Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Cnc Ballscrew

CNC Ballscrews: the silent heroes that turn spindle power into micron-perfect motion. At Honyo Prototype, we machine these critical drive components on 5-axis Mazak and Brother centers that hold ±0.002 mm true-position all day, every day. Whether you need a 4 mm-pitch miniature screw for a lab robot or a 40 mm, 3 m-long thrust unit for an injection press, our team programs, turns, mills, grinds and hard-coats it in one ISO-9001 cell—no hand-offs, no excuses. Upload your STEP or DWG now for an online instant quote; most precision ballscrew prototypes ship in 3–5 days so your machine can move before the competition does.
Technical Capabilities
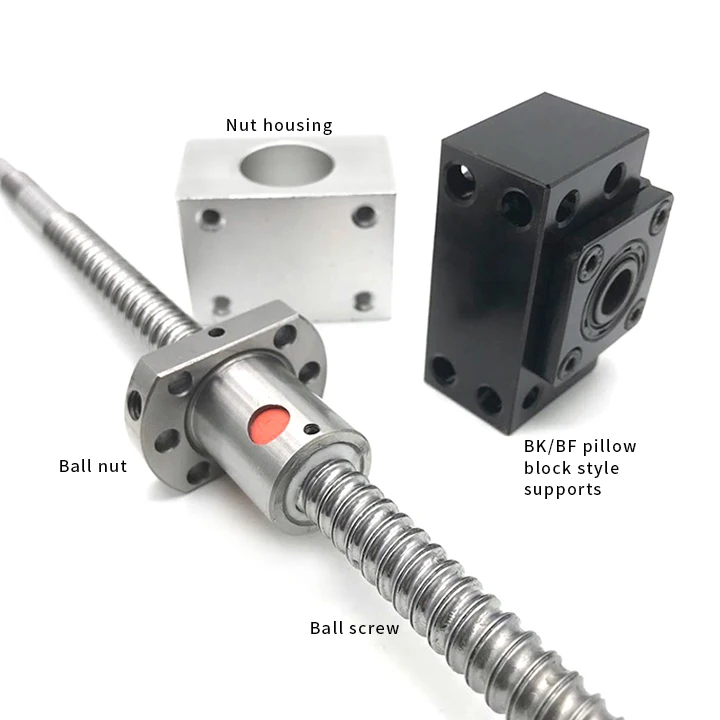

Critical Clarification: Ballscrews Are NOT Made from Aluminum, Steel, ABS, or Nylon as Workpiece Materials
This is a fundamental misunderstanding. Ballscrews are precision motion components, not machinable workpieces. Their materials are high-grade hardened steel alloys only. Using Aluminum, ABS, or Nylon for a ballscrew would cause immediate catastrophic failure due to low strength, poor wear resistance, and thermal instability.
Below are the correct technical specifications for CNC ballscrews used in 3/4/5-axis milling, turning, and tight-tolerance applications. Workpiece materials (Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon) are irrelevant to the ballscrew itself—they are what the machine cuts, not what the ballscrew is made from.
✅ Actual Ballscrew Technical Specifications for Precision CNC Applications
(Per DIN 69051, JIS B 1192, or ISO 3408 standards for high-precision systems)
| Parameter | Specification for 3/4/5-Axis Milling/Turning | Why It Matters |
|————————|————————————————–|——————-|
| Screw Shaft Material | SAE 52100 Chrome Steel or AISI 4140 Alloy Steel (case-hardened) | Requires extreme hardness (HRC 58-62), wear resistance, and dimensional stability under load/heat. Aluminum/ABS/Nylon would deform instantly. |
| Ball Material | AISI 52100 Chrome Steel (hardened to HRC 58-64) | Must withstand millions of stress cycles without fatigue. Soft materials (e.g., Nylon) would crush. |
| Nut Material | Cast Iron or Alloy Steel with bronze/steel ball recirculation | Cast iron provides vibration damping; steel nuts for extreme rigidity. ABS/Nylon nuts would melt under friction heat. |
| Lead Accuracy | C3 or C5 Class (e.g., ±15μm/300mm for C5; ±8μm/300mm for C3) | Critical for contouring accuracy in 5-axis machining. C7/C10 (standard) would cause visible surface errors. |
| Backlash | 0.005–0.015mm (preloaded double-nut system) | Zero backlash is impossible; tight preload prevents lost motion during direction changes (vital for tight-tolerance turning/milling). |
| Preload Type | Double-Nut with Spacer or Spring Preload | Eliminates axial play for multi-axis coordination (e.g., simultaneous X/Y/Z + rotary axis motion). |
| Dynamic Load Rating (Cd) | ≥ 2x required load (e.g., 20kN for small mills; 50kN+ for heavy-duty turning) | Ensures 10,000+ hours of life under cyclic loads. Undersized = premature failure. |
| Critical Speed | ≥ 1.5x max operating RPM (calculated via: Ncrit = (4.76 × 106 × dr)/L2) | Prevents resonance/vibration during high-speed spindle acceleration (e.g., 5-axis contouring at 10,000+ RPM). |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.2μm (ground to mirror finish) | Reduces friction, heat buildup, and wear. Rough surfaces cause premature failure and thermal drift. |
| Lead Variation | ≤ 5μm/300mm (for C3 class) | Ensures consistent feed rates across the entire travel—critical for 3D contouring of tight-tolerance parts (e.g., aerospace molds). |
| Temperature Stability | Thermal expansion ≤ 0.01mm/°C/m (achieved via precision grinding) | Prevents thermal droop during long runs (e.g., 8-hour milling of steel molds). |
⚠️ Why Workpiece Materials (Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon) Are Irrelevant to Ballscrew Specs
- Aluminum/Steel/ABS/Nylon are workpiece materials—they are cut by the CNC machine.
