Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc aircraft
In the ever-evolving landscape of aviation technology, sourcing CNC aircraft presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the demand for high-precision manufacturing and advanced aircraft technology escalating, businesses must navigate a complex web of suppliers, regulations, and technological specifications to make informed purchasing decisions. This guide aims to demystify the global market for CNC aircraft, providing a comprehensive overview of the various types available, their applications in diverse industries, and critical insights into supplier vetting and cost considerations.
By equipping international buyers with actionable knowledge, this guide empowers you to confidently engage with suppliers, ensuring that you select the right CNC aircraft tailored to your operational needs. From understanding the intricacies of CNC machining for aerospace applications to evaluating the benefits of advanced communication technologies integrated into modern aircraft, our resource is designed to streamline your procurement process. Whether you’re looking to enhance aerial surveillance capabilities or optimize your fleet’s performance, this guide will serve as your essential toolkit in navigating the global market landscape effectively.
Understanding cnc aircraft Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-Wing Aircraft | Rigid wings, typically faster, longer range | Cargo transport, aerial surveillance | Pros: Greater speed and range; Cons: Higher operational costs. |
| Rotary-Wing Aircraft | Rotor blades for lift, versatile in operations | Search and rescue, law enforcement | Pros: Excellent maneuverability; Cons: Limited range and speed. |
| Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) | Remote-controlled or autonomous, often smaller in size | Agriculture, mapping, surveillance | Pros: Cost-effective, flexible; Cons: Regulatory challenges. |
| Light Sport Aircraft | Simplified design, lower weight, often two-seater | Training, recreational flying | Pros: Affordable and accessible; Cons: Limited payload capacity. |
| Business Jets | Luxury interiors, high speed, and range | Corporate transport, private charters | Pros: Time-saving, comfort; Cons: High acquisition and operating costs. |
What are the Characteristics of Fixed-Wing Aircraft in B2B Operations?
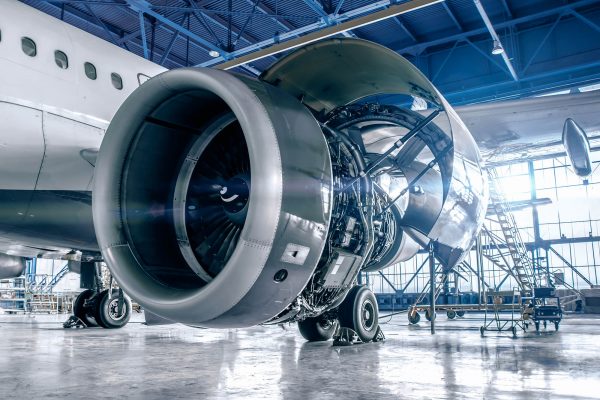
Fixed-wing aircraft are characterized by their rigid wings, which allow for faster flight speeds and longer ranges compared to rotary-wing options. These aircraft are ideal for B2B applications such as cargo transport and aerial surveillance, making them a preferred choice for logistics companies and government agencies. When considering fixed-wing aircraft, buyers should evaluate operational costs, maintenance requirements, and the specific range needed for their business operations.
How Do Rotary-Wing Aircraft Serve Diverse Business Needs?
Rotary-wing aircraft, commonly known as helicopters, are designed with rotor blades that provide lift, allowing for vertical takeoff and landing. This versatility is particularly beneficial for applications such as search and rescue missions and law enforcement operations. Buyers interested in rotary-wing aircraft should focus on factors like payload capacity, operational range, and maintenance support, as these will significantly impact their operational efficiency.
Why Choose Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) for Business Applications?
UAVs, or drones, are remote-controlled or autonomous flying devices that have gained popularity in various industries, including agriculture and mapping. Their ability to perform tasks without a pilot on board makes them cost-effective and flexible for businesses. However, buyers must navigate regulatory challenges and ensure compliance with local aviation laws when integrating UAVs into their operations.
What Makes Light Sport Aircraft an Attractive Option for Training?
Light sport aircraft are designed for simplicity and ease of use, often accommodating two passengers. These aircraft are particularly well-suited for training purposes and recreational flying, offering an affordable entry point for new pilots. When purchasing light sport aircraft, businesses should consider factors such as training programs, insurance costs, and the aircraft’s operational capabilities.
How Do Business Jets Enhance Corporate Travel Efficiency?
