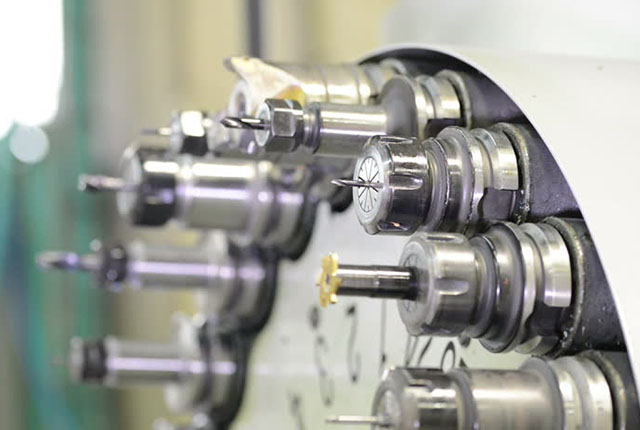
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc auto tool changer
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing the right CNC auto tool changer can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With varying standards, technological advancements, and a multitude of suppliers, making the best purchasing decision is crucial. This guide addresses these complexities by providing a comprehensive overview of CNC auto tool changers, including the different types available, their applications across various industries, and essential criteria for vetting suppliers.
As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—like Brazil and Germany—seek to enhance operational efficiency and productivity, understanding the nuances of CNC auto tool changers becomes imperative. This guide empowers buyers by offering actionable insights into cost considerations, compatibility with existing machinery, and the latest innovations in automatic tool changing systems. By equipping decision-makers with the knowledge needed to navigate the global market, this resource aims to facilitate informed choices that align with specific business needs and technological requirements. Whether you are upgrading your existing setup or investing in new machinery, this guide serves as your roadmap to successful procurement in the ever-evolving world of CNC technology.
Understanding cnc auto tool changer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pneumatic Tool Changer | Utilizes compressed air for tool changes; often has multiple tool positions. | Aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery. | Pros: Fast operation; high reliability. Cons: Requires air compressor; potential for air leaks. |
| Electric Tool Changer | Uses electric motors for tool engagement and disengagement; often quieter. | Woodworking, metalworking, and prototyping. | Pros: Lower maintenance; quieter operation. Cons: Potentially slower than pneumatic systems; higher initial cost. |
| Manual Tool Changer | Requires operator intervention to change tools; typically lower cost. | Small workshops, hobbyists, and prototyping. | Pros: Cost-effective; easy to implement. Cons: Increased downtime; less efficient for high-volume production. |
| Automatic Tool Changer (ATC) | Fully automated system with pre-set tool positions; integrates with CNC software. | Mass production, complex machining tasks. | Pros: Maximizes efficiency; reduces human error. Cons: Higher complexity; requires compatible CNC systems. |
| Hybrid Tool Changer | Combines pneumatic and electric mechanisms for enhanced flexibility. | Versatile manufacturing environments. | Pros: Offers the benefits of both systems; adaptable to various materials. Cons: More complex installation; potential for higher maintenance. |
What Are the Characteristics of Pneumatic Tool Changers?
Pneumatic tool changers are designed to operate using compressed air, allowing for quick and efficient tool changes. They typically feature multiple tool positions, making them ideal for applications that require frequent tool swaps, such as in aerospace and automotive manufacturing. When considering a pneumatic system, businesses should evaluate their air supply capabilities, as these systems require reliable compressors to function effectively. While they offer speed and reliability, potential air leaks can pose challenges.
How Do Electric Tool Changers Differ from Pneumatic Options?
Electric tool changers use electric motors to engage and disengage tools, providing a quieter alternative to pneumatic systems. They are particularly suited for woodworking and metalworking applications where noise reduction is a priority. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment, as electric systems may have a higher upfront cost but often lead to lower maintenance expenses. Their efficiency in quieter environments makes them a compelling choice for businesses focused on workplace comfort.
Why Choose Manual Tool Changers for Small Workshops?
Manual tool changers require operator intervention for tool changes, making them a cost-effective solution for small workshops or hobbyists. Their straightforward design allows for easy implementation without the need for complex systems. However, businesses should be aware that manual changers can lead to increased downtime and are less efficient for high-volume production environments. They are best suited for applications where flexibility and lower cost are prioritized over speed.
What Makes Automatic Tool Changers Ideal for Mass Production?
Automatic Tool Changers (ATCs) are fully automated systems that integrate seamlessly with CNC machines, allowing for pre-set tool positions and reducing the need for human intervention. They are particularly beneficial in mass production scenarios where efficiency and accuracy are paramount. B2B buyers must ensure compatibility with existing CNC systems, as the complexity of ATCs can be a drawback. However, their ability to minimize human error and maximize throughput makes them a top choice for complex machining tasks.
What Are the Advantages of Hybrid Tool Changers?