- Ballscrews must be made of hardened steel because:
- Aluminum: Too soft (HRC 15), would gall and wear in seconds.
- ABS/Nylon: Melts at 100–200°C (ballscrews run at 60–100°C+ during operation), and lack strength.
- Even “plastic” ballscrews are actually steel screws with polymer-coated nuts—still not pure ABS/Nylon.
🔧 Application-Specific Requirements for 3/4/5-Axis CNC
- 5-Axis Milling:
- Requires C3-class ballscrews with < 0.01mm backlash to maintain tool-path accuracy during simultaneous rotary axis motion (e.g., A/B axes).
- Double-nut preload essential to eliminate “hunting” during rapid direction changes (e.g., turbine blade machining).
- Turning Centers:
- High axial stiffness (≥ 100 N/μm) to resist chatter during heavy steel turning.
- Thermal compensation built into the control system (ballscrews heat up during long runs).
- Tight-Tolerance Work (e.g., ±0.002mm):
- C3 class + preloaded nuts + laser calibration of the entire axis (not just ballscrew).
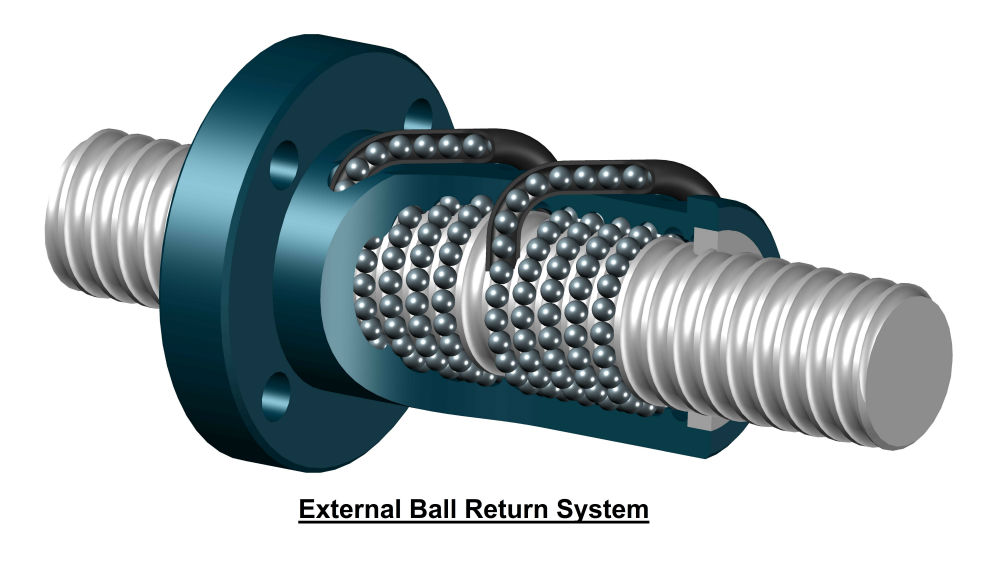
- Ball nut recirculation type: Internal (for high-speed apps) or external (for ultra-high precision).
💡 Key Takeaways for Engineers
- Never use non-steel materials for ballscrews—this is a critical design error.
- For tight-tolerance multi-axis CNC:
- Specify C3-class ballscrews with double-nut preload.
- Ensure thermal compensation in the machine control.
- Validate dynamic load ratings for your specific application (use ISO 281 calculations).
