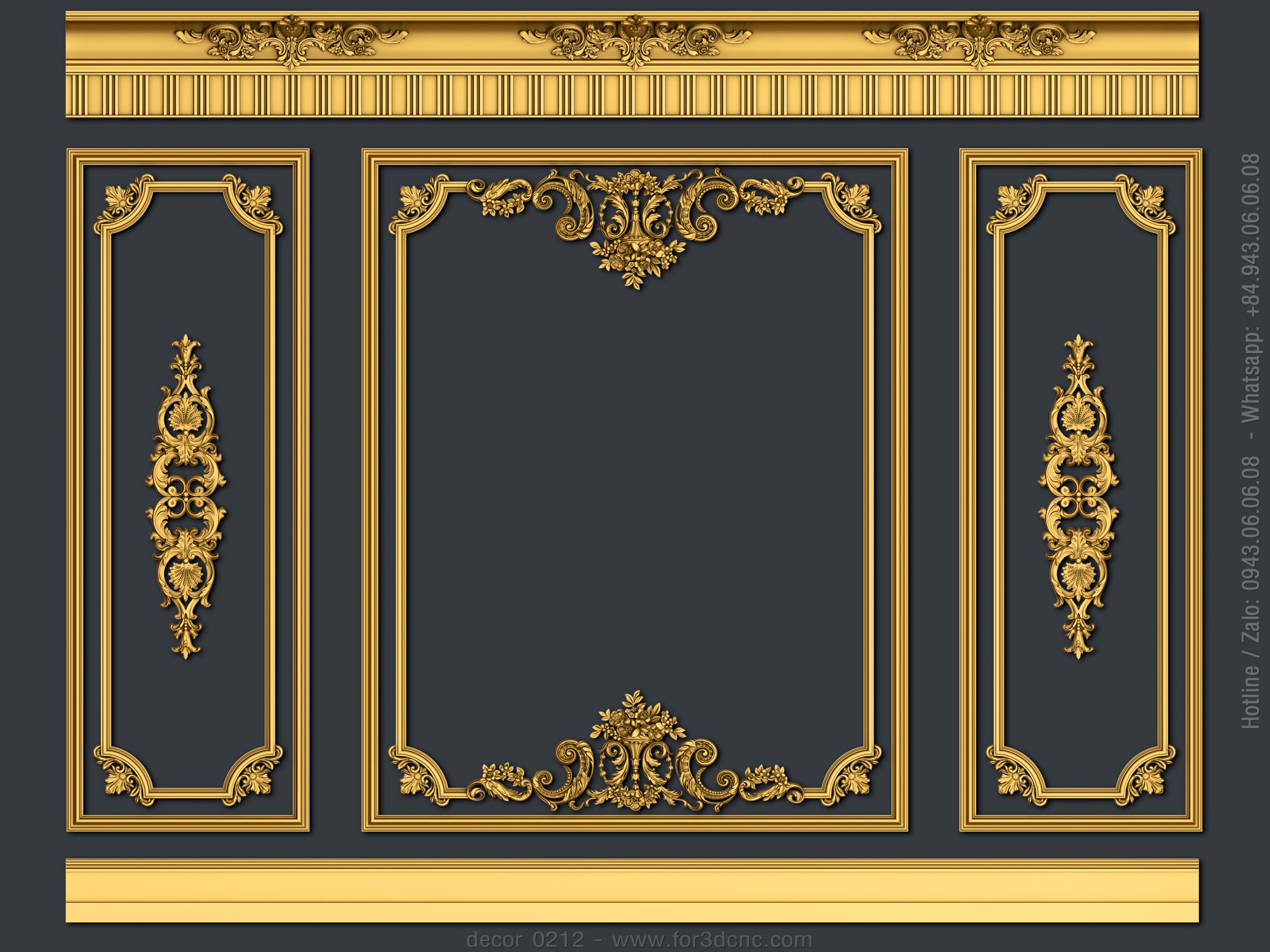
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc 3d files
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality CNC 3D files is crucial for manufacturers and designers looking to enhance production efficiency and innovate product offerings. As international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, you face the challenge of navigating a diverse market filled with varying quality standards, file formats, and supplier reliability. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of acquiring CNC 3D files by providing comprehensive insights into the types of files available, their applications across industries, and best practices for vetting suppliers.
Within these pages, you will discover a detailed exploration of STL and OBJ file formats, among others, and their implications for your CNC projects. We will also delve into the cost factors involved in sourcing these digital assets, helping you identify budget-friendly options without compromising on quality. Furthermore, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions by equipping you with essential criteria for evaluating suppliers, ensuring that you partner with reliable sources that meet your specific needs.
By leveraging the information presented here, you can streamline your procurement process, reduce risks associated with subpar files, and ultimately drive your business forward. Whether you’re looking to create intricate designs or functional components, understanding the global market for CNC 3D files is your first step toward unlocking new opportunities in manufacturing and design.