Business jets are distinguished by their luxurious interiors and high-speed capabilities, catering to corporate travel and private charters. They provide significant time savings for businesses needing to travel long distances quickly. However, potential buyers must weigh the high acquisition and operating costs against the benefits of increased productivity and comfort when considering a business jet for their travel needs.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc aircraft
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Aircraft | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace Manufacturing | Precision Component Fabrication | High accuracy and repeatability in producing complex parts | Certifications (e.g., AS9100), material specifications, lead time |
| Law Enforcement and Security | Aerial Surveillance and Reconnaissance | Enhanced situational awareness and real-time data collection | Integration with existing systems, training for operators |
| Emergency Services | Medical Evacuation and Transport | Rapid response capabilities and improved patient outcomes | Compliance with aviation regulations, reliability of equipment |
| Agricultural Aviation | Crop Monitoring and Aerial Spraying | Increased efficiency in farming operations and yield management | Cost of operation, maintenance support, and local regulations |
| Tourism and Charter Services | Scenic Flights and Private Charters | Enhanced customer experience and operational flexibility | Customization options, safety records, and service availability |
How is CNC Aircraft Used in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In aerospace manufacturing, CNC aircraft are utilized for precision component fabrication, producing everything from structural components to complex assemblies. This application addresses the industry’s need for high accuracy and repeatability, essential for ensuring safety and performance standards. International buyers must consider certifications like AS9100, material specifications, and lead times to meet their production schedules and compliance requirements.
What Role Does CNC Aircraft Play in Law Enforcement and Security?
CNC aircraft are critical for aerial surveillance and reconnaissance operations, providing law enforcement and security agencies with advanced capabilities for real-time data collection and enhanced situational awareness. This application solves challenges related to information gathering in difficult terrains or during large-scale events. Buyers in this sector should focus on the integration of CNC aircraft with existing systems and the training necessary for operators to utilize these technologies effectively.
How is CNC Aircraft Transforming Emergency Services?
In emergency services, CNC aircraft are deployed for medical evacuation and transport, significantly improving response times in critical situations. This application ensures rapid patient transport, which is vital for improving outcomes in emergencies. Buyers should prioritize compliance with aviation regulations, the reliability of equipment, and operational support to ensure that these aircraft can perform effectively under pressure.
What Benefits Do CNC Aircraft Offer in Agricultural Aviation?
CNC aircraft are increasingly used in agricultural aviation for crop monitoring and aerial spraying, enabling farmers to manage their fields more efficiently. This application enhances the precision of farming operations, leading to better yield management and reduced waste. Buyers in this sector should evaluate the cost of operation, ongoing maintenance support, and adherence to local regulations to maximize their investment.
How Do CNC Aircraft Enhance Tourism and Charter Services?
In the tourism sector, CNC aircraft are leveraged for scenic flights and private charters, providing unique experiences for customers and operational flexibility for service providers. This application allows businesses to cater to niche markets and enhance customer satisfaction. Key considerations for buyers include customization options, safety records, and the availability of services to ensure a competitive edge in the market.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc aircraft’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Regulatory Compliance for CNC Aircraft
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter significant challenges in ensuring compliance with various regulatory frameworks when procuring CNC aircraft. Different countries, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, have distinct aviation regulations and standards. This complexity can lead to delays in procurement processes, unexpected costs, and potential legal issues if compliance is not met. Buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by the need to understand not only local laws but also international standards, leading to a sense of uncertainty and frustration.
The Solution: To navigate this intricate landscape, buyers should engage with experienced legal and regulatory consultants who specialize in aviation compliance. Conducting a thorough audit of the specific regulations applicable to the regions where the aircraft will operate is essential. Buyers should also work closely with manufacturers who have a proven track record of compliance with both local and international standards. It’s beneficial to create a comprehensive checklist of regulatory requirements and ensure that all aircraft specifications align with these standards. Additionally, establishing a relationship with local aviation authorities can provide insights and updates on changing regulations, thus facilitating smoother compliance.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Operational Efficiency in CNC Aircraft Utilization
The Problem: After purchasing CNC aircraft, many B2B buyers face operational inefficiencies due to a lack of adequate training for their personnel. This can result in suboptimal use of the aircraft’s capabilities, leading to increased operational costs and reduced effectiveness in fulfilling missions. Companies may struggle to maximize the aircraft’s potential, which can hinder their competitive edge in the market.
The Solution: Investing in comprehensive training programs for all personnel involved in the operation and maintenance of CNC aircraft is crucial. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that offer robust training solutions, including hands-on workshops, online courses, and ongoing support. Implementing a structured training schedule that covers all operational aspects will empower staff to fully leverage the capabilities of the aircraft. Additionally, incorporating simulation-based training can provide practical experience without the risks associated with live operations. Regular assessments and refresher courses should also be part of the training strategy to ensure that skills are maintained and updated.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Supply Chain Disruptions for CNC Aircraft Parts
The Problem: Supply chain disruptions can severely impact the availability of essential parts for CNC aircraft, leading to extended downtimes and delayed operations. B2B buyers, especially in regions with less established supply chains, may struggle to source parts quickly, resulting in increased maintenance costs and potential loss of revenue. This unpredictability can undermine trust with clients who rely on timely operations.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, buyers should adopt a proactive sourcing strategy that includes diversifying their supplier base. Establishing relationships with multiple vendors for critical components can reduce dependency on a single source and enhance resilience against disruptions. Additionally, implementing inventory management software can help track parts availability and forecast needs based on operational demands. Buyers should also consider local suppliers to shorten lead times and reduce shipping costs. Engaging in long-term contracts with suppliers for essential parts can secure better pricing and ensure priority during shortages. Regularly reviewing and updating supplier agreements can further safeguard against supply chain issues.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc aircraft
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in CNC Aircraft Manufacturing?
Aluminum is a widely used material in the aerospace industry due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 150°C and can withstand moderate pressure, making it suitable for various aircraft components. Its low density contributes to overall fuel efficiency, a critical factor in aviation economics.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum in CNC Aircraft Applications
The advantages of aluminum include its lightweight nature, which enhances fuel efficiency, and its ease of machining, which can lower manufacturing costs. However, aluminum is not as strong as some other materials, such as titanium, and may require additional treatments to improve its fatigue resistance. This can complicate manufacturing processes and increase costs.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions may vary, aluminum’s corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial. International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM and JIS, which govern the quality and safety of aluminum components in aviation. Understanding local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact is also crucial.
How Does Titanium Enhance Performance in CNC Aircraft?
Titanium is renowned for its high strength and lightweight properties, with temperature ratings exceeding 400°C. It is highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for components exposed to harsh environments. Its ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions makes it a preferred choice for high-performance aircraft.
Pros and Cons of Titanium in CNC Aircraft Applications
The primary advantage of titanium is its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, which significantly improves aircraft performance. However, titanium is more expensive than aluminum and is more challenging to machine, leading to higher manufacturing costs. This complexity can also extend lead times for production, which may be a critical factor for international buyers.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, where high-performance aircraft are common, titanium’s properties align well with industry demands. Compliance with international standards, such as ASTM and DIN, is essential for ensuring safety and reliability. Additionally, understanding the local market’s willingness to invest in higher-cost materials is crucial for procurement strategies.
What Role Does Composite Materials Play in CNC Aircraft?
Composite materials, particularly carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP), are increasingly used in aircraft manufacturing due to their high strength and low weight. These materials can withstand temperatures up to 200°C and offer excellent fatigue resistance, making them suitable for various structural applications.
Pros and Cons of Composite Materials in CNC Aircraft Applications
The main advantage of composites is their superior strength-to-weight ratio and design flexibility, allowing for innovative shapes and structures. However, they can be more expensive than traditional materials and require specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate production. Additionally, their repair and recycling can pose challenges, impacting lifecycle costs.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Europe, where sustainability is a growing concern, the environmental impact of composites should be a consideration. Compliance with standards such as JIS and ASTM is necessary to ensure quality and safety. Buyers should also assess local capabilities for composite manufacturing and repair to avoid potential supply chain issues.
What Are the Benefits of Steel in CNC Aircraft Manufacturing?
Steel, particularly high-strength steel alloys, is used in specific applications within aircraft due to its durability and resistance to deformation. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for critical structural components.
Pros and Cons of Steel in CNC Aircraft Applications
Steel’s primary advantage is its strength, which allows for the construction of robust components. However, it is significantly heavier than aluminum and composites, which can negatively impact fuel efficiency. The complexity of machining steel can also lead to higher manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
In regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure may be less developed, the availability of steel can be an advantage. Buyers should consider the local supply chain and compliance with international standards to ensure that the steel used meets safety and performance requirements.
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc aircraft | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Airframes, wing structures | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | Lower strength compared to titanium | Medium |
| Titanium | Engine components, fasteners | High strength-to-weight ratio | High cost, difficult to machine | High |
| Composite | Fuselage, wing skins | Superior design flexibility, lightweight | Expensive, complex repair processes | High |
| Steel | Landing gear, structural supports | Exceptional strength | Heavier than alternatives, higher machining costs | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc aircraft
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for CNC Aircraft?
The manufacturing of CNC aircraft involves several critical stages that ensure precision, safety, and performance. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specific techniques tailored to the unique requirements of the aerospace industry.
How Does Material Preparation Impact CNC Aircraft Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in the CNC aircraft manufacturing process. It involves selecting high-quality materials, such as aluminum alloys, titanium, and composite materials, which are essential for reducing weight while maintaining strength. The materials undergo thorough inspection for defects and impurities, ensuring they meet the necessary specifications.
Once the materials are selected, they are cut into manageable sizes using CNC cutting tools. This process involves precise measurements to minimize waste and ensure that the parts fit together seamlessly during assembly. Advanced technologies, such as laser cutting and water jet cutting, may be employed for enhanced accuracy.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in CNC Aircraft Production?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into specific components. Techniques such as CNC machining, stamping, and forging are commonly utilized. CNC machining, in particular, is a hallmark of modern aircraft manufacturing, allowing for intricate designs and high tolerances.
During this stage, components are machined to exact specifications using computer-controlled tools. This not only ensures uniformity but also enables manufacturers to produce complex geometries that would be challenging with traditional methods. The use of multi-axis CNC machines enhances flexibility and precision, allowing for the production of parts that meet stringent aerospace standards.
How Is Assembly Conducted in the CNC Aircraft Manufacturing Process?
The assembly stage is where all the individual components come together to form the aircraft structure. This process often involves a combination of manual and automated techniques. Skilled technicians are essential for tasks that require a high degree of precision, such as aligning parts and ensuring that fasteners are correctly torqued.
In addition, manufacturers often utilize advanced assembly tools, including robotic arms and automated guided vehicles, to enhance efficiency and reduce the risk of human error. Quality control checks are integrated into the assembly process to verify that components meet specifications before moving on to the finishing stage.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Enhance CNC Aircraft Components?
Finishing is the final stage of the manufacturing process, where components are treated to enhance durability and performance. Techniques such as anodizing, painting, and coating are commonly used to protect against corrosion and wear. These processes not only improve the aesthetic appeal of the aircraft but also contribute to its longevity.
Surface treatments are essential for maintaining the integrity of the aircraft in harsh environments. For instance, anodizing aluminum parts creates a protective oxide layer that improves resistance to corrosion, while specialized coatings can enhance thermal and chemical resistance.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in CNC Aircraft Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of CNC aircraft manufacturing, ensuring that all products meet stringent safety and performance standards. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these processes.
What International Standards Are Relevant to CNC Aircraft Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are pivotal in establishing a quality management system. This standard provides a framework for consistent quality and customer satisfaction across manufacturing processes. Additionally, aerospace-specific standards such as AS9100 outline requirements for quality management systems in the aerospace sector, focusing on safety and reliability.
Other certifications may include CE marking, which indicates compliance with European safety standards, and API specifications for aircraft parts. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers hold these certifications as they reflect a commitment to quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Aircraft Manufacturing?
Quality control is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with several checkpoints established to ensure compliance with specifications. The main quality control checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components upon delivery to verify their quality before they enter the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the production process. This includes checking dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes at various stages of production.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the aircraft components are fully assembled, a comprehensive inspection is carried out to ensure that all specifications are met before delivery. This may include functional testing and performance evaluations.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in CNC Aircraft Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality of CNC aircraft components. Common methods include:
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, and magnetic particle inspection are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the components.
-
Destructive Testing: In some cases, components may undergo destructive testing to evaluate their strength and durability. This involves subjecting parts to extreme conditions until they fail, providing valuable data on material performance.
-
Functional Testing: This testing assesses the performance of the assembled aircraft, ensuring that it meets operational specifications under realistic conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is crucial. Buyers can take several actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Buyers should request access to audit reports and findings.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including certifications, inspection reports, and compliance records.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices and ensure compliance with industry standards.
-
Understand Regional Nuances: Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that their suppliers comply with them.
-
Establish Strong Communication: Building strong relationships with suppliers can foster transparency. Regular communication regarding quality issues and improvements can help buyers stay informed about their suppliers’ practices.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing CNC aircraft components, ensuring they partner with suppliers who prioritize quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc aircraft’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in the procurement of CNC aircraft. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, understanding the complexities of sourcing high-quality CNC aircraft is essential for operational success. This checklist will help you navigate the critical steps to ensure a seamless procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by outlining the specific technical requirements for the CNC aircraft you need. This includes size, weight capacity, engine type, and intended use (e.g., surveillance, cargo transport). Clear specifications will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure you receive suitable options.
- Consider regulatory compliance: Different regions may have specific aviation regulations that your aircraft must meet.
- Identify any customization needs: Determine if you require modifications to existing models to fit your operational requirements.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of CNC aircraft. Look for manufacturers with a solid reputation in the industry, particularly those with experience in your region.
- Check online platforms: Utilize resources like industry forums and trade publications to discover reputable suppliers.
- Attend aviation trade shows: Events provide opportunities to meet suppliers and assess their offerings firsthand.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, ensure that potential suppliers hold the necessary certifications and licenses. This includes compliance with international aviation standards such as ISO 9001 or AS9100.
- Request documentation: Ask for copies of their certifications and any relevant audit reports.
- Verify through third-party organizations: Consider contacting certifying bodies to confirm the validity of the supplier’s claims.
Step 4: Assess Manufacturing Capabilities
Understanding a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities is crucial for ensuring quality and timely delivery. Evaluate their production processes, technology, and capacity to handle your order volume.
- Inquire about quality control measures: Ask how they maintain quality throughout the production process.
- Consider lead times: Ensure they can meet your timeline without compromising quality.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, request samples or prototypes of the CNC aircraft. This step allows you to assess the quality and functionality of the aircraft before making a larger investment.
- Evaluate performance: Test the aircraft under conditions similar to your operational needs.
- Examine craftsmanship: Look for precision in machining and assembly, which are critical in aviation applications.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations to finalize the terms of your purchase, including pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Be clear about your budget constraints and seek to establish a mutually beneficial agreement.
- Consider total cost of ownership: Factor in maintenance, operational costs, and potential upgrades when evaluating pricing.
- Be open to long-term relationships: Establishing a partnership can lead to better pricing and support in the future.
Step 7: Plan for After-Sales Support and Training
Ensure that the supplier provides comprehensive after-sales support and training. This is vital for maximizing the operational efficiency of the CNC aircraft.
- Evaluate training programs: Assess the quality and extent of training offered to your team.
- Inquire about ongoing support: Understand the availability of technical support and spare parts post-purchase.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing CNC aircraft, ensuring they make informed decisions that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc aircraft Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Aircraft Sourcing?
When considering CNC aircraft sourcing, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost. High-strength alloys and composites, often used in aircraft manufacturing, can be expensive. Buyers should evaluate the material specifications required for their specific aircraft models.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass skilled machinists and technicians required for CNC machining. The complexity of the aircraft parts being produced can increase labor time and, consequently, costs. Labor rates vary significantly by region, impacting total expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient operations can mitigate these costs, but they remain a significant factor in overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific aircraft components can be a substantial upfront investment. Buyers must assess the tooling costs and factor them into their overall budget, especially for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with aviation standards necessitates rigorous QC processes. The costs associated with inspections, testing, and certifications can add to the overall expense.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, including international freight, customs duties, and insurance, can vary widely based on the geographic location of suppliers and buyers. These logistics costs must be factored into the total procurement price.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin, which can vary based on market conditions and competition. Understanding typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect CNC Aircraft Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC aircraft, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to bulk discounts, while smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs. Buyers should evaluate their purchasing strategy to leverage volume pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Highly customized parts typically command higher prices due to the additional time and resources required for production. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Material Selection: The choice of materials not only affects performance but also the cost. Buyers should balance between material quality and budget constraints, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
-
Quality and Certifications: Aircraft components must meet stringent regulatory requirements. Parts that require additional certifications or testing may incur higher costs. Buyers should inquire about certification processes and their associated costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but they often provide greater assurance of compliance and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can impact the overall pricing. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who bears the costs and risks during transport, influencing the final price.
What Buyer Tips Can Optimize CNC Aircraft Sourcing Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in thorough negotiations with suppliers to secure favorable terms. Understanding the cost components can empower buyers to negotiate effectively.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the entire lifecycle cost, including maintenance, operation, and resale value. This comprehensive view can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences due to labor and material costs. Buyers should conduct market research to identify competitive suppliers in various regions.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and priority service. Consider establishing partnerships that may yield discounts or preferential terms.
-
Cost-Effective Logistics: Evaluate shipping options and logistics providers to find the most cost-effective solutions. Consolidating shipments or selecting different Incoterms can lead to significant savings.
Disclaimer
Prices and cost structures are indicative and may vary based on specific project requirements, market fluctuations, and supplier conditions. It is advisable for buyers to conduct detailed due diligence and seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc aircraft With Other Solutions
Exploring Viable Alternatives to CNC Aircraft Solutions
In the realm of aviation technology, businesses often face the challenge of selecting the most appropriate solution for their operational needs. CNC aircraft represent a sophisticated option for aerial surveillance and communications, but it is essential to evaluate other technologies that may fulfill similar roles effectively. This analysis compares CNC aircraft with two notable alternatives: UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) and traditional manned aircraft. Understanding the nuances of each solution allows international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Aircraft | UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) | Traditional Manned Aircraft |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and control | Versatile, adaptable for various missions | Established reliability with robust payload capacity |
| Cost | High initial investment | Generally lower, with fewer operational costs | Higher operational costs due to crew and maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized training | User-friendly, often with extensive support | Complex due to regulations and crew training |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized service | Typically lower maintenance needs | High maintenance due to mechanical complexity |
| Best Use Case | Aerial surveillance and communication | Search and rescue, agriculture, mapping | Passenger and cargo transport, extensive surveillance |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of UAVs as an Alternative to CNC Aircraft?
UAVs, or drones, have gained significant traction in various sectors due to their versatility and lower operational costs. They can be deployed for a wide range of applications, such as agricultural monitoring, search and rescue operations, and environmental assessments. The ease of use associated with many UAVs is a notable advantage, as they often come equipped with user-friendly interfaces and robust support systems. However, UAVs can be limited in terms of payload capacity and flight time, which may not suit all operational requirements, particularly in high-demand situations.
How Do Traditional Manned Aircraft Compare to CNC Aircraft?
Traditional manned aircraft have a long-standing reputation for reliability and extensive operational capabilities. They can carry larger payloads and are often utilized in passenger transport and heavy cargo operations. Their established infrastructure and regulatory frameworks make them a familiar choice for many organizations. However, the costs associated with manned aircraft are significantly higher due to the need for crew members and more complex maintenance protocols. Furthermore, the implementation process can be cumbersome, requiring extensive training and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Select the Right Aviation Solution?
Choosing the right aviation solution hinges on a thorough assessment of operational requirements, budget constraints, and the specific use cases of the technology. For organizations prioritizing precision and advanced communication capabilities, CNC aircraft may be the best fit. Conversely, for those seeking lower costs and flexibility, UAVs could serve their needs effectively. Meanwhile, traditional manned aircraft remain a reliable option for businesses that require substantial payload capacities and established operational frameworks. By carefully weighing these factors, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that align with their unique operational goals and resource capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc aircraft
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Aircraft?
When considering CNC aircraft, understanding critical technical properties is essential for making informed procurement decisions. Below are some key specifications that impact performance, safety, and operational efficiency.
1. Material Grade
The material grade used in CNC aircraft components is paramount. Common materials include aluminum alloys, titanium, and composite materials. These materials are selected based on their strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and fatigue properties. B2B buyers should prioritize high-grade materials to ensure longevity and reliability in harsh operating conditions.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In the aerospace industry, tight tolerances (often within ±0.001 inches) are critical for ensuring that parts fit together correctly and function effectively. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels can help in evaluating supplier capabilities and ensuring that components meet stringent safety and performance standards.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish indicates the texture and quality of a surface after machining. It affects aerodynamics, corrosion resistance, and overall aesthetics. Buyers should consider the required surface finish when sourcing CNC parts, as smoother finishes can reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency, which is vital for operational cost-effectiveness.
4. Weight
The weight of aircraft components is a critical factor that influences performance, fuel efficiency, and payload capacity. CNC machining allows for the creation of lightweight structures without compromising strength. Buyers must evaluate weight specifications to ensure optimal aircraft performance and compliance with operational limits.
5. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes, such as annealing or hardening, enhance the mechanical properties of materials. These processes can improve strength, ductility, and wear resistance. Understanding the heat treatment specifications is crucial for B2B buyers looking for durable and reliable components that can withstand high-stress environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the CNC Aircraft Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother negotiations and clearer communications between buyers and suppliers. Here are several essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end products. In the CNC aircraft industry, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM or a third-party manufacturer can impact quality assurance and warranty considerations. Buyers should prioritize working with reputable OEMs to ensure high standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the aerospace sector, MOQs can significantly influence purchasing decisions, especially for smaller companies. Buyers need to assess their demand and negotiate terms that align with their inventory management practices.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. Crafting a clear RFQ can help buyers receive accurate quotes and streamline the procurement process. It’s essential to include detailed specifications to ensure responses meet expectations.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact overall costs. Buyers must be familiar with relevant Incoterms to avoid unexpected expenses and ensure smooth logistics.
5. CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
CAD refers to software used for creating precise drawings and models of parts before manufacturing. Understanding CAD capabilities is essential for buyers looking to collaborate closely with suppliers on custom designs. It allows for better visualization and iteration of components, enhancing the overall quality of the final product.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their investments in CNC aircraft components yield optimal performance and reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc aircraft Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the CNC Aircraft Sector?
The CNC aircraft sector is experiencing transformative growth driven by several global factors. Increased demand for lightweight and high-precision components in aerospace manufacturing is pushing international B2B buyers to seek advanced CNC machining solutions. Emerging technologies, such as additive manufacturing and Industry 4.0 practices, are redefining production processes, enabling greater customization and efficiency.