Hybrid tool changers combine the features of both pneumatic and electric systems, offering enhanced flexibility in various manufacturing environments. They can adapt to different materials and machining requirements, making them suitable for diverse applications. Businesses should consider the complexity of installation and maintenance when choosing a hybrid system, as these factors can influence overall operational efficiency. The adaptability of hybrid changers can lead to improved productivity across multiple processes.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc auto tool changer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Auto Tool Changer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision machining of complex components | Enhanced accuracy and reduced cycle times | Compatibility with high-precision materials |
| Automotive | Automated tool changes for mass production | Increased throughput and reduced labor costs | Robustness for high-volume operations |
| Furniture Manufacturing | Custom woodwork and design applications | Improved design flexibility and material handling | Versatility to handle various tooling requirements |
| Electronics | PCB milling and engraving | Higher precision and reduced manual intervention | Compatibility with delicate components |
| Medical Device Production | Manufacturing of intricate surgical instruments | Strict adherence to quality and safety standards | Certification compliance and precision requirements |
How is CNC Auto Tool Changer Used in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, CNC auto tool changers are essential for precision machining of complex components such as turbine blades and structural parts. These changers facilitate rapid tool switching, which is crucial for high-accuracy tasks that require different cutting tools for various materials. The ability to maintain tight tolerances while reducing cycle times is paramount for aerospace applications. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing auto tool changers that are compatible with high-performance materials and can operate in environments requiring stringent quality controls.
What Role Does CNC Auto Tool Changer Play in Automotive Mass Production?
In automotive manufacturing, CNC auto tool changers streamline the production process by automating tool changes during mass production runs. This not only increases throughput but also significantly reduces labor costs associated with manual tool changes. The automotive sector demands high reliability and durability from machinery, so sourcing a robust auto tool changer that can withstand the rigors of continuous operation is critical. Buyers should consider the changer’s compatibility with various machining tools and its ability to handle high-volume production efficiently.
How Does CNC Auto Tool Changer Enhance Furniture Manufacturing?
CNC auto tool changers are revolutionizing furniture manufacturing by enabling customized woodwork and intricate designs. These systems allow manufacturers to switch between various cutting tools quickly, enhancing design flexibility and material handling capabilities. This adaptability is essential for meeting the diverse demands of clients while maintaining high production rates. For businesses in this sector, sourcing an auto tool changer that supports a wide range of tooling options and can easily integrate with existing CNC systems is vital for maximizing operational efficiency.
In What Ways is CNC Auto Tool Changer Beneficial for Electronics Production?
In the electronics sector, CNC auto tool changers are used for tasks such as PCB milling and engraving. The automation of tool changes minimizes manual intervention, thereby increasing precision and reducing the risk of errors. As electronics manufacturing often involves intricate designs and tight tolerances, sourcing an auto tool changer that can handle delicate components and ensure high-quality output is crucial. Buyers should also evaluate the changer’s compatibility with specialized tools needed for different electronic applications.
Why is CNC Auto Tool Changer Critical in Medical Device Production?
CNC auto tool changers play a crucial role in the production of intricate surgical instruments within the medical device industry. The ability to switch tools automatically ensures that manufacturers can adhere to strict quality and safety standards while optimizing production efficiency. Given the high stakes involved, sourcing auto tool changers that comply with medical device regulations and provide exceptional precision is a must for buyers in this sector. Additionally, understanding the specific machining requirements for different medical devices can guide sourcing decisions effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc auto tool changer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Ensuring Compatibility with Existing CNC Systems
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when integrating an automatic tool changer (ATC) into their existing CNC setups. The compatibility between the ATC and various CNC controllers can lead to significant downtime and frustration. Buyers often find themselves unsure if the ATC will function seamlessly with their specific machine models, leading to risks of poor investment and operational inefficiencies. This issue is particularly prevalent among companies in regions like Africa and South America, where access to technical support and resources may be limited.
The Solution:
To address compatibility issues, it’s essential for buyers to conduct thorough research before making a purchase. This includes reviewing the specifications of the ATC and comparing them with the technical documentation of their CNC systems. Buyers should reach out to manufacturers for compatibility guidelines and leverage any available online forums or user groups for firsthand experiences from other users. Engaging a reputable supplier who provides a compatibility guarantee can also be beneficial. Additionally, investing in an ATC that offers a plug-and-play solution can significantly reduce integration challenges, allowing for a smoother transition with minimal technical adjustments required.
Scenario 2: Managing Maintenance and Downtime
The Problem:
Maintenance of CNC equipment, including automatic tool changers, is a common pain point for businesses striving to optimize production efficiency. Regular wear and tear can lead to unexpected breakdowns, resulting in costly downtime. B2B buyers often struggle with how to effectively manage maintenance schedules, causing anxiety over potential delays in production and missed deadlines for clients, which can harm their reputation in competitive markets.
The Solution:
To mitigate maintenance-related issues, buyers should adopt a proactive maintenance strategy tailored to their ATC systems. This includes creating a maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and actual usage patterns. Implementing a preventive maintenance checklist that covers key components such as tool holders, pneumatic systems, and electrical connections will help ensure that each part is functioning optimally. Additionally, investing in training for staff on basic troubleshooting techniques can empower teams to address minor issues before they escalate into major problems. Finally, establishing a relationship with a reliable service provider for regular check-ups and emergency support can further enhance operational reliability.