Understanding cnc 3d files Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| STL | Standard format for 3D models; represents geometry as triangles | Prototyping, custom part manufacturing | Pros: Widely supported, easy to use. Cons: Can lead to large file sizes if overly detailed. |
| OBJ | Similar to STL but supports color and texture; less common in CNC applications | Animation, visual effects | Pros: Rich detail representation. Cons: Limited compatibility with CNC software. |
| DXF | 2D vector format; widely used in CAD for 2D designs | Laser cutting, engraving | Pros: Excellent for 2D machining. Cons: Not suitable for complex 3D models. |
| 3MF | Modern format supporting textures and metadata; designed for 3D printing | Advanced prototyping | Pros: More efficient file size and quality. Cons: Less widely adopted in CNC applications. |
| AMF | Supports advanced features like color and texture; more flexible than STL | Complex assemblies | Pros: High fidelity in representation. Cons: Limited software support compared to STL. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of STL Files for B2B Buyers?
STL (Stereolithography) files are the most prevalent format in the CNC industry, characterized by their ability to represent 3D geometries as a mesh of triangles. This format is particularly suitable for rapid prototyping and custom part manufacturing, making it a go-to choice for B2B buyers looking to streamline their production processes. When purchasing STL files, buyers should consider the level of detail and accuracy required for their projects, as overly complex models can lead to increased file sizes and longer processing times.
How Do OBJ Files Differ and When Should They Be Used?
OBJ files, while similar to STL in their triangular representation of 3D models, also support color and texture information, making them valuable in animation and visual effects industries. However, their use in CNC applications is limited due to compatibility issues with CAM software. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of rich detail against the potential need for conversion to a more compatible format, which could add complexity to their workflow.
What are the Advantages of Using DXF Files in CNC Machining?
DXF (Drawing Exchange Format) files are primarily used for 2D designs and are excellent for applications like laser cutting and engraving. Their widespread use in CAD software makes them a reliable choice for businesses focused on 2D machining. However, DXF files are not suitable for complex 3D models, so B2B buyers should ensure that their projects align with the limitations of this format to avoid workflow disruptions.
What Makes 3MF and AMF Formats Suitable for Advanced Applications?
3MF (3D Manufacturing Format) and AMF (Additive Manufacturing File Format) are modern file types designed for 3D printing, offering advanced features such as color and texture support. These formats are more efficient in terms of file size and quality but are less commonly adopted in CNC applications. B2B buyers considering these formats should evaluate their specific needs for complex assemblies and ensure that their software supports these modern file types to maximize their investment.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc 3d files
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC 3D Files | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of complex components | Enhanced precision and lightweight designs reduce costs | Certification compliance, material compatibility, high precision requirements |
| Automotive | Prototyping vehicle parts | Rapid development cycles shorten time-to-market | Advanced material options, ability to handle complex geometries |
| Furniture and Decor | Custom furniture designs | Unique offerings increase competitive advantage | Design flexibility, precision cutting capabilities |
| Medical Device Manufacturing | Creating surgical instruments | High-quality standards improve patient outcomes | Material safety certifications, adherence to industry regulations |
| Defense and Security | Production of tactical gear | Increased durability and customization options | Reliability of materials, compliance with defense specifications |
How Are CNC 3D Files Transforming the Aerospace Industry?
In aerospace manufacturing, CNC 3D files are utilized to create intricate components such as brackets, fixtures, and structural parts from lightweight materials. These parts must meet stringent safety and performance criteria. High precision is critical to ensure proper fit and function, ultimately impacting aircraft performance and fuel efficiency. International buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East must prioritize suppliers that demonstrate adherence to aerospace certification standards, such as AS9100, along with a proven track record of quality inspections.
What Are the Benefits of CNC 3D Files in Automotive Prototyping?
For the automotive sector, CNC 3D files enable rapid prototyping of various vehicle parts, contributing to shorter development cycles. This method allows manufacturers to test and iterate designs faster, significantly speeding up time-to-market for new vehicles. When sourcing these files, buyers should seek out providers who offer a range of advanced materials suitable for different applications, as well as the capability to manage complex geometries inherent in modern automotive design.
Why Is CNC 3D File Usage Essential in Furniture and Decor?
In the furniture and decor industry, CNC 3D files facilitate the production of custom-designed furniture pieces that meet unique customer specifications. This capability offers businesses a competitive edge through the introduction of distinctive offerings. Buyers in this field should consider the flexibility of design options and precise cutting capabilities of the CNC machines used. Ensuring that the models are optimized for CNC machining helps to minimize waste and improve production efficiency.
How Are CNC 3D Files Beneficial for Medical Device Manufacturing?
CNC 3D files play a crucial role in producing surgical instruments and new medical device components that require high standards of quality and precision. These components must adhere strictly to regulatory requirements, ensuring safety and reliability in medical settings. B2B buyers in this lightning-paced industry need to vet suppliers based on their material safety certifications and adherence to medical regulations, ensuring that the components will perform optimally without compromising patient safety.
How Do CNC 3D Files Enhance the Defense and Security Sector?
In defense and security applications, CNC 3D files are key in producing durable and customizable tactical gear and equipment. This allows for enhancements in terms of both functionality and personalization to meet specific military or security needs. Buyers in this field should seek manufacturers with a robust understanding of material reliability and compliance with defense industry specifications to ensure the highest standards are met for critical application equipment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc 3d files’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulties with File Compatibility for CNC Projects
The Problem: A frequent challenge faced by B2B buyers using CNC 3D files is the frustration of file compatibility. Many businesses, especially those in regions with diverse software systems like Africa and the Middle East, often find that the CAD software they employ does not natively support the 3D file formats they purchase or download, such as STL or OBJ. This can lead to wasted time and resources as teams scramble to convert files or seek alternative models, which could result in delays in project timelines and increased costs.
The Solution: To combat these issues, it’s vital for buyers to prioritize standard file formats such as STL when sourcing CNC 3D files. When engaging with suppliers, ensure they provide detailed information about the file types and compatibility with your current hardware and software infrastructure. Additionally, utilizing a dedicated CAD software that supports a broad range of file formats will reduce compatibility issues. Consider investing in a robust conversion tool or service that efficiently transforms files into usable formats for your CNC machine, allowing seamless integration into your workflow without the complications of format discrepancies.
Scenario 2: High Costs Associated with Poor Quality 3D Files
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially in Europe and South America, encounter the issue of high costs stemming from investing in low-quality 3D files. Inadequate models can lead to machining errors, wasted materials, and the need for rework, which may significantly inflate production costs. Poor-quality designs often result in products that do not meet quality standards or specifications, causing dissatisfaction among end customers and potential reputational damage.
The Solution: To mitigate risks associated with low-quality 3D files, businesses should conduct thorough vetting of file suppliers. Look for platforms or providers that emphasize high-resolution, professionally designed 3D models with positive user feedback. Prioritize suppliers that offer sample files or previews to assess quality before making a purchase. Additionally, investing in proper training for your team on how to evaluate the finesse and details of CNC 3D models will ensure that files are fit for purpose, thereby safeguarding your process from unnecessary expenditures related to subpar files.
Scenario 3: Time-Consuming Adjustments and Preparations Before Use
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers in sectors like manufacturing is dedicating excessive time to prepare and adjust CNC 3D files before they can be used in production. Many users find the need to resize, reconfigure, or optimize the models due to compatibility issues with their specific CNC machinery or due to design limitations. This can slow down production processes, divert valuable resources, and disrupt workflow schedules, ultimately affecting profitability.
The Solution: To streamline the process, buyers should seek out providers that specialize in CNC 3D files specifically optimized for various machines. Understanding your CNC machine’s specifications is crucial; communicate these needs clearly to your file suppliers. Additionally, investing in CAM software that automates the preparation of 3D files can save time. These systems can handle file modifications efficiently, optimizing them for the desired machining operations with minimal manual adjustments. Lastly, fostering ongoing relationships with reliable design partners who can provide tailored support and revisions can further enhance efficiency and project continuity. By addressing these preparatory tasks proactively, companies can minimize delays and focus on productive output instead.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc 3d files
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for CNC 3D Files?
When selecting materials for CNC 3D files, it is crucial to understand the properties that affect performance, durability, and application suitability. Here, we analyze four common materials: wood, aluminum, plastic, and steel.
How Does Wood Perform as a Material for CNC 3D Files?
Wood is a popular choice for CNC machining due to its availability and ease of use. It offers excellent machinability, allowing for intricate designs and fine details. Key properties include natural insulation, lightweight nature, and a wide range of finishes. However, wood is susceptible to moisture, which can lead to warping or swelling, particularly in humid environments.
Pros: Cost-effective, easy to work with, and aesthetically pleasing.
Cons: Limited durability compared to metals, sensitive to environmental conditions.
Impact on Application: Suitable for decorative items, furniture, and prototypes, but less ideal for structural components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations regarding sustainable sourcing is crucial, especially in Europe, where environmental standards are stringent.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for CNC 3D Files?
Aluminum is favored in industrial applications due to its strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It is lightweight yet durable, making it suitable for both functional and decorative parts. Key properties include good thermal conductivity and resistance to oxidation, which enhances longevity.
Pros: High durability, excellent finish quality, and good machinability.
Cons: Higher cost than wood and may require specialized tooling for machining.
Impact on Application: Ideal for aerospace, automotive, and other high-performance applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM standards for aluminum alloys, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Europe.
How Do Plastics Compare in Terms of CNC 3D File Applications?
Plastics, such as acrylic and polycarbonate, are increasingly popular for CNC machining due to their versatility and range of properties. They can be engineered to provide specific characteristics, such as impact resistance or thermal stability. Key properties include lightweight, chemical resistance, and ease of coloring.
Pros: Cost-effective, lightweight, and available in various colors and finishes.
Cons: Generally less durable than metals and may degrade under UV exposure.
Impact on Application: Suitable for signage, prototypes, and consumer products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with JIS standards for plastics is essential, especially in Japan and South America, where specific regulations may apply.
What Role Does Steel Play in CNC 3D File Production?
Steel is known for its exceptional strength and durability, making it a preferred choice for heavy-duty applications. Key properties include high tensile strength, resistance to wear, and the ability to withstand high temperatures. However, steel can be challenging to machine and may require advanced tooling.
Pros: Extremely durable and suitable for high-stress applications.
Cons: Higher manufacturing complexity and cost, as well as potential for rusting if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Ideal for structural components, machinery parts, and tools.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must adhere to DIN standards for steel products, particularly in Europe, where quality and safety regulations are stringent.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC 3D Files
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc 3d files | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Decorative items, furniture, prototypes | Cost-effective and easy to work with | Limited durability and moisture sensitivity | Low |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive components | High durability and excellent finish | Higher cost and requires specialized tooling | High |
| Plastic | Signage, prototypes, consumer products | Lightweight and versatile | Less durable and may degrade under UV | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components, machinery parts | Extremely durable and high strength | High manufacturing complexity and potential for rust | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for CNC 3D files, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc 3d files
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for CNC 3D Files?
Creating CNC 3D files involves several key stages that adapt to the complexities of the desired outcomes. Each stage contributes to the overall quality and viability of the product. Here’s a breakdown of the typical manufacturing processes:
Material Preparation: Which Materials Are Optimal for CNC Projects?
Material selection is paramount, as it forms the foundation of any 3D model. Common materials used in CNC manufacturing include wood, plastic, metals (such as aluminum and steel), and composite materials. Before production, materials are sourced and inspected to ensure they meet specific criteria such as chemical composition and physical properties. This initial step often requires a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) to guarantee compliance with international safety standards.
What Techniques Are Commonly Used for Forming 3D Models?
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming, typically achieved through CNC machining or additive manufacturing techniques. CNC machining relies on subtractive methods where tools and cutters remove material to achieve the specifications of the STL files. Techniques such as milling, routing, and turning are often employed, with tools programmed according to the required precision of the model design.
Additive manufacturing techniques are becoming increasingly popular, offering flexibility and the ability to create complex shapes that may not be feasible with traditional methods. However, the choice of technique depends on project requirements and the characteristics of the materials used.
What Is the Importance of Assembly in CNC Manufacturing?
In certain projects, multiple components might need to be assembled to create the final product. The assembly stage ensures that all parts fit correctly and function intuitively. This can involve a range of techniques from mechanical fastening to welding or gluing, depending on the materials and design specifications. Proper assembly plays a critical role in achieving durability and performance.
How Is Finishing Achieved and Why Is It Critical?
Finishing processes, such as sanding, painting, or coating, are employed to enhance aesthetics and durability. These processes can also influence the functionality of the product by providing protective layers against environmental factors. Quality finishing is vital for ensuring that the product meets both visual and operational expectations, especially in industries such as consumer goods or automotive parts.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential in CNC Manufacturing Processes?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to ensuring that the final output of CNC manufacturing meets defined standards and customer satisfaction. Adhering to international standards not only bolsters the manufacturer’s reputation but also fosters trust among buyers.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
Adhering to established international standards, such as ISO 9001, helps ensure that manufacturing processes consistently produce quality products. Buyers should inquire whether suppliers have certifications that validate their compliance with these standards. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE for European markets or API for oil and gas components, should also be verified to confirm product compliance with local regulations and safety requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Manufacturing?
Typically, quality control involves various checkpoints during the production process to ensure compliance with specifications:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials for defects or deviations from standards before they are used in production.
-
In-process Quality Control (IPQC): Through this step, ongoing checks are performed throughout the manufacturing stage, ensuring that production processes remain within predetermined limits. This could involve measuring tolerances or conducting simple tests during machining.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection of products before delivery confirms that they meet all specifications and quality standards. This can include dimensional checks, functionality tests, and visual inspections.
Which Testing Methods Are Common in QC Processes?
Different conventional and advanced testing methods are employed to ensure the fidelity of the final product. These include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Verifying that parts adhere to specified dimensions using tools like calipers and micrometers.
-
Functional Testing: This step assesses whether the finished components perform as intended under operational conditions.
-
Visual Inspections: Techniques focusing on identifying cosmetic blemishes or deviations through human inspection or automated vision systems.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Adapting a thorough vetting process for manufacturing partners is crucial for international B2B buyers. Here are several actionable steps:
What Are the Audit and Reporting Protocols for Vendors?
Conducting regular audits of supplier facilities allows buyers to assess adherence to quality assurance standards actively. Auditors should look for records of past inspections, quality reports, and evidence of corrective actions taken where defects were identified. Buyers can also request regular quality reports that detail performance metrics, rejection rates, and customer feedback.
How Do Third-Party Inspections Benefit International Transactions?
Engaging third-party inspection services adds an extra layer of impartiality and credibility, ensuring that the supplier is not only reporting accurately but also adhering strictly to quality standards. These inspectors can provide full-quality reports before shipment.
What Are the QC/CERT Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may face unique challenges regarding quality certifications. It’s crucial to consider local regulations and customs requirements before accepting products. Familiarizing oneself with specific import/export rules in the target markets, along with international quality standards, can significantly reduce the risk of costly returns or compliance issues.
In conclusion, a robust understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is indispensable for B2B buyers in the CNC industry. By carefully considering each aspect from supplier audits to material selection, businesses can significantly enhance their chances of securing quality products that meet their project specifications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc 3d files’
To effectively procure CNC 3D files for your business needs, it’s essential to have a well-structured approach. This checklist will guide B2B buyers through the critical steps of sourcing high-quality 3D models optimized for CNC machining, ensuring you make informed decisions tailored to your specific requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Project Requirements
Before beginning your search, clearly outline your project specifications. Consider aspects such as the type of material you’ll be working with, the dimensions of the parts, and the complexity of the designs. This will help you narrow down potential suppliers that specialize in the particular files necessary for your applications.
Step 2: Choose the Appropriate File Format
The selection of file format directly impacts machining efficiency and quality. Common formats like STL and DXF should be prioritized due to their compatibility with most CNC machines. Ensure that the supplier provides clear descriptions of file types and their intended use to avoid compatibility issues later on.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Vetting suppliers thoroughly is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability. Request company profiles, case studies, and references to verify their experience in producing CNC 3D files. Look for feedback on design accuracy and the timeliness of file delivery to avoid disruptions in your project timeline.
Step 4: Review Quality and Detail of Models
Assess the level of detail and accuracy in the models offered by suppliers. High-resolution files are important for achieving precision in machining. Ask for sample files or portfolio examples to evaluate the visual and functional aspects of their designs, ensuring they meet your quality standards.
Step 5: Check for Optimization Features
Suppliers who optimize their models for CNC machining will enhance your production efficiency. Look for dimensions specified for your machine’s capabilities and ensure that the models are designed to minimize material waste. Optimized files can significantly speed up the machining process while improving the final product quality.
Step 6: Understand Licensing and Usage Rights
It’s vital to clarify licensing terms associated with the files you purchase. Ensure that you have the commercial rights necessary to utilize the designs within your business operations. Be cautious of suppliers who impose restrictions on resale or reproduction, which could limit your operational flexibility.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified suitable suppliers, discuss pricing and payment terms. Don’t hesitate to negotiate the cost based on your intended volume of orders or long-term partnerships. Ensure that delivery terms, guarantees, and support for potential adjustments post-purchase are clearly outlined in the agreement.
This checklist serves as a practical roadmap for sourcing CNC 3D files in a way that meets your manufacturing demands. Adhering to these steps will enable you to partner effectively with your suppliers, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc 3d files Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing CNC 3D Files?
When sourcing CNC 3D files, several cost components must be considered to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the overall expenditure. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: While digital files themselves do not have material costs, the choice of materials for the final product can significantly impact costs. For example, using high-quality wood or metal can increase the overall expense.
-
Labor: This includes the costs associated with skilled labor needed to operate CNC machines and ensure that the files are executed correctly. The expertise of the machinists can vary by region, affecting labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. These costs can vary widely depending on the supplier’s location and operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: CNC machining often requires specialized tools that can add to the cost. Depending on the complexity of the design, the tooling costs may fluctuate.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing quality assurance processes is critical to ensuring that the final products meet specifications. QC costs can include both testing and any rework required for parts that do not meet standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can be significant, particularly for international transactions. The method of shipping and the destination can greatly influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition, demand, and the perceived value of their designs.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of CNC 3D Files?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC 3D files, which are crucial for B2B buyers to understand:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it essential for buyers to negotiate based on their anticipated needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or complex specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly outline their requirements to receive accurate quotes.
-
Materials: The choice of materials for the final product can significantly affect pricing. For instance, premium materials often result in higher costs, while standard materials may keep expenses lower.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers offering certified high-quality files may charge a premium. Buyers should evaluate whether the added cost aligns with their quality requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and reliability, while newer entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade is crucial for international buyers. Different Incoterms can affect the total cost, including who bears responsibility for shipping and insurance.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing CNC 3D Files?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate prices and terms with suppliers. Many are willing to offer discounts or better terms for long-term partnerships or larger orders.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the long-term costs associated with sourcing CNC 3D files. This includes the quality of the files, potential rework costs, and the longevity of the final products.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, suppliers in Germany may have different cost structures compared to those in Saudi Arabia. Understanding these nuances can help in making more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Request Samples: Whenever possible, request samples or trial files before committing to a large order. This allows buyers to assess quality and suitability without incurring significant upfront costs.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize online platforms that specialize in CNC file sourcing to compare prices and designs efficiently. This can aid in finding competitive pricing and innovative designs.
Conclusion
While the digital nature of CNC 3D files may suggest lower costs, various factors influence the overall pricing structure. By understanding these cost components and price influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their sourcing strategies and enhance their competitive edge in the market.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc 3d files With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CNC 3D Files: A Comprehensive Comparison
In the realm of manufacturing and design, CNC 3D files represent a popular solution for creating intricate designs and components. However, businesses may find themselves evaluating alternative methods that could potentially offer better efficiency, cost savings, or operational flexibility. This section provides a comparative analysis of CNC 3D files against two viable alternatives: 2D CAD files and additive manufacturing (3D printing).
| Comparison Aspect | Cnc 3D Files | 2D CAD Files | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for complex shapes | Limited to flat designs | Excellent for complex geometries |
| Cost | Varies based on design complexity | Generally lower initial costs | Material costs can add up quickly |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific software and setup | Easier to generate and implement | Requires specialized equipment and software |
| Maintenance | Regular updates needed for files | Minimal ongoing maintenance | Equipment can require significant upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Intricate, multi-dimensional parts | Flat designs or layouts | Rapid prototyping and complex shapes |
Understanding the Pros and Cons of 2D CAD Files
2D CAD files serve as a foundational approach for many manufacturing processes. They are typically less expensive to create and implement than CNC 3D files, making them an attractive option for businesses focusing on simpler designs or those just starting out in CNC machining. However, their main limitation lies in their inability to handle complex 3D geometries, restricting their applicability in industries that require more sophisticated parts. Additionally, while they require less specialized software, they may not leverage the full potential of CNC technology.
Evaluating Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly referred to as 3D printing, has emerged as a revolutionary alternative to traditional machining methods. It excels in creating complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with CNC machining. This method allows for rapid prototyping, enabling businesses to iterate designs quickly and efficiently. However, the costs associated with materials and the need for specialized equipment can be significant drawbacks. Moreover, while 3D printing can produce high-quality parts, the production speed may not match that of CNC machining for larger batches.
Making the Right Choice: How to Select the Best Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between CNC 3D files and alternative solutions like 2D CAD files or additive manufacturing, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific project requirements. Considerations such as the complexity of the design, budget constraints, and the intended production volume play crucial roles in this decision-making process. For projects requiring intricate designs, CNC 3D files may provide the necessary precision and quality. Conversely, for simpler or flat designs, 2D CAD files could offer a more cost-effective and efficient solution. If rapid prototyping or unique geometries are paramount, exploring additive manufacturing may be the best route. Ultimately, aligning the chosen method with operational goals will ensure optimal results and resource utilization.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc 3d files
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of CNC 3D Files?
Understanding the essential properties of CNC 3D files is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility, functionality, and overall quality in production. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
File Format
The most common file formats for CNC machining are STL, OBJ, and DXF. STL files are the industry standard due to their ability to represent 3D geometry as a mesh of triangles, offering compatibility across various CAD and CAM software. Understanding which format is most suitable for your CNC machine can prevent costly mistakes in production. -
Resolution/ Triangle Count
This refers to the detail level in the 3D model, usually represented by the number of triangles used in the mesh. While higher triangle counts can provide more detail, they can also slow down processing and toolpath generation. For CNC machining, maintaining a balance—roughly 250,000 triangles—is often sufficient for high-quality outputs, making it essential for businesses to optimize files efficiently. -
Accuracy and Tolerance
Tolerance denotes the acceptable deviation in dimensions for manufactured parts. In CNC machining, tight tolerances ensure that components fit together as intended. Establishing clear tolerance specifications during the project kickoff can save time and resources, as deviations may require rework or scrapping of parts, impacting timelines and costs. -
Material Compatibility
Different materials—wood, metal, plastic—require specific considerations in the design of 3D files. Each material type affects the cutting speed, tooling, and tooling paths. Buyers should ensure that their 3D files are designed with the specific material in mind, facilitating a smoother machining process and enhancing end-product quality. -
Post-Processing Requirements
Some CNC files might require additional processing steps after machining, such as sanding or coating. Buyers need to discuss post-processing details with their vendors to determine if their chosen designs accommodate these requirements efficiently, helping to streamline production.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand When Dealing with CNC 3D Files?
Navigating the CNC landscape involves familiarizing oneself with industry jargon that can influence procurement and production processes. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM provides products or components that other companies use in their own products. Understanding this term is vital for buyers to identify potential suppliers who can fulfill specifications tailored to their specific industry needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, as understanding MOQ policies helps buyers avoid overcommitting or underserving market demands. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing for specified items or services. It’s an important tool in B2B transactions as it facilitates competitive bidding, enabling buyers to compare offers effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade definitions that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, risk, and insurance. Familiarity with Incoterms can help B2B buyers navigate international contracts and agreements with a clearer understanding of their obligations and liabilities. -
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
CAM software is used to create a toolpath and machine instructions from a CNC-compatible 3D file. Acknowledging the role of CAM can guide buyers in ensuring their 3D files are optimally designed for seamless downstream processing. -
Lead Time
This term reflects the time taken from placing an order to delivery. In the context of CNC machining, understanding lead time can assist buyers in managing project timelines and ensuring timely delivery of components.