In regions like Africa and South America, there’s a notable surge in investment in aviation infrastructure, which is fostering the need for reliable CNC aircraft components. Meanwhile, the Middle East and Europe are witnessing a trend towards the integration of smart technologies in aircraft manufacturing, enhancing operational efficiencies. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who not only provide high-quality products but also demonstrate the ability to innovate and adapt to these rapidly changing market conditions.
Moreover, the emphasis on data-driven decision-making is reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are leveraging analytics to assess supplier performance and material costs, ensuring they make informed choices that align with their operational goals. This data-centric approach is particularly vital for businesses in competitive markets, allowing them to optimize their supply chains and reduce lead times.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the CNC Aircraft Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of strategic sourcing in the CNC aircraft sector. As environmental concerns escalate, the aviation industry is under pressure to minimize its ecological footprint. This has led to a growing emphasis on ethical sourcing practices, where B2B buyers prioritize suppliers who adhere to environmental regulations and demonstrate a commitment to sustainable manufacturing processes.
Materials used in CNC machining are increasingly scrutinized for their environmental impact. Buyers are now seeking ‘green’ certifications for materials, such as recycled aluminum or bio-based composites, which not only reduce waste but also enhance the sustainability profile of their aircraft products. Furthermore, transparency in supply chains is paramount; businesses are expected to have clear visibility into the sourcing of their materials to ensure ethical practices throughout the production lifecycle.
The push for sustainability is not merely a regulatory compliance issue but also a competitive advantage. Companies that embrace eco-friendly practices can attract environmentally-conscious customers and differentiate themselves in the marketplace. As a result, international buyers are increasingly valuing suppliers who can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability through certifications and transparent sourcing practices.
How Has the CNC Aircraft Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the CNC aircraft sector has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in market demand. Initially, CNC machining was primarily focused on producing standard components with limited customization. However, as the aerospace industry grew more competitive, the need for precision and tailored solutions emerged. This led to the adoption of advanced CNC technologies capable of producing intricate designs with high accuracy.
In recent years, the integration of digital technologies has further transformed the landscape. The advent of automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning has streamlined manufacturing processes, enabling faster production cycles and reduced costs. Additionally, the rise of global supply chains has allowed B2B buyers to source CNC components from various regions, enhancing their flexibility and responsiveness to market changes.
Today, the CNC aircraft sector stands at the intersection of innovation and sustainability, with a strong focus on meeting the complex demands of the aviation industry while addressing environmental concerns. This ongoing evolution underscores the importance for international B2B buyers to stay informed about technological trends and sustainable practices that will shape the future of aircraft manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc aircraft
-
How do I ensure the quality of CNC aircraft before purchase?
To ensure the quality of CNC aircraft, conduct thorough supplier vetting by reviewing certifications such as AS9100 or ISO 9001. Request detailed product specifications, quality assurance reports, and conduct factory audits if possible. Establish communication with current clients of the supplier to gather feedback on their experiences. Additionally, consider sourcing samples for evaluation before committing to larger orders, allowing you to assess the craftsmanship and adherence to your specifications firsthand. -
What customization options are available for CNC aircraft?
Customization options for CNC aircraft can vary widely based on the manufacturer. Typically, buyers can request modifications in design, material, and technology features such as avionics and communication systems. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your customization needs without compromising safety and regulatory standards. Document all specifications in detail to avoid misunderstandings during production. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC aircraft?
Minimum order quantities for CNC aircraft can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of aircraft. Some manufacturers may have a MOQ of one unit for custom designs, while others may require orders in batches to optimize production costs. It is essential to clarify these details with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to align your purchasing strategy with their production capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing CNC aircraft internationally?
Payment terms for international CNC aircraft purchases typically include options like letters of credit, advance payments, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may request a deposit upfront, often ranging from 30% to 50%, with the balance due upon completion or delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that protect your interests while ensuring that the supplier has the necessary cash flow to meet production timelines. -
How can I effectively manage logistics for importing CNC aircraft?
Effective logistics management for importing CNC aircraft involves planning transportation routes, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Collaborate with logistics partners who have experience in handling aircraft shipments. Ensure all necessary documentation, such as bills of lading and customs declarations, are prepared in advance. Consider using freight forwarders who specialize in aviation to mitigate risks and streamline the import process, ensuring compliance with local regulations in your destination country. -
What regulatory considerations should I be aware of when purchasing CNC aircraft?
When purchasing CNC aircraft, it is vital to comply with both international aviation regulations and the specific regulations of your country. This includes understanding airworthiness standards, import permits, and any specific requirements set by aviation authorities. Engage with legal and regulatory experts to navigate these requirements effectively, ensuring that the aircraft meets all safety and operational standards before it enters service. -
How do I vet suppliers for CNC aircraft effectively?