Scenario 3: High Initial Investment with Uncertain ROI
The Problem:
For many businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, the high initial investment required for a quality automatic tool changer can be daunting. Buyers often grapple with the uncertainty of whether the ATC will deliver sufficient ROI to justify the expenditure. This concern is magnified in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where market competition is fierce and operational costs need careful management.
The Solution:
To ensure that investing in an ATC is worthwhile, buyers should perform a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis before purchasing. This analysis should consider not only the purchase price but also potential savings in labor, reduced tool change times, and increased production capacity. Buyers can enhance their decision-making by seeking testimonials and case studies from other businesses that have successfully integrated ATCs, providing real-world insights into expected performance improvements. Additionally, exploring financing options or leasing arrangements can help spread the cost over time, reducing the financial burden while still allowing for operational improvements. Engaging with suppliers who offer trial periods or satisfaction guarantees can also provide peace of mind and facilitate a more informed purchasing decision.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc auto tool changer
When selecting materials for CNC auto tool changers, it is essential to consider various factors such as durability, manufacturing complexity, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the production of CNC auto tool changers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Aluminum in CNC Auto Tool Changers?
Aluminum is widely used in CNC auto tool changers due to its favorable properties, including a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and good machinability. It can withstand temperatures up to 150°C, making it suitable for various machining applications.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, which enhances the speed and efficiency of tool changes. It is also relatively inexpensive and easy to fabricate, allowing for quick production cycles.
Cons: While durable, aluminum may not be suitable for high-stress applications compared to steel. It can also be more susceptible to wear over time, particularly in abrasive environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a range of media, making it versatile for various machining tasks. However, its wear characteristics may necessitate more frequent maintenance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN and ASTM for aluminum grades. Understanding local preferences for aluminum alloys can also influence sourcing decisions.
How Does Steel Compare for Use in CNC Auto Tool Changers?
Steel, particularly high-carbon and stainless steel, is another common material used in CNC auto tool changers. It boasts superior strength and durability, with temperature ratings that can exceed 300°C depending on the alloy.
Pros: Steel’s robustness makes it ideal for high-load applications, providing longevity and reliability. Its resistance to deformation under stress is a significant advantage in demanding environments.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which can slow down the tool-changing process. Additionally, it is more expensive and requires more complex manufacturing processes, including heat treatment.
Impact on Application: Steel is well-suited for applications involving hard materials, as it can withstand higher wear rates. However, its weight may limit its use in lightweight CNC machines.
Considerations for International Buyers: Steel products must often meet stringent quality standards, such as JIS in Japan or ASTM in the U.S. Buyers should also be aware of import tariffs that may affect the overall cost.
What Role Does Composite Material Play in CNC Auto Tool Changers?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics, are increasingly being used in CNC auto tool changers due to their lightweight and high strength properties. They can operate effectively at temperatures around 120°C.
Pros: Composites offer excellent corrosion resistance and are lighter than both aluminum and steel, enhancing machine speed and efficiency. They also provide good vibration dampening, which can improve machining accuracy.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost of composites, along with the complexity of manufacturing and repair. They may also not be as widely accepted in traditional manufacturing environments.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly effective in applications requiring high precision and minimal weight, making them suitable for advanced CNC setups.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with international standards for composite materials, as regulations can vary significantly by region. Awareness of local suppliers and their capabilities is also crucial.
How is Plastic Utilized in CNC Auto Tool Changers?
Plastics, such as nylon and polycarbonate, are used in non-load-bearing components of CNC auto tool changers. These materials are lightweight and can operate effectively in temperatures up to 80°C.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective and provide excellent chemical resistance. They are also easy to mold into complex shapes, which can enhance design flexibility.
Cons: Plastics generally have lower mechanical strength compared to metals, making them unsuitable for high-stress applications. They can also wear out more quickly under heavy use.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for components that require less strength, such as covers or guides, but may not be suitable for critical load-bearing parts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding plastics is essential, particularly in Europe where regulations are stringent. Buyers should also consider the availability of local suppliers for specific plastic grades.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Auto Tool Changers
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc auto tool changer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower wear resistance | Medium |
| Steel | Load-bearing components | High strength and durability | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Composite | Precision components | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Non-load-bearing components | Cost-effective and flexible design | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in CNC auto tool changers, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc auto tool changer
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of CNC Auto Tool Changers?
The manufacturing process for CNC auto tool changers involves several key stages that ensure precision, reliability, and efficiency. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to invest in high-quality equipment.
Material Preparation: How Are Components Selected and Prepared?
The first stage in manufacturing CNC auto tool changers is material preparation. Manufacturers typically choose high-strength materials such as aluminum alloys and stainless steel for their durability and resistance to wear. The materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet specifications, including tensile strength and corrosion resistance.
Once selected, the materials are cut to size using advanced CNC machining tools. This step is critical as it lays the foundation for the accuracy of the final product. Manufacturers may also use laser cutting or waterjet cutting techniques to achieve intricate designs and high tolerances.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape the Components?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming. This process includes various techniques such as machining, bending, and welding, which are employed to create the necessary shapes and configurations for the tool changers. CNC milling and turning are commonly used to ensure high precision in critical components like tool holders and mounting brackets.
Advanced forming techniques, such as injection molding for plastic components or die casting for aluminum parts, may also be utilized. These techniques not only enhance production efficiency but also ensure consistency in quality across batches.
Assembly: How Are Components Brought Together for Functionality?
The assembly stage is where all manufactured components come together. This process is often performed in a cleanroom environment to minimize contamination. Skilled technicians or automated systems assemble the components, ensuring that each part is correctly aligned and securely fastened.
During assembly, manufacturers pay particular attention to critical connections, such as pneumatic lines for tool clamping mechanisms and electrical connections for control systems. The integration of smart technology, such as sensors for tool detection and automated calibration, can also be part of this stage, enhancing the functionality of the tool changer.
Finishing: What Steps Ensure the Tool Changer Meets Quality Standards?
Finishing processes, including surface treatment and coating, are essential for enhancing the durability and aesthetics of the CNC auto tool changers. Common finishing techniques include anodizing, powder coating, and painting, which not only improve corrosion resistance but also provide a finished look.
Quality checks are conducted during this stage to ensure that the surface treatments meet the specified requirements. This includes checking for uniformity, adhesion, and appearance, which are critical for operational efficiency and longevity.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for CNC Auto Tool Changers?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing CNC auto tool changers, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. This process typically involves several checkpoints and testing methods.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant international standards that govern manufacturing quality. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that the manufacturer adheres to best practices in quality management, ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
In addition, specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe or API standards in the oil and gas sector may apply, depending on the intended use of the tool changer. Manufacturers may undergo third-party audits to verify compliance with these standards, providing assurance to buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) involves several critical checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint occurs when raw materials and components arrive at the manufacturing facility. Materials are inspected for defects and compliance with specifications before they enter production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, IPQC ensures that processes are being followed correctly and that components meet quality standards. This may involve regular checks of dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the assembly is complete, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the finished product. This includes functional tests, stress tests, and performance evaluations to ensure the tool changers operate as intended.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to validate the quality and performance of CNC auto tool changers. Common methods include:
-
Functional Testing: Verifying that all mechanical and electrical functions operate correctly under various conditions.
-
Load Testing: Assessing the tool changer’s ability to handle specified loads without failure, simulating real-world operating conditions.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Using precision measuring tools to ensure all components meet design specifications, focusing on critical tolerances.
-
Durability Testing: Subjecting the tool changer to prolonged use conditions to evaluate long-term performance and reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying supplier quality control practices is essential to ensure they receive high-quality CNC auto tool changers. Here are several strategies to consider:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Conduct Supplier Audits?
Buyers should conduct thorough supplier audits to assess the manufacturer’s quality management system. This includes reviewing documentation related to ISO certifications, quality control processes, and testing protocols. On-site visits can provide insight into the manufacturing environment and practices.
How Can Buyers Utilize Quality Reports and Certifications?
Requesting quality reports and certificates from suppliers can help buyers evaluate compliance with international standards. These documents should detail the results of inspections and tests performed at various stages of manufacturing, offering transparency into the supplier’s quality assurance efforts.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Ensuring Quality?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control processes. These inspectors can verify compliance with industry standards, perform random sampling of products, and conduct tests to ensure the tool changers meet required specifications.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for B2B Buyers from Different Regions?
B2B buyers from diverse regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific quality control considerations relevant to their markets.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulations governing product safety and performance. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with local regulations and standards.
-
Cultural Expectations: Understanding regional expectations regarding quality and service can influence supplier selection. Buyers may prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in their specific market.
-
Logistics and Support: Buyers should consider the supplier’s ability to provide ongoing support and spare parts, particularly in regions where access to technical services may be limited.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for CNC auto tool changers can empower B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on quality control practices and international standards, buyers can ensure they invest in reliable and efficient equipment tailored to their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc auto tool changer’
When sourcing a CNC automatic tool changer (ATC), it’s essential to approach the process methodically to ensure you select a system that meets your operational needs and business goals. This guide outlines critical steps for B2B buyers to consider while procuring an ATC, ensuring a successful investment in enhanced machining capabilities.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before exploring options, identify the specific requirements for your CNC operations. Consider factors such as the types of materials you’ll be machining, the complexity of your projects, and the desired speed and precision of tool changes.
– Tool Capacity: Determine how many tools you need the changer to accommodate.
– Compatibility: Ensure that the ATC is compatible with your existing CNC machine and its controller.
Step 2: Research Available Options
Take time to explore various ATC systems available in the market. Look for systems that align with your defined specifications while considering brand reputation and customer reviews.
– Product Features: Investigate features such as automatic vs. manual operation, tool measurement capabilities, and safety mechanisms.
– Supplier Reputation: Opt for suppliers known for reliability and customer service, as their support can be crucial during installation and operation.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
– Certifications and Standards: Verify that suppliers adhere to international manufacturing standards, which can assure product quality and safety.
– Technical Support: Assess the level of after-sales support and training provided by the supplier to facilitate smooth integration.
Step 4: Assess Cost vs. Value
While budget is a critical consideration, focus on the overall value of the ATC system rather than just the initial purchase price.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in installation, maintenance, and potential downtime savings from improved efficiency.
– Warranty and Service Plans: Look for comprehensive warranties and service agreements that can protect your investment over time.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Trials
If possible, arrange for product demonstrations or trials before finalizing your purchase. This hands-on experience can provide valuable insights into the ATC’s performance and compatibility with your workflow.
– Performance Metrics: Pay attention to the speed and reliability of tool changes during the demonstration.
– Ease of Use: Evaluate the user interface and controls to ensure they are intuitive for your team.
Step 6: Review Shipping and Installation Options
Understand the logistics involved in shipping and installing your ATC. Ensure that the supplier can meet your timeline and that you have the necessary resources for installation.
– Shipping Costs: Clarify any additional shipping costs, especially for international orders.
– Installation Support: Confirm whether the supplier offers installation support, either remotely or on-site, to facilitate a smooth setup process.
Step 7: Plan for Future Upgrades
Consider how the ATC system will fit into your long-term operational strategy. Choose a system that allows for future upgrades or expansions as your business grows.
– Modularity: Look for ATCs that can be easily upgraded with additional tools or features.
– Integration Capabilities: Ensure that the ATC can integrate with new technologies or CNC machines you may acquire in the future.
By following these steps, you can make informed decisions when sourcing a CNC automatic tool changer, ultimately enhancing your manufacturing efficiency and productivity.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc auto tool changer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for CNC Auto Tool Changer Sourcing?
When sourcing CNC auto tool changers, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality of materials used, such as high-grade steel or aluminum for structural components, significantly impacts the overall cost. Advanced materials can enhance durability and performance but may raise prices.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the assembly and quality assurance of CNC auto tool changers. Labor costs can vary widely based on the location of manufacturing and the complexity of the assembly process.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to the production facility, utilities, and equipment maintenance. High overhead costs can lead to increased pricing, particularly in regions with higher operational expenses.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom designs. This cost is amortized over production runs, affecting the pricing of smaller orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the products meet industry standards. Implementing robust QC measures adds to the overall cost but is essential for maintaining reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the supplier’s location and the destination. Incoterms and shipping methods chosen can significantly influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market competition, brand reputation, and perceived value.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Auto Tool Changer Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC auto tool changers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk orders often lead to discounts, as suppliers can spread fixed costs over a larger number of units. Understanding MOQs is essential for negotiating better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom tool changers tailored to specific applications or machinery may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that comply with international standards or certifications, such as ISO, may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence costs. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and service may charge more but offer better support and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can affect pricing. Buyers should be aware of who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs clearance to calculate the total cost accurately.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost Efficiency?
B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can employ several strategies to negotiate better prices:
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the market rates for CNC auto tool changers can empower buyers during negotiations. This knowledge helps in identifying reasonable pricing and potential suppliers.
-
Leverage Volume Purchases: If possible, consolidate orders to meet or exceed MOQs, thus gaining leverage for discounts. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate prices for larger orders.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs. A higher upfront investment in quality may lead to lower TCO over time.
-
Be Open to Alternative Suppliers: Engaging with multiple suppliers can create competitive tension, leading to better pricing and terms. This is particularly effective in regions with emerging markets.
-
Clarify Terms and Conditions: Ensure all costs associated with shipping, customs, and delivery are transparent. This avoids surprises that can inflate the total cost post-purchase.
What Should International Buyers Consider in Their Sourcing Strategy?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances when sourcing CNC auto tool changers:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can impact pricing significantly. Buyers should factor in potential fluctuations when budgeting for purchases.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Understanding local regulations regarding import duties can help in accurately calculating the total cost. This is particularly relevant for buyers in Africa and South America, where tariffs can vary widely.
-
Local Support and Service: Ensure that the supplier can provide after-sales support and service in the buyer’s region. This is crucial for maintaining equipment efficiency and minimizing downtime.
-
Cultural Considerations: Building relationships with suppliers and understanding local business practices can enhance negotiation outcomes and facilitate smoother transactions.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific product configurations. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc auto tool changer With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to CNC Auto Tool Changers
In the realm of CNC machining, the automatic tool changer (ATC) is a pivotal innovation that enhances productivity by minimizing downtime during tool changes. However, various alternatives exist, each presenting unique benefits and challenges. This analysis will compare the CNC auto tool changer with two viable alternatives: manual tool changers and semi-automated tool changers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Cnc Auto Tool Changer | Manual Tool Changer | Semi-Automated Tool Changer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, continuous operation | Moderate precision, frequent interruptions | Good precision, moderate interruptions |
| Cost | Higher initial investment (e.g., $3,700) | Lower upfront cost, no additional equipment needed | Moderate cost, often between manual and full ATC |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires integration with CNC systems | Simple installation, no special setup | Moderate complexity, may require some adjustments |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for reliability | Minimal maintenance | Moderate maintenance, depends on the system |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production, complex operations | Low-volume, simple machining tasks | Medium-volume operations needing flexibility |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Manual Tool Changer
Manual tool changers are the simplest form of tool changing, where operators physically replace tools as needed. This method is cost-effective, as it does not require specialized equipment or complex integration. However, it can lead to increased downtime and potential errors during tool changes, which can affect overall productivity. Manual changers are best suited for small workshops or businesses that handle low-volume production or projects that do not require rapid tool changes.
Semi-Automated Tool Changer
Semi-automated tool changers bridge the gap between manual and fully automated systems. They often involve a simple mechanism that allows for quicker tool changes with some degree of automation. While they are typically more expensive than manual changers, they still offer a lower cost option compared to full ATC systems. These systems provide improved efficiency and can be beneficial for medium-volume operations that require a balance of speed and cost. However, they may still necessitate operator intervention, leading to potential interruptions in workflow.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your CNC Needs
When selecting between a CNC auto tool changer and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, including production volume, budget constraints, and the complexity of machining tasks. For businesses engaged in high-volume production with intricate designs, investing in a CNC auto tool changer can significantly enhance efficiency and accuracy. Conversely, smaller operations or those with less demanding machining needs may find manual or semi-automated tool changers to be more appropriate, offering adequate performance without the higher costs associated with full automation. Ultimately, the choice should align with the company’s strategic goals and operational capabilities, ensuring maximum return on investment and productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc auto tool changer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Auto Tool Changers?
CNC auto tool changers (ATCs) are essential components in modern machining processes, enhancing efficiency and precision. Understanding their technical properties is vital for B2B buyers looking to invest in these systems.
1. Material Grade
The material used in the construction of an ATC significantly influences its durability and performance. Common materials include high-grade aluminum and stainless steel, which resist corrosion and wear. For buyers, selecting a tool changer made from robust materials ensures longevity and reduces maintenance costs, providing better ROI.
2. Tool Capacity
Tool capacity refers to the number of tools that an ATC can hold and manage during operations. Systems typically range from 5 to 10 tools, with some advanced models accommodating more. Higher tool capacity allows for greater versatility in machining operations, enabling manufacturers to switch between different tasks without manual intervention. This flexibility can lead to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
3. Precision and Tolerance
Precision in tool change operations is measured in microns, affecting the overall accuracy of the machining process. Tolerance levels should be minimal to ensure that tools are correctly positioned each time they are changed. For businesses, investing in ATCs with high precision minimizes errors in production, thereby enhancing product quality and reducing waste.
4. Drive Mechanism
The drive mechanism can be pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric, each offering distinct advantages. Pneumatic systems are known for their speed and efficiency, while hydraulic systems provide greater force for heavy tools. Electric drive systems are quieter and require less maintenance. Buyers must assess the specific needs of their machining processes to select the most appropriate drive mechanism, balancing speed, force, and operational costs.
5. Interface Compatibility
ATCs must be compatible with existing CNC controllers to function effectively. This compatibility includes communication protocols and power requirements. Buyers should verify that the ATC integrates seamlessly with their current machinery to avoid costly upgrades or modifications, ensuring a smooth operational workflow.
6. Safety Features
Safety is paramount in CNC operations. ATCs should include emergency stop switches and fail-safes to prevent accidents during tool changes. Understanding these safety features is crucial for businesses to protect their workforce and machinery, as well as to comply with industry regulations.
Which Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know for CNC Auto Tool Changers?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and decision-making in B2B transactions involving CNC auto tool changers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces components or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CNC ATCs, buyers should consider OEMs for reliable parts and systems, ensuring that they source quality components that fit their machines.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers as it affects inventory management and initial investment. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to avoid excess inventory costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It specifies the product requirements, quantities, and delivery expectations. Submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping goods. Understanding these terms helps buyers clarify shipping costs, insurance, and risks associated with transportation, ensuring that they are adequately prepared for international transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. For CNC ATCs, understanding lead times is essential for production planning. Buyers should factor in lead times when scheduling their manufacturing processes to avoid disruptions.
6. Calibration
Calibration involves adjusting the ATC to ensure accurate tool positioning and performance. Regular calibration is necessary for maintaining precision in machining. Buyers should prioritize systems that offer easy calibration procedures to reduce downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when investing in CNC auto tool changers, ultimately enhancing their production capabilities and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc auto tool changer Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the CNC Auto Tool Changer Sector?