In summary, grasping the technical properties and industry-specific terminology surrounding CNC 3D files enables B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, align product specifications with manufacturing capabilities, and optimize their production strategies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc 3d files Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Impacting the CNC 3D Files Sector?
The CNC 3D files market is experiencing dynamic growth, driven by the increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies and the demand for personalized and intricate designs across diverse industries. Key trends include the proliferation of customizable designs, with businesses seeking unique, tailor-made solutions that cater to specific customer needs. With the rise of Industry 4.0, businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly looking for 3D files that can be seamlessly integrated with automated CNC systems, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
Furthermore, globalization is enabling suppliers from different regions to compete effectively, resulting in lower costs for high-quality files. For instance, international buyers can leverage competitive pricing from suppliers in emerging markets while also finding niche designs from European producers renowned for their craftsmanship. The digital transformation of B2B transactions is also notable, as online platforms simplify the sourcing of 3D STL files, facilitating immediate downloads and reducing lead times.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are further shaping the landscape, with companies increasingly using these tools to optimize file creation and production processes. As buyers prioritize speed, quality, and affordability, the market dynamics are continually evolving to meet these demands through innovative design practices and advanced file optimization techniques.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in CNC 3D Files?
In the wake of growing environmental concerns, B2B buyers are prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing in the acquisition of CNC 3D files. The environmental impact of sourcing materials for CNC manufacturing, particularly plastics and metals, is substantial. Therefore, companies are urged to explore and support suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. These practices may include the use of recycled materials for digital file creation or engaging in sustainable waste management practices.
Buyers should also consider suppliers who possess ‘green’ certifications, demonstrating their commitment to environmental sustainability. Such certifications often indicate that a supplier utilizes environmentally friendly materials that reduce carbon footprints. Additionally, collaborating with suppliers that uphold ethical labor practices within their supply chains ensures that businesses not only meet consumer demand for responsibly sourced products but also adhere to increasingly stringent regulatory requirements.
Moreover, adopting a circular economy approach by sourcing designs that facilitate recycling or can be reused in new products can be an excellent strategy for enhancing sustainability. By carefully selecting partners that emphasize these principles, businesses can fortify their market position while attracting environmentally conscious customers.
What Is the Evolution of CNC 3D Files and Its Significance for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of CNC 3D files reflects broader advancements in technology and digital manufacturing. Initially, CNC machining was primarily focused on 2D designs, limiting creativity and execution in production processes. As 3D printing technology advanced in the late 20th century, file formats like STL emerged, enabling more complex geometric designs to be executed through CNC machines.
The embrace of STL files signifies a pivotal moment in the CNC landscape: providing a standard for consistent, high-quality outputs while enabling a greater degree of customization—an essential aspect for B2B buyers today. As industries increasingly demand precise and intricate components, the evolution toward sophisticated 3D modeling and CNC capabilities continues to shape sourcing strategies for B2B buyers.
In summary, understanding the historical context of CNC 3D files helps international buyers recognize the technological advancements that influence current sourcing trends and market dynamics, ultimately assisting them in making informed purchasing decisions that align with their business objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc 3d files
-
1. How do I choose the right CNC 3D files for my project?
Selecting the right CNC 3D files involves understanding your specific project requirements. Consider the intended application, material compatibility, and the level of detail needed. Ensure that the files are in a compatible format (e.g., STL) and optimized for your CNC machine. Additionally, evaluate the complexity of the design and whether it matches your machining capabilities. Look for suppliers that offer a variety of models and allow you to preview the designs before purchasing. -
2. What is the best file format for CNC 3D models?
The most widely recommended file format for CNC 3D models is STL (Stereolithography). It is compatible with most CAD and CAM software and is specifically optimized for CNC machining processes. While OBJ and DXF formats exist, they may not be as universally accepted in CNC applications. When sourcing files, prioritize STL formats to ensure seamless integration with your machinery and software. -
3. How can I verify the quality of CNC 3D files before purchasing?
To verify the quality of CNC 3D files, check for customer reviews and ratings from previous buyers. Look for detailed descriptions and images of the models provided by the supplier. Some reputable suppliers offer a sample or preview option, allowing you to assess the design before making a purchase. Additionally, inquire about the file’s specifications, such as polygon count and machining compatibility, to ensure it meets your standards. -
4. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC 3D files?
Minimum order quantities for CNC 3D files can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the designs. Many digital file suppliers do not impose a MOQ since files are sold as digital downloads. However, for customized or bespoke designs, suppliers may require a minimum order to justify the design effort. Always confirm MOQ policies with potential suppliers before finalizing your order. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when buying CNC 3D files internationally?
Payment terms for purchasing CNC 3D files internationally typically include options such as credit card, PayPal, or bank transfers. Many suppliers require upfront payment for digital products due to the instant access provided upon purchase. Some may offer discounts for bulk purchases or extended payment plans. Always clarify payment terms and conditions with your supplier to avoid misunderstandings. -
6. How can I ensure timely delivery of CNC 3D files across international borders?
To ensure timely delivery of CNC 3D files, choose suppliers that provide instant digital downloads. This eliminates shipping delays associated with physical products. Confirm the supplier’s operating hours and response times, especially if you are in different time zones. It’s also advisable to ask about their customer support availability for any potential issues that might arise during the transaction. -
7. What should I consider when vetting suppliers of CNC 3D files?
When vetting suppliers of CNC 3D files, consider their reputation, experience, and customer feedback. Check if they provide support for file customization and whether they have a wide range of designs. Evaluate their policies on refunds and exchanges for files that do not meet expectations. Additionally, look for suppliers who adhere to international quality standards and offer comprehensive technical support. -
8. How can I customize CNC 3D files to meet my specific needs?
Customizing CNC 3D files typically requires access to CAD software that allows for editing of STL files. Many suppliers offer customization services for an additional fee, which can include alterations in size, detail, or design features. When requesting customization, provide clear specifications and reference models to guide the supplier. Always confirm the turnaround time and any additional costs associated with customization before proceeding.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Cnc 3D Files Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. 3D Wave – CNC-Ready STL Models
Domain: 3dwave.us
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: 3D STL Models for CNC Router and 3D illusion laser-ready files. High-quality 3D models designed specifically for CNC machining. Instant download available in STL format. Optimized for CNC with high detail and precision. Compatible with most CNC software and machines. Wide variety of models including animals, religious figures, decorative pieces, and functional parts. Digital download only, for per…
2. Carbide 3D – CNC Models
Domain: carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Carbide 3D offers 3D models for CNC machines, specifically for their Shapeoko CNC Router and Nomad Desktop CNC. The primary file types for 3D models include STL, OBJ, and DXF, with STL being the most common and preferred format for CNC applications. STL files represent 3D models as a series of triangles and can accurately convey the model’s shape for CNC machining. OBJ files are similar but are pr…
3. Etsy – CNC STL Files
Domain: etsy.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This company, Etsy – CNC STL Files, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. CNC Clipart – 3D Relief Models
Domain: cncclipart.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: CNC Clipart offers 3D relief models for CNC projects, compatible with software such as Carveco, Vectric, MasterCAM, and Fusion 360. The product categories include Animals (284 items), Badges (106 items), Banners (40 items), Buildings (46 items), Decorative (206 items), Fantasy (17 items), Frames (63 items), Food & Drink (77 items), People (63 items), Music (25 items), Nautical (33 items), Objects …
5. Cults3D – Premium STL Files for 3D Printing
Domain: cults3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Cnc best STL files for 3D printer; 30.4k free models to download; Various categories including Art, Fashion, Jewelry, Home, Architecture, Gadget, Game, Tools, and more; Supported file formats: STL, OBJ, STEP, 3MF, SCAD for 3D printing; DXF, SVG, PDF, AI for CNC machining & laser cutting; Community of 199k designers; Payment options include credit card, PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay.
6. 3DModelsArt – Mega 3D STL Models Collection
Domain: 3dmodelsart.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: 3D STL Models for CNC Routers and 3D Printers. Instant Downloads. Support You Can Trust. Products include: 7000+ PCS MEGA 3D STL MODELS COLLECTION SET for CNC Routers – $165.00 (originally $400.00), 3000 PCS MEGA BIG 3D STL MODELS COLLECTION SET for CNC Routers – $105.00 (originally $155.00), 500+ PCS 3D STL MODELS COLLECTION – $15.00 (originally $150.00), 121 PCS ANIMALS 3D STL MODELS COLLECTION …
7. Dezin – 3D Engraving & Cut Models
Domain: dezin.info
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: This company, Dezin – 3D Engraving & Cut Models, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc 3d files
In the rapidly evolving landscape of CNC machining, strategic sourcing of 3D files is paramount for international buyers seeking to enhance their production capabilities. By prioritizing high-quality STL files optimized for CNC applications, businesses can significantly improve their manufacturing efficiency and product quality. The ability to access a diverse range of 3D models, from intricate designs to functional components, empowers companies to innovate and meet the growing demands of their markets.
Furthermore, embracing a proactive sourcing strategy not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also fosters partnerships that enhance competitiveness. As industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for modernization, investing in reliable 3D file resources will be instrumental in driving growth and operational excellence.
Looking ahead, the demand for customized and precision-engineered products will only intensify. B2B buyers are encouraged to explore reputable sources for CNC 3D files, ensuring they remain at the forefront of technological advancements. By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can not only fulfill current project requirements but also position themselves for future success in an increasingly competitive global market.