To effectively vet suppliers for CNC aircraft, conduct a comprehensive review of their credentials, including certifications, production capabilities, and industry reputation. Request references from previous clients and check for any reviews or complaints. It’s beneficial to visit their facilities if possible, observing their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Establishing a solid relationship with the supplier and clear communication channels is also crucial for long-term collaboration. -
What after-sales support should I expect from CNC aircraft suppliers?
After-sales support is a critical aspect of the procurement process for CNC aircraft. Expect suppliers to offer training for your team on aircraft operation and maintenance, along with access to ongoing technical support. Inquire about warranty terms, spare parts availability, and service agreements for repairs. Establishing clear expectations regarding after-sales support will ensure that you have the necessary resources to maintain operational efficiency and address any issues that may arise post-purchase.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Cnc Aircraft Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CNC Technologies – Custom Aviation Solutions
Domain: cnctechnologies.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: CNC Technologies offers custom aviation technology and wireless communication solutions, including a Mission Suite Design for aerial surveillance with real-time distribution, comprehensive and ongoing training for clients, and 24/7 support from qualified staff in the US and Europe. Their CNC.Live platform provides a secure interface for agencies to access helicopter, fixed wing, and UAV footage fr…
2. Cessna – CNC Aircraft
Domain: seatlink.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This company, Cessna – CNC Aircraft, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. FlightAware – AeroAPI, Firehose & Foresight
Domain: flightaware.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: AeroAPI: Flight data API with on-demand flight status and flight tracking data. FlightAware Firehose: Streaming flight data feed for enterprise integrations with real-time, historical and predictive flight data. FlightAware Foresight: Predictive technology to strengthen customer trust in operations. Rapid Reports: Quickly purchase historical reports delivered via email. Custom Reports: Consultativ…
4. Owens Industries – Precision Aircraft Components
Domain: owensind.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Owens Industries specializes in CNC machining components for the aircraft industry, offering precision aircraft parts manufactured to the highest standards. Key services include 5-axis machining, Wire EDM, CNC lathes, turning, milling, and deburring. The company provides custom components from scratch and replicates specific parts, with micromachining capabilities achieving resolutions up to 0.1 m…
5. HG-Grimme – CNC Machining Centres for Aviation
Domain: hg-grimme.de
Introduction: CNC machining centres for aviation, specifically designed for precise milling of lightweight materials such as aluminum, CFRP, GFRP, and other composite materials. Features include 5-axis CNC milling technology for efficient and economical production, custom-designed CNC machines tailored to specific components and materials, and capabilities for dynamic machining with a gantry design. The machine…
6. Aerostar Manufacturing – Precision CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: aerostarmfg.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Aerostar Manufacturing specializes in CNC production machining, precision CNC machining, machined castings, prototype and low volume CNC machining, machined forgings, sheet metal fabrication, stamping, aluminum extrusions, gear manufacturing, and machined assemblies. They also offer supplemental services including inspection services. Their operations include global manufacturing with locations in…
7. 3DS – CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: 3ds.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: CNC machining is a precision production technique using computer-controlled machines to cut, shape, and form parts from materials like metal, plastic, or wood. It includes processes such as cutting, milling, turning, drilling, grinding, routing, and polishing. Key advantages in the aerospace sector include: precision and accuracy for critical components, efficiency and productivity through automat…
8. CreatingWay – Precision CNC Machining for Aircraft Components
Domain: creatingway.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: CNC machining can create a variety of aircraft components including engine parts, landing gear components, airframe components, and interior components. It is capable of producing complex parts such as turbine blades and impellers that require precise tolerances. The manufacturing process ensures high accuracy, reduces failures and defects, and allows for quick design modifications using CAD softw…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc aircraft
In navigating the complex landscape of CNC aircraft sourcing, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic partnerships that align with their operational needs and mission goals. The integration of advanced CNC technology not only enhances precision and efficiency in aircraft manufacturing but also significantly reduces lead times. Buyers are encouraged to leverage suppliers that offer comprehensive training and robust support systems, ensuring seamless implementation and operation.
Furthermore, a thorough understanding of the global supply chain dynamics is crucial. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider local suppliers who can provide tailored solutions and responsive service. This localized approach can mitigate risks associated with international logistics while promoting sustainable business practices.
As the aerospace industry continues to evolve with technological advancements, the demand for high-quality CNC aircraft solutions will only increase. Buyers are urged to stay informed about emerging trends and innovations that can enhance their operational capabilities. By investing in strategic sourcing now, businesses can position themselves to capitalize on future opportunities and maintain a competitive edge in the market. Embrace this moment to refine your sourcing strategies and connect with partners who can help elevate your aerospace initiatives.