The CNC auto tool changer (ATC) sector is witnessing a surge in demand driven by several global factors. The push for automation across manufacturing industries is paramount, as businesses seek to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. This trend is particularly prominent in developing regions such as Africa and South America, where manufacturers are increasingly investing in advanced technologies to compete in global markets. In Europe, particularly Germany, the focus is on precision engineering and integrating Industry 4.0 technologies, making ATCs a vital component for achieving efficiency and quality in production processes.
Emerging technologies, including IoT integration and AI-driven analytics, are shaping sourcing trends for CNC ATC systems. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for solutions that offer real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities, which can drastically reduce downtime. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms has made it easier for international buyers to source these components from global suppliers, providing access to a wider range of products and competitive pricing.
Furthermore, customization is becoming a key differentiator in the CNC ATC market. Manufacturers are now offering modular systems that allow for easy upgrades and integration with existing CNC machinery, catering to the specific needs of small workshops and large-scale production facilities alike. This trend reflects the growing demand for flexibility in manufacturing processes, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer preferences.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the CNC Auto Tool Changer Market?
Sustainability has become a critical concern in the CNC auto tool changer sector, as manufacturers and buyers alike recognize the environmental impacts of their sourcing decisions. The production of ATC systems often involves materials and processes that can contribute to carbon footprints, making it imperative for companies to prioritize eco-friendly practices. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through the use of recycled materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and reduced waste generation.
Ethical sourcing has gained traction, particularly in regions like Europe, where regulations and consumer expectations around corporate responsibility are stringent. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can provide transparency in their supply chains, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and that labor practices meet ethical standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade practices are becoming essential criteria for procurement decisions.
Moreover, the adoption of “green” technologies in CNC ATC systems, such as energy-efficient motors and materials that minimize environmental impact, is influencing purchasing decisions. Companies that invest in sustainable practices not only enhance their brand reputation but also position themselves favorably in a market where consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context of the CNC Auto Tool Changer Development?
The evolution of CNC auto tool changers can be traced back to the early days of computer numerical control technology in the 1960s and 1970s. Initially, CNC machines operated with manual tool changes, which limited efficiency and productivity. The introduction of ATCs revolutionized the manufacturing landscape by automating the tool change process, significantly reducing downtime and improving machining accuracy.
Over the decades, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated ATC systems, including those capable of handling multiple tools and supporting various machining operations. The integration of automation and robotics has further enhanced the capabilities of CNC ATCs, making them indispensable for modern manufacturing processes. Today, with the advent of smart technologies and Industry 4.0, the CNC ATC market continues to evolve, focusing on enhanced performance, connectivity, and customization options that cater to the diverse needs of B2B buyers worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc auto tool changer
-
1. How can I ensure compatibility between the CNC auto tool changer and my existing equipment?
To guarantee compatibility, first, check the specifications of your CNC machine, including its controller type and available power supply. Most manufacturers provide detailed compatibility lists for their auto tool changers. It’s advisable to consult with your supplier or manufacturer regarding specific models and configurations. Additionally, consider reaching out for technical support to discuss your setup and confirm that all components will work seamlessly together. -
2. What factors should I consider when selecting a CNC auto tool changer?
When choosing a CNC auto tool changer, evaluate several key factors: the number of tools it can hold, the type of spindle required (air or water-cooled), and the overall automation level. Assess the quality of materials used, ease of installation, and the manufacturer’s reputation for reliability and support. Ensure that the tool changer fits your machining needs, such as the types of materials you will be working with and the precision required for your operations. -
3. What are the typical payment terms for purchasing CNC auto tool changers in international trade?
Payment terms can vary by supplier but often include options such as a deposit followed by payment upon shipping or delivery. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or even letters of credit for larger orders. It is crucial to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfer, credit card) and to understand any currency exchange implications. Discussing payment terms upfront can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smoother transaction. -
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC auto tool changers?
Minimum order quantities can differ significantly among suppliers. Some manufacturers might have MOQs of one unit for standard products, while others may require larger quantities for custom solutions. It’s essential to inquire about MOQs before placing an order, as this can impact your initial investment. If you’re a smaller operation, consider discussing potential exceptions or options for combining orders to meet MOQ requirements. -
5. How can I vet suppliers when sourcing CNC auto tool changers internationally?
Vetting suppliers involves several steps: researching their business history, checking reviews and testimonials from other customers, and verifying their certifications and compliance with international standards. Request references and consider visiting their facilities if feasible. Additionally, assess their responsiveness to inquiries and willingness to provide technical support. Engaging in discussions about their manufacturing processes can also give insight into their quality assurance practices. -