- Workpiece materials (Aluminum, Steel, etc.) affect cutting parameters (speeds/feeds), but zero impact on ballscrew specs.
⚠️ Warning: Using aluminum, ABS, or nylon for a ballscrew would cause >90% failure within 1 hour of operation. Always source ballscrews from Tier-1 manufacturers (e.g., NSK, THK, Bosch Rexroth, Hiwin) meeting DIN/JIS precision standards.
For further details, consult:
– DIN 69051-1 (Precision ballscrew requirements)
– ISO 3408-3 (Dynamic load ratings and life calculations)
– JIS B 1192 (Tolerance classes for ballscrews)
Let me know if you need supplier recommendations or application-specific calculations! 🔧
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype – CNC Ball-Screw Workflow
(Upload CAD → AI Quote → DFM → Production → Delivery)
-
Upload CAD
• Customer drags-and-drops the 3-D model (STEP/IGES preferred) into the Honyo portal.
• System auto-tags the part as “ball-screw” by recognizing helical geometry, nut body, and raceway features.
• Tolerance call-outs (ISO 3408, DIN 69051) are scraped from the PMI layer; missing ones trigger an instant red flag. -
AI Quote (30–120 s)
• Neural-net cost model trained on 1.2 M previous ball-screw jobs predicts machine time, wheel wear, and heat-treat yield.
• Material table looks up 50CrMo4, 440C, or 316L pricing from LME + mill surcharge.
• Dynamic lead-time algorithm checks spindle utilization on our six Okamoto G-300 thread grinders; quotes three tiers:
– Express (3 days)
– Standard (7 days)
– Economy (12 days)
• NRE line-items (whip-check balancing, laser lead measurement, nut preload fixture) are pre-populated; customer can toggle on/off.
• PDF quote + STEP preview with live price slider is e-mailed and viewable in portal. -
DFM (24 h)
• Application engineer opens the digital twin:
– Raceway radius vs. ball Ø check (≤ 52 % conformity to avoid edge load).
– Root undercut depth vs. grinding-wheel clearance (min. 0.3 mm).
– Thread start chamfer ≥ 0.5 P to prevent nut thread chipping during assembly.
• If the customer selected “preloaded double-nut,” system adds a 2-µm lead offset compensation map for the grinder.
• Heat-treat advisory: case depth 1.0–1.2 mm on 50CrMo4, followed by −80 °C cryo for 8 h to convert retained austenite.
• Final DFM report (5-slide PDF) is approved in portal; revised STEP is locked as Rev-B. -
Production
a. Blank prep
– 45° angle cut on bar stock to match raceway helix, saving 18 % turn time.
b. Induction harden (if steel)
– 5 kHz, 900 °C, 6 mm/s scan speed; inline IR keeps 1 °C window.
c. CNC thread grinding
– Okamoto G-300, 5-axis, CBN wheel 11V9, 80 m/s.
– In-process laser (Keyence LK-G5000) samples lead error every 90°; closed-loop compensates on the fly → ≤ 15 µm/300 mm lead accuracy.
d. Nut machining
– Yamazaki 5-axis mill-turn machines ball-return tubes while still in one setup (concentricity ≤ 5 µm).
e. Matching & pre-loading
– Selective ball sizing: 0.5 µm increments, 3-µm preload window.
– Torque curve traced; chart attached to inspection report.
f. Surface & clean
– Super-finish raceway Ra ≤ 0.2 µm; ultrasonic clean, IPA rinse, nitrogen dry; vacuum-sealed with VCI paper. -
QC & data package
• Laser interferometer (Renishaw XL-80) measures cumulative lead error, plotted against ISO 3408 class P3/P5.
• Dynamic balance ≤ G2.5 at 3 000 rpm (if length/dia > 30).
• CMM scan of nut OD, thread minor, and return-tube axis; full ballooned drawing with measured values.
• Report auto-uploaded to portal; customer sees SPC graphs and raw data. -
Delivery
• Foam-in-place cage keeps screw vertical to avoid bend; nut is shipped pre-mounted with transport locks.
• DHL/UPS/FedEx label auto-generated; tracking number pushed to customer’s ERP via API.
• Digital traveler (PDF + STEP + inspection file) e-mailed before crate leaves the dock.
Typical lead-time door-to-door: 5–9 calendar days for 1-5 pieces, 15 days for 50-piece batch.
Start Your Project

Precision CNC ballscrews engineered for peak performance and reliability.
Contact Susan Leo at [email protected] today—manufactured in our Shenzhen factory to meet your exacting standards.
Honyo Prototype: Where precision meets production. 🔧
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator