling, drilling, turning, etc.). Evaluate online reviews and user feedback to gain insights into usability and effectiveness.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for established suppliers who demonstrate a strong track record of customer satisfaction and technical support. This evaluation can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing from less reputable providers.
Step 4: Check for Software Compatibility and Integration
Ensure that the CNC calculator you choose is compatible with your existing systems and machinery. This includes compatibility with your CNC machine controller and any CAD/CAM software you use. A seamless integration will enhance workflow efficiency and minimize disruptions during implementation.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications and Support Services
Assess the credentials and certifications of your potential suppliers. Look for industry-standard certifications that indicate quality assurance and compliance with international machining standards. Additionally, evaluate the level of customer support offered, including training resources and technical assistance, which can be crucial for successful adoption.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Before finalizing your purchase, request demonstrations or trial versions of the CNC calculators. This allows you to test the functionality and ease of use in real-world scenarios relevant to your operations. Pay attention to the interface, speed of calculations, and whether the tool meets your expectations for performance.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Value-Added Features
Finally, compare the pricing structures of different CNC calculators, but don’t focus solely on cost. Consider the value-added features offered, such as advanced analytics or customization options. Assessing the total cost of ownership, including potential savings from improved machining efficiency, will help you make a more informed decision.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for CNC calculators, ensuring they choose a solution that aligns with their operational goals and enhances their machining capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc calculator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for CNC Calculator Sourcing?
When sourcing a CNC calculator, understanding the cost structure is paramount for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. High-quality materials like carbide or specialized alloys often command higher prices, while standard metals may be more economical. It’s essential to assess the material requirements based on the specific applications of the CNC calculator.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for the design, development, and production of CNC calculators. Labor costs can vary dramatically based on geographic location, skill level, and labor market conditions. Outsourcing to regions with lower labor costs can provide significant savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient processes can reduce overhead and contribute to overall cost savings.
-
Tooling: The tooling required for CNC calculator production, such as molds and cutting tools, represents a significant upfront investment. The complexity of the product design may necessitate custom tooling, which can escalate costs.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring precision in CNC calculations is crucial; therefore, robust QC measures must be in place. This can involve additional testing and certification processes, which contribute to overall costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary based on the supplier’s location and the destination market. Factors such as customs duties and tariffs can also influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary depending on the competitiveness of the market and the perceived value of the CNC calculator.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Calculator Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC calculators, especially for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to lower per-unit costs. Many suppliers have minimum order quantities (MOQs) that can affect pricing structures. Negotiating favorable terms for larger orders can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specific requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and adherence to specific industry standards or certifications can raise costs. However, these investments often result in better performance and longevity, making them worthwhile.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher quality and better support, while newer entrants might provide lower prices but with increased risk.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery is crucial. Incoterms dictate who bears the costs and risks associated with shipping and delivery, influencing the final price. Buyers should clarify these terms to avoid unexpected costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in CNC Calculator Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency, B2B buyers should consider several strategies:
-
Negotiation: Always engage in negotiations with suppliers. Many are open to discussing prices, especially for larger orders or long-term partnerships.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront costs but also the TCO. This includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtimes, which can significantly impact the overall investment.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local taxes when sourcing CNC calculators from international suppliers. These factors can affect the final cost and should be factored into budgeting.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on different suppliers. Comparing prices, materials, and service levels can lead to better purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for CNC calculators can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct a comprehensive analysis before making a purchasing decision. Always ensure that you are working with reputable suppliers who can provide accurate pricing based on your specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc calculator With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CNC Calculators: What Are the Options?
In the evolving landscape of CNC machining, businesses are increasingly looking for efficient tools to optimize their operations. While CNC calculators offer a reliable way to determine cutting speeds and feeds, several alternative solutions can also enhance machining performance. This section compares CNC calculators with notable alternatives, providing insights that can guide B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Calculator | FSWizard Speed and Feed Calculator | Kennametal Speed and Feed Calculator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy; customizable | Comprehensive with built-in database | Reliable; tailored to specific tools |
| Cost | Varies (often low or free) | Free basic version; PRO version available | Free with registration; additional features may incur costs |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly interface | Intuitive design; web-based access | Requires account creation; some learning curve |
| Maintenance | Minimal; software updates | Regular updates; community support | Regular updates; may require user training |
| Best Use Case | General machining applications | Versatile for various materials and operations | Best for specialized machining needs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
FSWizard Speed and Feed Calculator
The FSWizard calculator is a robust online tool that excels in providing precise calculations for cutting parameters across various materials and machining operations. Its built-in database includes a wide range of materials, making it versatile for different applications. Users benefit from an intuitive interface that simplifies complex calculations. However, while the basic version is free, the PRO version comes at a cost, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious businesses. Additionally, its reliance on internet access can be a limitation in areas with unstable connectivity.
Kennametal Speed and Feed Calculator
Kennametal’s calculator is tailored for precision machining and offers detailed insights based on the specific tools and materials used. It allows users to create customized assemblies and collaborate with teams, making it a strong choice for larger operations. The tool’s accuracy is enhanced by its focus on theoretical values, allowing for better planning. However, users must register to access the full features, and there may be a learning curve for those unfamiliar with the platform. The need for an account can also be a barrier for smaller businesses looking for quick solutions.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between a CNC calculator and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and the technical expertise of their teams. For businesses focused on general machining applications, a CNC calculator may suffice due to its simplicity and low cost. However, for those requiring advanced features and comprehensive material databases, tools like FSWizard and Kennametal’s calculator offer enhanced capabilities that can drive efficiency and precision. Ultimately, the best choice will depend on a careful evaluation of the features that align with the company’s machining needs and operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc calculator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a CNC Calculator in B2B Applications?
When selecting a CNC calculator, understanding its technical properties is crucial for optimizing machining processes. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Compatibility
CNC calculators must support a wide range of materials, such as aluminum, steel, and plastics. Each material has unique machining characteristics, which impact cutting speeds and feed rates. Knowing the material type helps manufacturers optimize tool life and minimize waste, ultimately improving productivity and cost-effectiveness.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified measurement. In CNC machining, precise tolerances are critical for ensuring that parts fit and function correctly. A CNC calculator should help users determine appropriate machining parameters to achieve desired tolerances, enhancing product quality and reducing the likelihood of rework.
3. Cutting Speed and Feed Rate Calculations
Cutting speed (often expressed in Surface Feet per Minute or SFM) and feed rate (measured in inches per minute or IPM) are vital metrics for any machining operation. CNC calculators should provide accurate calculations based on material properties and tooling specifications, allowing machinists to optimize their processes for efficiency and effectiveness.
4. Tool Geometry and Engagement
Tool geometry, including diameter, number of teeth, and flute design, significantly impacts machining performance. A CNC calculator should allow users to input these parameters to ensure accurate calculations for spindle speed and chip load. This ensures that the machining process is efficient and that the tools operate within their optimal ranges, extending tool life.
5. Machining Power Requirements
Understanding the power requirements for machining operations is essential for equipment selection and energy management. A CNC calculator should help users estimate the required power based on cutting conditions, material properties, and tool specifications. This can lead to better machine choices and more efficient operations.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Calculators for B2B Buyers?
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B contexts. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the CNC industry, OEMs often provide the machines and tools that buyers need. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable sources for high-quality equipment.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the minimum quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. It’s important to negotiate favorable MOQs that align with production needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific products or services. In CNC machining, an RFQ allows businesses to compare pricing and terms from multiple vendors, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. These terms clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is vital for B2B transactions involving CNC equipment. Understanding Incoterms helps businesses manage logistics and costs effectively.
5. G-Code
G-Code is a language used to instruct CNC machines on how to move and operate. It is essential for programming machining operations. Familiarity with G-Code enables buyers to understand machining capabilities and communicate effectively with suppliers.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when selecting CNC calculators and negotiating with suppliers, ultimately enhancing their manufacturing processes and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc calculator Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Impacting the CNC Calculator Sector?
The CNC calculator sector is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in automation, the growing demand for precision machining, and the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies. Global buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking solutions that enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. The rise of smart manufacturing systems has catalyzed the development of sophisticated CNC calculators that utilize real-time data analytics to optimize cutting parameters. This capability not only improves efficiency but also minimizes waste, making it a critical factor for businesses looking to remain competitive.
Moreover, the shift towards digitalization is leading to the emergence of cloud-based CNC calculators that facilitate remote access and collaborative features. These tools allow users to calculate speeds and feeds, analyze machining processes, and share insights across teams, regardless of geographical location. As a result, international B2B buyers are prioritizing software that not only meets their immediate needs but also scales with their operations. This trend is particularly pronounced in developing markets, where businesses are increasingly adopting advanced technologies to leapfrog traditional manufacturing practices.
In response to these dynamics, suppliers are focusing on developing user-friendly interfaces and integrating machine learning algorithms to provide predictive analytics. This evolution aims to empower users with actionable insights, enabling them to make data-driven decisions that enhance their manufacturing processes. For B2B buyers, staying informed about these trends is crucial for selecting the right CNC calculator solutions that align with their operational goals.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Addressed in the CNC Calculator Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the CNC calculator sector, influencing sourcing strategies and product development. As environmental concerns continue to escalate globally, B2B buyers are increasingly scrutinizing the sustainability practices of their suppliers. This includes evaluating the lifecycle impact of CNC calculators, from material sourcing to end-of-life disposal. Suppliers are being urged to adopt ‘green’ certifications and utilize eco-friendly materials to appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining traction, with companies prioritizing suppliers that uphold fair labor standards and transparent supply chains. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America are particularly attentive to these factors, as they seek to foster partnerships that reflect their commitment to social responsibility. The integration of sustainability into sourcing not only mitigates environmental impact but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty.
To meet these demands, manufacturers are exploring alternative materials and processes that reduce waste and energy consumption. Innovations in CNC calculator technology, such as energy-efficient algorithms and materials that minimize carbon footprints, are becoming increasingly prevalent. By investing in sustainable solutions, B2B buyers can ensure compliance with regulatory standards while enhancing their competitive edge in the market.
What Is the Evolution of CNC Calculators and Its Significance for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of CNC calculators has been marked by significant technological advancements, transitioning from basic manual calculations to sophisticated digital solutions. Initially, machinists relied on simple formulas and charts to determine cutting speeds and feeds, a process that was often time-consuming and prone to human error. As computer technology advanced, the introduction of software-based calculators revolutionized the industry, allowing for more accurate and efficient calculations.
Today, CNC calculators are equipped with features that account for a multitude of variables, including material types, tool geometry, and machining conditions. This evolution has significantly improved machining precision and productivity, making it indispensable for modern manufacturing operations. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context underscores the importance of investing in advanced CNC calculators that leverage current technologies to enhance their machining capabilities and drive operational efficiency. As the sector continues to innovate, staying abreast of these developments will be essential for maintaining a competitive advantage in the global marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc calculator
-
How do I solve CNC speed and feed calculation problems?
To solve CNC speed and feed calculation problems, first identify the material being machined and the type of cutting tool used. Utilize a CNC speed and feed calculator that takes into account factors such as tool diameter, cutting speed (SFM or SMM), and chip load. Input the relevant parameters, and the calculator will provide you with the optimal RPM and feed rate for efficient machining. Always cross-reference results with manufacturer recommendations for accuracy and best practices. -
What is the best CNC calculator for my specific machining needs?
The best CNC calculator depends on your specific machining requirements, including the type of materials you work with and the operations you perform (milling, drilling, or turning). Look for calculators that feature comprehensive databases for materials and tools, like FSWizard or Kennametal’s Speed and Feed Calculator. A good calculator should also provide customization options for unique projects and allow for adjustments based on machine capabilities and tooling conditions. -
How can I ensure accurate calculations when using a CNC calculator?
To ensure accurate calculations, always input precise data regarding the material type, tool specifications, and machine settings. Familiarize yourself with the calculator’s interface and the underlying formulas it uses. It’s also beneficial to consult tool manufacturers’ guidelines for recommended speeds and feeds, as they often provide specific parameters for various materials. Regularly reviewing and updating your input data based on recent experiences can further enhance accuracy. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing a CNC calculator for international use?
When sourcing a CNC calculator for international use, consider factors such as software compatibility with local machines, language support, and the ability to handle multiple measurement units (imperial and metric). Additionally, ensure the calculator can accommodate various materials prevalent in your region. Supplier reputation, customer support availability, and any potential tariffs or trade regulations affecting software imports should also be evaluated. -
What are typical payment terms when purchasing CNC calculators from international suppliers?
Typical payment terms vary by supplier but often include options like advance payment, net 30, or net 60 days. For international transactions, consider methods such as wire transfers or letters of credit to ensure security. It’s essential to clarify payment terms before finalizing the purchase, including any additional fees for currency conversion or transaction processing. Discussing payment terms upfront can help avoid delays and misunderstandings later. -
How can I vet suppliers of CNC calculators effectively?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by researching their reputation through online reviews and industry forums. Request references from other businesses that have used their products and inquire about their customer service track record. Evaluate their technical support capabilities, including response times and availability of user manuals or training resources. Additionally, consider requesting a demonstration or trial of the CNC calculator to assess its functionality and ease of use before committing to a purchase. -
What customization options should I look for in a CNC calculator?
When evaluating CNC calculators, look for customization options that allow you to tailor the tool to your specific machining processes. Features like custom material databases, adjustable cutting parameters, and the ability to save and retrieve previous calculations can enhance efficiency. Additionally, check if the calculator supports integration with existing CAD/CAM software, enabling seamless transitions from design to machining. -
What logistics considerations are important when importing CNC calculators?
When importing CNC calculators, logistics considerations include shipping methods, estimated delivery times, and customs clearance procedures. Ensure the supplier provides clear documentation to facilitate smooth importation, including invoices and packing lists. Also, consider potential tariffs or duties that may apply to your purchase. Working with a reliable freight forwarder can help navigate these complexities and ensure your equipment arrives on time and in good condition.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Cnc Calculator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Zero-Divide – FSWizard CNC Speed and Feed Calculator
Domain: zero-divide.net
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: FSWizard is a CNC Speed and Feed Calculator designed for high-performance CNC machinists. Key features include: a built-in material and tool database, support for various machining operations (Milling, Drilling, Tapping, Turning), calculation of Cutting Speed (SFM), Chip Load (ipt), RPM, Feed Rate, required Machining Power, optimal Depth and Width of Cut, and Chip Thinning for High-Speed Machining…
2. Kennametal – Feeds and Speeds Calculator
Domain: kennametal.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Kennametal – Feeds and Speeds Calculator, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. CNC Dirt – Machinist Calculator Pro
Domain: cncdirt.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
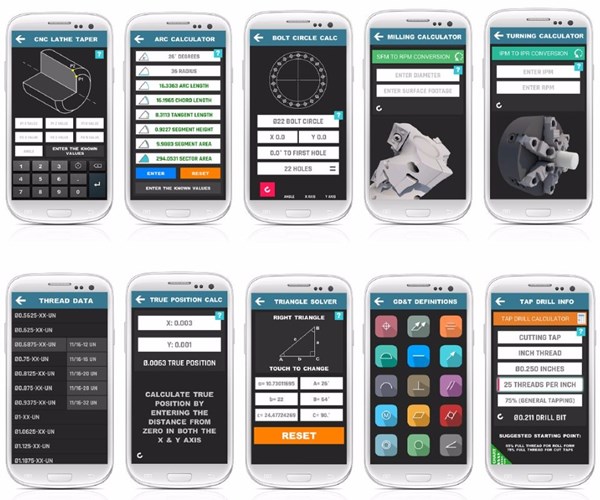
Introduction: CNC Machinist Calculator Pro is a machining app designed for CNC programmers and operators. Key features include: 1. Turning Calculators 2. Milling Calculators 3. Drilling Calculators 4. Gun Drilling Calculator 5. Thread Calculators 6. True Position Calculator 7. Bolt Pattern Calculator 8. Surface Finish Calculators 9. Drill & Tap charts 10. Thread Pitch charts 11. Center drill data 12. Unit conve…
4. IDC Woodcraft – Chipload Calculator
Domain: idcwoodcraft.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Chipload Calculator: A tool for calculating optimal chip load for CNC tooling. Users can input tool diameter, spindle speed, and feed rate to obtain precise values that enhance tool life and cutting performance. Ideal for machinists, hobbyists, and professionals. Typical chiploads provided for various materials (hardwood, softwood, MDF) and diameters (1/8″, 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″ and their metric equiva…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc calculator
What Are the Key Takeaways for International B2B Buyers of CNC Calculators?
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, leveraging a CNC calculator is essential for optimizing machining processes. These tools empower businesses to accurately calculate speeds and feeds, ensuring efficient material usage and minimizing waste. By understanding the specific requirements of various materials and tooling options, companies can significantly enhance their production capabilities and reduce operational costs.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your CNC Operations?
Strategic sourcing not only provides access to high-quality CNC calculators but also fosters relationships with reliable suppliers. This approach enables buyers to secure the best pricing and service, which is particularly crucial for companies operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By investing in advanced CNC technologies, organizations can improve their machining precision and ultimately drive profitability.
What Should International Buyers Do Next?
As you consider your sourcing strategy for CNC calculators, evaluate your specific needs and the local market conditions. Embrace innovation and seek out suppliers that offer comprehensive tools tailored to your operational demands. By making informed decisions today, you can position your business for success in the evolving global manufacturing arena. Engage with industry experts, explore cutting-edge solutions, and take the next step toward enhancing your machining efficiency.