6. What are the logistics considerations when importing CNC auto tool changers?
Logistics considerations include understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or taxes applicable in your country. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with importing machinery to handle documentation and ensure compliance with local laws. Assess shipping costs and lead times to plan your production schedules effectively. It’s also wise to have a contingency plan for any unforeseen delays during transit. -
7. How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for CNC auto tool changers?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and test results from the manufacturer. Many reputable suppliers provide documentation of their QA processes, including bench tests and performance metrics. Consider sourcing from manufacturers that adhere to international quality standards like ISO 9001. Implementing a robust inspection process upon delivery can also help identify any issues before integrating the tool changer into your operations. -
8. Can CNC auto tool changers be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for CNC auto tool changers to meet specific application requirements. Customizations may include the number of tool holders, spindle types, or integration with existing machinery. It’s essential to communicate your specific needs clearly and collaborate with the supplier during the design phase. Be prepared to discuss potential lead times and additional costs associated with custom orders.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Cnc Auto Tool Changer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Affordable Automatic Tool Changer Options
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Affordable Automatic Tool Changer (ATC) options discussed in the Reddit thread include a mechanical ATC priced between $500 to $600, which does not require compressed air. Users mention the RapidChange ATC, which is compatible with non-ATC spindles and integrates with FluidNC, Mach3, and UCCNC software. Other options include small tool changers for Kress type spindles around $500, with additional …
2. PWN CNC – ATC Solutions for Enhanced Productivity
Domain: pwncnc.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: ATC (Automatic Tool Changer) for CNC machines, designed to enhance productivity and efficiency. Features include quick tool changes, compatibility with various CNC models, and robust construction for durability. Ideal for high-volume production environments.
3. ShopBot – Desktop MAX ATC CNC
Domain: shopbottools.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Product Name: ShopBot Desktop MAX ATC CNC
Starting Price: $19,694
Features:
– 1HP Automatic tool change spindle with pneumatically actuated draw bar
– 7 position tool bar with 7 ISO20 tool holders compatible with ER20 collets (up to 1/2″ shank)
– Requires compressed air (4 scfm at 90 psi recommended)
– Solid machined aluminum frame with pinned/bolted joints
– Aluminum T-slot and Vacuum deck optio…
4. Tormach – Automatic Tool Changers
Domain: tormach.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘8-Pocket Automatic Tool Changer for PCNC 440’, ‘price’: ‘$3,995.00’, ‘part_number’: ‘PN: 35900’}, {‘name’: ’12-Pocket Automatic Tool Changer for the 1100M’, ‘price’: ‘$5,995.00’, ‘part_number’: ‘PN: 38400’}, {‘name’: ’10-Pocket Automatic Tool Changer for the 770M’, ‘price’: ‘$5,995.00’, ‘part_number’: ‘PN: 38401’}, {‘name’: ’10-Pocket Automatic Tool Changer for the 770MX (BT30)’, ‘price…
5. STEPCRAFT – Automatic Tool Changer
Domain: toolstoday.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Automatic Tool Changer for STEPCRAFT MM-1000 Spindle\n- Brand: STEPCRAFT\n- SKU: #20981\n- Price: $899.00\n- Ships direct from manufacturer; shipping fees may apply\n- Coupon codes are not applicable for this item\n- Overview: Automates tool exchange, reducing manual effort. Parameters defined in machine control software.\n- Magazine capacity: Holds up to 6 tools (extendable to 12)\n- Includes: To…
6. Onefinity – CNC Machine Specifications
Domain: forum.onefinitycnc.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Desired machine specifications include: 2.2 kW liquid cooled spindle, ability to hold 4-5 tools, working area of 48×32 inches (preferably 48×48). Additional requirements for upgrade: spindle mount, potential need for Z-20 Heavy duty slider, new controller (considering Masso G3), possible addition of limit switches, replacement of motors, and all associated tool changer gear. Estimated costs for a …
7. STEPCRAFT – Automatic Tool Changers
Domain: shop.stepcraft-systems.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: 1. Automatic Tool Changer for AMB-1400 FME-P DI: Price range 569,00 € – 698,00 €, Delivery time: 3 – 4 Days (DE – int. shipments may differ)
2. Automatic Tool Changer for STEPCRAFT MM-1000 / KRESS / AMB: Price range 539,00 € – 668,00 €, Delivery time: 3 – 4 Days (DE – int. shipments may differ)
3. Automatic Tool Changer HF Spindle: Price range 489,00 € – 618,00 €, Delivery time: 3 – 4 Days (DE…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc auto tool changer
The integration of CNC automatic tool changers (ATCs) into manufacturing processes offers substantial advantages for businesses seeking efficiency and precision. By adopting ATCs, companies can significantly reduce downtime, enhance production speed, and ensure consistent quality in their outputs. The strategic sourcing of these systems not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also enables businesses to leverage technological advancements that improve operational capabilities.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in high-quality ATC solutions is essential for staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market. When sourcing, consider factors such as compatibility, ease of integration, and after-sales support to maximize your investment.
Looking ahead, the global demand for automated solutions is poised to grow, making now the perfect time to explore partnerships with reliable suppliers. Engage with manufacturers that provide robust support and customization options to align with your specific operational needs. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, you position your business for sustained growth and innovation in the CNC landscape. Embrace the future of manufacturing—start your journey toward operational excellence today.